Zero-Sequence Voltage Outperforms MCSA-STFT for a Robust Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in Three-Phase Induction Motors: A Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Short-Time Fourier Transform Method
3. The Spectral Analysis of the Stator Current
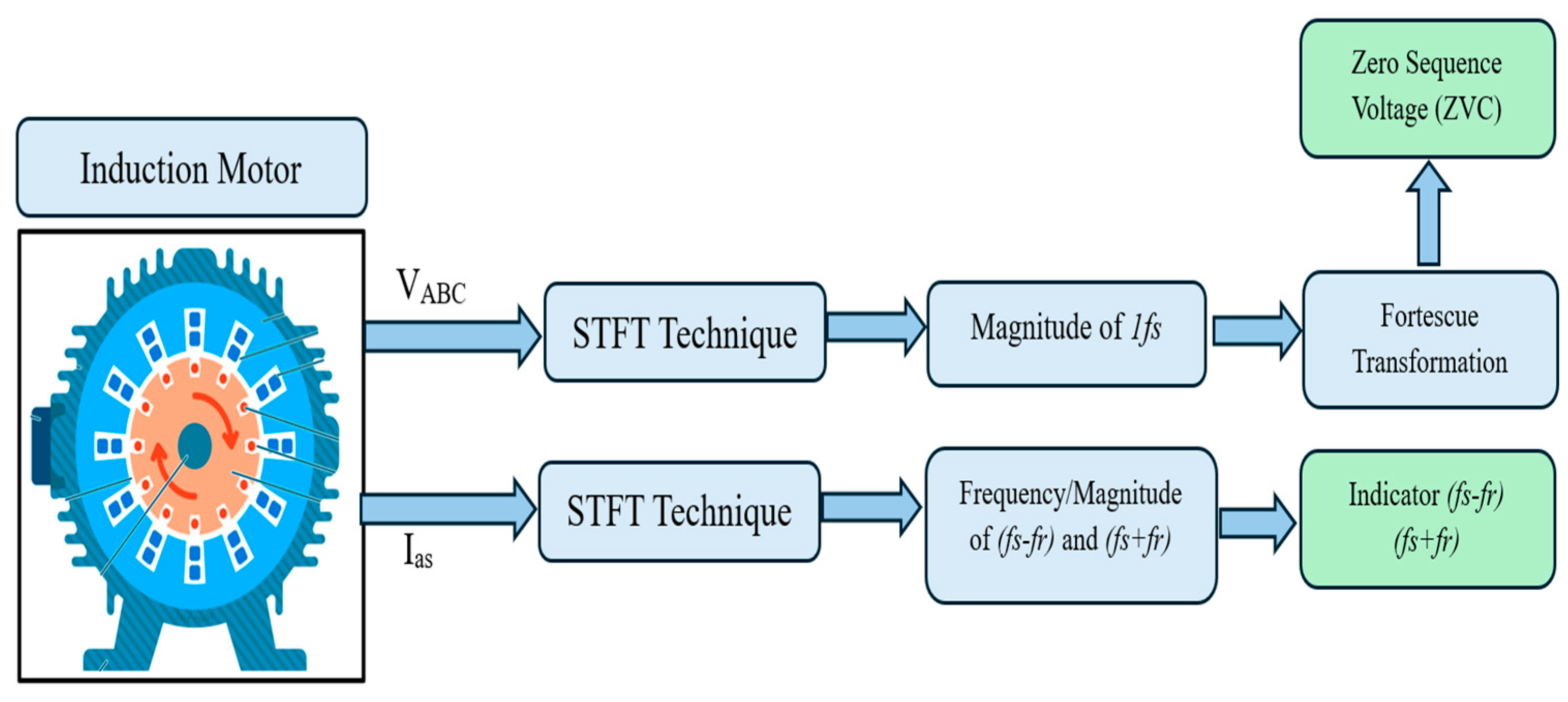
4. The Analysis of the Symmetrical Components
- ✓
- Step 01: The acquisition of the three-phase voltages (Va, Vb, Vc).
- ✓
- Step 02: The fundamental harmonic magnitudes and phase angles of the three-phase voltages are extracted using the short-time Fourier transform (STFT). This signal processing technique accurately estimates and tracks the frequency, amplitude, and phase of each harmonic, accommodating the non-stationary nature of the voltage signals.
- ✓
- Step 03: The calculation of the positive-, negative-, and zero-sequence components related to the supply voltages ()
- ✓
- Step 04: The calculation of the magnitude of the zero-sequence voltage component. Hence, the proposed approach can be outlined by the following steps (Figure 1).
