Spatio-Temporal Expression Pattern of Ki-67, pRB, MMP-9 and Bax in Human Secondary Palate Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Processing and Immunofluorescence Staining
2.2. Quantitative and Semi-Quantitative Analysis
3. Results
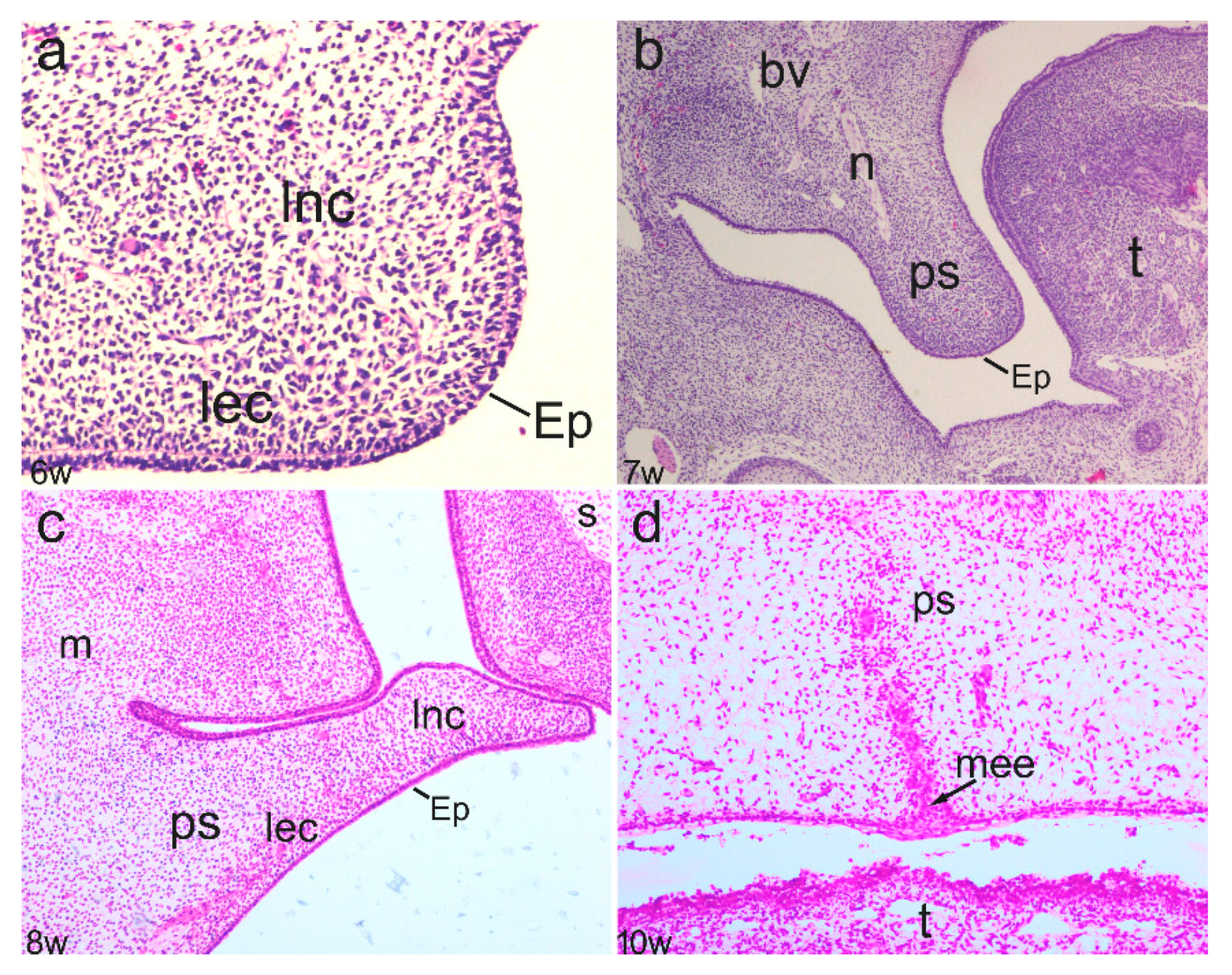
3.1. Phases of Normal Secondary Palate Development
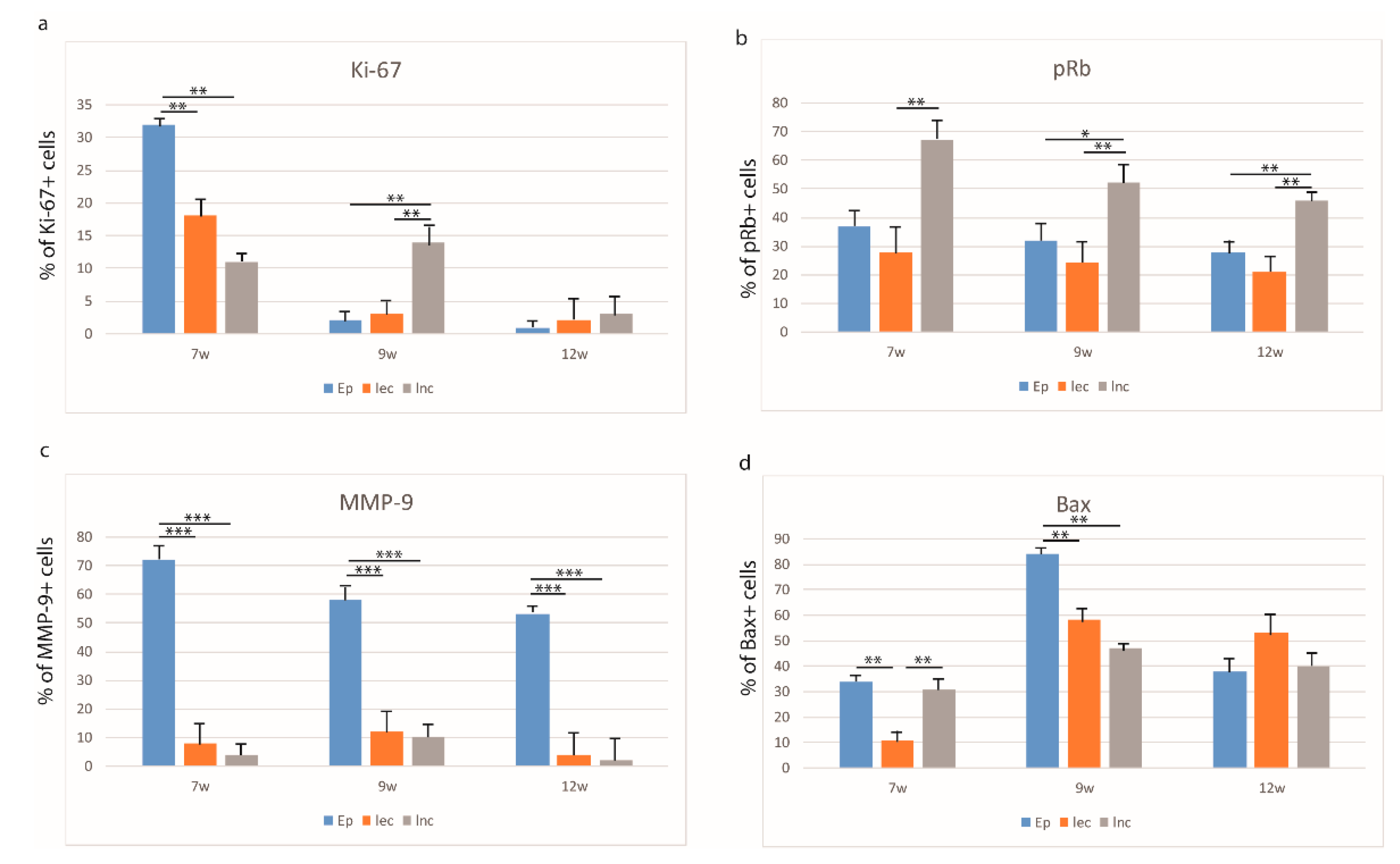
3.2. Expression Patterns of Ki-67, pRb, Bax, and MMP-9 in the Embryonic and Early Fetal Development of the Human Secondary Palate Formation (Figure S1)
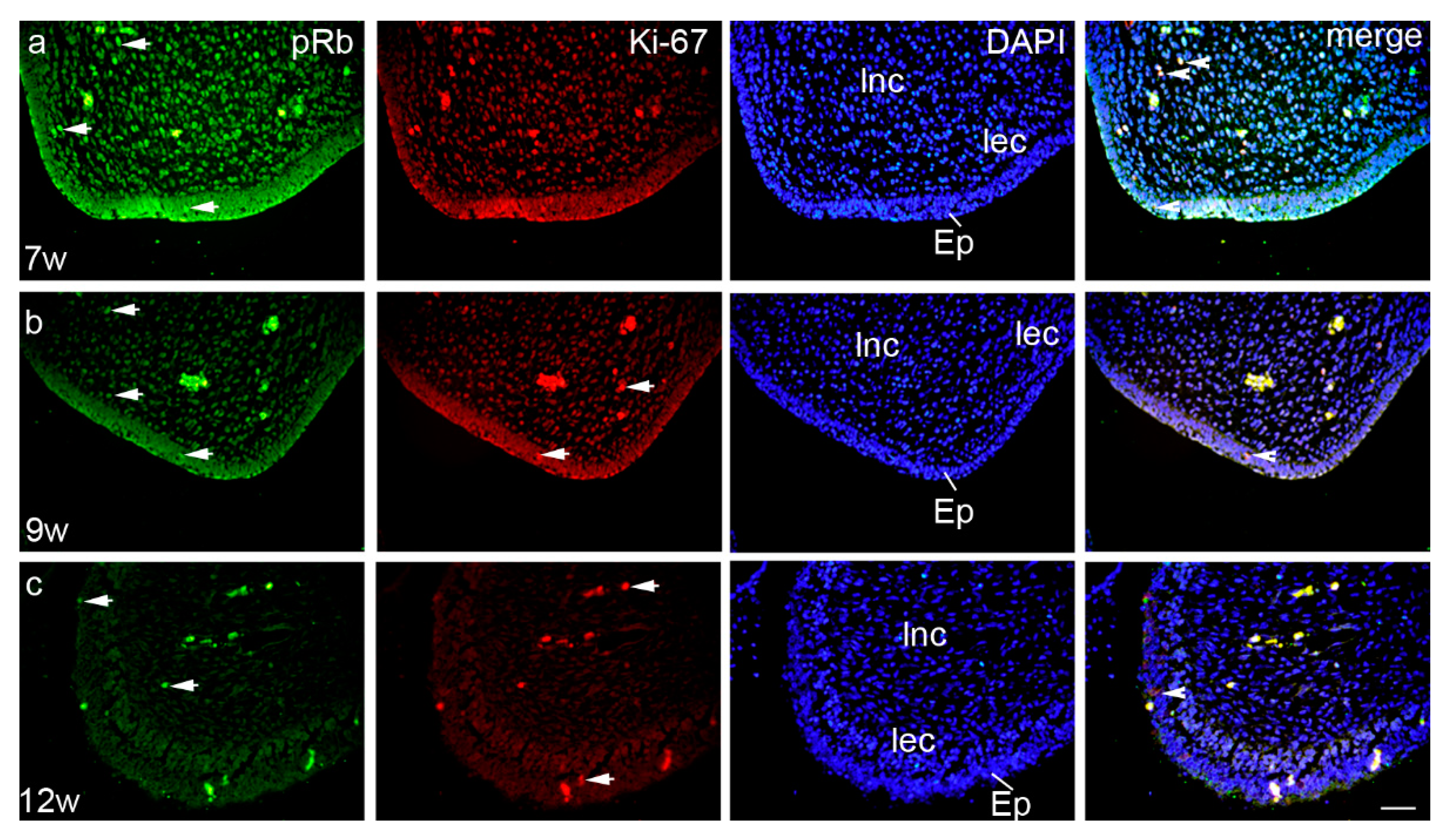
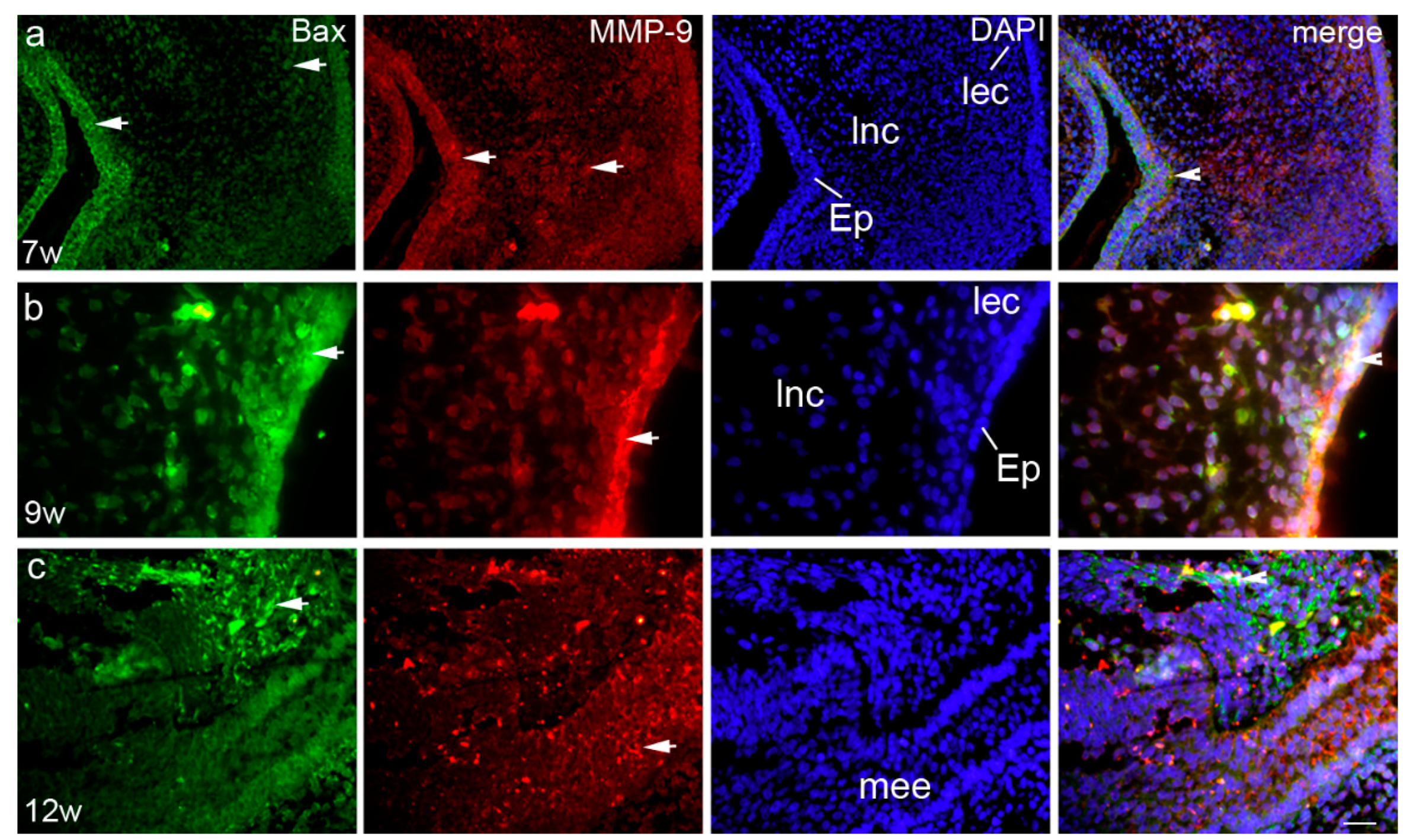
3.2.1. The Sixth to Seventh Week of Development
3.2.2. The Eighth to Ninth Week of Development
3.2.3. The 12th Week of Development
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vukojevic, K.; Kero, D.; Novakovic, J.; Kalibovic Govorko, D.; Saraga-Babic, M. Cell proliferation and apoptosis in the fusion of human primary and secondary palates. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2012, 120, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanier, P.; Moore, G.E. Genetics of cleft lip and palate: Syndromic genes contribute to the incidence of non-syndromic clefts. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, R73–R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, J.O.; Jiang, R. Palatogenesis: Morphogenetic and molecular mechanisms of secondary palate development. Development 2012, 139, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakovic, J.; Mardešić-Brakus, S.; Vukojević, K.; Saraga-Babić, M. Developmental patterns of Ki-67, bcl-2 and caspase-3 proteins expression in the human upper jaw. Acta Histochem. 2011, 113, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozario, T.; DeSimone, D.W. The extracellular matrix in development and morphogenesis: A dynamic view. Dev. Biol. 2010, 341, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesa, P.; Ellies, D.L.; Trainor, P.A. Comparative analysis of neural crest cell death, migration, and function during