Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine with Magnetic Saliency Tracking Based on Voltage Signal Injection †
Abstract
Notation
- ud, uq = dq axis stator voltages
- id, iq = dq axis stator currents
- λd, λq = dq axis stator magnetic fluxes
- λm = rotor magnetic flux
- Ld, Lq = dq axis inductances
- ΣL =(Ld+Lq)/2 = average inductance
- ΔL = (Ld-Lq)/2 = differential inductance
- rs = stator resistance
- uγ, uδ= γδ axis stator voltages
- iγ, iδ= γδ axis stator currents
- λγ, λδ= γδ axis stator magnetic fluxes
- p = number of pole pairs
- θ = θe = electrical angular position
- ω = ωe = electrical angular speed
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of Modified Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine (PMSM) Model
2.1. Modified PMSM Voltage and Flux/Current Model in Synchronous Reference Frame dq
2.2. Modified PMSM Voltage and Flux/Current Model in γδ
2.3. Modified PMSM Voltage and Flux/Current Model in γδ
2.4. PMSM Inductance Matrix Lγδ and Magnetic Saliency
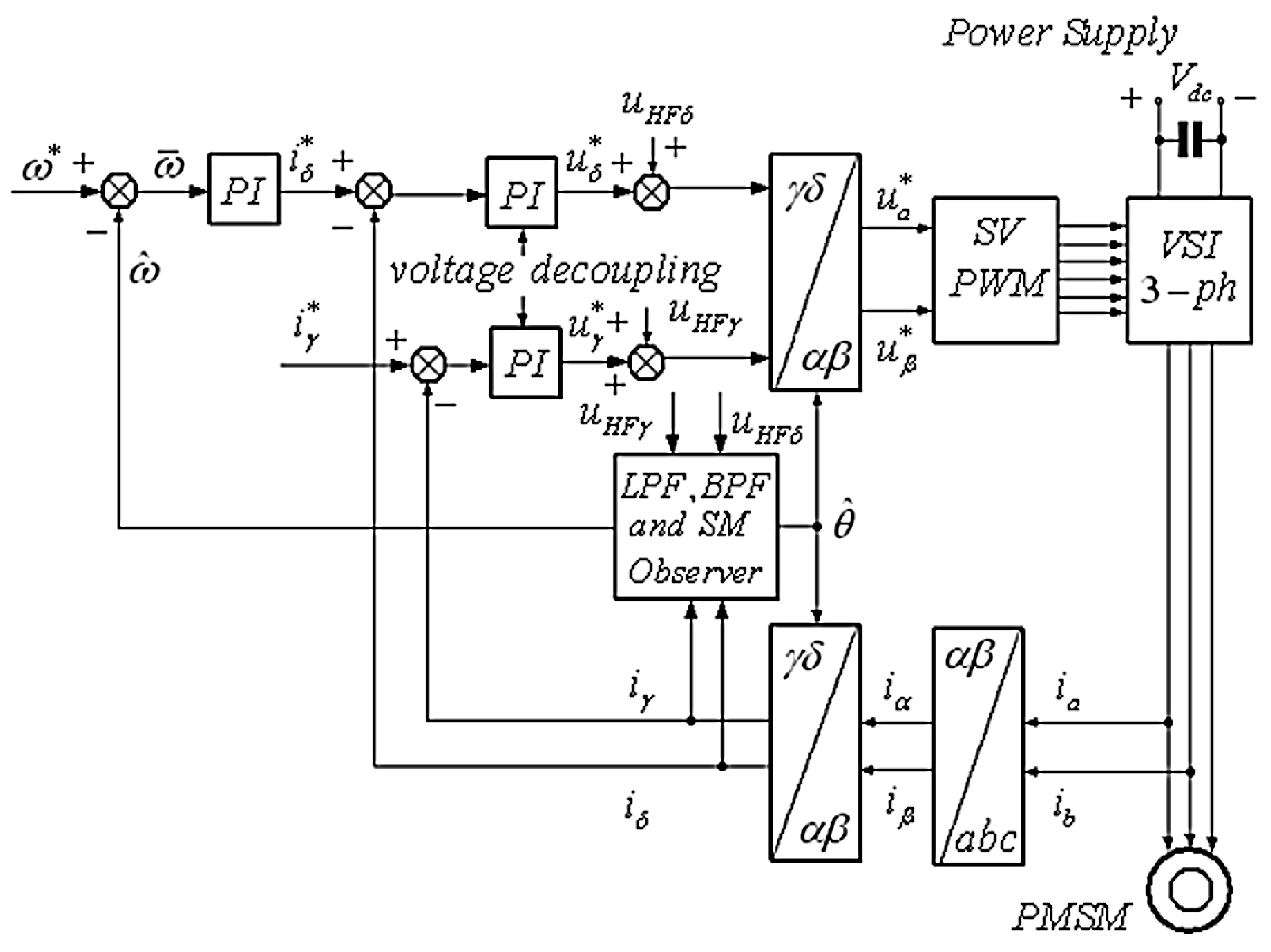
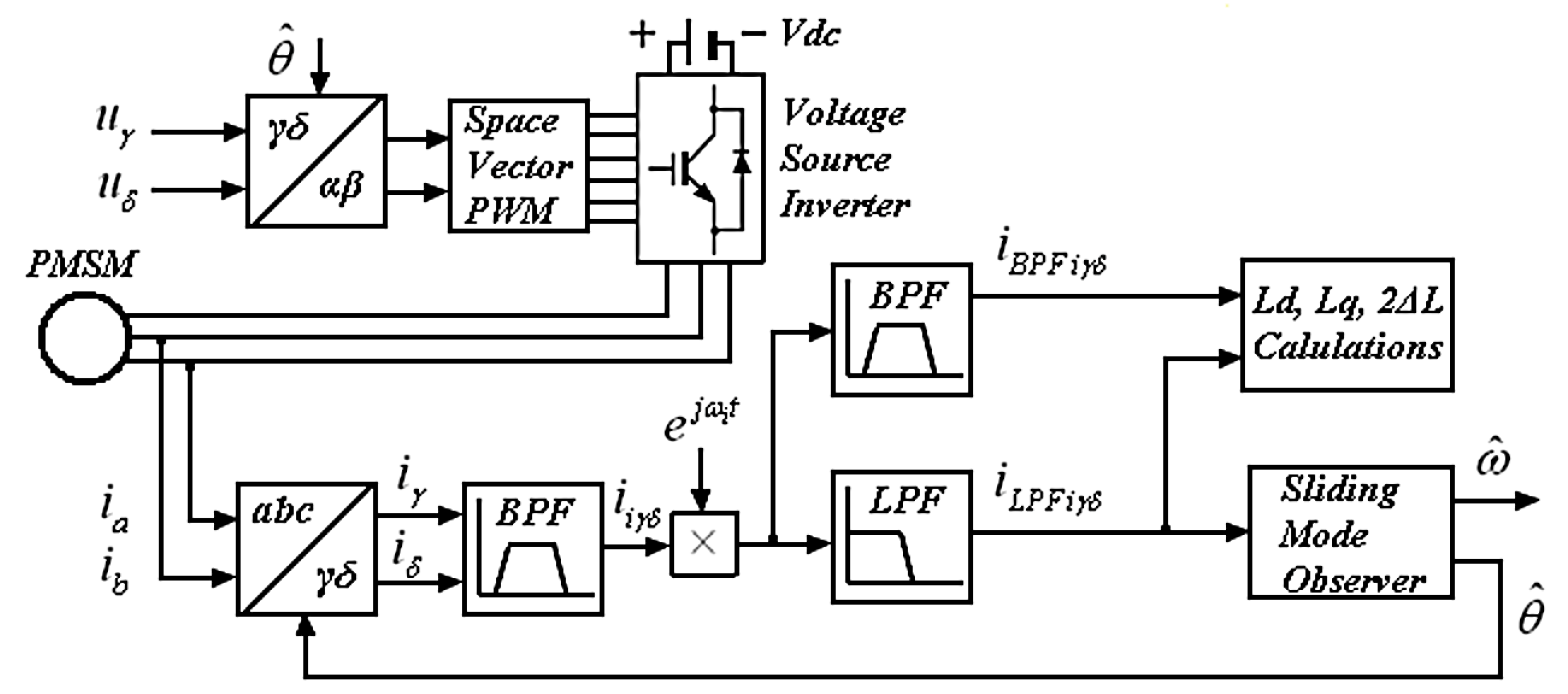
3. High-Frequency Injection (HFI) of Stator Voltage for Rotor Position Estimation
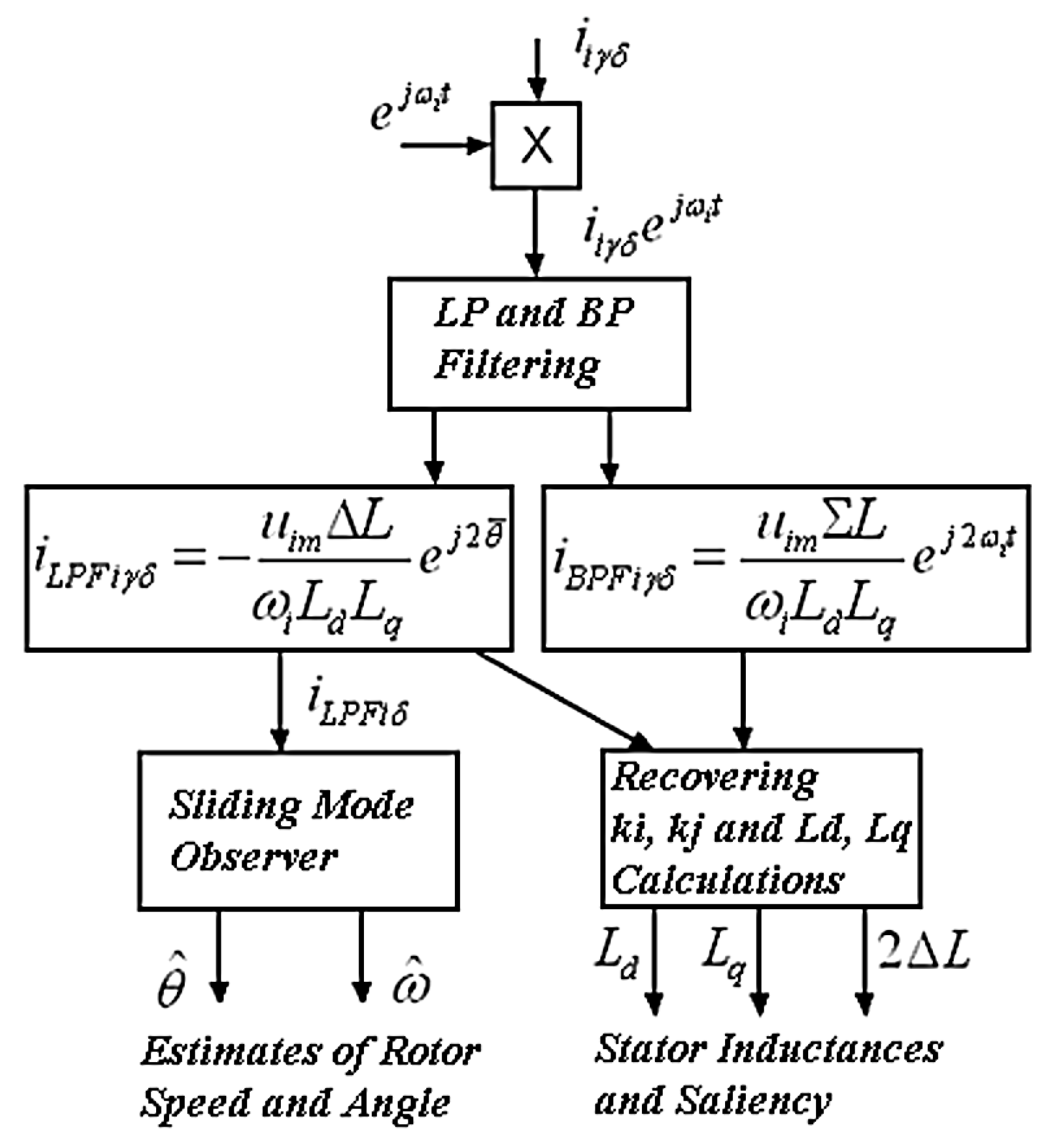
3.1. Analysis of High Frequency Stator Current in γδ Reference Frame
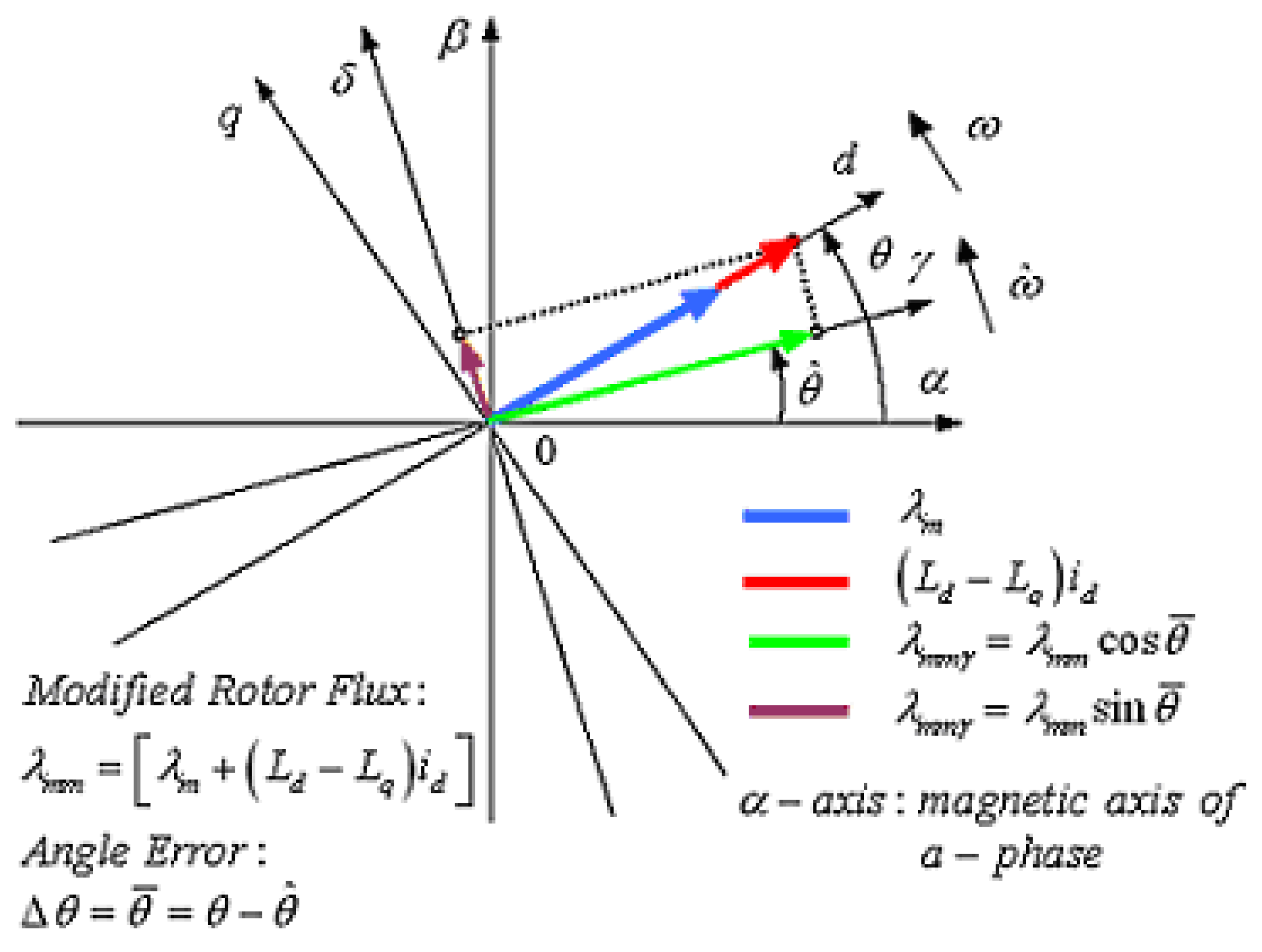
3.2. Angle Error between dq and γδ Reference Frames
3.3. Angle Error of PMSM Rotor Flux in γδ Reference Frame
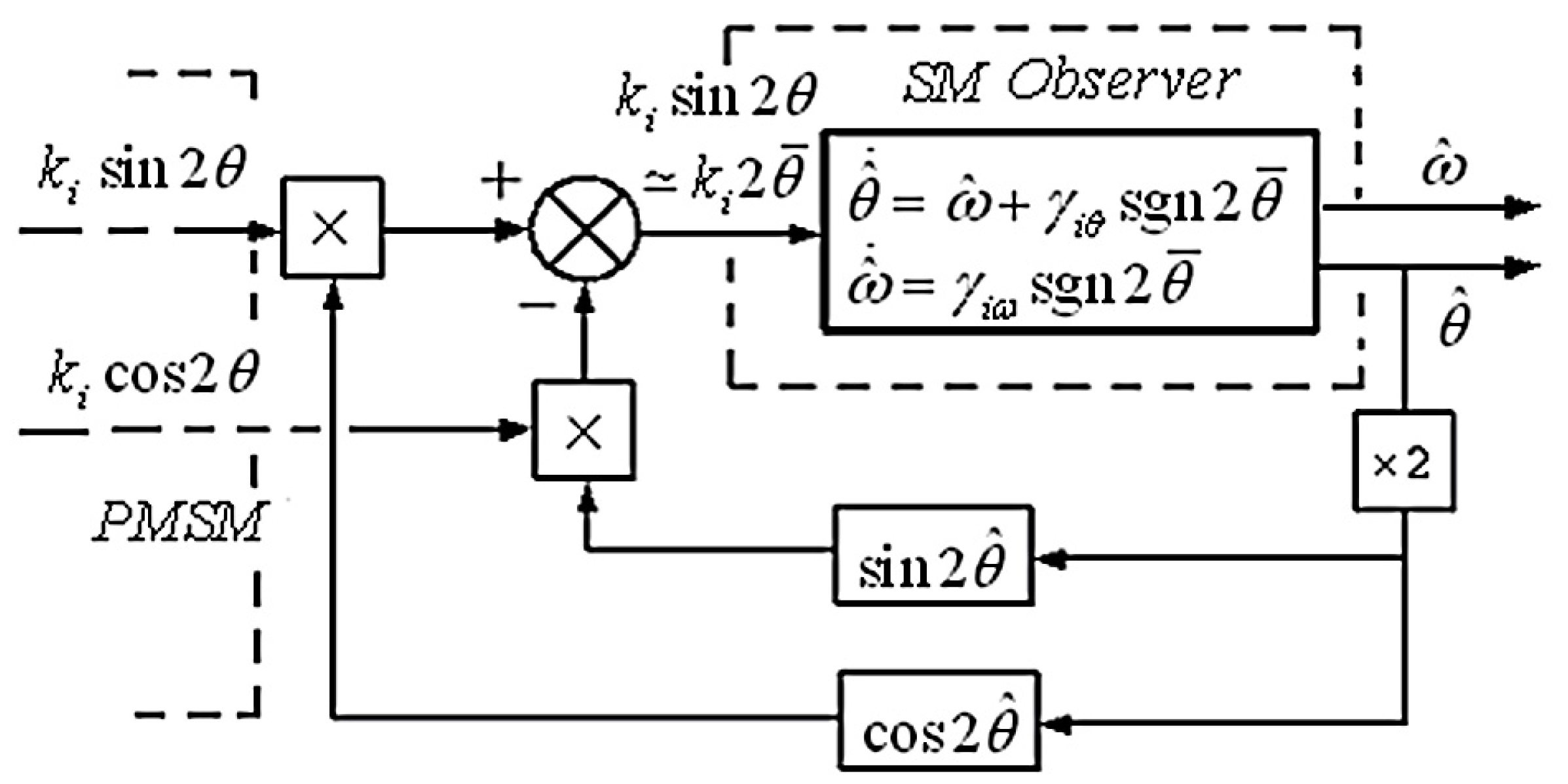
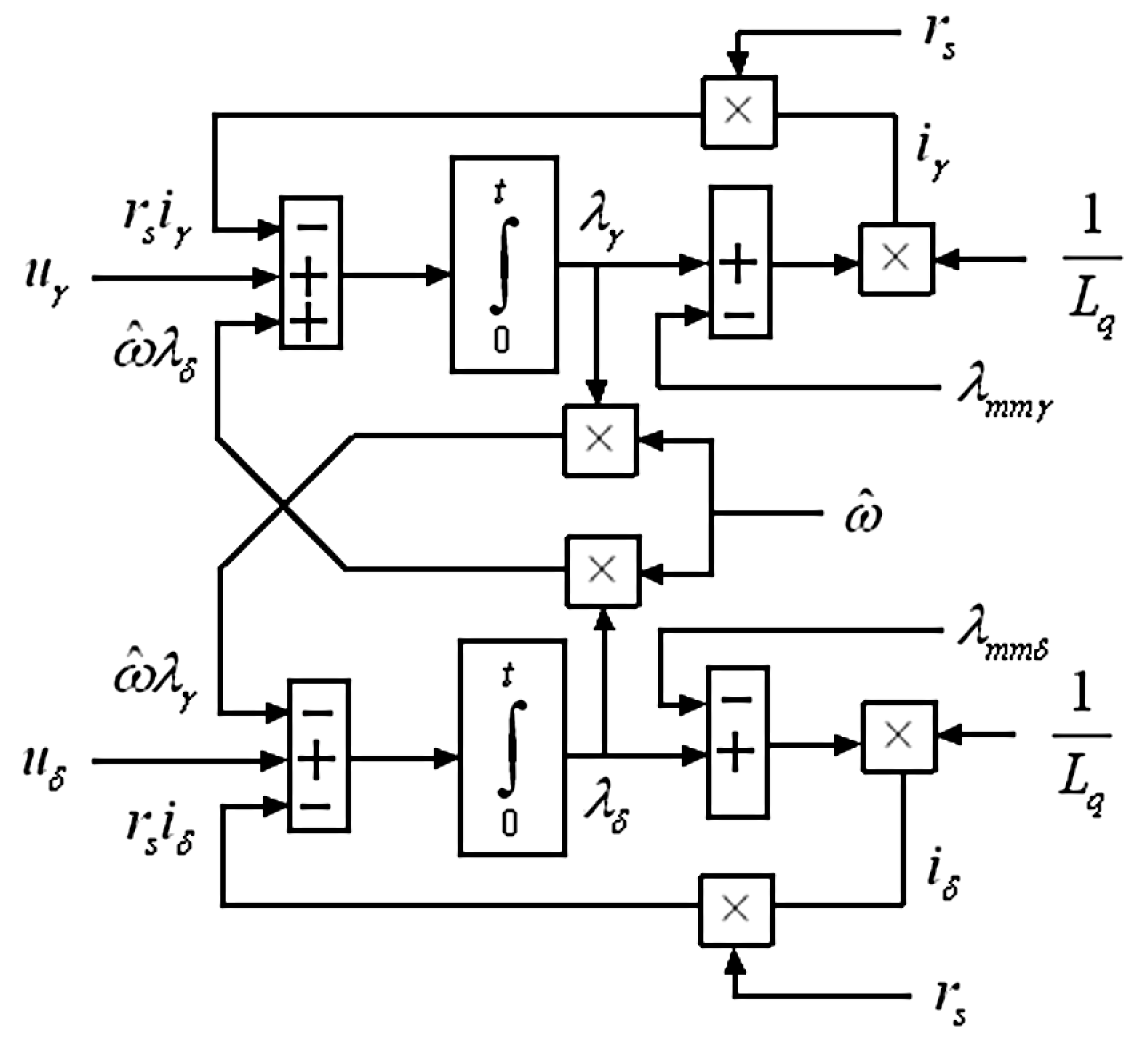