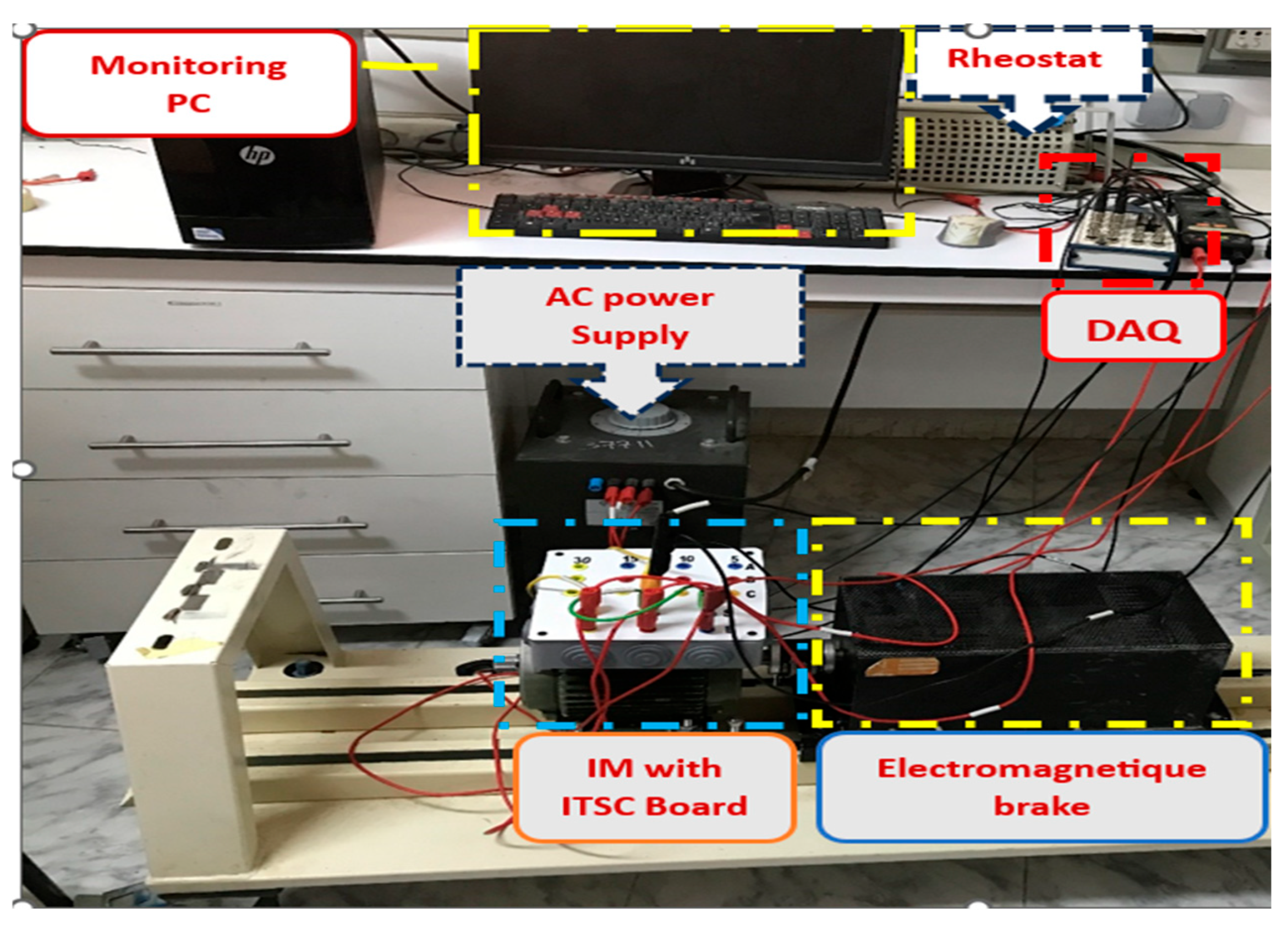
5. Experimental Validation
- A.
- The Sensitivity to the ITSC fault
