An Analytical Method for Generating Determined Torque Ripple in Synchronous Machine with Interior Magnets by Harmonic Current Injection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals
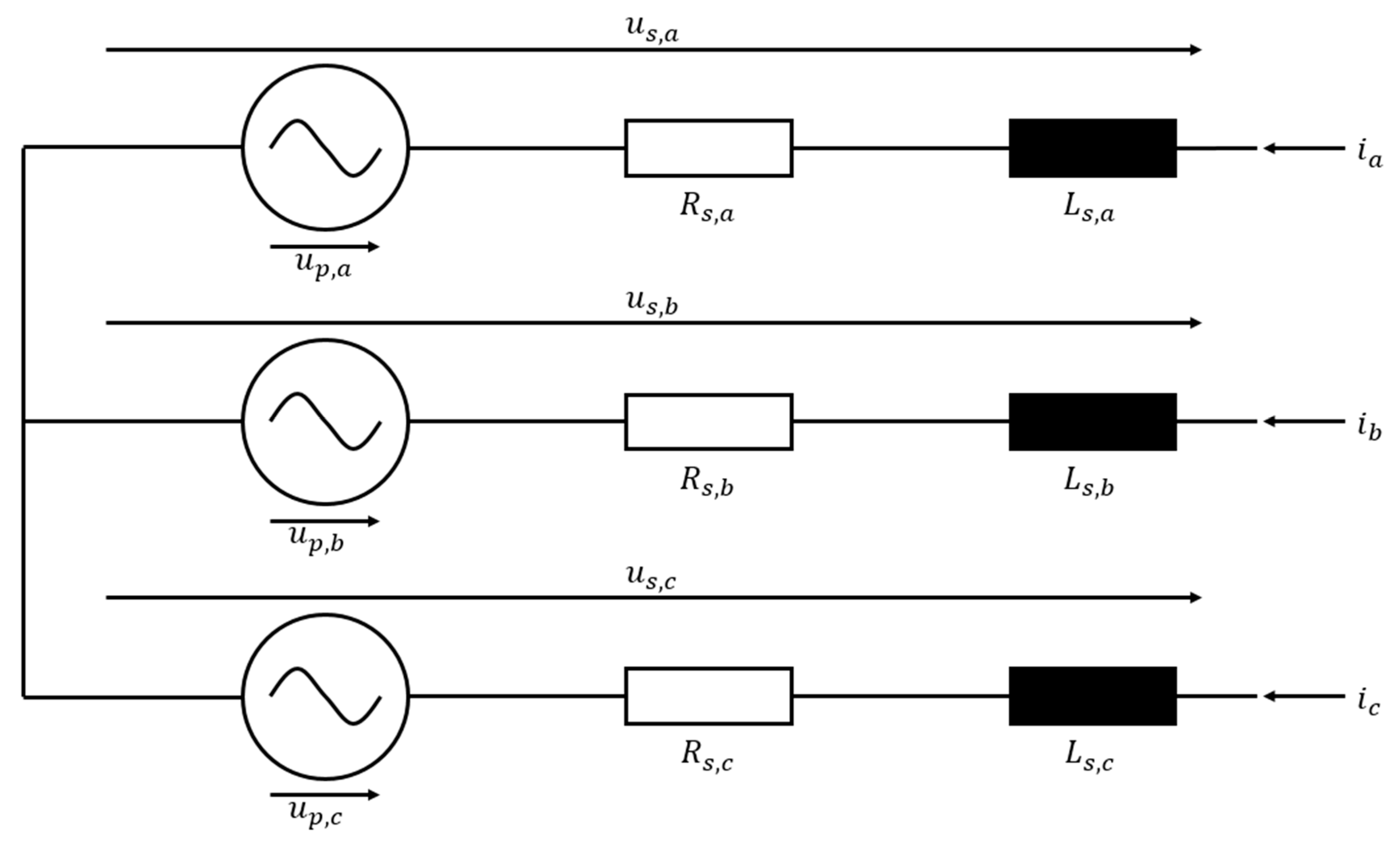
2.1. Machine Equations for Permanent Magnet Excited Synchronous Machines with Interior Magnets
- -
- The magnetic permeability, , of the iron is close to infinity, so there should be almost no saturation of the iron;
- -
- Due to the large difference, , it is acceptable that the field lines are perpendicular at the air–iron transition;
- -
- Edge effects on the front side of the rotor and stator are neglected;
- -
- The magnetic behavior of the permanent magnets is linear;
- -
- The given equations are applied in the armature range without field weakening.
