ANN-Based Pattern Recognition for Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bar Monitoring under Supply Frequency Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modelling of Rotor Bar Crack Fault
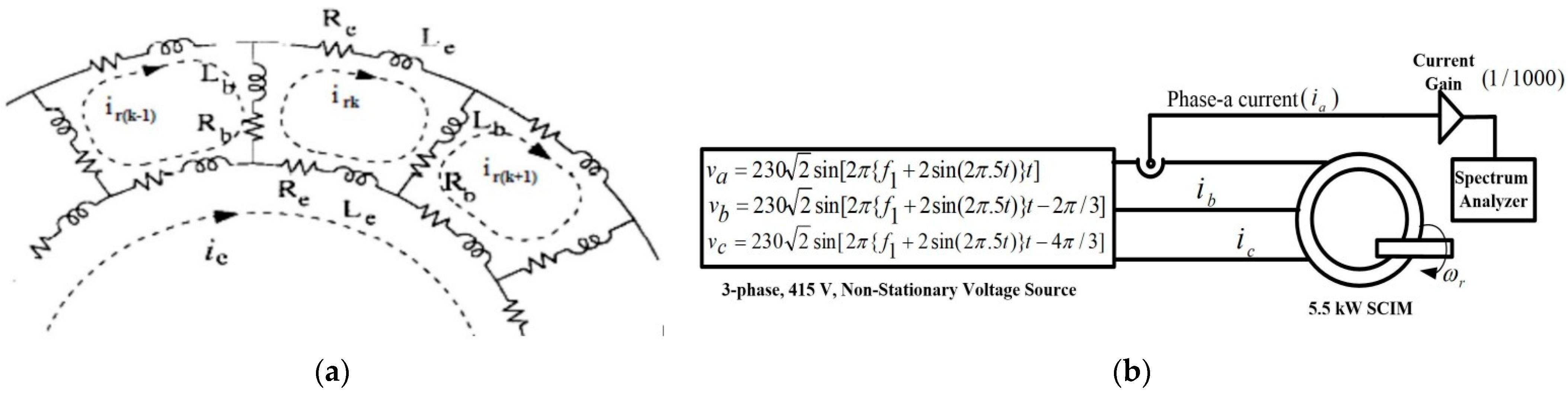
2.1. Winding Function Theory-Based Modelling of SCIM
2.2. Modelling of SCIM Subjected to Frequency Regulation
2.3. Modelling of Rotor Bar Crack
3. Simulation Results
3.1. FFT-Based Analysis
3.1.1. Choice of Sampling Frequency
3.1.2. Analysis of Stationary Current Signal Using FFT
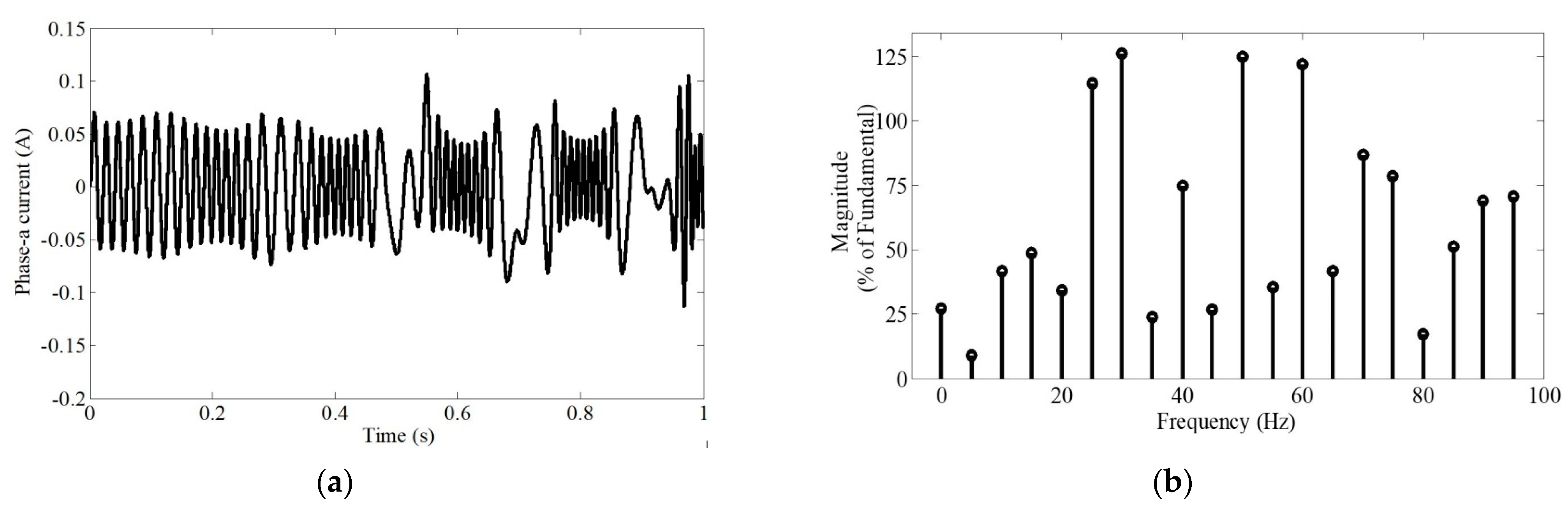
3.1.3. Analysis of Non-Stationary Current Signal
3.2. DWT-Based MULTI-Resolution Analysis
3.2.1. Choice of Sampling Frequency for DWT Analysis
3.2.2. Choice of Mother Wavelet and Number of Decomposition Levels
3.2.3. Analysis of Stationary and Non-Stationary Current Signals by DWT for a Motor operating at Variable Load
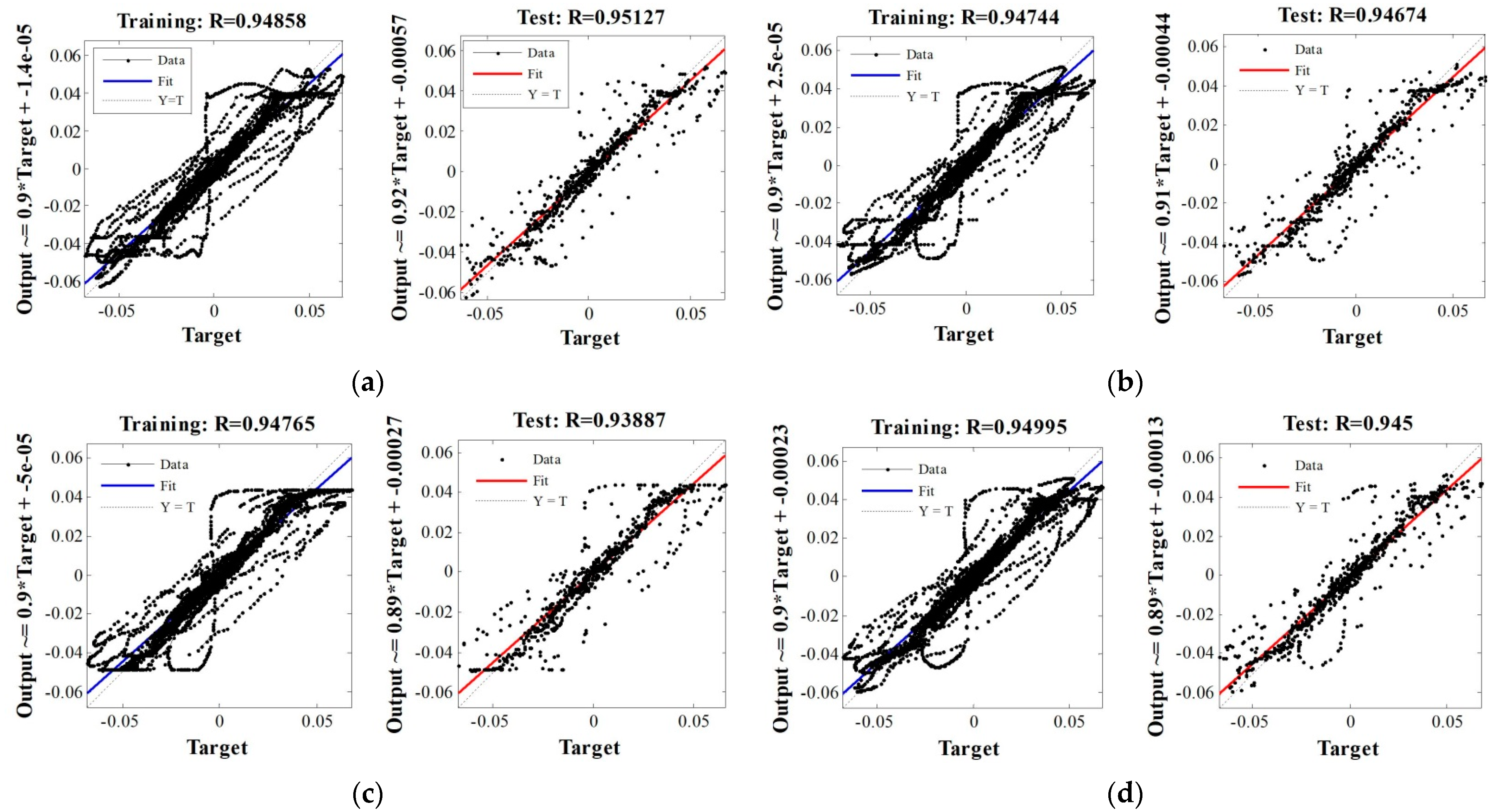
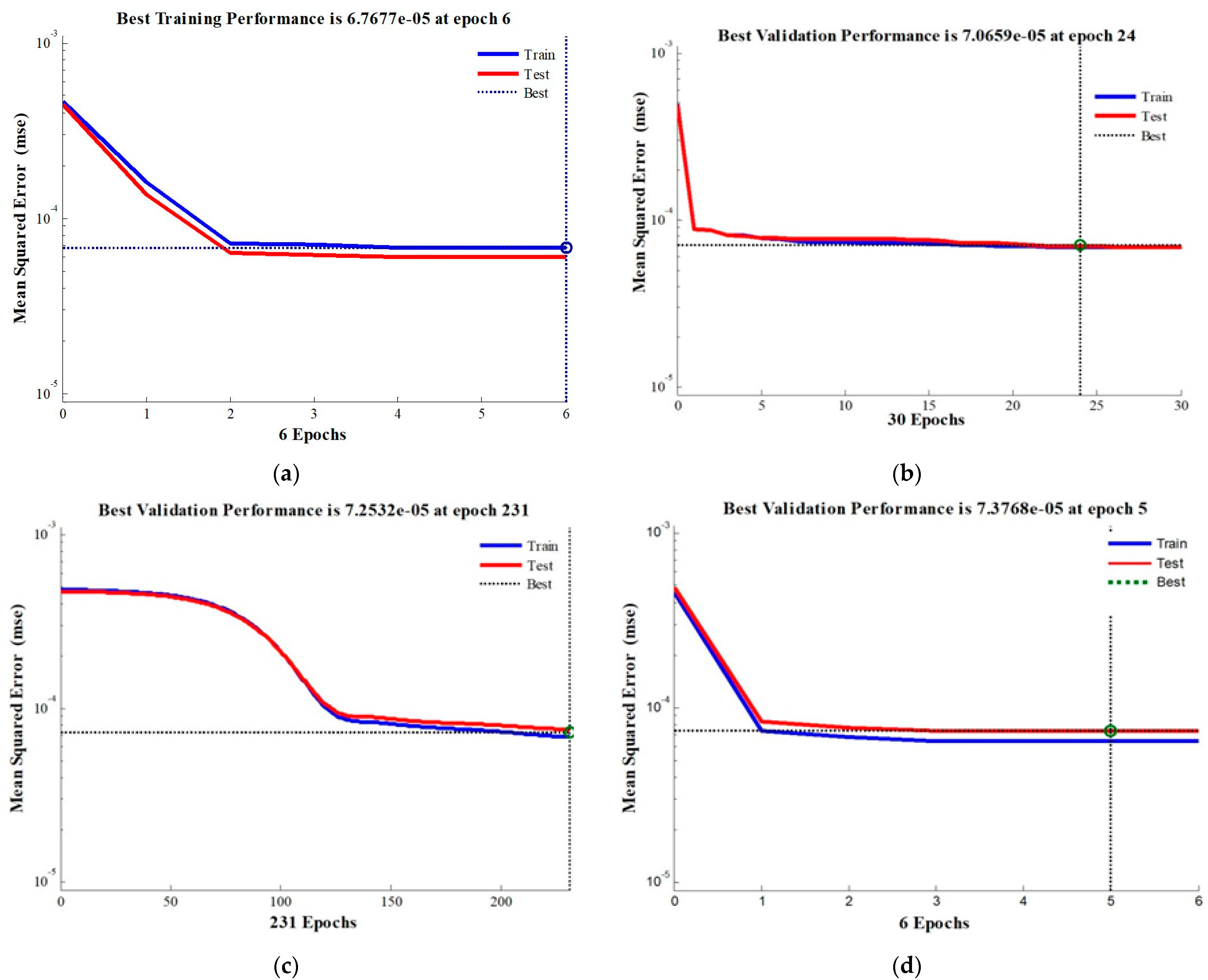
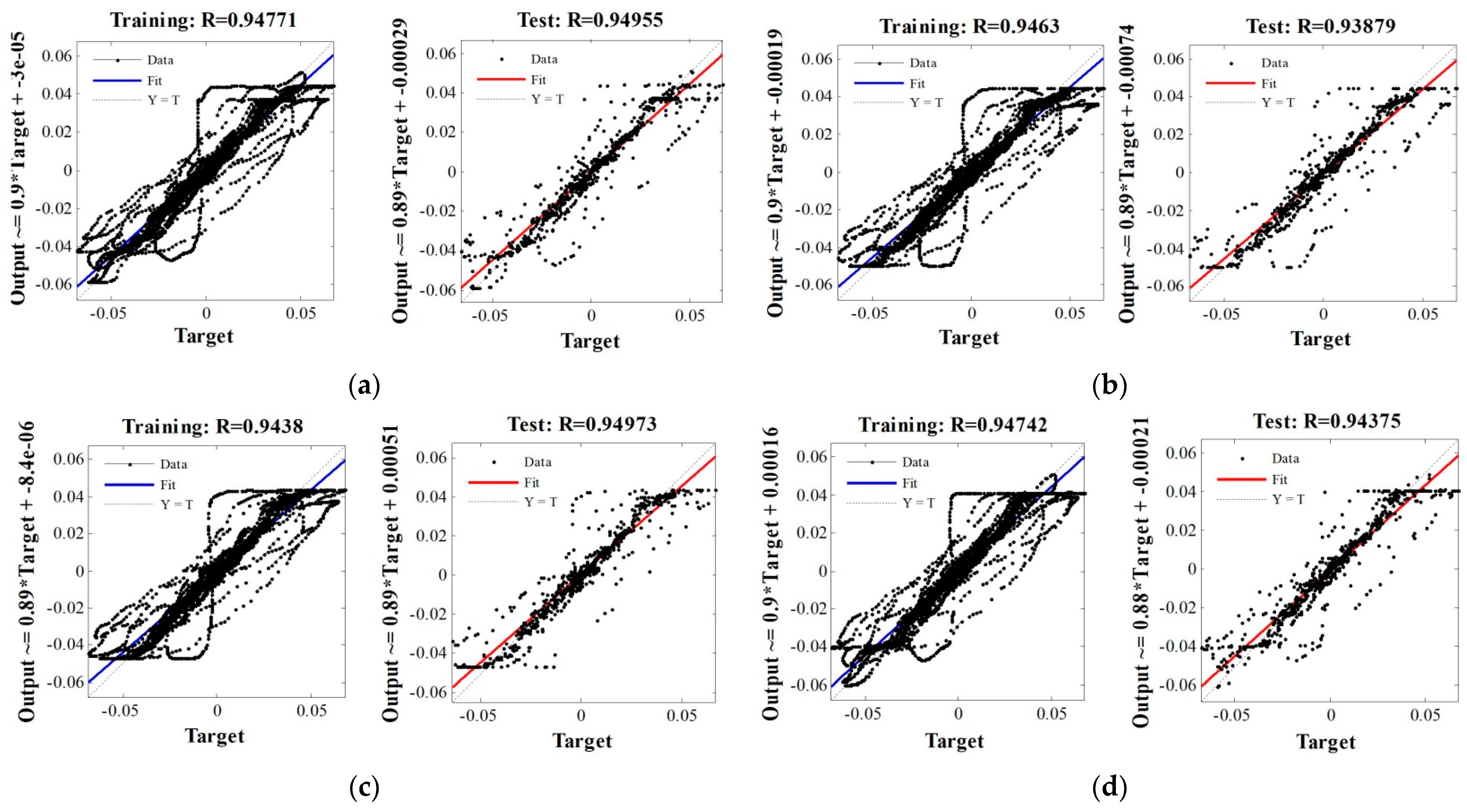
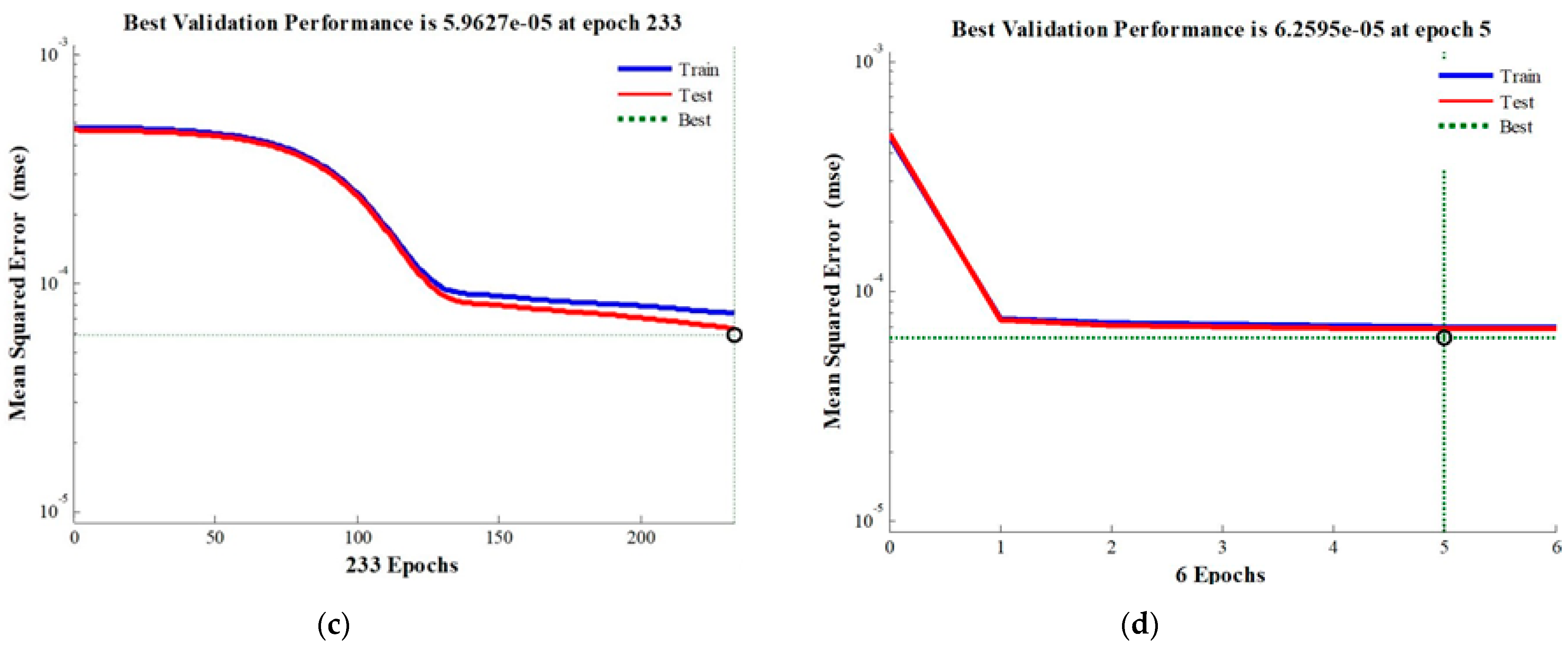
3.3. ANN-Based Analysis
3.4. Modelling of DWT-Based Fault Detection Scheme
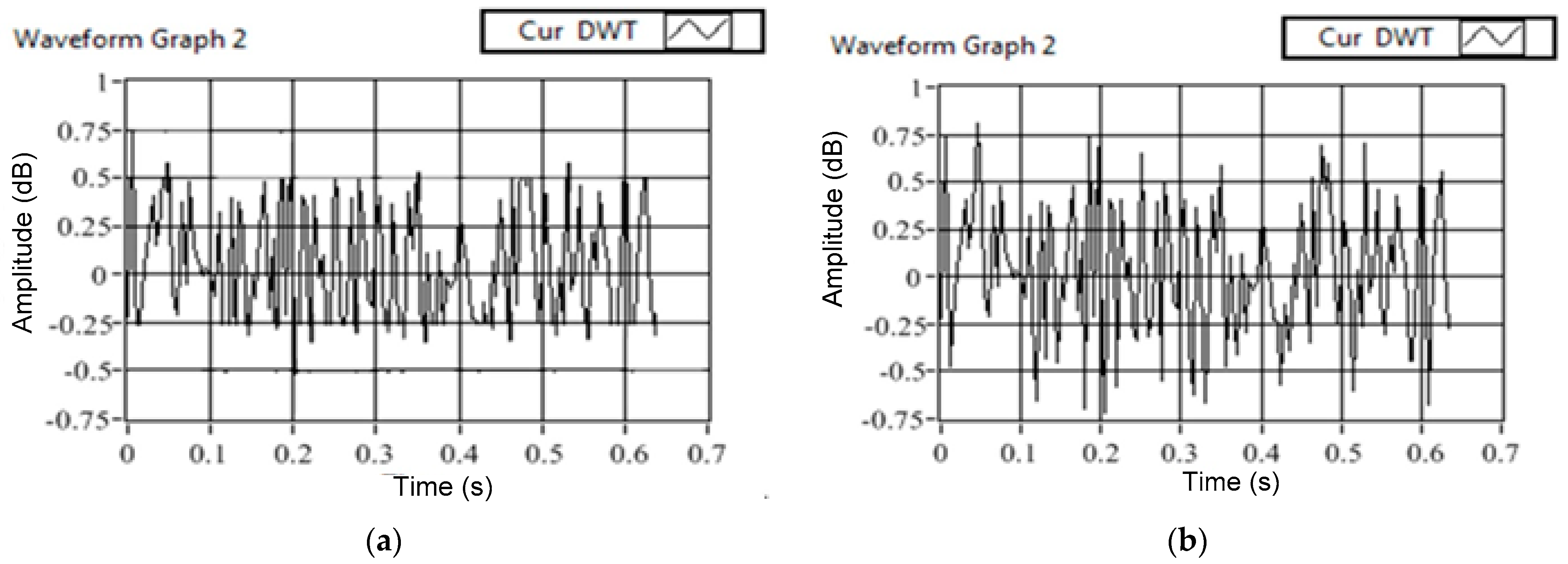
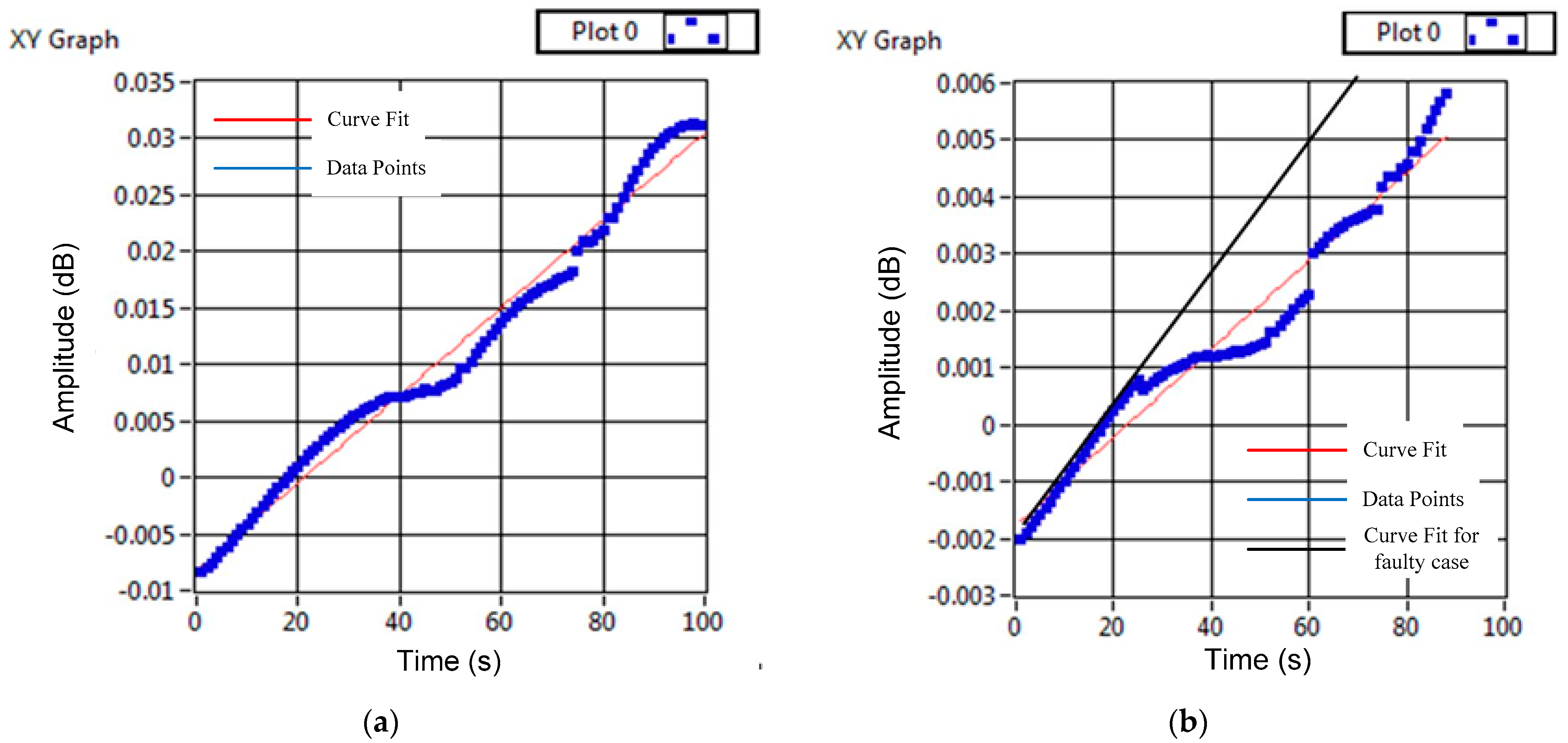
4. Real-Time Validation
4.1. LabVIEW-Based Laboratory Prototype
4.2. Results of Fault Detection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description |
| s | Slip of the machine (%) |
| f1 | Supply frequency (Hz) |
| p | Number of pole pairs |
| Ωr | Rotor speed (rad/s) |
| Rb,Lb | Rotor bar resistance (Ω), inductance (H) |
| Rinc | Increase in rotor resistance () |
| Re, Le | End-ring resistance (), inductance (H) |
| N1 | Turn number of one stator winding |
| N | Total number of rotor bars |
| Nb | Contiguous number of cracked bars |
| fsb | Higher-order slot harmonics |
| [Vs][Ir] | Stator voltage, rotor loop current matrices |
| [Rr][Lr] | Rotor resistance, inductance matrices |
| Φs, Φr | Total flux linkages of stator and rotor winding |
| θr | Angular rotor position |
| Φ | Particular point along the air-gap |
