Abstract
Abrasive belt grinding is the key technology in high-end precision manufacturing field, but the working condition of abrasive particles on the surface of the belt will directly affect the quality and efficiency during processing. Aiming at the problem of the inability to monitor the wearing status of abrasive belt in real-time during the grinding process, and the challenge of time-consuming control while shutdown for detection, this paper proposes a method for predicating the wear of abrasive belt while the grinding process based on back-propagation (BP) neural network. First, experiments are carried out based on ultra-depth-of-field detection technology, and different parameter combinations are used to measure the degree of abrasive belt wear. Then the effects of different grinding speeds, different contact pressures, and different work piece materials on the abrasive belt wear rate are obtained. It can be concluded that the abrasive belt wear rate gradually increases as the grinding speed of the abrasive belt increases. With the increase of steel grade, the hardness of the steel structure increases, which intensifies the abrasive belt wear. As the contact pressure increases, the pressure on a single abrasive particle increases, which ultimately leads to increased wear. With the increase of contact pressure, the increase of the wear rate of materials with higher hardness is greater. By utilizing the artificial intelligence BP neural network method, 18 sets of experiment data are used for training BP neural network while 9 sets of data are used for verification, and the nonlinear mapping relationship between various process parameter combinations such as grinding speed, contact pressure, workpiece material, and wear rate is established to predict the wear degree of abrasive belt. Finally, the results of verification by examples show that the method proposed in this paper can fulfill the purpose of quickly and accurately predicting the degree of abrasive belt wear, which can be used for guiding the manufacturing processing, and greatly improving the processing efficiency.
1. Introduction
Since the 1960s, the technology of abrasive belt grinding has been greatly developed. It has already been considered as another classic processing method after traditional turning, wheel grinding, and milling. Its production efficiency is 5–20 times higher than that of wheel grinding [1], whether it is surface grinding, internal and external cylindrical grinding, or complex surface grinding, can make the entire process more efficient and rapid [2,3]. However, the single-layer abrasive grain structure of the abrasive belt will bring about short life problems. The life of the abrasive belt is related to its performance and effective grinding area. In order to extend the service life of the abrasive belt, on the one hand, it is necessary to select an abrasive belt with stable grinding performance and high durability under the premise of meeting the grinding requirements, and optimize the grinding process to increase the wear. On the other hand, it is necessary to design a special abrasive belt grinding mechanism to increase the effective grinding area of the abrasive belt. However, the former is limited by abrasive belt manufacturing technology, while the latter is restricted by the space of polishing equipment, and both have certain limitations. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately determine the degree of abrasive belt wear on the basis of the above requirements, avoid premature replacement when the abrasive belt still has the grinding ability, and at the same time prevent the continued service of the abrasive belt that is reaching its life limitation [4].
2. State of the Art
Abrasive belt will inevitably wear in the process of grinding materials, and the wear of abrasive belt is the result of multiple factors, such as grinding pressure, abrasive belt speed, workpiece materials, etc., the wear forms of abrasive belt will also be different in grinding different materials or under different grinding conditions. Namba et al. [5] obtained the current grinding coefficient through the online tangential force method, and then adjusted the process parameters to ensure that the grinding depth remains unchanged. LeMaster et al. [6] used acoustic emission signal to monitor the wear state of the abrasive belt. It was found that when the workpiece surface is smooth, the acoustic emission signal can monitor the abrasive belt grinding process, and the abrasive belt wear degree, abrasive particle size, and processing parameters will affect the acoustic emission signal. Chen et al. [7] studied the grinding sound signal of abrasive belt by using FFT and wavelet decomposition method, and found that the grinding sound signal has a strong correlation with the wear state of abrasive belt. Under the constant pressure grinding condition, the grinding sound signal energy decreases gradually with the wear of abrasive belt. Ferguson et al. [8] evaluated the wear rate of composites by changing the abrasive particle size, grinding pressure, sliding speed, and sliding distance. Malinov et al. [9] found that with the increase of grinding pressure, the wear resistance of Fe-B alloy decreased, and the wear mechanism changed from micro cutting to the mixed mode of micro cutting and micro tillage. Carrano et al. [10] divided the life cycle of the abrasive belt into four stages: crushing period, stable period, abrasion period, and terminal period, at the same time, they determined the duration of these four wear stages. After identifying the wear state of the abrasive belt, its remaining service life is the sum combining the time duration of the remaining wears stage. This method can only roughly estimate the remaining life of the abrasive belt. Shu et al. [11] used four parameters as variables: the difference in thickness of the skin, the amplitude of the grinding wheel, the temperature of the knife roller, and the output power of the knife roller motor, which are closely related to the grinding wheel wear status of the sharpening system of the smoother. These variables equip with a characteristics of good availability and strong operation, then by using the gray GM (1, N) model, they predicted the wear status of the grinding wheel in the grinding system of the leveler. Zhi [12] implied CBN materials to grind superalloys, and observed the microscopic morphology with SEM, revealing the mechanism of surface quality changing with time. Wang et al. [13] explored the wear mechanism and degree of change of the abrasive belt while using them to grind metallic nickel. At the same time, this experiment also generated five ways to improve the service life of the abrasive belt (reduce the initial wear amount, use grinding aids or cooling lubricants, gradually increase the contact pressure, increase the length of the abrasive belt, and select high-quality Abrasives). Xiao et al. [14] took the diamond flexible grinding wheel as the research object, and explored the influence of the grinding wheel rotation speed, contact pressure, abrasive concentration, and abrasive particle size on the wear of the grinding wheel. Based on the CMOS system, McGibbon et al. [15] conducted data acquisition and data analysis on the grinding contact area and optimized the abrasive belt wear model. Some other studies focused on the abrasive belt wear process which can be used to predict the remaining life of the abrasive belt. Maxence et al. [16] established the micro wear model of sand belt. Mezghani [17] outlined a method by which belt condition can be illustrated graphically on plots of grit size against abrasion energy or applied pressure in connection with the produced surface state (i.e., roughness) for a given wear rate. Peter [18] researched the development of grinding models for titanium metal-matrix composites by investigating possible relationships between their indentation hardness, low-stress belt abrasion, high-stress belt abrasion, and the surface grinding characteristics. Cui et al. [19] built a grinding force test experimental platform based on LabVIEW and calibrated the sensor. Boehm et al. [20] studied the method of using light scattering to monitor the surface roughness, morphology, and vibration trace of workpiece after abrasive belt processing, and found that the vibration wavelength is affected by process parameters such as abrasive belt speed through frequency domain analysis. Zawada et al. [21] studied the method of monitoring the grinding surface of workpiece by using image sensor to monitor the microstructure of abrasive belt, and the grinding time can be estimated according to the workpiece surface image. Through these studies, the change curve of certain wear characteristics with grinding time can be obtained, then according to the identified current abrasive belt wear degree determines the current wear time of the abrasive belt, thus a result can be reached that the difference between the current wear time and the life of the abrasive belt is the remaining life of a belt. However, due to the microscopic complexity and difficulty for observing the abrasive belt wear, various prediction models and derivation models have certain errors and uncertainties. Furthermore, on account of the limitations of the processing environment, it is difficult to achieve real-time detection and the equipment can only be suspended during the manual inspection, which is a waste for both time, cost, and labor costs.
Considering that there is no literature to solve the above problems up to now, this paper proposes a method for predicting abrasive belt wear based on back-propagation (BP) neural network. First, the experiment will be based on ultra-depth-of-field detection technology, different parameter combinations are used to measure the degree of abrasive belt wear, and the effects of different grinding speeds, different contact pressures, and different work piece materials on the abrasive belt wear rate are obtained. Then by utilizing the artificial intelligence BP neural network method, the degree of abrasive belt wears is predicted. Finally, the surface quality inspection technology is employed to evaluate the surface quality of work pieces processed by abrasive belts with different degrees of wear.
3. Wear Prediction Based on BP Neural Network
3.1. BP Neuron Structure
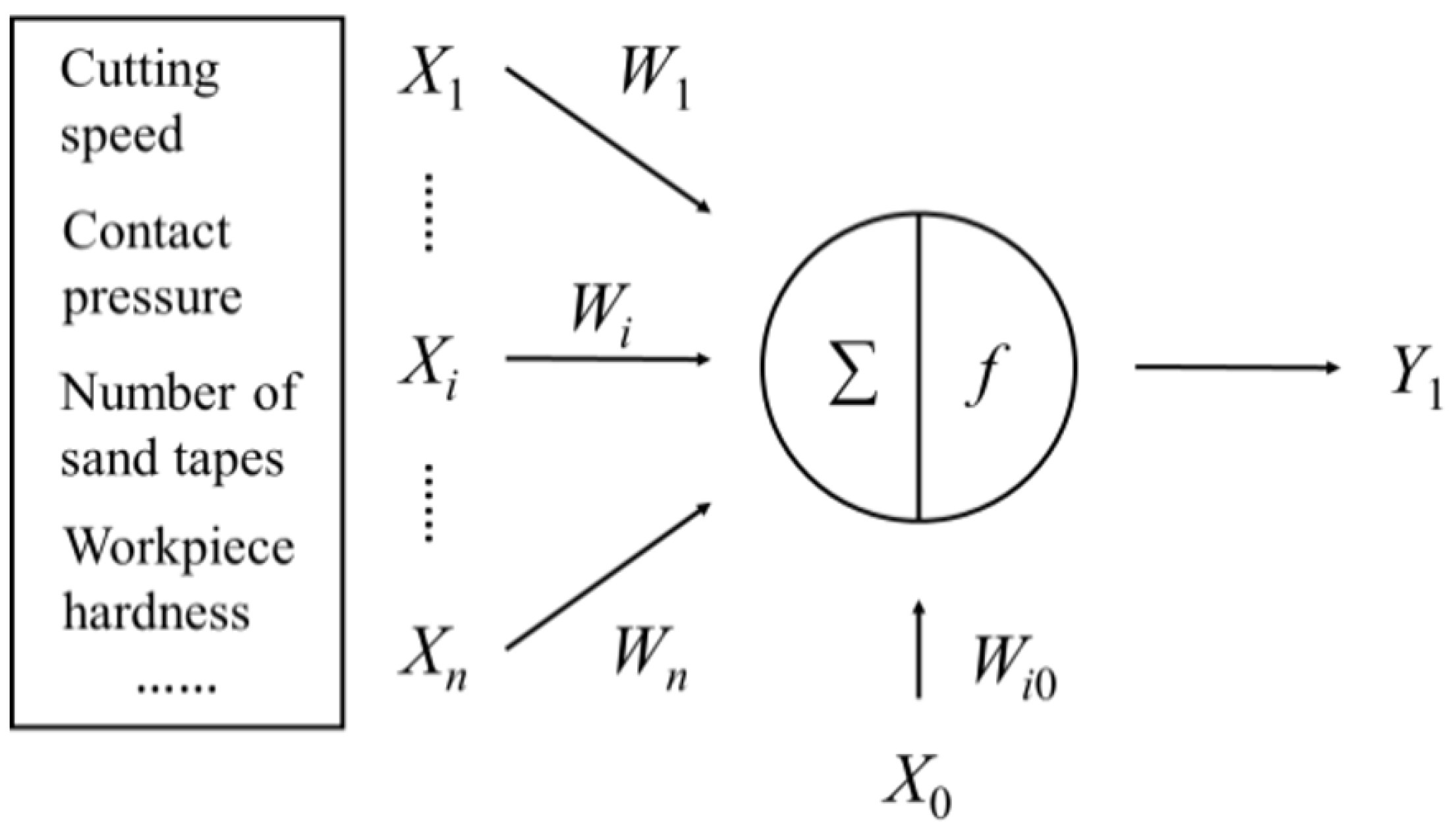
The BP neural network algorithm is based on the method of biological neuron information exchange, simplification, and simulation. The basis of the entire algorithm network is the information processing unit-neuron [22], as shown in Figure 1.
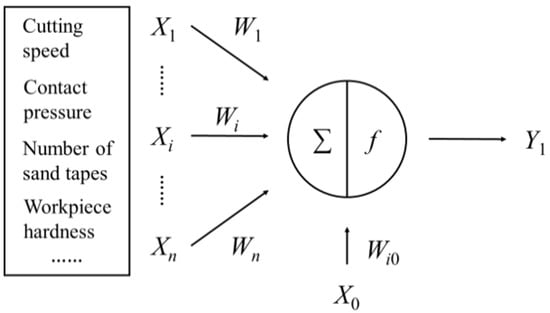
Figure 1.
Neuron schematic.
The neuron is a multi-input single-output non-linear processing unit, which weights the signal transmitted by the upper level, and performs summation under the action of the excitation function [22]:
where Xi is the input signal, f(netj) is the excitation function, i = 1, 2, 3, …, n, and Wi is the connection weight. When i = 0, the weight of X0 is W0 = −1.