2.2. System of Currents
2.3. Back Electromotive Force
2.4. Analytical Model of the Inductances
2.5. Torque Generation
2.5.1. Alignment Torque
2.5.2. Cogging Torque
2.5.3. Reluctance Torque
3. Approach
4. Validation
4.1. Machine Parameters
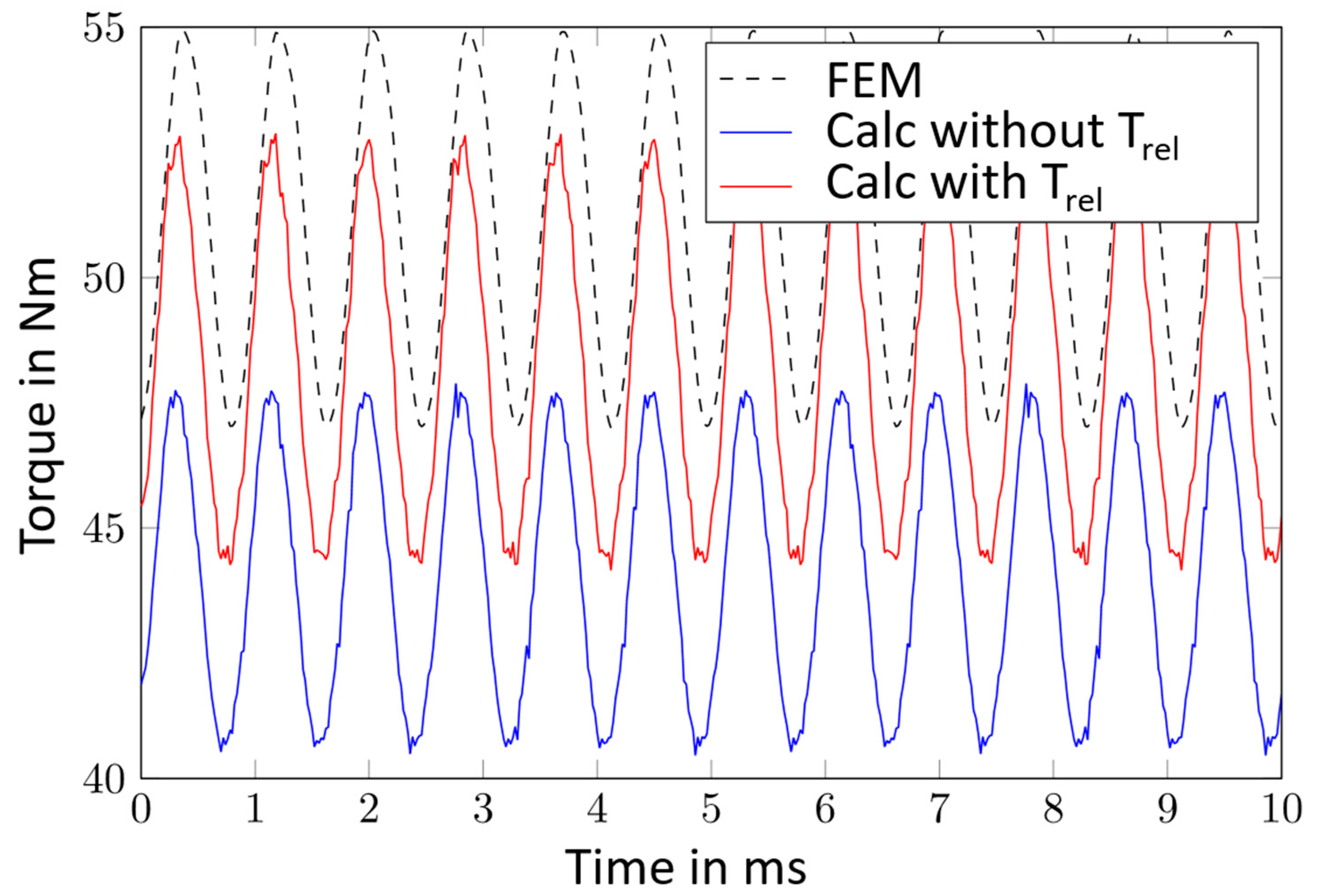
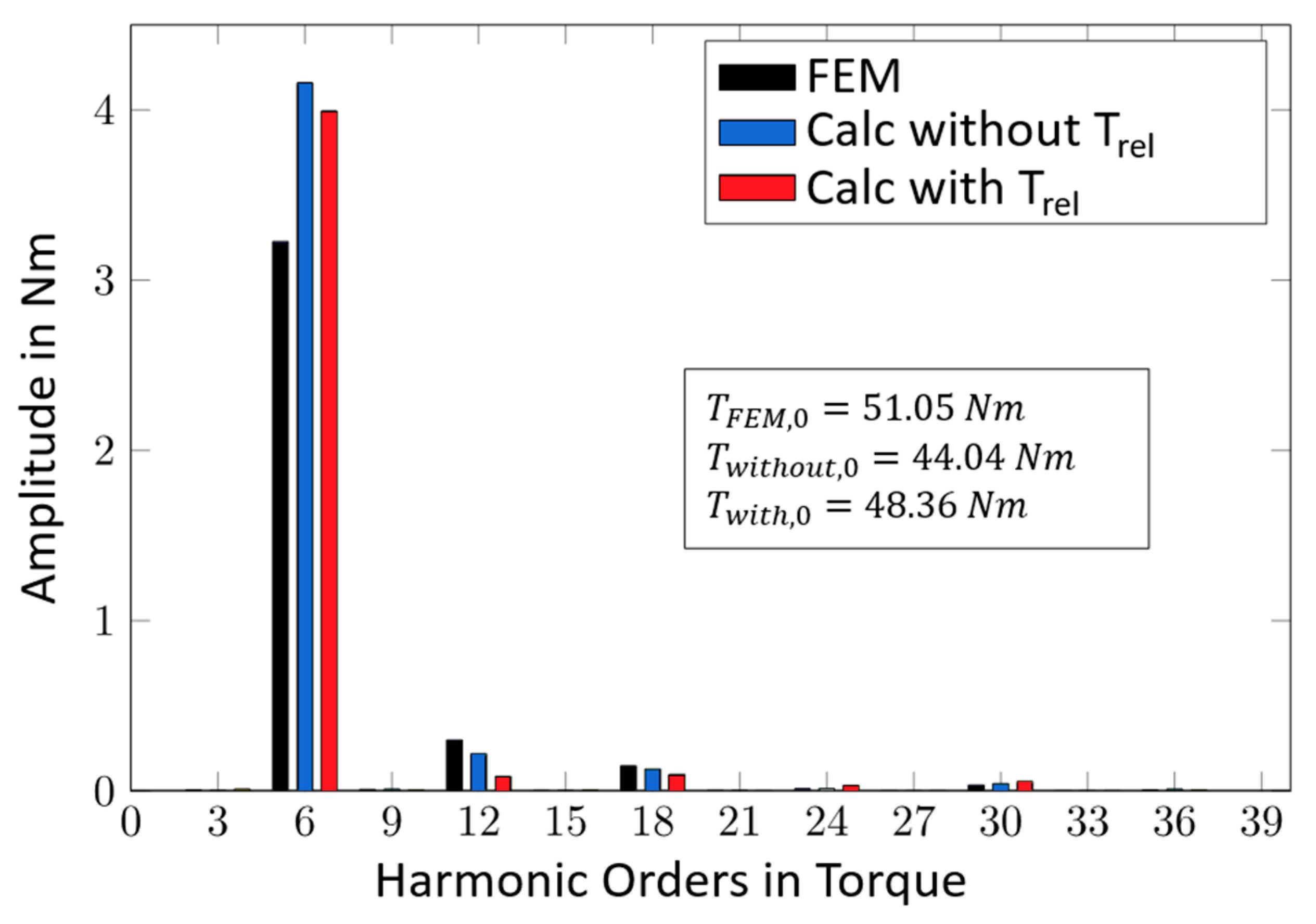
4.2. Validation of the Torque Calculation Method for Permanent Magnet Excited Synchronous Machines with Interior Magnets
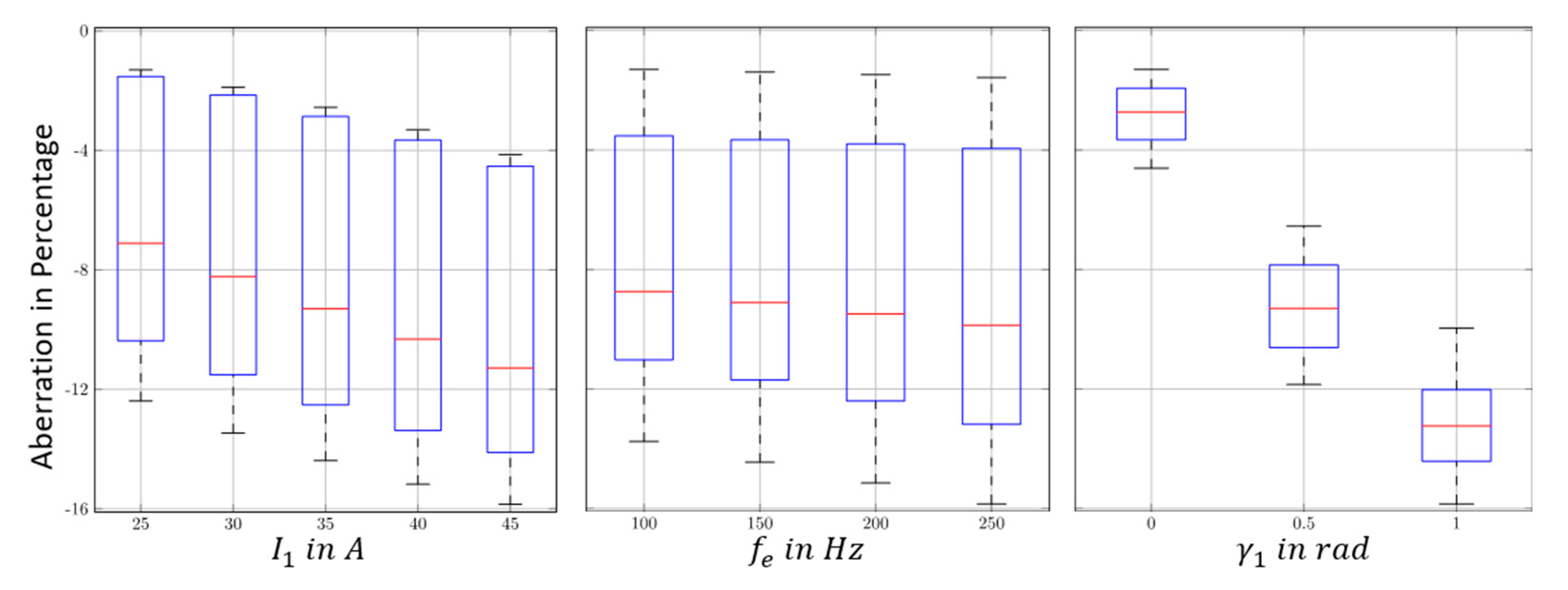
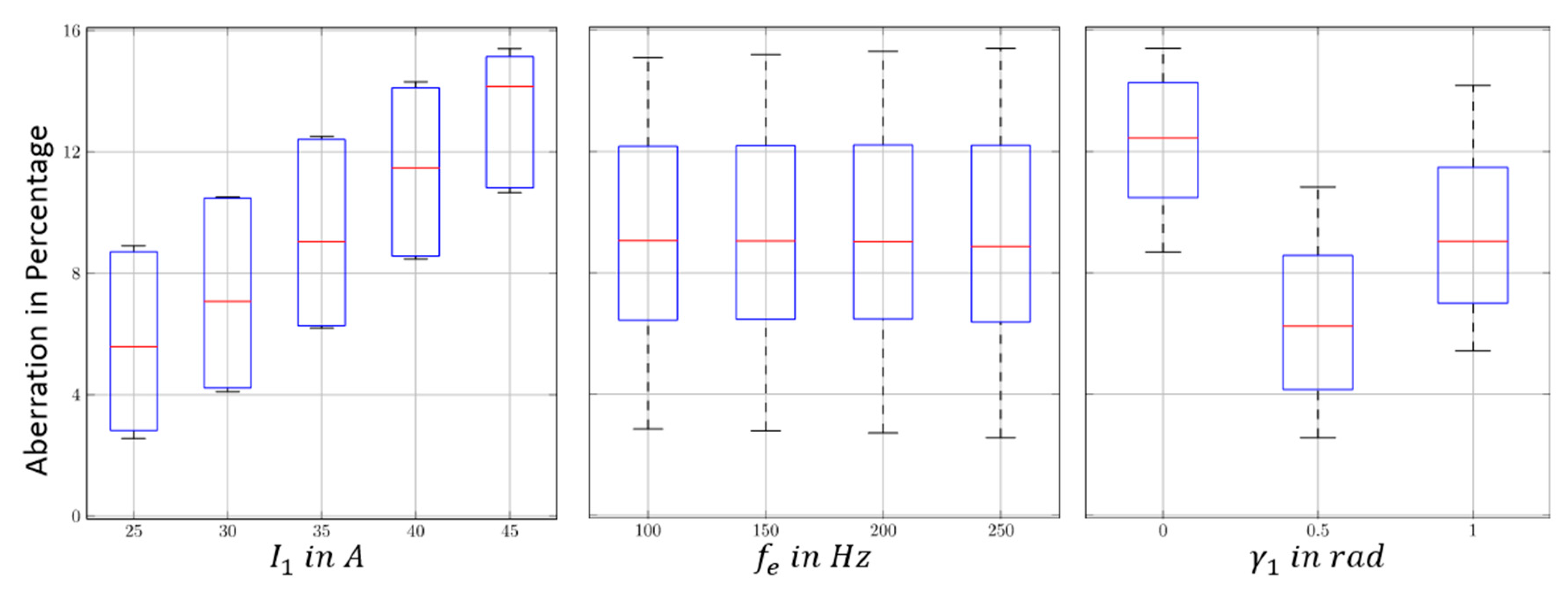
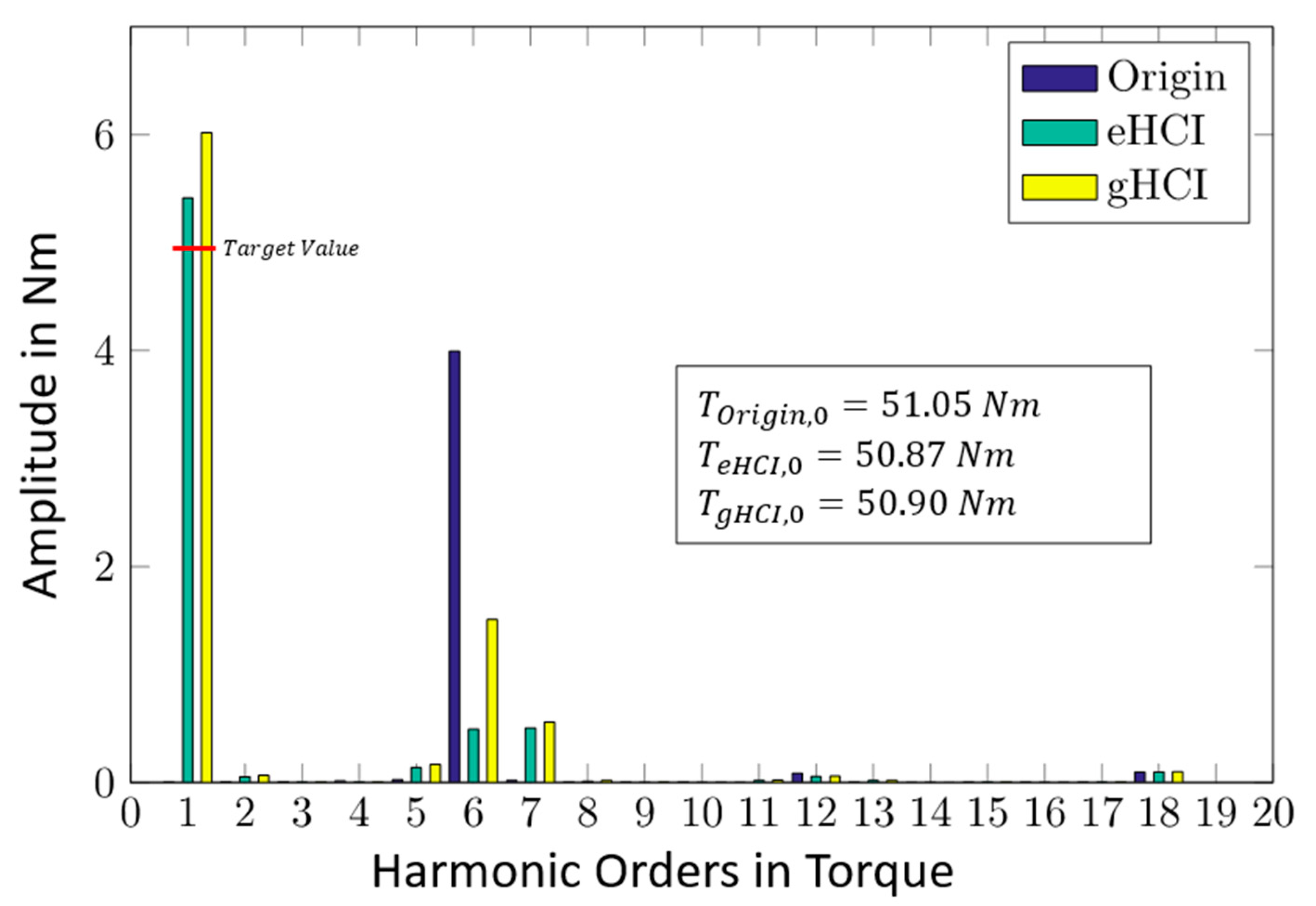
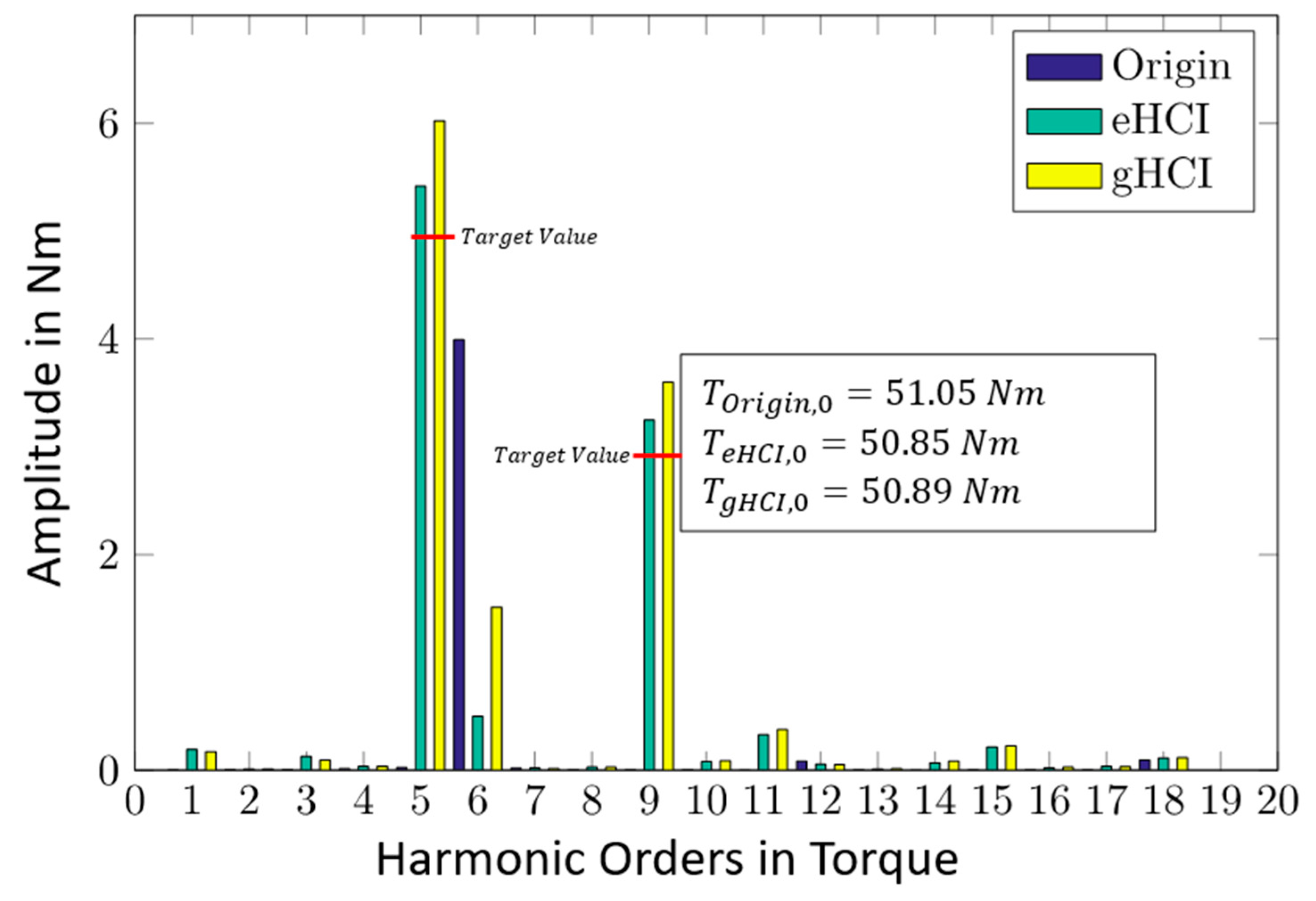
4.3. Validation of Generative Harmonic Current Injection for Permanent Magnet Excited Synchronous Machines with Interior Magnets
5. Conclusions
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeraoulia, M.; Benbouzid, M.E.H.; Diallo, D. Electric Motor Drive Selection Issues for HEV Propulsion Systems: A Comparative Study. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2006, 55, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangkang, Z.; Jianqiu, L.; Minggao, O.; Jing, G.; Yan, M. Electric braking performance analysis of PMSM for electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electronic & Mechanical Engineering and Information Technology, Harbin, China, 12–14 August 2011; pp. 2596–2599. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gerling, D.; Ma, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, Q. The Comparison of Control Strategies for the Interior PMSM Drive Used in the Electric Vehicle. World Electr. Veh. J. 2010, 4, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Saitou, R.; Kubo, K.; Nakatsu, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Sasaki, K. High-power-density inverter technology for hybrid and electric vehicle applications. Hitachi Rev. 2014, 63, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, E. Advances in Converter Control and Innovative Exploitation of Additional Degrees of Freedom for Multiphase Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.; Springob, L. Identification and compensation of torque ripple in high-precision permanent magnet motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, F.; Thelin, P.; Sadarangani, C. Performance evaluation of permanent magnet synchronous machines with concentrated and distributed windings including the effect of field-weakening. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2004), Edinburgh, UK, 31 March–2 April 2004; p. v2-679. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.-H.; Jahns, T.M.; Soong, W.L. Torque Ripple Reduction in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Using the Principle of Mutual Harmonics Exclusion. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Industry Applications Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–27 September 2007; pp. 558–565. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.-H.; Jahns, T.M.; Soong, W.L.; Guven, M.K.; Illindala, M.S. Torque Ripple Reduction in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Using Stators with Odd Number of Slots Per Pole Pair. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Bolognani, S.; Pre, M.D.; Grezzani, G. Design considerations for fractional-slot winding configurations of synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 42, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.-W.; You, Y.-M. Cogging Torque Reduction in Permanent-Magnet Brushless Generators for Small Wind Turbines. J. Magn. 2015, 20, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwack, J.; Min, S.; Hong, J.-P. Optimal Stator Design of Interior Permanent Magnet Motor to Reduce Torque Ripple Using the Level Set Method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2108–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-C. A Novel Method for Minimization of Cogging Torque and Torque Ripple for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Xu, Q.; Li, Q. Asymmetrical V-Shape Rotor Configuration of an Interior Permanent Magnet Machine for Improving Torque Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajaku, G.; Gerling, D. New methods for reducing the cogging