Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Human Gut Microbiome and Body Metabolism
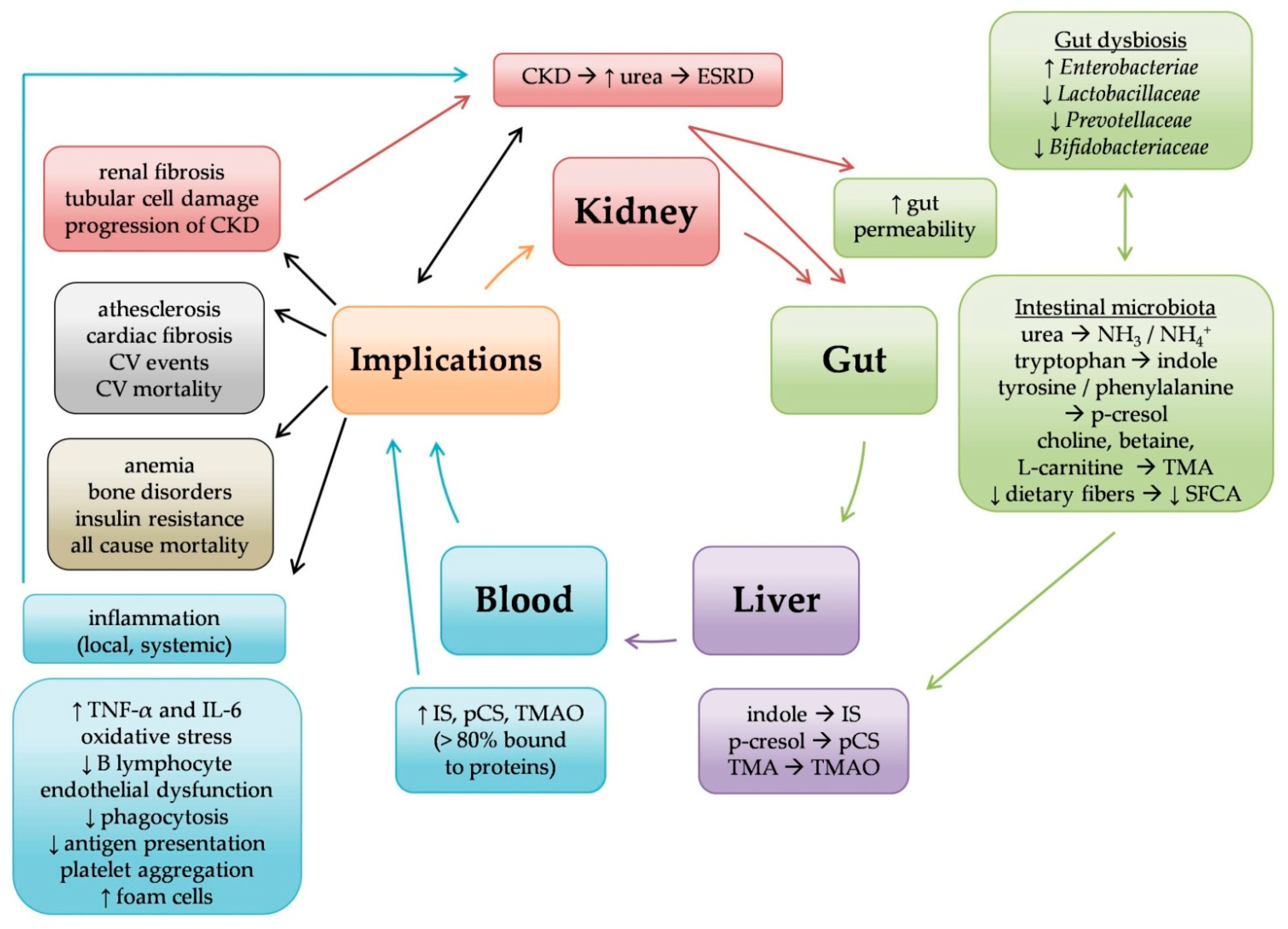
3. Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease
3.1. Microbiome in CKD (at Pre-Dialysis Stages)
| Increase/Growth | Decrease/Reduction | Authors, Year, Type of Study | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-dialysis CKD | Enterobacteriae [38,43] Enterococci [43] Lachnospiraceae [38] Ruminococcaceae [38] | Lactobacillaceae [38,43] Prevotellaceae [38,43] Bacteroidaceae [38] Bifidobacterium species [38] | Sampaio-Maia et al. [38], 2016, review Vaziri et al. [43], 2013, cohort study (n = 24) |
| Hemodialysis | Proteobacteria(mainly Gammaproteobacteria [43,51]) Actinobacteria [43,51] Firmicutes [43,51,52] (mainly Clostridium, Enterococcus) | Lactobacillaceae [53] Prevotellaceae [53] | Vaziri et al. [43], 2013, cohort study (n = 36) Chen at al. [51], 2019, review Shi et al. [52], 2014, cohort study (n = 52) Wong et al. [53], 2014, cohort study (n = 24) |
| Peritoneal dialysis | Proteobacteria [54] (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) [55] | Actinobacteria [56] Firmicutes [56] Lactobacillaceae [55] Bifidobacterium species [55] | Crespo-Salgado et al. [54], 2016, cross-sectional study (n = 39) Wang et al. [55], 2012, cohort study (n = 29) Simões-Silva et al. [56], 2020, cross-sectional study (n = 20) |
| Kidney transplantation | Proteobacteria [57,58] | Actinobacteria [58] | Lee at al. [57], 2014, pilot study (n = 26) Swarte et al. [58], 2020, cohort study (n = 139) |
3.2. Microbiome in Hemodialysis
3.3. Microbiome in Peritoneal Dialysis
3.4. Microbiome in Kidney Transplantation
4. Microbiome and Clinical Implications (Table 2)
| Clinical Implications | Authors, Year, Type of Study | |
|---|---|---|
| CKD | atheromatosis [34,71] vascular calcification [34] anemia [35] bone disorders [78] progression of CKD [45] systemic inflammation [26] cardiovascular risk factor [38] | Opdebeeck et al. [34], 2019, cohort study (n = 42) Hung et al. [71], 2017, review Chiang et al. [35], 2011, laboratoty cohort study Lin et al. [78], 2014, cohort study (n = 80) Lim et al., 2021, review Missailidis et al. [26], 2016, prospective cohort study (n = 179) Sampaio-Maia et al. [38], 2016, review |
| ESRD | systemic inflammation [26] cardiovascular mortality [72] all cause mortality [72] | Missailidis et al. [26], 2016, prospective cohort study (n = 179) Graboski et al. [72], 2020, review |
| Hemodialysis | acute coronary syndrome [74] cardiovascular events [26,74] systemic inflammation [26] all cause mortality [26,74] | Wu et al. [74], 2021, cross-sectional study (n = 333) Missailidis et al. [26], 2016, prospective cohort study (n = 179) |
| Peritoneal dialysis | peritoneal infection [76,77] cardiovascular mortality [76] | Chang et al. [76], 2021, prospective cohort study (n = 513) Zhang et al. [77], 2022, cohort study |
| Kidney transplantation | allograft rejection (possible) [67] | Baghai Arassi et al. [67], 2020, review |
5. Microbiome and Immune Reactions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobby, G.P.; Karaduta, O.; Dusio, G.F.; Singh, M.; Zybailov, B.L.; Arthur, J.M. Chronic Kidney Disease and the Gut Microbiome. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 316, F1211–F1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrek, Ł. Potential therapeutic options targeting the gut dysbiosis in chronic kidney disease. Wiad. Lek. 2022, 75, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, M. Impact of the Gut Microbiome in Cardiovascular and Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 2387–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, C.; Ferris, A.H. Chronic Kidney Disease. Prim. Care 2020, 47, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Chronic Kidney Disease Guideline Development Work Group Members Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: Synopsis of the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelfarb, J.; Vanholder, R.; Mehrotra, R.; Tonelli, M. The Current and Future Landscape of Dialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golper, T.A.; Fissell, R.; Fissell, W.H.; Hartle, P.M.; Sanders, M.L.; Schulman, G. Core Curriculum in Dialysis 2013 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, M.C.C.; Totoli, C. Peritoneal Dialysis. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. (1992) 2020, 66 (Suppl. S1), s37–s44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondran-Tellier, B.; Baboudjian, M.; Lechevallier, E.; Boissier, R. Renal transplantation, for whom, why and how? Prog. Urol. 2020, 30, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulou, E.; Kantartzi, K.; Tsigalou, C.; Aftzoglou, K.; Voidarou, C.; Konstantinidis, T.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Thodis, E.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Microbiome, Immunosenescence, and Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 661203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.-C.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome Definition Re-Visited: Old Concepts and New Challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barko, P.C.; McMichael, M.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Williams, D.A. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: A Review. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.W.; Kitai, T.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasselman, L.J.; Vernice, N.A.; DeLeon, J.; Reiss, A.B. The Gut Microbiome and Elevated Cardiovascular Risk in Obesity and Autoimmunity. Atherosclerosis 2018, 271, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, A.; Raj, D.S. The Gut Microbiome, Kidney Disease, and Targeted Interventions. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Yang, H. Factors Affecting the Composition of the Gut Microbiota, and Its Modulation. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human Gut Microbiota/Microbiome in Health and Diseases: A Review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Wijmenga, C.; Fu, J.; Zhernakova, A. Host Genetics and Gut Microbiome: Challenges and Perspectives. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Jernberg, C.; Andersson, A.F.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. Short-Term Antibiotic Treatment Has Differing Long-Term Impacts on the Human Throat and Gut Microbiome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, S.; Scher, J.U.; Djukovic, A.; Jiménez, N.; Littman, D.R.; Abramson, S.B.; Pamer, E.G.; Ubeda, C. Short- and Long-Term Effects of Oral Vancomycin on the Human Intestinal Microbiota. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.M.; Finlay, B.B. Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallu, A.; Sharma, S.; Ramezani, A.; Muralidharan, J.; Raj, D. Gut Microbiome in CKD: Challenges and Opportunities. Transl. Res. 2017, 179, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranton, F.; Cohen, G.; De Smet, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Jankowski, J.; Vanholder, R.; Argiles, A. Normal and Pathologic Concentrations of Uremic Toxins. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, P.; Dou, L.; Cerini, C.; Berland, Y. Protein-Bound Uremic Retention Solutes. Adv. Ren. Replace Ther. 2003, 10, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missailidis, C.; Hällqvist, J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Barany, P.; Heimbürger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P.; Bergman, P. Serum Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Is Strongly Related to Renal Function and Predicts Outcome in Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0141738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdebeeck, B.; D’Haese, P.C.; Verhulst, A. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms That Induce Arterial Calcification by Indoxyl Sulfate and P-Cresyl Sulfate. Toxins 2020, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ke, B.; Du, J. TMAO: How Gut Microbiota Contributes to Heart Failure. Transl. Res. 2021, 228, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, N.; Anteyi, E. The Role of Dietary Fiber and Gut Microbiome Modulation in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2022, 14, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Ma, K.; Wang, J.; Ding, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Song, L.; Liu, C. The Immunomodulatory Effect of the Gut Microbiota in Kidney Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 5516035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.L.; Vaziri, N.D. The Leaky Gut and Altered Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2017, 27, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões-Silva, L.; Araujo, R.; Pestana, M.; Soares-Silva, I.; Sampaio-Maia, B. The Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.L.; Savoj, J.; Nakata, M.B.; Vaziri, N.D. Altered Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease: Systemic Effects of Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdebeeck, B.; Maudsley, S.; Azmi, A.; De Maré, A.; De Leger, W.; Meijers, B.; Verhulst, A.; Evenepoel, P.; D’Haese, P.C.; Neven, E. Indoxyl Sulfate and P-Cresyl Sulfate Promote Vascular Calcification and Associate with Glucose Intolerance. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.-K.; Tanaka, T.; Inagi, R.; Fujita, T.; Nangaku, M. Indoxyl Sulfate, a Representative Uremic Toxin, Suppresses Erythropoietin Production in a HIF-Dependent Manner. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppe, L.; Pillon, N.J.; Vella, R.E.; Croze, M.L.; Pelletier, C.C.; Chambert, S.; Massy, Z.; Glorieux, G.; Vanholder, R.; Dugenet, Y.; et al. P-Cresyl Sulfate Promotes Insulin Resistance Associated with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 24, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espi, M.; Koppe, L.; Fouque, D.; Thaunat, O. Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Immune Dysfunctions: Impact of Protein-Bound Uremic Retention Solutes on Immune Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio-Maia, B.; Simões-Silva, L.; Pestana, M.; Araujo, R.; Soares-Silva, I.J. The Role of the Gut Microbiome on Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 96, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, T.; Dong, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Raza, H.K.; Lei, G. Association between Gut Dysbiosis and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Narrative Review of the Literature. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 03000605211053276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Onal, E.M.; Afsar, B.; Dagel, T.; Yerlikaya, A.; Covic, A.; Vaziri, N.D. The Crosstalk of Gut Microbiota and Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Inflammation, Proteinuria, Hypertension, and Diabetes Mellitus. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata, C.; Cruz, C.; Cervantes, L.G.; Ramírez, V. The Gut Microbiota and Its Relationship with Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 2209–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lim, S.Y.; Ko, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Oh, S.W.; Kim, M.G.; Cho, W.Y.; Jo, S.K. Intestinal Barrier Disruption and Dysregulated Mucosal Immunity Contribute to Kidney Fibrosis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Wong, J.; Pahl, M.; Piceno, Y.M.; Yuan, J.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Ni, Z.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Andersen, G.L. Chronic Kidney Disease Alters Intestinal Microbial Flora. