Protein-Coding Genes in Euarchontoglires with Pseudogene Homologs in Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
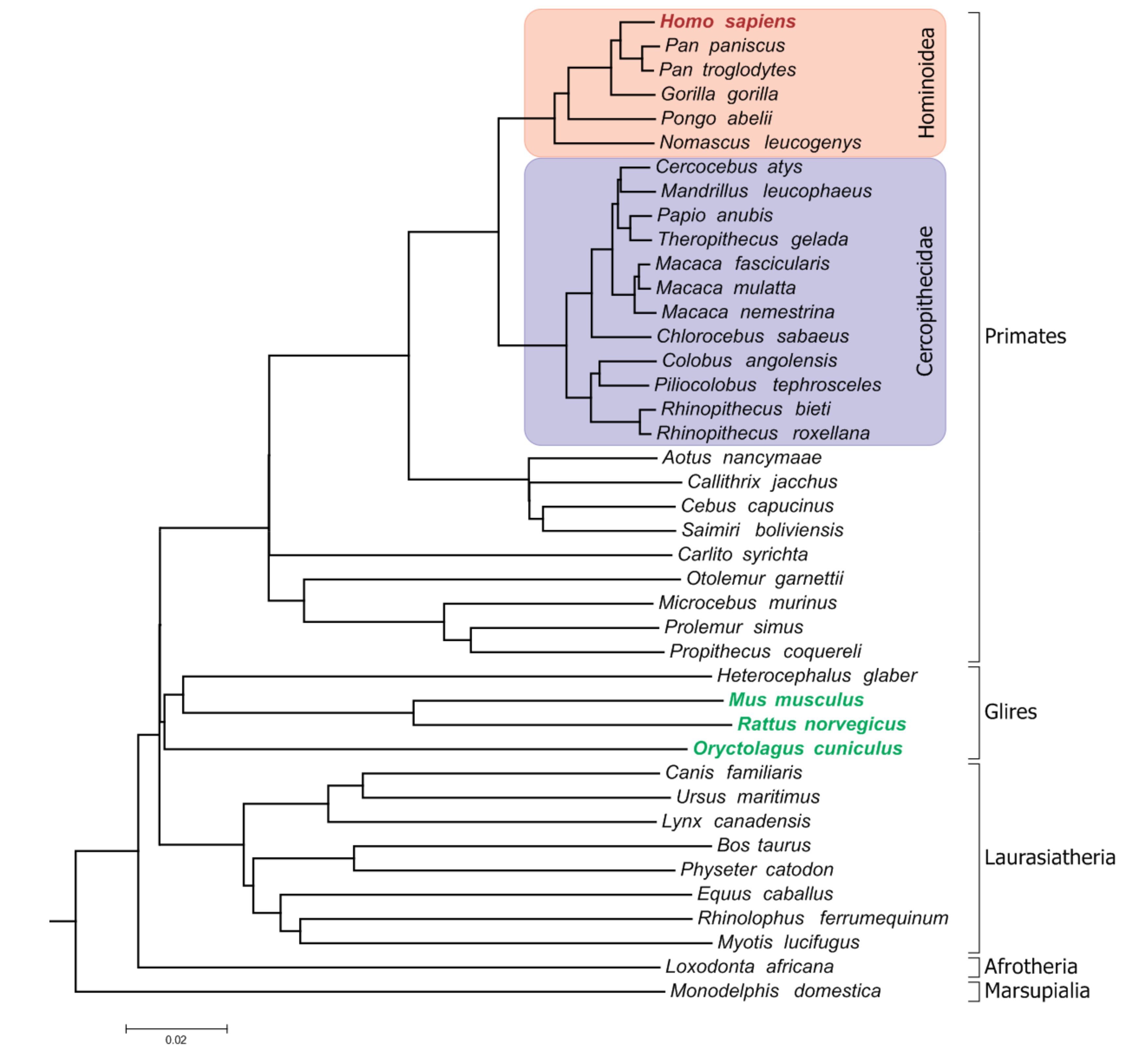
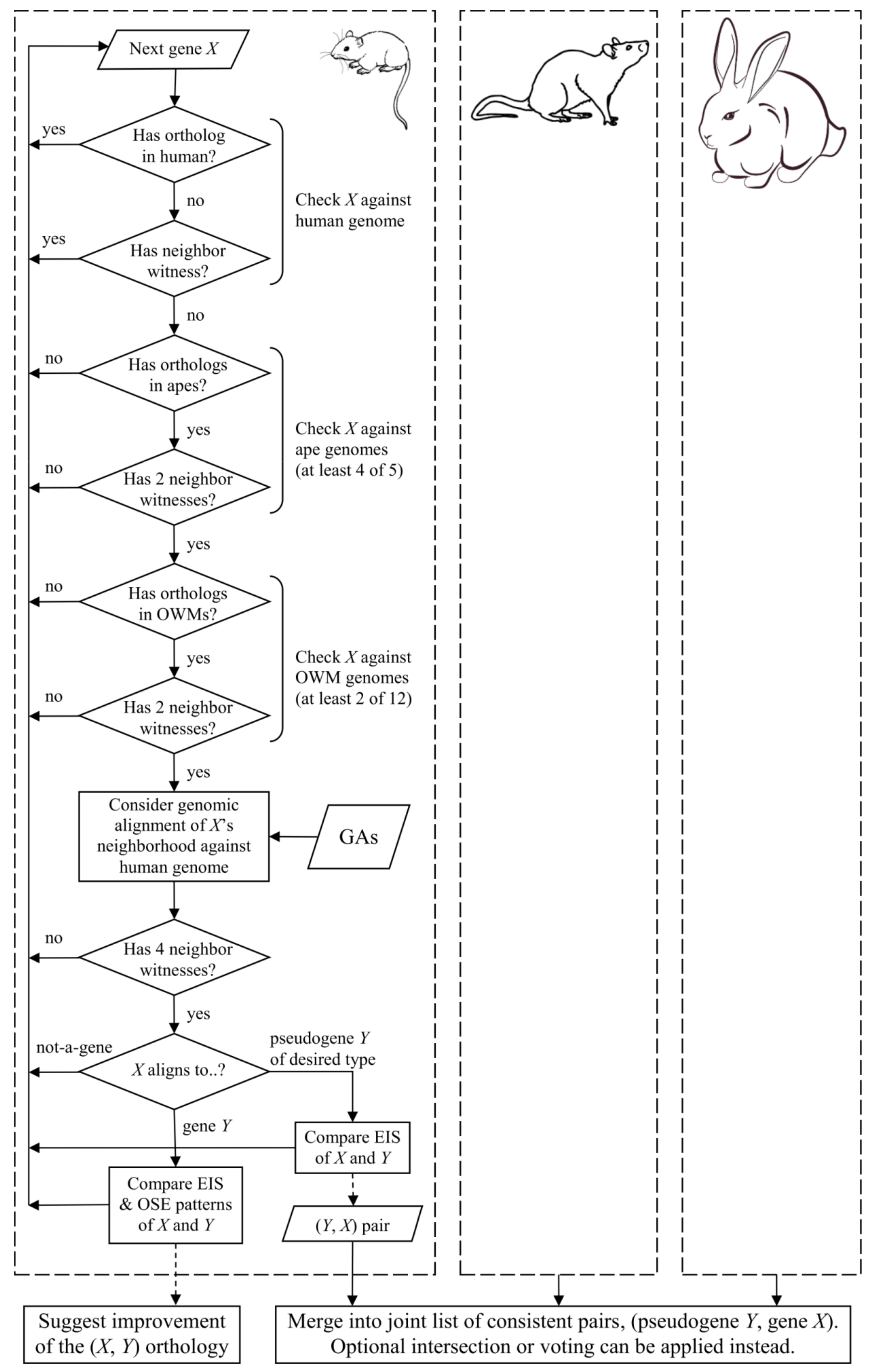
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Consistent Pseudogene Gene Pairs Identified
3.2. Consistent Genes of the Reference Species and Their Counterparts in Other Species
3.3. Human Pseudogenes Independently Pseudogenized or Lost in Exactly One Nonhuman Hominoid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheetham, S.W.; Faulkner, G.J.; Dinger, M.E. Overcoming challenges and dogmas to understand the functions of pseudogenes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, T.F.; Patrushev, L.I. Pseudogenes as functionally significant elements of the genome. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2018, 83, 1332–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Edgerton, M.E.; Diao, L.; Xu, Y.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Liang, H. The pan-cancer analysis of pseudogene expression reveals biologically and clinically relevant tumour subtypes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Shankar, S.; Robinson, D.R.; Wu, Y.M.; Cao, X.; Asangani, I.A.; Kothari, V.; Presner, J.R.; Lonigro, R.J.; et al. Expressed pseudogenes in the transcriptional landscape of human cancers. Cell 2012, 149, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karreth, F.A.; Reschke, M.; Ruocco, A.; Ng, C.; Chapuy, B.; Leopold, V.; Sjoberg, M.; Keane, T.M.; Verma, A.; Ala, U.; et al. The BRAF pseudogene functions as a competitive endogenous RNA and induces lymphoma in vivo. Cell 2015, 161, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliseno, L.; Salmena, L.; Zhang, J.; Carver, B.; Haveman, W.J.; Pandolfi, P.P. A coding-independent function of gene and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature 2010, 465, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiefari, E.; Iiritano, S.; Paonessa, F.; Pera, I.L.; Arcidiacono, B.; Filocamo, M.; Foti, D.; Liebhaber, S.A.; Brunetti, A. Pseudogene-mediated posttranscriptional silencing of HMGA1 can result in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.D.; Frankish, A.; Hunt, T.; Harrow, J.; Gerstein, M. Identification and analysis of unitary pseudogenes: Historic and contemporary gene losses in humans and other primates. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Hecker, N.; Roscito, J.G.; Foerster, L.; Langer, B.E.; Hiller, M. A genomics approach reveals insights into the importance of gene losses for mammalian adaptations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razin, S.V.; Gavrilov, A.A. Structural-functional domains of the eukaryotic genome. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2018, 83, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LossgainRSL. A Program for Prediction of Gene Losses and Gains between Several Groups of Species. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/software/lossgainRSL_a_program_for_prediction_of_gene_losses_and_gains_between_several_groups_of_species/9173243 (accessed on 15 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Korotkova, D.D.; Lyubetsky, V.A.; Ivanova, A.S.; Rubanov, L.I.; Seliverstov, A.V.; Zverkov, O.A.; Martynova, N.Y.; Nesterenko, A.M.; Tereshina, M.B.; Peshkin, L.; et al. Bioinformatics screening of genes specific for well-regenerating vertebrates reveals c-answer, a regulator of brain development and regeneration. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubanov, L.I.; Zaraisky, A.G.; Shilovsky, G.A.; Seliverstov, A.V.; Zverkov, O.A.; Lyubetsky, V.A. Screening for mouse genes lost in mammals with long lifespans. BioData Min. 2019, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, A.D.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Azov, A.G.; Bennett, R.; et al. Ensembl 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D682–D688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodorou, I.; Fonseca, N.A.; Keays, M.; Tang, Y.A.; Barrera, E.; Bazant, W.; Burke, M.; Füllgrabe, A.; Fuentes, A.M.; George, N.; et al. Expression Atlas: Gene and protein expression across multiple studies and organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D246–D251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, M.; Iwamura, C.; Miki-Hosokawa, T.; Shinoda, K.; Endo, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Shinnakasu, R.; Hosokawa, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Motohashi, S.; et