Anticancer Effects of Midazolam on Lung and Breast Cancers by Inhibiting Cell Proliferation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.3. MTT Assay
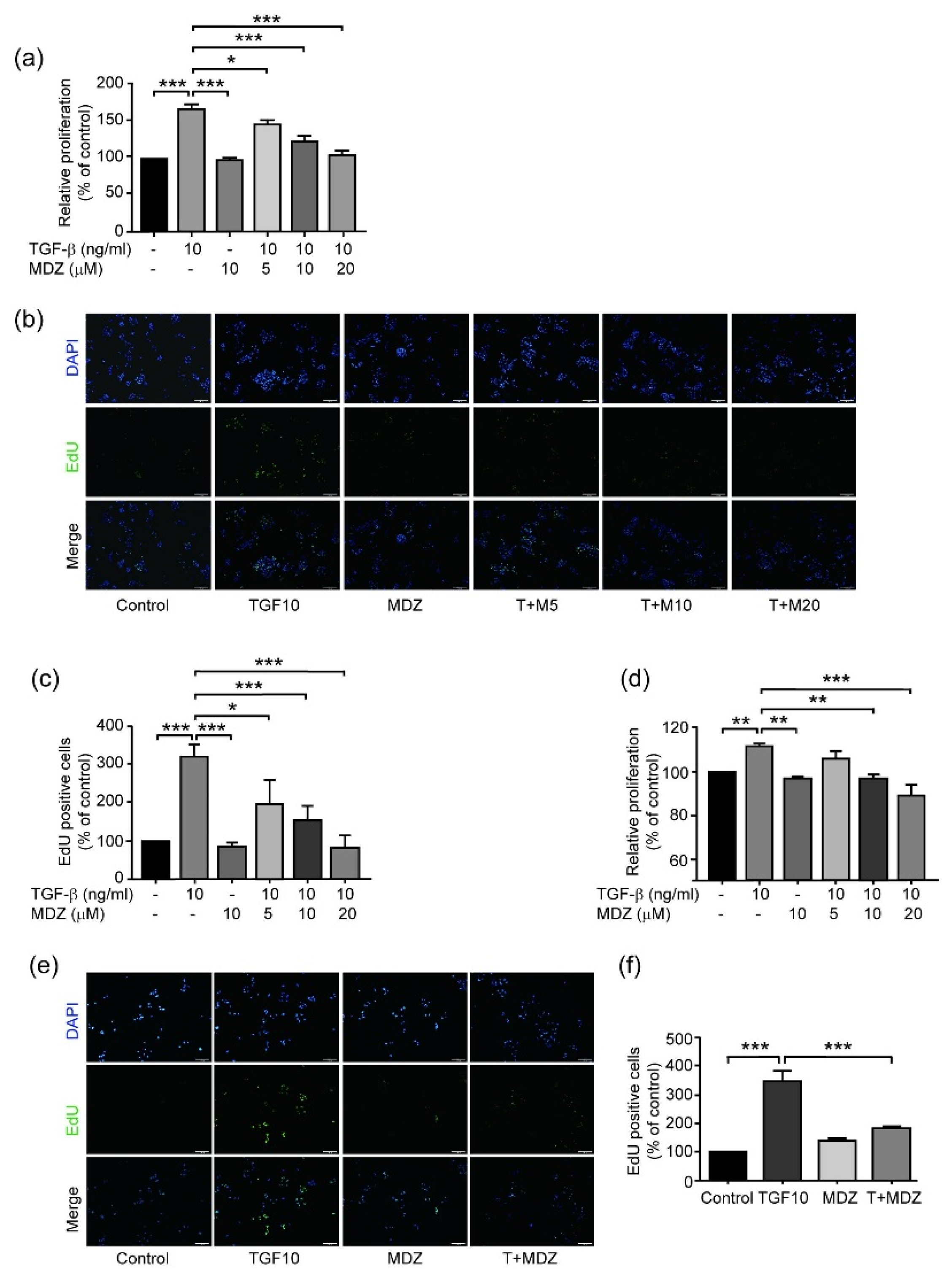
2.4. EdU Cell Proliferation Assay
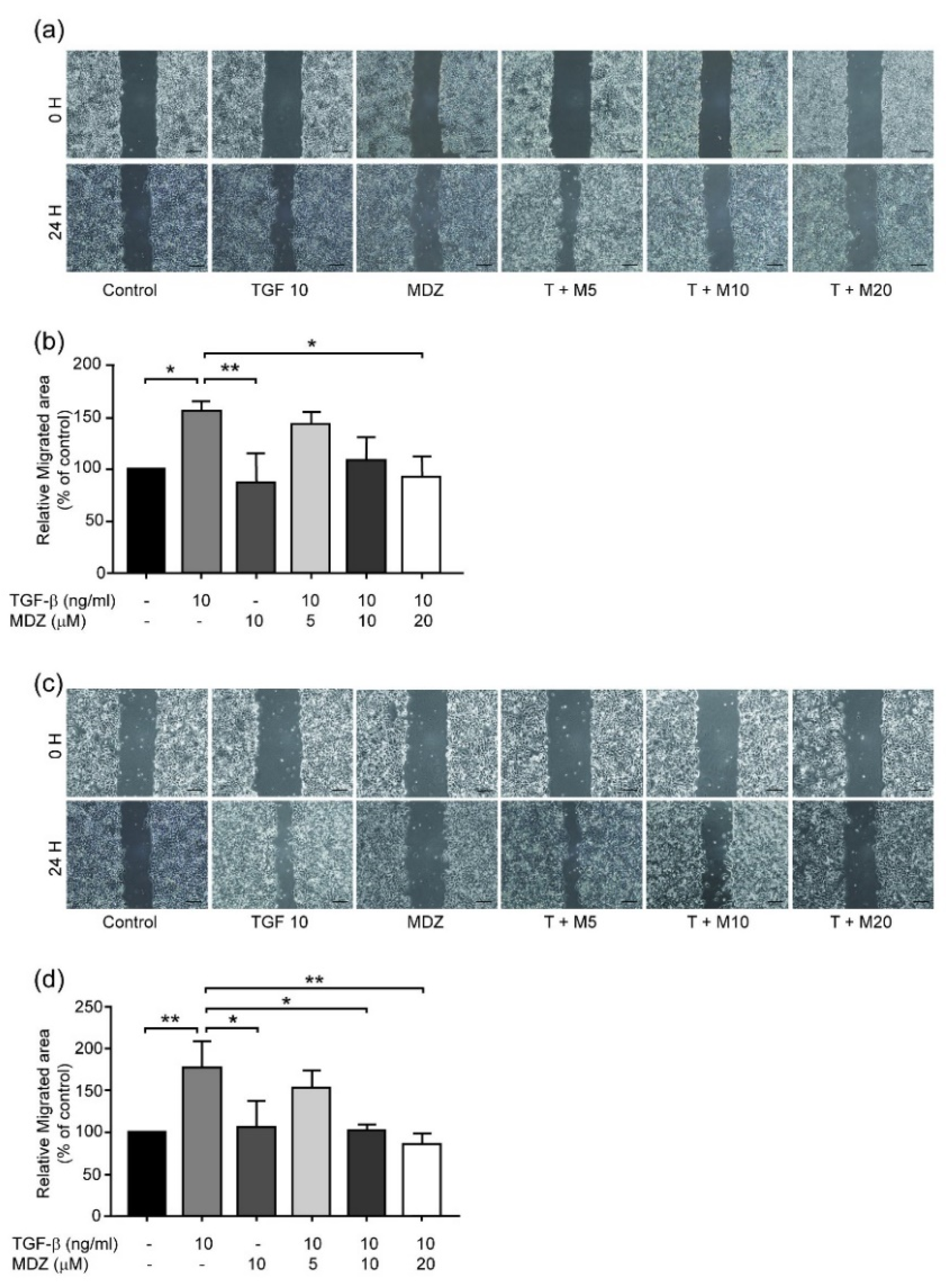
2.5. Wound Healing Assay
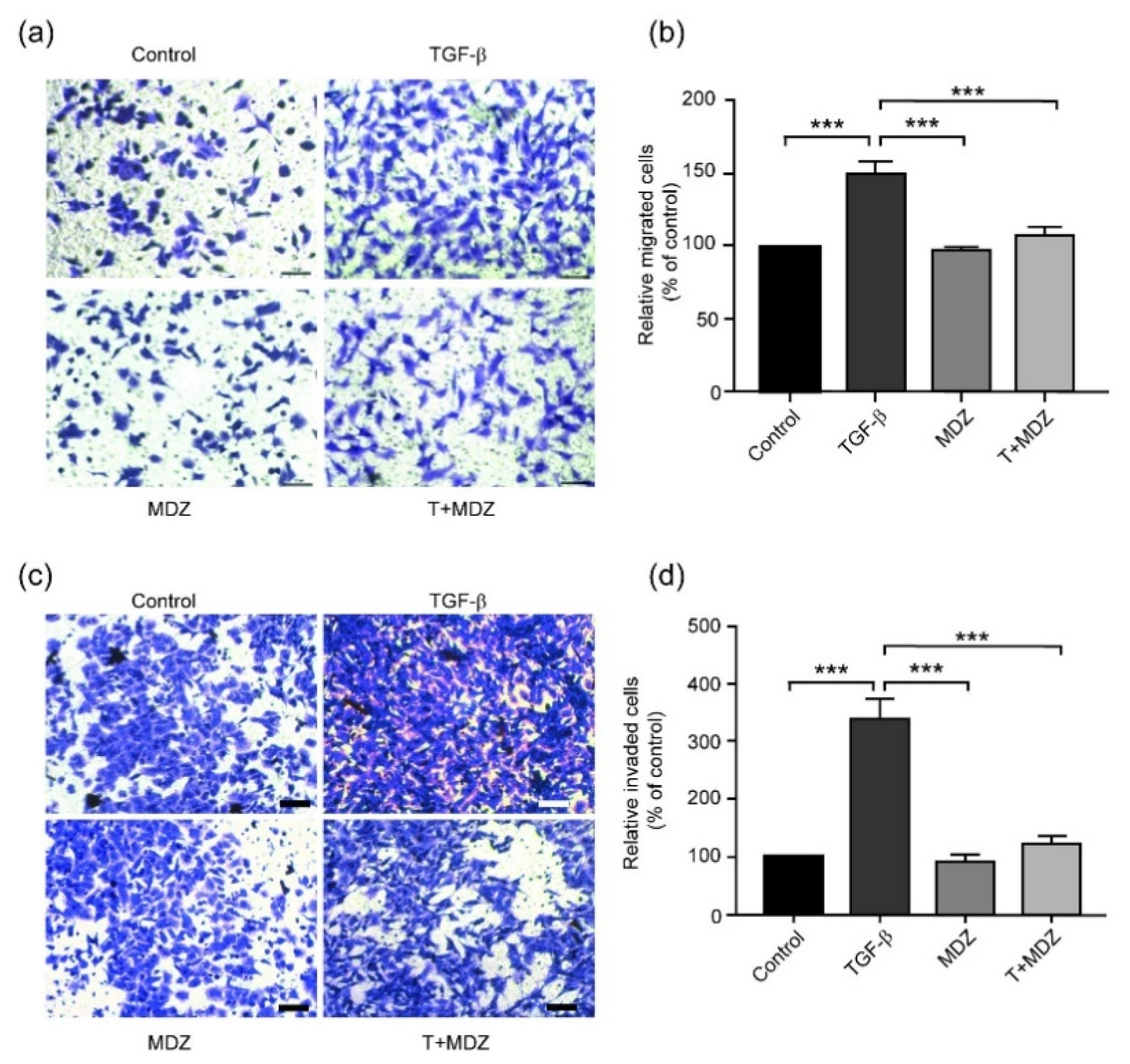
2.6. Transwell Migration and Invasion Assay
2.7. Western Blotting
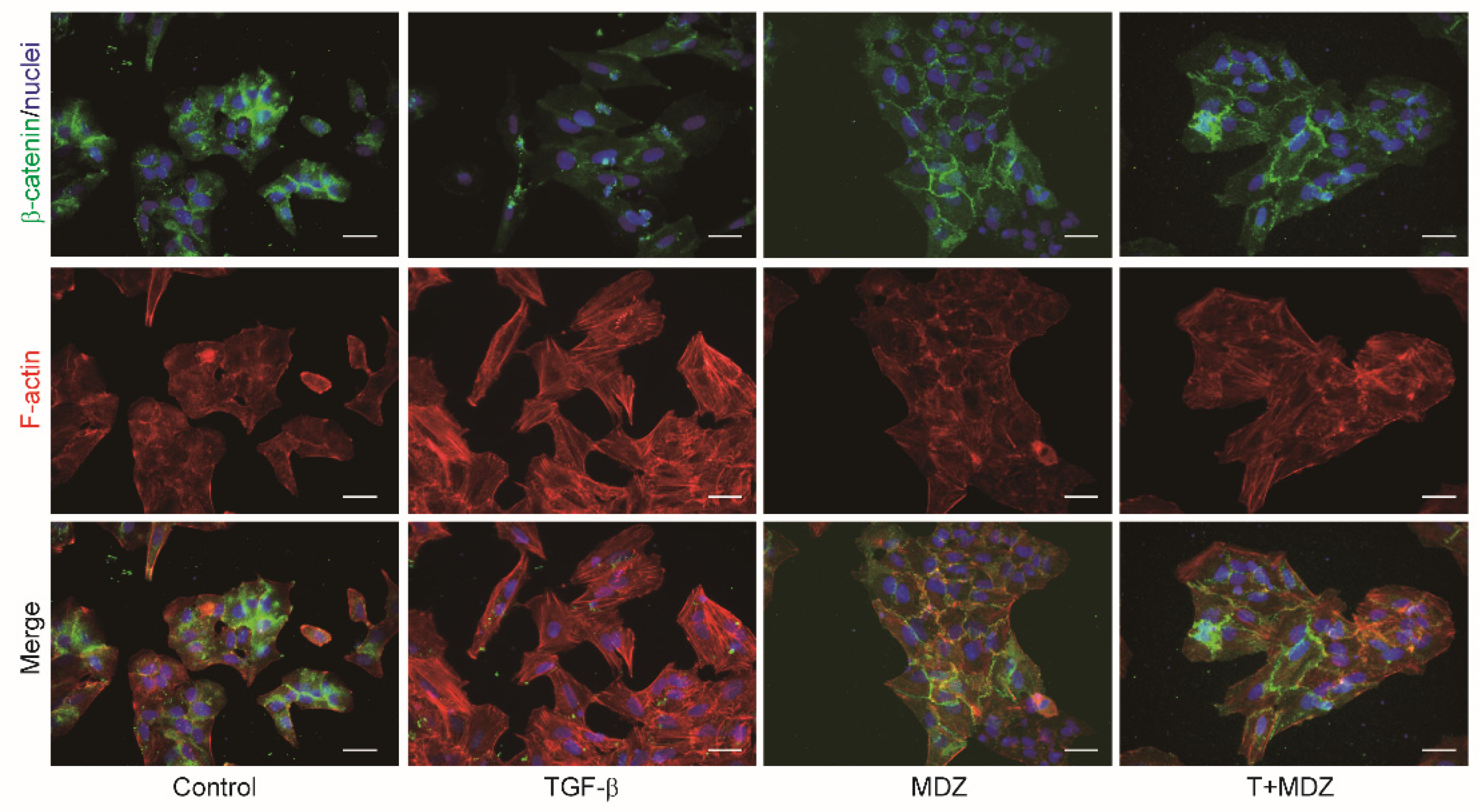
2.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
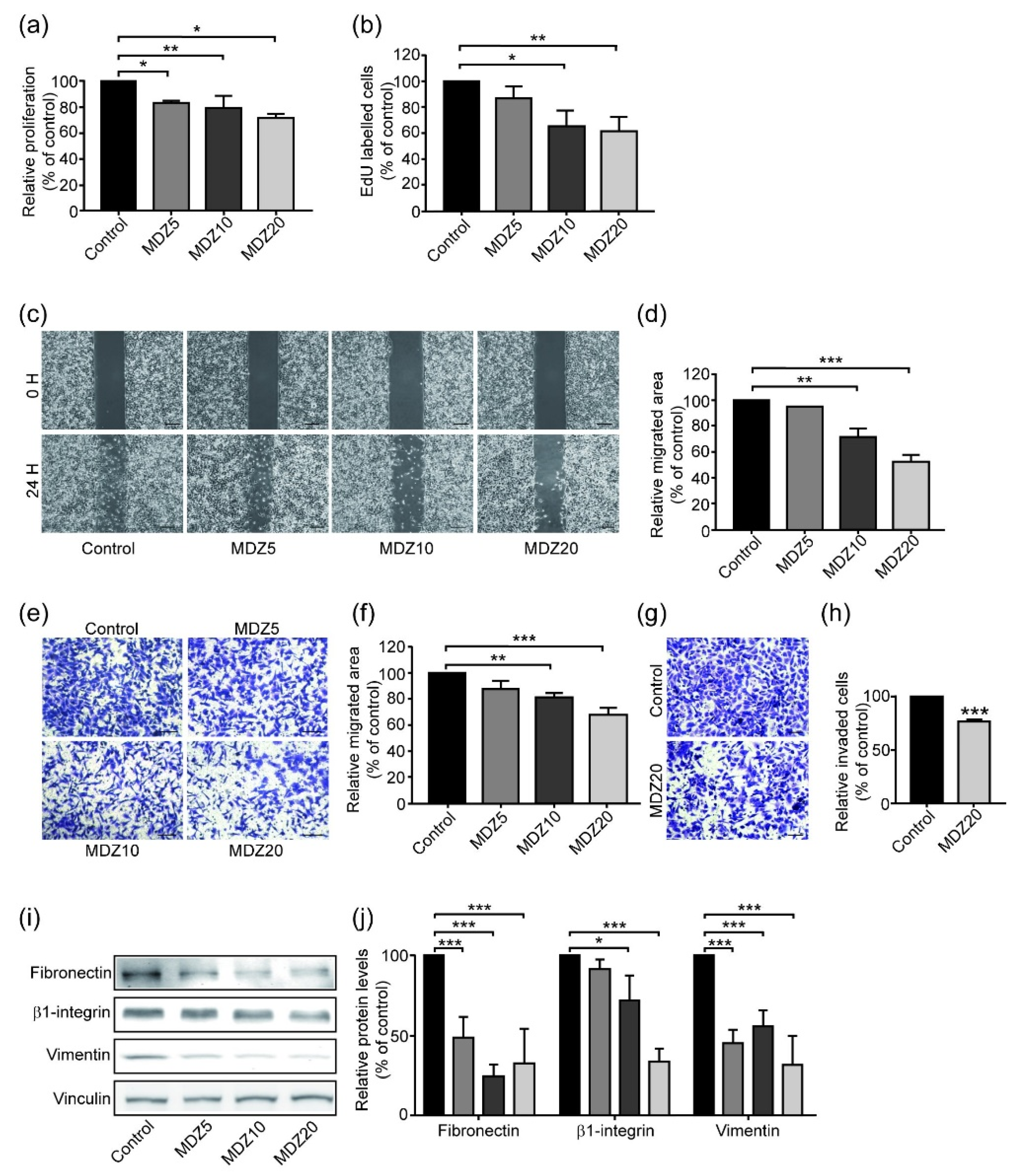
3.1. Midazolam Inhibits TGF-β-Induced Cancer Cell Proliferation
3.2. Midazolam Inhibits TGF-β-Induced Cancer Cell Migration
3.3. Midazolam Inhibits TGF-β-Induced Cell Invasion
3.4. Midazolam Suppresses TGF-β-Induced EMT in Cancer Cells
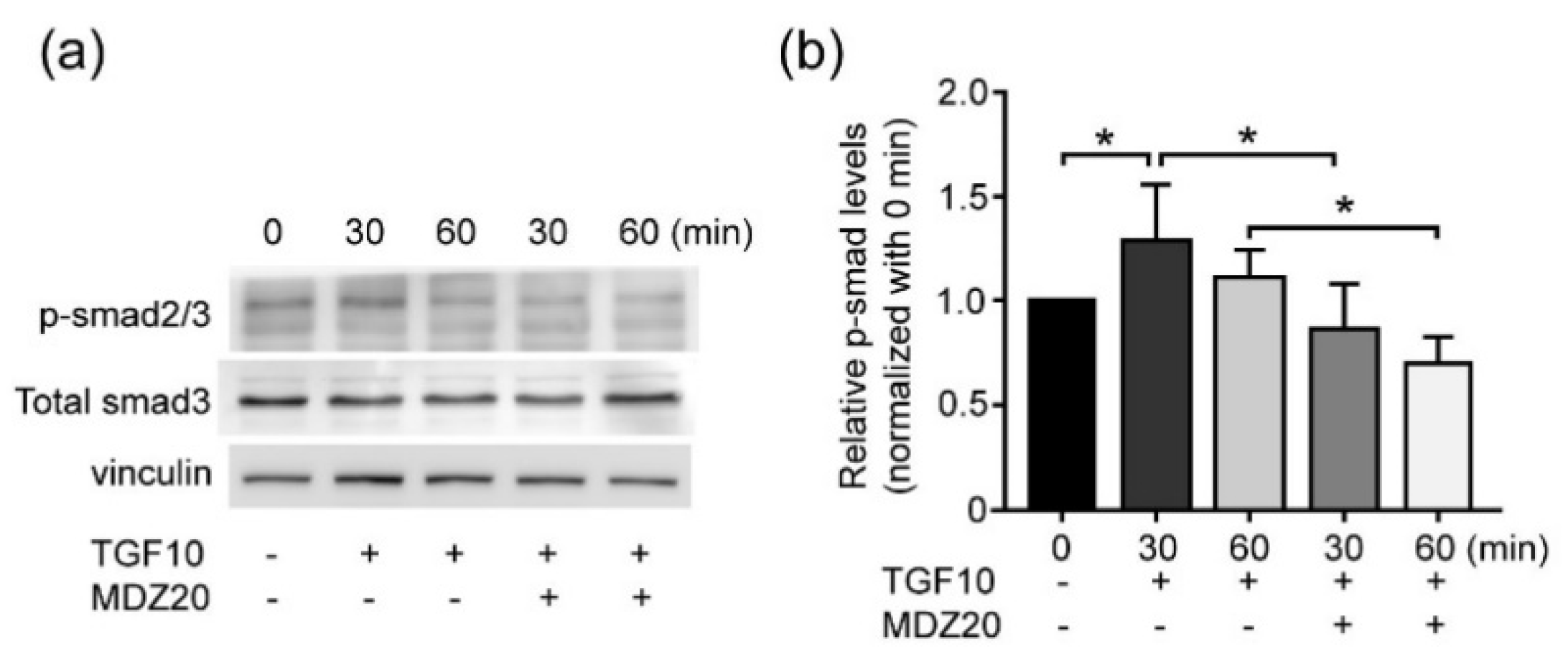
3.5. Midazolam Inhibits TGF-β-Induced Smad Signaling
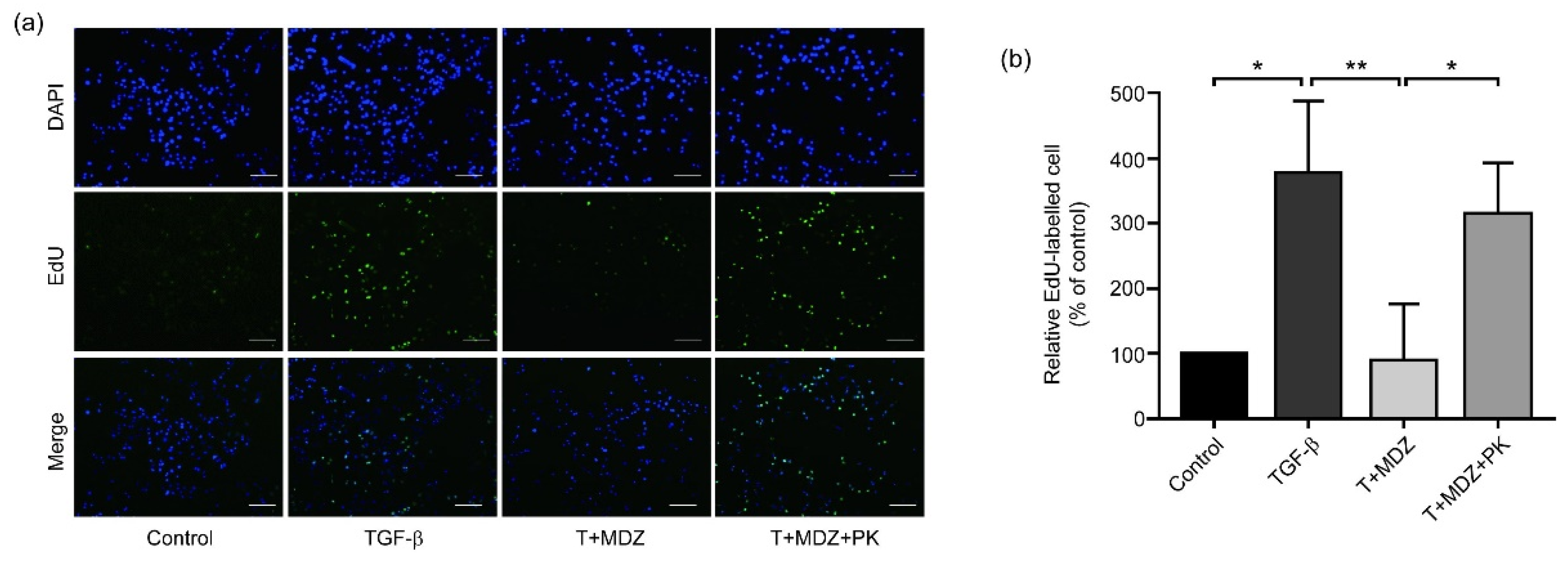
3.6. Midazolam Inhibits Cancer Cell Proliferation via Peripheral Benzodiazepine Receptor
3.7. Midazolam Inhibits Proliferation and Mesenchymal Marker Expression of MDA-MB 231
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clinc. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feitelson, M.A.; Arzumanyan, A.; Kulathinal, R.J.; Blain, S.W.; Holcombe, R.F.; Mahajna, J.; Marino, M.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Nawroth, R.; Sanchez-Garcia, I.; et al. Sustained proliferation in cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S25–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldin, C.H.; Landström, M.; Moustakas, A. Mechanism of TGF-beta signaling to growth arrest, apoptosis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Alexander, P.B.; Wang, X.F. TGF-beta Family Signaling in the Control of Cell Proliferation and Survival. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blobe, G.C.; Schiemann, W.P.; Lodish, H.F. Role of transforming growth factor beta in human disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Blobe, G.C. Dichotomous roles of TGF-beta in human cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, G.S.; Condeelis, J.S.; Oktay, M.H. Chemotherapy-induced metastasis: Mechanisms and translational opportunities. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2018, 35, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Brabletz, T.; Kang, Y.; Longmore, G.D.; Nieto, M.A.; Stanger, B.Z.; Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Upholding a role for EMT in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2017, 547, E1–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, N.A.; Zent, R.; Ghiassi, M.; McDonnel, M.; Moses, H.L. Integrin beta 1 signaling is necessary for transforming growth factor-beta activation of p38MAPK and epithelial plasticity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 46707–46713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Biomarkers for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Gomez, S.J.; Maziveyi, M.; Alahari, S.K. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yi, B.R.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, K.C. Role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its effects on embryonic stem cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzegrzolka, J.; Biala, M.; Wojtyra, P.; Kobierzycki, C.; Olbromski, M.; Gomulkiewicz, A.; Piotrowska, A.; Rys, J.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Dziegiel, P. Expression of EMT Markers SLUG and TWIST in Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 3961–3968. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.T.; Yang, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuno, Y.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordt, S.P.; Clark, R.F. Midazolam: A review of therapeutic uses and toxicity. J. Emerg. Med. 1997, 15, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.Z.; Miao, Y.L.; An, L.N.; Wang, X.Y.; Pan, N.L.; Ma, Y.Q.; Chen, H.X.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.F.; et al. Midazolam provides cytoprotective effect during corticosterone-induced damages in rat astrocytes by stimulating steroidogenesis. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 547, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkola, K.T.; Ahonen, J. Midazolam and other benzodiazepines. Mod. Anesth. 2008, 182, 335–360. [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup, C.; Squires, R.F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H) diazepam binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 74, 3805–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anholt, R.R.; Pedersen, P.L.; De Souza, E.B.; Snyder, S.H. The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor. Localization to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanova, C. Peripheral Benzodiazepine Receptors in Health and Disease. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2009, 23, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Jiang, X. Insights into the Roles of Midazolam in Cancer Therapy. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 3826506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.F.; Werdehausen, R.; Gaza, N.; Hermanns, H.; Kremer, D.; Bauer, I.; Küry, P.; Hollmann, M.W.; Braun, S. Midazolam activates the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis independent of benzodiazepine and death receptor signaling. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2011, 36, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, E.