Transcription Factor Activity Inference in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Selection and Preprocessing
2.2. Inferring Transcription Factor Activities
2.3. Subgroup Identification
2.4. Differential Activity and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of TF Activity Revealed Two Main Groups of SLE Patients
3.2. TFs with Differential Activity in SLE and Healthy Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moulton, V.R.; Suarez-Fueyo, A.; Meidan, E.; Li, H.; Mizui, M.; Tsokos, G.C. Pathogenesis of Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cellular Perspective. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasef, S.Z.Y. Gender differences in systemic lupus erythematosus. Gend. Med. 2004, 1, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikdashi, J.; Nived, O. Measuring disease activity in adults with systemic lupus erythematosus: The challenges of administrative burden and responsiveness to patient concerns in clinical research. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, B.; Olsen, N.J. Systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis and management. Rheumatology 2016, 56, i3–i13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruel, M.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E. The genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus: What are the risk factors and what have we learned. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 74, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambino, C.M.; Di Bona, D.; Aiello, A.; Carru, C.; Duro, G.; Guggino, G.; Ferrante, A.; Zinellu, A.; Caruso, C.; Candore, G.; et al. HLA-C1 ligands are associated with increased susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum. Immunol. 2018, 79, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechler, E.C.; Batliwalla, F.M.; Karypis, G.; Gaffney, P.M.; Ortmann, W.A.; Espe, K.J.; Shark, K.B.; Grande, W.J.; Hughes, K.M.; Kapur, V.; et al. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2610–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, L.; Palucka, A.K.; Arce, E.; Cantrell, V.; Borvak, J.; Banchereau, J.; Pascual, V. Interferon and Granulopoiesis Signatures in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Blood. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchereau, R.; Hong, S.; Cantarel, B.; Baldwin, N.; Baisch, J.; Edens, M.; Cepika, A.-M.; Acs, P.; Turner, J.; Anguiano, E.; et al. Personalized Immunomonitoring Uncovers Molecular Networks that Stratify Lupus Patients. Cell 2016, 165, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Domínguez, D.; Martorell-Marugán, J.; Goldman, D.; Petri, M.; Carmona-Sáez, P.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E. Stratification of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients into Three Groups of Disease Activity Progression According to Longitudinal Gene Expression. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barturen, G.; Babaei, S.; Català-Moll, F.; Martínez-Bueno, M.; Makowska, Z.; Martorell-Marugán, J.; Carmona-Sáez, P.; Toro-Domínguez, D.; Carnero-Montoro, E.; Teruel, M.; et al. Integrative Analysis Reveals a Molecular Stratification of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 2326–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozmorov, M.G.; Wren, J.D.; E Alarcón-Riquelme, M. Epigenomic elements enriched in the promoters of autoimmunity susceptibility genes. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, J.B.; Chen, X.; Pujato, M.; Miller, D.; Maddox, A.; Forney, C.; Magnusen, A.F.; Lynch, A.; Chetal, K.; Yukawa, M.; et al. Transcription factors operate across disease loci, with EBNA2 implicated in autoimmunity. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaghir, A.; Toffalini, F.; Knoops, L.; Kallin, A.; Van Helden, J.; Demoulin, J.-B. Transcription factor regulation can be accurately predicted from the presence of target gene signatures in microarray gene expression data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, M.M.; Bleda, M.; Carbonell-Caballero, J.; Dopazo, J. The pan-cancer pathological regulatory landscape. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Alonso, L.M.; Iorio, F.; Matchan, A.; A Fonseca, N.; Jaaks, P.; Peat, G.; Pignatelli, M.; Falcone, F.; Benes, C.H.; Dunham, I.; et al. Transcription Factor Activities Enhance Markers of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Alonso, L.; Holland, C.H.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Turei, D.; Saez-Rodriguez, J. Benchmark and integration of resources for the estimation of human transcription factor activities. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Diaz, J.; Isenberg, D.; Ramsey-Goldman, R. Measures of adult systemic lupus erythematosus: Updated Version of British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG 2004), European Consensus Lupus Activity Measurements (ECLAM), Systemic Lupus Activity Measure, Revised (SLAM-R), Systemic Lupus Activity Questi. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, S37–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zollars, E.; Courtney, S.M.; Wolf, B.J.; Allaire, N.; Ranger, A.; Hardiman, G.; Petri, M. Clinical Application of a Modular Genomics Technique in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Progress towards Precision Medicine. Int. J. Genom. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Narayan, R.; Corsello, S.M.; Peck, D.D.; Natoli, T.E.; Lu, X.; Gould, J.; Davis, J.F.; Tubelli, A.A.; Asiedu, J.K.; et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles. Cell 2017, 171, 1437–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, P.; Khalifa, C.; Defour, J.-P.; Latinne, D.; Van Pel, M.-C.; De Kock, M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zhao, X.; Bai, J.; Gery, S.; Sun, H.; Lin, D.-C.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Z.; Mack, L.; Yang, H.; et al. Circadian clock cryptochrome proteins regulate autoimmunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12548–12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.-J.; Huang, S.-H.; Chen, S.-J.; Wang, C.-H.; Chang, D.-M.; Sytwu, H.-K. Modulation by Melatonin of the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 11742–11766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolgin, E. Lupus in crisis: As failures pile up, clinicians call for new tools. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E. New Attempts to Define and Clarify Lupus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.K.; Kaplan, M.J. The role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulos, D.; Proudman, S.M.; Metcalf, R.G.; McWilliams, L.; Hall, C.; Wicks, I.P. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in early rheumatoid arthritis and its ability to predict subsequent failure of triple therapy. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, E.; Zanghì, A.; Romano, A.; Sciandra, M.; Palumbo, G.A.M.; Patti, F. The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio is Related to Disease Activity in Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Cells 2019, 8, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.L.; Paliogiannis, P.; Castagna, F.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; Passiu, G.; Zinellu, A. Meta-analysis of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaki, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kassai, Y.; Takeshita, M.; Murota, A.; Kondo, Y.; Ando, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Okuzono, Y.; Takiguchi, M.; et al. Multi-omics monitoring of drug response in rheumatoid arthritis in pursuit of molecular remission. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handunnetthi, L.; Ramagopalan, S.V.; Ebers, G.C.; Knight, J.C. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class II gene expression, genetic variation and disease. Genes Immun. 2009, 11, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambayashi, T.; Laufer, T.M. Atypical MHC class II-expressing antigen-presenting cells: Can anything replace a dendritic cell? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, J.C.; Zavolan, M. Patterns of ribosomal protein expression specify normal and malignant human cells. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goropevšek, A.; Holcar, M.; Avčin, T. The Role of STAT Signaling Pathways in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 52, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, L.; Song, L.; Ephrem, E.; Petri, M.; Sullivan, K.E. Interferon regulatory factor 1 marks activated genes and can induce target gene expression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 67, 785–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.-C.; Chang, J.-H.; Jin, J. Regulation of nuclear factor-κB in autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.-M.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Tsokos, G.C. Targeting Syk in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatikos, A.P.; Ghosh, D.; Devlin, A.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Tsokos, G.C. Spleen Tyrosine Kinase (Syk) Regulates Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) T Cell Signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyttaris, V.C.; Zhang, Z.; Kampagianni, O.; Tsokos, G.C. Calcium signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus T cells: A treatment target. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischbutter, S.; Schultheis, K.; Pätzel, M.; Radbruch, A.; Baumgrass, R. Evaluation of calcineurin/NFAT inhibitor selectivity in primary human Th cells using bar-coding and phospho-flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2012, 81, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C. Calcineurin inhibitors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukundan, L.; Odegaard, J.I.; Morel, C.R.; Heredia, J.E.; Mwangi, J.W.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Goh, Y.S.; Eagle, A.R.; Dunn, S.E.; Awakuni, J.U.; et al. PPAR-δ senses and orchestrates clearance of apoptotic cells to promote tolerance. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handono, K.; Firdausi, S.N.; Pratama, M.Z.; Endharti, A.T.; Kalim, H. Vitamin A improve Th17 and Treg regulation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, L.; Luo, X.M. Retinoic Acid, Leaky Gut, and Autoimmune Diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liao, X.; Sparks, J.B.; Luo, X.M. Dynamics of Gut Microbiota in Autoimmune Lupus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7551–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Yoshida, N.; Finn, G.; Kozono, S.; Nechama, M.