3.2. Setting of BP Neuron Topology Parameter
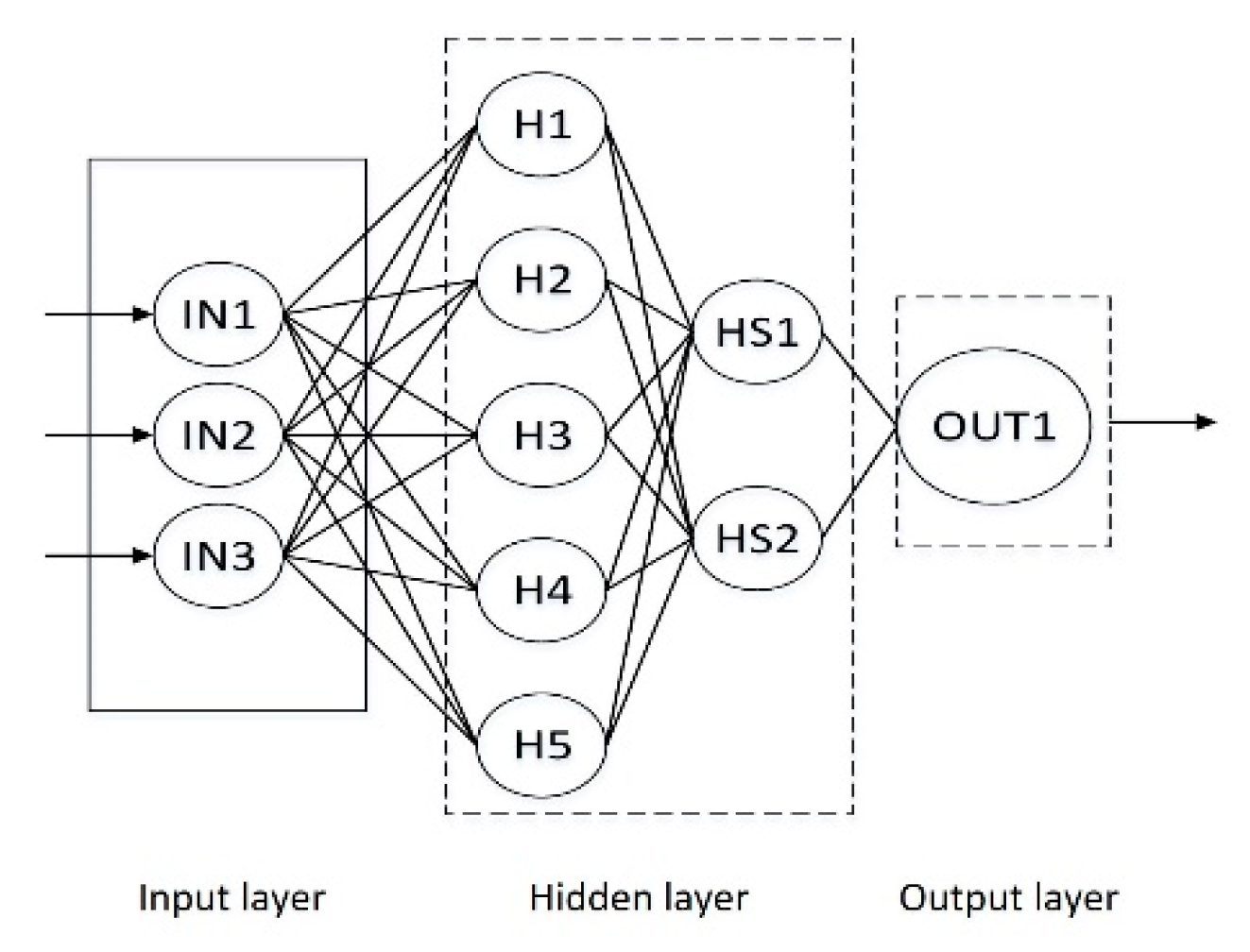
The topology of the neural network is shown in Figure 2, which is divided into output layer, hidden layer, and input layer. The non-linear mapping method between the three layers is used to approximate the result value with the set accuracy. For the set root mean square error value, the back propagation algorithm is adopted, therefore the samples are required for training, followed by input forward transmission, forming a complete closed-loop feedback system, and constantly improving the accuracy of the weight of each neuron to meet the accuracy requirements [23].
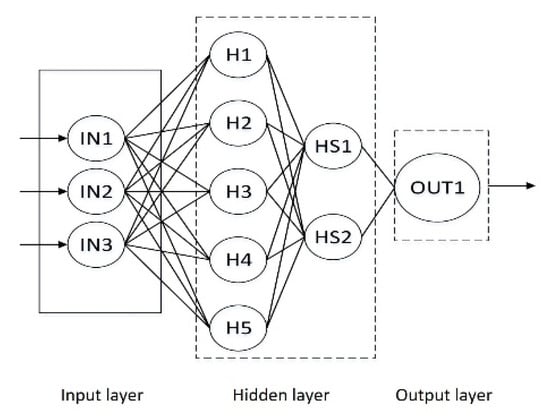
Figure 2.
Topology of the neural network.
(1) Determine the number of nodes in the input and output layer
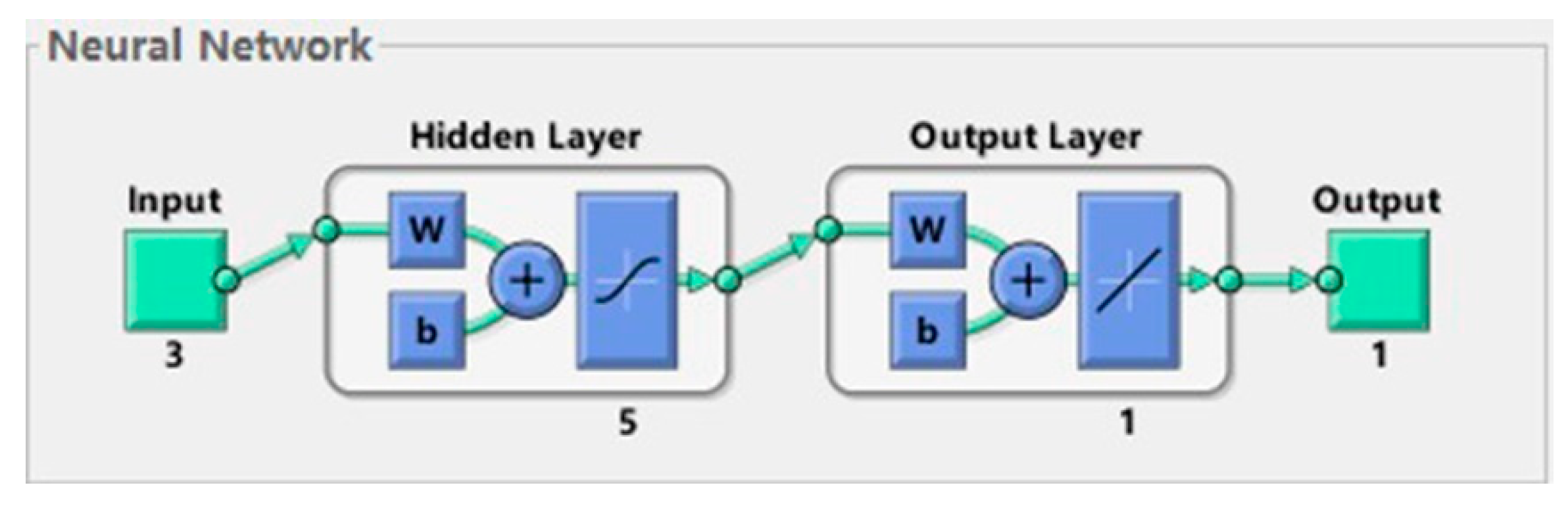
Since there are three input parameters, contact pressure, grinding speed, and material (characterized by elastic modulus), the number of nodes in the input layer n = 3, the wear rate of abrasive belt is the output parameter, so the number of nodes in the output layer is m = 1.
(2) Determine the number of nodes in the hidden layer
The number of hidden layers is related to the processing capacity of the network, which means more complex grid training and extended solution time. When there are too many hidden layer neurons, the network can learn well and achieve the expected network accuracy, but the generalization ability of the network will become worse due to the over fitting of the network to the weights. When the number of neurons is too small, the network performance cannot be brought into full play and it is difficult to complete sample learning [24]. The number of hidden layer neurons in the network is directly related to the complexity of the actual problem, the number of neurons in the input and output layers, and the setting of expected errors. At present, there is still a lack of a general calculation method, mainly referring to empirical formulas which are as follows [25]:
where n is the number of input layer nodes, m is the number of output layer nodes, and a is a constant between one and ten.
(3) Excitation function
The commonly used excitation functions of BP neural network are ramp function and Sigmoid function. Due to the limited output range of Sigmoid excitation function, it is not easy to diverge during data transmission. Therefore, this article chooses the Sigmoid excitation function [26].
3.3. BP Process and Data Processing
(1) Disruption processing
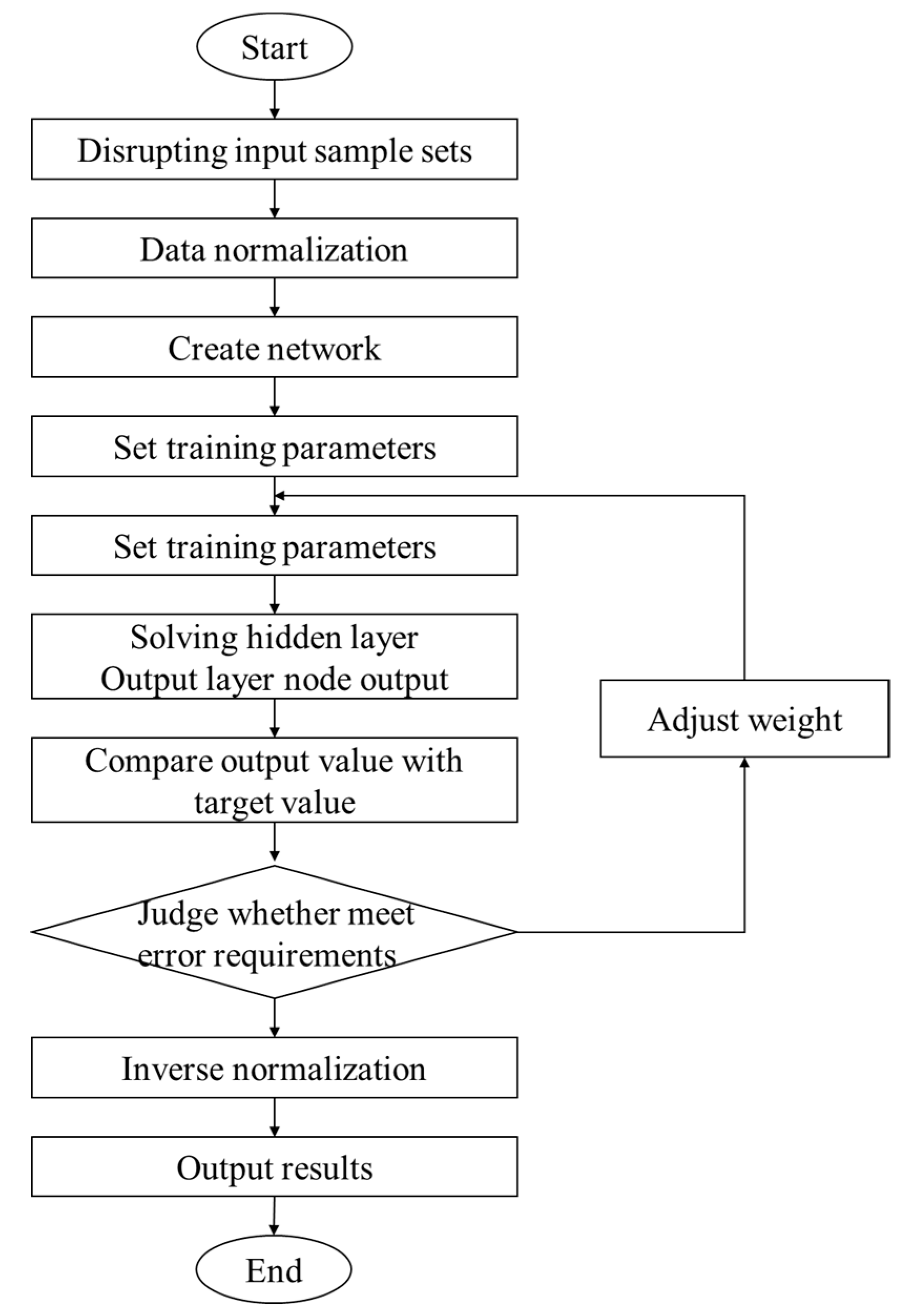
The BP neural network algorithm programming flowchart is shown in Figure 3. In order to reduce the influence of the input data sequence on the result, the input sample set needs to be randomly disrupted by using the “randperm” command in MATLAB.
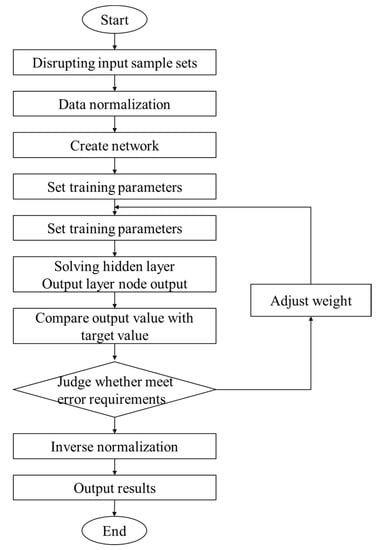
Figure 3.
Programming flowchart of BP neural network algorithm.
(2) Normalization and anti-normalization processing
The BP neural network uses numerical calculations. Because of the difference in the nature of the input data types of different types of data, there will be a very large gap in the order of magnitude. In order to prevent this influence in the data training process, it is necessary to normalize the input data, and the output result is also in the interval [0, 1], then the output result needs to be anti-normalized as follows:
where xi and yi are the normalized data, Xi and Yi are the data before normalization, Xmax and Ymax are the input data respectively, the maximum value of the calculation result data, Xmin, Ymin are the input data respectively, and the calculation result data is the smallest value.
(3) Other parameter settings
In order to verify the accuracy of the BP neural network prediction model, 60–80% data sets are usually used as the training set [27]. Therefore, distribute 27 sets of data, use 18 sets of data for training, and 9 sets of data for verification, which is shown as follows.
P_train = NIR(temp(1:18),:)’;
T_train = octane(temp(1:18),:)’;
P_test = NIR(temp(19:end),:)’;
T_test = octane(temp(19:end),:)’;
The number of iterations and the learning rate are determined by engineering experience. The number of iterations are usually 500–1000. The larger the learning rate, the greater the weight change and the faster the convergence. However, if the learning rate is too large, it will cause system oscillation [28]. In this paper, the number of iterations is set to 500 net, that is trainParam.epochs = 500, and the learning rate is set to 0.01, that is net.trainParam.lr = 0.01.
4. Abrasive Belt Wear Measurement Test
The measurement of abrasive belt wear is the key step to quantify wear, and is also the main indicator of the main assessment of the accuracy of neural network prediction. Therefore, in the abrasive belt wear measurement experiment, high-end testing equipment, as well as specific fixtures and testing methods are used to ensure the reliability and accuracy of data.