al. Enhanced Th2 cell differentiation and allergen-induced airway inflammation in Zfp35-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5388–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, K.; Dhar, C.; Do, R.; Varki, N.; Gordts, P.L.S.M.; Varki, A. Human species-specific loss of CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase enhances atherosclerosis via intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16036–16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.E.; Flenniken, A.M.; Ji, X.; Teboul, L.; Wong, M.D.; White, J.K.; Meehan, T.F.; Weninger, W.J.; Westerberg, H.; Adissu, H.; et al. High-throughput discovery of novel developmental phenotypes. Nature 2016, 537, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wakamiya, M.; Vaishnav, S.; Geske, R.; Montgomery, C., Jr.; Jones, P.; Bradley, A.; Caskey, C.T. Hyperuricemia and urate nephropathy in urate oxidase-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, L.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.Y.; Martin, F.; Grant, D.; Solloway, M.; Parker, L.; Ye, W.; et al. A mouse knockout library for secreted and transmembrane proteins. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H.; Castaneda, J.M.; Fujihara, Y.; Yu, Z.; Archambeault, D.R.; Isotani, A.; Kiyozumi, D.; Kriseman, M.L.; Mashiko, D.; Matsumura, T.; et al. Genome engineering uncovers 54 evolutionarily conserved and testis-enriched genes that are not required for male fertility in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7704–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardente, H.; Mendoza, J.; Fustin, J.M.; Challet, E.; Hazlerigg, D.G. Implication of the F-Box protein FBXL21 in circadian pacemaker function in mammals. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, A.; Yumimoto, K.; Tsunematsu, R.; Matsumoto, M.; Oyama, M.; Kozuka-Hata, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Lanjakornsiripan, D.; Nakayama, K.I.; Fukada, Y. FBXL21 regulates oscillation of the circadian clock through ubiquitination and stabilization of cryptochromes. Cell 2013, 152, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulachev, V.P.; Holtze, S.; Vyssokikh, M.Y.; Bakeeva, L.E.; Skulachev, M.V.; Markov, A.V.; Hildebrandt, T.B.; Sadovnichii, V.A. Neoteny, prolongation of youth: From naked mole rats to “naked apes” (humans). Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 699–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Li, W.; Fei, S.; Guo, M.; Chen, H.; Sun, L.; Han, Z.; Tao, J.; Ju, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms of ubiquitin-related genes were associated with allograft fibrosis of renal transplant fibrosis. Ann. Transplant. 2019, 24, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Yamada, K.; Watanabe, A.; Ohba, H.; Sakaguchi, T.; Honma, Y.; Iwayama, Y.; Toyota, T.; Maekawa, M.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Ablation of Mrds1/Ofcc1 induces hyper-γ-glutamyl transpeptidasemia without abnormal head development and schizophrenia-relevant behaviors in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Human Pseudogene | Consistent Mouse Gene(s) | Consistent Rat Gene(s) | Consistent Rabbit Gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| A2MP1 | A2ml1 | A2ml1 | ENSOCUG00000000313 |
| ABCC13 | ENSOCUG00000012802 | ||
| AC063977.5 | 4931406B18Rik | LOC690483 | |
| ADAM20P1 | Gm4787 | ENSOCUG00000008563 | |
| ADAM5 | Adam5 | Adam5 | ENSOCUG00000005475 |
| AHSA2P | Ahsa2 | Ahsa2 | ENSOCUG00000017817 |
| AL160191.3 | Adam4 | ||
| AL589987.1 | RGD1560171 | ENSOCUG00000012140 | |
| ALOX12P2 | Alox12e | Alox12e | |
| C4BPAP1 | Zp3r | Zp3r | ENSOCUG00000023993 |
| CCDC162P | Ccdc162 | ENSOCUG00000006035 | |
| CCDC92B | Ccdc92b | Ccdc92b | ENSOCUG00000027623 |
| CLCA3P | Clca3a1, Clca3a2, Clca3b | Clca5, Clca4l | ENSOCUG00000003548 |
| CMAHP | Cmah | Cmahp | ENSOCUG00000004430 |
| CRYGFP | ENSOCUG00000010967 | ||
| CST13P | Cst13 | Cst13 | ENSOCUG00000026263 |
| CTF2P | Ctf2 | Ctf2 | ENSOCUG00000027802 |
| CYMP | Cym | Cym | ENSOCUG00000026023 |
| CYP2G1P | Cyp2g1 | Cyp2g1 | ENSOCUG00000005745 |
| CYP2G2P | Cyp2g1 | Cyp2g1 | ENSOCUG00000005745 |
| DPY19L2P1 | Dpy19l2 | Dpy19l2 | ENSOCUG00000009890 |
| FBXL21P | Fbxl21 | Fbxl21 | |
| FER1L4 | Fer1l4 | Fer1l4 | ENSOCUG00000012872 |
| FMO6P | Fmo6 | Fmo6 | ENSOCUG00000005169 |
