High-Definition Map Change Regions Detection Considering the Uncertainty of Single-Source Perception Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A multi-object detection and tracking method based on a hybrid model is proposed, which enables real-time perception and tracking of ground lane markings and arrows.
- A feature matching algorithm based on geometric proximity and shape consistency is proposed, allowing for accurate matching between perception results and HD maps.
- A probabilistic update model that considers the uncertainty of single-vehicle perception data is developed, which integrates multi-source data to achieve precise map change detection.
2. Related Work
2.1. HD Map Construction and Update
2.2. HD Map Update Based on Crowdsourced Data
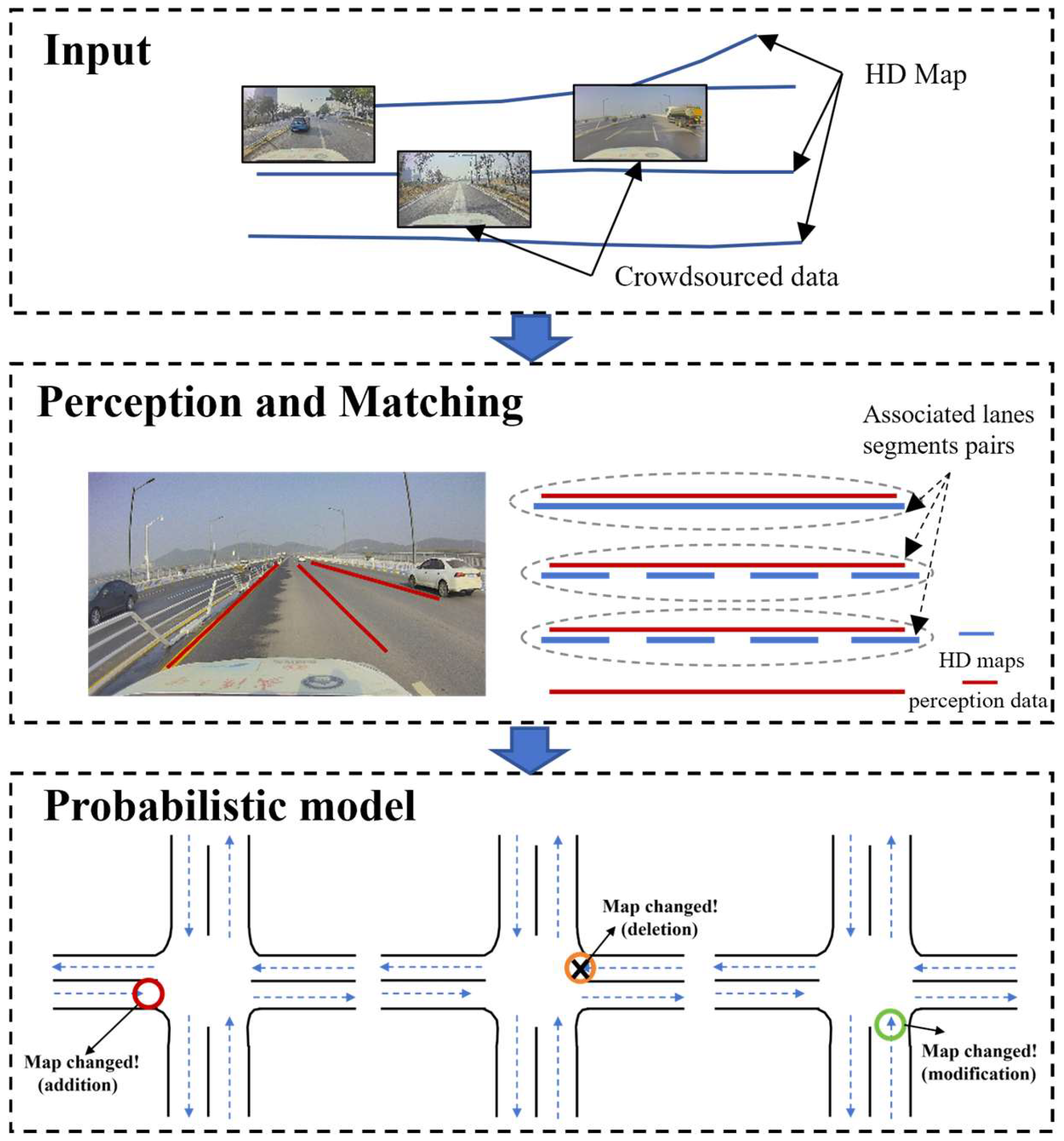
3. Method
3.1. Framework Overview
3.2. Road Information Perception and Matching
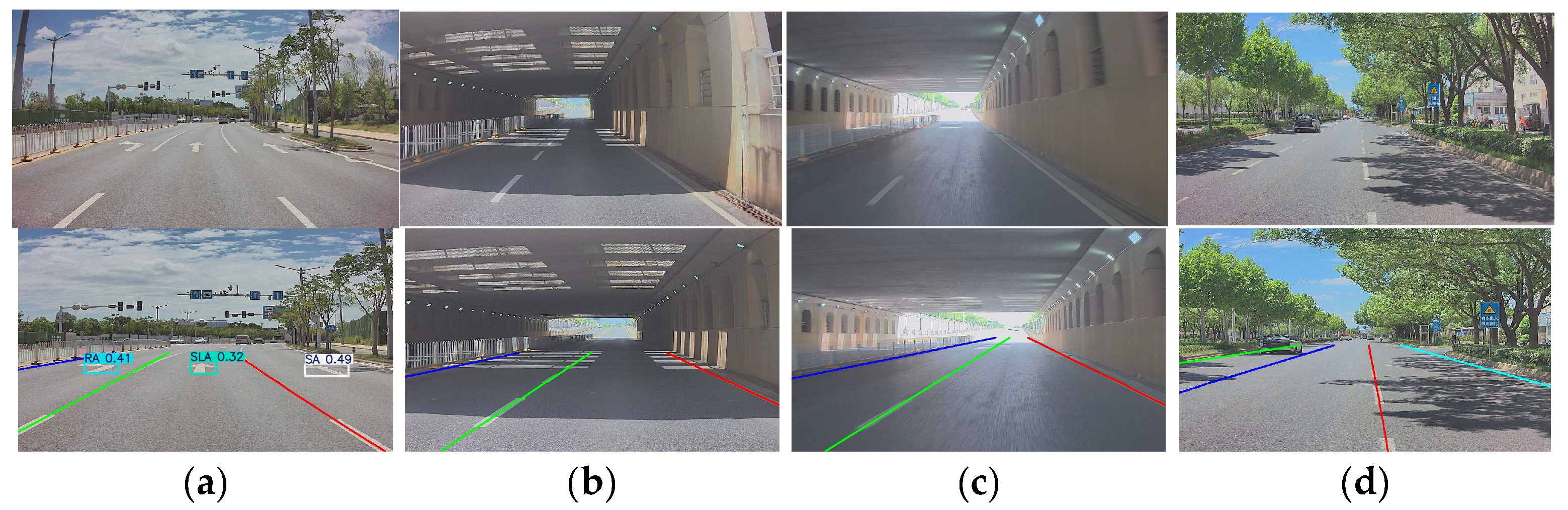
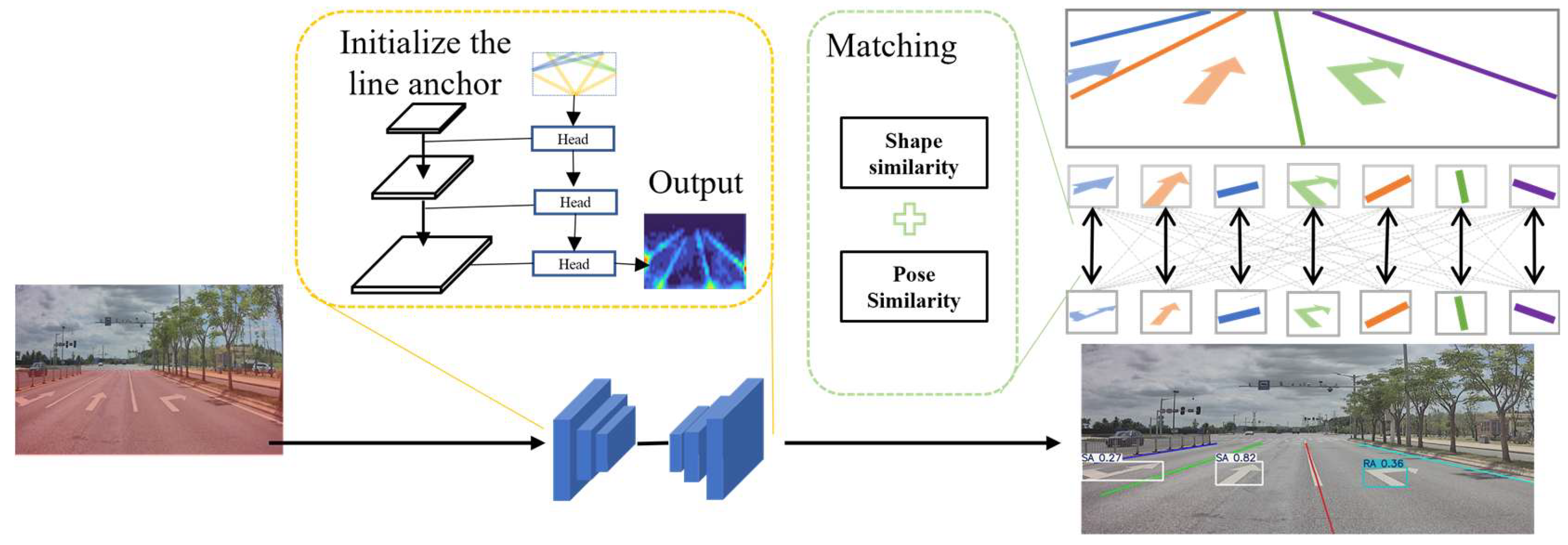
3.2.1. Road Information Perception
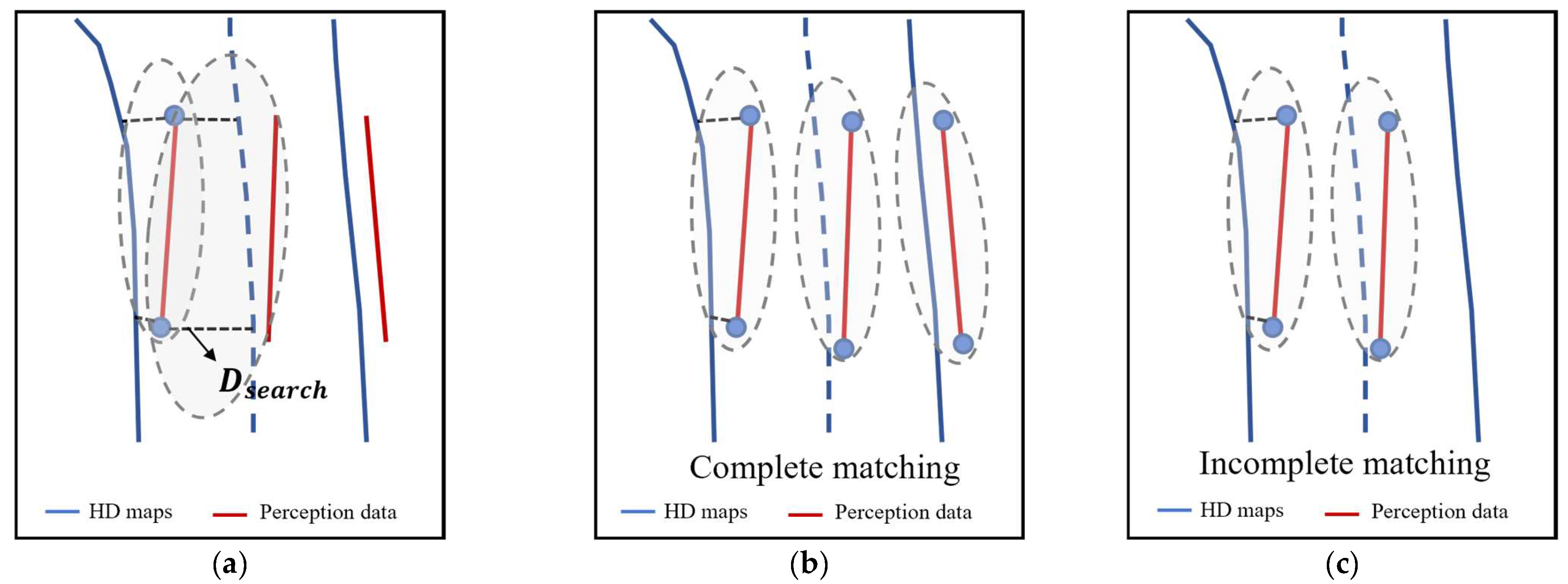
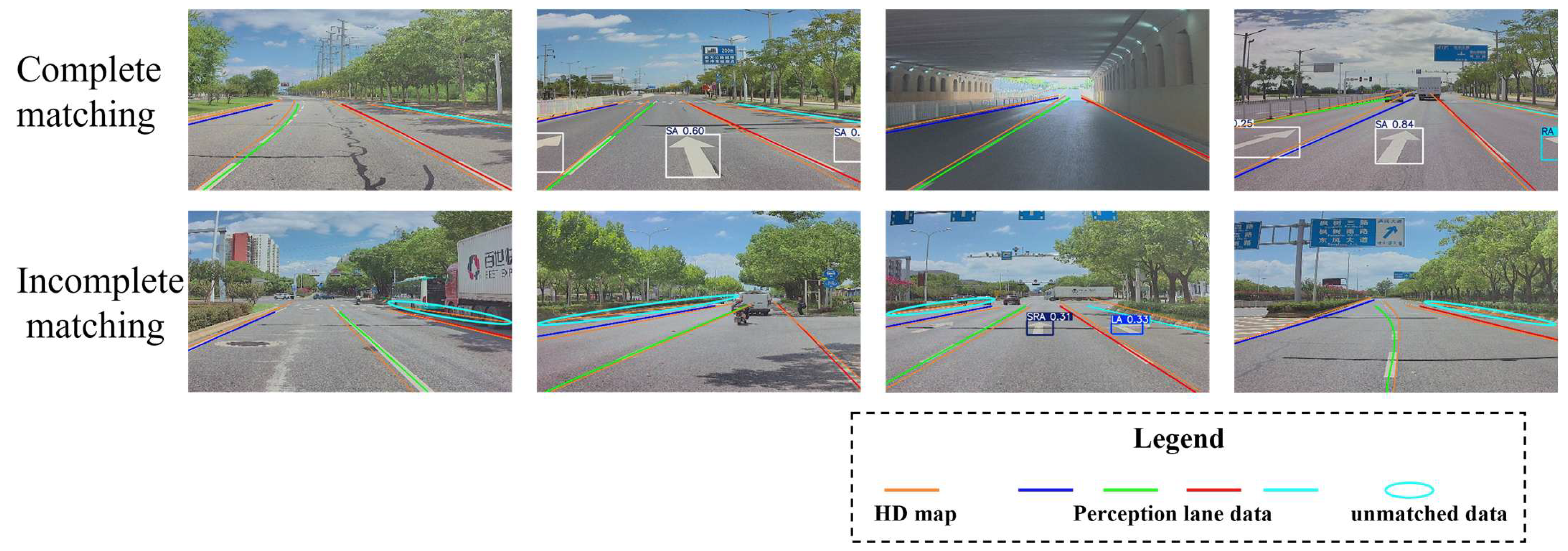
3.2.2. Road Information Matching
| Algorithm 1: Lane Matching between Perception Data and HD Map |
| Input: Set of perceived lanes ; Set of HD map lanes |
| Output: Matched lane pairs between perception and HD map |
| 1: Initialize matched set |
| 2: for each perceived lane do |
| 3: // Find candidate set |
| 4: if and lanes can be topologically aligned then |
| 5: for each candidate do |
| 6: |
| 7: |
| 8: Normalize and and compute matching cost |
| 9: Apply Hungarian algorithm to minimize total matching cost |
| 10: Add matched pairs to |