| l | Effective length of the motor |
| Ntsp, Nspp | Number of turns/slot/phase, number of slots/pole/phase |
| Nk (θr, φ) | Winding function of rotor windings |
| La, Lb, Lc, Lab, Lbc, Lca | Elements of |
| Lk1……Lkk | Elements of |
| Lak, Lbk, Lck | Elements of |
| θk | Angular position of bar ‘k’ |
| Alsb, Ausb | Lower, upper fault side-band amplitude (%) |
| va, vb, vc | Voltages of phase-a, phase-b, phase-c (V) |
| ia, ib, ic | Currents of phase-a, phase-b, phase-c (A) |
| Fs | Sampling frequency (Hz) |
| t | Time (s) |
| L | Number of decomposition levels |
| nf | Detailed coefficient containing 50 Hz |
| flsb, fusb | Lower, upper side-band frequency (Hz) |
| [Is] | Stator current vector |
| [Rs] | Stator winding resistance matrix |
| [Ls] | Stator winding inductance matrix |
| [Lsr] | Stator to rotor mutual inductance matrix |
| Tem, TL | Electromagnetic, load torques (Nm) |
| J | Rotor inertia (Kg-m2) |
| F | Coefficient of friction |
| μ0 | Permeability of air |
| r | Air-gap average radius (mm) |
| Ns, Ns1 | Effective, the actual number of turns of the stator winding |
| g | Air-gap length (mm) |
| N1 (θr, φ), Nj (θr, φ) | Winding function of circuit and |
| Kp, Kd, Ks | Pitch, distribution, skew factors |
| Na, Nb, Nc | Winding function of stator windings |
| αr | Angle between any two adjacent bars |
Appendix A. Motor Parameters
| Parameters | Ratings |
| Shaft power | 5.5 kW |
| Rated voltage | 415 V |
| Frequency | 50 Hz |
| Synchronous speed | 1500 rpm |
| Stator resistance/phase | 1.83 Ω |
| Stator inductance/phase | 0.0074 H |
| Rotor resistance referred to stator/phase | 1.26 Ω |
| Rotor inductance referred to stator/phase | 0.007 H |
| Mutual inductance | 0.198 H |
| Number of stator slots | 36 |
| Number of rotor slots | 28 |
| Number of poles | 4 |
References
