Association of Glomerular Filtration Rate and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease Patients over a 4-Year Follow-Up
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Study Design and Protocol
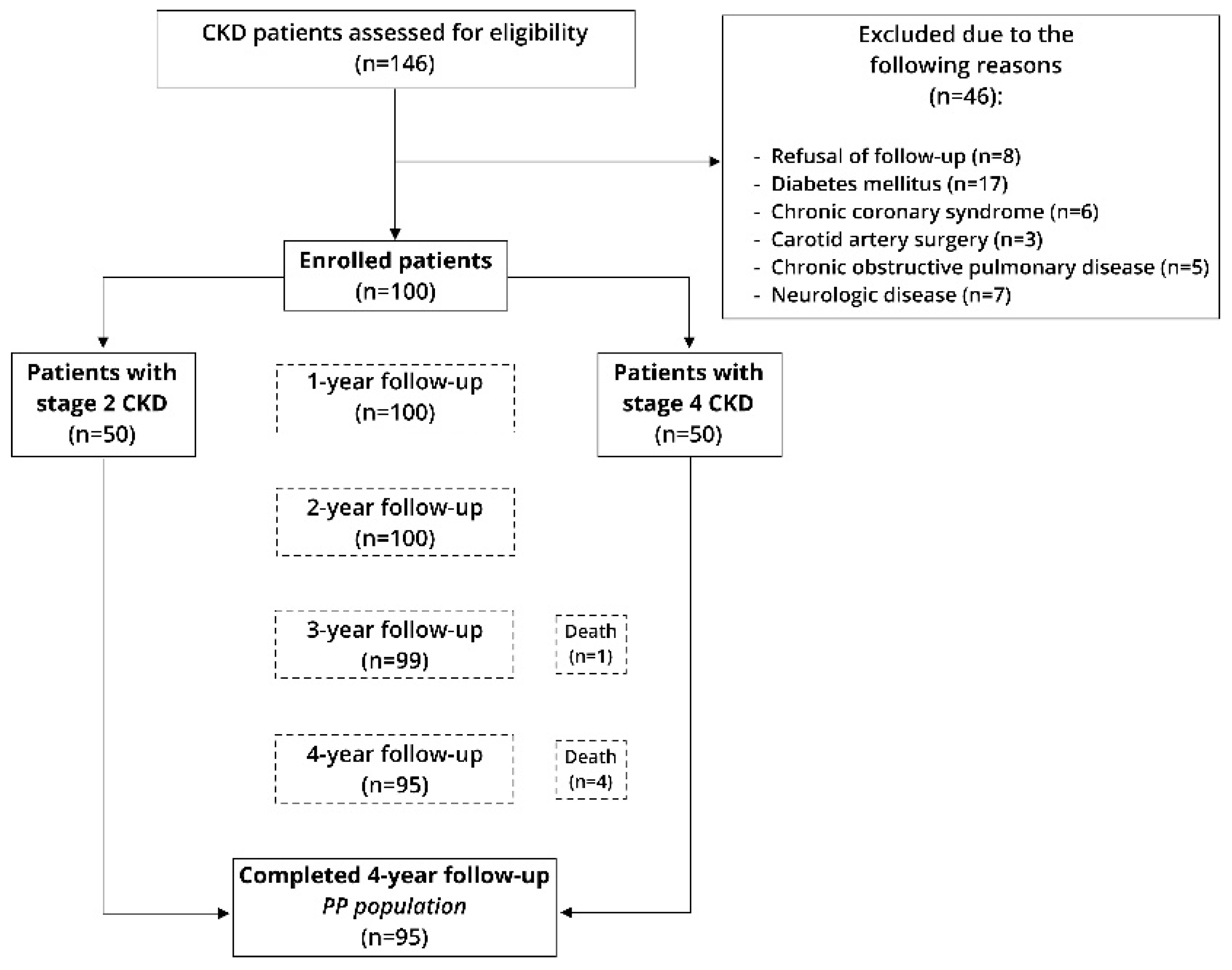
2.3. Subjects
2.4. Clinical Assessment and Anthropometric Measurements
2.5. Laboratory Analysis
2.6. Measurements of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subjects’ Characteristics
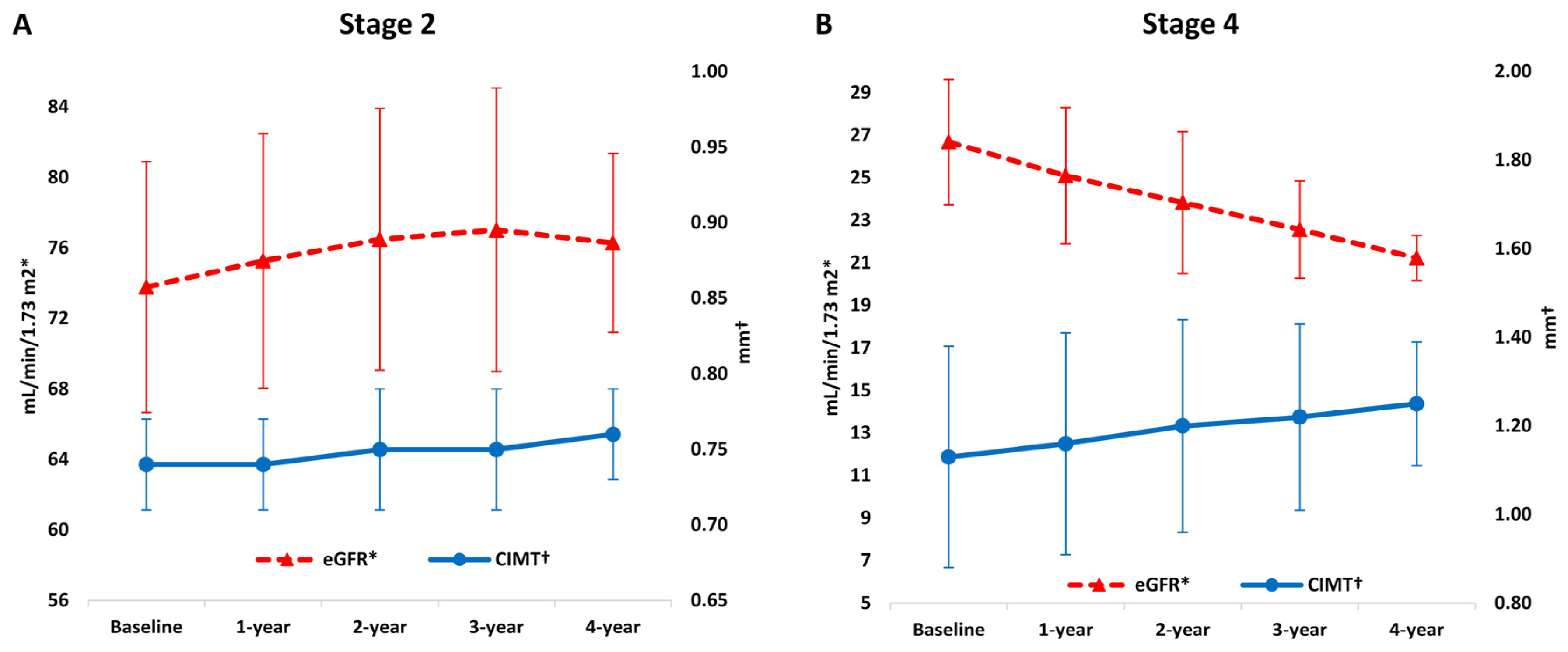
3.2. eGFR and CIMT Values
3.3. Bivariate Correlation Analysis of eGFR and CIMT Parameters during Follow-Up
3.4. Bivariate Correlation Analysis of Selected Baseline Parameters
3.5. Multivariable Linear Regression Analysis of Selected Independent Variables in the Prediction of CIMT
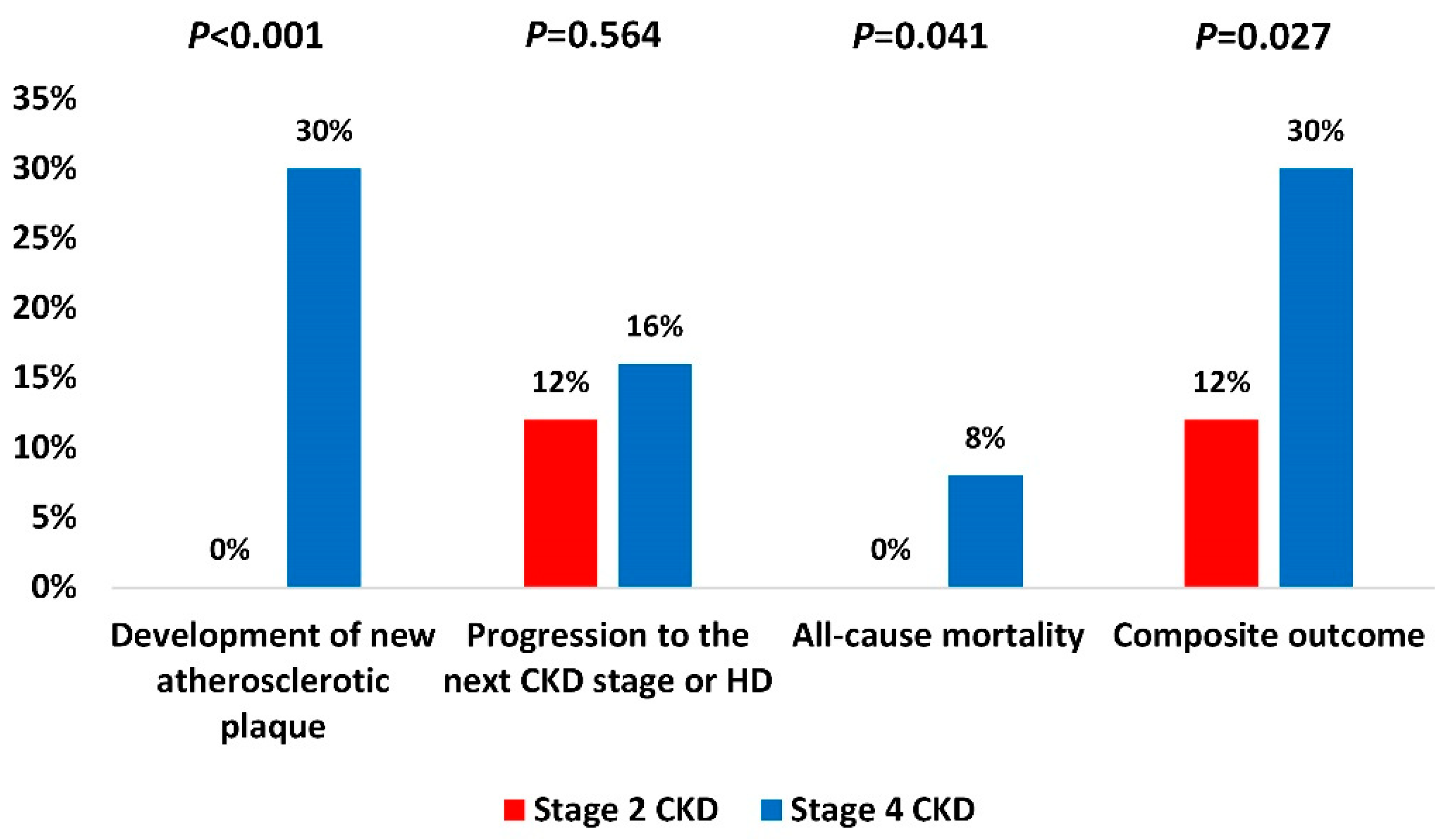
3.6. Adverse Events during Follow-Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease–A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucquemont, J.; Loubère, L.; Metzger, M.; Combe, C.; Stengel, B.; Leffondre, K.; The NephroTest Study Group. Identifying subgroups of renal function trajectories. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 32, ii185–ii193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosansky, S.J. Renal Function Trajectory Is More Important than Chronic Kidney Disease Stage for Managing Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, D.; Betriu, A.; Martinez-Alonso, M.; Vidal, T.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Fernández, E. Observational multicenter study to evaluate the prevalence and prognosis of subclinical atheromatosis in a Spanish chronic kidney disease cohort: Baseline data from the NEFRONA study. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansevoort, R.T.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Jafar, T.H.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Mann, J.F.; Matsushita, K.; Wen, C.P. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 2013, 382, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswami, J.; Bhalla, V.; Ronco, C.; Tang, W.W.; McCullough, P.A.; Blair, J.E.; Chang, T.I.; Costa, S.; Lentine, K.L.; On behalf of the American Heart Association Council on the Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease and Council on Clinical Cardiology; et al. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Classification, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e840–e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.W.; Price, J.F.; Robertson, C.; Bots, M.L.; Polak, J.F.; Poppert, H.; Kavousi, M.; Dörr, M.; Stensland, E.; Ducimetiere, P.; et al. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression and Risk of Vascular Events in People With Diabetes: Results From the PROG-IMT Collaboration. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, M.C.; Gassett, A.; Korcarz, C.E.; Gepner, A.D.; Kaufman, J.D.; Liu, K.J.; Astor, B.C.; Sheppard, L.; Kronmal, R.A.; Stein, J.H. Predictors of Carotid Thickness and Plaque Progression During a Decade. Stroke 2014, 45, 3257–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.W.; Markus, H.S.; Bots, M.L.; Rosvall, M.; Sitzer, M. Prediction of Clinical Cardiovascular Events with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness. Circulation 2007, 115, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, F.A.; Tripepi, G.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. Rate of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation Predicts Cardiovascular Events in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, C.C.; Chow, K.-M.; Woo, K.-S.; Chook, P.; Kwan, B.C.-H.; Leung, C.-B.; Li, P.K.-T. Carotid Intima Media Thickness Predicts Cardiovascular Diseases in Chinese Predialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, S. Correlation between Carotid Intima–Media Thickness and Early-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease: Results from Asymptomatic Polyvascular Abnormalities in Community Study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhajed, N.; Chandra, B.J.S.; Shetty, M.S.; Shetty, C. Correlation of carotid intimal-medial thickness with estimated glomerular filtration rate and cardiovascular risk factors in chronic kidney disease. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2014, 25, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Benedetto, F.; Mallamaci, F.; Tripepi, G.; Zoccali, C. Prognostic value of ultrasonographic measurement of carotid intima media thickness in dialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 2458–2464. [Google Scholar]