4.1. Test Equipment and Testing Equipment
(1) Test equipment
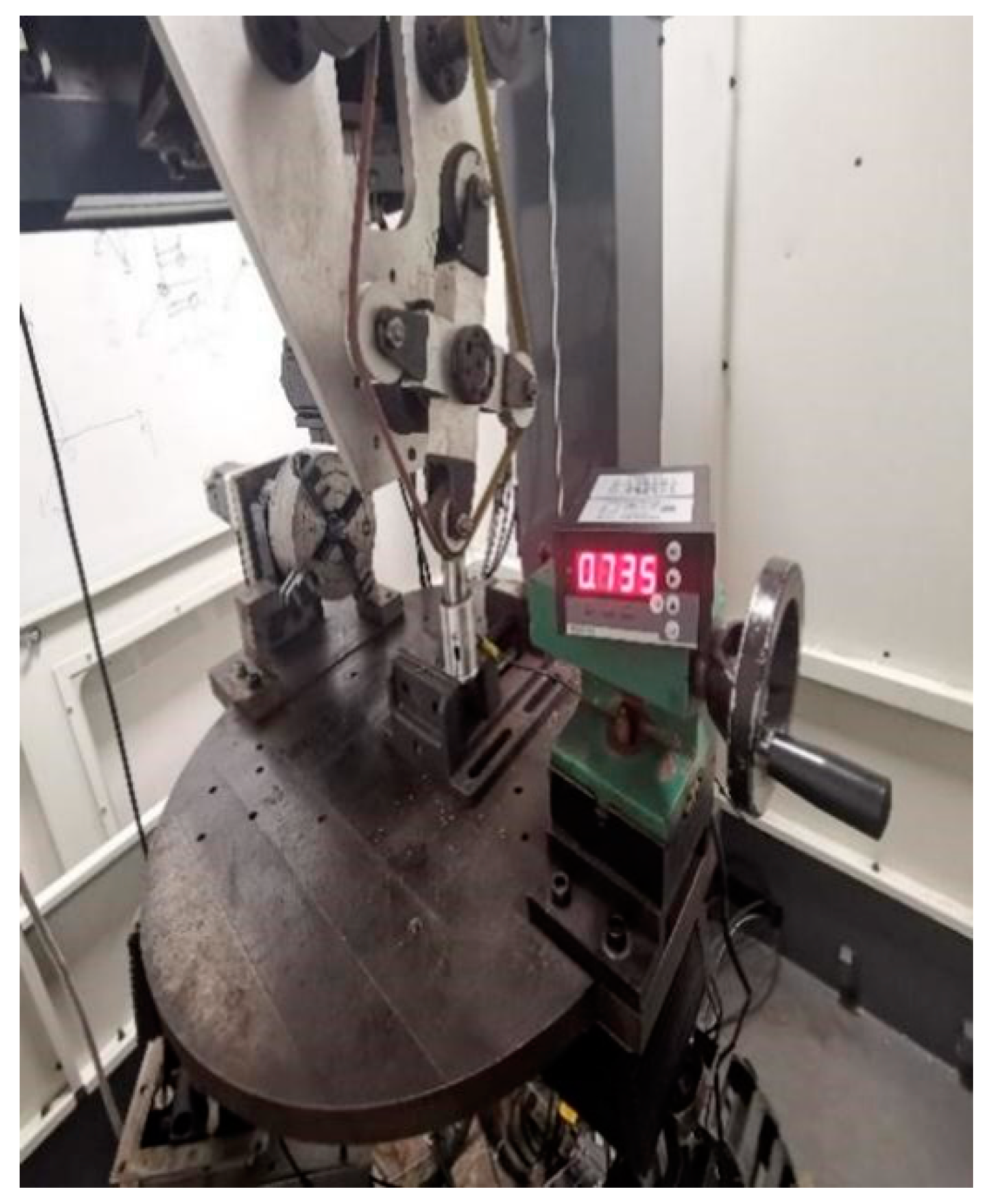
The self-developed series-parallel hybrid belt grinding machine is shown in Figure 4, and the constant force control display adopts the BSCC-H2 ZN4S integrator, as shown in Figure 5.
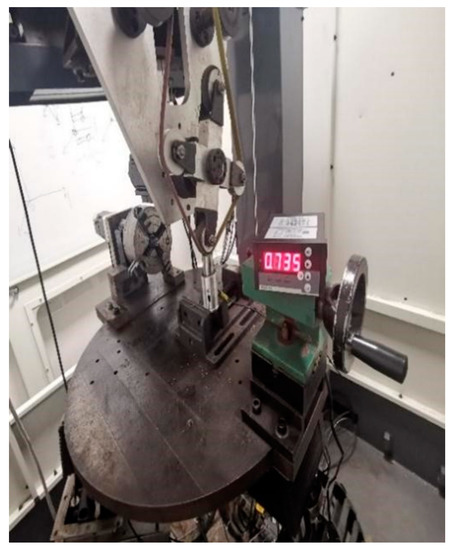

Figure 4.
BSCC-H2 ZN4S integrator.
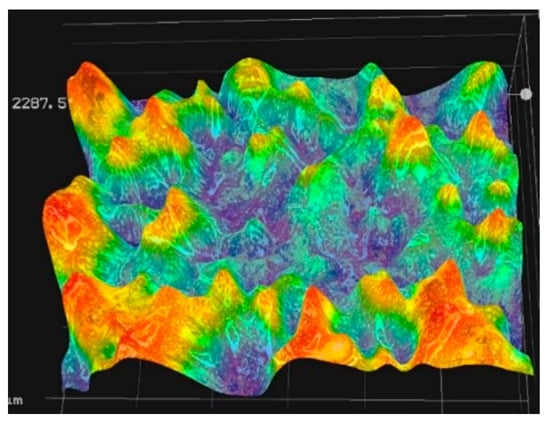
Figure 5.
#80 initial contour morphology of the #80 mesh belt.
(2) Testing equipment
The testing equipment uses a VHK-900 Keneyce ultra-depth-of-field microscope and 3D display plug-in to measure the amount of change in abrasive belt wear.
4.2. Experimental Parameters
Total of 27 sets of experiments were carried out. The three factors are cutting speed, contact pressure, and experimental material (using the elastic modulus of the experimental material as a parameter index to highlight the recognizability of the material, and the experimental parameter table is represented by steel number # instead). The elastic modulus of #20 is 206 GPa, the elastic modulus of #45 is 209 GPa, and the elastic modulus of #65 is 210 GPa. See Table 1 for details.

Table 1.
Experimental parameters.
4.3. Detection Error Control
(1) Pre-wear of abrasive belt
Due to the unevenness and randomness of the abrasive belt sand planting process, it will inevitably lead to the unevenness and randomness of the initial height of the abrasive grains. Therefore, a five-minutes process of pre-wearing is required, which helps to maintain the uniformity of the initial abrasive grain height and reduce random experiment errors.
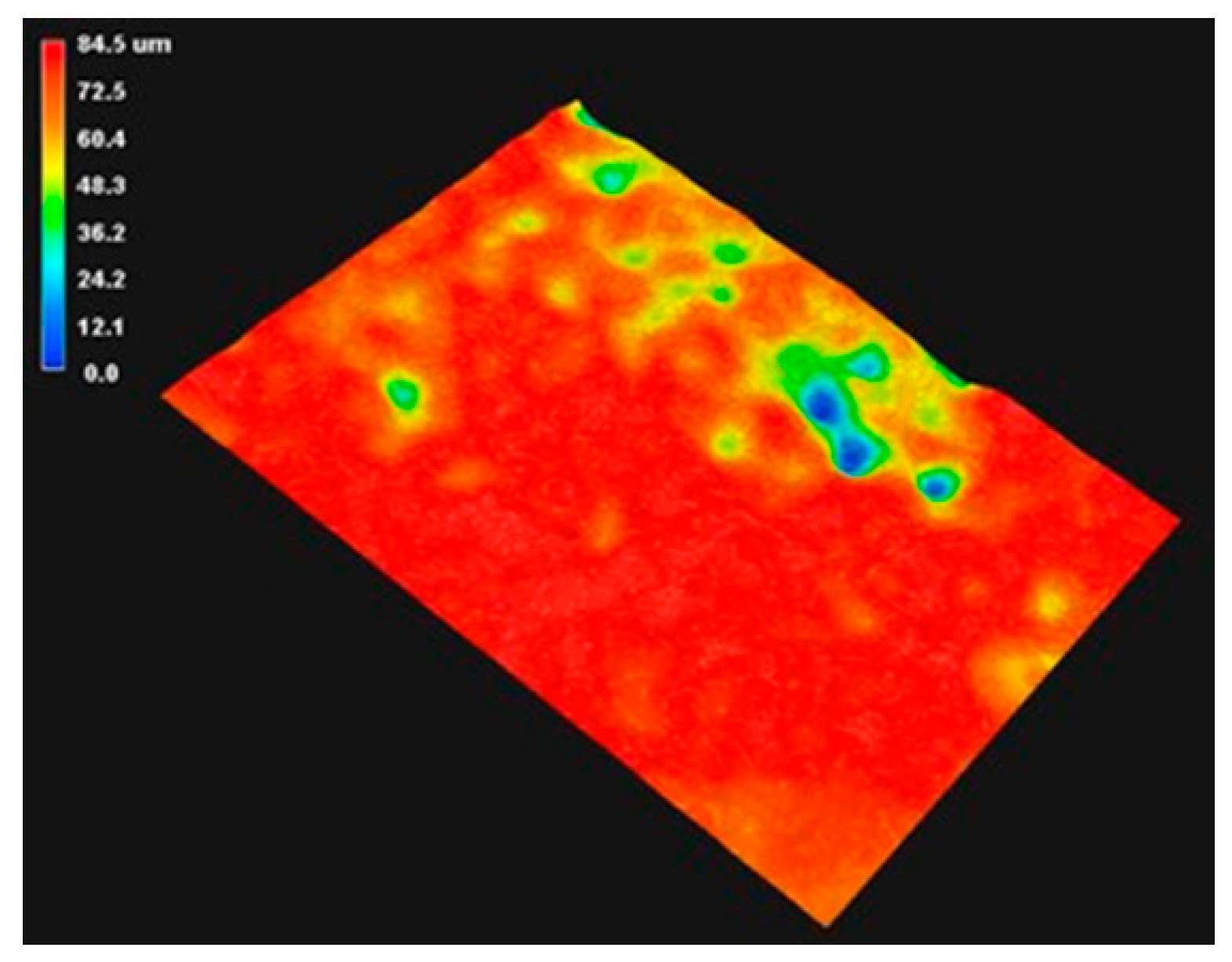
Figure 5 shows the initial contour morphology of the #80 mesh belt. The uneven distribution of the abrasive grain height can be clearly seen, which further reflects the necessity of initial pre-wear. Figure 6 shows the surface contour of the belt near the end of the severe wear stage. According to the color of height spectrum, it can be seen that the overall height of the abrasive grains is reduced, and the surface height is almost the same. However, as the amount of wear increases, the contact area between the abrasive belt and the workpiece increases during the grinding process, which will generate a lot of heat. On the one hand, it will accelerate the abrasive belt wear, and on the other hand, it may burn the surface of the workpiece. Therefore, it is very critical to accurately predict the degree of abrasive belt wear.
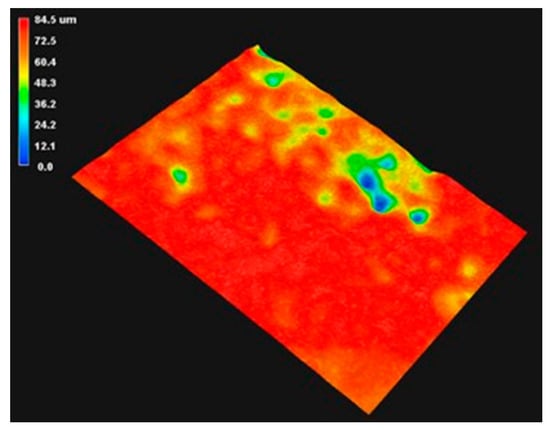
Figure 6.
End of the severe wear stage.