3.4. Design of Sliding Mode Observer (SMO) for Estimation of Rotor Flux Angle and Speed
3.4.1. SMO Dynamics and Stability
3.4.2. Approximation of sgn(.) Function-Chattering Reduction
4. Estimation of PMSM Inductances and Magnetic Saliency
4.1. Calculating the Parameters ki and kj
4.2. Expressing dq Impedances as Functions of the ki and kj Parameters
4.3. Expressing the PMSM Magnetic Saliency (Ld − Lq) as Function of Parameters ki and kj
5. Simulation Results and Discussion
5.1. Description of Simulated PMSM Model and Control System
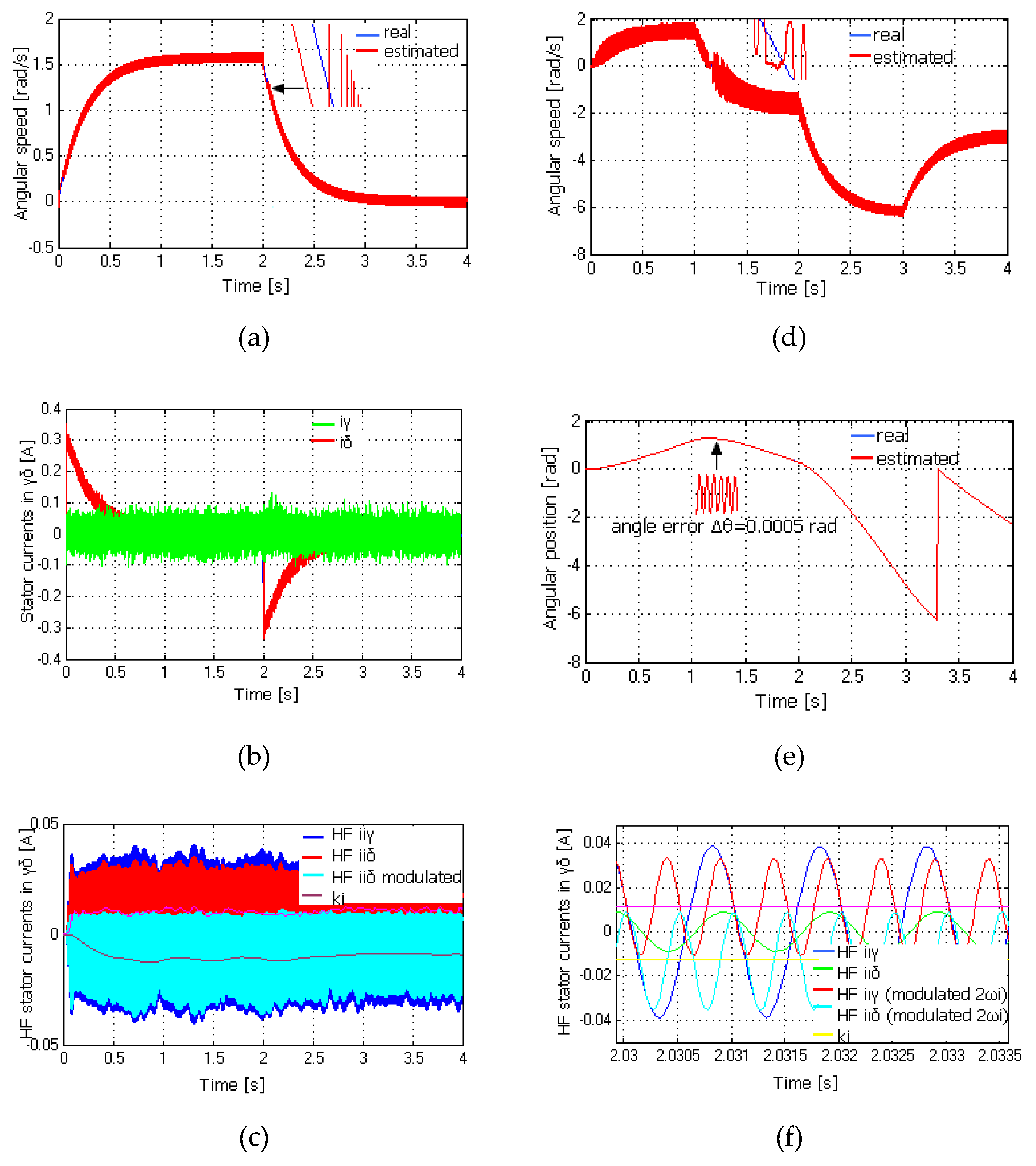
5.2. Response at Very Low Speed and Standstill
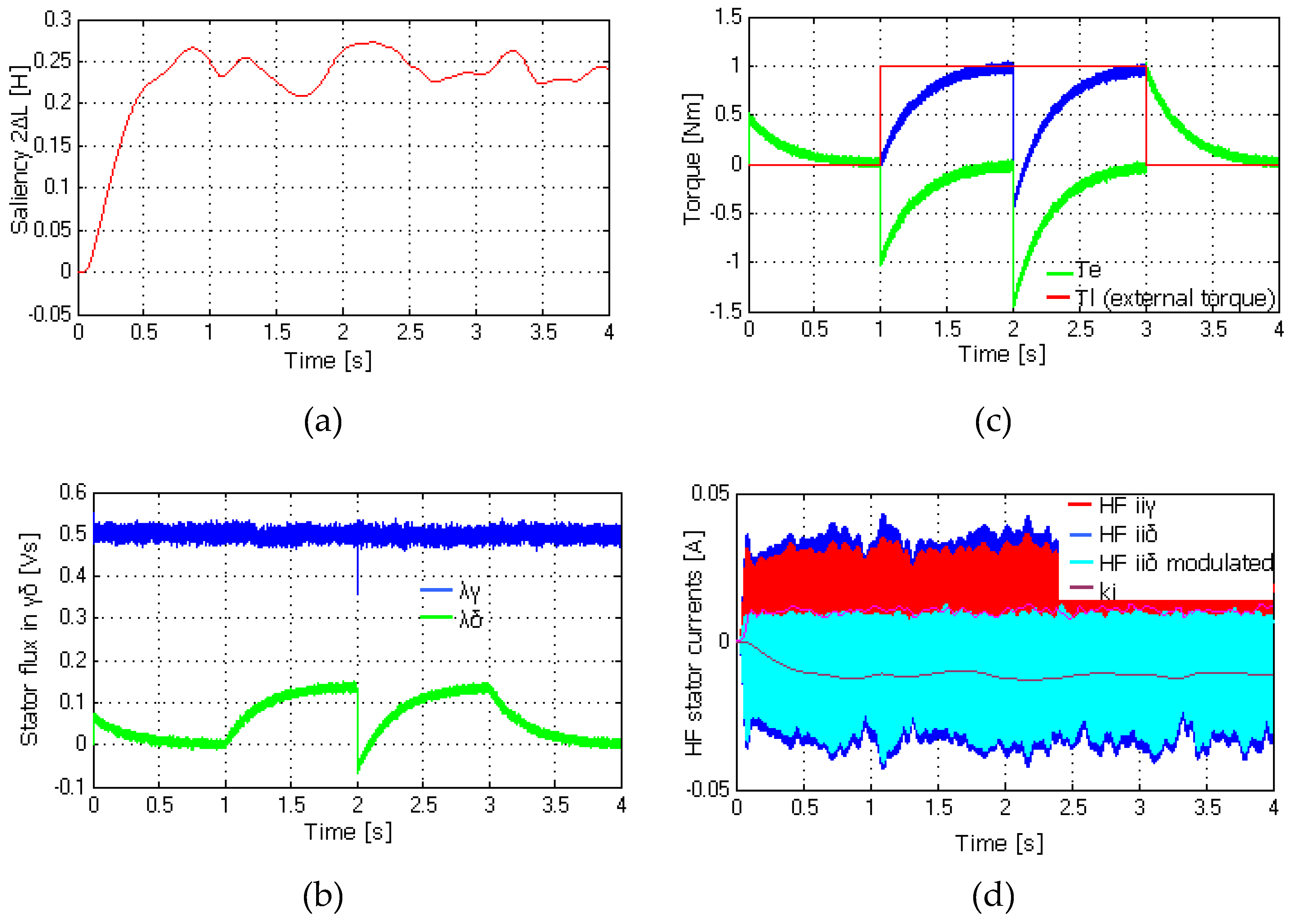
5.3. Very Low Speed Response with Torque Load
5.4. Flux and Torque Response with Saliency Estimation at Very Low Speed
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morimoto, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Sanada, M.; Takeda, Y. Sensorless control strategy for salient-Pole PMSM based on extended EMF in rotating reference frame. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lorenz, R. Surface permanent-magnet machine self-Sensing at zero and low speeds using improved observer for position, velocity, and disturbance torque estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kennel, R.M. Analysis of permanent-Magnet machine for sensorless control based on high-frequency signal injection. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC 2012), Harbin, China, 2–5 June 2012; pp. 2367–2371. [Google Scholar]