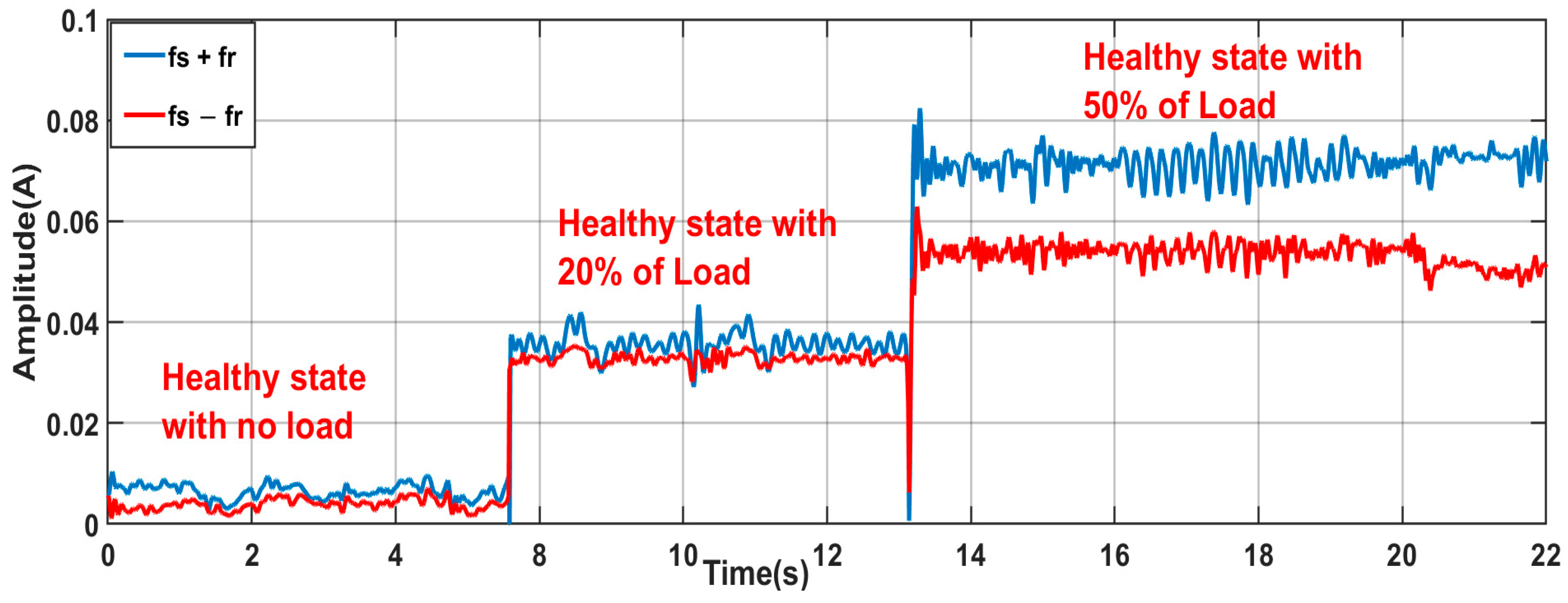
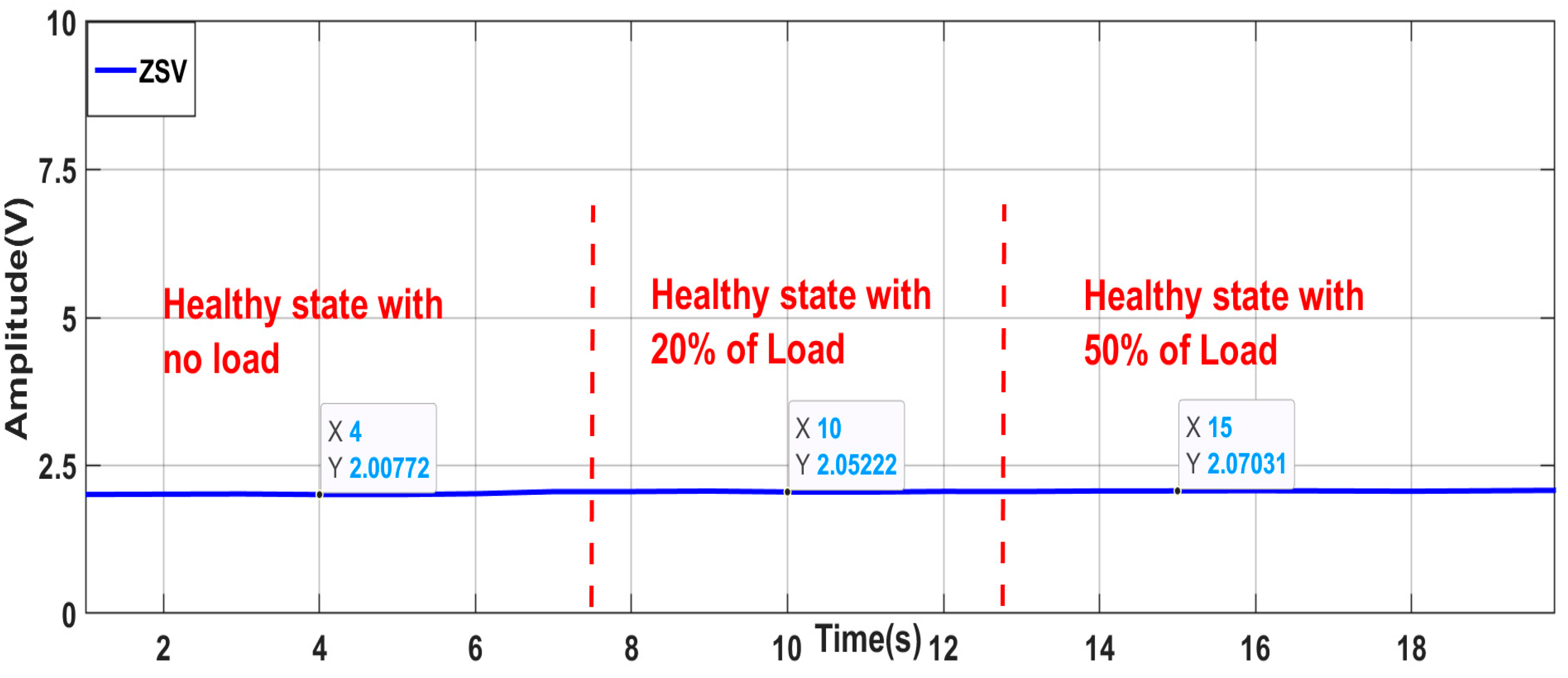
- B.
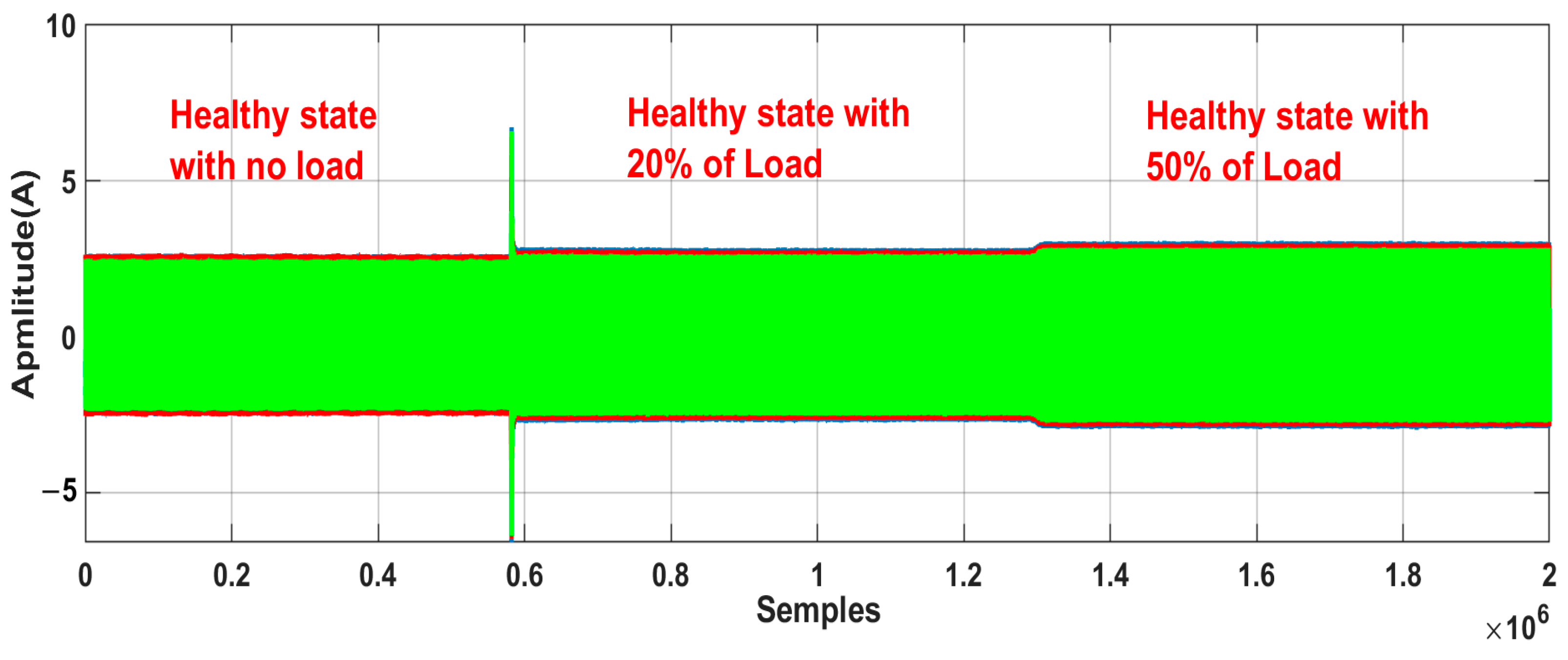