| 11: else each candidate do |
| 12: Compute and |
| 13: |
| 14: Normalize all metrics to [0,1] |
| 15: Compute total score |
| 16: Select candidate with maximum as match |
| 17: if , mark as unreliable |
| 18: end for |
| 19: return |
3.3. Probabilistic Model
3.3.1. Problem Definition
3.3.2. Single-Observation Probability
3.3.3. Multi-Vehicle Observation Fusion Probability
4. Experiments and Analysis
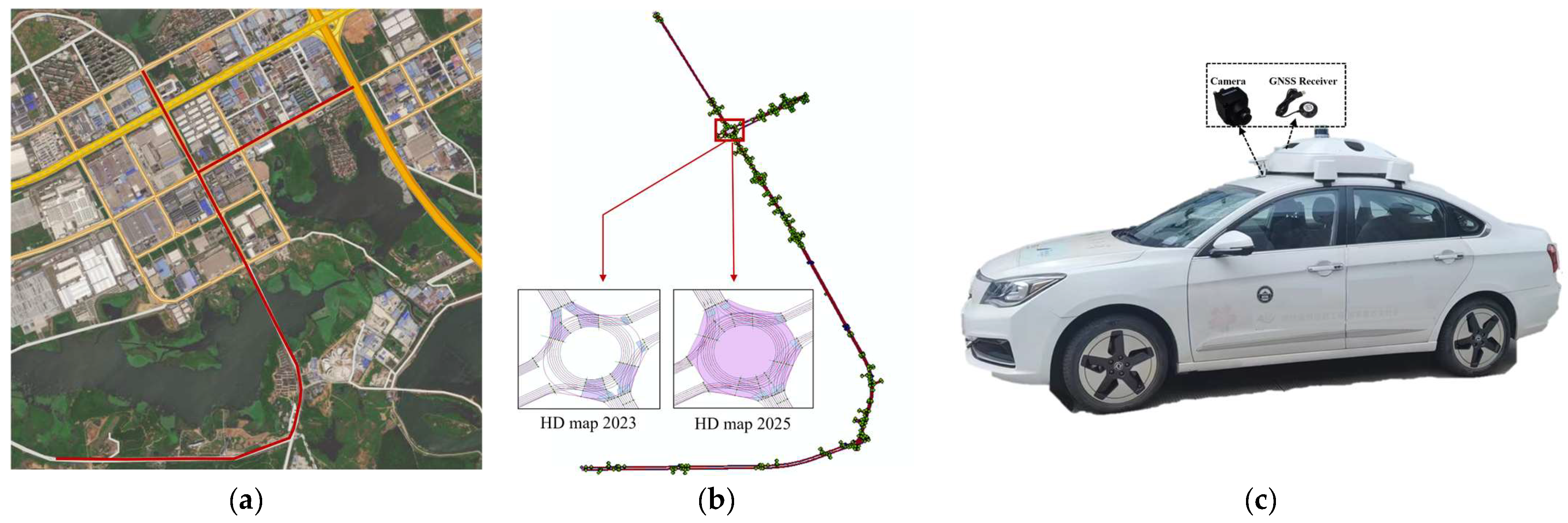
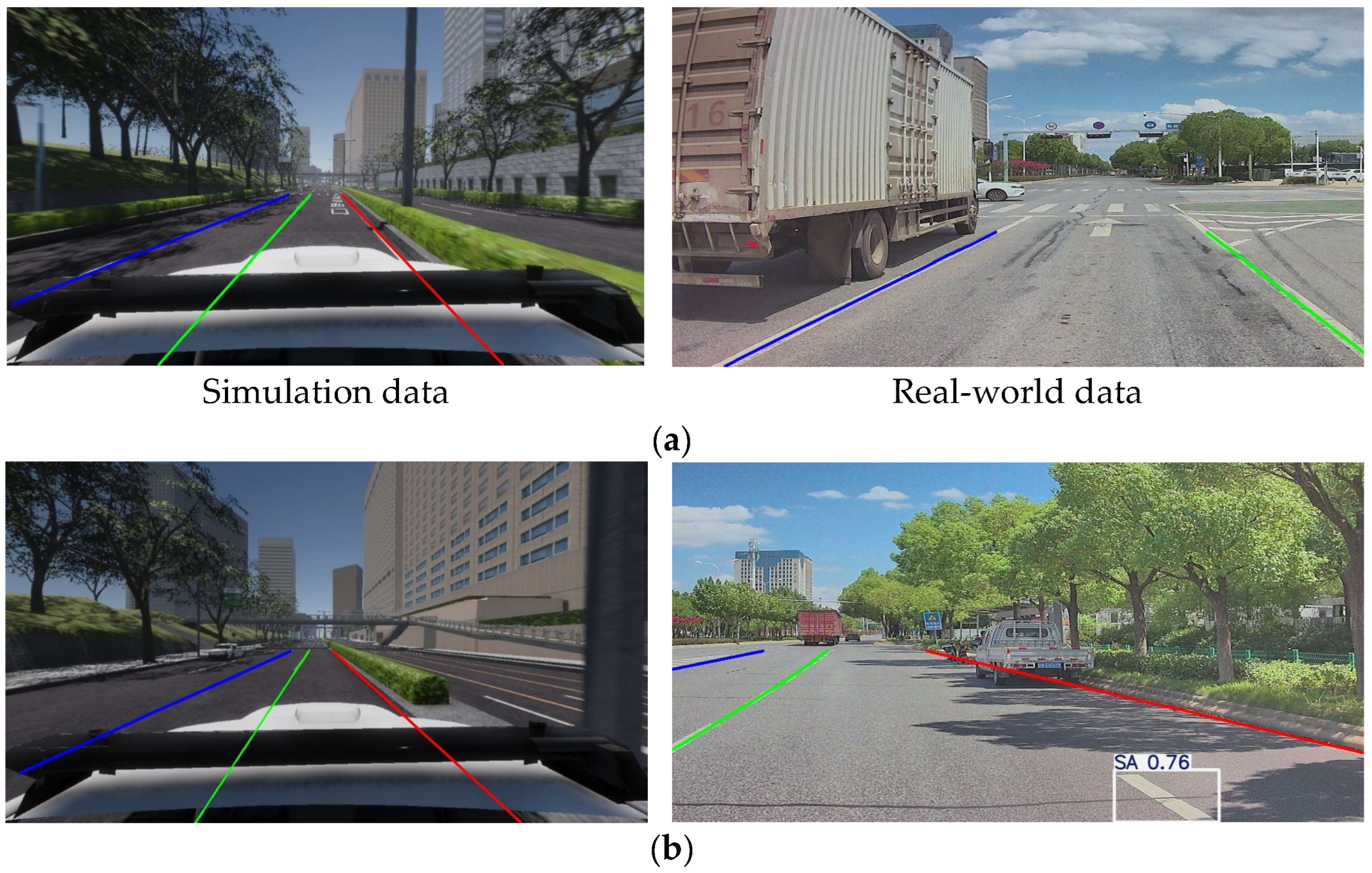
4.1. Study Area and Data
4.2. Experiment Setting and Accuracy Evaluation
4.2.1. Experiment Setting
4.2.2. Accuracy Evaluation
4.3. Experiment Results
4.3.1. Matching Evaluation
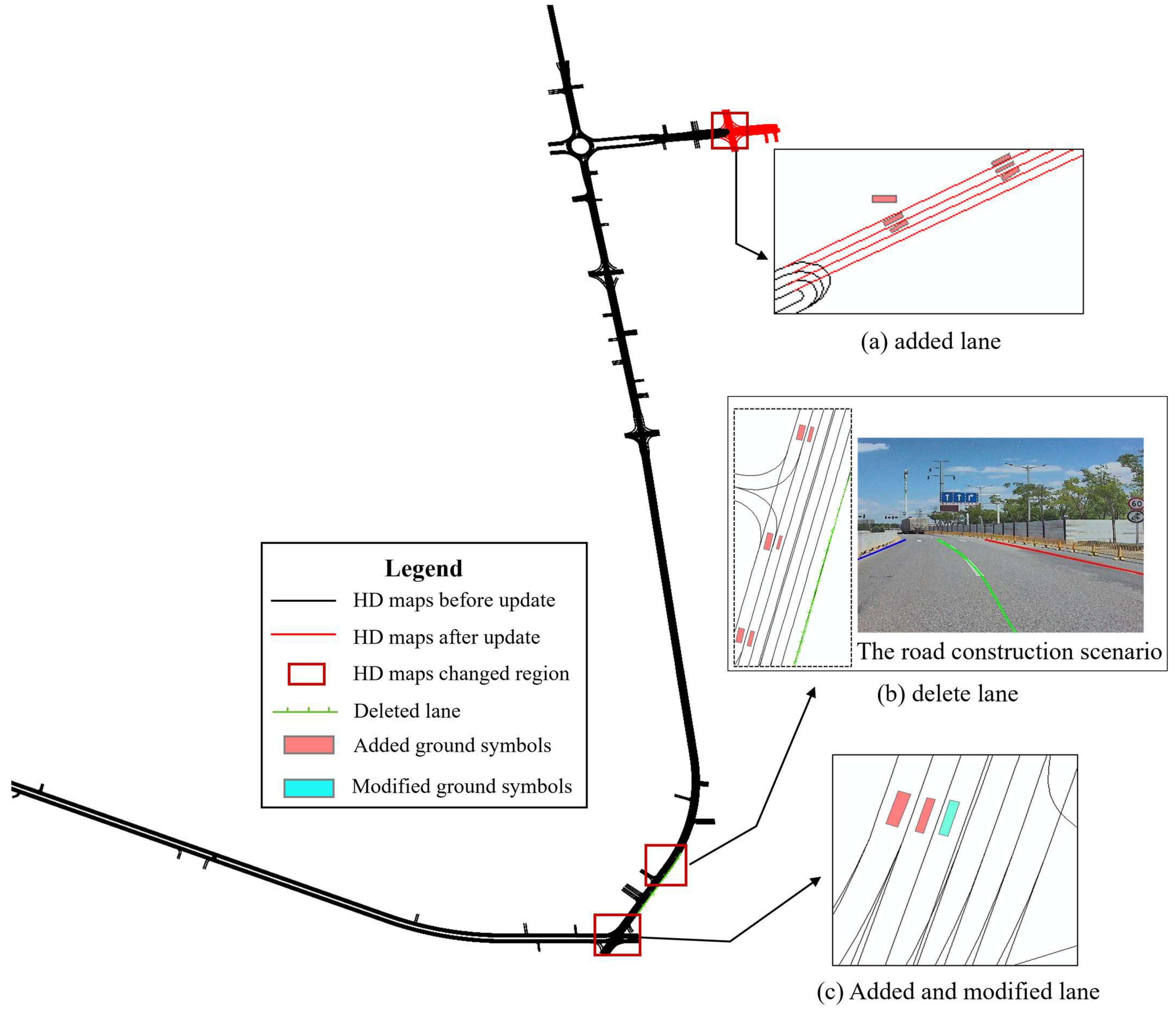
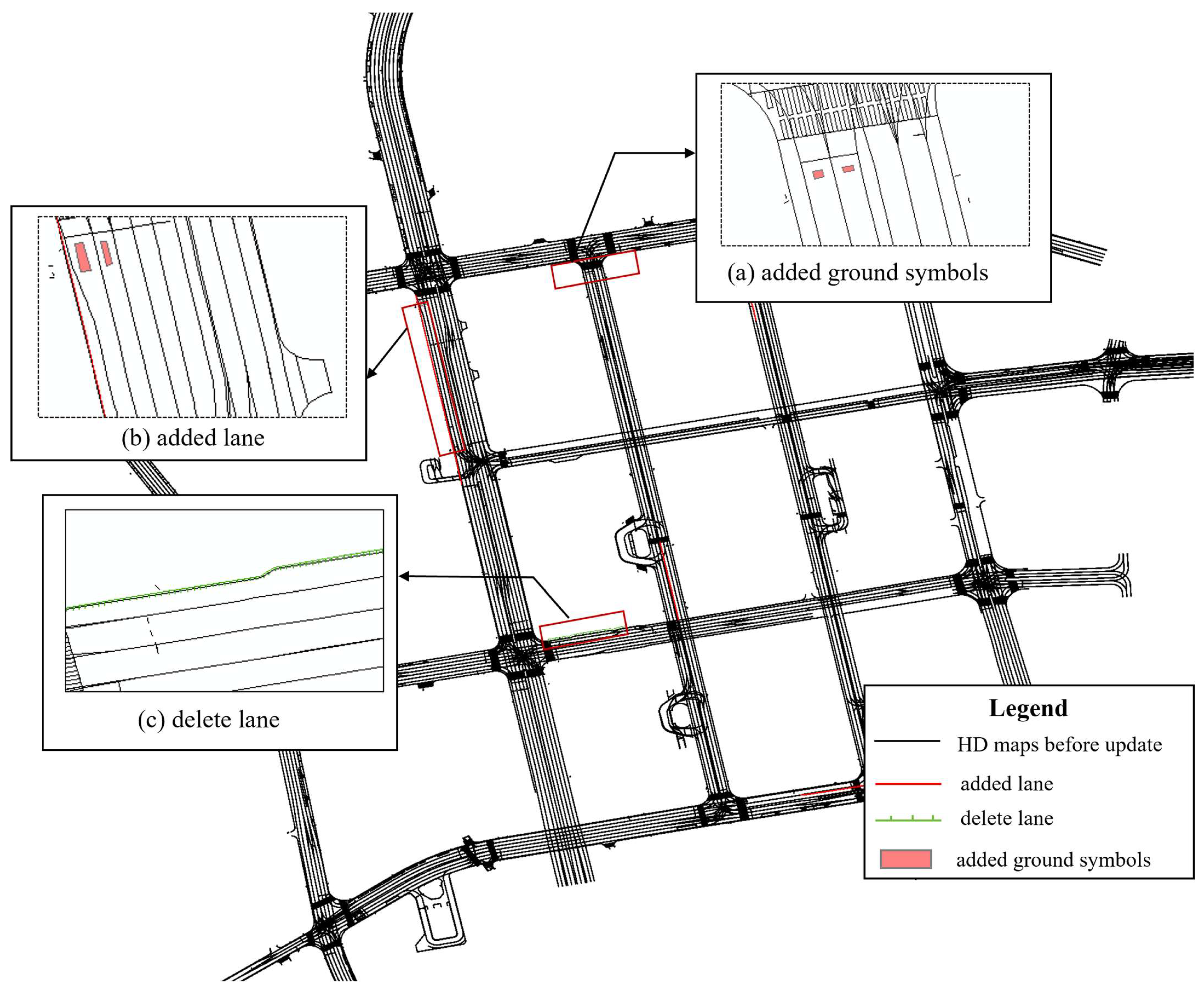
4.3.2. Map Change Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HD map | High-definition map |
| SD map | Standard-definition map |
| MMS | Mobile mapping systems |
| SLAM | Simultaneous localization and mapping |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
References
- Jia, Z.; Yin, J.; Cao, Z.; Wei, N.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, H. Sustainable Transportation Emission Reduction through intelligent transportation systems: Mitigation drivers, and temporal trends. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 112, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Ma, W. The influence of digital intelligence transformation on carbon emission reduction in manufacturing firms. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 121987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotopoulos, I.; Dimitrakopoulos, G. An empirical investigation on consumers’ intentions towards autonomous driving. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 95, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, G.; Sun, C.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Tian, L.; Li, F. Multi-Environment Vehicle Trajectory Automatic Driving Scene Generation Method Based on Simulation and Real Vehicle Testing. Electronics 2025, 14, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Sun, C.; Li, H.; Zheng, S. Real-Time Center of Gravity Estimation for Intelligent Connected Vehicle Based on HEKF-EKF. Electronics 2023, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, H.; Qian, C.; Fan, X. Real-Time Scan-to-Map Matching Localization System Based on Lightweight Pre-Built Occupancy High-Definition Map. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Hossain, S.; Lang, H.; Lin, X. High-Definition Map Generation Technologies for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.05400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Lv, Z. A Review of Crowdsourcing Update Methods for High-Definition Maps. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, Q.; Bian, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J. A lane-level localization method via the lateral displacement estimation model on expressway. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 243, 122848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. High Definition Map for Automated Driving: Overview and Analysis. J. Navig. 2020, 73, 324–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghazaly, G.; Frank, R.; Harvey, S.; Safko, S. High-Definition Maps: Comprehensive Survey, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. IEEE Open J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 4, 527–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, Q.; Li, B.; Xiao, J.; Li, Z. Refined high-definition map model for roadside rest area. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2025, 195, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, G.; Sun, C.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Li, F. A Shared-Road-Rights Driving Strategy Based on Resolution Guidance for Right-of-Way Conflicts. Electronics 2024, 13, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, W.; Chen, M.; Huang, W.; Liu, X. Open HD map service model: An interoperable high-definition map data model for autonomous driving. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 2089–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannen, D.; Liebner, M.; Hempel, W.; Burgard, W. How to Keep HD Maps for Automated Driving Up to Date. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 2288–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Cho, S.; Chung, W. HD Map Update for Autonomous Driving with Crowdsourced Data. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, L. CenterLineDet: CenterLine Graph Detection for Road Lanes with Vehicle-Mounted Sensors by Transformer for HD Map Generation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 3553–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, B. Lane Information Extraction for High Definition Maps Using Crowdsourced Data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 7780–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebner, M.; Jain, D.; Schauseil, J.; Pannen, D.; Hackelöer, A. Crowdsourced HD Map Patches Based on Road Model Inference and Graph-Based SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 9–12 June 2019; pp. 