- Basiratnia, M.; Fazel, M.; Lotfi, M.; Al-Hashemi, G.H.; Fallahzadeh, M.H.; Derakhshan, A.; Salehipour, M. Subclinical atherosclerosis and related risk factors in renal transplant recipients. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, T.M.; Schneider, M.F.; Flynn, J.T.; Cox, C.; Samuels, J.; Saland, J.; White, C.T.; Furth, S.; Warady, B.A.; Mitsnefes, M. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Children with CKD: Results from the CKiD Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, I.; Poyrazoglu, H.M.; Gunduz, Z.; Ulger, H.; Yykylmaz, A.; Dusunsel, R.; Patyroglu, T.; Gurgoze, M. The relationship between circulating endothelial microparticles and arterial stiffness and atherosclerosis in children with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, M.; Wühl, E.; Jourdan, C.; Niemirska, A.; Schenk, J.P.; Jobs, K.; Grenda, R.; Wawer, Z.T.; Rajszys, P.; Mehls, O.; et al. Evolution of large-vessel arteriopathy in paediatric patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2552–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwin, M.; Wühl, E.; Jourdan, C.; Trelewicz, J.; Niemirska, A.; Fahr, K.; Jobs, K.; Grenda, R.; Wawer, Z.T.; Rajszys, P.; et al. Altered Morphologic Properties of Large Arteries in Children with Chronic Renal Failure and after Renal Transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, D.J.D.A.; Dos Santos, E.M.; Dias, R.S.C.; Calado, I.L.; Silva, G.E.B.; Lages, J.S.; Júnior, F.D.C.M.; Dos Santos, A.M.; Filho, N.S. Association between renal damage markers and carotid atherosclerosis in Afro-descendants with hypertension belonging to a minority ethnic group from Brazil. Ren. Fail. 2018, 40, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbien, A.M.; Chonchol, M.; Gnahn, H.; Sander, D. Kidney Function and Progression of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in a Community Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, A.; Roumeliotis, S.; Panagoutsos, S.; Theodoridis, M.; Argyriou, C.; Tavridou, A.; Georgiadis, G.S. Carotid intima-media thickness is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular morbidity in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 and chronic kidney disease. Ren. Fail. 2019, 41, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, M.; Chowdhury, M.N.