- Preindl, M.; Schaltz, E. Sensorless Model Predictive Direct Current Control Using Novel Second-Order PLL Observer for PMSM Drive Systems. Ind. Electron. IEEE Trans. 2011, 58, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piippo, A.; Salomäki, J.; Luomi, J. Signal injection in sensorless PMSM drives equipped with inverter output filter. In Proceedings of the Fourth Power Conversion Conference (PCC 2007), Nagoya, Japan, 2–5 April 2007; pp. 1105–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Hammel, W.; Kennel, R.M. Position sensorless control of PMSM by synchronous injection and demodulation of alternating carrier voltage. In Proceedings of the 2010 First Symposium on Sensorless Control for Electrical Drives (SLED 2010), Padova, Italy, 9–10 July 2010; pp. 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Trancho, E.; Ibarra, E.; Arias, A.; Salazar, C.; Lopez, I.; de Guereñu, A.D.; Peña, A. A novel PMSM hybrid sensorless control strategy for EV applications based on PLL and HFI. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conf. of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2016), Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tuovinen, T.; Hinkkanen, M.; Harnefors, L.; Luomi, J. Comparison of a reduced-Order observer and a full-Order observer for sensorless synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Sul, S. Sensorless control method for PMSM based on frequency-adaptive disturbance observer. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, G.; Gui, X.; Xu, D. Adaptive compensation method of position estimation harmonic error for EMF-based observer in sensorless IPMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 3055–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betin, F.; Capolino, G.A.; Casadei, D.; Kawkabani, B.; Bojoi, R.I.; Harnefors, L.; Levi, E.; Parsa, L.; Fahimi, B. Trends in electrical machines control samples for classical, sensorless, and fault-Tolerant techniques. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2014, 8, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, T.; Huang, S. An enhanced reliability method for initial angle detection on surface mounted permanent magnet synchronous motors. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 1, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bolognani, S.; Calligaro, S.; Petrella, R. Design issues and estimation errors analysis of back-EMF-Based position and speed observer for SPM synchronous motors. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacas, M. Sensorless drives in industrial applications. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2011, 5, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, G.; Rahman, M.F. Sensorless sliding mode MTPA control of an IPM synchronous motor drive using a sliding-mode observer and HF signal injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staines, C.S.; Caruana, C.; Raute, R. A review of saliency-based sensorless control methods for alternating current machines. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2014, 3, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yang, S.; Hsu, Y.; Li, K. Position and Speed Estimation of Permanent Magnet Machine Sensorless Drive at High Speed Using an Improved Phase-Locked Loop. Energies 2017, 10, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tomita, M.; Ichikawa, S.; Doki, S.; Okuma, S. Sensorless control of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor by estimation of an extended electromotive force. Conf. Rec. IEEE-IAS Annu. Meet. 2000, 3, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, ZC.; Tomita, M.; Doki, S.; Okuma, S. An extended electromotive force model for sensorless control of interior permanent-Magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2003, 50, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Harke, M.C.; Lorenz, R.D. Sensorless control of interior permanent-magnet machine drives with zero-Phase lag position estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Ilioudis Vasilios, C. Sensorless Control Applying Signal Injection Methodology on Modified Model of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. In Proceedings of the Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT 2019), Paris, France, 23–26 April 2019; pp. 1935–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y. Improved Sensorless Control of Interior Permanent Magnet Sensorless Motors Using an Active Damping Control