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, S.C.; Wu, C.C.; Huang, M.C.; Lai, M.S.; Pan, B.S.; Kang, F.C.; Huang, B.M. Midazolam regulated caspase pathway, endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and cell cycle to induce apoptosis in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 2519–2533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, F.C.; Wang, S.C.; Chang, M.M.; Pan, B.S.; Wong, K.L.; Cheng, K.S.; So, E.C.; Huang, B.M. Midazolam activates caspase, MAPKs and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways, and inhibits cell cycle and Akt pathway, to induce apoptosis in TM3 mouse Leydig progenitor cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 1475–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justus, C.R.; Leffler, N.; Ruiz-Echevarria, M.; Yang, L.V. In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 88, 51046. [Google Scholar]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radisky, D.C. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4325–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.K.; Li, M.S.; He, J.L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.H.; Lai, S.; Ma, J.C.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.W.; et al. Translocator protein mediates the anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of midazolam. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 139, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavish, M.; Bachman, I.; Shoukrun, R.; Katz, Y.; Veenman, L.; Weisinger, G.; Weizman, A. Enigma of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 629–650. [Google Scholar]
- Azarashvili, T.; Krestinina, O.; Yurkov, I.; Evtodienko, Y.; Reiser, G. High-affinity peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand, PK11195, regulates protein phosphorylation in rat brain mitochondria under control of Ca(2+). J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Wu, K.C.; Huang, B.M.; So, E.C.; Wang, Y.K. Midazolam inhibits chondrogenesis via peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2896–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Lin, H.H.; Tang, M.J.; Wang, Y.K. Vimentin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition cancer cell mechanics by mediating cytoskeletal organization and focal adhesion maturation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15966–15983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, J.; Salari, K.; Bocanegra, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Girard, L.; Gandhi, J.; Kwei, K.A.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Wang, P.; Gazdar, A.F.; et al. Molecular profiling of breast cancer cell lines defines relevant tumor models and provides a resource for cancer gene discovery. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yu, P.; Tang, J. Characterization of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cell Spheroid Model. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 5395–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrobin, D.F.; Trosko, J.E. The possible effect of diazepam on cancer development and growth. Med. Hypotheses 1981, 7, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, U.; Nguyen, P.A.; Syed-Abdul, S.; Yang, H.C.; Huang, C.W.; Jian, W.S.; Hsu, M.H.; Yen, Y.; Li, Y.C.J. Is long-term use of benzodiazepine a risk for cancer? Medicine 2015, 94, e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, A.P.; Maaser, K.; Hopfner, M.; Barthel, B.; Grabowski, P.; Faiss, S.; Carayon, P.; Zeitz, M.; Scherübl, H. Specific ligands of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human