(2) Calibration of belt position interval
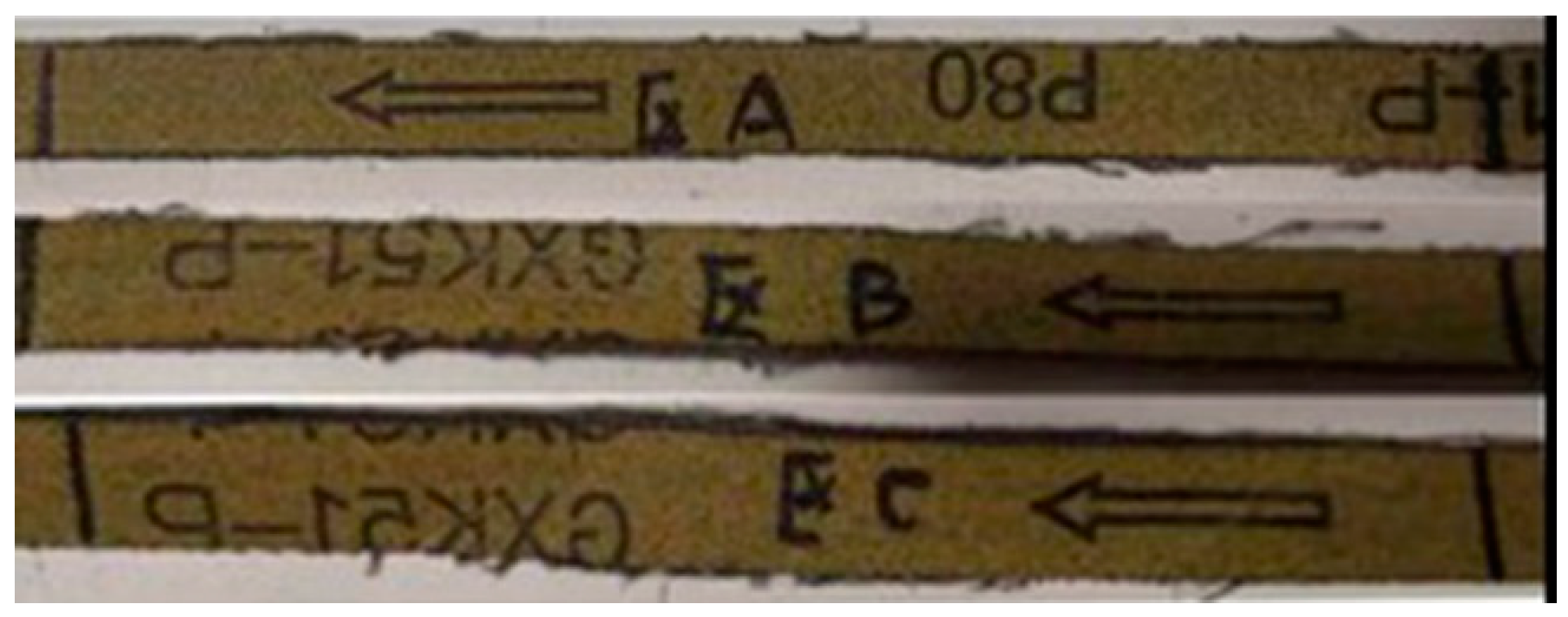
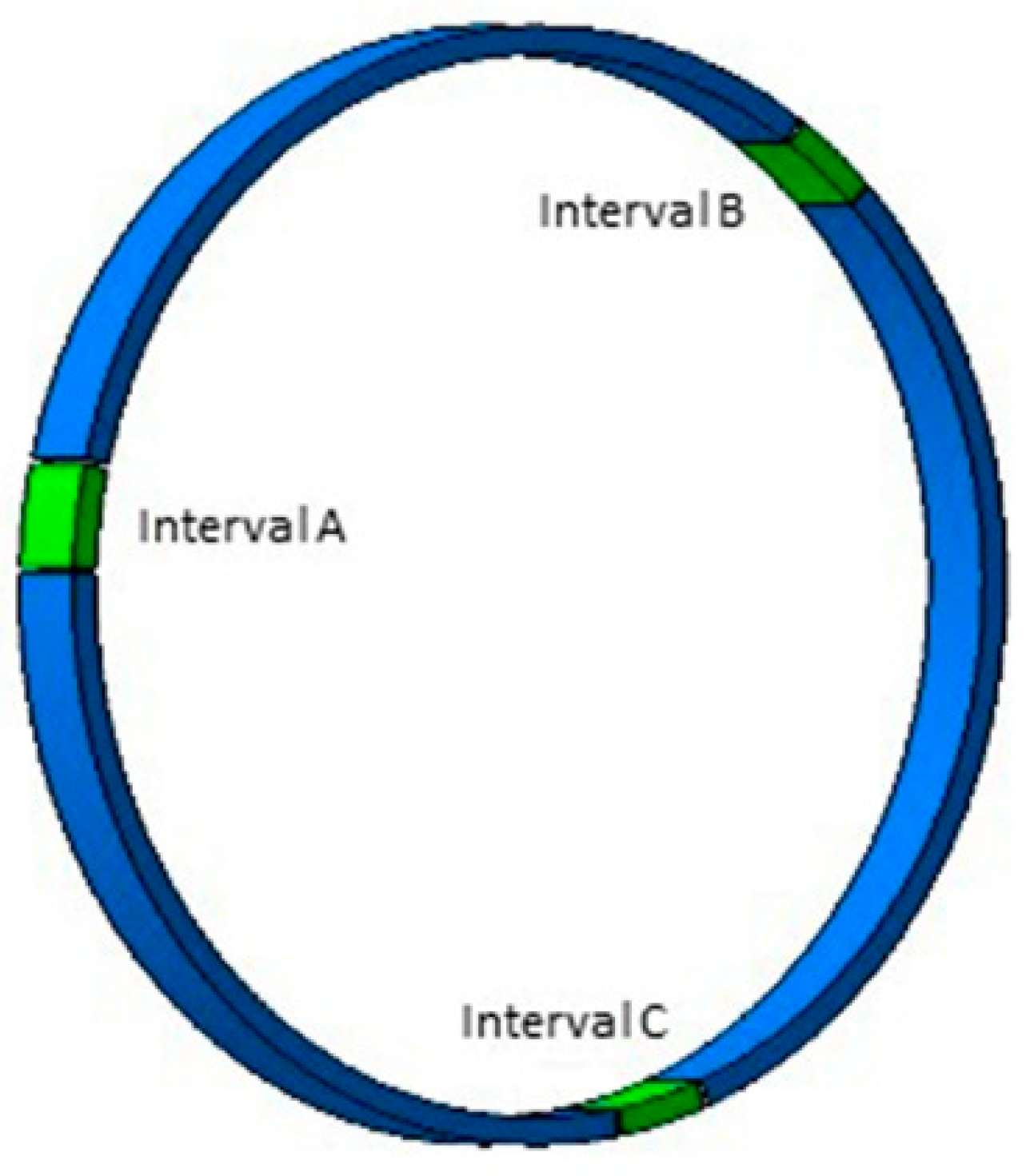
In order to reduce the influence of random errors, ensure the consistency and integrity of the measurement, and improve the credibility of the data, it is required to calibrate three intervals A, B, and C at equal intervals for the entire belt, as shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8. For each measurement of wear, three points are taken in this area. For example, points taken in area A are recorded as NA1, NA2, and NA3, and the three sets of interval data with better stability are taken as the actual measured value of wear Δ.
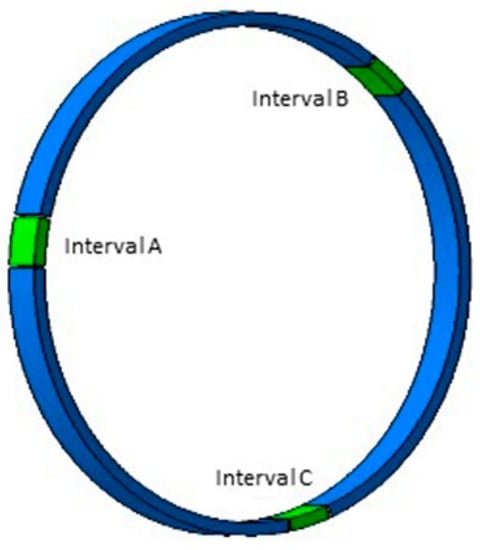
Figure 7.
Interval labeling.

Figure 8.
Actual interval labeling.
(3) Abrasive belt fixture
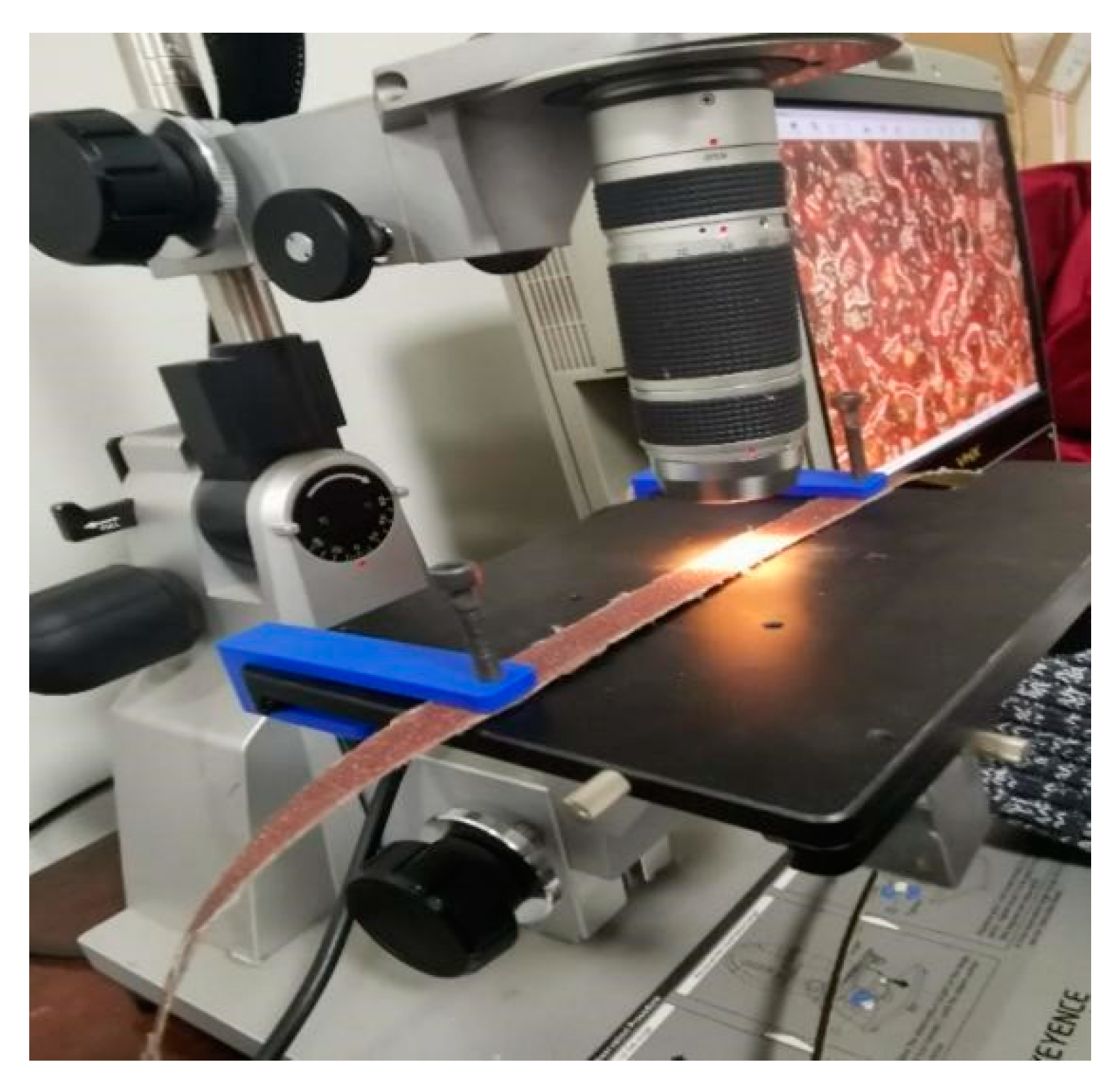
For the sanding belt within the interval length, researchers should fix the space position of the microscope lens and the position of the operating platform while framing. Meantime, the belt should be fixed by the self-designed special 3D printing fixture, as shown in Figure 9. The fixture is made of PLA material, which will avoid the damage of the microscope table due to touch and friction. By choosing this material, the repeatability of the measurement field will be maximized and the influence of random errors can be reduced, which will ensure the consistency and integrity of the measurement, as well as improve the data credibility.
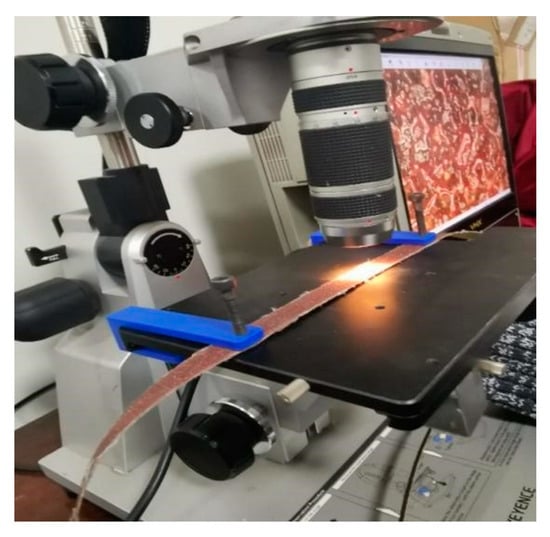

Figure 9.
3D printing fixture.
(4) Strategy of taking points under the mirror image
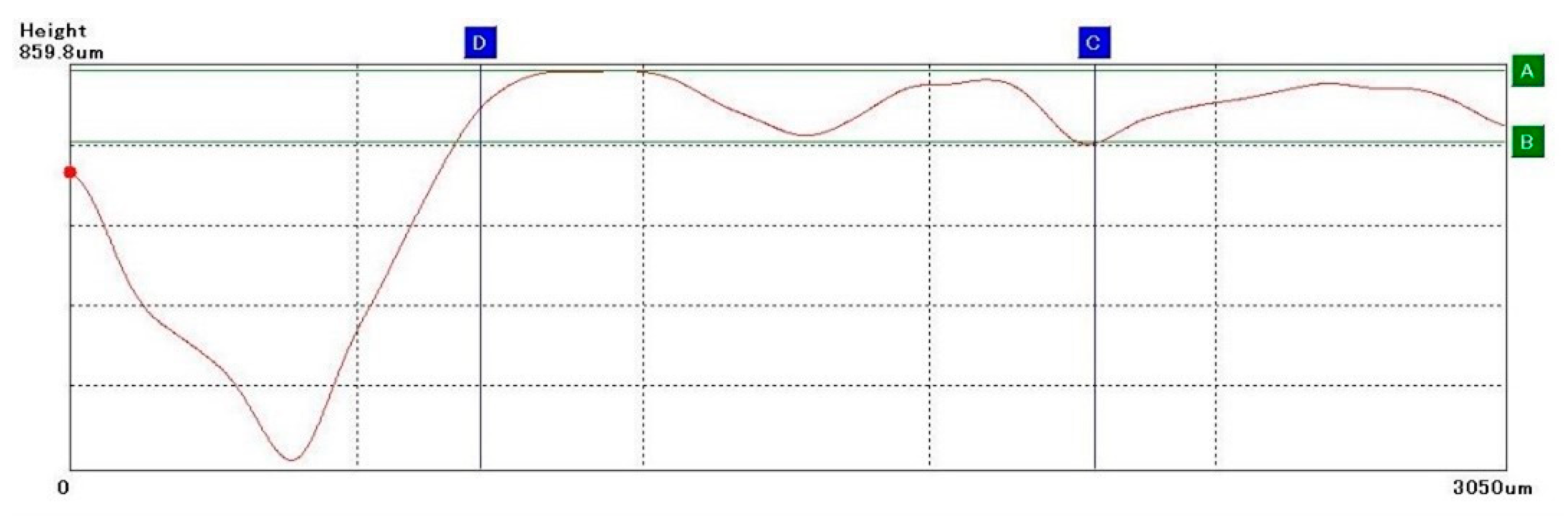
As shown in Figure 10, there will be huge fluctuations on the height curve at the sampling front end. This is because the VHK-900 Keneyce is a manually adjusted microscrew. It is difficult to achieve a uniform speed when the initial rotation speed is applied, so huge fluctuations will occur. Data removal processing is required to remove invalid information. When taking HorLine and VertLine, points should be taken at the peak and valley stages of smooth changes to calculate the amount of change in wear and thus improve the accuracy of wear measurement.
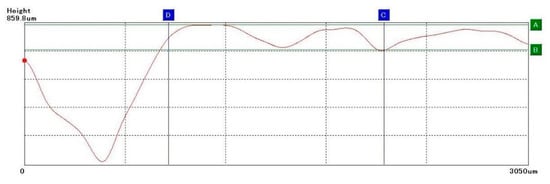
Figure 10.