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Zhou, X.Z.; Tsokos, G.C.; Lu, K.P. Pin1-Targeted Therapy for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2503–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Geng, L.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Hou, Y.; Lu, L.; Shi, S.; Zeng, X.; et al. Activated NF-κB in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation Through Downregulating Smad Signaling. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, V.F.-S.; Davis-Turak, J.; Macal, M.; Huang, J.Q.; Ponomarenko, J.; Kearns, J.D.; Yu, T.; Fagerlund, R.; Asagiri, M.; Zuniga, E.I.; et al. Control of RelB during dendritic cell activation integrates canonical and noncanonical NF-κB pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lo, Y.; Chan, A.; Law, K.S.; Mok, M.Y. Rel B-modified dendritic cells possess tolerogenic phenotype and functions on lupus splenic lymphocytes in vitro. Immunology 2016, 149, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Ushiyama, C.; Suzuki, S.; Hara, M.; Shimada, N.; Sekizuka, K.; Ebihara, I.; Koide, H. Urinary Podocytes for the Assessment of Disease Activity in Lupus Nephritis. Am. J. Med Sci. 2000, 320, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemoto, K.; Takahashi, S.; Shu, Y.; Usui, J.; Tomari, S.; Yan, K.; Hamazaki, Y.; Nagata, M. Variable expression of podocyte-related markers in the glomeruloid bodies in Wilms tumor. Pathol. Int. 2003, 53, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, J.; Peng, W.; Kong, Q.; He, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, W.; Tang, X.; et al. Tacrolimus Protects Podocytes from Injury in Lupus Nephritis Partly by Stabilizing the Cytoskeleton and Inhibiting Podocyte Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, S.N.; Tellier, J.; Liao, Y.; Trezise, S.; Light, A.; O’Donnell, K.; Garrett-Sinha, L.A.; Shi, W.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Nutt, S.L. Environmental sensing by mature B cells is controlled by the transcription factors PU.1 and SpiB. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.M.; Dao, K.H.; Han, B.K.; Kornu, R.; Lakhanpal, S.; Mobley, A.B.; Li, Q.-Z.; Lian, Y.; Wu, T.; Reimold, A.M.; et al. SLE Peripheral Blood B Cell, T Cell and Myeloid Cell Transcriptomes Display Unique Profiles and Each Subset Contributes to the Interferon Signature. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Pan, J.-H.; Han, J. A critical role of E2F transcription factor 2 in proinflammatory cytokines-dependent proliferation and invasiveness of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Wu, W.; Yang, D.; Xiao, C.; Huang, M.; Long, F.; Su, Z.; Qin, M.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.Z. GATA4 regulates angiogenesis and persistence of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyssenko, V.; Lupi, R.; Marchetti, P.; Del Guerra, S.; Orho-Melander, M.; Almgren, P.; Sjögren, M.; Ling, C.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Lethagen, υsa-L.; et al. Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

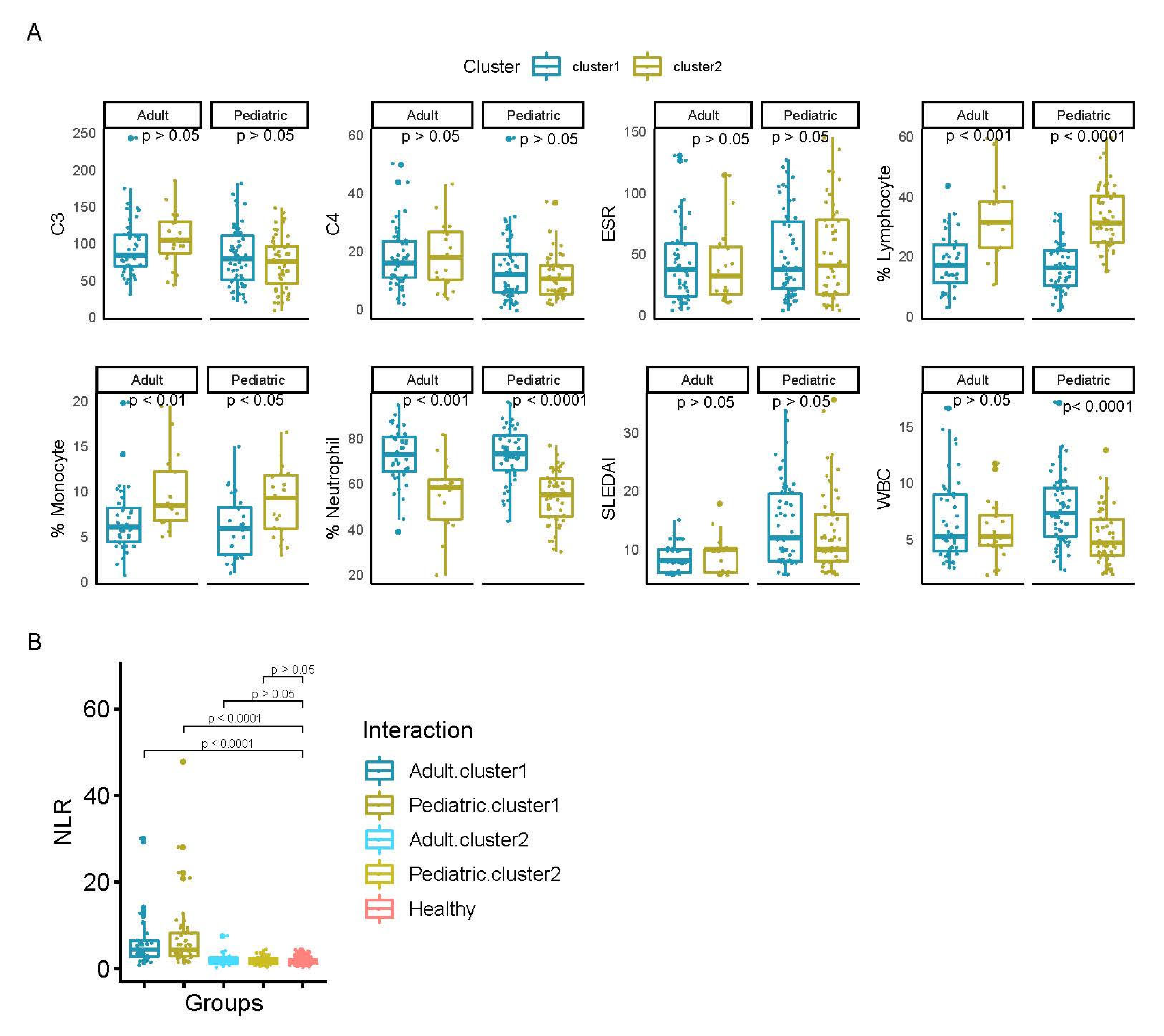
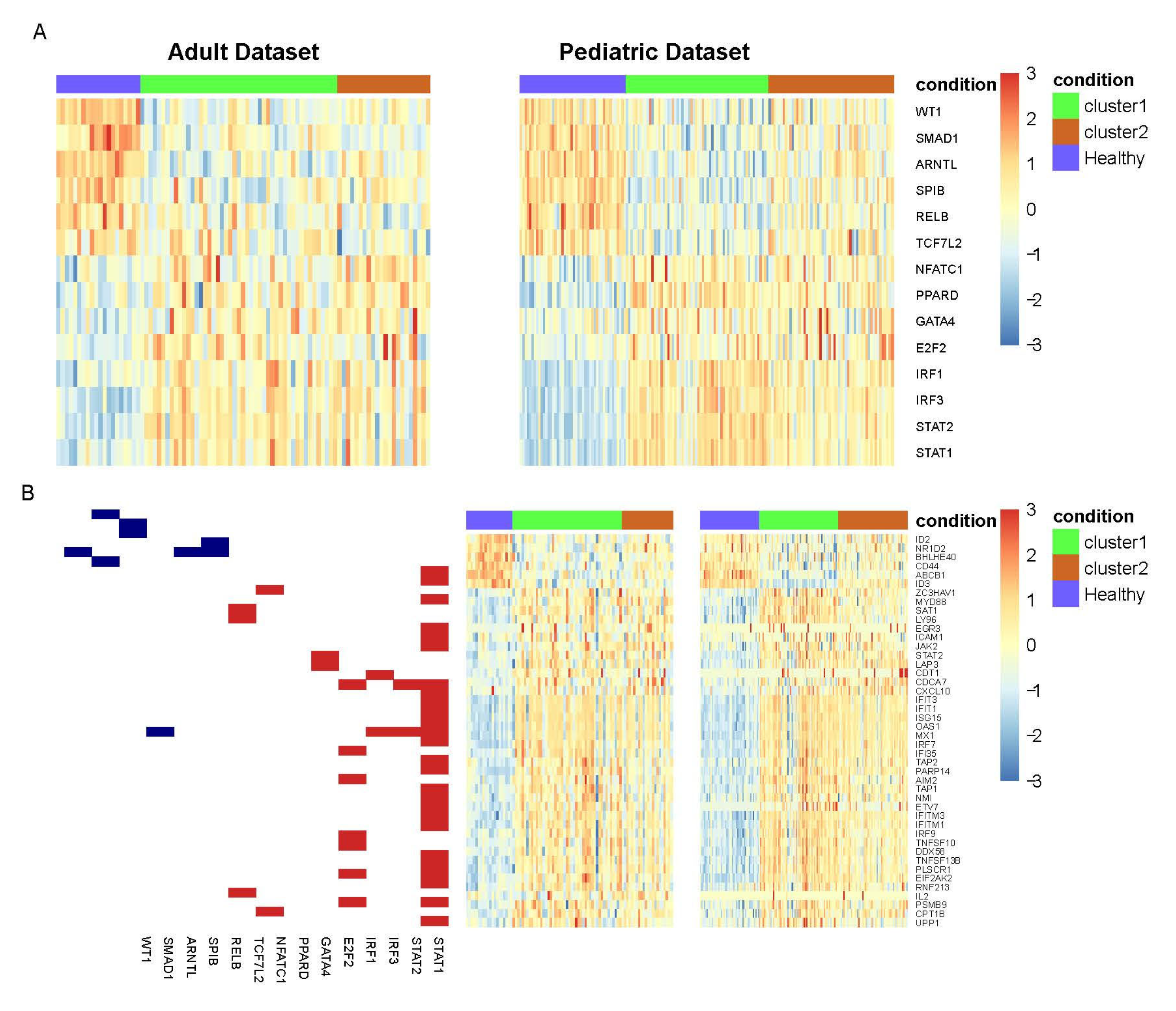
