Modelling Combined Intravenous Thrombolysis and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischaemic Stroke: Understanding the Relationship between Stent Retriever Configuration and Clot Lysis Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Arterial Geometry and Clot Composition
2.2. Computational Model Overview
2.3. Numerical Details
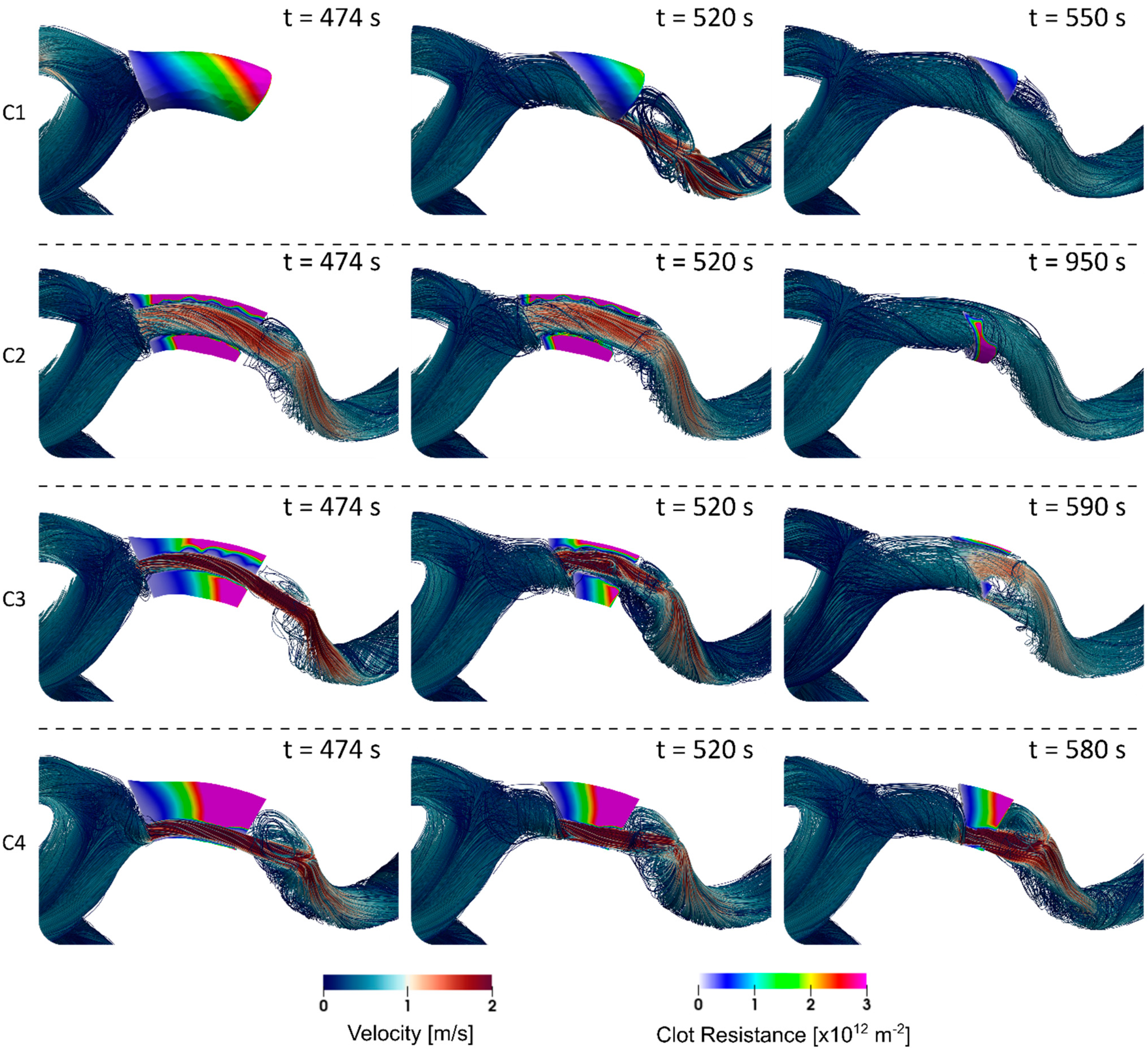
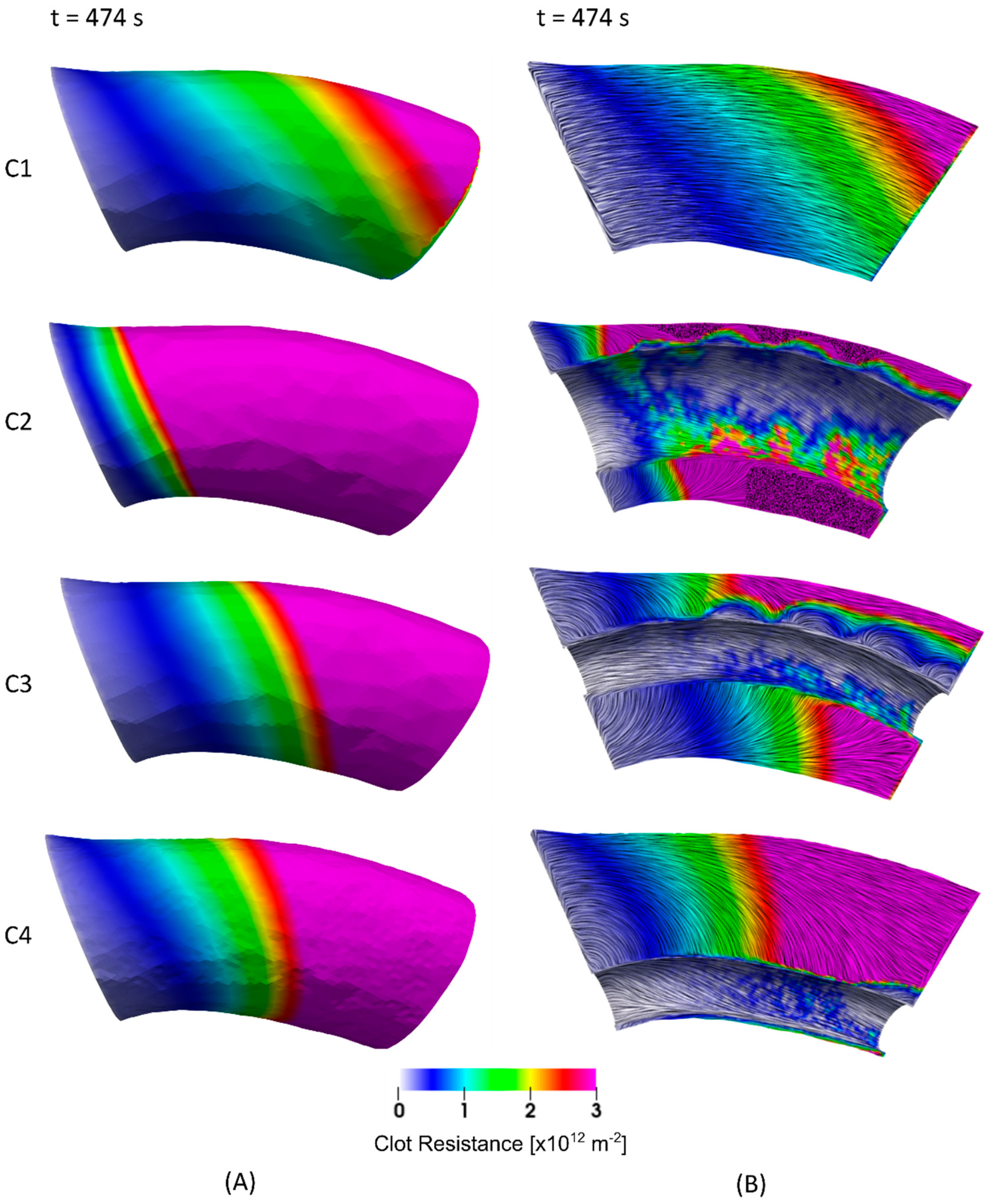
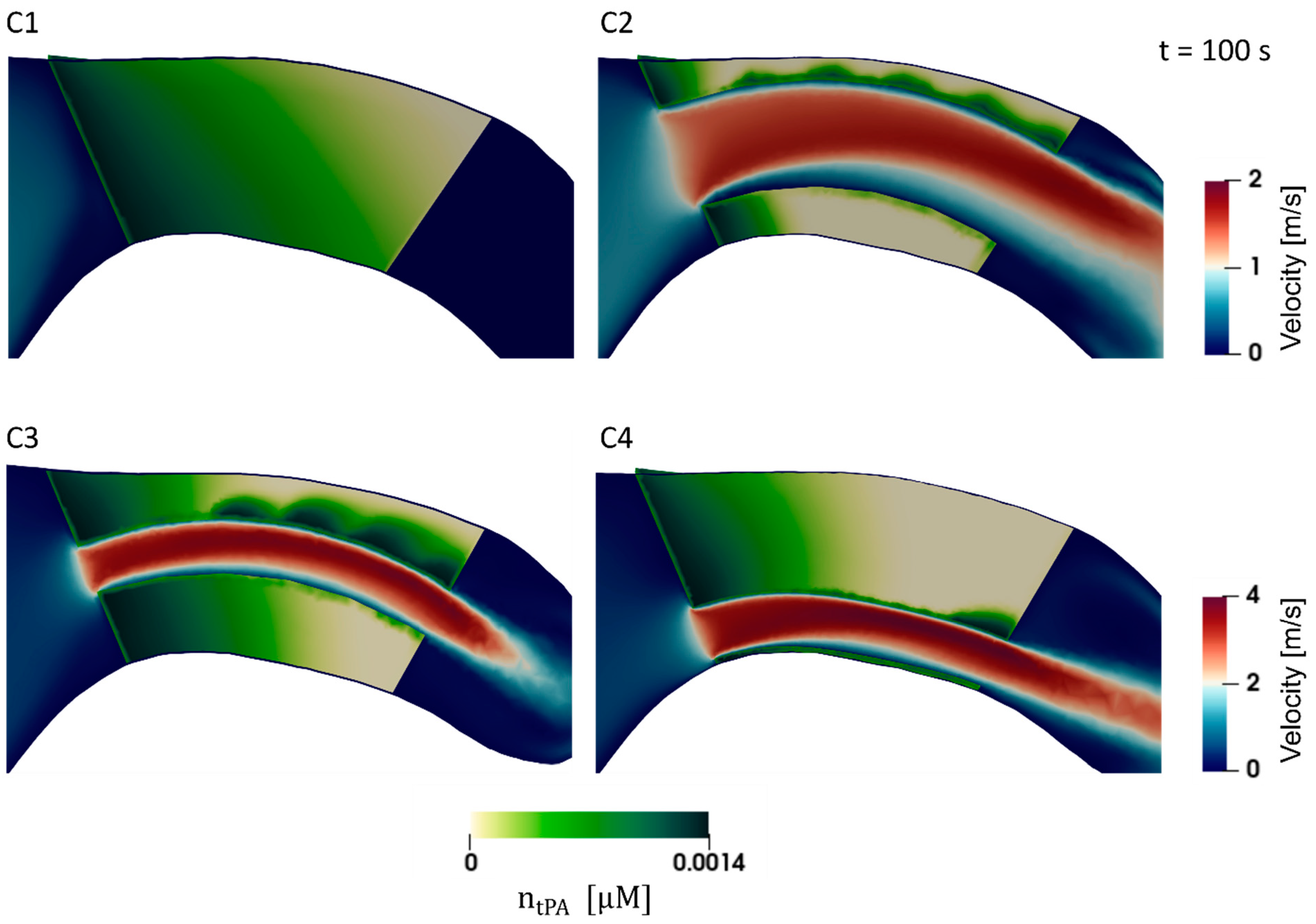
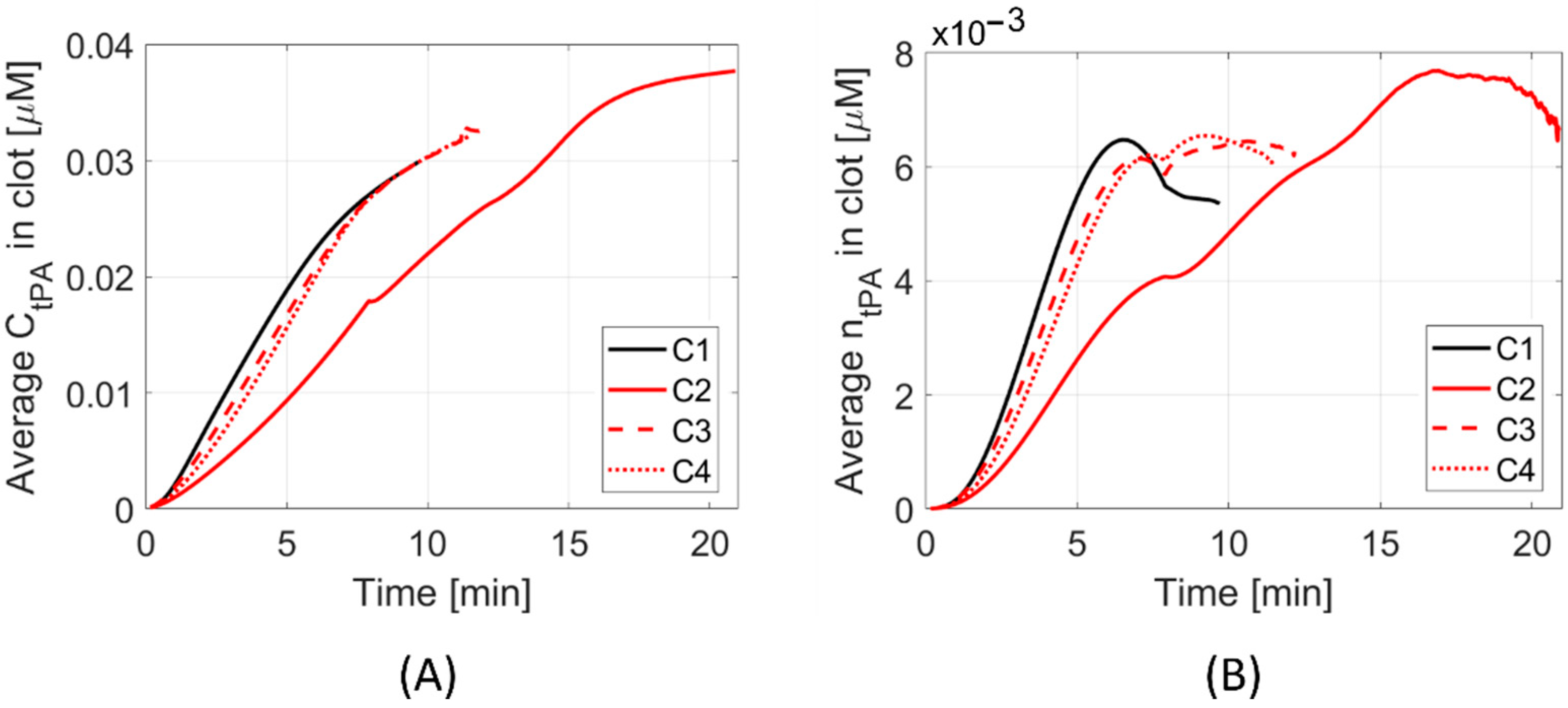
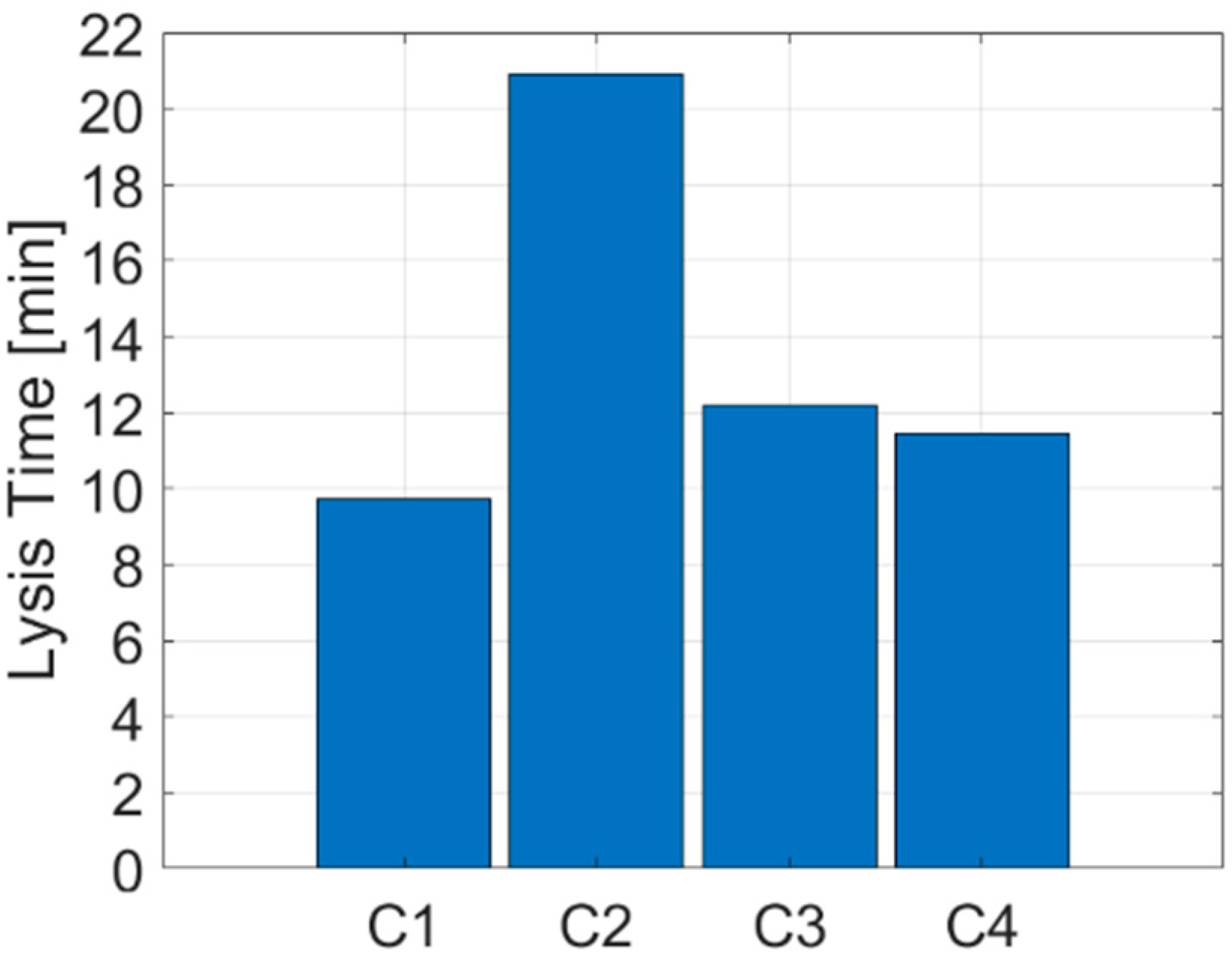
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Clot Lysis
4.2. Clinical Evaluation
4.3. Limitations and Future Work
4.3.1. Thrombolysis Model and Clot Properties
4.3.2. Mechanical Thrombectomy
4.3.3. Translation to Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Mensah, G.A.; Connor, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990-2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2014, 383, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, E.A.; Mistry, A.M.; Nakawah, M.O.; Chitale, R.V.; James, R.F.; Volpi, J.J.; Fusco, M.R. Mechanical thrombectomy outcomes with and without intravenous thrombolysis in stroke patients: A meta-analysis. Stroke 2017, 48, 2450–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhu, C.