vertebrate embryogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 2003, 229, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Yeo, J.Y.; Chytil, A.; Han, J.; Bringas, P.; Nakajima, A.; Shuler, C.F.; Moses, H.L.; Chai, Y. Conditional inactivation of Tgfbr2 in cranial neural crest causes cleft palate and calvaria defects. Development 2003, 130, 5269–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritli-Linde, A. Molecular control of secondary palate development. Dev. Biol. 2007, 301, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, S. Disintegration of the medial epithelial seam: Is cell death important in palatogenesis? Dev. Growth Differ. 2011, 53, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smane-Filipova, L.; Pilmane, M.; Akota, I. MMPs and TIMPs expression in facial tissue of children with cleft lip and palate. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016, 160, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritli-Linde, A. The mouse as a developmental model for cleft lip and palate research. Front. Oral Biol. 2012, 16, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalibovic Govorko, D.; Bečić, T.; Vukojević, K.; Mardešić-Brakus, S.; Biocina-Lukenda, D.; Saraga-Babić, M. Spatial and temporal distribution of Ki-67 proliferation marker, Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in the developing human tooth. Arch. Oral Biol. 2010, 55, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kero, D.; Kalibovic Govorko, D.; Vukojevic, K.; Cubela, M.; Soljic, V.; Saraga-Babić, M. Expression of cytokeratin 8, vimentin, syndecan-1 and Ki-67 during human tooth development. J. Mol. Histol. 2014, 45, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kero, D.; Novakovic, J.; Vukojevic, K.; Petricevic, J.; Kalibovic Govorko, D.; Biocina-Lukenda, D.; Saraga-Babic, M. Expression of Ki-67, Oct-4, gamma-tubulin and alpha-tubulin in human tooth development. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kero, D.; Vukojevic, K.; Stazic, P.; Sundov, D.; Mardesic Brakus, S.; Saraga-Babic, M. Regulation of proliferation in developing human tooth germs by MSX homeodomain proteins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p19INK4d. Organogenesis 2017, 13, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citterio, H.L.; Gaillard, D.A. Expression of transforming growth factor alpha (TGF alpha), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) and cell proliferation during human palatogenesis: An immunohistochemical study. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1994, 38, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, T.C. Taking it to the max: The genetic and developmental mechanisms coordinating midfacial morphogenesis and dysmorphology. Clin. Genet. 2004, 65, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.J.; Dyson, N.J. Retinoblastoma protein partners. Adv. Cancer Res. 2001, 82, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, A.S.; Weinberg, R.A. Control of the cell cycle and apoptosis. Eur. J. Cancer 1999, 35, 1886–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Sheng, G.; Warner, B.W. Epidermal growth factor-induced rapid retinoblastoma phosphorylation at Ser780 and Ser795 is mediated by ERK1/2 in small intestine epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35992–35998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacinti, C.; Giordano, A. RB and cell cycle progression. Oncogene 2006, 25, 5220–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leezer, J.L.; Hackmiller, R.C.; Greene, R.M.; Pisano, M.M. Expression of the retinoblastoma family of tumor suppressors during murine embryonic orofacial development. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2003, 6, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakus, S.M.; Govorko, D.K.; Vukojević, K.; Jakus, I.A.; Carev, D.; Petricevic, J.; Saraga-Babic, M. Apoptotic and anti-apoptotic factors in early human mandible development. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 118, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, M.; Mai, J.K.; Zapata, J.M.; Ashwell, K.W.S.; Schendel, S.L.; Reed, J.C.; Krajewski, S. Dynamics of expression of apoptosis-regulatory proteins Bid, Bcl-2, Bcl-X, Bax and Bak during development of murine nervous system. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadler-Olsen, E.; Fadnes, B.; Sylte, I.; Uhlin-Hansen, L.; Winberg, J.-O. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase activity in health and disease. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, G.S.; Overall, C.M. Updated biological roles for matrix metalloproteinases and new “intracellular” substrates revealed by degradomics. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 10830–10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbardella, D.; Fasciglione, G.F.; Gioia, M.; Ciaccio, C.; Tundo, G.R.; Marini, S.; Coletta, M. Human matrix metalloproteinases: An ubiquitarian class of enzymes involved in several pathological processes. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 119–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Steen, P.E.; Dubois, B.; Nelissen, I.; Rudd, P.M.; Dwek, R.A.; Opdenakker, G. Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 37, 375–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blavier, L.; Delaissé, J.M. Matrix metalloproteinases are obligatory for the migration of preosteoclasts to the developing marrow cavity of primitive long bones. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 3649–3659. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R. The Declaration of Helsinki and public health. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnić, I.; Filipovic, N.; Vukojević, K.; Saraga-Babić, M.; Vrdoljak, M.; Grković, I. Effects of isoflurane postconditioning on chronic phase of ischemia–reperfusion heart injury in rats. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2015, 24, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojević, K.; Petrovič, D.; Saraga-Babić, M. Nestin expression in glial and neuronal progenitors of the developing human spinal ganglia. Gene Expr. Patterns 2010, 10, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojević, K.; Skobic, H.; Saraga-Babić, M. Proliferation and differentiation of glial and neuronal progenitors in the development of human spinal ganglia. Differentiation 2009, 78, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, S.; Williams, B.; Ksouri, S.; Hardung, L.; Filipovic, N.; Hamzic, L.F.; Puljak, L.; Ghahramani, N.; Vukojevic, K. Changes in snail and SRF expression in the kidneys of diabetic rats during ageing. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizdrak, M.; Filipović, N.; Vukojević, K.; Čapkun, V.; Mizdrak, I.; Durdov, M.G. Prognostic value of connective tissue growth factor and c-Myb expression in IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura—A pilot immunohistochemical study. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racetin, A.; Jurić, M.; Filipović, N.; Šolić, I.; Kosović, I.; Durdov, M.G.; Kunac, N.; Tomaš, S.Z.; Saraga, M.; Šoljić, V.; et al. Expression and localization of DAB1 and Reelin during normal human kidney development. Croat. Med. J. 2019, 60, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperber, G.; Sperber, S.M.; Guttmann, G. Craniofacial Embryogenetics and Development, 2nd ed.; People’s Medical Publishing House: Shelton, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.-L.; Lin, J.-X.; Xiao, Y.; Han, J. [Retinoic acid induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in mouse embryonic palatal mesenchymal cells]. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu = J. Hyg. Res. 2005, 34, 566–569. [Google Scholar]
- Okano, J.; Suzuki, S.; Shiota, K. Involvement of apoptotic cell death and cell cycle perturbation in retinoic acid-induced cleft palate in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 221, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Álvarez, C.; Tudela, C.; Pérez-Miguelsanz, J.; O’Kane, S.; Puerta, J.; Ferguson, M. Medial edge epithelial cell fate during palatal