esophageal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 102, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaudin, D. Peripheral benzodiazepine receptor and its clinical targeting. Anticancer Drugs 2004, 15, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, J.H.; Ramirez, A.M.; Lin, L.; Oracion, A.; Agarwal, R.P.; Norenberg, M.D. Peripheral-type benzodiazepines inhibit proliferation of astrocytes in culture. Brain Res. 1991, 564, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, M.; Cavalli, L.R.; Barlow, K.D.; Haddad, B.R.; Papadopoulos, V. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) gene amplification in MDA-MB-231 aggressive breast cancer cells. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2002, 139, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Guillory, B.; Mukherjee, S.; Das, S.K. Antiproliferative effect of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor antagonist PK11195 in rat mammary tumor cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2010, 340, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardwick, M.; Fertikh, D.; Culty, M.; Li, H.; Vidic, B.; Papadopoulos, V. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor (PBR) in human breast cancer: Correlation of breast cancer cell aggressive phenotype with PBR expression, nuclear localization, and PBR-mediated cell proliferation and nuclear transport of cholesterol. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohno, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Uchida, S.; Amano, O.; Sakagami, H.; Nagasaka, H. Cytotoxicity and type of cell death induced by midazolam in human oral normal and tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 4737–4747. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, A.; Lantigua, H.; Lesch, C.; Shao, B.; Foreman, B.; Schmidt, J.M.; Hirsch, L.J.; Mayer, S.A.; Claassen, J. High-dose midazolam infusion for refractory status epilepticus. Neurology 2014, 82, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, D.C.; Pestotnik, S.L.; Evans, R.S.; Burke, J.P. Intensive surveillance of midazolam use in hospitalized patients and the occurrence of cardiorespiratory arrest. Pharmacotherapy 1992, 12, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Frei, E.; Karon, M., 3rd; Levin, R.H.; Freireich, E.J.; Taylor, R.J.; Hananian, J.; Selawry, O.; Holland, J.F.; Hoogstraten, B.; Wolman, I.J.; et al. The effectiveness of combinations of antileukemic agents in inducing and maintaining remission in children with acute leukemia. Blood 1965, 26, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Yoh, K.; Goto, K.; Niho, S.; Umemura, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; Ohe, Y. Safety and efficacy of platinum agents plus etoposide for patients with small cell lung cancer with interstitial lung disease. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, B.A.; Dash, R.; Sarkar, S.; Azab, B.; Bhoopathi, P.; Das, S.K.; Emdad, L.; Wei, J.; Pellecchia, M.; Sarkar, D.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Combination Therapy Using a BH3 Mimetic and a Synthetic Tetracycline. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat Mokhtari, R.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.A.; Coward, J.I. Chemotherapy advances in small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5 (Suppl. 5), S565–S578. [Google Scholar]