torque and torque ripples of PMSM. In Proceedings of the 4th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Nuremberg, Germany, 30 September–1 October 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, M.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Cha, H.-R. Analysis of Torque Ripple and Cogging Torque Reduction in Electric Vehicle Traction Platform Applying Rotor Notched Design. Energies 2018, 11, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Islam, R.; Sebastian, T. Experimental Verification of Design Techniques of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors for Low-Torque-Ripple Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, I.; Ponomarev, P.; Alexandrova, Y.; Pyrhonen, J. Unequal Teeth Widths for Torque Ripple Reduction in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines with Fractional-Slot Non-Overlapping Windings. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, E.; Cardoletti, L.; Jufer, M. Permanent-magnet synchronous motors: A comprehensive approach to cogging torque suppression. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1993, 29, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmabadi, A.; Xu, W.; Degner, M. A Sensitivity Analysis on the Fifth and the Seventh Harmonic Current Injection for Sixth Order Torque Ripple Reduction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC), Miami, FL, USA, 21–24 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Wu, L.J.; Xia, Z.P. An Accurate Subdomain Model for Magnetic Field Computation in Slotted Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 1100–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baodong, C.; Gang, L.; Kun, M. Harmonic current suppression for high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor with sensorless control. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiba, Japan, 13–16 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Kar, N.C. Practical Testing Solutions to Optimal Stator Harmonic Current Design for PMSM Torque Ripple Minimization Using Speed Harmonics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 5181–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollat, M.; Hartmann, D.; Gauterin, F. An Analytical Method for Generating Determined Torque Ripple in Synchronous Machines with Surface Magnets by Harmonic Current Injection. Machines 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanselman, D. Brushless Permanent Magnet Motor Design; Magna Physics Pub: Lebanon, OH, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, P.C.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S.D.; Pekarek, S. Analysis of Electric Machinery and Drive Systems, 3rd ed.; Wiley IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, D. Elektrische Antriebe–Regelung