Abstract
A novel synchronous generator is proposed for wind power generation. The field flux is generated by the half-wave rectified excitation method. The generator does not require slip rings and brushes for field power supply, as well as permanent magnets. In this paper, the excitation method is explained, and then, the basic characteristics are calculated using the finite element method analysis. Furthermore, the generator is designed for increasing the output power and efficiency.
1. Introduction
As demand for clean power generation increases, projects for onshore and offshore wind power generation have been widely drawn up.
For wind power generation, an induction generator, especially the doubly-fed type, has been mainly used as a generator. It generates a constant frequency unrelated to the wind speed. The problem is as follows; it needs periodic maintenance, because it has slip rings and brushes. It needs a gear box, because the speed rating of the generator is high. The efficiency is lower than that of a permanent magnet synchronous generator.
Consequently, a permanent magnet synchronous generator is expected to be suitable for the generation system, because of the high efficiency and easy maintenance, due to its brushless rotor configuration. The generator, however, will be expensive, because of the sharp increase in the price of rare-earth magnets. It is possible for the generator to be a direct drive system without a gear box, and this makes the system maintenance free; however, the generator becomes very large and expensive. Furthermore, its cut-in speed is high, because of its high detent torque, and the cut-out speed is low because of its high induced voltage.
The author, Higuchi, and his colleagues previously presented a half-wave rectified brushless synchronous motor as an AC servo motor [1,2]. The conventional three-phase winding was used for the armature, and the field rotor winding was just short-circuited with a diode. By superposing excitation current on the three-phase armature torque current, the armature winding generated an excitation magnetic field with a rotating magnetic field. The excitation magnetic field induced current in the rotor field winding. The current was rectified by the diode, so that a constant magnetic flux through the winding was retained. In this way, the field current in the rotor was induced from the stator. The field flux was controllable by varying the amplitude of the excitation current superposed on the armature torque current. The controllability made it possible to perform the field weakening operation easily at the high speed region. The half-wave rectified brushless synchronous motor possesses a simple and robust structure and is less expensive than a permanent magnet motor.
The origin of the half-wave rectified brushless excitation method is the brushless self-excitation synchronous generator proposed by S. Nonaka. For example, a single-phase generator modified with a wound rotor induction machine was proposed [3]. The negative-phase-sequence component of the rotating magnetic field produced the induced voltage at the rotor field windings. The field flux was produced by rectifying the induced voltage by the diode.
The authors proposed a novel, half-wave rectified brushless synchronous generator for wind power generation [4]. The brushless excitation system is based on the above half-wave rectified excitation method. Since the method needs no slip rings and brushes for field magnetic flux, nor permanent magnets, the generator achieves a maintenance-free, simple and robust brushless structure. Since the field flux is also controllable from zero to the rated value, the generator has no detent torque when standing still, and so, the generator is able to start generation at a very low cut-in speed. An excessive voltage rise can be prevented by weakening the field flux, and so, the generator can keep generating until a high cut-out speed without pitch control. This generator will be suitable for a vertical axis wind turbine that is able to work for wind from all directions and that is hard to operate with a pitch control.
In this paper, the basic characteristics of the proposed generator are estimated by using finite element method (FEM) analysis. Furthermore, the generator is designed for increasing output power and efficiency.
2. Principle of Half-Wave Rectified Excitation
2.1. Generator Model
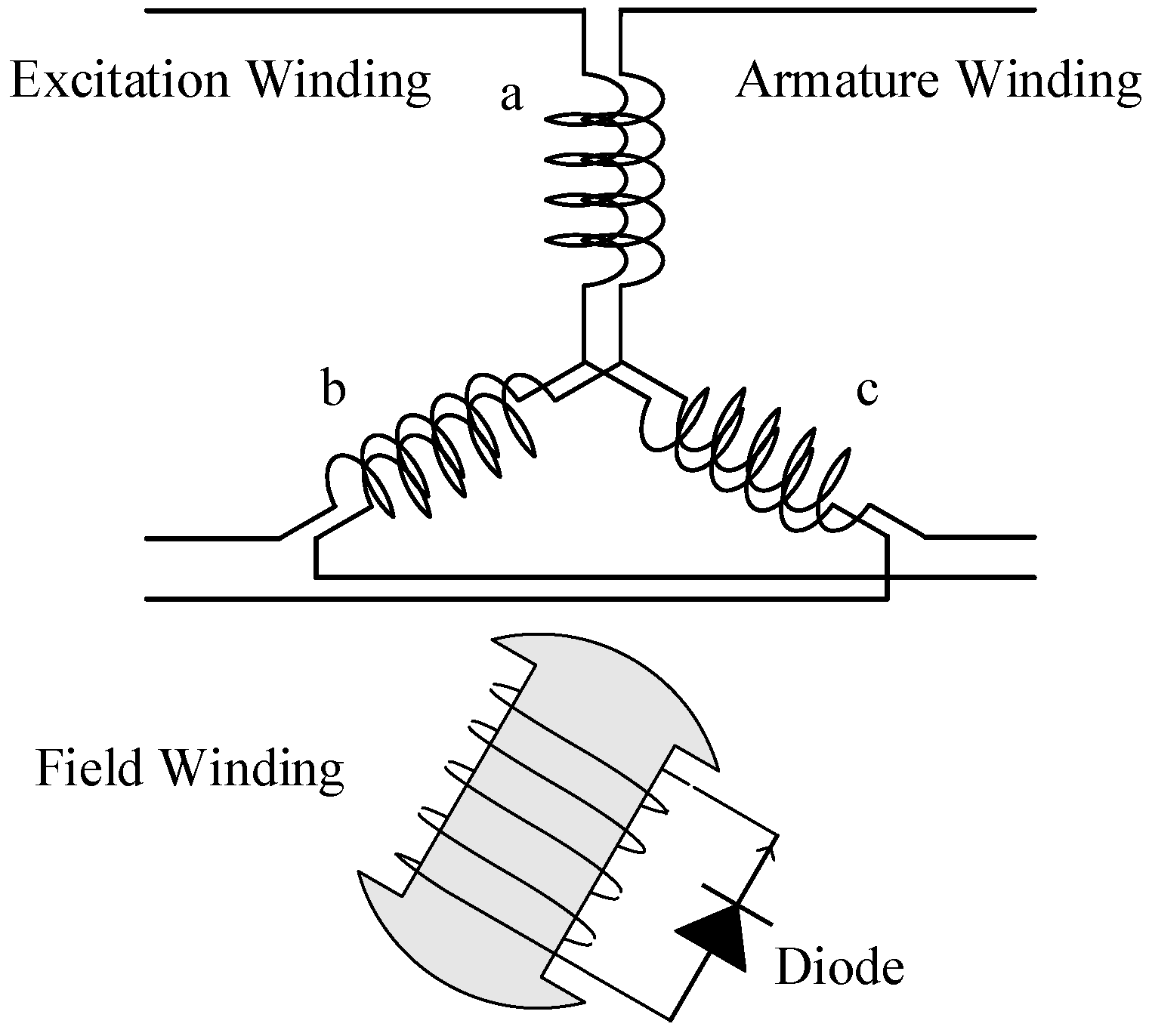
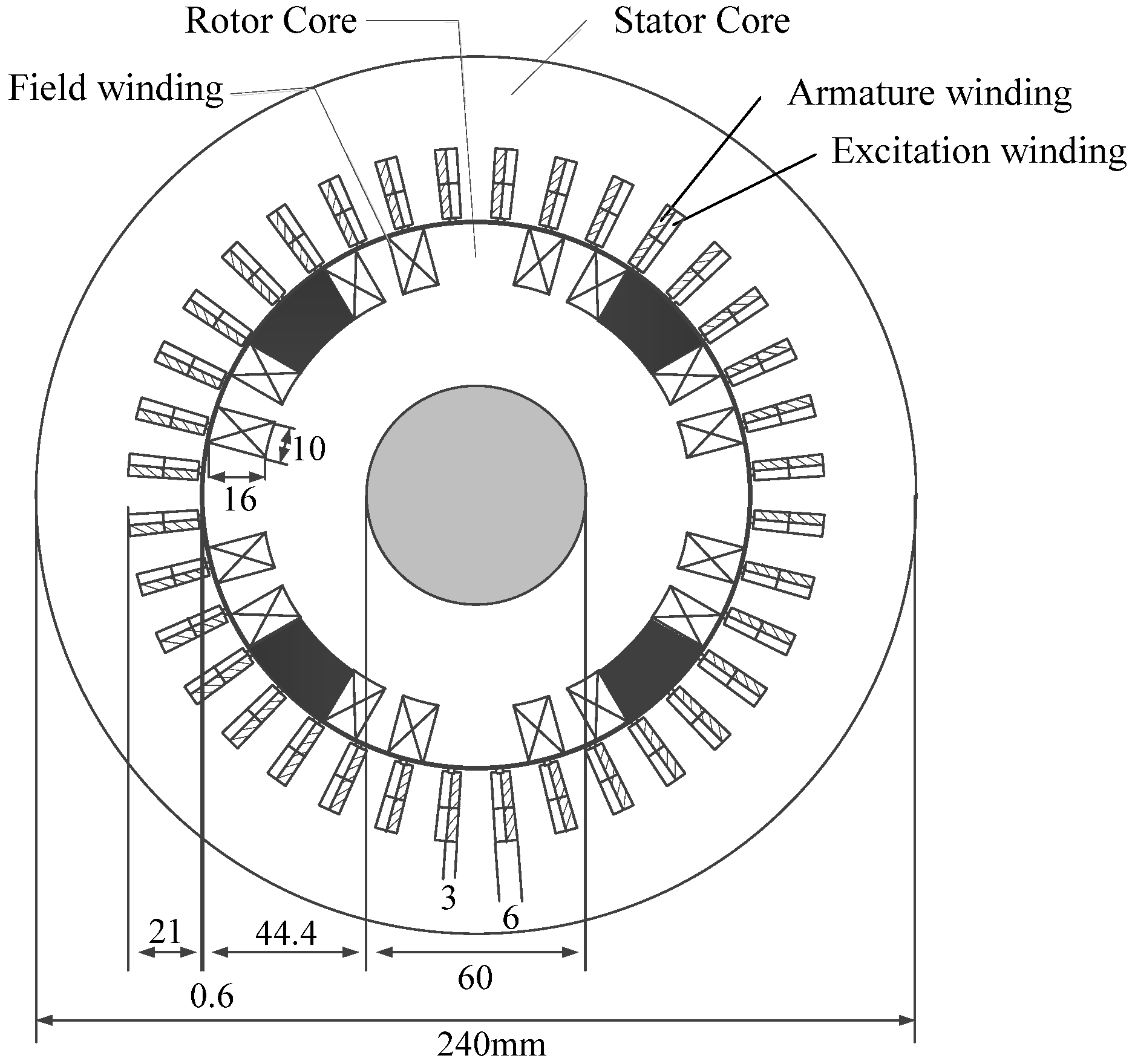
Figure 1 shows the winding configuration of the half-wave rectified brushless synchronous generator. The structure is the same as a conventional salient pole rotor-type synchronous generator, except the rotor field winding. The field winding is short-circuited with a diode. In this paper, we separate the excitation windings and the armature windings that are arranged in the same stator slots.
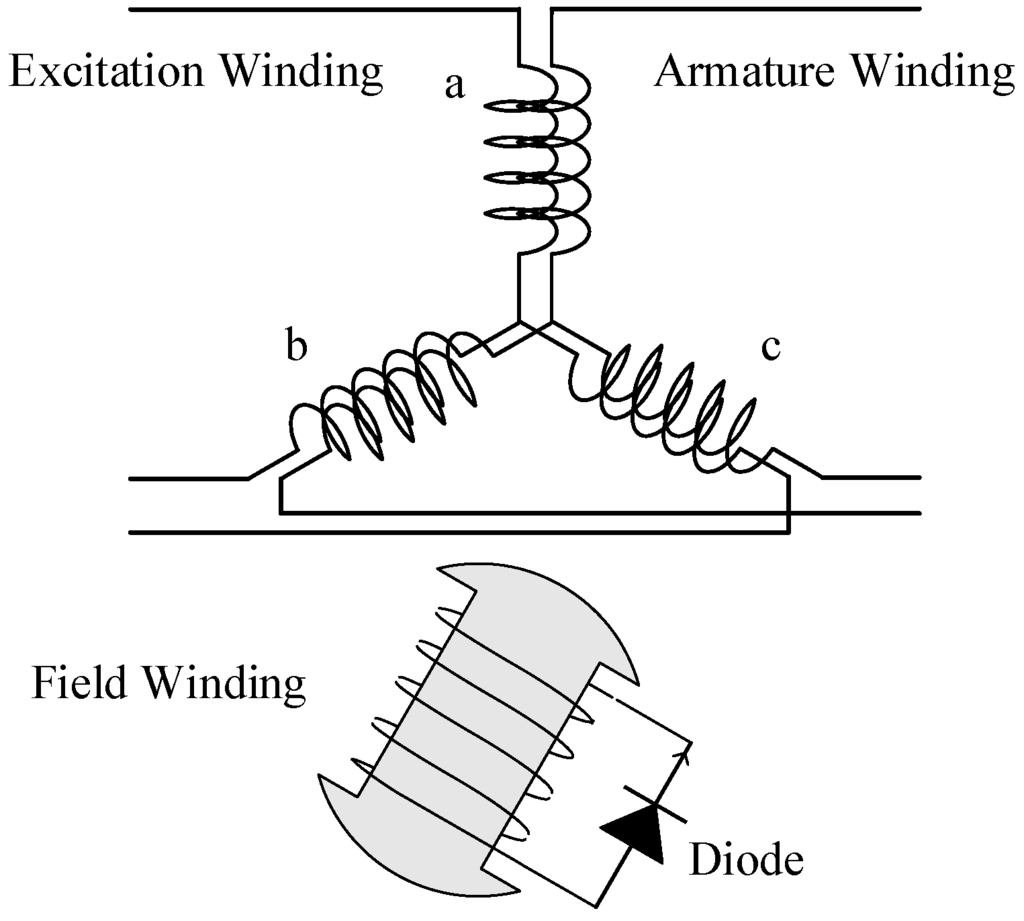
Figure 1.
Winding configuration.
Figure 1.
Winding configuration.