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Islam, S.; Hasan, R.; Zakir, H.; Saeed, A.; Masum, A.S. Association of Estimated GFR (By MDRD) with the Carotid Intima Media Thickness (CIMT) in Different Stages of CKD among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Mymensingh Med. J. 2020, 29, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; Bosch, J.P.; Lewis, J.B.; Greene, T.; Rogers, N.; Roth, D.R. A More Accurate Method to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine: A New Prediction Equation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touboul, P.-J.; Hennerici, M.; Meairs, S.; Adams, H.; Amarenco, P.; Bornstein, N.; Csiba, L.; Desvarieux, M.; Ebrahim, S.; Fatar, M.; et al. Mannheim Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Consensus (2004–2006). Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2006, 23, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Gao, P.; Seshasai, S.R.; Gobin, R.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Ingelsson, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Selvin, E.; Stampfer, M.; et al. Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brohall, G.; Oden, A.; Fagerberg, B. Carotid artery intima-media thickness in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance: A systematic review. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscemi, S.; Geraci, G.; Massenti, F.; Costa, F.; D’Orio, C.; Rosafio, G.; Maniaci, V.; Parrinello, G. Renal function and carotid atherosclerosis in adults with no known kidney disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.S.; Nichols, G.A.; Gullion, C.M.; Brown, J.B.; Smith, D.H. Longitudinal Follow-up and Outcomes Among a Population With Chronic Kidney Disease in a Large Managed Care Organization. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellam, T.J.; Chico, T.J. Phosphate: The new cholesterol? The role of the phosphate axis in non-uremic vascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | CKD Stage | Total (n = 100) | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 2 (n = 50) | Stage 4 (n = 50) | |||