Sampling positioning diagram.
4.4. Test Results
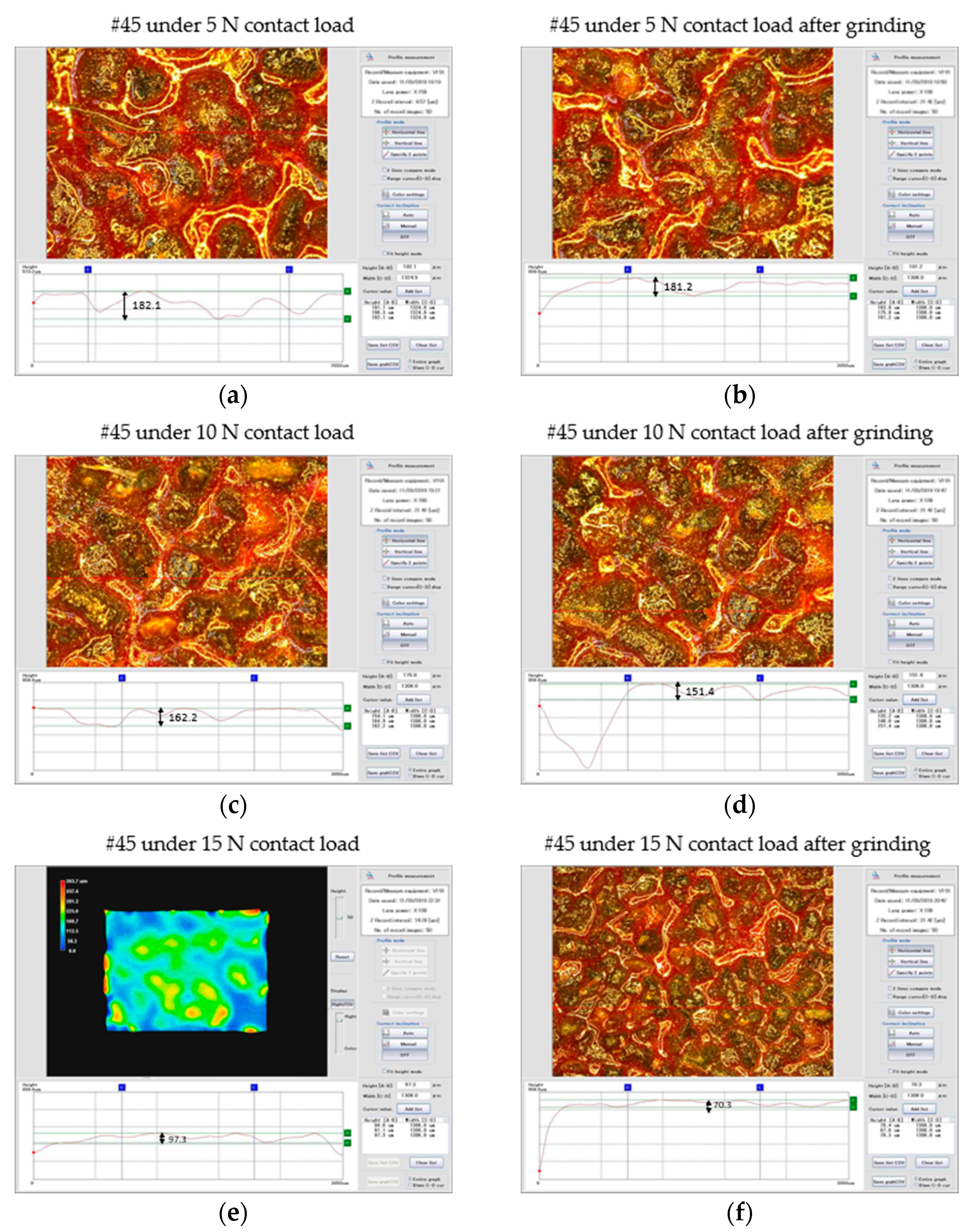
In the test, a total of 27 sets of tests were carried out for #20, #45, and #65 steels. Due to the consistency of the test process, the test process was analyzed with #45 as an example. The initial belt contour interval takes points NA1, NA2, and NA3. Figure 11 shows the measurement process example of abrasive height at NA3, and all measured data of abrasive heights for #45 steels are listed in Table 2.
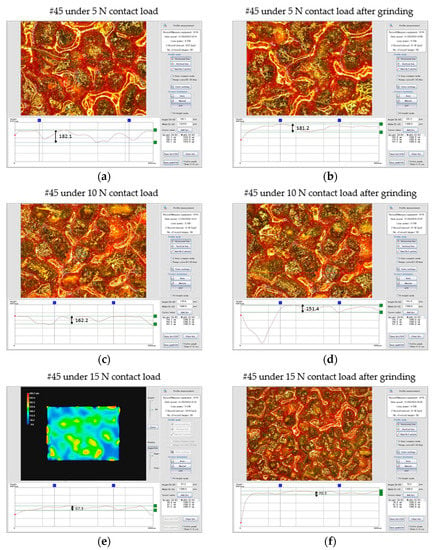
Figure 11.
Abrasive height measurement example.

Table 2.
Measured data of abrasive heights for #45 steels (μm).
Figure 11a shows that #45 is under a contact load of 5 N, and the initial belt contour interval takes points NA1, NA2, and NA3. The measured heights are 191.1 μm, 198.3 μm, 182.1 μm, and the average value is 190.5 μm.
Figure 11b shows that after grinding with parameters (No.10 in Table 1) for 15 min, the measured heights of abrasive grains are 183.9 μm, 175.8 μm, and 181.2 μm, respectively, with an average value of 180.3 μm.
Figure 11c shows #45 under a 10 N contact load, the initial belt contour interval takes points NA1, NA2, and NA3, and the measured heights are 154.1 μm, 164.9 μm, 162.2 μm, and the average value is 160.4 μm.
Figure 11d shows that after grinding for 15 min with parameters (No.13 in Table 1), the measured heights of abrasive grains are 135.2 μm, 146 μm, 151.4 μm, and the average value is 144.2 μm.
Figure 11e shows #45 under the contact load of 15 N, the initial belt contour interval takes the points NA1, NA2, and NA3. The measured heights are 84.6 μm, 81.1 μm, 97.3 μm, and the average value is 91.0 μm. According to the cloud chart chromatogram, it can be clearly seen that after a series of grinding processes in the early stage, the overall height of the abrasive particles has dropped a lot.
Figure 11f shows that after grinding for 15 min with the parameters (No. 16 in Table 1), the measured heights of abrasive grains are 78.4 μm, 67.6 μm, 70.3 μm, and the average value is 72.1 μm.
The grinding record data of #45 steel material: the initial height is 190.5 μm. According to the test sequence in Table 1, it is 180.3 μm, 174.6 μm, 170.1 μm, 160.4 μm, 144.2 μm, 122.6 μm, 91.0 μm, 72.1 μm, and 62.3 μm respectively, and then the amount of change in the height of abrasive grains Δh can be obtained. The final changes in the tip of the abrasive particles in each group of experiments are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Amount of change in the tip of the experimental abrasive grain μm).
4.5. Test Data Analysis
This group of experiments uses a single factor independent variable to study the relationship between the abrasive belt wear rate and the grinding parameters (grinding speed and contact pressure) and the workpiece material. The characteristic parameter is the abrasive belt height wear rate. Due to the high randomness of sanding belt’s abrasive height, in order to reduce the error as much as possible, 15 min is used as the unit time, and the wear amount is counted every 15 min.
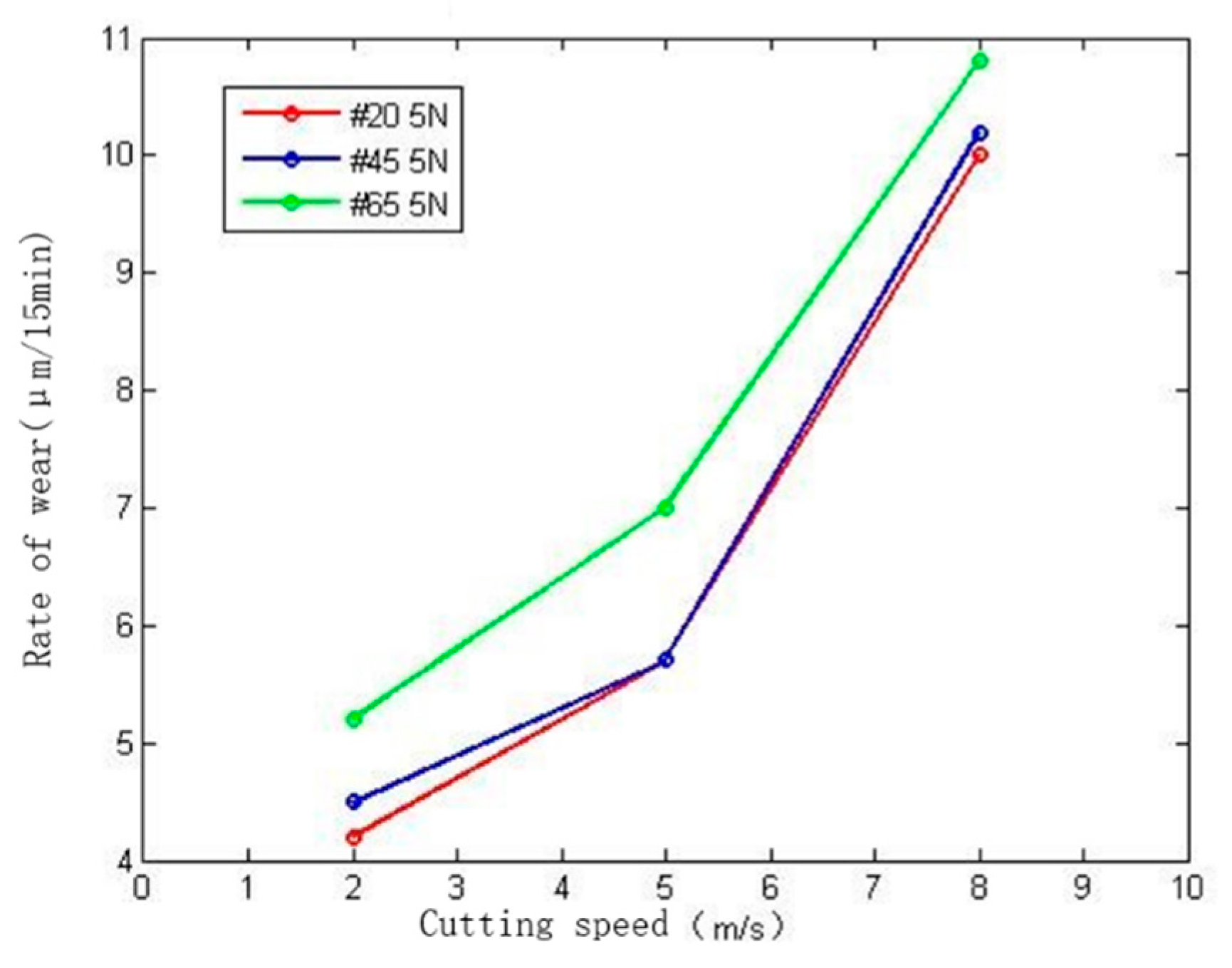
(1) The influence of grinding speed on wear rate
Figure 12 is a graph showing the change in the wear rate of different materials with the grinding speed under a contact pressure of 5 N. It can be seen from the figure that the abrasive belt wear rate gradually increases as the grinding speed v of the abrasive belt changes from 2 m/s to 8 m/s. The reason is that increasing the grinding speed of the abrasive belt within the same time will increase the number of abrasive particles contacting the workpiece. As the speed continues to increase, the increase in the wear rate increases accordingly. Meanwhile, different materials also have a certain impact on the wear rate. With the increase of steel grade, the hardness of the steel structure increases, which intensifies the abrasive belt wear. With the increase of grinding speed, the increase of the wear rate of hard materials is relatively stable. Therefore, the difference in materials has less superimposed effect on the change of grinding speed.
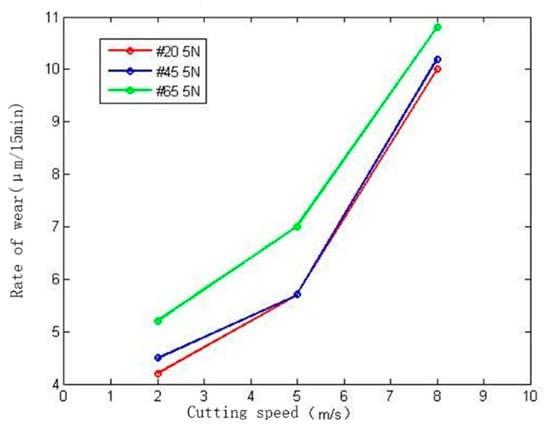
Figure 12.
Effect of grinding speed on rate of wear.