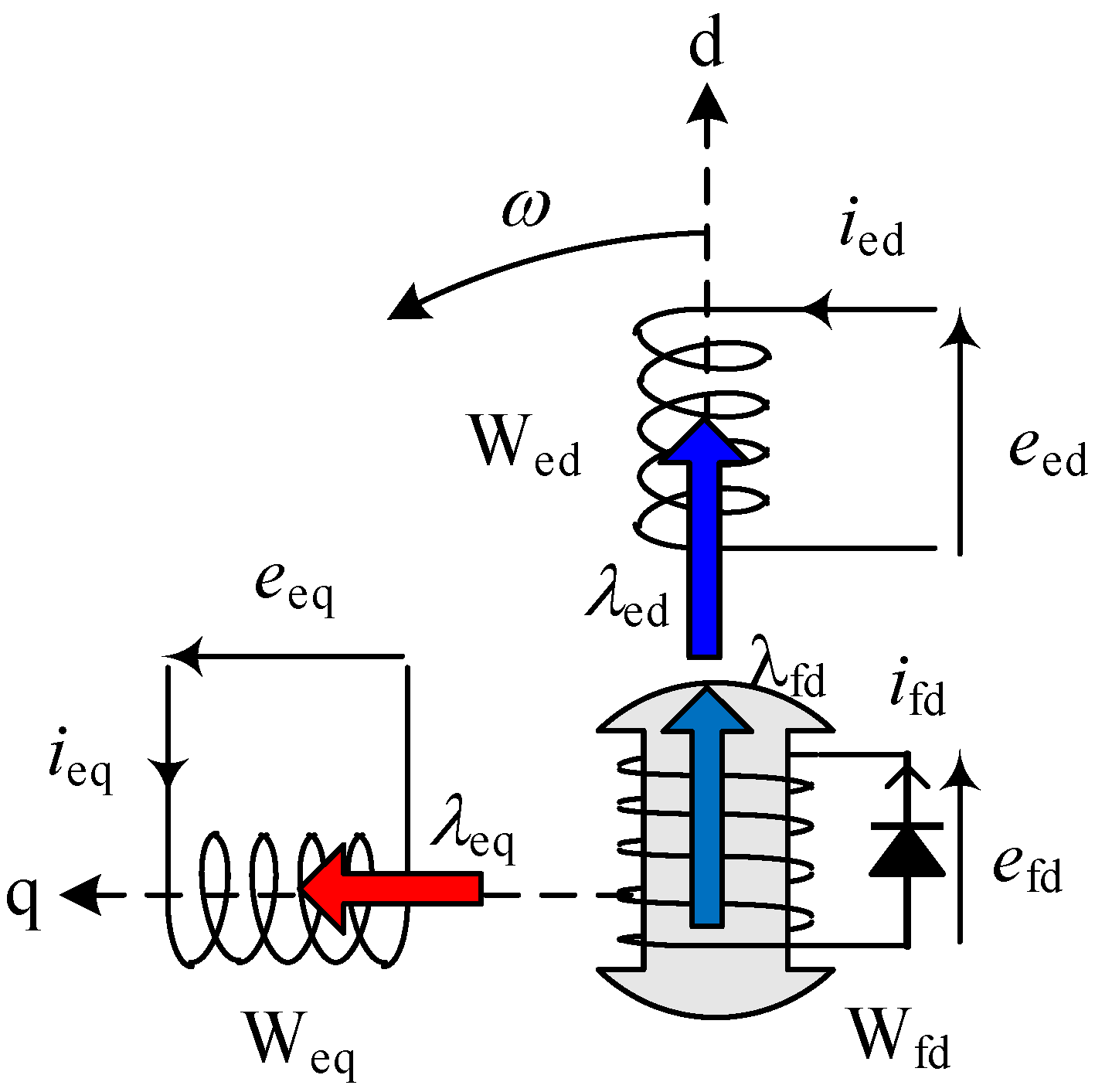
2.2. Voltage Equation
Figure 2 shows the dq-axis model of the stator excitation windings and rotor field windings in the no load condition. The voltage equations for the dq-axis model are:
where the subscripts, ed, eq and fd, of the variables and the constants represent the direct axis and the quadrature axis of the excitation and field windings, respectively. re stands for the resistance of the stator excitation winding and rfd, that of the rotor field winding.
eed = reied + dλed / dt − ωλeq
eeq = reieq + dλeq / dt + ωλed
efd = rfdifd + dλfd / dt
eeq = reieq + dλeq / dt + ωλed
efd = rfdifd + dλfd / dt
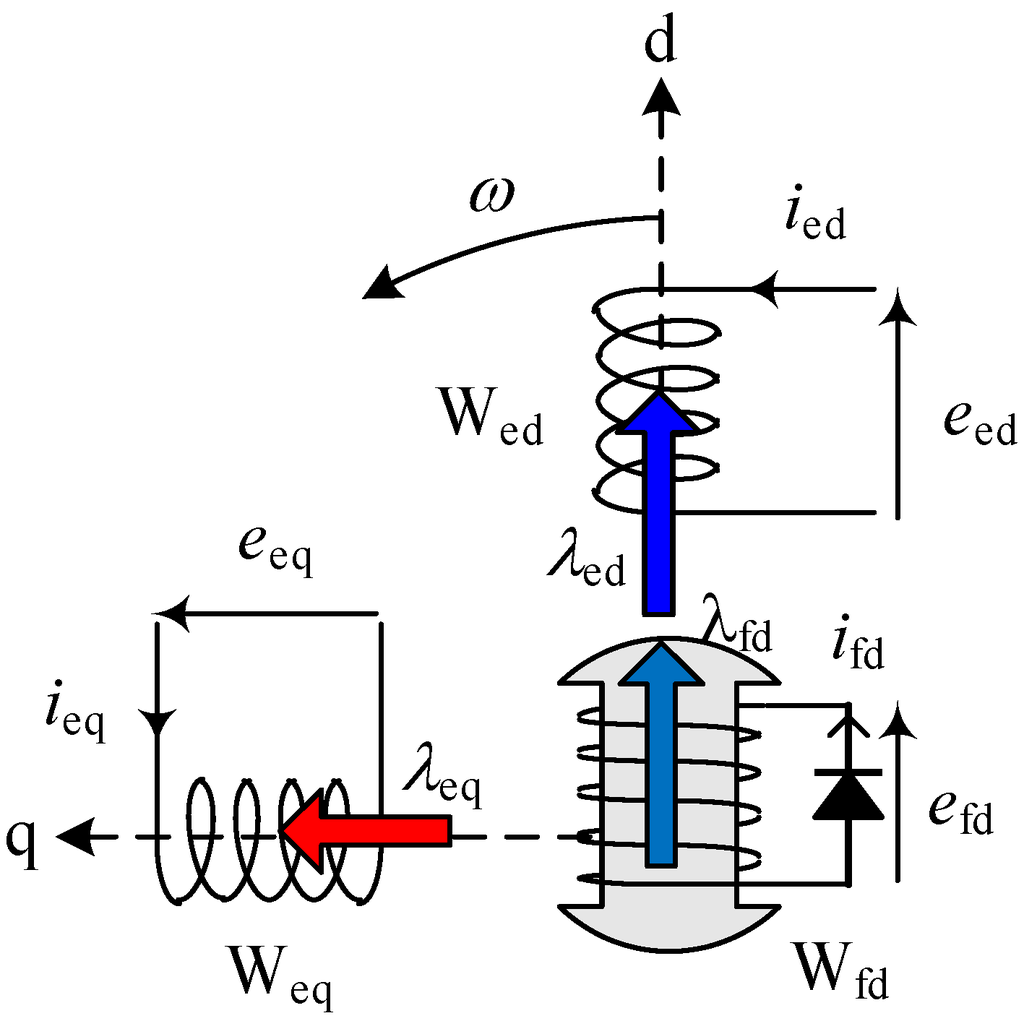
Figure 2.
dq-axis model of excitation windings.
Figure 2.
dq-axis model of excitation windings.
The flux linkages are expressed in terms of self- and mutual inductance as follows:
where L denotes the self-inductance of each winding indicated by the subscript; Mfd is the mutual inductance between the direct axis winding and the field winding.
λed = Ledied + Mfdifd
λeq = Leqieq
λfd = Mfdied + Lfdifd
λeq = Leqieq
λfd = Mfdied + Lfdifd
2.3. Principle of Brushless Excitation
In the proposed excitation method, the field flux is induced by the three-phase excitation current as shown in Equation (3).
iea = Af (t) sin θ
ieb = Af (t) sin (θ − 2π / 3)
iec = Af (t) sin (θ − 4π / 3)
ieb = Af (t) sin (θ − 2π / 3)
iec = Af (t) sin (θ − 4π / 3)
The excitation current is formed by controlling the amplitude of the three-phase current with the function Af(t). From Equation (3), the dq-axis currents are described by:
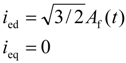
Figure 3 shows the wave forms of the currents and the field flux linkage. The function Af(t) of Equation (3) is a triangular wave in this figure. Since ieq equals zero, λeq becomes zero. When the flux linkage through the field winding λfd increases, the negatively-biased diode turns off in the field circuit. When the flux linkage decreases, the diode turns on, and the field current ifd flows to compensate for the decrease of the flux linkage. The field flux linkage λfd becomes the sum of the flux linkage Mfdied produced by the d-axis excitation current ied and the flux linkage Lfdifd produced by the above field current ifd. If the time constant related with the decreasing flux is large enough, the flux is almost kept constant.
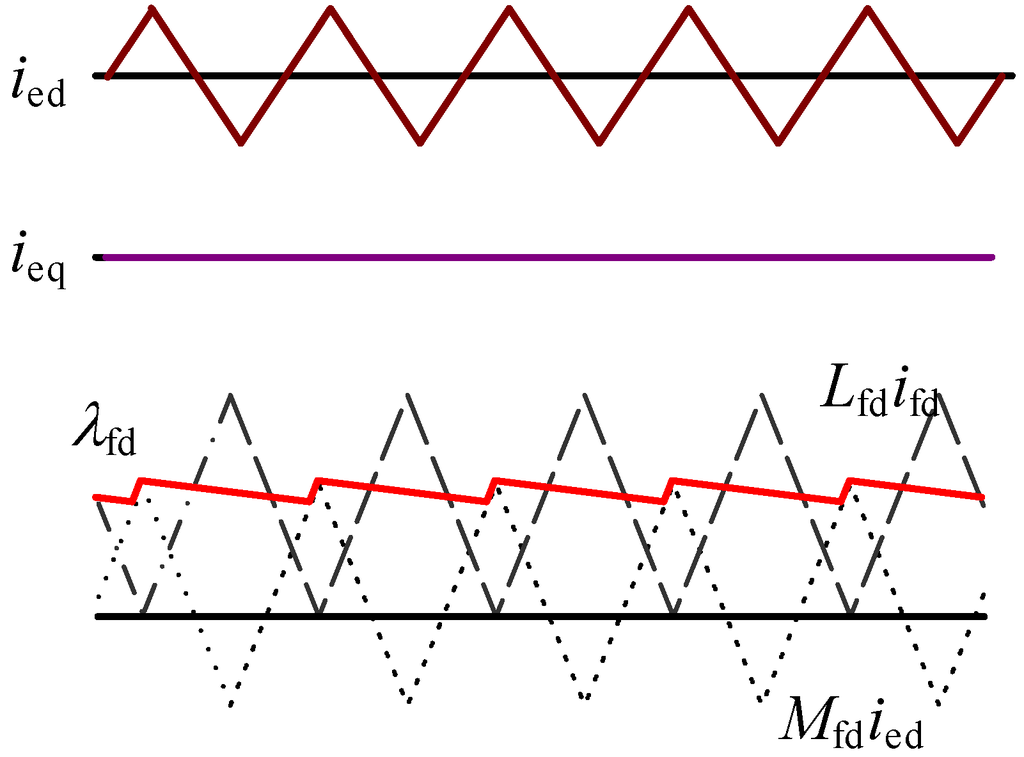
Figure 3.
Waveforms of dq currents and field flux linkage.
Figure 3.
Waveforms of dq currents and field flux linkage.
3. Fundamental Performances of a Half-Wave Rectified Brushless Synchronous Generator
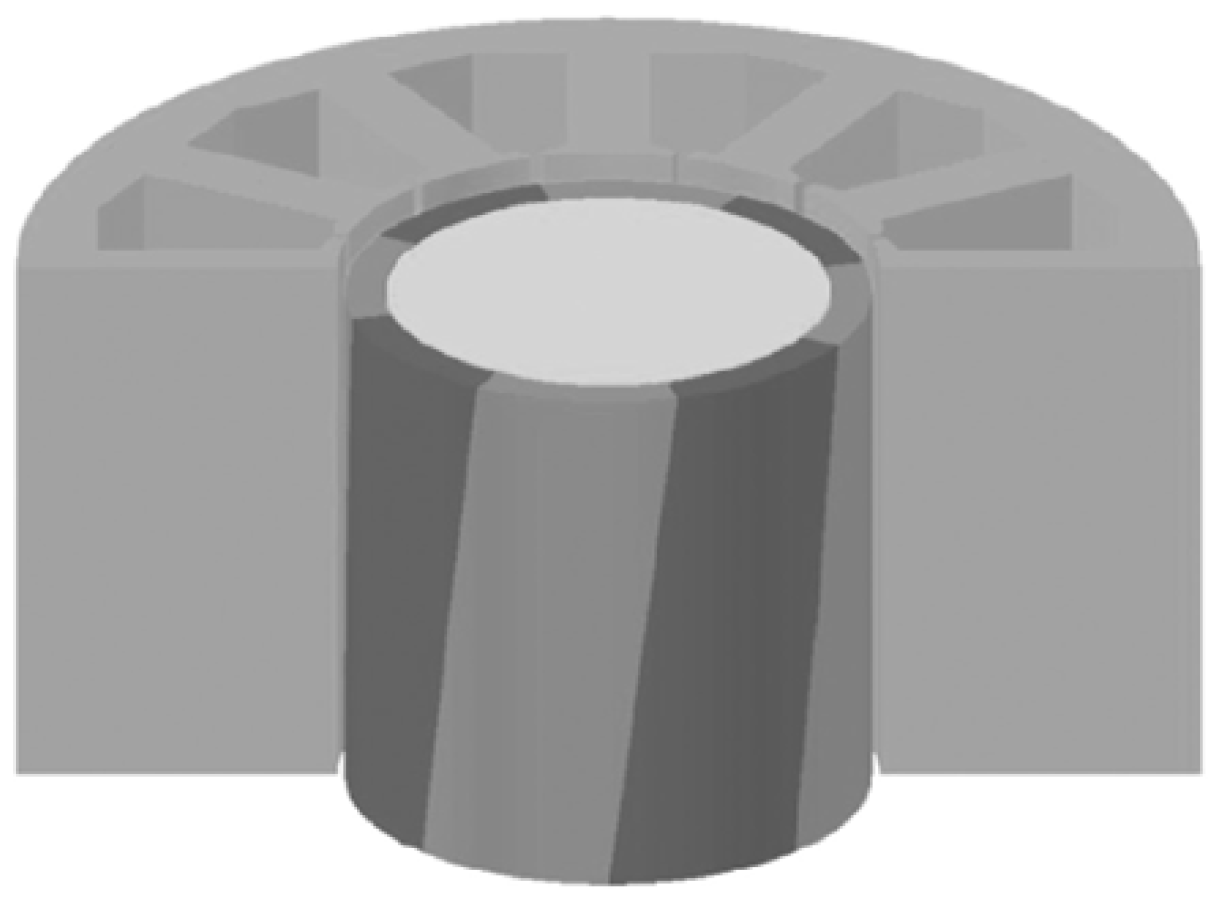
Figure 4 shows the prototype of the proposed four-pole, three-phase and 2-kW generator. The outer diameter is 240 mm; the motor length is 60 mm, and the air gap length is 0.6 mm. In the generator, the excitation winding is separated from the armature winding. The two groups of the winding coils are short pitch distributed windings and are arranged in the same stator slots. The four-pole rotor field windings are connected in series and are short-circuited with a diode.
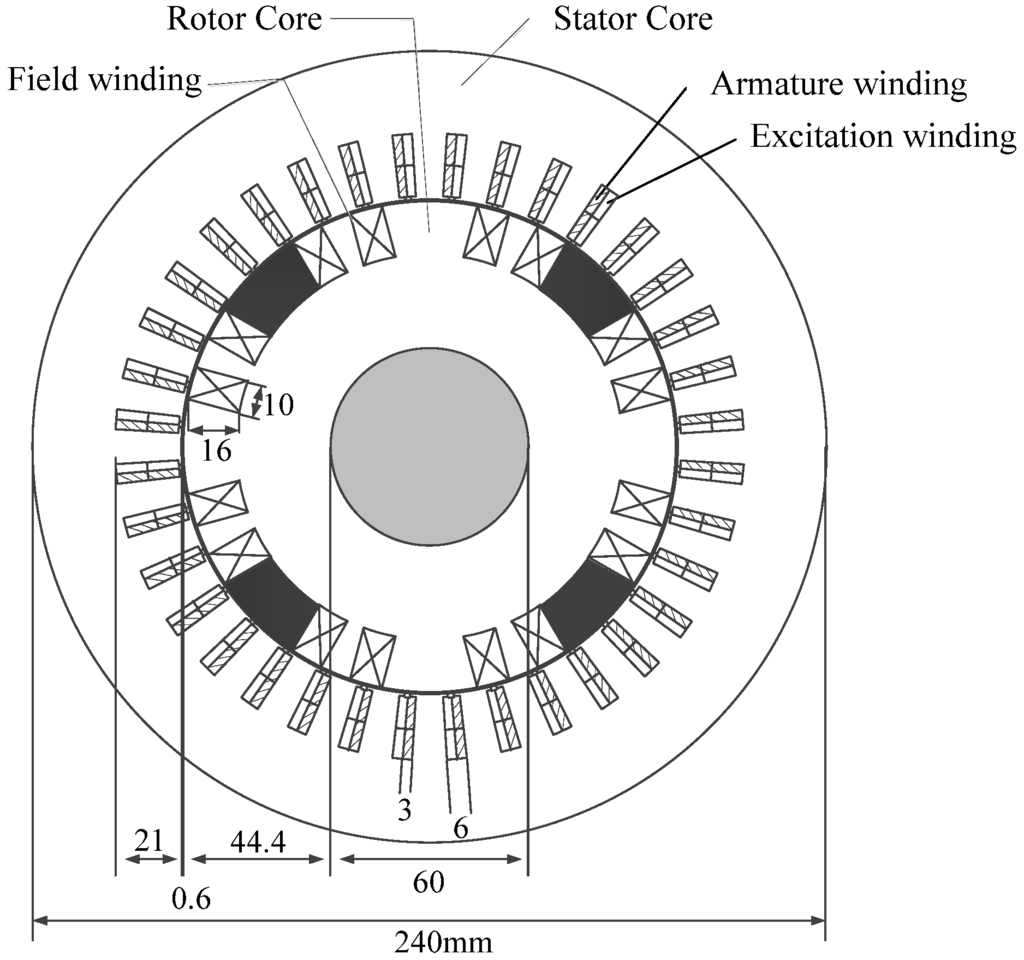
Figure 4.