| GUCY1B2 | Gucy1b2 | Gucy1b2 | |
| H1-9 | Hils1 | Hils1 | ENSOCUG00000012304 |
| H2BU2P | H2bu2 | Hist3h2ba | |
| HTR5BP | Htr5b | Htr5b | ENSOCUG00000016884 |
| KLRA1P | Klra2 | Ly49i7 | ENSOCUG00000007301 |
| KRT43P | ENSOCUG00000011173 | ||
| LINC00643 | ENSOCUG00000026292 | ||
| METTL21EP | Mettl21e | Mettl21cl1 | ENSOCUG00000012425 |
| OFCC1 | AABR07027339.1 | ENSOCUG00000016635 | |
| OR10AA1P | Olfr433 | ENSOCUG00000036381 | |
| OR13C6P | Olfr159 | Olr836 | |
| OR2S1P | Olfr155 | Olr840 | |
| PCDHB17P | Pcdhb14 | Pcdhb14 | |
| PRORSD1P | Prorsd1 | Prorsd1 | ENSOCUG00000011673 |
| PRSS40A | Prss40 | ||
| PRSS40B | Prss40 | ENSOCUG00000006394 | |
| PRSS46P | Prss46 | Prss46 | ENSOCUG00000039130 |
| SKINT1L | Skint1 | Skint1 | |
| SLC22A20P | Slc22a20 | Slc22a20 | ENSOCUG00000003132 |
| TAAR4P | Taar4 | Taar4 | ENSOCUG00000024372 |
| TDH | Tdh | Tdh | ENSOCUG00000011294 |
| TMED11P | Tmed11 | Tmed11 | |
| TMEM198B | Tmem198b | Tmem198b | ENSOCUG00000027671 |
| TMEM30CP | Tmem30c | Tmem30c | ENSOCUG00000027470 |
| UOX | Uox | Uox | ENSOCUG00000027397 |
| ZNF271P | Zfp35 | Zfp35 | ENSOCUG00000029705 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubanov, L.I.; Zverkov, O.A.; Shilovsky, G.A.; Seliverstov, A.V.; Lyubetsky, V.A. Protein-Coding Genes in Euarchontoglires with Pseudogene Homologs in Humans. Life 2020, 10, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090192
Rubanov LI, Zverkov OA, Shilovsky GA, Seliverstov AV, Lyubetsky VA. Protein-Coding Genes in Euarchontoglires with Pseudogene Homologs in Humans. Life. 2020; 10(9):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090192
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubanov, Lev I., Oleg A. Zverkov, Gregory A. Shilovsky, Alexandr V. Seliverstov, and Vassily A. Lyubetsky. 2020. "Protein-Coding Genes in Euarchontoglires with Pseudogene Homologs in Humans" Life 10, no. 9: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090192
APA StyleRubanov, L. I., Zverkov, O. A., Shilovsky, G. A., Seliverstov, A. V., & Lyubetsky, V. A. (2020). Protein-Coding Genes in Euarchontoglires with Pseudogene Homologs in Humans. Life, 10(9), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090192