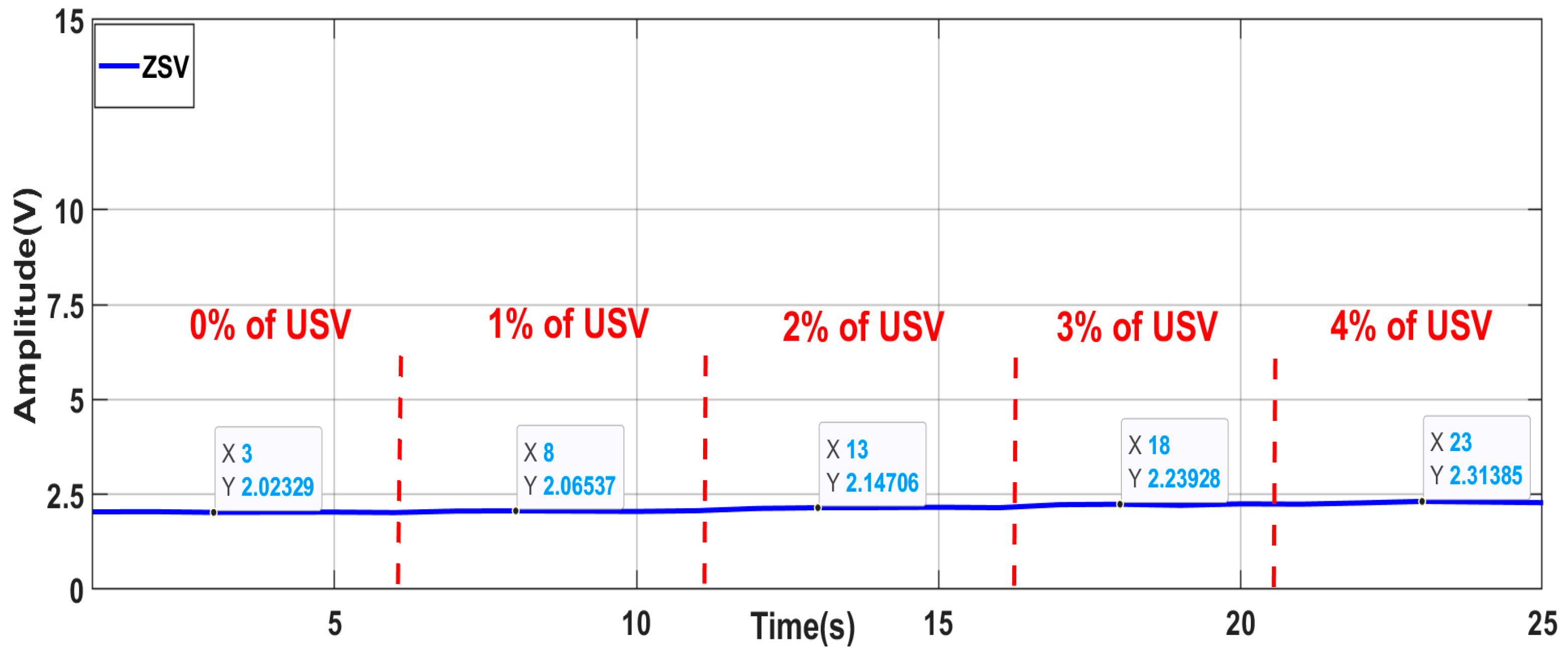
- Robustness against load variation