Generator model.
Figure 4.
Generator model.
3.1. Under DC Excitation
At first, the electro-motive force or voltage induced in the stator armature windings is calculated when a direct current (DC) is externally supplied for the rotor field windings, as shown in Figure 5. It is equivalent to a typical wound-field synchronous generator. The direct current is 0.82 A, and the total resistance of the excitation windings is 3.24 Ω.
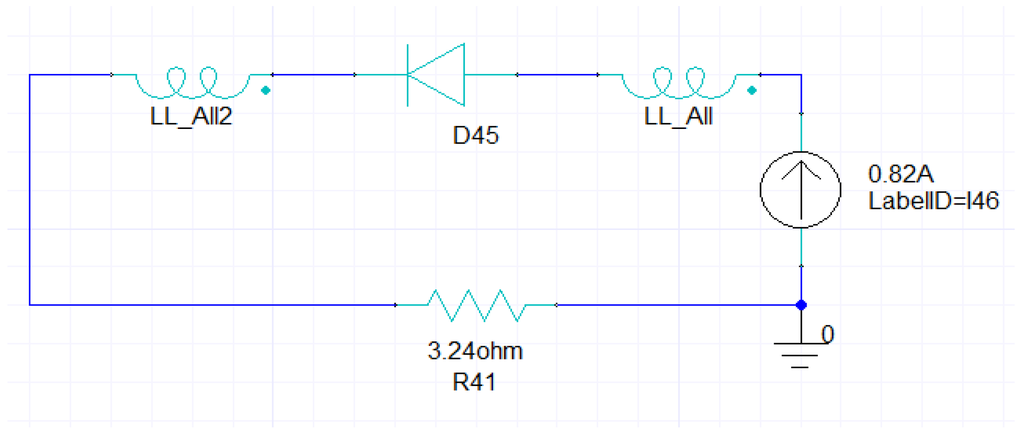
Figure 5.
External circuit for rotor field windings under DC excitation.
Figure 5.
External circuit for rotor field windings under DC excitation.
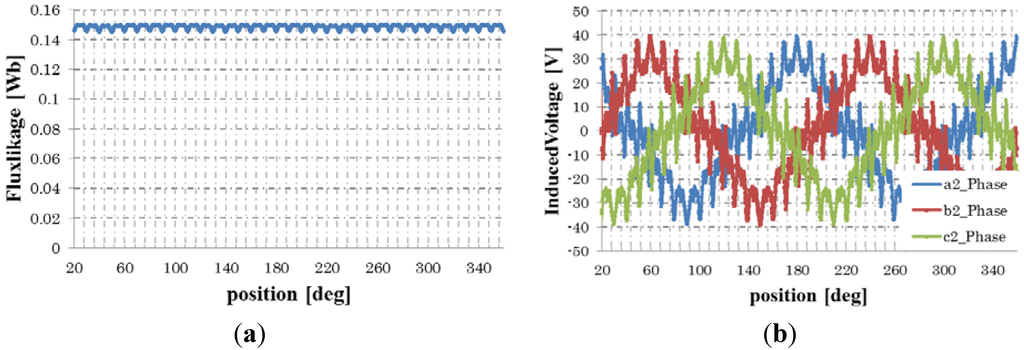
Figure 6.
Flux linkage and induced voltage under DC current excitation. (a) Flux linkage; (b) induced voltage.
Figure 6.
Flux linkage and induced voltage under DC current excitation. (a) Flux linkage; (b) induced voltage.
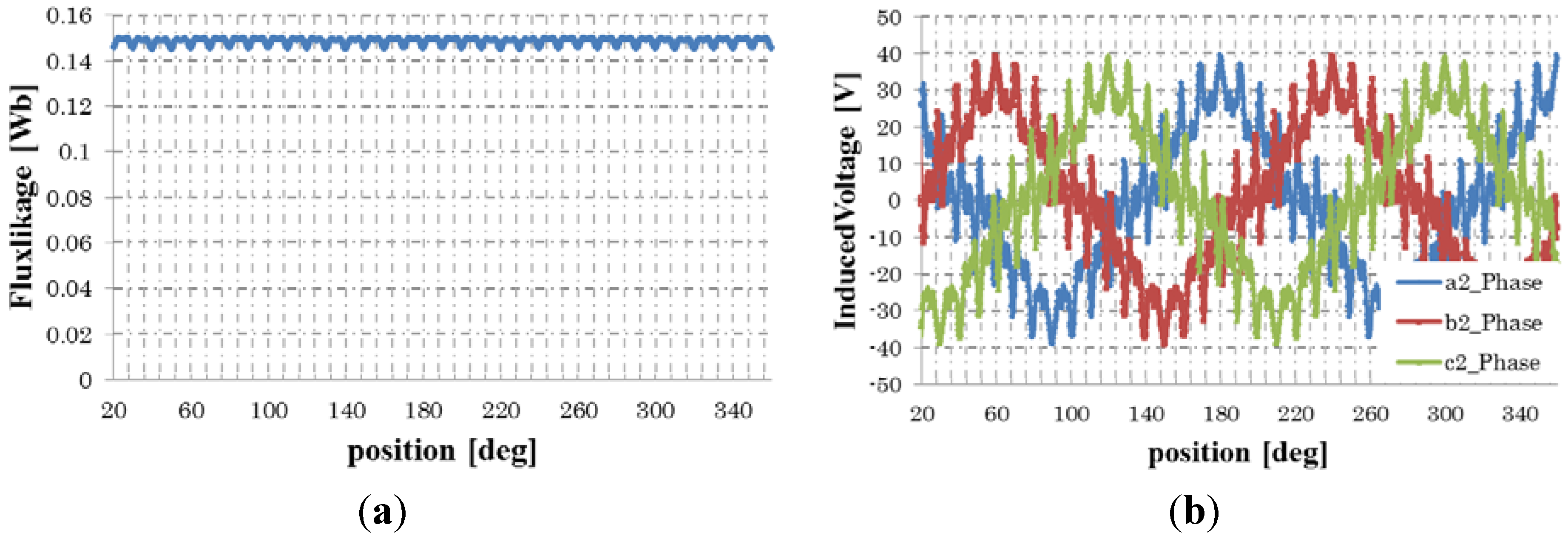
The flux linkage of the rotor field winding and the voltage induced in the stator armature winding at 1500 rpm is shown in Figure 6. They pulsate every 10 degrees of the rotor positions. The pulsation is attributed to an angular variation in the stator magnetic reluctance at the slots. Figure 7 shows the phase-a induced voltage for applying 10 degree skewing to the rotor field cores as shown in Figure 8. It is shown that the ripple on the induced voltage is reduced well.
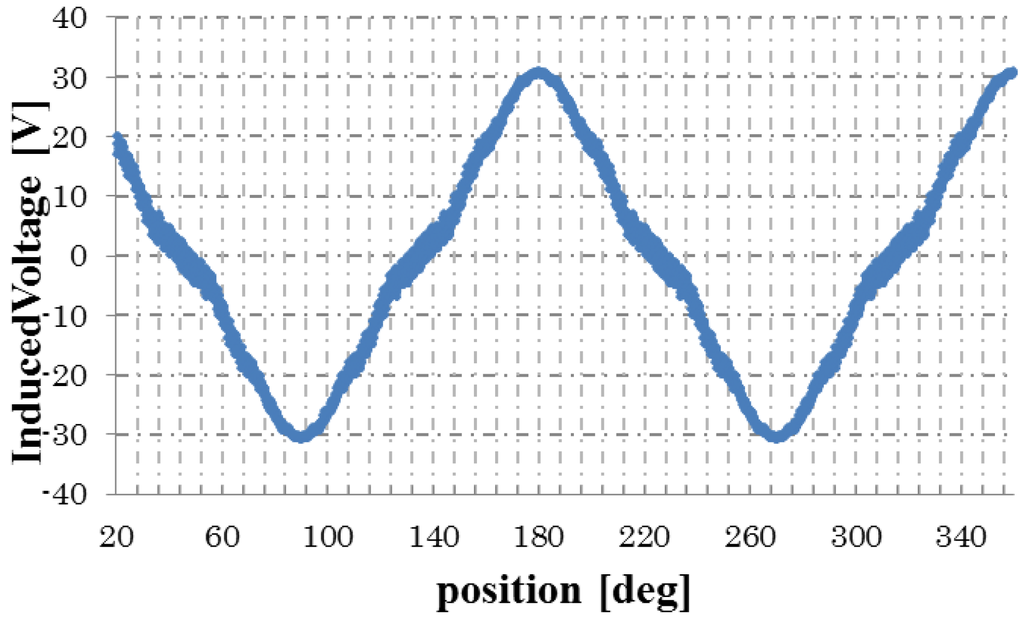
Figure 7.
Induced voltage of a skewed rotor (Phase-a).
Figure 7.
Induced voltage of a skewed rotor (Phase-a).
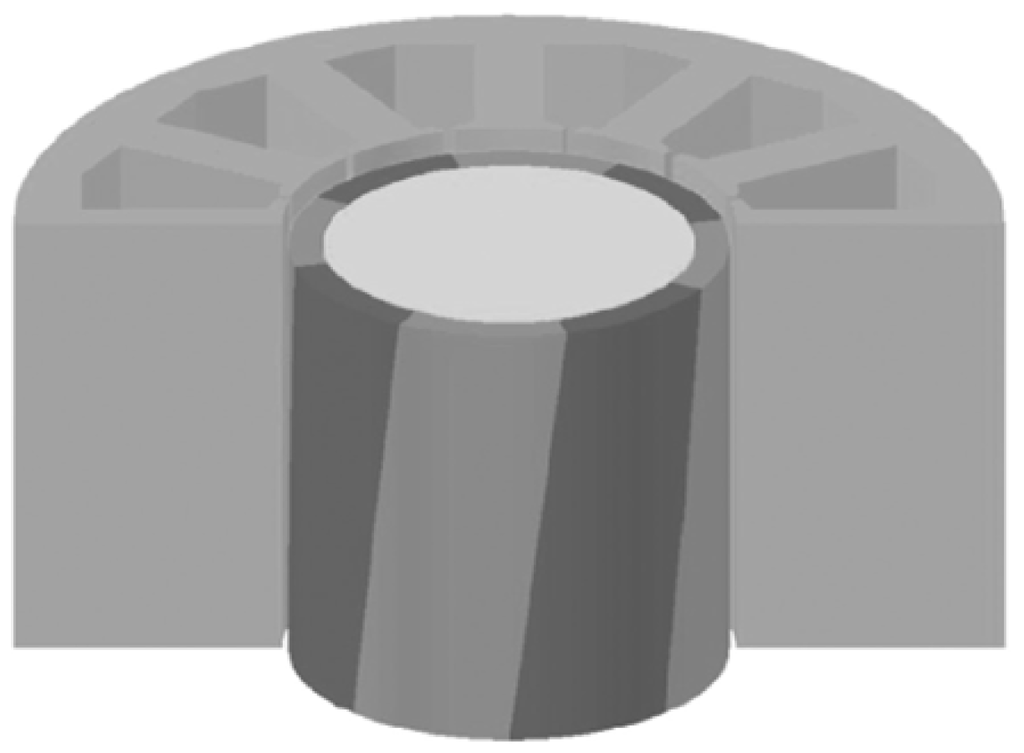
Figure 8.
Rotor skew.
Figure 8.
Rotor skew.
3.2. Under Half-Wave Rectified Excitation
3.2.1. No-Load Condition
Next, the voltage induced in the stator armature windings is calculated in no-load condition and at the rated speed of 1800 rpm, when the field current is produced by the half-wave rectified excitation.
Figure 9a shows the flux linkage of the rotor field winding when the three-phase excitation currents of Equation (3) are supplied to the stator excitation windings. The amplitude Af(t) is controlled to a triangular wave with an effective value of 1.1 A and a frequency of 250 Hz. The induced voltage of Phase-a is shown in Figure 9b. It is shown that the flux linkage is almost constant, but the induced voltage includes many harmonics. Figure 9c shows the induced voltage for the 10-degree skewed rotor. The small pulsations or harmonic components are reduced; however, high-level pulses are not reduced. The high-level pulses are generated at every turn-on time of the diode connected with the rotor field windings, and they are not able to be reduced by the rotor skew.
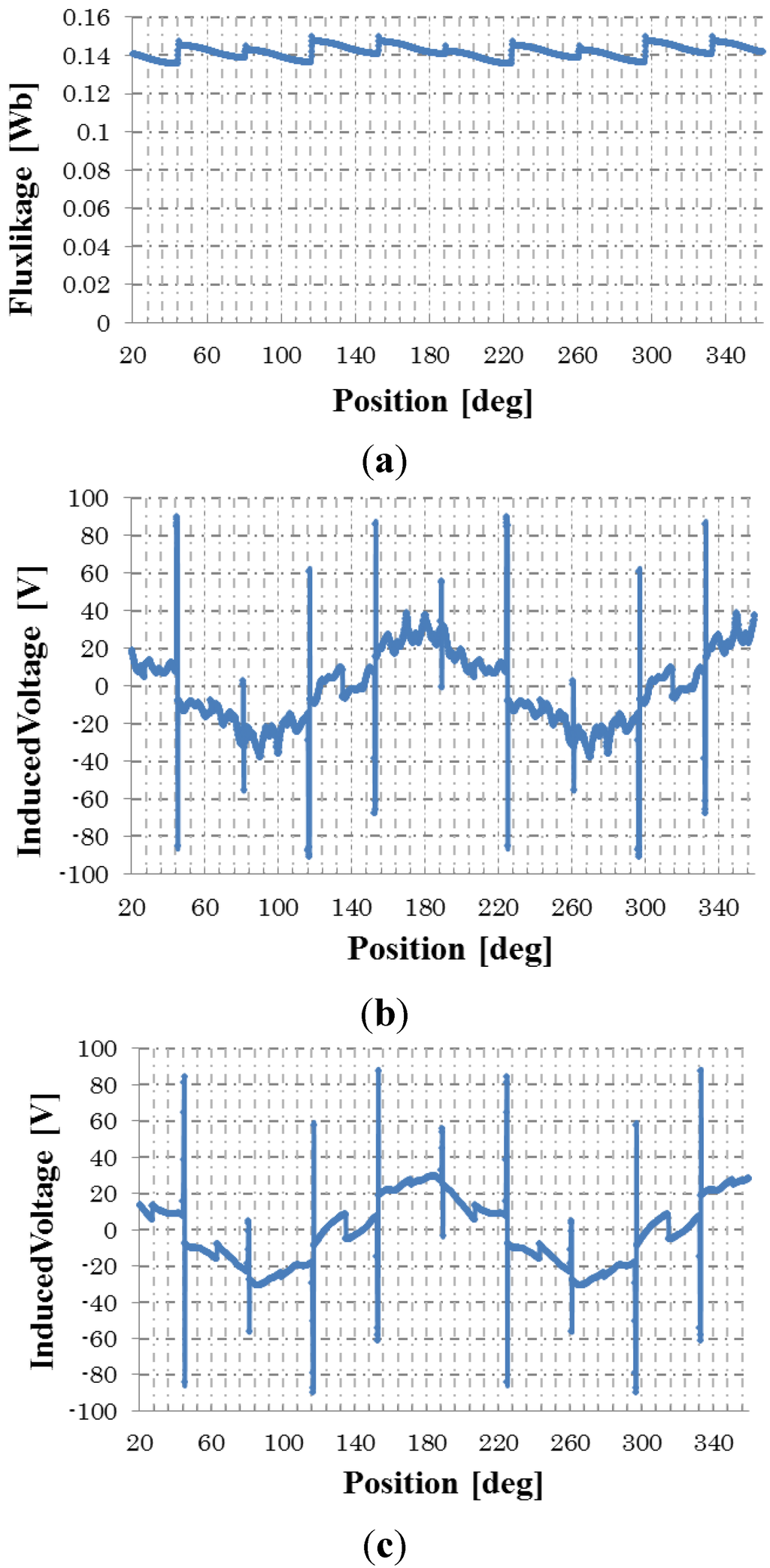
Figure 9.