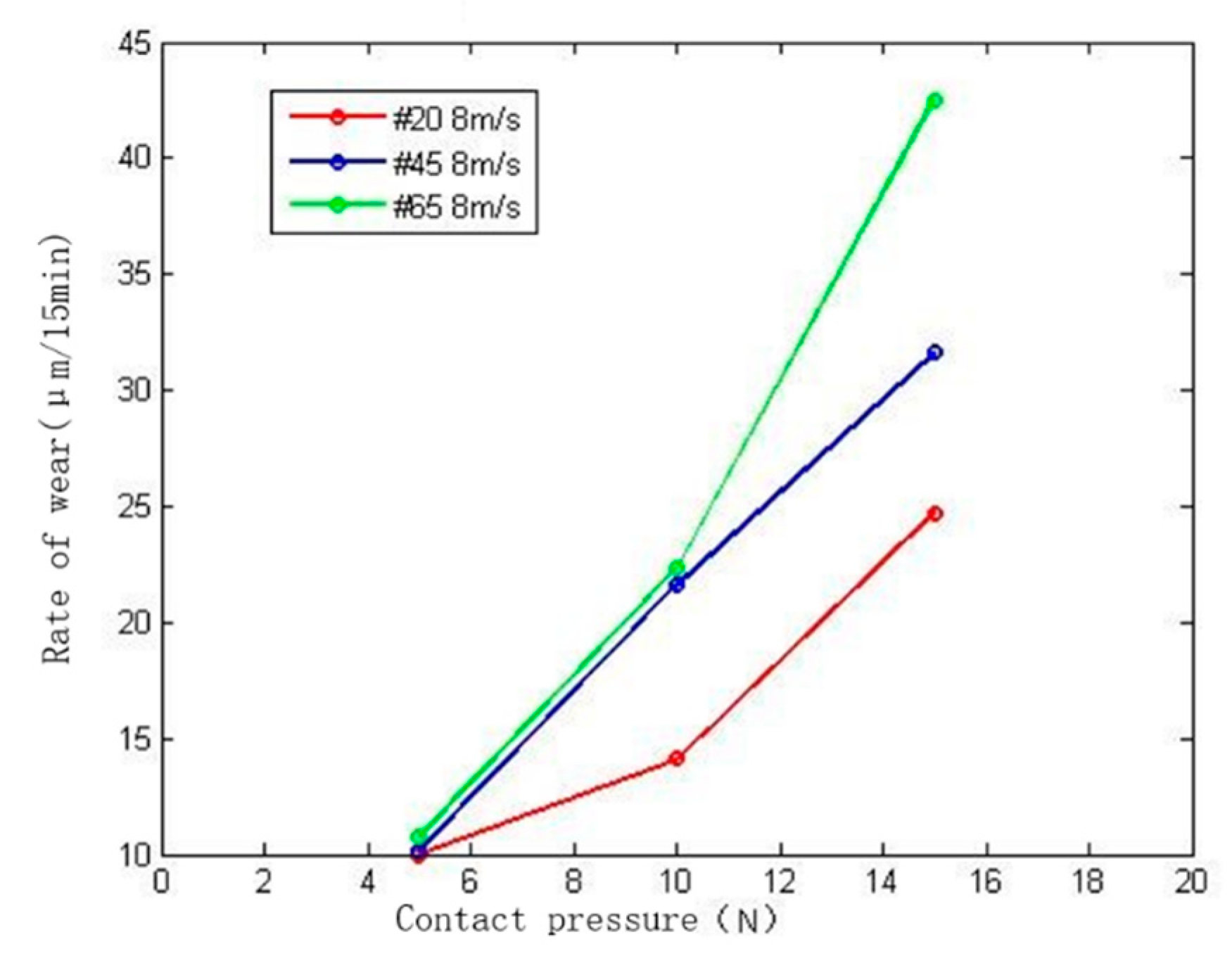
(2) Influence of contact pressure on wear rate
Figure 13 shows the change curve of wear rate with contact pressure for different materials at a grinding speed of 8 m/s. According to the figure, it can be seen that when the contact pressure of the abrasive belt is 5–15 N, the high wear rate of the abrasive belt has a huge increase with the increase of the pressure. The contact pressure increases by 10 N, and the wear amount increases by nearly 70%. As the contact pressure increases, the pressure on a single abrasive particle increases, the cutting depth also increases, and the temperature in the contact area increases faster, which ultimately leads to increased wear. At the same time, it can be seen that with the increase of contact pressure, the increase of the wear rate of materials with higher hardness is greater, so the difference of materials has a greater superimposition effect on the change of contact pressure.
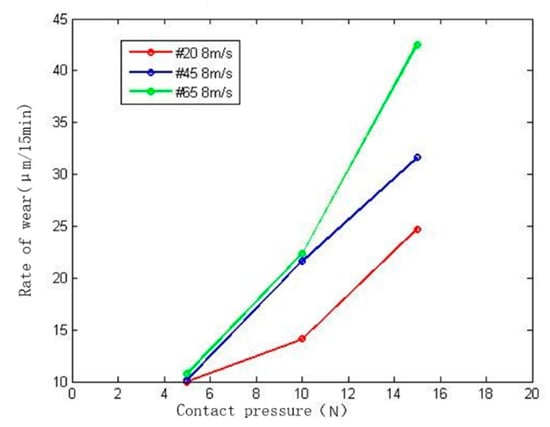
Figure 13.
Influence of contact pressure on wear rate.
5. BP Neural Network Experimental Analysis
5.1. Data Analysis
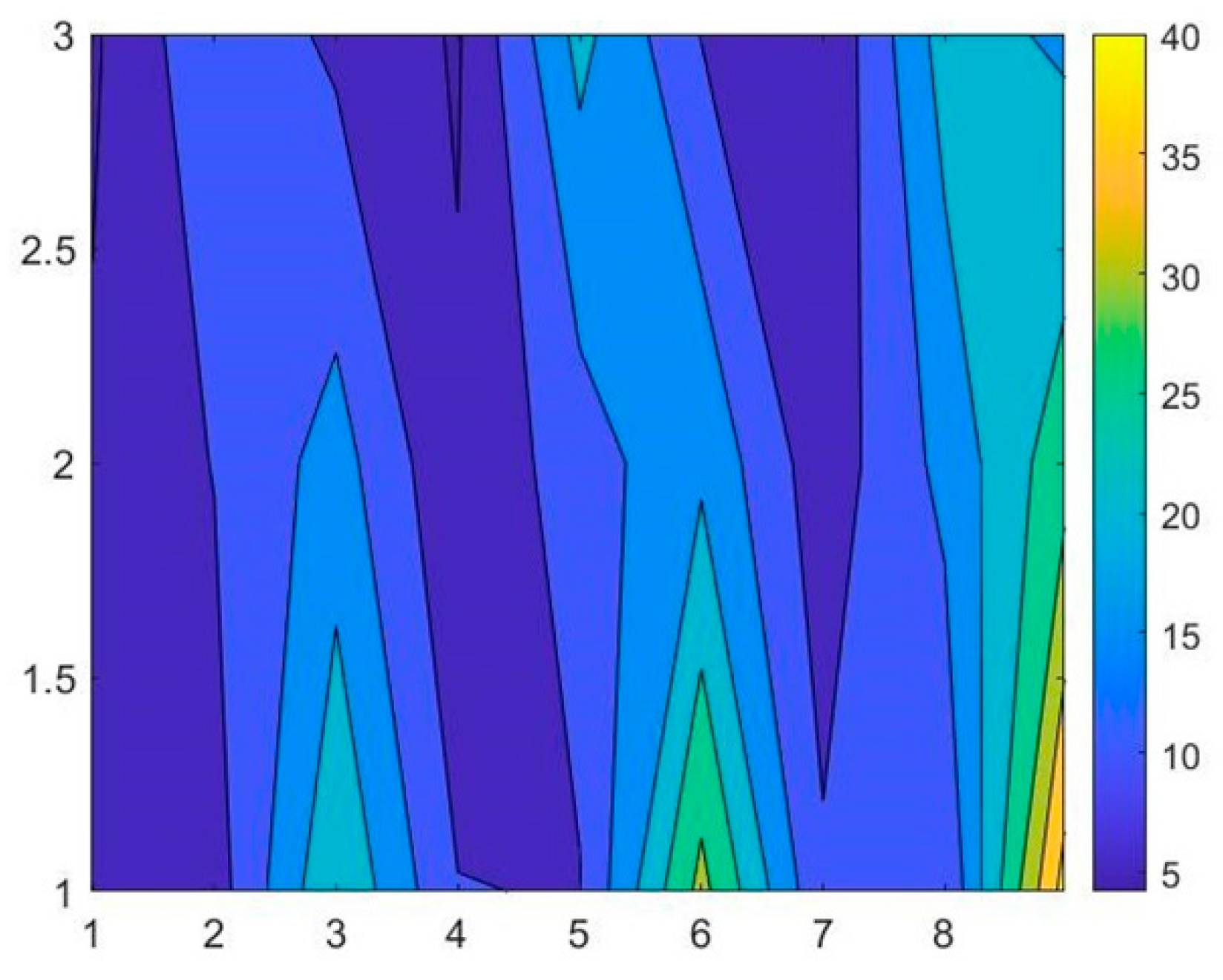
The employment of the neural network algorithm module in MATLAB is based on the experimental parameters and results obtained in Table 3. The contour plots of the final changes in the tip of the abrasive particles are shown in Figure 14. The complexity of collected data can be seen in the Figure 15, which verifies the necessity to use BP neural network to train the data sets. First, a certain number of data will be selected in order to train the neural network. And then other groups of data should be used for verification and testing to prove the BP neural network’s reliability and effectiveness.
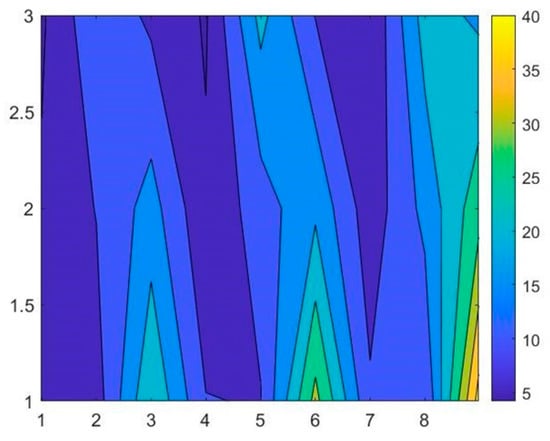
Figure 14.
Contour plots of experimental data.
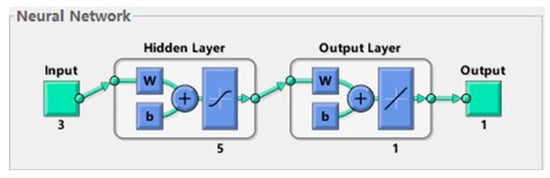
Figure 15.
Schematic diagram of neuron parameter setting.
According to Equation (5), the number of L is between 3 and 12. To determine the number of hidden layer neurons, the training accuracy are compared under different numbers of hidden layer neurons, which is shown in Table 4. It can be seen that it has the best training effect when L = 5. Therefore, the number of hidden layer neurons is chosen as L = 5, therefore, the number of nodes in the hidden layer is set as 5, as shown in Figure 15.

Table 4.
Training accuracy under different numbers of hidden layer neurons.
5.2. Principles of Experimental Analysis
In the evaluation of result output, the correlation coefficient R2 is used to characterize the accuracy of the prediction. The calculation method of R2 is as shown in Equation (15). When the result of R2 is closer to 1, it means that the prediction effect is better, the prediction accuracy is higher, and closer to the actual value [29].
where xi and yi represent predicted data and measured data, and , represent the arithmetic average of predicted data and measured data.
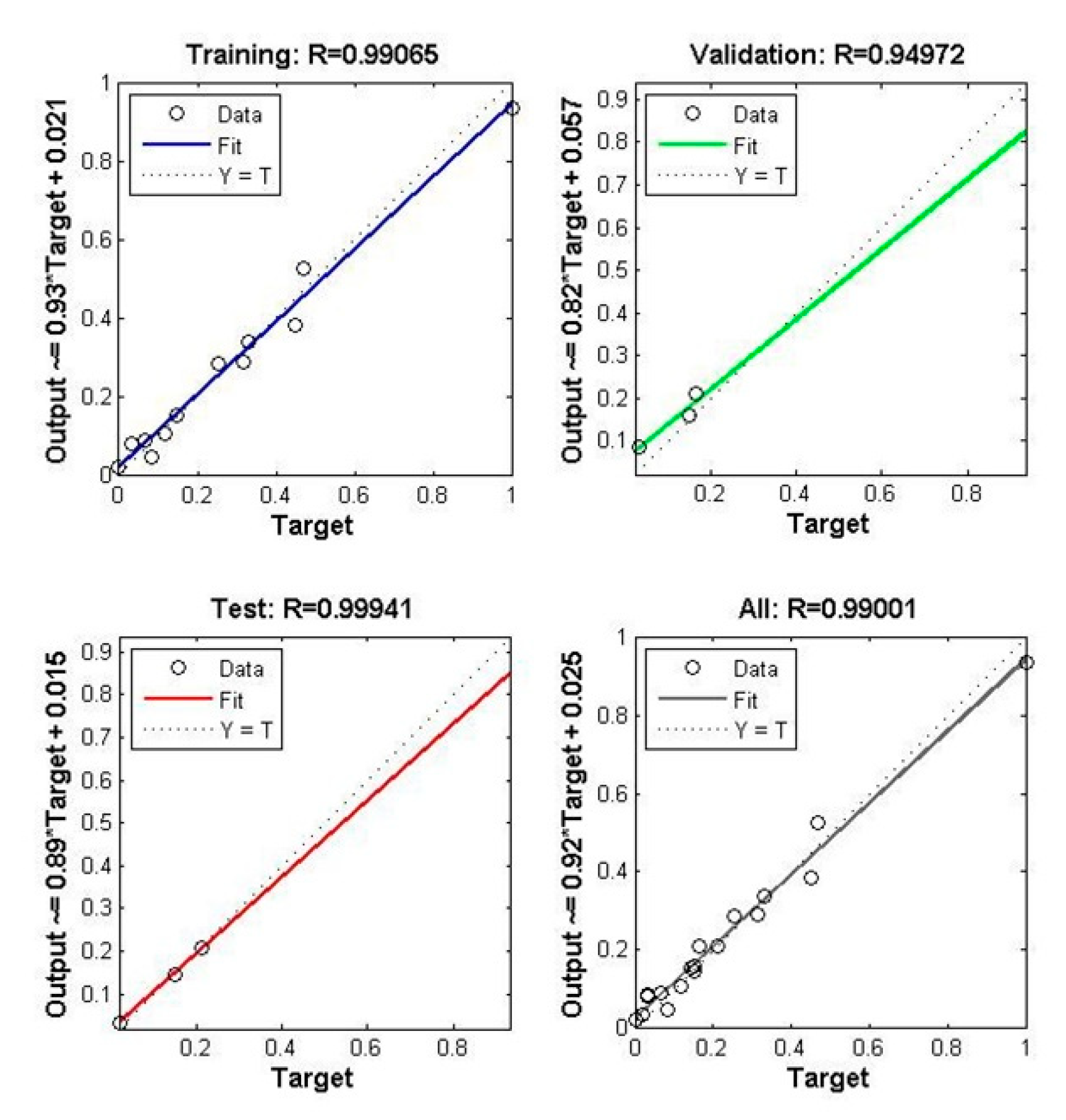
It can be seen from the two figures on the left side of Figure 16 that the training set and test set of the model have a high degree of fit and a good linear relationship. From the perspective of the complete set, it still has a good degree of fit. Therefore, it can be concluded that the prediction accuracy using BP neural network is very high.