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Ding, W. Traffic Flow-Based Crowdsourced Mapping in Complex Urban Scenario. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 5077–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, J.; Yuan, Z.; Aslam, N. Enhancement of High-Definition Map Update Service Through Coverage-Aware and Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.14582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Mahnaz, F.; Bulan, O.; Mengistu, Y.; Mahesh, S.; Losh, M.A. Creating Semantic HD Maps from Aerial Imagery and Aggregated Vehicle Telemetry for Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2022, 23, 15382–15395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, B.; Yang, M.; Wen, T.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Tang, X.; Sigomo, D.O.; Miao, J.; Yang, D. Multi-Session High-Definition Map-Monitoring System for Map Update. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J. Real-Time HD Map Change Detection for Crowdsourcing Update Based on Mid-to-High-End Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Ai, R.; Gu, W.; Lu, H.; Kannala, J.; Chen, X. SuperFusion: Multilevel LiDAR-Camera Fusion for Long-Range HD Map Generation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2211.15656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Hu, M.; Dou, Q.; Ouyang, W.; Ma, G.; Li, Y.; Qin, H. HD Map Construction and Update System for Autonomous Driving in Open-Pit Mines. IEEE Syst. J. 2023, 17, 6202–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Azimi, S.M.; Roschlaub, R.; Krauß, T. Towards HD Maps from Aerial Imagery: Robust Lane Marking Segmentation Using Country-Scale Imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagahit, M.L.R.; Liu, X.; Xiu, H.; Kim, T.; Kim, K.-S.; Matsuoka, M. Learnable Resized and Laplacian-Filtered U-Net: Better Road Marking Extraction and Classification on Sparse-Point-Cloud-Derived Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Fu, J.; Shen, Y.; Jing, H.; Chen, S.; Zheng, N. Complementing Onboard Sensors with Satellite Maps: A New Perspective for HD Map Construction. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 11103–11109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, S. HD Map Change Detection with Cross-Domain Deep Metric Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 10218–10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathla, G.; Bhadane, K.; Singh, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Aluvalu, R.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Kumar, A.; Thakur, R.N.; Basheer, S. Autonomous Vehicles and Intelligent Automation: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, e7632892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Cho, S.; Sunwoo, M.; Resende, P.; Bradaï, B.; Jo, K. Cloud Update of Geodetic Normal Distribution Map Based on Crowd-Sourcing Detection against Road Environment Changes. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, e4486177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zhao, H.; Ma, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Chapman, M.A.; Junior, J.M.; Li, J. Robust Lane Extraction from MLS Point Clouds Towards HD Maps Especially in Curve Road. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, L. Road-Model-Based Road Boundary Extraction for High Definition Map via LIDAR. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 18456–18465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, N.; Jiang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Ying, S. Vision-HD: Road change detection and registration using images and high-definition maps. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 38, 454–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. HDMapNet: An Online HD Map Construction and Evaluation Framework. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 4628–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. VectorMapNet: End-to-End Vectorized HD Map Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2206.08920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.; Carballo, A.; Cano, A.M.; Narksri, P.; Wong, D.; Takeuchi, E.; Takeda, K. Performance Analysis of 10 Models of 3D LiDARs for Automated Driving. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 131699–131722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Z.; Cai, D.; He, X. CLRNet: Cross Layer Refinement Network for Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 898–907. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2022/html/Zheng_CLRNet_Cross_Layer_Refinement_Network_for_Lane_Detection_CVPR_2022_paper.html (accessed on 5 December 2022).


| Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|
| Simulation | 95.1% | 85.2% |
| Real-world | 91.1% | 76.3% |
| Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|
| Simulation | 76.3% | 53.5% |
| Real-world | 74.5% | 52.1% |
| 0.7 | 0.75 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simu | Real | Simu | Real | Simu | Real | Simu | Real | Simu | Real | Simu | Real | |
| precision | 0.802 | 0.751 | 0.829 | 0.773 | 0.862 | 0.832 | 0.883 | 0.853 | 0.885 | 0.856 | 0.886 | 0.859 |
| recall | 0.827 | 0.824 | 0.808 | 0.802 | 0.791 | 0.757 | 0.782 | 0.742 | 0.756 | 0.731 | 0.745 | 0.719 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Qiao, X.; Zhao, J.; Yin, P.; Zhou, J.; Li, B. High-Definition Map Change Regions Detection Considering the Uncertainty of Single-Source Perception Data. Machines 2025, 13, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13121080
Zhang Z, Li Q, Qiao X, Zhao J, Yin P, Zhou J, Li B. High-Definition Map Change Regions Detection Considering the Uncertainty of Single-Source Perception Data. Machines. 2025; 13(12):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13121080
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhihua, Qingjian Li, Xiangfei Qiao, Jun Zhao, Peng Yin, Jian Zhou, and Bijun Li. 2025. "High-Definition Map Change Regions Detection Considering the Uncertainty of Single-Source Perception Data" Machines 13, no. 12: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13121080
APA StyleZhang, Z., Li, Q., Qiao, X., Zhao, J., Yin, P., Zhou, J., & Li, B. (2025). High-Definition Map Change Regions Detection Considering the Uncertainty of Single-Source Perception Data. Machines, 13(12), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13121080