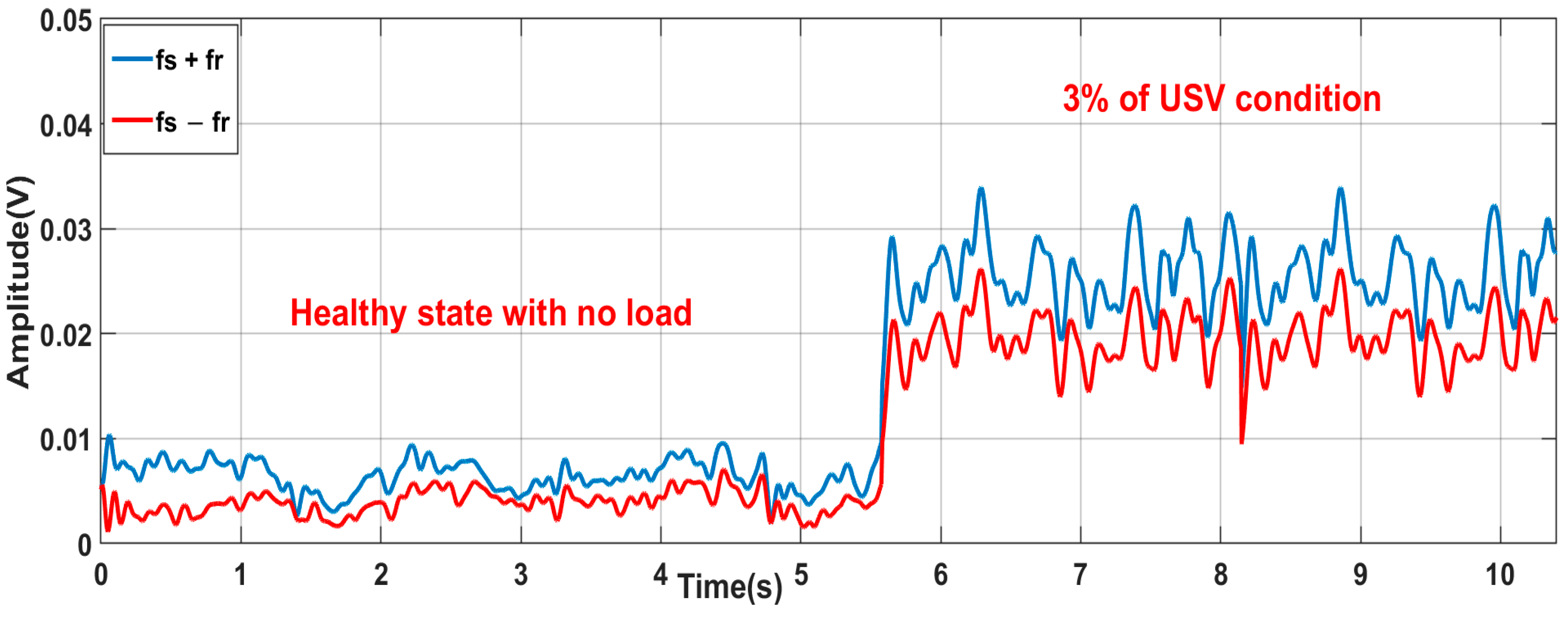
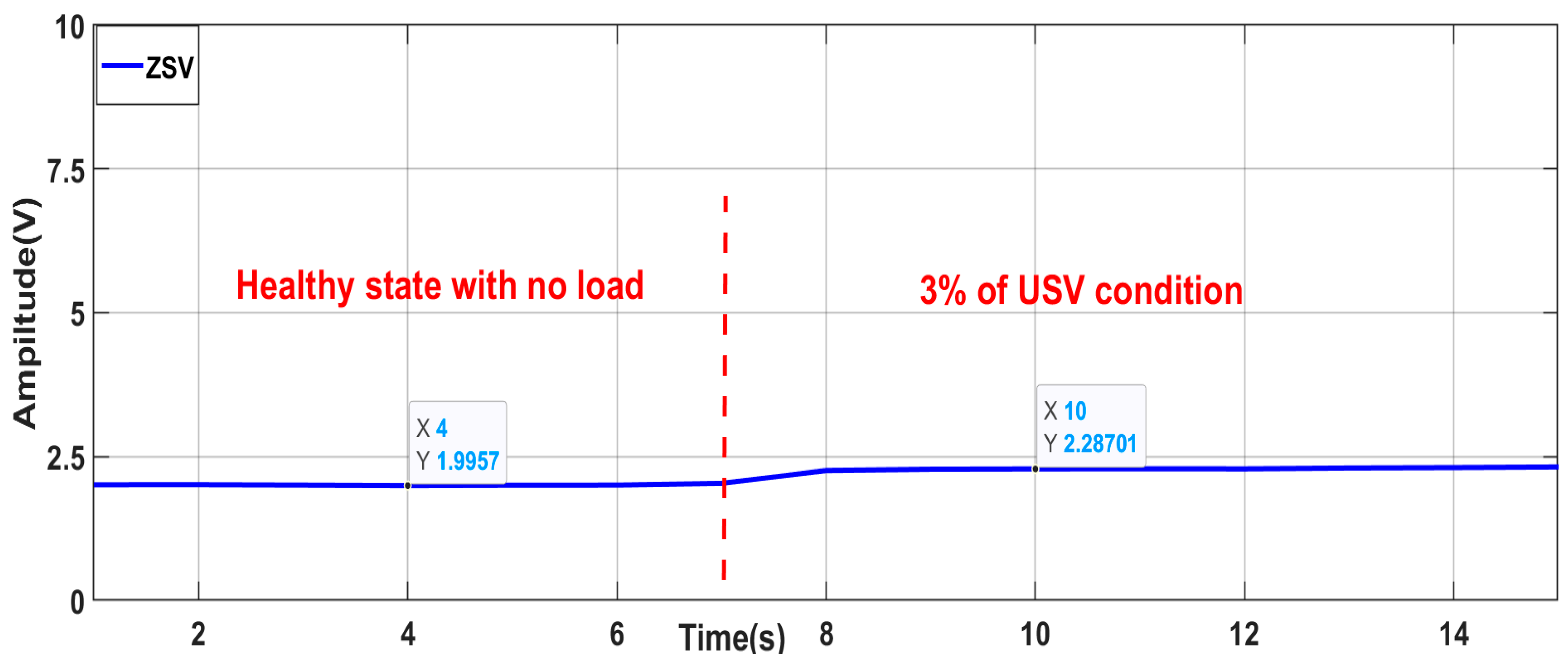
- C.
- Robustness against similar faults
- D.