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Goto, S.; Fukagawa, M. Role of Uremic Toxins for Kidney, Cardiovascular, and Bone Dysfunction. Toxins 2018, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.J.; Sidor, N.A.; Tonial, N.C.; Che, A.; Urquhart, B.L. Uremic Toxins in the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Toxins 2021, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, J. Role of Intestinal Microbiota and Metabolites on Gut Homeostasis and Human Diseases. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, M.; Tsalouchos, A. Microbiota, Renal Disease and Renal Transplantation. World J. Transplant. 2021, 11, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Chang, S.-C.; Wu, M.-S. Uremic Toxins Induce Kidney Fibrosis by Activating Intrarenal Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Associated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Bolati, D.; Adijiang, A.; Adelibieke, Y.; Muteliefu, G.; Enomoto, A.; Higashiyama, Y.; Higuchi, Y.; Nishijima, F.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl Sulfate Downregulates Renal Expression of Klotho through Production of ROS and Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 33, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Caetano-Pinto, P.; Seegers, A.E.M.; Dankers, A.C.A.; van den Broek, P.H.H.; Wetzels, J.F.M.; van den Brand, J.A.J.G.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Wilmer, M.J.G.; et al. Proximal Tubular Efflux Transporters Involved in Renal Excretion of P-Cresyl Sulfate and p-Cresyl Glucuronide: Implications for Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Chen, D.-Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.-R.; Vaziri, N.D.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Microbiome–Metabolome Reveals the Contribution of Gut–Kidney Axis on Kidney Disease. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Wang, F.; Jiang, H.; Liu, H.; Wei, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, L. Gut Bacterial Translocation May Aggravate Microinflammation in Hemodialysis Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; Piceno, Y.M.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Pahl, M.; Andersen, G.L.; Vaziri, N.D. Expansion of Urease- and Uricase-Containing, Indole- and p-Cresol-Forming and Contraction of Short Chain Fatty Acid-Producing Intestinal Microbiota in ESRD. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 39, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Salgado, J.; Vehaskari, V.M.; Stewart, T.; Ferris, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Blanchard, E.E.; Taylor, C.M.; Kallash, M.; Greenbaum, L.A.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota in Pediatric Patients with End Stage Renal Disease: A Midwest Pediatric Nephrology Consortium Study. Microbiome 2016, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.-K.; Lai, H.-C.; Yu, C.-J.; Liang, C.-C.; Chang, C.-T.; Kuo, H.-L.; Yang, Y.-F.; Lin, C.-C.; Lin, H.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; et al. Real-Time PCR Analysis of the Intestinal Microbiotas in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões-Silva, L.; Araujo, R.; Pestana, M.; Soares-Silva, I.; Sampaio-Maia, B. Peritoneal Microbiome in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients and the Impact of Peritoneal Dialysis Therapy. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.R.; Muthukumar, T.; Dadhania, D.; Toussaint, N.C.; Ling, L.; Pamer, E.; Suthanthiran, M. Gut Microbial Community Structure and Complications Following Kidney Transplantation: A Pilot Study. Transplantation 2014, 98, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarte, J.C.; Douwes, R.M.; Hu, S.; Vich Vila, A.; Eisenga, M.F.; van Londen, M.; Gomes-Neto, A.W.; Weersma, R.K.