| Adult | Pediatric | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | 67 female and 2 male | 102 female and 14 male |
| SLEDAI | 8.493 ± 2.5 | 13.371 ± 6.6 |
| % Neutrophil | 67.289 ± 15.4 | 63.963 ± 14.8 |
| % Lymphocyte | 22.641 ± 12.9 | 24.808 ± 12.4 |
| % Monocyte | 7.68 ± 4.0 | 7.415 ± 3.8 |
| C3 (mg/dL) | 99.667 ± 39.0 | 78.645 ± 37.5 |
| C4 (mg/dL) | 17.87 ± 10.2 | 12.495 ± 9.5 |
| WBC (K/cu mm) | 6.396 ± 3.3 | 6.507 ± 2.9 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 41.765 ± 31.2 | 50.038 ± 37.0 |
| Proteinuria | 20 patients with proteinuria and 49 without | 69 patients with proteinuria and 47 without |
| Pyuria | 11 patients with pyuria and 58 without | 41 patients with pyuria and 75 without |
| Drug | Mechanisms of Action (MoA) | TF Target | Indication | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bezafibrate | PPAR receptor agonist | PPARD | Cholesterol | Launched |
| DG-172 | PPAR receptor inverse agonist | PPARD | Preclinical | |
| Elafibranor | PPAR receptor agonist | PPARD | Phase 3 | |
| FH-535 | PPAR receptor antagonist, WNT signaling inhibitor | PPARD | Preclinical | |
| GSK-0660 | PPAR receptor antagonist | PPARD | Preclinical | |
| GSK3787 | PPAR receptor antagonist | PPARD | Preclinical | |
| GW-0742 | PPAR receptor agonist | PPARD | Preclinical | |
| GW-501516 | PPAR receptor agonist | PPARD | Phase 2 | |
| Icosapent | Platelet aggregation inhibitor | PPARD | Hypertriglyceridemia | Launched |
| L-165041 | PPAR receptor agonist | PPARD | Preclinical | |
| Sulindac | Cyclooxygenase inhibitor | PPARD | Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis | Launched |
| Tretinoin | Retinoid receptor agonist, retinoid receptor ligand | PPARD | Leukemia | Launched |
| INCA-6 | Calcineurin inhibitor | NFATC1 | Preclinical | |
| piceatannol | SYK inhibitor | IRF3 | Preclinical | |
| CKD-712 | NFkB pathway inhibitor | STAT1 | Phase 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez-Dominguez, R.; Toro-Dominguez, D.; Martorell-Marugan, J.; Garcia-Moreno, A.; Holland, C.H.; Saez-Rodriguez, J.; Goldman, D.; Petri, M.A.; Alarcon-Riquelme, M.E.; Carmona-Saez, P. Transcription Factor Activity Inference in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Life 2021, 11, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11040299
Lopez-Dominguez R, Toro-Dominguez D, Martorell-Marugan J, Garcia-Moreno A, Holland CH, Saez-Rodriguez J, Goldman D, Petri MA, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Carmona-Saez P. Transcription Factor Activity Inference in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Life. 2021; 11(4):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11040299
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez-Dominguez, Raul, Daniel Toro-Dominguez, Jordi Martorell-Marugan, Adrian Garcia-Moreno, Christian H. Holland, Julio Saez-Rodriguez, Daniel Goldman, Michelle A. Petri, Marta E. Alarcon-Riquelme, and Pedro Carmona-Saez. 2021. "Transcription Factor Activity Inference in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Life 11, no. 4: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11040299
APA StyleLopez-Dominguez, R., Toro-Dominguez, D., Martorell-Marugan, J., Garcia-Moreno, A., Holland, C. H., Saez-Rodriguez, J., Goldman, D., Petri, M. A., Alarcon-Riquelme, M. E., & Carmona-Saez, P. (2021). Transcription Factor Activity Inference in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Life, 11(4), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11040299