No-load induced voltage under half-wave rectified excitation with triangular wave modulation. (a) Flux linkage; (b) induced voltage; (c) induced voltage for skewed rotor.
Figure 9.
No-load induced voltage under half-wave rectified excitation with triangular wave modulation. (a) Flux linkage; (b) induced voltage; (c) induced voltage for skewed rotor.
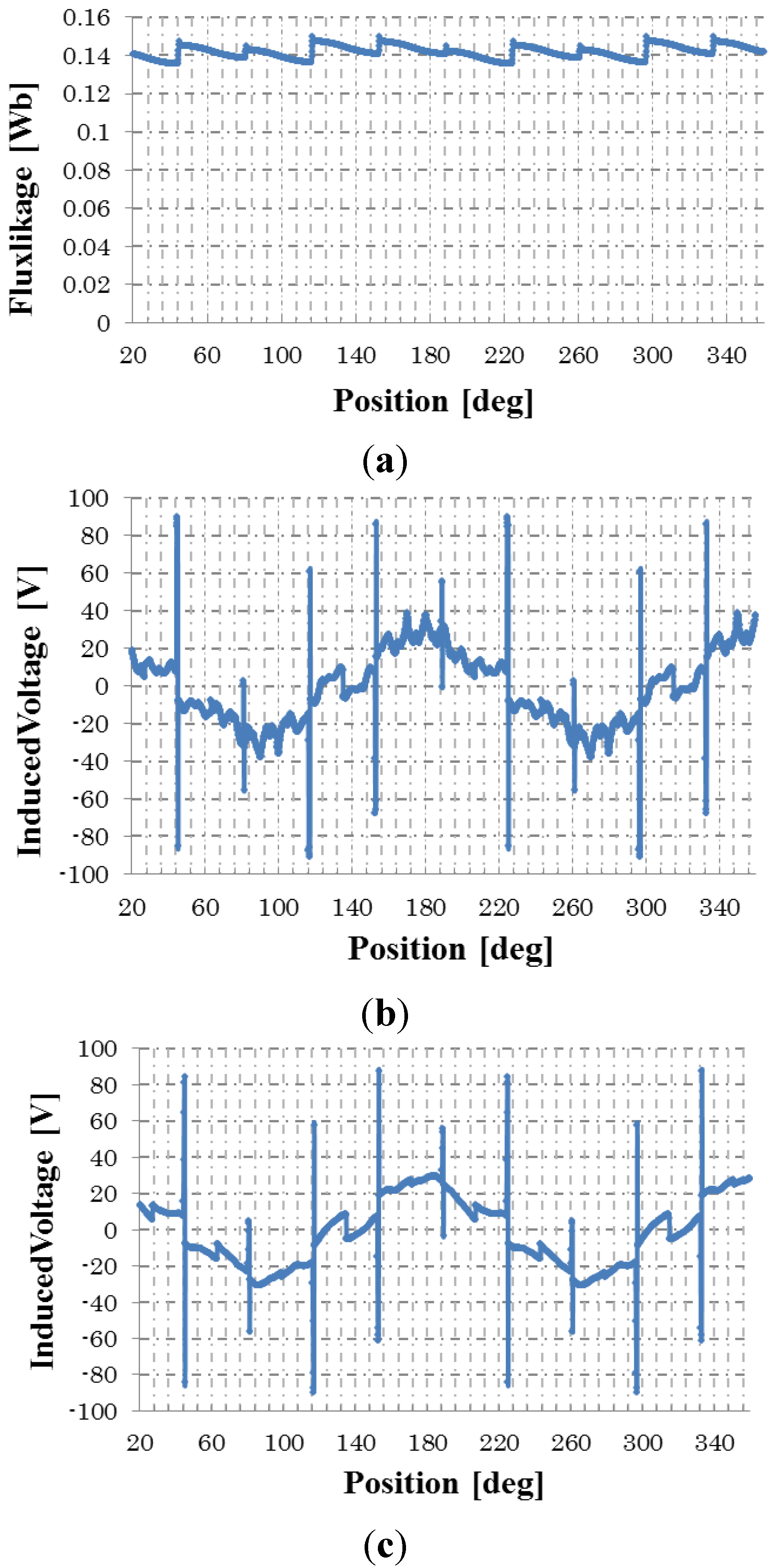
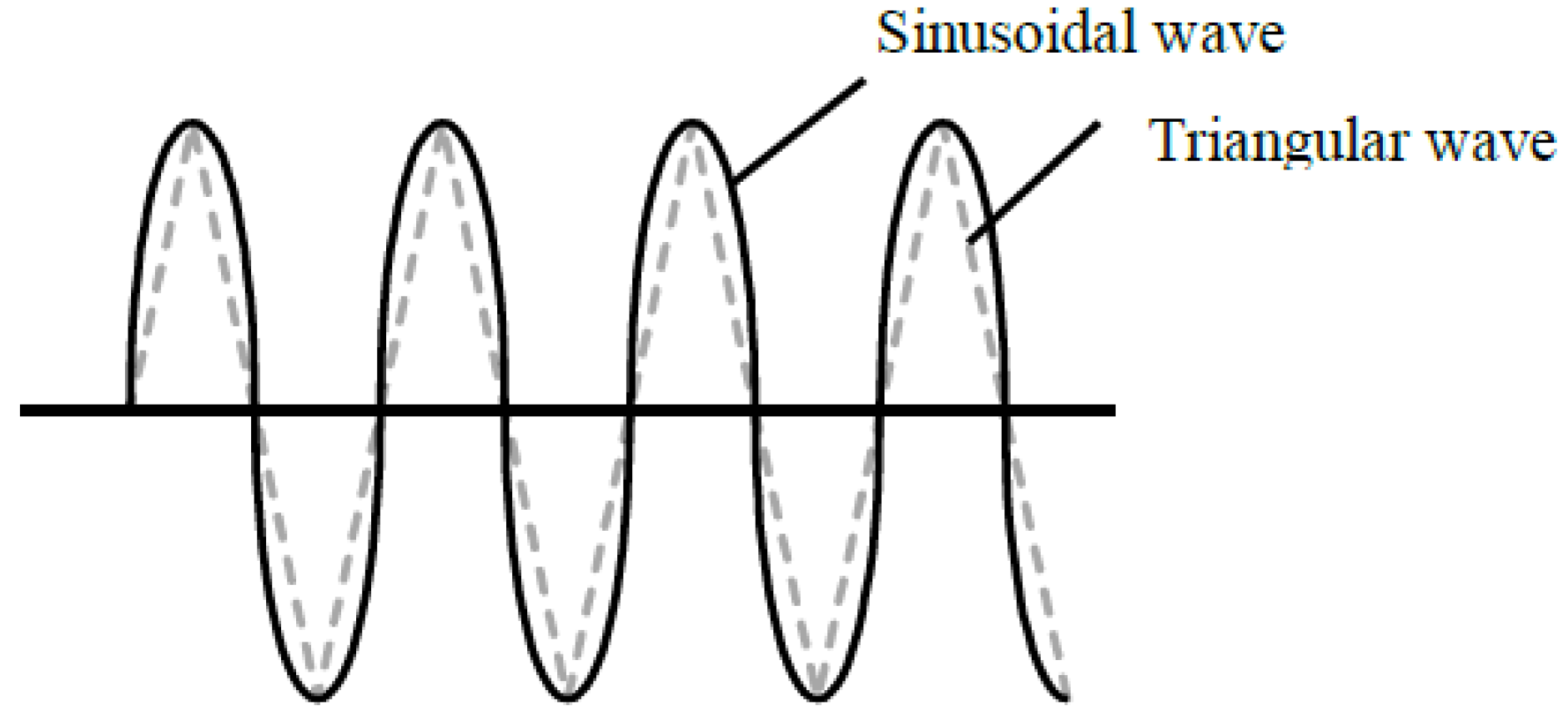
The high-level pulses are reduced by adjusting the waveform of the modulation function Af(t) of Equation (3). Figure 10a shows the flux linkage when Af(t) is a sinusoidal wave whose peak value and bias frequency are the same as the triangular wave, shown in Figure 11. Figure 10b,c shows the induced voltages for without and with the rotor skew, respectively. In both induced voltages, the harmonic components exist. However, the high-level pulses generated by the switching of the diode are reduced in comparison with that of the triangular wave in Figure 9b,c.
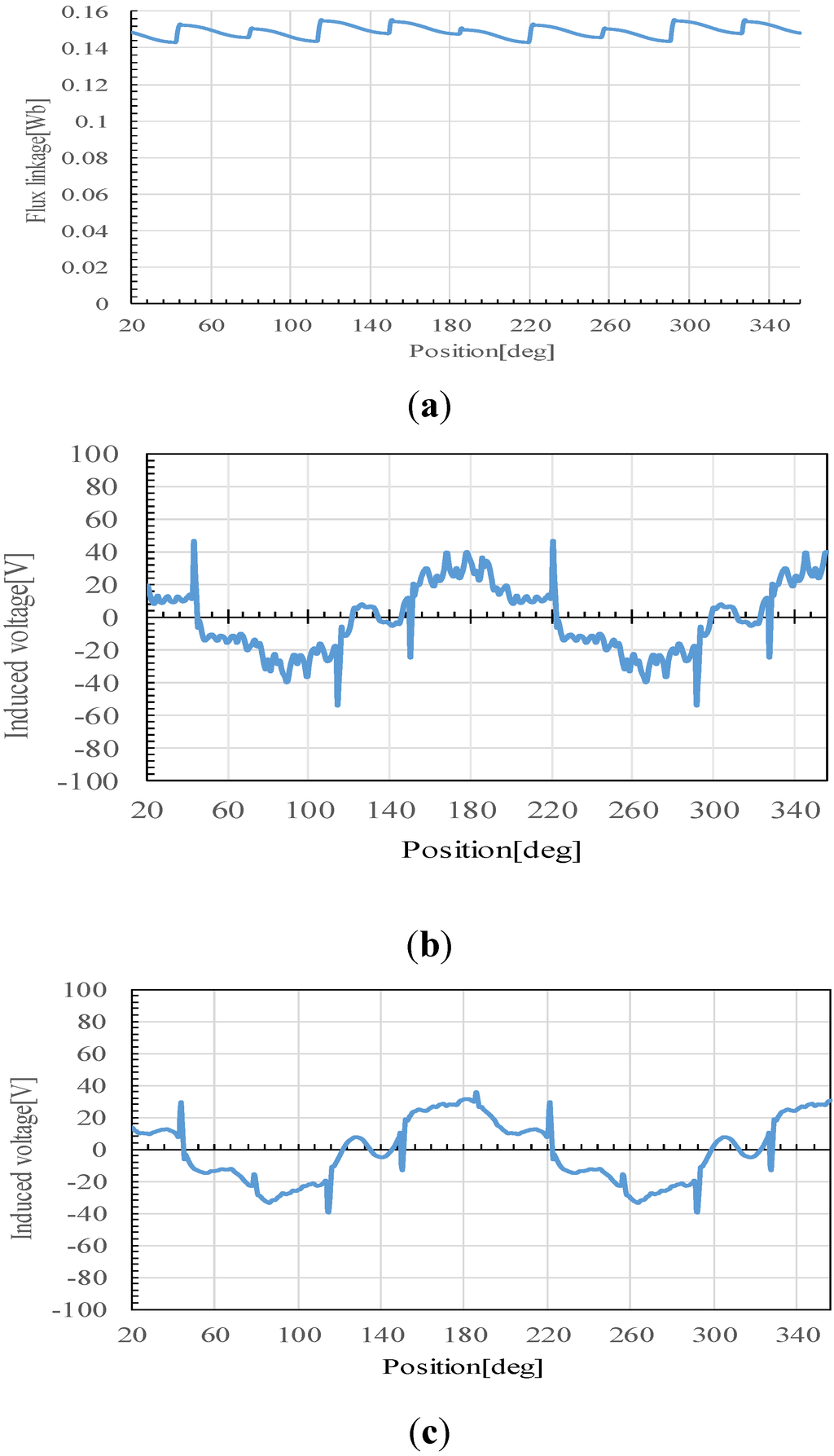
Figure 10.
No-load induced voltage under half-wave rectified excitation with sinusoidal wave modulation. (a) Flux linkage; (b) induced voltage; (c) induced voltage for skewed rotor.
Figure 10.
No-load induced voltage under half-wave rectified excitation with sinusoidal wave modulation. (a) Flux linkage; (b) induced voltage; (c) induced voltage for skewed rotor.
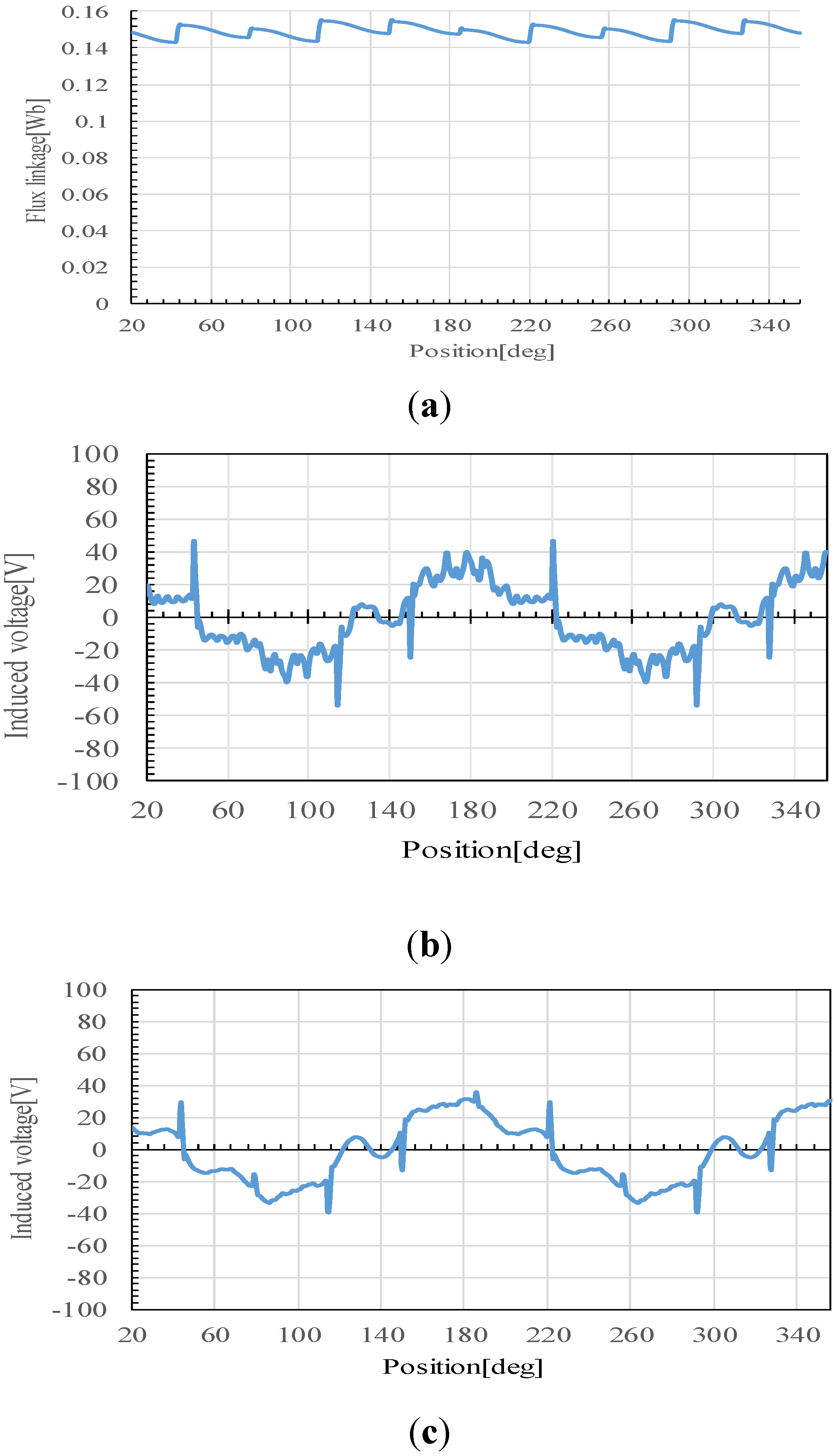
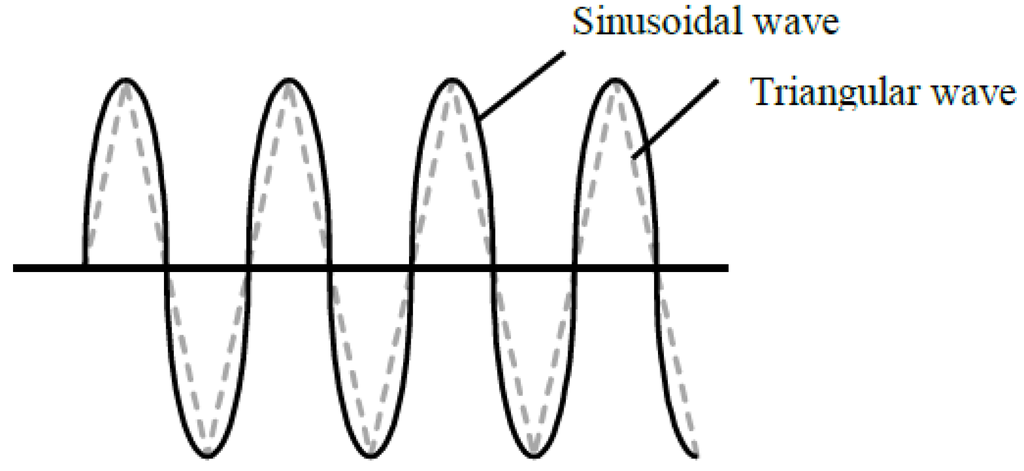
Figure 11.