| Age (years) | 48 (36, 54) | 60 (53, 63) | 53 (43, 62) | <0.001 1 |
| Male sex | 30 (60%) | 34 (68%) | 64 (64%) | 0.405 2 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.56 ± 2.67 | 27.46 ± 3.36 | 25.01 ± 3.90 | <0.001 3 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 127.80 ± 9.80 | 149.30 ± 18.24 | 138.55 ± 18.14 | <0.001 3 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 79.92 ± 7.64 | 82.20 ± 9.75 | 81.06 ± 8.79 | 0.196 3 |
| Active smoking | 20 (40%) | 31 (62%) | 51 (51%) | 0.085 2 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 5.04 ± 1.35 | 12.61 ± 1.73 | 8.83 ± 4.11 | <0.001 3 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 87.20 ± 12.30 | 171.48 ± 17.14 | 129.34 ± 44.88 | <0.001 3 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 73.78 ± 7.12 | 26.86 ± 2.95 | 50.32 ± 24.19 | <0.001 3 |
| CRP (mmol/L) | 2.73 ± 1.30 | 4.04 ± 1.61 | 3.39 ± 1.60 | <0.001 3 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.85 ± 1.28 | 5.85 ± 1.08 | 5.35 ± 1.28 | <0.001 3 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 0.89 ± 0.11 | 1.10 ± 0.16 | 1.00 ± 0.17 | <0.001 3 |
| LDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.55 ± 1.03 | 3.04 ± 0.68 | 2.80 ± 0.90 | 0.006 3 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.77 ± 0.54 | 2.09 ± 0.79 | 1.93 ± 0.69 | 0.023 3 |
| Serum phosphorus (mmol/L) | 1.23 ± 0.07 | 1.52 ± 0.21 | 1.37 ± 0.22 | <0.001 3 |
| Serum total calcium, corrected (mg/dL) | 10.47 ± 0.54 | 9.85 ± 0.28 | 10.16 ± 0.53 | <0.001 3 |
| Serum PTH (pg/mL) | 45.29 ± 5.58 | 157.65 ± 23.93 | 101.47 ± 59.05 | <0.001 3 |
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D (nmol/L) | 32.61 ± 2.01 | 15.81 ± 2.43 | 24.21 ± 8.73 | <0.001 3 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 42.96 ± 1.55 | 39.10 ± 1.15 | 41.03 ± 2.37 | <0.001 3 |
| Carotid intima media thickness (mm) | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 1.13 ± 0.25 | 0.96 ± 0.27 | <0.001 3 |
| Carotid atherosclerotic plaque (>1.5 mm) | 0 (0%) | 13 (26%) | 13 (13%) | <0.001 4 |
| Variables | Follow-Up 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1-Year | 2-Year | 3-Year | 4-Year | |
| Stage 2 | |||||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 73.78 ± 7.12 | 75.27 ± 7.23 | 76.49 ± 7.43 | 77.02 ± 8.05 | 76.28 ± 5.07 |