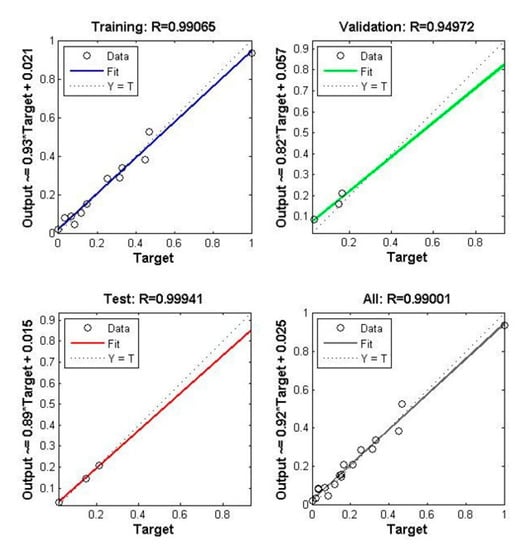
Figure 16.
Fitting degree of BP neural network.
5.3. Comparison of Experimental Results
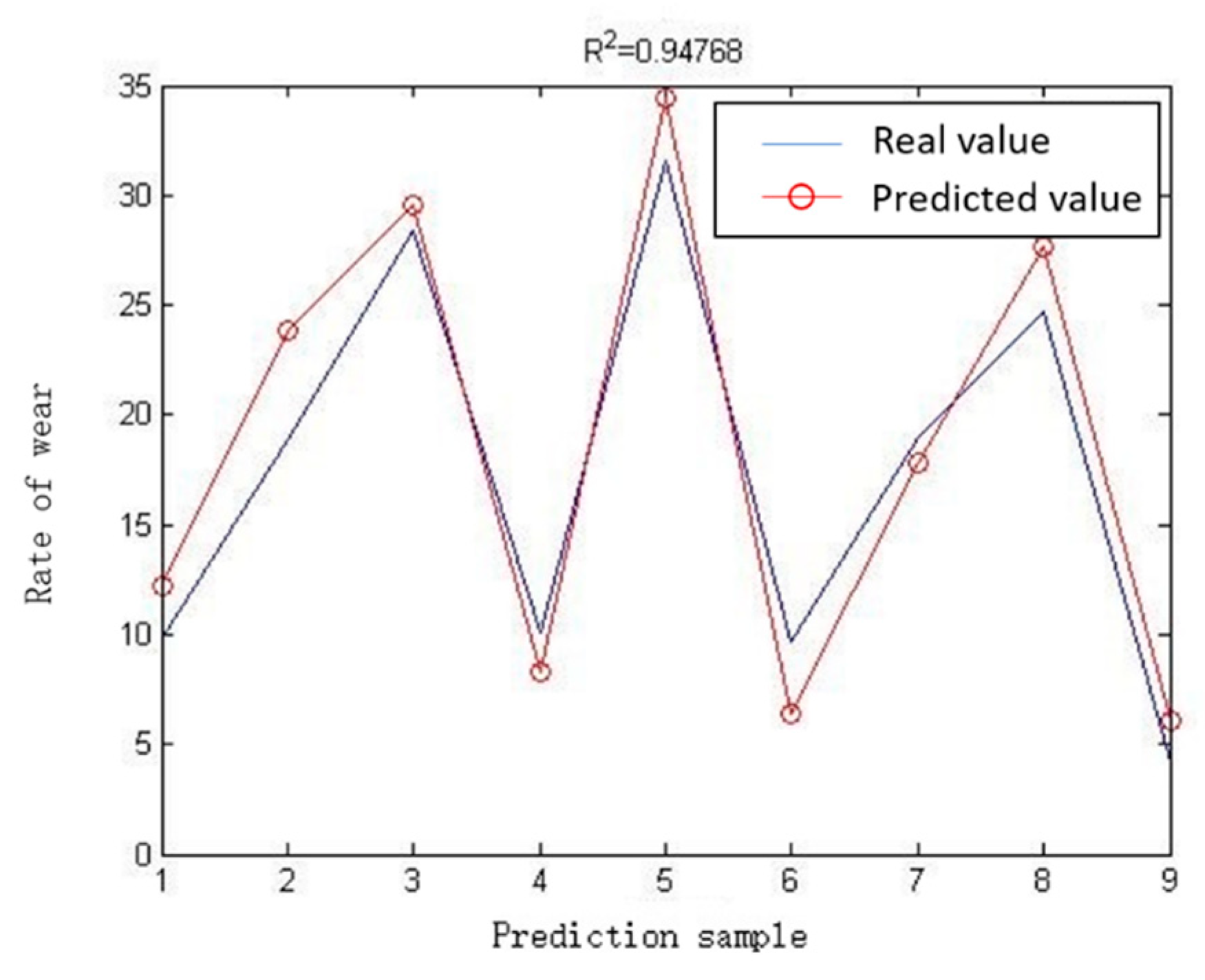
Among the 27 sets of data in Table 3, 18 sets of data were randomly selected by the program for algorithm training, and then the results of the remaining 9 sets of experiments were used for verification and comparison. The comparison of the true value and the predicted value of the 9 sets of verification results is shown in Figure 17 and Table 5. R2 reaches 0.94768, which shows that the prediction accuracy of abrasive belt wear is very high.
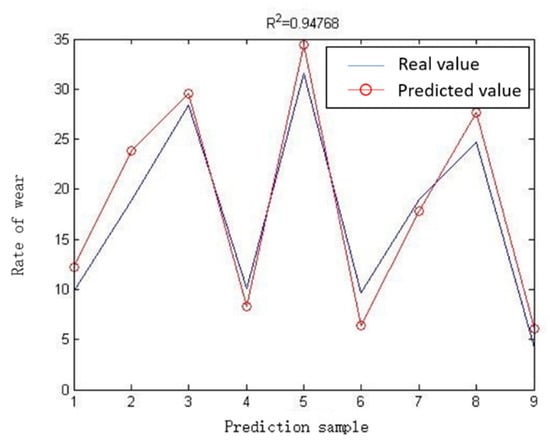
Figure 17.
Comparison of the true value of the test sample and the predicted value.

Table 5.
Comparison of predicted result and true value.
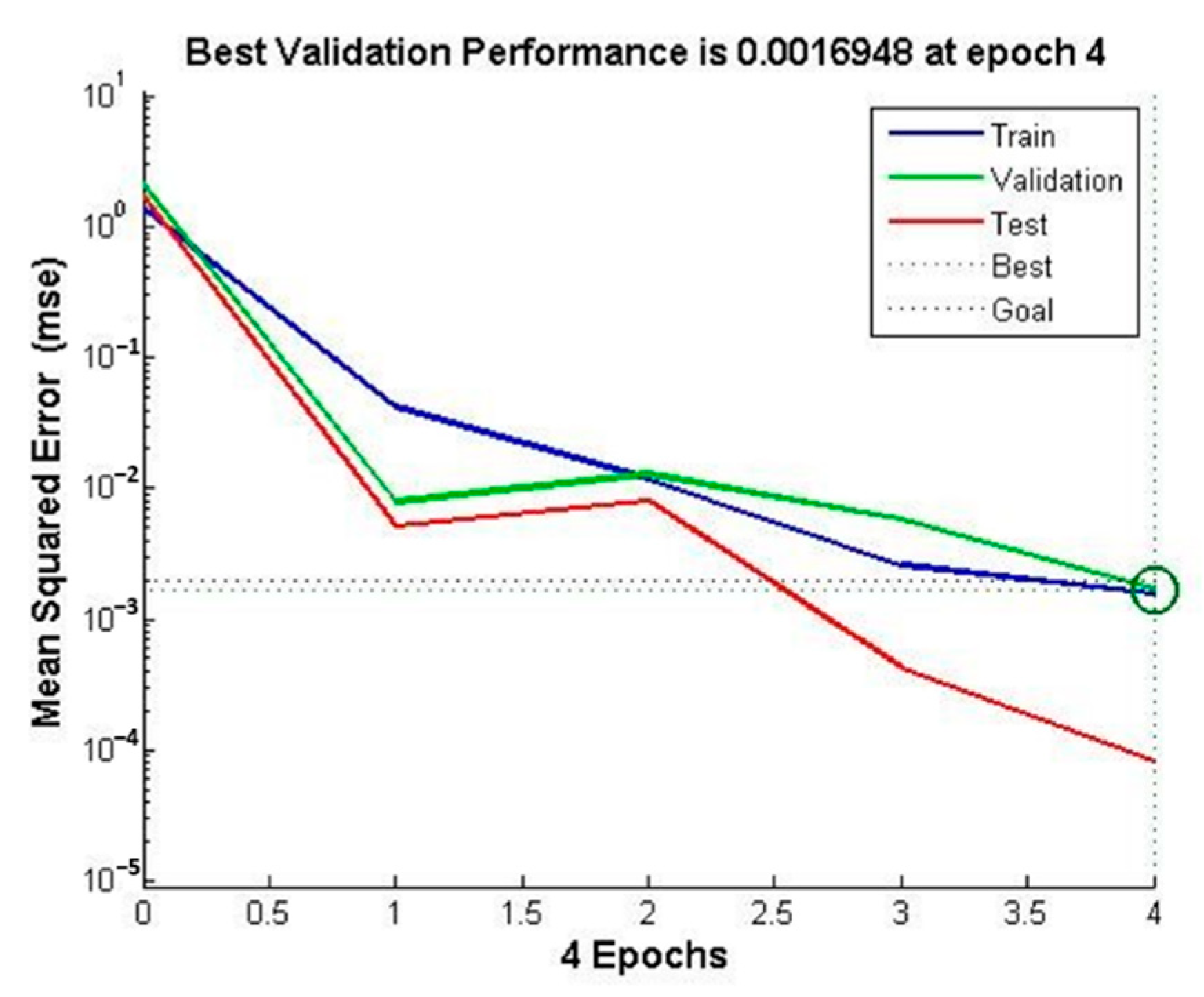
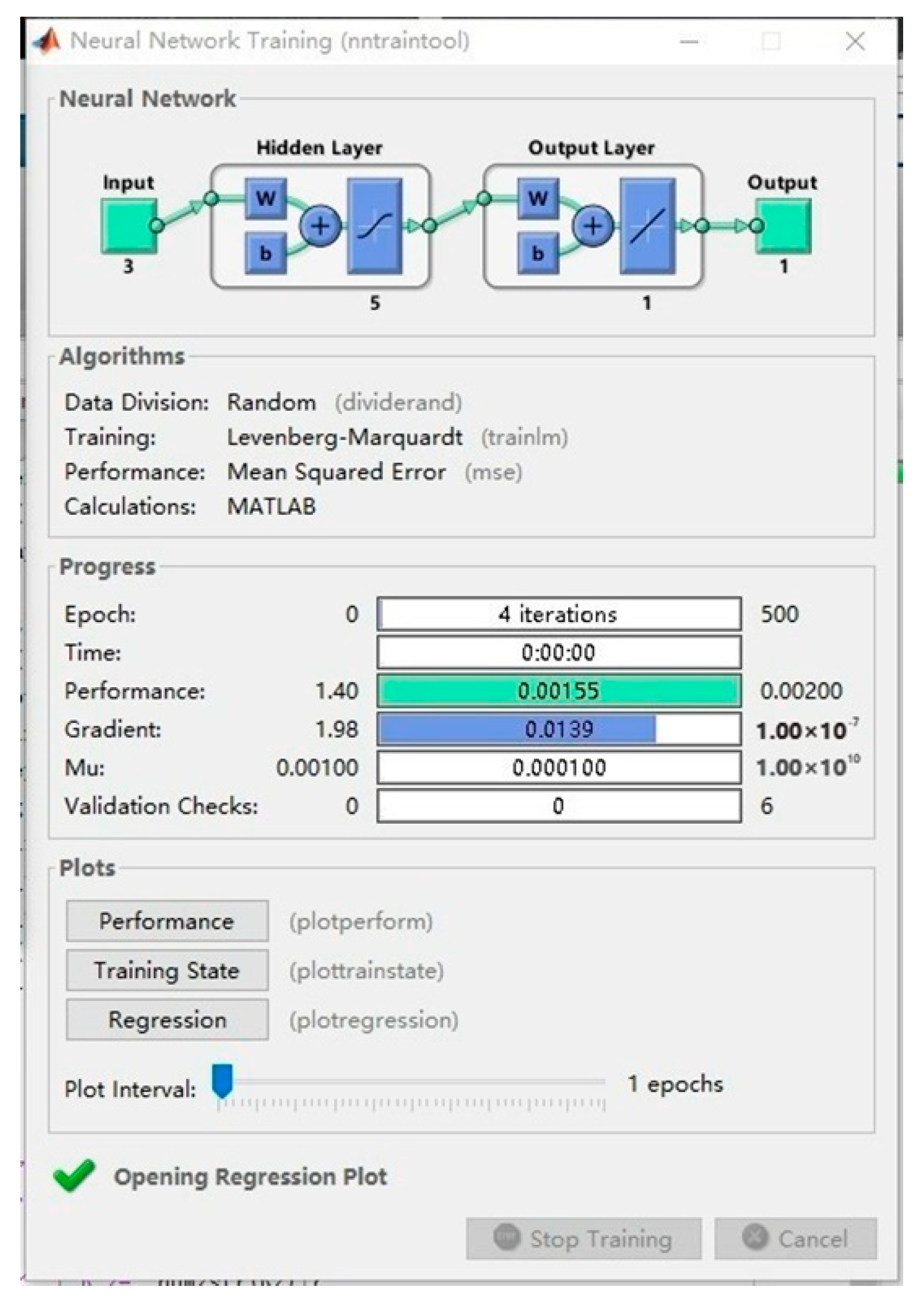
At the same time, the BP neural network-based model used in this article has a fast convergence speed. As shown in Figure 18 and Figure 19, the convergence accuracy can be achieved by using four iterations of calculation. This plays an important role in the use of abrasive belts for grinding processing, the detailed calculation of the material removal calculation of the workpiece, and the intelligent planning of the grinding residence time. In addition, the frequency of real-time monitoring of the workpiece surface processing depth and surface profile determination can be greatly reduced, and the efficiency of the processing and inspection process can be improved.