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Bakker, S.J.L. Characteristics and Dysbiosis of the Gut Microbiome in Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossola, M.; Sanguinetti, M.; Scribano, D.; Zuppi, C.; Giungi, S.; Luciani, G.; Torelli, R.; Posteraro, B.; Fadda, G.; Tazza, L. Circulating Bacterial-Derived DNA Fragments and Markers of Inflammation in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly-Y, M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The Microbial Metabolites, Short Chain Fatty Acids, Regulate Colonic Treg Cell Homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B.; Ławiński, J.; Olszewski, R.; Ciałkowska-Rysz, A.; Gluba-Brzózka, A. The Impact of CKD on Uremic Toxins and Gut Microbiota. Toxins 2021, 13, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.C.; Sirich, T.L. Indoxyl Sulfate—Review of Toxicity and Therapeutic Strategies. Toxins 2016, 8, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T. Removal of Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins by Haemodialysis. Blood Purif. 2013, 35 (Suppl. S2), 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, X.; Landeras, V.; Dobre, M.A.; DeOreo, P.; Meyer, T.W.; Hostetter, T.H. Mechanism of Prominent Trimethylamine Oxide (TMAO) Accumulation in Hemodialysis Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, B.; Cataldi, M.; Riccio, E.; Grumetto, L.; Pota, A.; Borrelli, S.; Memoli, A.; Barbato, F.; Argentino, G.; Salerno, G.; et al. Plasma P-Cresol Lowering Effect of Sevelamer in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: Evidence from a Cross-Sectional Observational Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xie, T.; Bao, M.; Zhang, P.; Jiao, X.; Zou, J.; Ding, X.; Cao, X.; Yu, X. Serum Concentration of Indoxyl Sulfate in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients and Low-Flux Hemodialysis Patients. Blood Purif. 2019, 48, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghai Arassi, M.; Zeller, G.; Karcher, N.; Zimmermann, M.; Toenshoff, B. The Gut Microbiome in Solid Organ Transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2020, 24, e13866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial Signature of Dysbiosis in Gut Microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liabeuf, S.; Cheddani, L.; Massy, Z.A. Uremic Toxins and Clinical Outcomes: The Impact of Kidney Transplantation. Toxins 2018, 10, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, R.; Evenepoel, P.; de Loor, H.; Bammens, B.; Claes, K.; Sprangers, B.; Naesens, M.; Kuypers, D.; Augustijns, P.; Meijers, B. The Influence of Renal Transplantation on Retained Microbial-Human Co-Metabolites. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.; Kuo, K.; Wu, C.; Tarng, D. Indoxyl Sulfate: A Novel Cardiovascular Risk Factor in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graboski, A.L.; Redinbo, M.R. Gut-Derived Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.-W.; Hsu, K.-H.; Lee, C.-C.; Sun, C.-Y.; Hsu, H.-J.; Tsai, C.-J.; Tzen, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, M.-S. P-Cresyl Sulphate and Indoxyl Sulphate Predict Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chiu, Y.-W.; Baldanzi, G.; Huang, J.-C.; Liang, S.-S.; Lee, S.-C.; Chen, S.-C.; Hsu, Y.-L.; Kuo, M.-C.; et al. The Relationship of Indoxyl Sulfate and P-Cresyl Sulfate with Target Cardiovascular Proteins in Hemodialysis Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, M.K.; Middel, I.R.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; Bots, M.L.; Verhaar, M.C.; Masereeuw, R.; Grooteman, M.P.; Nubé, M.J.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Blankestijn, P.J.; et al. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins in Hemodialysis Patients Relate to Residual Kidney Function, Are Not Influenced by Convective Transport, and Do Not Relate to Outcome. Toxins 2020, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, Z.; Ma, T.; Nie, J.; Dong, J. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease Receiving Peritoneal Dialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2021, 8968608211051809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, F.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhong, X.; Gong, N.