Low Levels of Serum Fetuin-A and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Correlate with Lipoprotein Subfractions in Morbid Obese and Lean Non-Diabetic Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Sample Collection and Biochemical Measurements
2.3. ELISA Measurements
2.4. Determination of PON1 Enzyme Activities
2.5. Lipoprotein Subfraction Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analyses
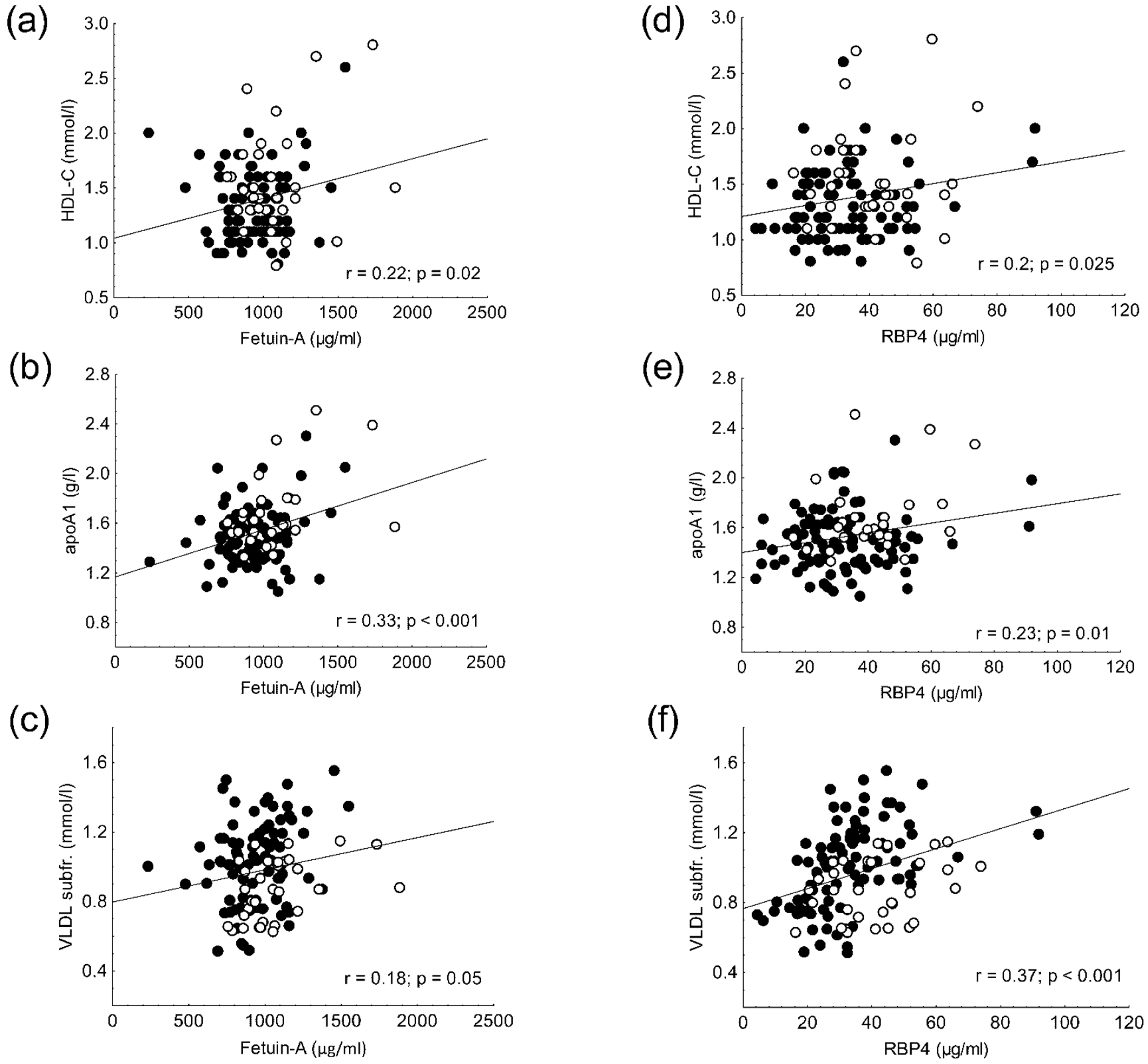
2.7. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Satish, M.; Saxena, S.K.; Agrawal, D.K. Adipokine Dysregulation and Insulin Resistance with Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease: Metabolic Syndrome or Independent Sequelae? J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2019, 12, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.N.; Teran-Garcia, M. From infancy to aging: Biological and behavioral modifiers of Fetuin-A. Biochimie 2016, 124, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roumeliotis, S.; Roumeliotis, A.; Dounousi, E.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Liakopoulos, V. Biomarkers of vascular calcification in serum. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 98, 91–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Cai, W.J.; Chang, X.Y.; Li, J.; Su, X.H.; Zhu, L.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Sun, K. Association between fetuin-A levels with insulin resistance and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Rep. 2014, 2, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Himmetoglu, S.; Teksoz, S.; Zengin, K.; Yesim, T.; Taskın, M.; Dincer, Y. Serum levels of fetuin A and 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in morbidly obese subjects. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2013, 121, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, F.; Ahsan, N.; Nasim, A.; Alam, F. Association of fetuin-A with dyslipidemia and insulin resistance in type-II Diabetics of Pakistani population. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dogru, T.; Genc, H.; Tapan, S.; Aslan, F.; Ercin, C.N.; Ors, F.; Kara, M.; Sertoglu, E.; Karslioglu, Y.; Bagci, S.; et al. Plasma fetuin-A is associated with endothelial dysfunction and subclinical atherosclerosis in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 78, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Wen, S.W.; Bestman, P.L.; Kaminga, A.C.; Acheampong, K.; Liu, A. Fetuin-A in Metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi-Noori, E.; Salehi, N.; Mozafari, H.; Elieh Ali Komi, D.; Saidi, M.; Bahrehmand, F.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Elahirad, S.; Moini, A.; Kiani, A. Association of AHSG gene polymorphisms with serum Fetuin-A levels in individuals with cardiovascular calcification in west of Iran. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychter, A.M.; Skrzypczak-Zielińska, M.; Zielińska, A.; Eder, P.; Souto, E.B.; Zawada, A.; Ratajczak, A.E.; Dobrowolska, A.; Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. Is the Retinol-Binding Protein 4 a Possible Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Diseases in Obesity? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yin, S.; Lin, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, N.; Bai, X.; Ke, Q.; Shen, J.; You, L.; Lin, X.; et al. Association of Serum Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels and the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes in Subjects With Prediabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nono Nankam, P.A.; Blüher, M. Retinol-binding protein 4 in obesity and metabolic dysfunctions. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 531, 111312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, I.; Straczkowski, M.; Adamska, A.; Nikolajuk, A.; Karczewska-Kupczewska, M.; Otziomek, E.; Górska, M. Serum retinol binding protein 4 is related to insulin resistance and nonoxidative glucose metabolism in lean and obese women with normal glucose tolerance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2786–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Si, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Sun, L. The correlation of retinol-binding protein-4 and lipoprotein combine index with the prevalence and diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome. Heart Vessel. 2020, 35, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somodi, S.; Seres, I.; Lőrincz, H.; Harangi, M.; Fülöp, P.; Paragh, G. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Level Correlates with Lipoprotein Subfractions in Obese Nondiabetic Subjects. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 9596054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubinow, K.B.; Henderson, C.M.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Himmelfarb, J.; de Boer, I.H.; Vaisar, T.; Kestenbaum, B.; Hoofnagle, A.N. Kidney function is associated with an altered protein composition of high-density lipoprotein. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Kern, S.; Birner-Grünberger, R.; Curcic, S.; Heinemann, A.; Marsche, G. Refined purification strategy for reliable proteomic profiling of HDL. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lőrincz, H.; Katkó, M.; Harangi, M.; Somodi, S.; Gaál, K.; Fülöp, P.; Paragh, G.; Seres, I. Strong correlations between circulating chemerin levels and lipoprotein subfractions in nondiabetic obese and nonobese subjects. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefner, D.M.; Hodel, S.D.; O’Brien, J.F.; Branum, E.L.; Sun, D.; Meissner, I.; McConnell, J.P. Development of a rapid, quantitative method for LDL subfractionation with use of the Quantimetrix Lipoprint LDL System. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.C.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.W. Predominance of small dense LDL differentiates metabolically unhealthy from metabolically healthy overweight adults in Korea. Metabolism 2014, 63, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.S.; Heink, A.; Sexmith, H.; Dolan, L.M.; Gordon, S.M.; Otvos, J.D.; Melchior, J.T.; Elder, D.A.; Khoury, J.; Geh, E.; et al. Obesity is associated with an altered HDL subspecies profile among adolescents with metabolic disease. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woudberg, N.J.; Goedecke, J.H.; Blackhurst, D.; Frias, M.; James, R.; Opie, L.H.; Lecour, S. Association between ethnicity and obesity with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) function and subclass distribution. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, Y.S.; Kang, M.J.; Oh, Y.J.; Baek, J.W.; Yang, S.; Hwang, I.T. Fetuin-A as an Alternative Marker for Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk in Prepubertal Children. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismail, N.A.; Ragab, S.; El Dayem, S.M.; Elbaky, A.A.; Salah, N.; Hamed, M.; Assal, H.; Koura, H. Fetuin-A levels in obesity: Differences in relation to metabolic syndrome and correlation with clinical and laboratory variables. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadir, A.; Kavalakatt, S.; Madhu, D.; Hammad, M.; Devarajan, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Tiss, A. Fetuin-A levels are increased in the adipose tissue of diabetic obese humans but not in circulation. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismail, T.A.; Soliman, M.M.; Nassan, M.A. Molecular and immunohistochemical effects of metformin in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kadoglou, N.P.; Kottas, G.; Lampropoulos, S.; Vitta, I.; Liapis, C.D. Serum levels of fetuin-A, osteoprotegerin and osteopontin in patients with coronary artery disease: Effects of statin (HMGCoA-reductase inhibitor) therapy. Clin. Drug Investig. 