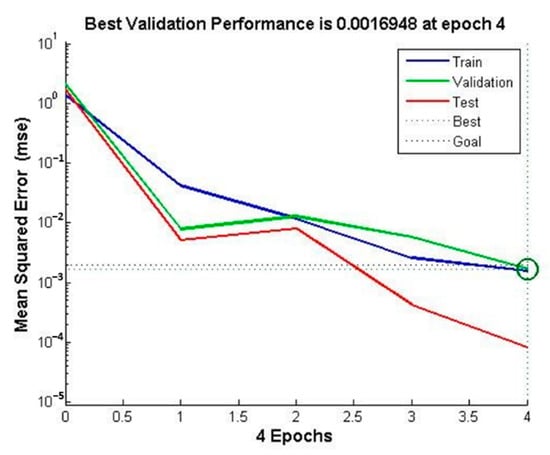
Figure 18.
Iterations of calculation.
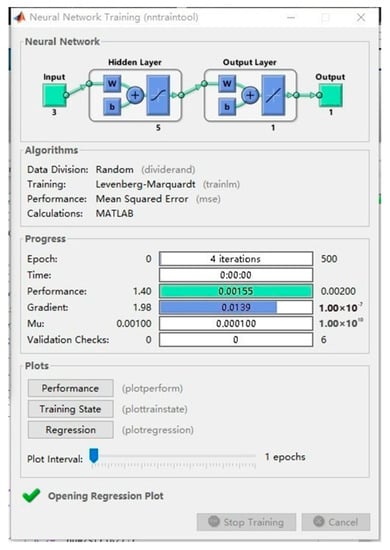
Figure 19.
BP Neural network control process.
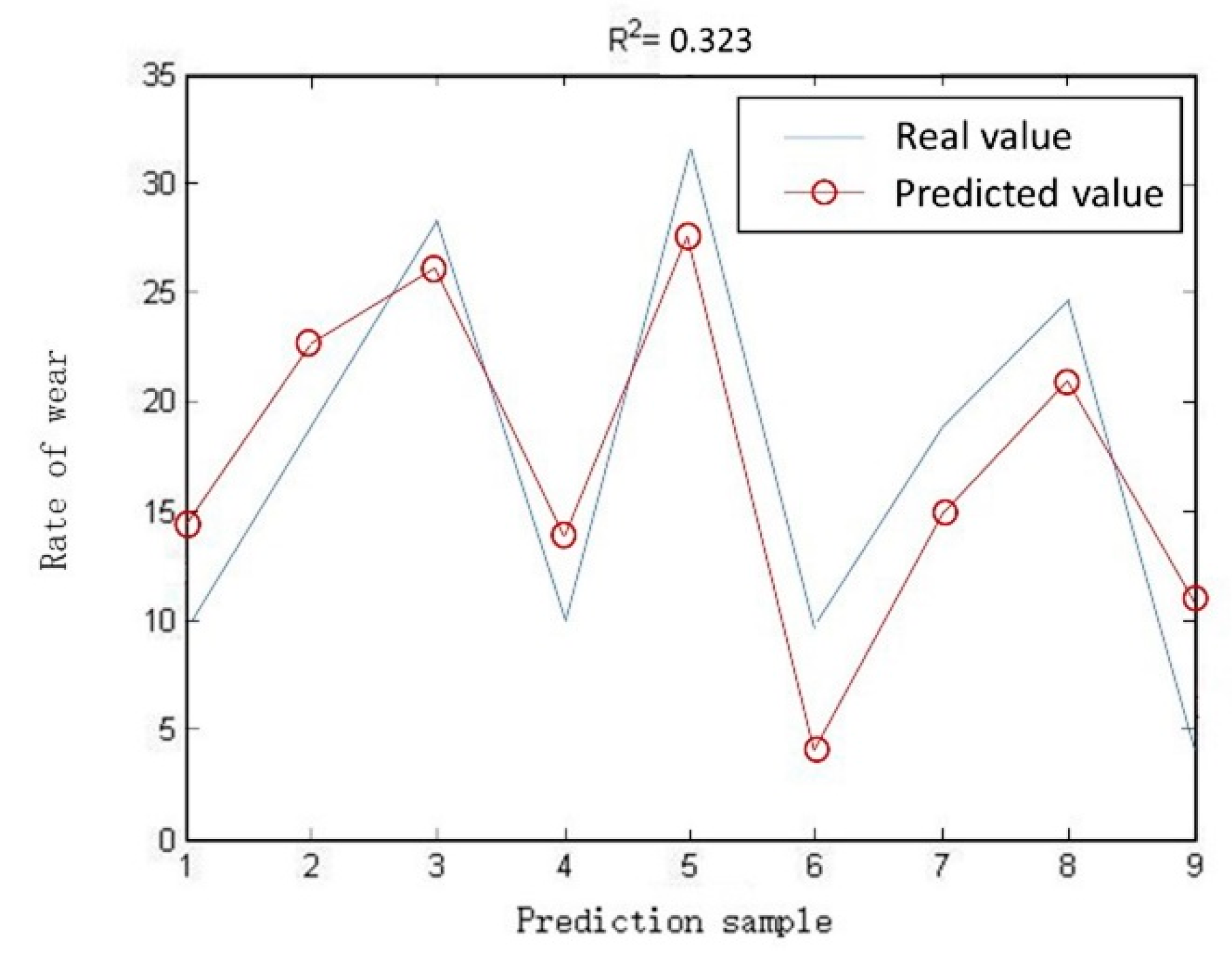
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, the wear rate model of abrasive belt is established based on power exponential function [30,31,32,33], which is generally used in the other research.
where r is the wear rate, Fn is the contact pressure, vb is the grinding speed, a, b, c, d, e are unknown parameters, which can be estimated by the maximum likelihood estimation method.
According to the experiment data, the unknown parameters are calculated as a = 1.134, b = 0.356, c = 1.132, d = 0.956, e = 0.987. The comparison of the true value and the predicted value based on other method is shown in Figure 20. R2 reaches 0.323, which shows that the prediction accuracy of abrasive belt wear is very high. It can be concluded that the proposed prediction method of abrasive belt wear based on BP neural network is effectiveness and has accurate prediction result.
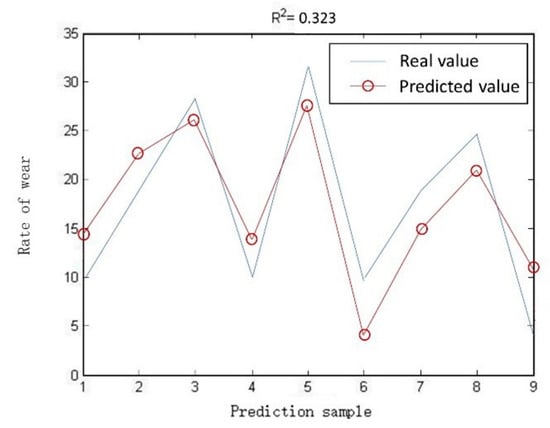
Figure 20.
Comparison of the true value of the test sample and the predicted value based on other method.
6. Conclusions
The wear of the abrasive belt has a great impact on the processing efficiency and processing accuracy, so it is necessary to accurately judge the wear degree of the abrasive belt. However, at present, due to the limitation of the processing environment, it is difficult to achieve real-time detection, so the equipment can only be suspended for manual detection, wasting time, cost, and labor cost. Therefore, this paper proposes a method for predicting abrasive belt wear based on back-propagation (BP) neural network, which greatly simplifies the detection process and reduce the cost. First, the experiment was based on ultra-depth-of-field detection technology, different parameter combinations are used to measure the degree of abrasive belt wear, and the effects of different grinding speeds, different contact pressures and different work piece materials on the abrasive belt wear rate are obtained. Then by utilizing the artificial intelligence BP neural network method, the degree of abrasive belt wears was predicted. Finally, the surface quality inspection technology was employed to evaluate the surface quality of work pieces processed by abrasive belts with different degrees of wear.
Based on the proposed method, experiments in this paper are conducted with different experimental parameter combinations. Total of 18 sets of data are selected for BP neural network training and to establish the combination of various process parameters, such as the non-linear mapping relationship between grinding speed, contact pressure, belt type, etc., and wear rate, which are verified by 9 sets of data. By utilizing this artificial intelligence method, the wear of the abrasive belt can be predicted more quickly and accurately. Therefore, the manufacturing processing guided through this method greatly improves the processing efficiency.
In the future, further research will be carried out from the following two aspects:
On the one hand, in the sand belt wear measurement experiment, due to the non-uniformity and randomness of sand belt planting process and the instability of measuring equipment, there exist the errors in the experimental measurement data. In the future research, effective methods will be studied to reduce the impact of experimental errors on the prediction results.
On the other hand, when using artificial intelligence BP neural network for predictive analysis, the fixed learning rate is used for training, and the idea of gradient descent is used to find the best weight to reduce the network error. The learning rate of the network determines the weight change in the learning process. If the learning rate is too high, oscillation will occur; if the learning rate is too small, it will increase the training time, reduce the convergence ability of the network, and the iterative effect is not ideal. In the future, the remaining life prediction method of sand belt based on the improved BP neural network or other deep learning algorithm can be studied to further improve the prediction accuracy and stability.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.C.; conceptualization, J.Z.; formal analysis, X.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, B.L.; writing—review and editing, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51135006.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xiao, G.; Song, K.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W. Comprehensive investigation into the effects of relative grinding direction on abrasive belt grinding process. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 62, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, J. Steel Wire Grinding Testing Based on New Type Abrasive Belt Grinding Machine. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 602–604, 2273–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, J.; Moisan, A. Belt grinding: A way to optimize the surface integrity of cut surfaces. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Machining and Measurements of Sculptured Surfaces (MMSS), Kraków, Poland, 20–22 September 2003; pp. 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Denkena, B.; Grove, T.; Suntharakumaran, V. New profiling approach with geometrically defined cutting edges for sintered metal bonded CBN grinding layers. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 278, 116473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, Y.; Tsuwa, H. Evaluation of Abrasive Belt Performance. J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng. 1976, 42, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaster, R.; Dornfeld, D. The use of acoustic emission to monitor an abrasive machining process. In Proceedings of the 11th International Wood Machining Seminar, Honne, Norway, 25–27 May 1993; pp. 231–245. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cao, F.; Chen, X. Acoustic signal-based tool wear monitoring system for belt grinding of superalloys. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Siem Reap, Cambodia, 18–20 June 2017; pp. 1281–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, D.C.; Kolecki, J.C.; Siebert, M.W.; Wilt, D.M.; Matijevic, J.R. Evidence for Martian electrostatic charging and abrasive wheel wear from the wheel abrasion experiment on the Pathfinder Sojourner Rover. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 8747–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malinov, L.S.; Malysheva, I.E.; Klimov, E.S.; Kukhar, V.V.; Balalayeva, E.Y. Effect of particular combinations of quenching, tempering and carburization on abrasive wear of low-carbon manganese steels with metastable austenite. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 945, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, A.L.; Vora, B.S.; Sahin, F.; Lemaster, R.L. Monitoring of abrasive loading for optimal belt cleaning or replacement. For. Prod. J. 2007, 57, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhua, S. Prediction of grinding wheel life of shaving machine based on improved gray GM (1, N) model. China Leather 2016, 45, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, G.; Li, X.; Qian, Z.; Liu, H.; Rong, Y. Experimental study of time-dependent performance in superalloy high-speed grinding with cBN wheels. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2016, 20, 615–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanshan, W.; Ruilan, S. A Study on the Wear Mechanism of Abrasive Belt in Grinding Nickel Metal. Diamond Abrasives Eng. 1990, 4, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Leyin, X.; Feng, L.; Delong, X.; Xiaoyi, P. Study of the Influences of Different Factors on Diamond Soft Grinding Wheel Abrasion. Superhard Mater. Eng. 2016, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- McGibbon, T.R.; Amundson, S.E.; Lokken, R.C. CAMOS: A computer-aided system for establishing optimal parameters for achieving uniform abrasive wear during high-rate grinding. Wear 1976, 37, 1–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxence, B.; Benjamin, H. Mechanical modeling of micro-scale abrasion in superfinish belt grinding. Tribology 2008, 41, 992–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Mezghani, S.; Sura, M. Wear mechanism maps for the belt finishing of steel and cast iron. Wear 2009, 267, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.B.; Brian, C.J. Relationships between abrasive wear, hardness and grinding characteristics of Titanium-based Metal-Matrix composites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 18, 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Detecting grinding force of abrasive belt based on LabVIEW. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2014, 34, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, J.; Vernes, A.; Vorlaufer, G.; Vellekoop, M. Online monitoring of a belt grinding process by using a light scattering method. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5891–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawada, A.; Sciegienka, R. Monitoring of a micro-smoothing process with the use of machined surface images. Metrol. Meas. Syst. 2011, 18, 419–428. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Xiong, X.; Wu, X.; Xue, Z. Modeling the SOFC by BP neural network algorithm. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 20065–20077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagias, J.D.; Tsiolikas, A.; Petousis, M.; Ninikas, K.; Vidakis, N.; Tzounis, L. A robust methodology for optimizing the topology and the learning parameters of an ANN for accurate predictions of laser-cut edges surface roughness. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2022, 114, 102414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, I.A.; Haimeer, M. Artificial neural networks: Fundamentals, computing, design, and application. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 43, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Choi, S. Restricted deep belief networks for multi-view learning. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Discov. Databases 2011, 130–145. [Google Scholar]
- Hajduk, Z. Hardware Implementation of Hyperbolic Tangent and Sigmoid Activation Function. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2018, 66, 563–577. [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshiri, R.R.; Ma, C. Multivariate gated recurrent unit for battery remaining useful life prediction: A deep learning approach. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 16633–16648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Chen, J. Summarize of Parameter Improve Methods for BP Neural Network. Digit. Commun. World 2009, 1, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Guo, J.; Yang, X.; Xia, Z. Grinding roughness prediction model based on evolutionary artificial neural network. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2013, 19, 2855–2859. [Google Scholar]
- Namba, Y.; Tsuwa, H. Machining Efficiency on Centerless Belt Grinding. J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng. 1976, 42, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, K.; Tanaka, Y. Grinding Temperature and Affected Layer. J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng. 1978, 44, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Li, J.Y.; Fan, W.G.; He, Z. Abrasion Process Modeling of Abrasive Belt Grinding in Rail Maintenance. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2017, 52, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, S.K.; Srinivas, P. Tool wear prediction in turning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 153, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).