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tian, J.; et al. Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Increases Peritoneal Inflammation and Peritonitis Risk in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Transl. Res. 2022, 240, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J.; Pan, C.-F.; Chuang, C.-K.; Liu, H.-L.; Sun, F.-J.; Wang, T.-J.; Chen, H.-H.; Wu, C.-J. Association of Indoxyl Sulfate with Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 347, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Liu, C.H.; Tzianabos, A.O.; Kasper, D.L. An Immunomodulatory Molecule of Symbiotic Bacteria Directs Maturation of the Host Immune System. Cell 2005, 122, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, M.T.; Cosola, C.; Ranieri, E.; Gesualdo, L. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins and Immunity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2325, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletinck, A.; Glorieux, G.; Schepers, E.; Cohen, G.; Gondouin, B.; Van Landschoot, M.; Eloot, S.; Rops, A.; Van de Voorde, J.; De Vriese, A.; et al. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins Stimulate Crosstalk between Leukocytes and Vessel Wall. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1981–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, M.L.V.; Bonan, N.B.; Dias, G.; Brehm, F.; Steiner, T.M.; Souza, W.M.; Stinghen, A.E.M.; Barreto, F.C.; Elifio-Esposito, S.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; et al. P-Cresyl Sulfate Affects the Oxidative Burst, Phagocytosis Process, and Antigen Presentation of Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 263, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiba, T.; Kawakami, K.; Sasaki, T.; Makino, I.; Kato, I.; Kobayashi, T.; Uchida, K.; Kaneko, K. Effects of Intestinal Bacteria-Derived p-Cresyl Sulfate on Th1-Type Immune Response In Vivo and In Vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 274, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Katsuki, S.; Chen, M.; Decano, J.L.; Halu, A.; Lee, L.H.; Pestana, D.V.S.; Kum, A.S.T.; Kuromoto, R.K.; Golden, W.S.; et al. Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate Promotes Pro-Inflammatory Macrophage Activation via the Interplay of OATP2B1 and Dll4-Notch Signaling. Circulation 2019, 139, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Saldanha, J.F.; Yi, D.; Mafra, D.; Fouque, D.; Soulage, C.O. The Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate Exacerbates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Inflammation in 3T3-L1 Adipose Cells. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaier, M.; Leick, A.; Uhlmann, L.; Kälble, F.; Morath, C.; Eckstein, V.; Ho, A.; Mueller-Tidow, C.; Meuer, S.; Mahnke, K.; et al. End-Stage Renal Disease, Dialysis, Kidney Transplantation and Their Impact on CD4+ T-Cell Differentiation. Immunology 2018, 155, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tourountzis, T.; Lioulios, G.; Fylaktou, A.; Moysidou, E.; Papagianni, A.; Stangou, M. Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease. Life 2022, 12, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101513
Tourountzis T, Lioulios G, Fylaktou A, Moysidou E, Papagianni A, Stangou M. Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease. Life. 2022; 12(10):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101513
Chicago/Turabian StyleTourountzis, Theodoros, Georgios Lioulios, Asimina Fylaktou, Eleni Moysidou, Aikaterini Papagianni, and Maria Stangou. 2022. "Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease" Life 12, no. 10: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101513
APA StyleTourountzis, T., Lioulios, G., Fylaktou, A., Moysidou, E., Papagianni, A., & Stangou, M. (2022). Microbiome in Chronic Kidney Disease. Life, 12(10), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101513