- Krichen, M.; Elbouchikhi, E.; Benhadj, N.; Chaieb, M.; Benbouzid, M.E.H.; Neji, R. Motor current signature analysis-based permanent magnet synchronous motor demagnetisation characterisation and detection. Machines 2020, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavizadeh, S.A.; Mousavi, S.M.G. A review on condition monitoring and diagnostic techniques of rotating electrical machines. J. Phys. Sci. 2014, 310–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbouchikhi, E.; Choqueuse, V.; Benbouzid, M.E.H. Induction machine faults detection using stator current parametric spectral estimation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 52, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Du, Y.; Habetler, T.G.; Lu, B. A survey of condition monitoring and protection methods for medium-voltage induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Toliyat, H.A. Condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of electrical motors—A review. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavner, P.; Ran, L.; Penman, J.; Sedding, H. Condition Monitoring of Rotating Electrical Machines; IET: London, UK, 2008; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- Gritli, Y.; Bellini, A.; Rossi, C.; Casadei, D.; Filippetti, F.; Capolino, G.A. Condition monitoring of mechanical faults in in-duction machines from electrical signatures: Review of different techniques. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th international symposium on diagnostics for electrical machines, power electronics and drives (SDEMPED), Tinos, Greece, 29 August–1 September 2017; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Jigyasu, R.; Sharma, A.; Mathew, L.; Chatterji, S. A review of condition monitoring and fault diagnosis methods for induction motor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 14–15 June 2018; pp. 1713–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Cabanas, M.F.; Pedrayes, F.; González, M.R.; Melero, M.G.; Rojas, C.H.; Orcajo, G.A.; Cano, J.M.; Nuno, F. A New Electronic Instrument for the Early Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Asynchronous Motors Working Under Arbitrary Load Conditions. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electric Machines, Power Electronics, and Drives (SDEMPED), Vienna, Austria, 7–9 September 2005; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, H.; Pillay, P.; Ziarani, A.K. Broken rotor bar detection in induction machines with transient operating speeds. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbouzid, M.E.H. (Ed.) Signal Processing for Fault Detection and Diagnosis in Electric Machines and Systems; IET: London, UK, 2020; p. 284. ISBN 978-1-83953-025-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, P.J.; Belahcen, A.; Arkkio, A. Signatures of electrical faults in the force distribution and vibration pattern of induction motors. IEEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2006, 163, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippetti, F.; Franceschini, G.; Tassoni, C.; Vas, P. AI techniques in induction machines diagnosis including the speed ripple effect. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehala, N.; Dahiya, R. A Comparative Study of FFT, STFT and Wavelet Techniques for Induction Machine Fault Diagnostic Analysis. In Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Man-Machine Systems and Cybernetics, Cairo, Egypt, 29–31 December 2008; Volume 2931. [Google Scholar]
- Riera-Guasp, M.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Roger-Folch, J.; Palomares, M.P.M. The use of the wavelet approximation signal as a tool for the diagnosis of rotor bar failures. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Hernandez, J.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.; Pons-Llinares, J.; Climente-Alarcon, V.; Frances-Galiana, V. Transient-based rotor cage assessment in induction motors operating with soft starters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3734–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Z.; Wang, W.; Ismail, F. A spectrum synch technique for induction motor health condition monitoring. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, A.; Samanta, A.K.; Routray, A.; Deb, A.K. A method for detecting half-broken rotor bar in lightly loaded induction motors using current. IEEE Trans Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 1614–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritli, Y.; Lee, S.B.; Filippetti, F.; Zarri, L. Advanced diagnosis of outer cage damage in double-squirrel-cage induction motors under time-varying conditions based on wavelet analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonino-Daviu, J.; Riera-Guasp, M.; Pons-Llinares, J.; Park, J.; Lee, S.B.; Yoo, J.; Kral, C. Detection of broken outer-cage bars for double-cage induction motors under the start-up transient. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Llinares, J.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Riera-Guasp, M.; Lee, S.B.; Kang, T.J.; Yang, C. Advanced induction motor rotor fault diagnosis via continuous and discrete time-frequency tools. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskes, H.; Braham, A. Recursive undecimated wavelet packet transform and DAG SVM for induction motor diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Kang, T.J.; Hyun, D.; Lee, S.B.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Pons-Llinares, J. Reliable detection of induction motor rotor faults under the rotor axial air duct influence. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 2493–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kim, J.M. Reliable fault diagnosis of multiple induction motor defects using a 2-D representation of shannon wavelets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonino-Daviu, J.; Aviyente, S.; Strangas, E.G.; Riera-Guasp, M. Scale invariant feature extraction algorithm for the automatic diagnosis of rotor asymmetries in induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hati, A.S. Deep convolutional neural network based on adaptive gradient optimiser for fault detection in SCIM. ISA Trans. 2021, 111, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hati, A.S. Convolutional neural network with batch normalisation for fault detection in squirrel cage induction motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 15, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Jain, A.; Radhika, S. Neuro-fuzzy Classifier for Identification of Stator Winding Inter-Turn Fault for Industrial Machine. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Modelling, Simulation and Intelligent Computing, Dubai, UAE, 29–31 January 2020; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Hati, A.S. Review on machine learning algorithm based fault detection in induction motors. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.K.; Marei, M.I.; El-Gohary, H.S.; Shehata, S.A.M. Modeling of induction motor based on winding function theory to study motor under stator/rotor internal faults. In Proceedings of the 14th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON’10), Cairo, Egypt, 19–21 December 2010; pp. 494–500. [Google Scholar]
- Taher, S.A.; Malekpour, M. A novel technique for rotor bar failure detection in single-cage induction motor using FEM and MATLAB/SIMULINK. Math. Probl. Eng. 2011, 2011, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Alger, P.L. Induction Machines; Gordon and Breach: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Bellini, A.; Filippetti, F.; Franceschini, G.; Tassoni, C.; Kliman, G.B. Quantitative evaluation of induction motor broken bars by means of electrical signature analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.K.; Das, S.; Chatterjee, T.K. Empirical relation for broken bar determination in SCIM. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 37, 242–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halem, N.; Zouzou, S.E.; Srairi, K. Analysis of induction motor with broken bars and constant speed using circuit-field coupled method. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2011, 3, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marcelo, C.; Fossatti, J.P.; Terra, J.I. Fourier Transform-Signal Processing; Salih, S., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Burrus, C.S.; Guo, H. Introduction to Wavelets and Wavelet Transforms: A Primer; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Shashidhara, S.M.; Raju, P.S. Tradeoff analysis of wavelet transform techniques for the detection of broken rotor bars in induction motors. Adv. Electron. Electr. Eng. 2013, 3, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Chen, Z.; Vagapov, Y. Wavelet transform based broken rotor-bar fault detection and diagnosis performance evaluations. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 69, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Neural Networks and Deep Learning; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Chong, K.T. Induction Machine Condition Monitoring Using Neural Network Modeling. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Nagpal, S.; Desai, A.; Sudha, R. An efficient neural-network model for real-time fault detection in industrial machine. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 1297–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mathew, L.; Chatterji, S.; Goyal, D. Artificial Intelligence-Based Fault Diagnosis for Condition Monitoring of Electric Motors. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 2059043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serin, G.; Sener, B.; Ozbayoglu, A.M.; Unver, H.O. Review of tool condition monitoring in machining and opportunities for deep learning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 109, 953–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, T.; Yerchuru, J.; Krishnan, H.; Aravind, R.N.; Yameni, R. Development of tool condition monitoring system in end milling process using wavelet features and Hoelder’s exponent with machine learning algorithms. Measurement 2021, 173, 108671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| [dn]/[an] | Sampling Frequency Fs (Hz) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6100 | 6150 | 6200 | 6250 | 6300 | 6350 | |
| d1 | 1525–3050 | 1537–3075 | 1550–3100 | 1562–3125 | 1575–3150 | 1588–3175 |
| d2 | 762–1525 | 769–1537 | 775–1550 | 781–1562 | 788–1575 | 794–1588 |