Modulation function.
Figure 11.
Modulation function.
3.2.2. Load Condition
Output characteristics of the generator are simulated using the circuit model of Figure 12.
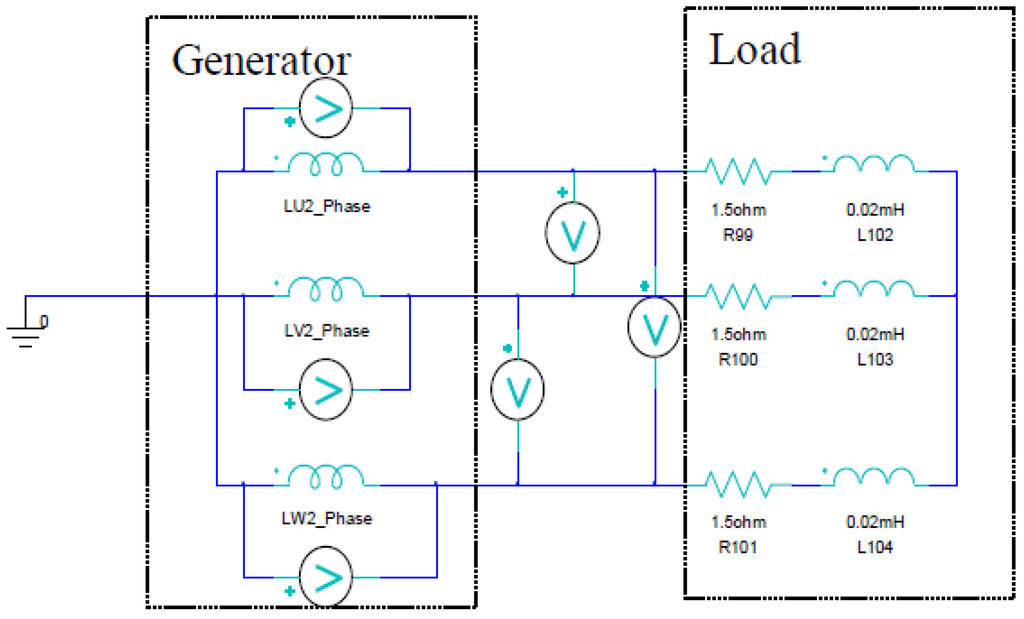
Figure 12.
Circuit model.
Figure 12.
Circuit model.
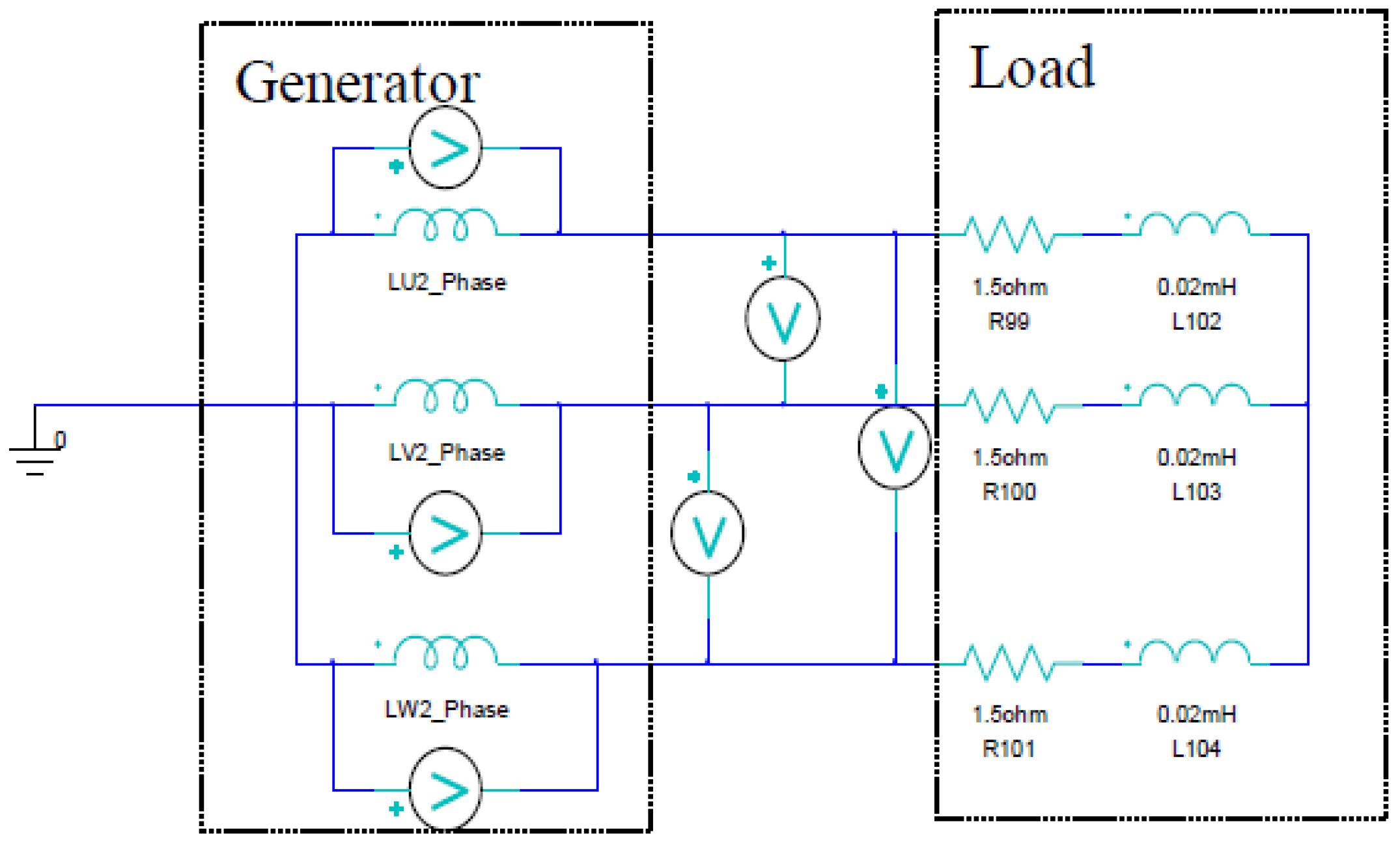
Resistance and inductance loads are connected to the armature windings. FEM analysis is carried out with varying the load resistance. As the modulation function Af(t) of Equation (3), two functions are selected. One is the triangular wave function with an effective value of 12.9 A and a frequency of 250 Hz. Another is the sinusoidal wave function with the same peak value and frequency as the triangular function.
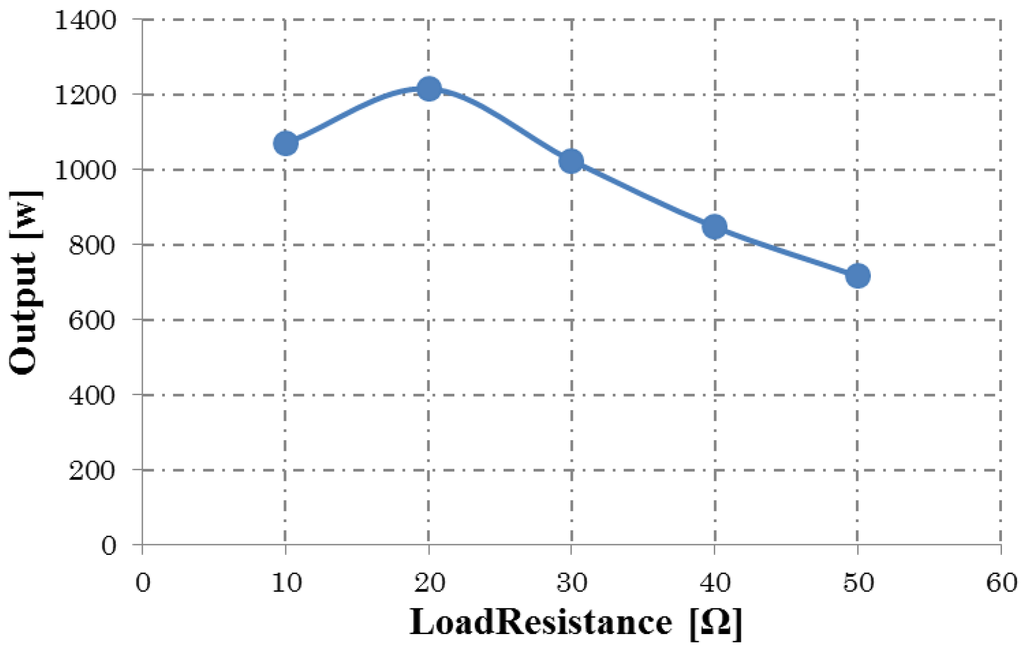
Figure 13.
Output characteristics (triangular wave modulation).
Figure 13.
Output characteristics (triangular wave modulation).
Figure 13 shows the output power characteristics for the triangular wave modulation when the load resistance R is varied. The rotational speed is 1800 rpm. The self-inductance L is constant at 0.01 mH. The flux linkage becomes very small at small R, because the stator armature windings prevent the time varying of the flux linkage of the rotor field winding. The output power is highest at about 20 Ω of R when the copper loss becomes equal to the iron loss.
Table 1 shows the induced voltage, output power and efficiency on the triangular wave modulation. Table 2 shows the characteristics on the sinusoidal wave modulation. The efficiency is calculated by using the following formula.
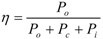 where Po is output active power at the load circuit of Figure 12, Pi is iron loss and Pc is the sum of copper loss of the excitation winding and the armature winding. Mechanical loss is ignored.
where Po is output active power at the load circuit of Figure 12, Pi is iron loss and Pc is the sum of copper loss of the excitation winding and the armature winding. Mechanical loss is ignored.
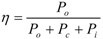

Table 1.
Output power and efficiency (triangular wave).
| Load Resistance (Ω) | Induced Voltage (Vrms) | Load Current (Arms) | Output Power (W) | Iron Loss (W) | Copper Loss (W) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 70.1 | 6.4 | 1069.9 | 77.8 | 126.4 | 86.6 |
| 20 | 103.0 | 4.9 | 1215.5 | 122.3 | 121.5 | 86.9 |
| 30 | 114.9 | 3.7 | 1024.2 | 125.3 | 119.2 | 84.9 |
| 40 | 120.3 | 2.9 | 847.2 | 132.7 | 119.1 | 82.1 |
| 50 | 123.4 | 2.4 | 715.7 | 137.3 | 120.3 | 79.1 |

Table 2.
Output power and efficiency (sinusoidal wave).
| Load Resistance (Ω) | Induced Voltage (Vrms) | Load Current (Arms) | Output Power (W) | Iron Loss (W) | Copper Loss (W) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 79.9 | 7.0 | 1348.8 | 87.4 | 168.3 | 86.4 |
| 20 | 111.7 | 5.3 | 1432.1 | 127.8 | 164.6 | 86.2 |
| 30 | 121.7 | 3.9 | 1149.3 | 137.8 | 161.3 | 83.3 |
| 40 | 126.0 | 3.1 | 930.6 | 143.7 | 161.7 | 79.5 |
| 50 | 127.8 | 2.5 | 768.3 | 144.5 | 160.1 | 76.8 |
The maximum output power on the sinusoidal wave modulation is larger, and the efficiency is slightly smaller than the triangular wave modulation. This depends on choosing the same peak values of the two modulation functions.
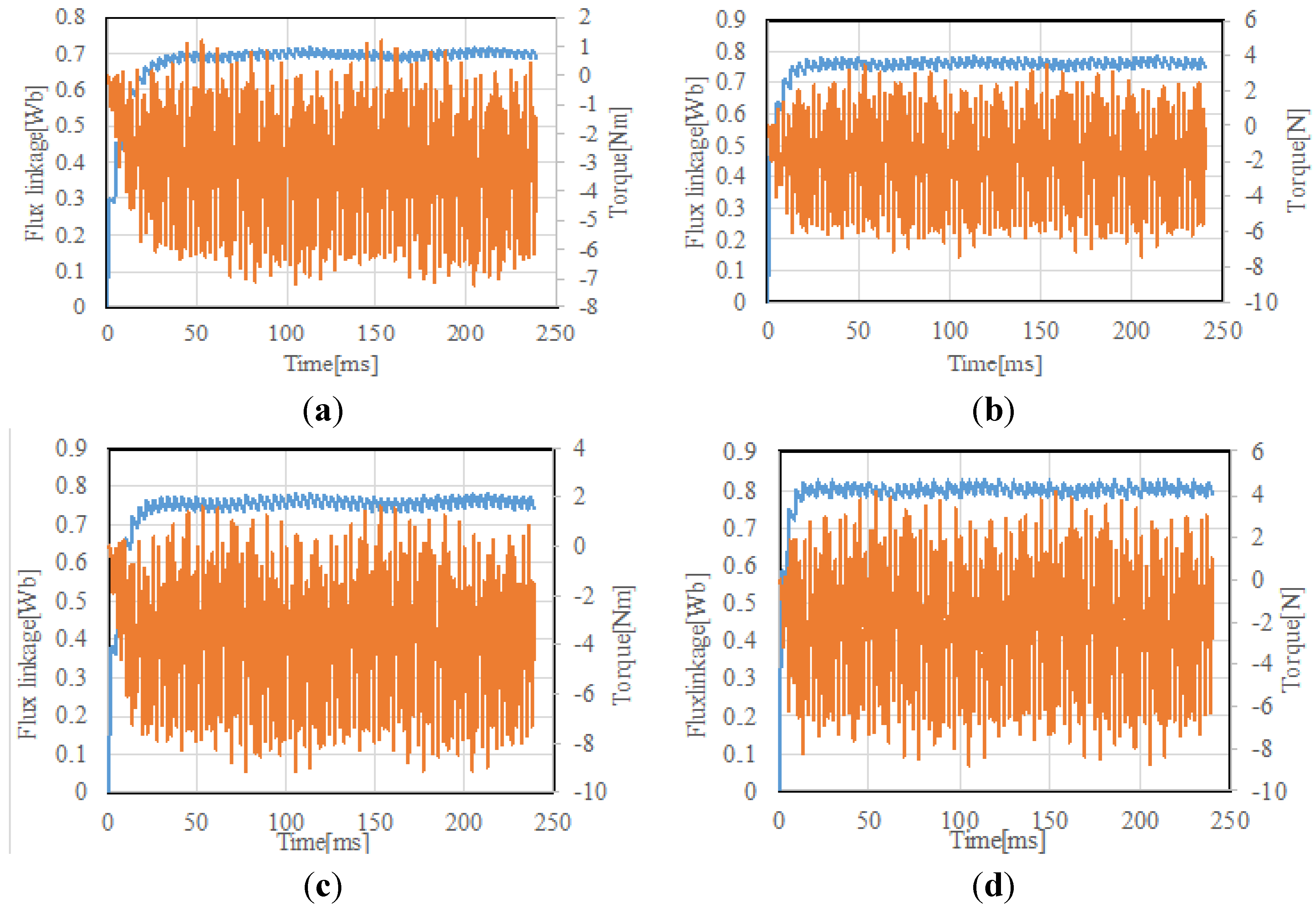
Figure 14 shows the time-flux linkage and time-torque characteristics for different modulation function and load resistance R. The rotational speed is 1800 rpm. Figure 15 shows the simulation results at 600 rpm. It is shown that the time-invariant flux linkage is produced independently of the speed or modulation function. Though the torque is pulsating with time, the average value is constant.