- Massague, J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell 2008, 134, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Hill, C.S. Tgf-beta superfamily signaling in embryonic development and homeostasis. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.H.; Shin, H.S.; Choi, H.S.; Ryu, E.S.; Kim, M.J.; Min, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, D.H. Effects of dexamethasone on the TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, T.; Uwabe, K.; Naito, S.; Higashino, K.; Nakano, T.; Numata, Y.; Kihara, A. AM251 Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, H.-L.; Wu, K.-C.; Chen, C.-W.; Weng, H.-K.; Huang, B.-M.; Lin, T.-Y.; Liu, M.-H.; So, E.-C.; Lin, R.-M.; Wang, Y.-K. Anticancer Effects of Midazolam on Lung and Breast Cancers by Inhibiting Cell Proliferation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Life 2021, 11, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121396
Lu H-L, Wu K-C, Chen C-W, Weng H-K, Huang B-M, Lin T-Y, Liu M-H, So E-C, Lin R-M, Wang Y-K. Anticancer Effects of Midazolam on Lung and Breast Cancers by Inhibiting Cell Proliferation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Life. 2021; 11(12):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121396
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Hsin-Ling, King-Chuen Wu, Char-Wen Chen, Hung-Kai Weng, Bu-Miin Huang, Ting-Yu Lin, Ming-Hsin Liu, Edmund-Cheung So, Ruey-Mo Lin, and Yang-Kao Wang. 2021. "Anticancer Effects of Midazolam on Lung and Breast Cancers by Inhibiting Cell Proliferation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition" Life 11, no. 12: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121396
APA StyleLu, H.-L., Wu, K.-C., Chen, C.-W., Weng, H.-K., Huang, B.-M., Lin, T.-Y., Liu, M.-H., So, E.-C., Lin, R.-M., & Wang, Y.-K. (2021). Anticancer Effects of Midazolam on Lung and Breast Cancers by Inhibiting Cell Proliferation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Life, 11(12), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121396