| d3 | 381–762 | 384–769 | 388–775 | 390–781 | 394–788 | 397–794 |
| d4 | 191–381 | 192–384 | 194–388 | 195–390 | 197–394 | 198–397 |
| d5 | 95–191 | 96–192 | 97–194 | 98–195 | 97–197 | 99–198 |
| d6 | 48–95 | 48–96 | 48–97 | 49–98 | 49–98 | 49–98 |
| d7 | 24–48 | 24–48 | 24–48 | 25–49 | 25–49 | 25–49 |
| d8 | 12–24 | 12–24 | 12–24 | 13–25 | 13–25 | 13–25 |
| a8 | 0–12 | 0–12 | 0–12 | 0–13 | 0–13 | 0–13 |
| Correlation Coefficient Value (R) | Mean Square Error Epoch Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cascaded Forward Backdrop | Feed-Forward Backdrop | Cascaded Forward Backdrop | Feed-Forward Backdrop | |
| Bayesian Regulation | 0.95127 | 0.94955 | 6 | 8 |
| Polak-Ribiere Restarts | 0.945 | 0.95373 | 24 | 5 |
| Gradient Descent with momentum and adaptive learning rate | 0.94557 | 0.95264 | 231 | 233 |
| Levenberg-Marquardt | 0.94935 | 0.94925 | 5 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sinha, A.K.; Hati, A.S.; Benbouzid, M.; Chakrabarti, P. ANN-Based Pattern Recognition for Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bar Monitoring under Supply Frequency Regulation. Machines 2021, 9, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9050087
Sinha AK, Hati AS, Benbouzid M, Chakrabarti P. ANN-Based Pattern Recognition for Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bar Monitoring under Supply Frequency Regulation. Machines. 2021; 9(5):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9050087
Chicago/Turabian StyleSinha, Ashish Kumar, Ananda Shankar Hati, Mohamed Benbouzid, and Prasun Chakrabarti. 2021. "ANN-Based Pattern Recognition for Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bar Monitoring under Supply Frequency Regulation" Machines 9, no. 5: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9050087
APA StyleSinha, A. K., Hati, A. S., Benbouzid, M., & Chakrabarti, P. (2021). ANN-Based Pattern Recognition for Induction Motor Broken Rotor Bar Monitoring under Supply Frequency Regulation. Machines, 9(5), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9050087