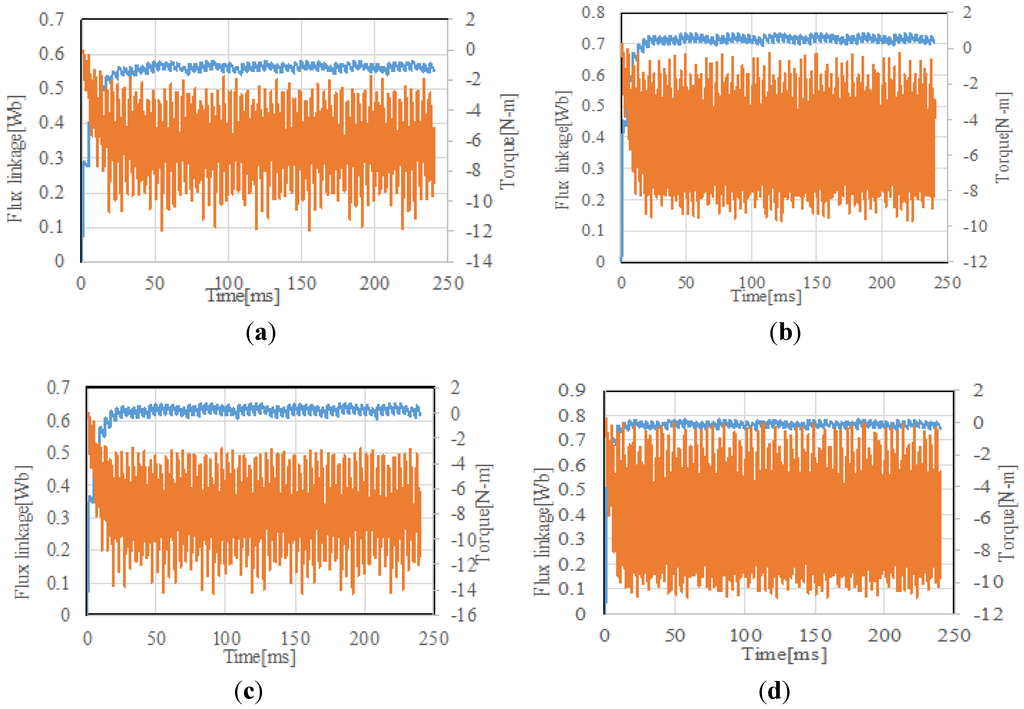
Figure 14.
Flux linkage and torque wave form at 1800 rpm. (a) Triangular wave modulation (R = 20 Ω); (b) triangular wave modulation (R = 40 Ω); (c) sinusoidal wave modulation (R = 20 Ω); (d) sinusoidal wave modulation (R = 40 Ω).
Figure 14.
Flux linkage and torque wave form at 1800 rpm. (a) Triangular wave modulation (R = 20 Ω); (b) triangular wave modulation (R = 40 Ω); (c) sinusoidal wave modulation (R = 20 Ω); (d) sinusoidal wave modulation (R = 40 Ω).
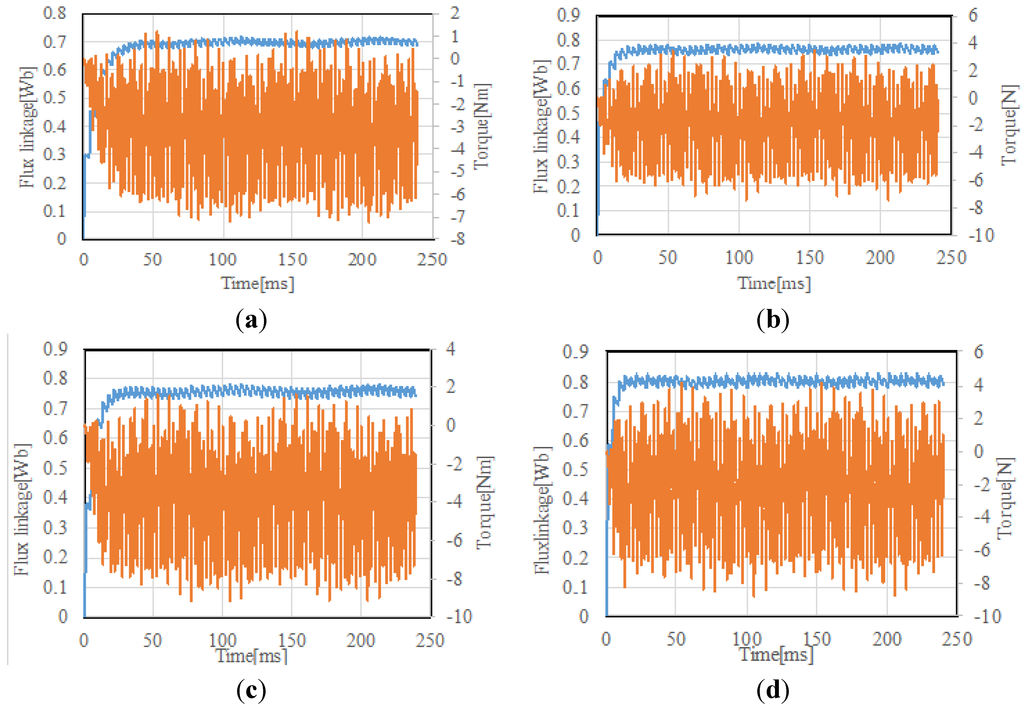
Figure 15.
Flux linkage and torque wave form at 600 rpm. (a) Triangular wave modulation (R = 20 Ω); (b) triangular wave modulation (R = 40 Ω); (c) sinusoidal wave modulation (R = 20 Ω); (d) sinusoidal wave modulation (R = 40 Ω).
Figure 15.
Flux linkage and torque wave form at 600 rpm. (a) Triangular wave modulation (R = 20 Ω); (b) triangular wave modulation (R = 40 Ω); (c) sinusoidal wave modulation (R = 20 Ω); (d) sinusoidal wave modulation (R = 40 Ω).
4. Design Analysis for Improving Performance
4.1. Rotor Diameter
Design analysis is carried out for achieving higher output power and efficiency on the condition that the stator outer diameter is constant. Here, three designs are investigated. Design 1, shown in Figure 16, is the basic model. The rotor radius is set at 74.4 mm. The rotor radius of Design 2 is decreased to 69.4 mm. The height of the stator slots is increased, so that the electric loading is increased to 1.17-times as large as Design 1. The rotor radius of Design 3 is decreased to 64.4 mm. The function Af(t) of Equation (3) is the triangular wave with the effective value of 12.9 A. The rotational speed is 1800 rpm. The resistance R of the load circuit is 20 Ω.
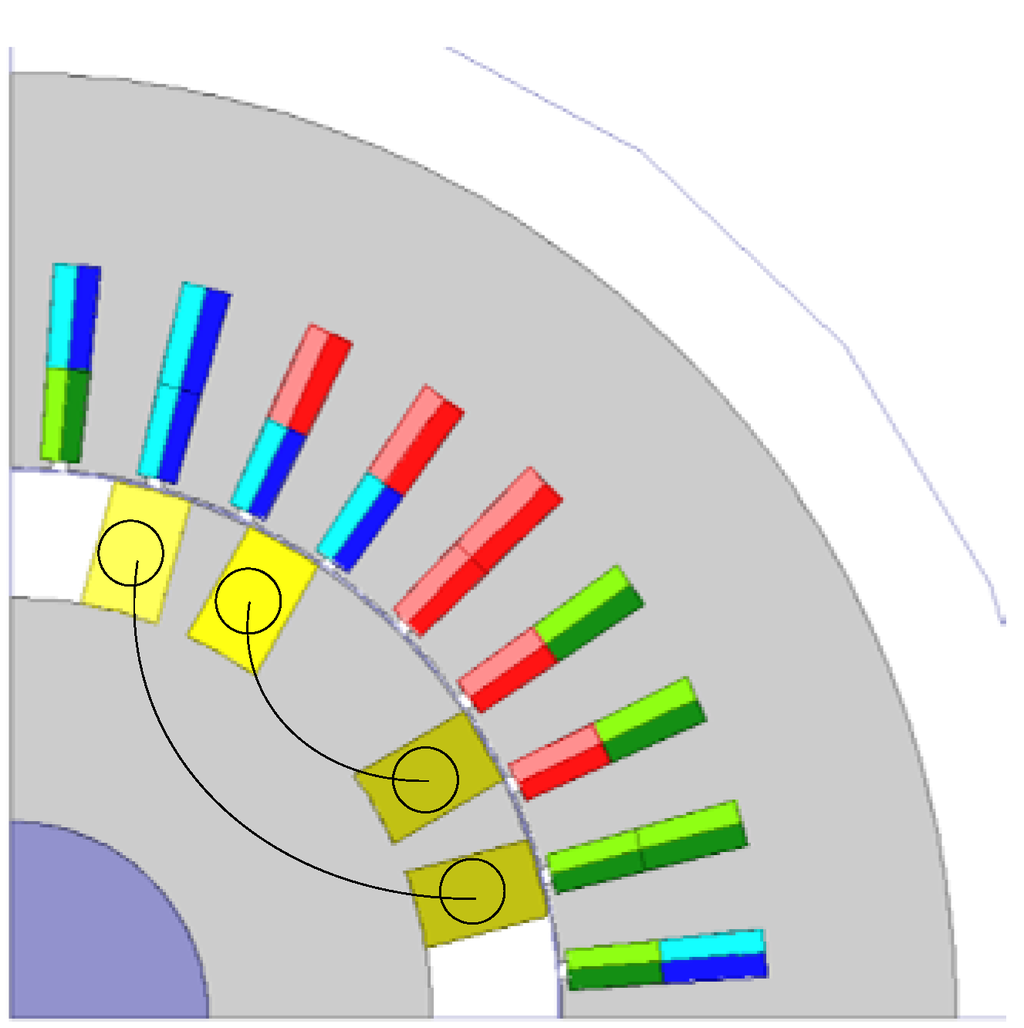
Figure 16.
Design 1 (rotor radius: 74.4 mm).
Figure 16.
Design 1 (rotor radius: 74.4 mm).
The induced voltage, output power and efficiency are listed in Table 3. The output power of Design 2 increases by 26%, and the efficiency increases by 0.6% compared with Design 1.

Table 3.
Output power and efficiency.
| Design Model (Rotor Radius (mm)) | Induced Voltage (V) | Output Power (W) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design 1 (74.4) | 103.01 | 1215 | 86.9 |
| Design 2 (69.4) | 116.01 | 1530 | 87.4 |
| Design 3 (64.4) | 115.14 | 1471 | 82.2 |
The output power of Design 3 increases by 21%, but the efficiency decreases by 5.4% compared with Design 1, because of the magnetic saturation of the rotor iron under the high electric loading.
4.2. Rotor Configuration
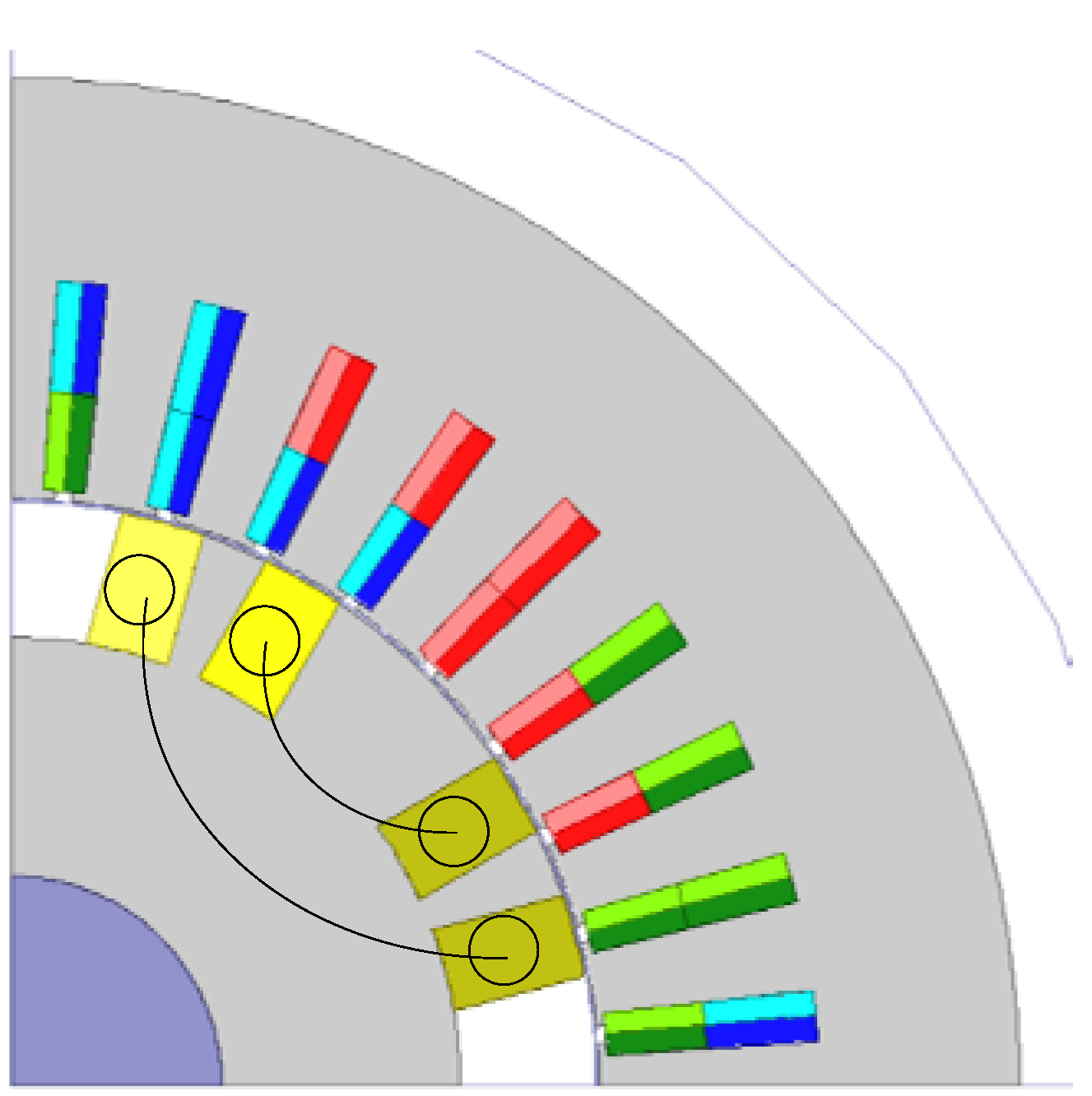
The rotor field windings of Designs 1–3 are distributed windings, the field flux distribution being sinusoidal. Figure 17 shows for Design 4 that the field windings are changed to concentrated windings. The total cross-sectional area of the winding and the iron core are equal to those of Design 1. Design 5 and Design 6 are designed in the same way as Design 4, for Design 2 and Design 3, respectively.
Table 4 shows the output characteristics of the designs. The output power of Design 4 increases by 25.3%, and the efficiency increases by 1.4% compared with Design 1. In this comparison, the same electric loadings for the excitation windings are assumed.
The output power of Design 5 increases by 70%, and the efficiency increases by 3.2% compared with Design 1. The output power of Design 6 increases by 77.4%, and the efficiency increases by 0.6% compared with Design 1.