- Discussion
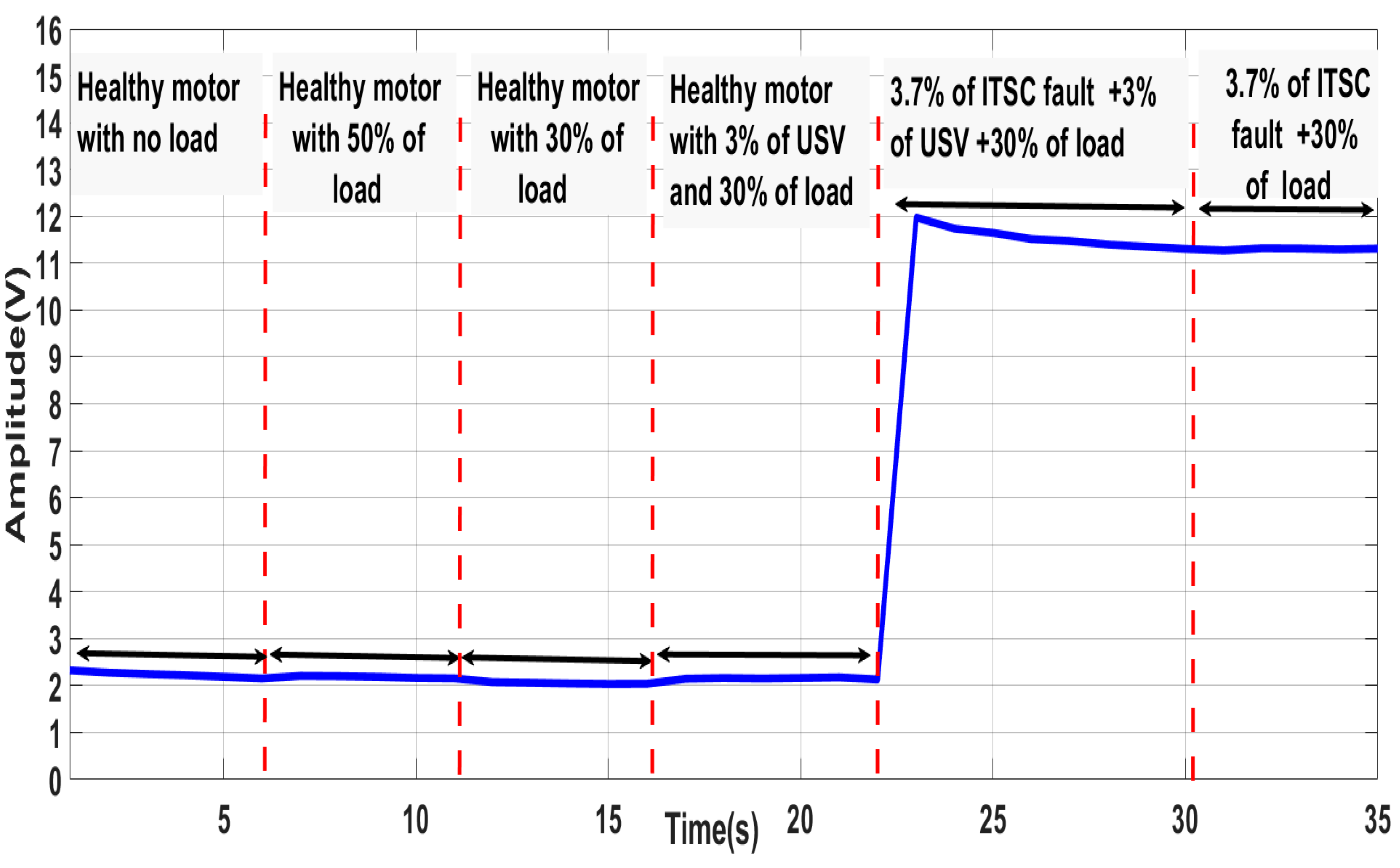
6. ITSC Fault Detection Based on ZSV Under Complex Operating Conditions
- ▪
- Start the motor in a healthy state, with balanced supply voltages, with no load;
- ▪
- Increase the motor load by 50% (the motor is always in a healthy state);
- ▪
- Return to the operation under a motor load of 30% (a healthy motor with a balanced supply);
- ▪
- Introduce a USV of 3% in phase “a”, under 30% of the load (healthy motor);
- ▪
- Short 3.7% of the ITSC fault in phase “a” under a USV of 3% and 30% of the load;
- ▪
- Eliminate the USV while the motor remains with the 3.7% of the ITSC fault and 30% of the load.
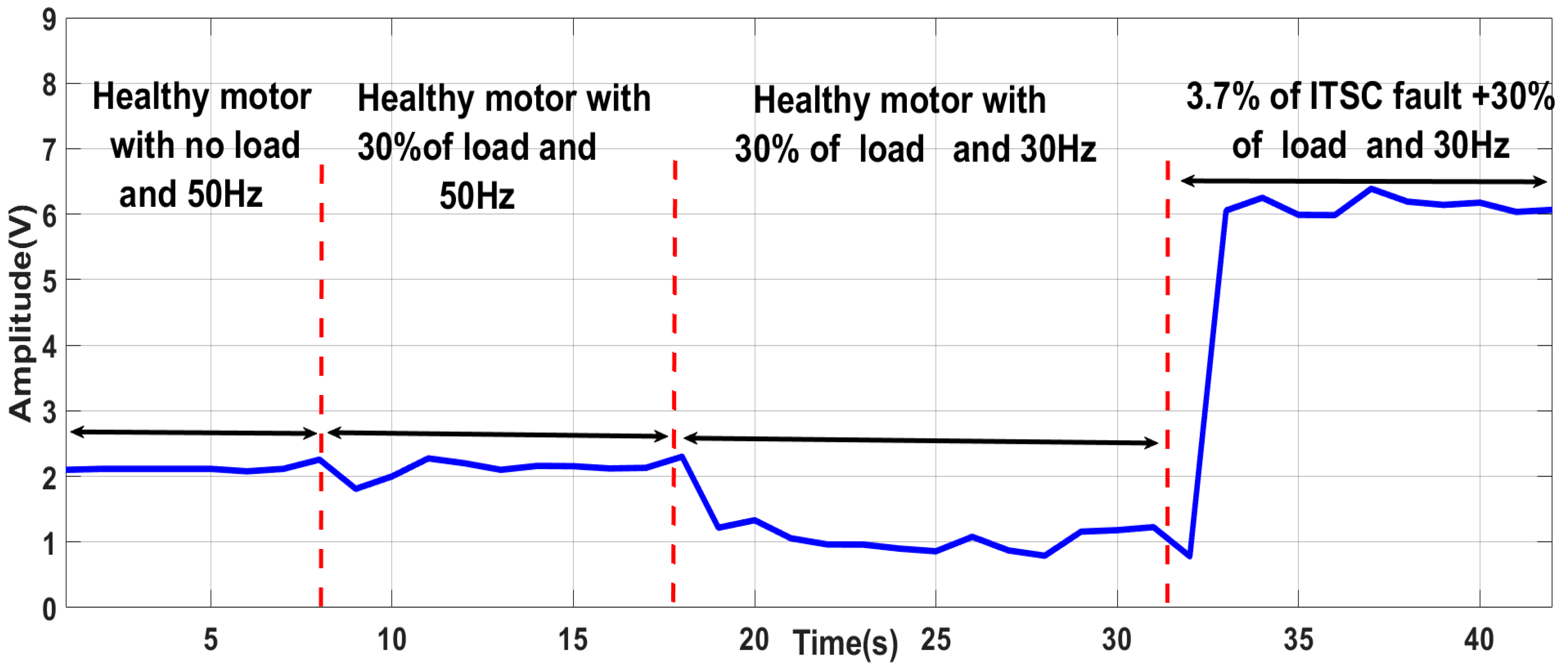
- ▪
- Start the motor in a healthy state, with 50 Hz, with no load;
- ▪
- Increase the motor load by 30% (healthy motor with 50 Hz);
- ▪
- Decrease the frequency of the motor to 30 Hz (healthy motor at 30% of the load);
- ▪
- Introduce 3.7% of the ITSC fault in phase “a”, under 30% of the load and 30 Hz.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Guchhait, P.K.; Banerjee, R.; Srivastava, A.K.; Vishwakarma, D.N.; Saket, R.K. A Comprehensive Review of Condition Based Prognostic Maintenance (CBPM) for Induction Motor. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 90690–90704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangsar, P.; Tiwari, R. Signal based condition monitoring techniques for fault detection and diagnosis of induction motors: A state-of-the-art review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Calva, T.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Fernandez-Cavero, V.; Romero-Troncoso, R. Early Detection of Faults in Induction Motors—A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 7855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyftakis, K.N.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Reliable Detection of Stator Interturn Faults of Very Low Severity Level in Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, M.B.K.; Champenois, G. New Expressions of Symmetrical Components of the Induction Motor Under Stator Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, H.; Benakcha, A.; Khechekhouche, A.; Menacer, A.; Chehaidia, S.E.; Panchal, H. Experimental diagnosis of inter-turns stator fault and unbalanced voltage supply in induction motor using MCSA and DWER. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2020, 8, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Dongare, U.V.; Umre, B.S.; Ballal, M.S. Voltage–current locus-based stator winding inter-turn fault detection in induction motors. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2023, 51, 2889–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Cornejo, J.-J.; Ibarra-Manzano, M.-A.; González-Parada, A.; Castro-Sanchez, R.; Almanza-Ojeda, D.-L. Classification of inter-turn short-circuit faults in induction motors based on quaternion analysis. Measurement 2023, 222, 113680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaedi, M.A. Fault Diagnosis of Three-Phase Induction Motor: A Review. Optics 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, B.H.; Elhay, E.A.; Elkholy, M.M. Advanced fault detection technique of three phase induction motor: Comprehensive review. Discov. Electron. 2024, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhni, M.F.; Cauet, S.; Sakout, A.; Assoum, H.; Etien, E.; Rambault, L.; El-Gohary, M. Variable speed induction motors’ fault detection based on transient motor current signatures analysis: A review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 184, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraoui, M.; Ghoggal, A.; Guedidi, S.; Zouzou, S.E. Detection of inter-turn short-circuit in induction motors using Park–Hilbert method. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2014, 5, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, B.H.; Elhay, E.A.; Sutikno, T.; Elkholy, M.M. Revolutionizing motor maintenance: A comprehensive survey of state-of-the-art fault detection in three-phase induction motors. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. IJPEDS 2024, 15, 1968–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, P.; Wolkiewicz, M. Stator Winding Fault Detection of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on the Short-Time Fourier Transform. Power Electron. Drives 2022, 7, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, T.Y.; Li, M.S.; Wu, Q.H. Application of morphological max-lifting scheme for identification of induction motor stator inter-turn short circuit. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 1, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, G.N.; Khan, Z.J.; Ballal, M.S.; Suryawanshi, H.M. A Simplified Frequency-Domain Detection of Stator Turn Fault in Squirrel-Cage Induction Motors Using an Observer Coil Technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacz, A.; Glowacz, W.; Głowacz, Z.; Kozik, J. Early fault diagnosis of bearing and stator faults of the single-phase induction motor using acoustic signals. Measurement 2017, 113, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadrinath, J.