2014, 34, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ix, J.H.; Shlipak, M.G.; Brandenburg, V.M.; Ali, S.; Ketteler, M.; Whooley, M.A. Association between human fetuin-A and the metabolic syndrome: Data from the Heart and Soul Study. Circulation 2006, 113, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Lamendola, C.; Ariel, D.; Abbasi, F.; Kim, S.H.; Cardell, J.; Tomasso, V.; Xu, S.; Patel, S.; Mojaddidi, H.; et al. Usefulness of fetuin-A to predict risk for cardiovascular disease among patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Lee, H.; Zivkovic, A.M.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Rivera, N.; German, J.B.; Lebrilla, C.B. Glycomic analysis of high density lipoprotein shows a highly sialylated particle. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Retinol binding protein 4 correlates with and is an early predictor of carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J. Biomed. Res. 2015, 29, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wessel, H.; Saeed, A.; Heegsma, J.; Connelly, M.A.; Faber, K.N.; Dullaart, R.P.F. Plasma Levels of Retinol Binding Protein 4 Relate to Large VLDL and Small LDL Particles in Subjects with and without Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocha, M.; Bañuls, C.; Bellod, L.; Rovira-Llopis, S.; Morillas, C.; Solá, E.; Víctor, V.M.; Hernández-Mijares, A. Association of serum retinol binding protein 4 with atherogenic dyslipidemia in morbid obese patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Xu, A.; Hui, X.; Zhou, P.; Li, X.; Zhong, H.; Tang, W.; Huang, G.; Zhou, Z. Circulating lipocalin-2 and retinol-binding protein 4 are associated with intima-media thickness and subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhang, K.Z.; Yan, J.J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.Y.; Sun, H.X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, C.; He, H.W.; et al. Serum retinol-binding protein 4 as a predictor of cardiovascular events in elderly patients with chronic heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kailemia, M.J.; Wei, W.; Nguyen, K.; Beals, E.; Sawrey-Kubicek, L.; Rhodes, C.; Zhu, C.; Sacchi, R.; Zivkovic, A.M.; Lebrilla, C.B. Targeted Measurements of O- and N-Glycopeptides Show That Proteins in High Density Lipoprotein Particles Are Enriched with Specific Glycosylation Compared to Plasma. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Obese | Control | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects (n) | 100 | 32 | |
| Female (n, %) | 83 (83) | 27 (84) | 0.8 |
| Male (n, %) | 17 (17) | 5 (16) | 0.8 |
| Age (years) | 44.7 ± 12.5 | 41.8 ± 6 | 0.2 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 42.5 ± 8.1 | 24.5 ± 2.5 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 122.3 ± 16.7 | 83.6 ± 9.3 | <0.001 |
| Medications | |||
| ACEI/ARB (n, %) | 49 (49) | 0 (0) | |
| CCB (n, %) | 22 (22) | 0 (0) | |
| Statin (n, %) | 14 (14) | 0 (0) | |
| Metformin (n, %) | 12 (12) | 0 (0) | |
| Diuretics (n, %) | 33 (33) | 0 (0) | |
| Laboratory parameters | |||
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 8.1 (3.5–15.7) | 1.6 (0.6–2.9) | <0.001 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| OGTT 120 min (mmol/L) | 6.5 ± 1.8 | na | |
| Fasting insulin (mU/L) | 17.6 ± 9.5 | na | |
| HOMA-IR | 3.6 (2.5–5.5) | na | |
| C-peptide (pmol/L) | 1110 (775–1394) | na | |
| Fructoseamine (μmol/L) | 224.5 ± 28.2 | 229 ± 11.7 | 0.4 |
| Haemoglobin A1C (%) | 5.6 (5.2–6.1) | 5 (4.8–5.3) | <0.001 |
| GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 90 (90–90) | 90 (90–90) | 0.2 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.1 ± 1.6 | 4.6 ± 1.3 | 0.2 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 66.3 ± 17.5 | 68.3 ± 14.5 | 0.6 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.0 ± 0.8 | 5.1 ± 0.8 | 0.7 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 0.002 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.2 ± 0.7 | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 0.04 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.45 (1.1–1.95) | 1 (0.7–1.4) | <0.001 |
| Apolipoprotein AI (g/L) | 1.48 ± 0.24 | 1.68 ± 0.3 | 0.003 |
| Apolipoprotein B (g/L) | 0.87 ± 0.2 | 0.94 ± 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone (mU/L) | 1.95 (1.48–2.67) | 1.94 (1.26–2.11) | 0.1 |
| AST (U/L) | 20 (17–27) | 18 (16.5–21) | 0.02 |
| GGT (U/L) | 28 (19–43) | 19 (16–28.5) | 0.01 |
| ALT (U/L) | 25 (18–32) | 17 (12.5–23.5) | <0.001 |
| PON1 paraoxonase activity (U/L) | 56.7 (37.3–139.2) | 83 (47.9–167.4) | 0.04 |
| PON1 salt stimulated paraoxonase activity (U/L) | 149.8 (105.1–293.3) | 169.4 (97.3–297.4) | 0.9 |
| PON1 arylesterase activity (U/L) | 124.3 ± 22.1 | 135.3 ± 36.8 | 0.04 |
| Obese | Control | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDL Subfraction Analysis | |||
| VLDL subfraction (%) | 19.9 ± 4.3 | 17.1 ± 2.3 | <0.001 |
| IDL subfraction (%) | 25.0 ± 3.9 | 29.6 ± 5.0 | <0.001 |
| Large LDL subfraction (%) | 28.0 ± 4.7 | 21.1 ± 5.8 | <0.001 |
| Small-dense LDL subfraction (%) | 1.3 (0.0–2.4) | 0.5 (0.0–0.85) | <0.01 |
| VLDL subfraction (mmol/L) | 1.004 ± 0.243 | 0.866 ± 0.172 | <0.01 |
| IDL subfraction (mmol/L) | 1.242 ± 0.296 | 1.508 ± 0.373 | <0.001 |
| Large LDL subfraction (mmol/L) | 1.417 ± 0.359 | 1.074 ± 0.351 | <0.001 |
| Small-dense LDL subfraction (mmol/L) | 0.069 (0.0–0.129) | 0.028 (0.0–0.046) | <0.01 |
| Mean LDL size (nm) | 27.1 (26.8–27.3) | 27.35 (27.2–27.5) | <0.001 |
| HDL subfraction analysis | |||
| Large HDL subfraction (%) | 23.2 ± 7.1 | 29.8 ± 9.0 | <0.001 |
| Intermediate HDL subfraction (%) | 51.2 ± 3.8 | 50.8 ± 4.7 | 0.6 |
| Small HDL subfraction (%) | 25.6 ± 6.7 | 19.3 ± 5.3 | <0.001 |
| Large HDL subfraction (mmol/L) | 0.308 ± 0.143 | 0.495 ± 0.287 | <0.001 |
| Intermediate HDL subfraction (mmol/L) | 0.679 ± 0.171 | 0.774 ± 0.169 | <0.01 |
| Small HDL subfraction (mmol/L) | 0.340 ± 0.108 | 0.287 ± 0.062 | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lőrincz, H.; Csige, I.; Harangi, M.; Szentpéteri, A.; Seres, I.; Szabó, Z.; Paragh, G.; Somodi, S. Low Levels of Serum Fetuin-A and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Correlate with Lipoprotein Subfractions in Morbid Obese and Lean Non-Diabetic Subjects. Life 2021, 11, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090881
Lőrincz H, Csige I, Harangi M, Szentpéteri A, Seres I, Szabó Z, Paragh G, Somodi S. Low Levels of Serum Fetuin-A and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Correlate with Lipoprotein Subfractions in Morbid Obese and Lean Non-Diabetic Subjects. Life. 2021; 11(9):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090881
Chicago/Turabian StyleLőrincz, Hajnalka, Imre Csige, Mariann Harangi, Anita Szentpéteri, Ildikó Seres, Zoltán Szabó, György Paragh, and Sándor Somodi. 2021. "Low Levels of Serum Fetuin-A and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Correlate with Lipoprotein Subfractions in Morbid Obese and Lean Non-Diabetic Subjects" Life 11, no. 9: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090881
APA StyleLőrincz, H., Csige, I., Harangi, M., Szentpéteri, A., Seres, I., Szabó, Z., Paragh, G., & Somodi, S. (2021). Low Levels of Serum Fetuin-A and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Correlate with Lipoprotein Subfractions in Morbid Obese and Lean Non-Diabetic Subjects. Life, 11(9), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090881