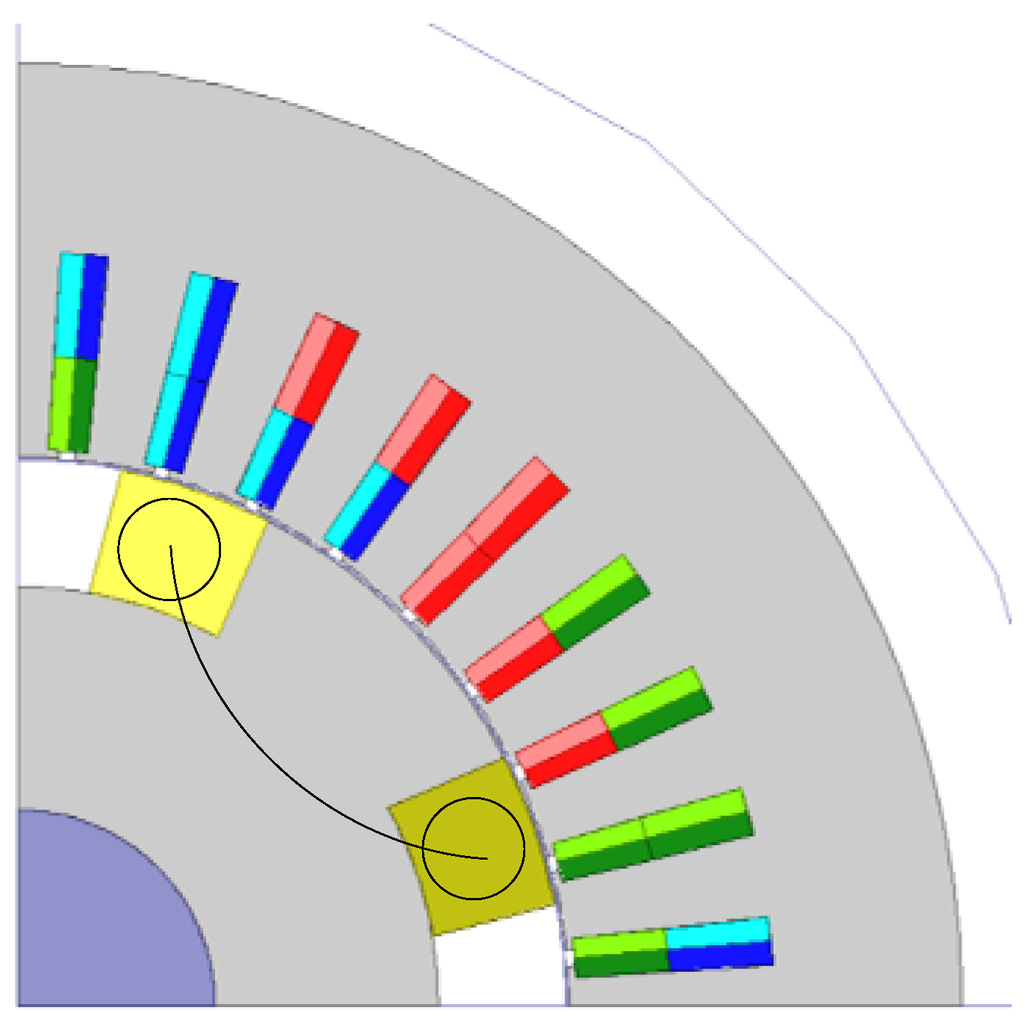
Figure 17.
Design 4 (rotor radius: 74.4 mm).
Figure 17.
Design 4 (rotor radius: 74.4 mm).
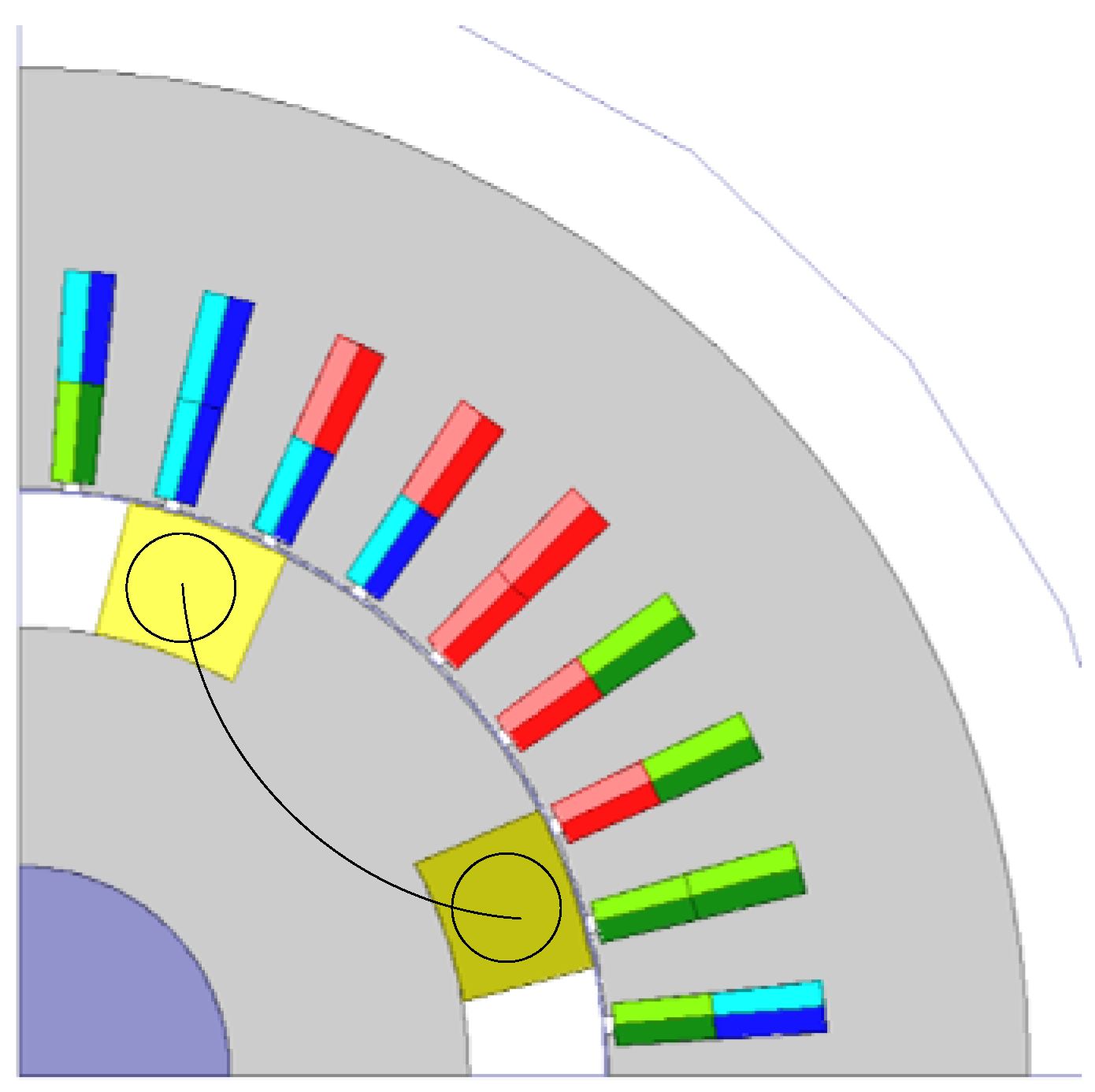

Table 4.
Output power and efficiency.
| Design Model (Rotor Radius (mm)) | Induced Voltage (V) | Output Power (W) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design 4 (74.4) | 115.10 | 1,523 | 88.1 |
| Design 5 (69.4) | 134.26 | 2,064 | 89.7 |
| Design 6 (64.4) | 138.17 | 2,156 | 87.4 |
Figure 18 shows the flux density distribution of Design 6. It is confirmed that magnetic saturation of the rotor iron is not serious. Figure 19 shows the induced voltage of Design 2 and Design 5. The harmonics are detected, but they will be decreased by the rotor skew. The high-level pulse detected in the no-load condition, for example, Figure 9b, is not so serious under the load condition.
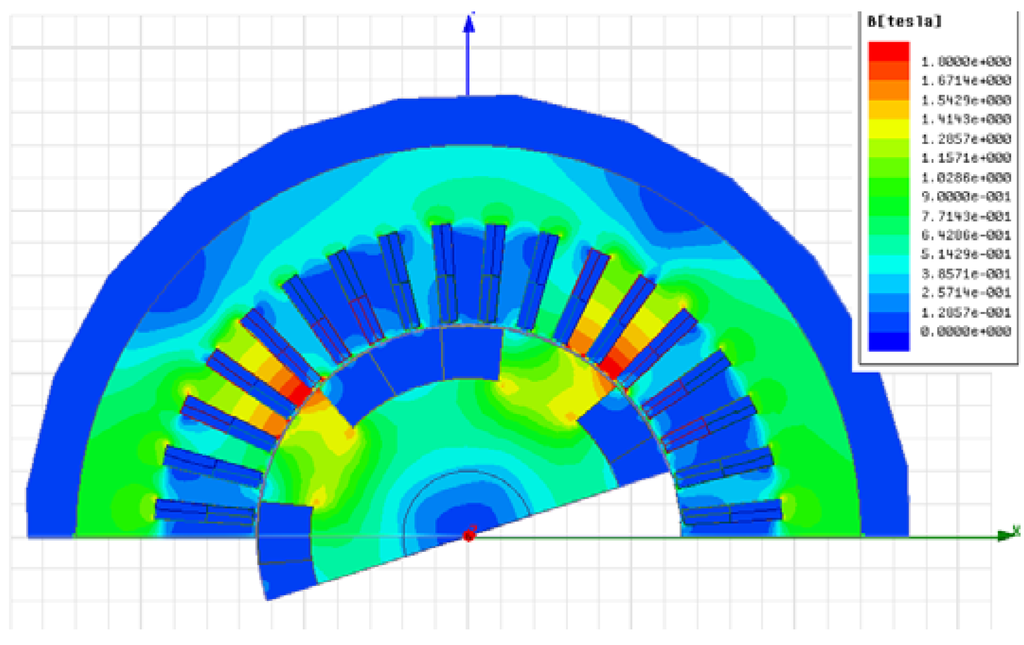
Figure 18.
Flux distribution of Design 6.
Figure 18.
Flux distribution of Design 6.
4.3. Air Gap Length
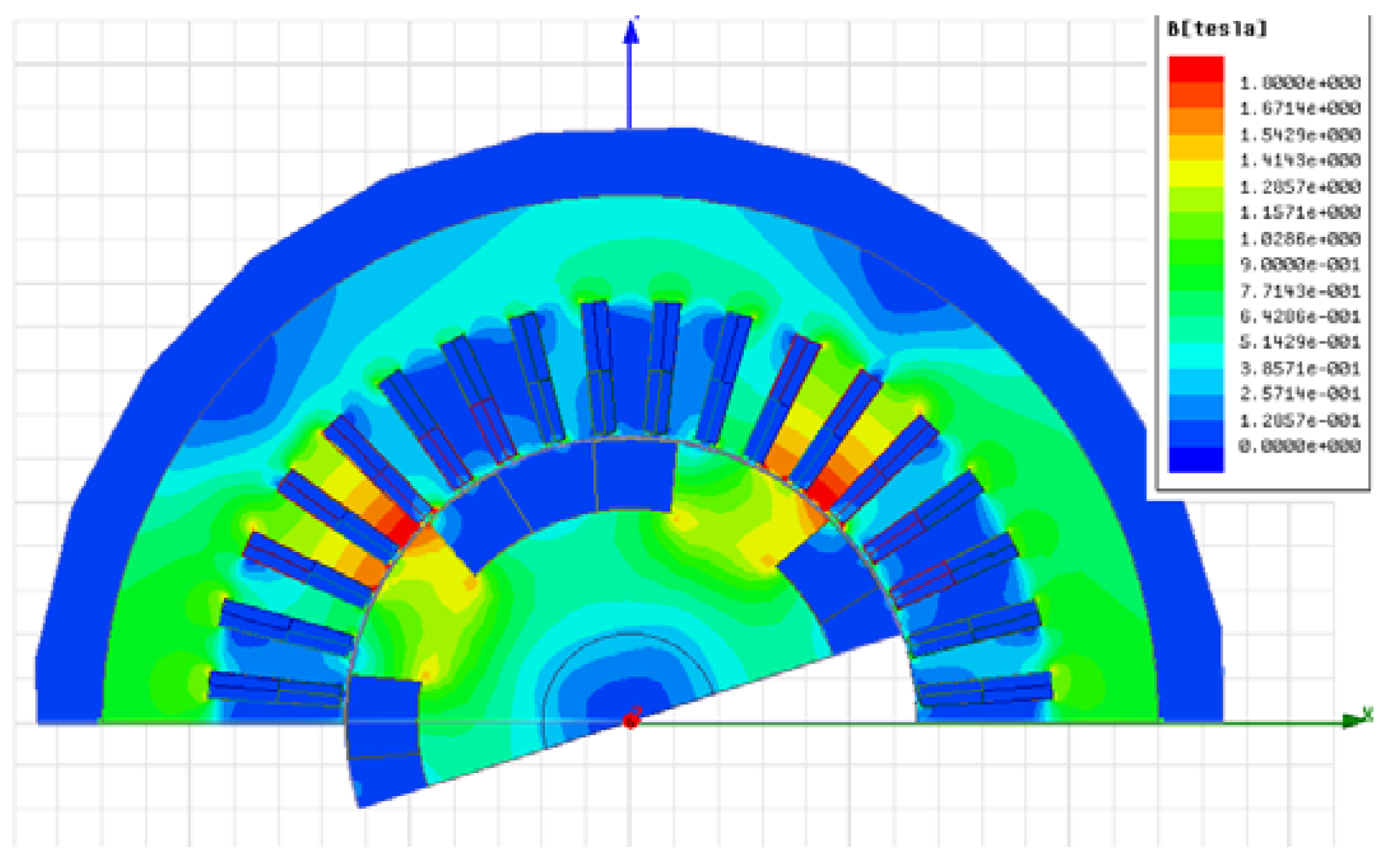
The rotor field current of the proposed generator is induced by the stator excitation current. Therefore, the air gap is an important parameter for the performance. The air gap length of Design 4 to Design 6 is 0.6 mm. They are redesigned as Design 7 to Design 9, respectively, with an air gap of 0.3 mm. Figure 20 shows the flux linkage and induced voltage of Design 4 and Design 7. It is shown that the flux linkage and induced voltage are increased by decreasing the air gap. Table 5 shows the output power and efficiency. It is shown that the output power of Design 9 is about 2.65 kW and the efficiency is about 92%.
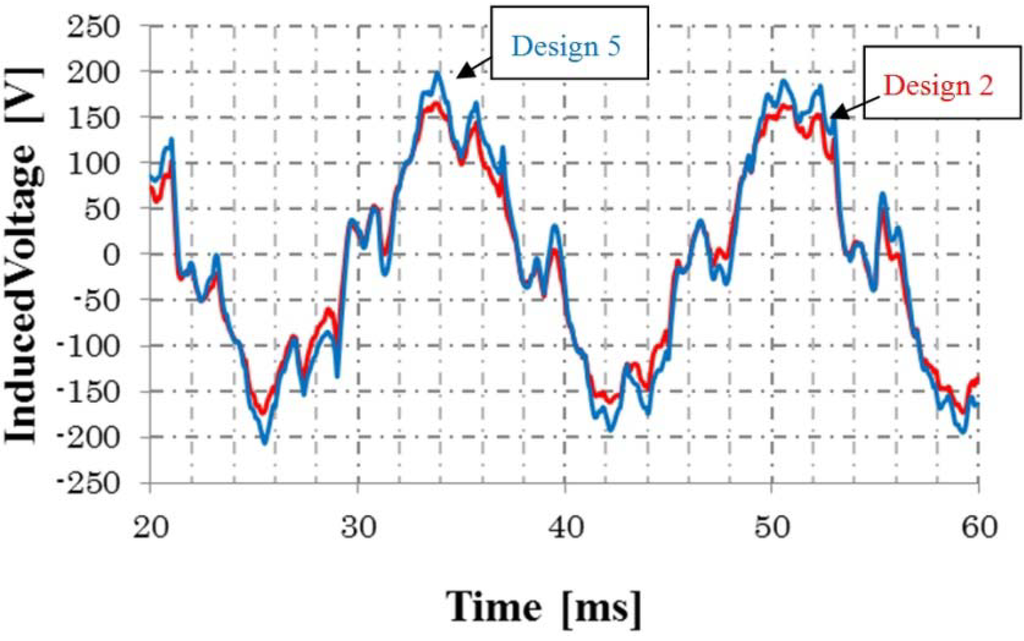
Figure 19.
Induced voltages of Design 2 and Design 5.
Figure 19.
Induced voltages of Design 2 and Design 5.