fusion. Dev. Biol. 2000, 220, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Liu, C.C.; Nawshad, A. Mechanisms of palatal epithelial seam disintegration by transforming growth factor (TGF) beta3. Dev. Biol. 2007, 309, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawshad, A. Palatal seam disintegration: To die or not to die? that is no longer the question. Dev. Dyn. 2008, 237, 2643–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, F.; Tang, L.; Tang, R.; Li, W. Apoptotic effect of mtrix metalloproteinases 9 in the development of diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10452–10459. [Google Scholar]
- Vaillant, C.; Meissirel, C.; Mutin, M.; Belin, M.F.; Lund, L.R.; Thomasset, N. MMP-9 deficiency affects axonal outgrowth, migration, and apoptosis in the developing cerebellum. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 24, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.E.; Hewitt, R.E.; Kleiner, D.E.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Molecular regulation of cellular invasion—role of gelatinase A and TIMP--2. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 74, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris-Wiman, J.; Burch, H.; Basco, E. Temporospatial distribution of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases during murine secondary palate morphogenesis. Anat. Embryol. 2000, 202, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demarchi, A.C.C.D.O.; Zambuzzi, W.F.; Paiva, K.B.S.; Silva-Valenzuela, M.D.G.D.; Nunes, F.D.; de Cassia Savio Figueira, R.; Sasahara, R.M.; Demasi, M.A.A.; Winnischofer, S.M.B.; Sogayar, M.C.; et al. Development of secondary palate requires strict regulation of ECM remodeling: Sequential distribution of RECK, MMP-2, MMP-3, and MMP-9. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 340, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Age (weeks) | CRL (mm) | Carnegie Stage | Biparietal Diameter (mm) | No. of Conceptuses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 13–14 | 16–17 | / | 5 |