| CIMT (mm) | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 0.75 ± 0.04 | 0.75 ± 0.04 | 0.76 ± 0.03 |
| Stage 4 | |||||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 26.68 ± 2.95 | 25.10 ± 3.20 | 23.84 ±3.33 | 22.57 ± 2.29 | 21.23 ± 1.06 |
| CIMT (mm) | 1.13 ± 0.25 | 1.16 ± 0.25 | 1.20 ± 0.24 | 1.22 ± 0.21 | 1.25 ± 0.14 |
| Parameters | Parameter Estimates 1 (95% CI) | t-Value | P | Bayesian Information Criteria | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 2 | |||||
| eGFR | 1-year | 2.51 (1.10, 3.92) | 3.56 | 0.001 | 1034.25 |
| 2-year | 3.25 (2.47, 4.01) | 8.46 | <0.001 | ||
| 3-year | 2.71 (2.17, 3.25) | 10.09 | <0.001 | ||
| 4-year | 1.50 (1.24, 1.75) | 11.81 | <0.001 | ||
| CIMT | 1-year | 0.03 (−0.02, 0.04) | 5.02 | 0.340 | −1094.66 |
| 2-year | 0.01 (−0.01, 0.02) | 4.60 | 0.061 | ||
| 3-year | 0.01 (−0.01, 0.01) | 2.60 | 0.073 | ||
| 4-year | 0.01 (−0.01, 0.02) | 1.43 | 0.160 | ||
| Stage 4 | |||||
| eGFR | 1-year | −6.69 (−7.13, −6.25) | −31.79 | <0.001 | 686.67 |
| 2-year | −5.12 (−5.37, −4.87) | −41.02 | <0.001 | ||
| 3-year | −3.18 (−3.47, −2.89) | −21.96 | <0.001 | ||
| 4-year | −1.77 (−1.94, −1.60) | −20.94 | <0.001 | ||
| CIMT | 1-year | 0.20 (0.17, 0.23) | 12.28 | <0.001 | −516.70 |
| 2-year | 0.14 (0.11, 0.17) | 9.99 | <0.001 | ||
| 3-year | 0.07 (0.06, 0.09) | 9.09 | <0.001 | ||
| 4-year | 0.03 (0.02, 0.03) | 8.95 | <0.001 | ||
| r 1 (P 2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 2 | ||||
| Parameters | CIMT 1-year | CIMT 2-year | CIMT 3-year | CIMT 4-year |
| eGFR 1-year | −0.73 (<0.001) | |||
| eGFR 2-year | −0.74 (<0.001) | |||
| eGFR 3-year | −0.78 (<0.001) | |||
| eGFR 4-year | −0.36 (0.045) | |||
| Stage 4 | ||||
| Parameters | CIMT 1-year | CIMT 2-year | CIMT 3-year | CIMT 4-year |
| eGFR 1-year | −0.90 (<0.001) | |||
| eGFR 2-year | −0.89 (<0.001) | |||
| eGFR 3-year | −0.71 (<0.001) | |||
| eGFR 4-year | −0.44 (0.006) | |||
| r 1 (P 2) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Baseline eGFR | Baseline CIMT | BMI | Cholesterol | CRP | Calcium | 25-hydroxyvitamin D | PTH | Phosphorus |
| Baseline eGFR | −0.77 (<0.001) | −0.63 (<0.001) | 0.44 (<0.001) | −0.37 (<0.001) | 0.57 (<0.001) | 0.95 (<0.001) | −0.94 (<0.001) | −0.67 (<0.001) | |