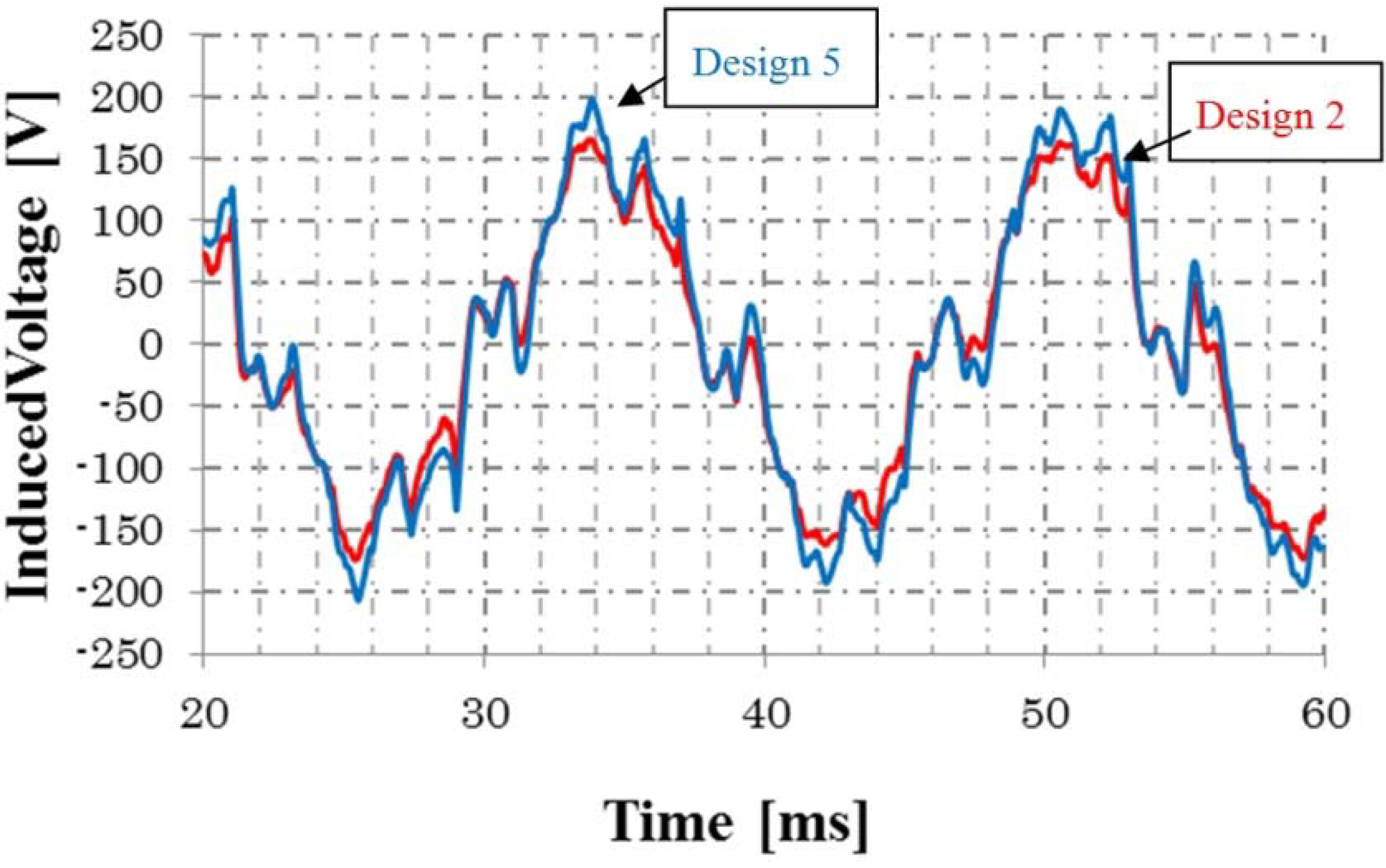
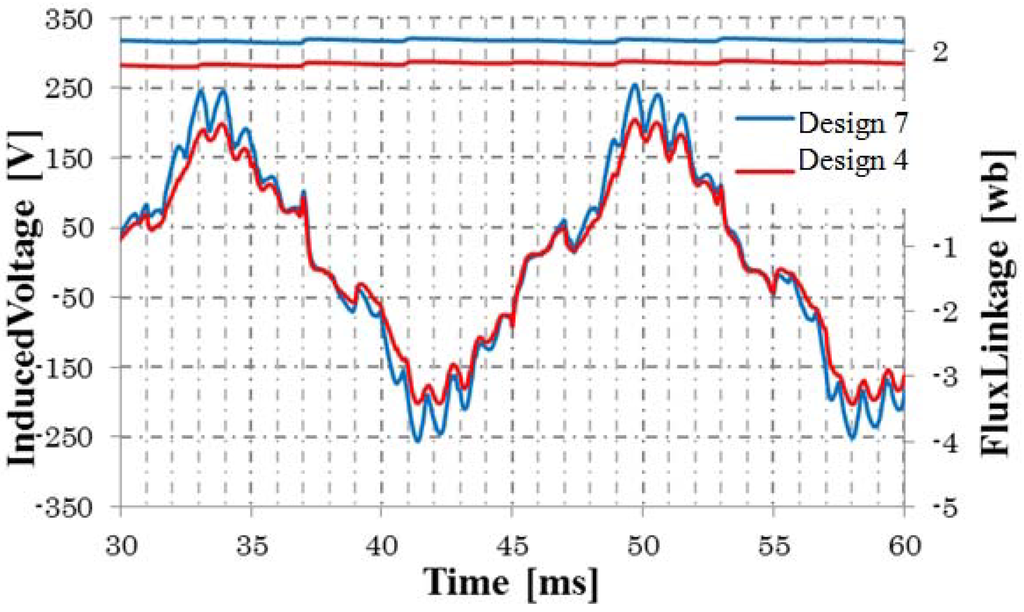
Figure 20.
Flux linkage and induced voltage of Design 1 and Design 4.
Figure 20.
Flux linkage and induced voltage of Design 1 and Design 4.
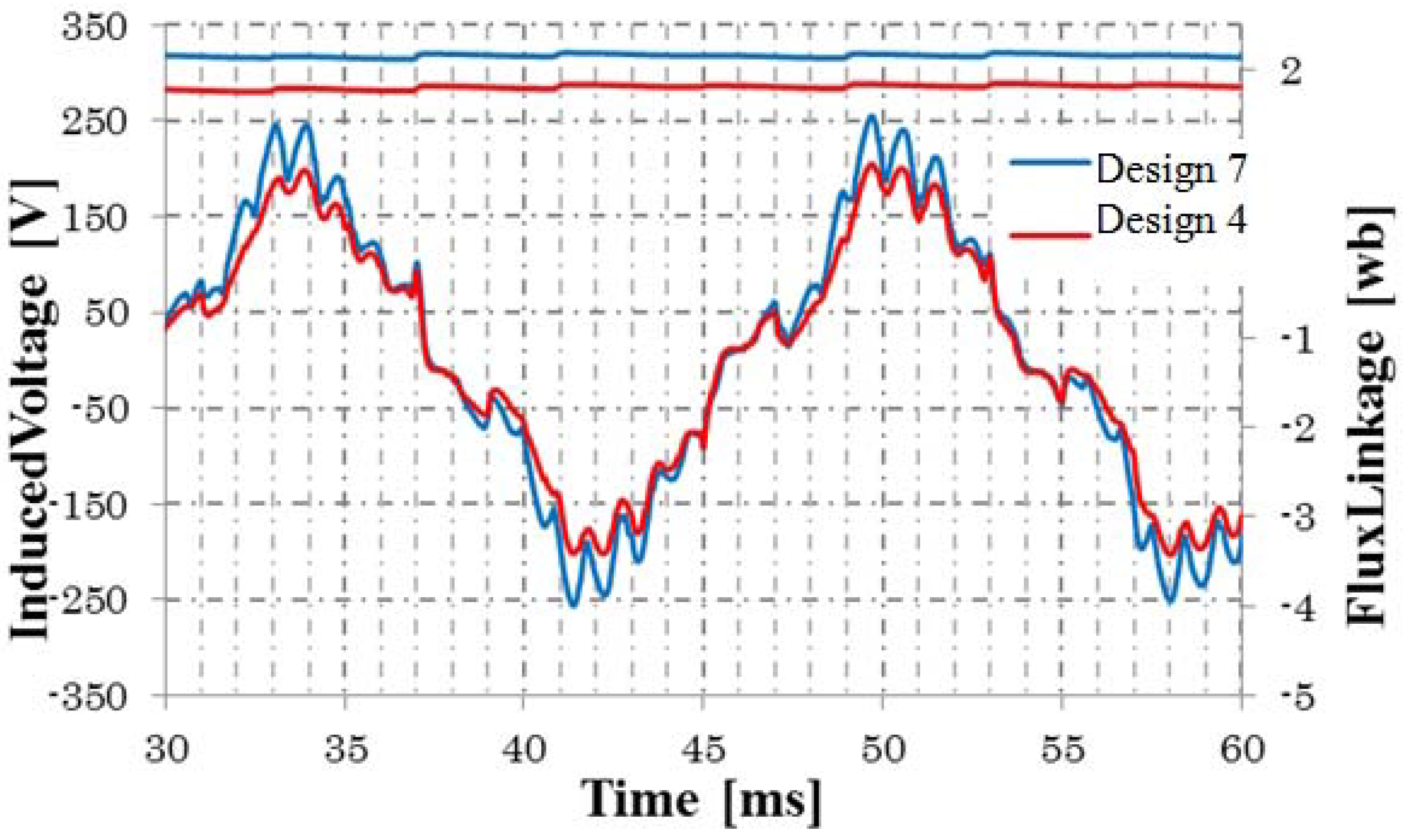

Table 5.
Output power and efficiency.
| Design model (Rotor Radius (mm)) | Induced Voltage (V) | Output Power (W) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design 7 (74.4) | 139.11 | 2285 | 90.7 |
| Design 8 (69.4) | 149.33 | 2640 | 91.7 |
| Design 9 (64.4) | 149.67 | 2646 | 91.9 |
5. Speed Characteristics
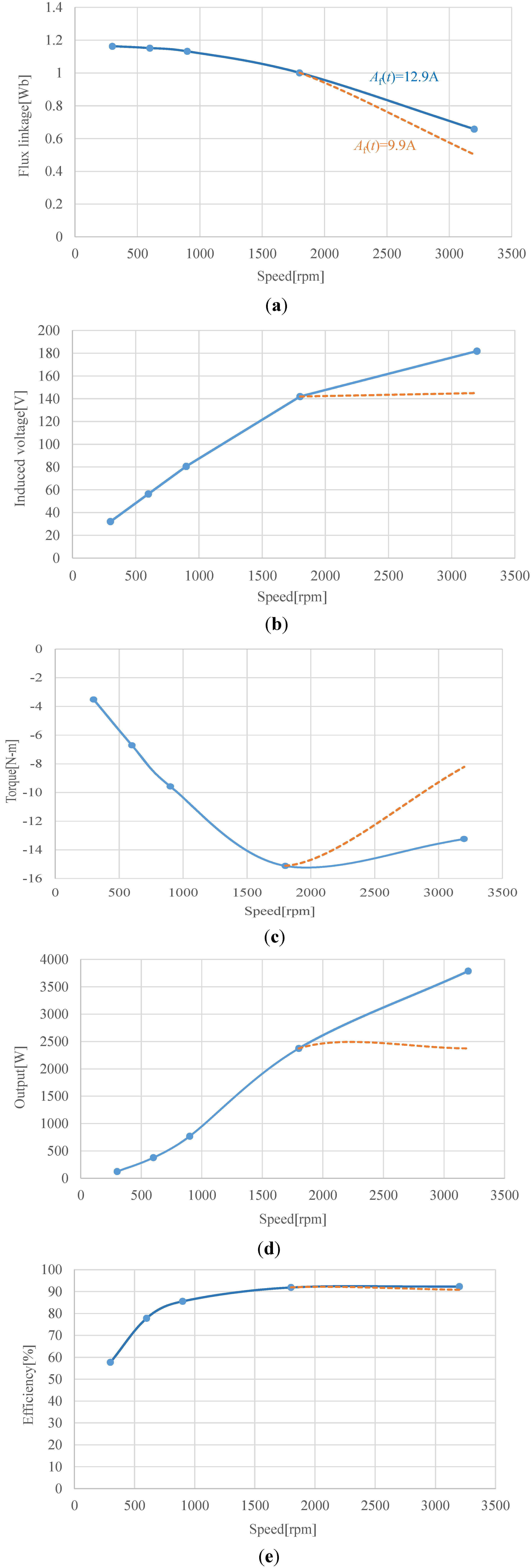
Figure 21 show the speed characteristic curves of Design 8. The modulation function Af(t) of Equation (3) is the triangular wave. A solid line shows the characteristics when the amplitude of Af(t) is kept constant at 12.9 A. The induced voltage and output power increases with increasing the rotational speed. A dotted line shows the characteristics when the amplitude of Af(t) is decreased to 9.9 A at 3200 rpm. The flux linkage is decreased to 0.5 Wb, and the induced voltage is controlled with 140 V constant.
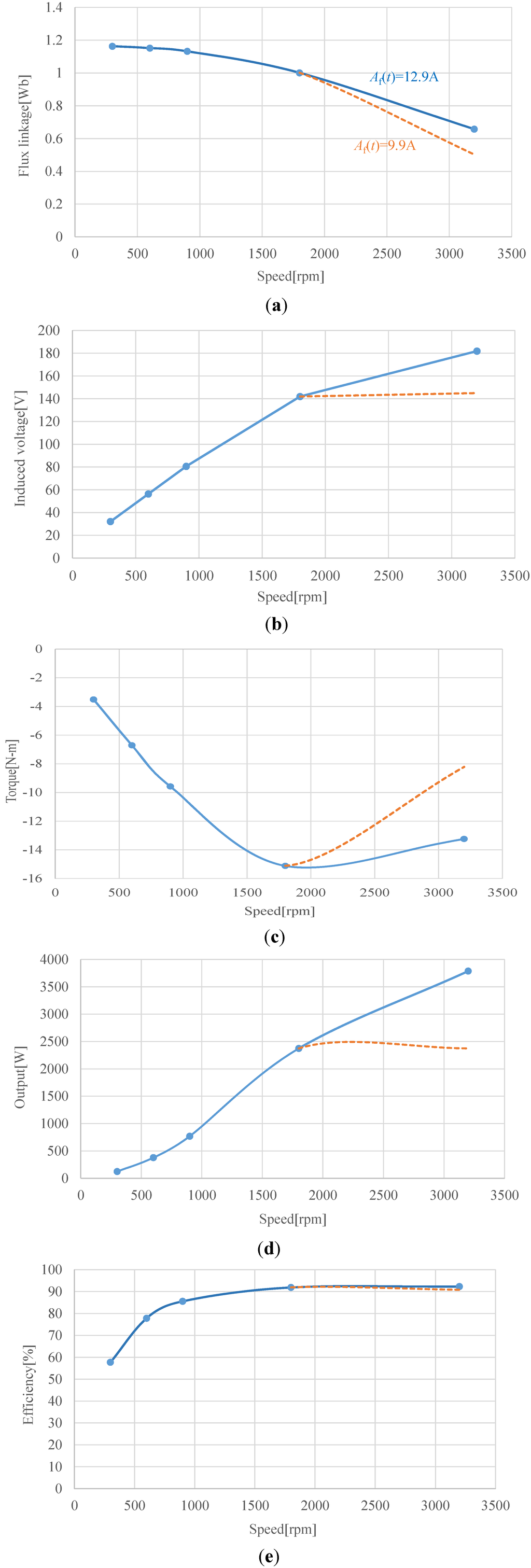
Figure 21.
Speed characteristics of Design 8. (a) Flux linkage; (b) induced voltage; (c) torque; (d) output power; (e) efficiency.
Figure 21.
Speed characteristics of Design 8. (a) Flux linkage; (b) induced voltage; (c) torque; (d) output power; (e) efficiency.
6. Conclusions
A novel synchronous generator is proposed for wind power generation. The generator does not require the slip rings and brushes for excitation, nor permanent magnets. Design analysis is carried out, and the performances are presented by using FEM analysis. The output power and efficiency are expected to be the same as those of a permanent magnet-type generator. Furthermore, the field flux can be controlled very easily during wind power generation. In future work, the experimental performances will be shown.
Conflicts of Interest
State any potential conflicts of interest here or “The authors declare no conflict of interest”.
References
- Oyama, J.; Toba, S.; Higuchi, T.; Yamada, E. The characteristics of half-wave rectified brushless synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the Beijing International Conference on Electrical Machines, Beijing, China, 10–14 August 1987; pp. 654–657.
- Oyama, J.; Toba, S.; Higuchi, T.; Yamada, E. The principle and fundamental characteristics of half-wave rectified brushless synchronous motor. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 1987, 107, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, S.; Kesamaru, K. Brushless self-excited type single-phase synchronous generator using wound-rotor type three-phase induction machine. Trans. IEEE Jpn 1981, 101, 743–750. [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura, K.; Higuchi, T.; Yuichi, Y.; Abe, T. Principle and characteristic analysis of a half-wave rectified brushless synchronous generator. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Busan, Korea, 26–29 October 2013; pp. 708–711.
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