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Malhotra, A. Bridging thrombolysis achieved better outcomes than direct thrombectomy after large vessel occlusion: An updated meta-analysis. Stroke 2021, 52, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, Y. Direct endovascular treatment versus intravenous alteplase followed by endovascular treatment in acute stroke due to a large vessel occlusion. In Proceedings of the International Stroke Conference, Online, 17–19 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Treurniet, K.M.; Chen, W.; Peng, Y.; Han, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Endovascular thrombectomy with or without intravenous alteplase in acute stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1981–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, W.; Qiu, Z.; Li, F.; Sang, H.; Wu, D.; Luo, W.; Liu, S.; Yuan, J.; Song, J.; Shi, Z.; et al. Effect of endovascular treatment alone vs intravenous alteplase plus endovascular treatment on functional independence in patients with acute ischemic stroke: The DEVT randomized clinical trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Matsumaru, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Morimoto, M.; Kanazawa, R.; Takayama, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Shigeta, K.; Okubo, S.; Hayakawa, M.; et al. Effect of mechanical thrombectomy without vs with intravenous thrombolysis on functional outcome among patients with acute ischemic stroke: The SKIP randomized clinical trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Saver, J.L.; Ovbiagele, B.; Huang, W.-Y.; Lee, M. Endovascular thrombectomy without versus with intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: A non-inferiority meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piebalgs, A.; Gu, B.; Roi, D.; Lobotesis, K.; Thom, S.; Xu, X.Y. Computational simulations of thrombolytic therapy in acute ischaemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, B.; Piebalgs, A.; Huang, Y.; Roi, D.; Lobotesis, K.; Longstaff, C.; Hughes, A.D.; Chen, R.; Thom, S.A.; Xu, X.Y. Computational simulations of thrombolysis in acute stroke: Effect of clot size and location on recanalisation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2019, 73, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Baek, J.H.; Park, H.; Song, D.; Kim, K.; Hwang, I.G.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Ahn, S.H.; et al. Thrombus volume as a predictor of nonrecanalization after intravenous thrombolysis in acute stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 2108–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, P.J.; Watanabe, S.M.; Passos, M.A.R.F.; Lemos, P.A.; Feijóo, R.A. An anatomically detailed arterial network model for one-dimensional computational hemodynamics. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 736–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Piebalgs, A.; Huang, Y.; Longstaff, C.; Hughes, A.D.; Chen, R.; Thom, S.A.; Xu, X.Y. Mathematical modelling of intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke: Effects of dose regimens on levels of fibrinolytic proteins and clot lysis time. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 33, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhof, N.; Lankhaar, J.W.; Westerhof, B.E. The arterial windkessel. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2009, 47, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diamond, S.L.; Anand, S. Inner clot diffusion and permeation during fibrinolysis. Biophys. J. 1993, 65, 2622–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Kudallur, V.; Pitman, E.B.; Diamond, S.L. Mechanisms by which thrombolytic therapy results in nonuniform lysis and residual thrombus after reperfusion. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1997, 25, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serša, I.; Tratar, G.; Mikac, U.; Blinc, A. A mathematical model for the dissolution of non-occlusive blood clots in fast tangential blood flow. Biorheology 2007, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gariel, F.; Lapergue, B.; Bourcier, R.; Berge, J.; Barreau, X.; Mazighi, M.; Kyheng, M.; Labreuche, J.; Fahed, R.; Blanc, R.; et al. Mechanical thrombectomy outcomes with or without intravenous thrombolysis insight from the ASTER randomized trial. Stroke 2018, 49, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, A.V.; Burgin, W.S.; Demchuk, A.M.; El-Mitwalli, A.; Grotta, J.C. Speed of intracranial clot lysis with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator therapy: Sonographic classification and short-term improvement. Circulation 2001, 103, 2897–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.A.; Ribo, M.; Rubiera, M.; Montaner, J.; Santamarina, E.; Delgado-Mederos, R.; Arenillas, J.F.; Huertas, R.; Purroy, F.; Delgado, P.; et al. Microbubble administration accelerates clot lysis during continuous 2-MHz ultrasound monitoring in stroke patients treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 2006, 37, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, C.H.; Zimmermann, P.; Jensen-Kondering, U.; Stingele, R.; Deuschl, G.; Jansen, O. The importance of size: Successful recanalization by intravenous thrombolysis in acute anterior stroke depends on thrombus length. Stroke 2011, 42, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.G.; Ariëns, R.A.S. Insights into the composition of stroke thrombi: Heterogeneity and distinct clot areas impact treatment. Haematologica 2020, 105, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, X.; Ma, T.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Dong, Z.; Xu, X.Y. Patient-specific simulation of stent-graft deployment in type B aortic dissection: Model development and validation. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2021, 20, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luraghi, G.; Matas, J.F.R.; Dubini, G.; Berti, F.; Bridio, S.; Duffy, S.; Dwivedi, A.; McCarthy, R.; Fereidoonnezhad, B.; McGarry, P.; et al. Applicability assessment of a stent-retriever thrombectomy finite-element model. Interface Focus 2021, 11, 