| 7 | 15 | 18 | / | 5 |
| 8 | 18–19 | 21–23 | / | 5 |
| 9 | 20 | / | / | 5 |
| 10 | / | / | 18–21 | 5 |
| 12 | / | / | 26–28 | 5 |
| Structure | Antibodies | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pRb | Ki-67 | MMP-9 | Bax | |||||||||
| 7w | 9w | 12w | 7w | 9w | 12w | 7w | 9w | 12w | 7w | 9w | 12w | |
| Ep | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| lec | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| lnc | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šimić Bilandžija, T.; Vukojević, K.; Ćorić, A.; Vuković Kekez, I.; Medvedec Mikić, I.; Lasić Arapović, L.; Filipović, N.; Anđelić, J.; Saraga-Babić, M.; Kalibović Govorko, D. Spatio-Temporal Expression Pattern of Ki-67, pRB, MMP-9 and Bax in Human Secondary Palate Development. Life 2021, 11, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020164
Šimić Bilandžija T, Vukojević K, Ćorić A, Vuković Kekez I, Medvedec Mikić I, Lasić Arapović L, Filipović N, Anđelić J, Saraga-Babić M, Kalibović Govorko D. Spatio-Temporal Expression Pattern of Ki-67, pRB, MMP-9 and Bax in Human Secondary Palate Development. Life. 2021; 11(2):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020164
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠimić Bilandžija, Tanja, Katarina Vukojević, Anka Ćorić, Ivna Vuković Kekez, Ivana Medvedec Mikić, Lidija Lasić Arapović, Natalija Filipović, Jasminka Anđelić, Mirna Saraga-Babić, and Danijela Kalibović Govorko. 2021. "Spatio-Temporal Expression Pattern of Ki-67, pRB, MMP-9 and Bax in Human Secondary Palate Development" Life 11, no. 2: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020164
APA StyleŠimić Bilandžija, T., Vukojević, K., Ćorić, A., Vuković Kekez, I., Medvedec Mikić, I., Lasić Arapović, L., Filipović, N., Anđelić, J., Saraga-Babić, M., & Kalibović Govorko, D. (2021). Spatio-Temporal Expression Pattern of Ki-67, pRB, MMP-9 and Bax in Human Secondary Palate Development. Life, 11(2), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11020164