von Antriebssystemen, Version 4; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Farshadnia, M. Advanced Theory of Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Wound Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, J.Y.; Ding, Z. Design of currents to reduce torque ripple in brushless permanent magnet motors. IEEE Proc. B Electr. Power Appl. UK 1993, 140, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamiti, T.; Lubin, T.; Baghli, L.; Rezzoug, A. Modeling of a synchronous reluctance machine accounting for space harmonics in view of torque ripple minimization. Math. Comput. Simul. 2010, 81, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
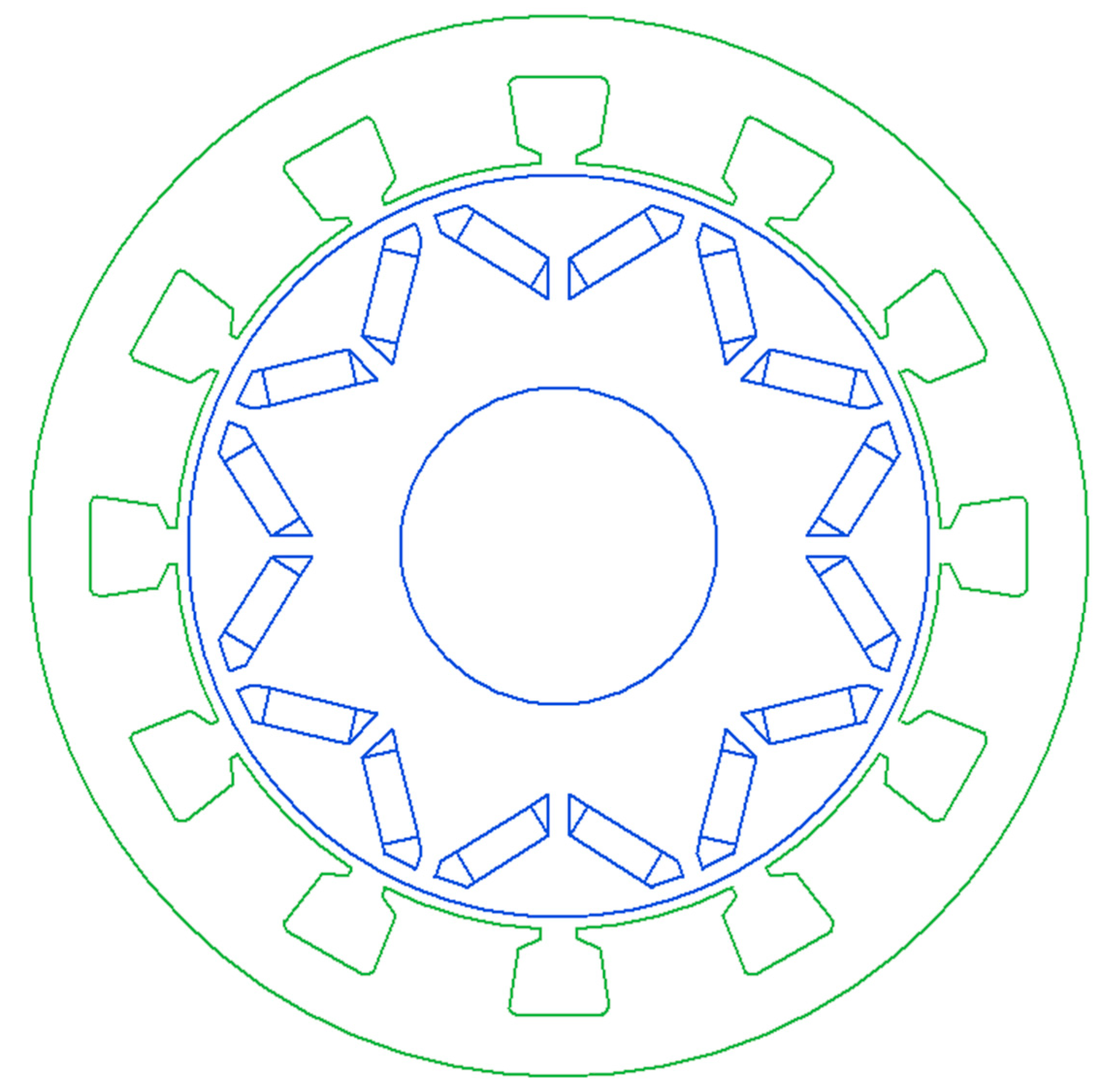
| Rated Output Power | 20 kW | Number of Slots | 12 |
| Rated Voltage | 320 V | Number of Conductors per Slot | 58 |
| Rated Speed | 3400 rpm | Outer Diameter of Rotor | 210 mm |
| Number of Poles | 8 | Length of Rotor Core | 75 mm |
| Outer Diameter of Stator | 300 mm | Length of Stator Core | 75 mm |
| Inner Diameter of Stator | 217 mm |
| Residual Flux Density | 1.40 T |
| Coercive Force | 1115 kA/m |
| Maximum Energy Density | 390.57 kJ/m3 |
| Relative Recoil Permeability | 1.00 |
| Demagnetized Flux Density | 0 T |
| Recoil Residual Flux Density | 1.40 T |
| Recoil Coercive Force | 1115 kA/m |
| Current amplitude | {25 A, 30 A, 35 A, 40 A, 45 A} |