| Baseline CIMT | 0.39 (<0.001) | 0.32 (0.002) | 0.25 (0.020) | −0.45 (<0.001) | −0.73 (<0.001) | 0.72 (<0.001) | 0.46 (<0.001) | ||
| BMI | 0.23 (0.023) | 0.27 (0.006) | −0.37 (<0.001) | −0.62 (<0.001) | 0.57 (<0.001) | 0.50 (<0.001) | |||
| Cholesterol | 0.11 (0.265) | −0.20 (0.043) | −0.40 (<0.001) | 0.33 (0.001) | 0.19 (0.059) | ||||
| CRP | −0.31 (0.002) | −0.40 (<0.001) | 0.35 (<0.001) | 0.33 (0.001) | |||||
| Calcium | 0.57 (<0.001) | −0.58 (<0.001) | −0.33 (0.001) | ||||||
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D | −0.94 (<0.001) | −0.67 (<0.001) | |||||||
| PTH | 0.68 (0.001) | ||||||||
| Parameters | B 1 (t 2) | P | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline eGFR | −0.85 (−8.27) | <0.001 | R2 adjusted = 0.590 F ratio = 21.87 P < 0.001 |
| Age | 0.11 (1.20) | 0.235 | |
| BMI | −0.17 (−1.75) | 0.085 | |
| Systolic blood pressure | 0.03 (0.38) | 0.704 | |
| LDL-cholesterol | −0.07 (−0.96) | 0.341 | |
| CRP | −0.04 (−0.59) | 0.555 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizikalo, A.; Coric, S.; Matetic, A.; Vasilj, M.; Tocilj, Z.; Bozic, J. Association of Glomerular Filtration Rate and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease Patients over a 4-Year Follow-Up. Life 2021, 11, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030204
Rizikalo A, Coric S, Matetic A, Vasilj M, Tocilj Z, Bozic J. Association of Glomerular Filtration Rate and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease Patients over a 4-Year Follow-Up. Life. 2021; 11(3):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030204
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizikalo, Azer, Slavica Coric, Andrija Matetic, Mirjana Vasilj, Zoran Tocilj, and Josko Bozic. 2021. "Association of Glomerular Filtration Rate and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease Patients over a 4-Year Follow-Up" Life 11, no. 3: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030204
APA StyleRizikalo, A., Coric, S., Matetic, A., Vasilj, M., Tocilj, Z., & Bozic, J. (2021). Association of Glomerular Filtration Rate and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease Patients over a 4-Year Follow-Up. Life, 11(3), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030204