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, B.K. Investigation of Vibration Signatures for Multiple Fault Diagnosis in Variable Frequency Drives Using Complex Wavelets. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Liu, Z.; Vong, C.-M.; Pecht, M. A Rotating Machinery Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Feature Learning of Thermal Images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 12348–12359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdar, A.; Nasiri-Gheidari, Z. Detection of Stator Interturn Fault in Induction Motors Using SNR Concept. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 9925–9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, M.; Petridis, S.; Karachalios, I.; Rakopoulos, D. A Review on Distribution System State Estimation Algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarchała, G.; Wolkiewicz, M. Performance of the Stator Winding Fault Diagnosis in Sensorless Induction Motor Drive. Energies 2019, 12, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, W.F.; Silva, I.N.; Goedtel, A.; Palácios, R.H.C.; Lopes, T.D. Application of intelligent tools to detect and classify broken rotor bars in three-phase induction motors fed by an inverter. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Hamdy, R.A.; Massoud, A.M.; Ahmed, S. Postfault Control of Scalar (V/f) Controlled Asymmetrical Six-Phase Induction Machines. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 59211–59220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, H.R.P.; Fonseca, D.S.B.; Cardoso, A.J.M. The Use of Line Impedance Symmetrical Components for Stator Faults Diagnostics in Symmetrical Six-Phase Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2025, 61, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, P.; Wolkiewicz, M. Stator winding fault detection of permanent magnet synchronous motors based on the bispectrum analysis. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2022, 70, 140556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dalahmeh, M.; Al-Greer, M.; Bashir, I.; El-Dalahmeh, M.; Demirel, A.; Keysan, O. Autonomous fault detection and diagnosis for permanent magnet synchronous motors using combined variational mode decomposition, the Hilbert-Huang transform, and a convolutional neural network. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 110, 108894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, S.; He, B.; Meng, G. Fault Diagnosis under Variable Working Conditions Based on STFT and Transfer Deep Residual Network. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 1274380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almounajjed, A.; Sahoo, A.K.; Kumar, M.K. Diagnosis of stator fault severity in induction motor based on discrete wavelet analysis. Measurement 2021, 182, 109780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias Martínez, M.E.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Dunai, L.; Conejero, J.A.; Fernández De Córdoba, P. Higher-Order Spectral Analysis and Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosing Faults in Electrical Machines: An Overview. Mathematics 2024, 12, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedidi, A.; Laala, W.; Guettaf, A.; Arif, A. Early detection and localization of stator inter-turn short circuit faults based on variational mode decomposition and deep learning in induction motor. Diagnostyka 2023, 24, 2023401. Available online: https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/yadda/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-e5ff46fe-d64a-45b5-a474-41f8df649a0e (accessed on 6 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, P.; Wolkiewicz, M. Comparison of selected methods for the stator winding condition monitoring of a PMSM using the stator phase currents. Energies 2021, 14, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, L.; Ma, J. Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on STFT-Deep Learning and Sound Signals. Shock Vib. 2016, 2016, 6127479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkedjouh, T.; Zerhouni, N.; Rechak, S. Deep Learning for Fault Diagnosis based on short-time Fourier transform. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Smart Communications in Network Technologies (SaCoNeT), El Oued, Algeria, 27–31 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Laadjal, K.; Sahraoui, M.; Cardoso, A.J.M. On-Line Fault Diagnosis of DC-Link Electrolytic Capacitors in Boost Converters Using the STFT Technique. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 6303–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Arredondo, P.A.; Garcia-Perez, A.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Avina-Cervantes, J.G.; Rostro-Gonzalez, H.; Romero-Troncoso, R.D.J. Comparative Study of Time-Frequency Decomposition Techniques for Fault Detection in Induction Motors Using Vibration Analysis during Startup Transient. Shock Vib. 2015, 2015, 708034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Tapia, S.; Avalos-Almazan, G.; Rangel-Magdaleno, J.D.J.; Ramirez-Cortes, J.M. Physical Variable Measurement Techniques for Fault Detection in Electric Motors. Energies 2023, 16, 4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y. Motor Fault Diagnostics Based on Current Signatures: A Review. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 3520919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Din Memon, T.; Hussain, I.; Ahmed Memon, Z.; Kumar, D. Fault Detection and Identification Using Deep Learning Algorithms in Induction Motors. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2022, 133, 435–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almounajjed, A.; Sahoo, A.K.; Kumar, M.K.; Subudhi, S.K. Stator Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Based on Discrete Wavelet Analysis and Neural Network Technique. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2023, 9, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamany, G.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajamany, K.; Natarajan, R.K. Induction Motor Stator Interturn Short Circuit Fault Detection in Accordance with Line Current Sequence Components Using Artificial Neural Network. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4825787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, M.; Champenois, G. A novel reliable indicator of stator windings fault in induction motor extracted from the symmetrical components. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Gdansk, Poland, 27–30 June 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Llinares, J.; Antonino-Daviu, J.; Roger-Folch, J.; Moríñigo-Sotelo, D.; Duque-Pérez, O. Mixed eccentricity diagnosis in Inverter-Fed Induction Motors via the Adaptive Slope Transform of transient stator currents. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2014, 48, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cavero, V.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Duque-Perez, O.; Pons-Llinares, J. A Comparison of Techniques for Fault Detection in Inverter-Fed Induction Motors in Transient Regime. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 8048–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, P.; He, S.; Huang, J. A Review of Modeling and Diagnostic Techniques for Eccentricity Fault in Electric Machines. Energies 2021, 14, 4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bazzi, A.M. A review and comparison of fault detection and diagnosis methods for squirrel-cage induction motors: State of the art. ISA Trans. 2017, 70, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houili, M.; Sahraoui, M.; Laadjal, K.; Cardoso, A.J.M.; Alloui, A. A Comparative Study of MCSA and ZSV-Based Methods for Diagnosing Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Faults in Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence & Green Energy (ICAIGE), Yasmine Hammamet, Tunisia, 10–12 October 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–5. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10776654/ (accessed on 12 January 2025).



| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Poles | 4 | / |
| Rated Power | 1.1 | kW |
| Rated Voltage | 230/400 | V |
| Rated Current | 2.5/4.3 | A |
| Rated Frequency | 50 | Hz |
| Rated Speed | 1450 | rpm |
| Number of Turns/Phases | 396 | turns |
| Indicators | Healthy State | Faulty State | Variation (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Turns | 15 Turns | 5 Turns | 15 Turns | ||
| (fs − fr) | 0.0071 (A) | / | 0.025 (A) | / | 252% |
| (fs + fr) | 0.0115 (A) | / | 0.04 (A) | / | 247% |
| ZSV | 2 (v) | 3.5 (v) | 11.5 (v) | 75% | 475% |
| Fault Indicator | (fs − fr) and (fs + fr) | ZSV |
|---|---|---|
| Signal processing technique | STFT | STFT |
| Online implementation |  Yes Yes |  Yes Yes |
| Sensitivity to the ITSCFs |  Yes Yes |  Yes Yes |
| Robustness against load variation |  No No |  Yes Yes |
| Robustness against USV condition |  No No |  Yes Yes |
| Robustness against a speed transition |  No No |  Yes Yes |
| Number of sensors | 1 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Houili, M.; Sahraoui, M.; Marques Cardoso, A.J.; Alloui, A. Zero-Sequence Voltage Outperforms MCSA-STFT for a Robust Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in Three-Phase Induction Motors: A Comparative Study. Machines 2025, 13, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060501
Houili M, Sahraoui M, Marques Cardoso AJ, Alloui A. Zero-Sequence Voltage Outperforms MCSA-STFT for a Robust Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in Three-Phase Induction Motors: A Comparative Study. Machines. 2025; 13(6):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060501
Chicago/Turabian StyleHouili, Mouhamed, Mohamed Sahraoui, Antonio J. Marques Cardoso, and Abdeldjalil Alloui. 2025. "Zero-Sequence Voltage Outperforms MCSA-STFT for a Robust Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in Three-Phase Induction Motors: A Comparative Study" Machines 13, no. 6: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060501
APA StyleHouili, M., Sahraoui, M., Marques Cardoso, A. J., & Alloui, A. (2025). Zero-Sequence Voltage Outperforms MCSA-STFT for a Robust Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in Three-Phase Induction Motors: A Comparative Study. Machines, 13(6), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060501