| Stator field frequency | {100 Hz, 150 Hz, 200 Hz, 250 Hz} |
| Phase shift of fundamental wave | {0 rad, 0.5 rad 1 rad} |
| Scenario | Amplitude | Phase | Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | - | ||
| S1 | 8.25% | ||
| S2 | 6.56% | ||
| S3 | 7.49% | ||
| S4 | 8.36% 8.90% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vollat, M.; Li, J.; Gauterin, F. An Analytical Method for Generating Determined Torque Ripple in Synchronous Machine with Interior Magnets by Harmonic Current Injection. Machines 2020, 8, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040062
Vollat M, Li J, Gauterin F. An Analytical Method for Generating Determined Torque Ripple in Synchronous Machine with Interior Magnets by Harmonic Current Injection. Machines. 2020; 8(4):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040062
Chicago/Turabian StyleVollat, Matthias, Junchao Li, and Frank Gauterin. 2020. "An Analytical Method for Generating Determined Torque Ripple in Synchronous Machine with Interior Magnets by Harmonic Current Injection" Machines 8, no. 4: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040062
APA StyleVollat, M., Li, J., & Gauterin, F. (2020). An Analytical Method for Generating Determined Torque Ripple in Synchronous Machine with Interior Magnets by Harmonic Current Injection. Machines, 8(4), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040062