20190123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manchester, E.L.; Roi, D.; Gu, B.; Xu, X.Y.; Lobotesis, K. Modelling Combined Intravenous Thrombolysis and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischaemic Stroke: Understanding the Relationship between Stent Retriever Configuration and Clot Lysis Mechanisms. Life 2021, 11, 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111271
Manchester EL, Roi D, Gu B, Xu XY, Lobotesis K. Modelling Combined Intravenous Thrombolysis and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischaemic Stroke: Understanding the Relationship between Stent Retriever Configuration and Clot Lysis Mechanisms. Life. 2021; 11(11):1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111271
Chicago/Turabian StyleManchester, Emily Louise, Dylan Roi, Boram Gu, Xiao Yun Xu, and Kyriakos Lobotesis. 2021. "Modelling Combined Intravenous Thrombolysis and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischaemic Stroke: Understanding the Relationship between Stent Retriever Configuration and Clot Lysis Mechanisms" Life 11, no. 11: 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111271
APA StyleManchester, E. L., Roi, D., Gu, B., Xu, X. Y., & Lobotesis, K. (2021). Modelling Combined Intravenous Thrombolysis and Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischaemic Stroke: Understanding the Relationship between Stent Retriever Configuration and Clot Lysis Mechanisms. Life, 11(11), 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111271