Strategy. Energies 2016, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piippo, A.; Luomi, J. Inductance harmonics in permanent magnet synchronous motors and reduction of their effects in sensorless control. In Proceedings of the XVII International Conference on Electric Machines (ICEM 2006), Chania, Crete Island, Greece, 2–5 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Corley, M.; Lorenz, R.D. Rotor Position and Velocity Estimation for a Salient-Pole Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine at Standstill and High Speeds. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Gong, L.M. Investigation of effectiveness of sensorless operation in carrier signal injection based sensorless control Methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 8, 3431–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Shita, T.; Ohto, M.; Ide, K. Encoderless servo drive with adequately designed IPMSM for pulse-voltage-injection-Based position detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 48, 1922–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonhoven, G.; Uddin, M.N. Harmonic Injection-Based adaptive control of IPMSM motor drive for reduced motor current THD. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Jy.; Yang, Sh.; Tu, Ka. Comparative Evaluation of a Permanent Magnet Machine Saliency-Based Drive with Sine-Wave and Square-Wave Voltage Injection. Energies 2018, 11, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejny, R.W.; Lorenz, R.D. Evaluating the practical low-Speed limits for back-EMF tracking-Based sensorless speed control using drive stiffness as a key metric. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtessel, Y.B. Sliding Mode Control with Applications: Tutorial. In Proceedings of the ICEECSAS-2008, UNAM, Mexico City, Mexico, 12 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zidat, F.; Lecointe, J.P.; Morganti, F.; Brudny, J.F.; Jacq, T.; Streiff, F. Non Invasive Sensors for Monitoring the Efficiency of AC Electrical Rotating Machines. Sensors 2010, 10, 7874–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao, H.; Capolino, G.A.; Razik, H. Analytical Approach of the Stator Current Frequency Harmonics Computation for Detection of Induction Machine Rotor Faults. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Diagnostic for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives, SDEMPED, Atlanta, GA, USA, 24–26 August 2003; pp. 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Briz, F.; Degner, M.W.; Zamarrón, A.; Guerrero, J.M. Online Diagnostics in Inverter-Fed AC Machines Using High-Frequency Signal Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.; Huang, K.; Wang, L. Sensorless Speed Control with Initial Rotor Position Estimation for Surface Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 11030–11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Guo, H.; Cao, D.; Wang, Fe. Simultaneous Observation of Hybrid States for Cyber-Physical Systems: A Case Study of Electric Vehicle Powertrain. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar]
| Symbol | Quantity | Expressed in SI |
|---|---|---|
| S | Apparent power | 5.5 kVA |
| cosφ | Electric power coefficient | 0.8 |
| Vl-l | Line to line voltage | 380 V |
| rs | Stator resistance | 2.5 Ω |
| Lmd | d-axis magnetizing inductance | 0.360 H |
| Ld | d-axis inductance | 0.400 H |
| Lq | q-axis inductance | 0.210 H |
| λm | Permanent Magnet Flux | 0.5 Vs (or Wb) |
| J | Moment of inertia | 0.089 kgm2 |
| p | Magnetic pole pairs | 1 |
| ωm | Mechanical angular speed | 3000 rpm |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilioudis, V.C. Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine with Magnetic Saliency Tracking Based on Voltage Signal Injection. Machines 2020, 8, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8010014
Ilioudis VC. Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine with Magnetic Saliency Tracking Based on Voltage Signal Injection. Machines. 2020; 8(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlioudis, Vasilios C. 2020. "Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine with Magnetic Saliency Tracking Based on Voltage Signal Injection" Machines 8, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8010014
APA StyleIlioudis, V. C. (2020). Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine with Magnetic Saliency Tracking Based on Voltage Signal Injection. Machines, 8(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8010014




