Finite Speed-Set Model Reference Adaptive System Based on Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generators for Wind Turbines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Model
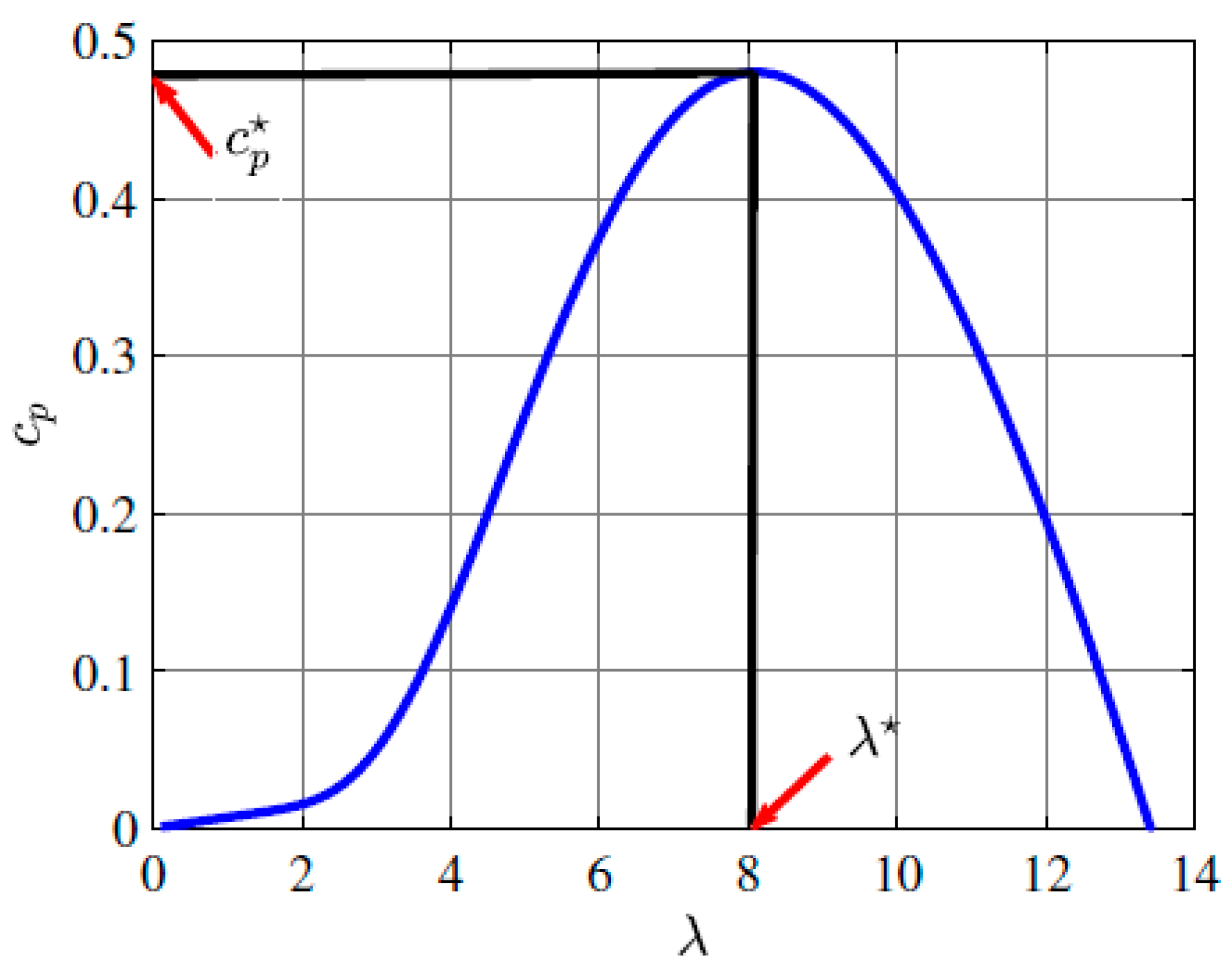
2.1. Wind Turbine Modeling
2.2. Modeling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
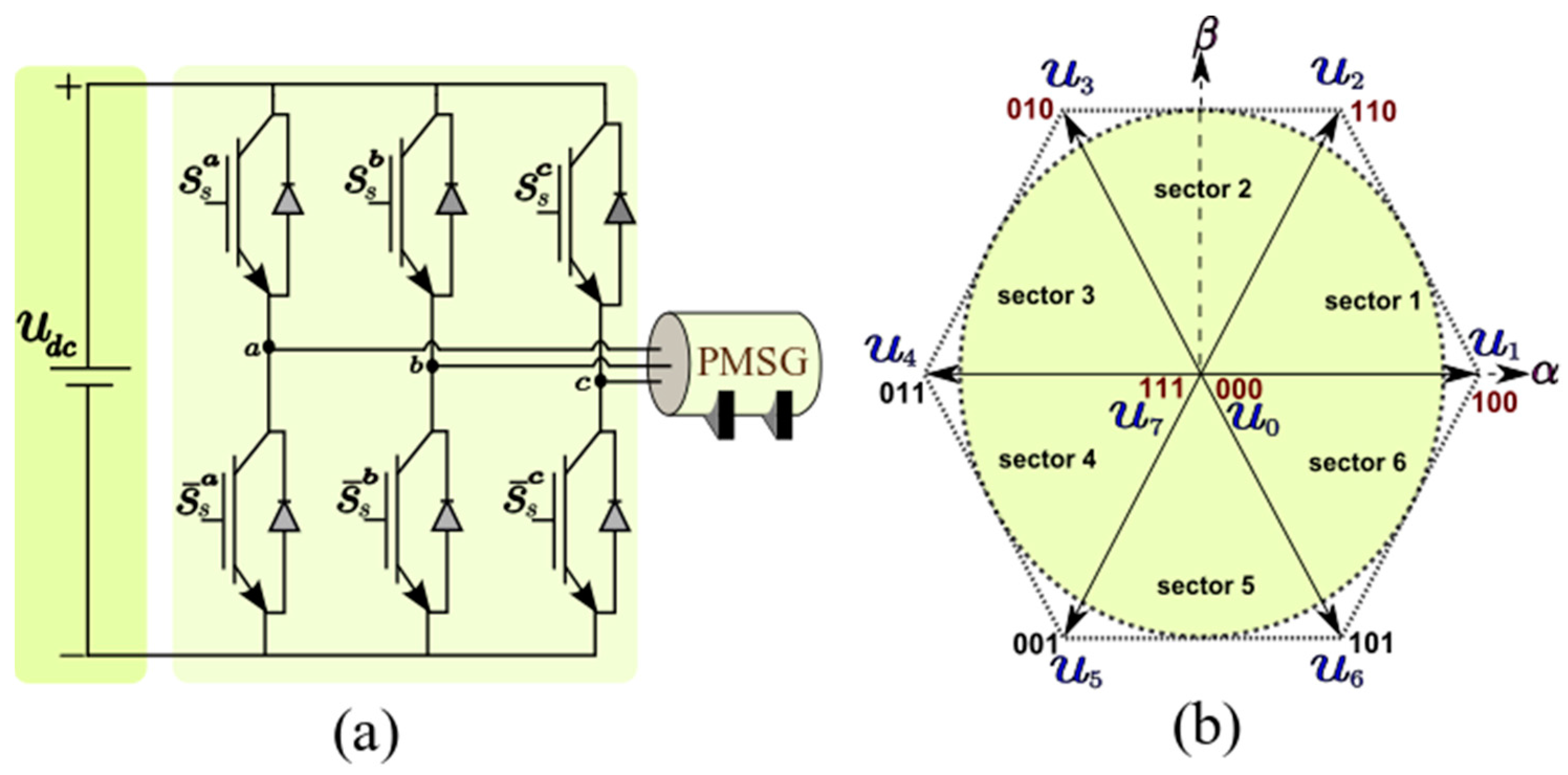
2.3. Inverter Model
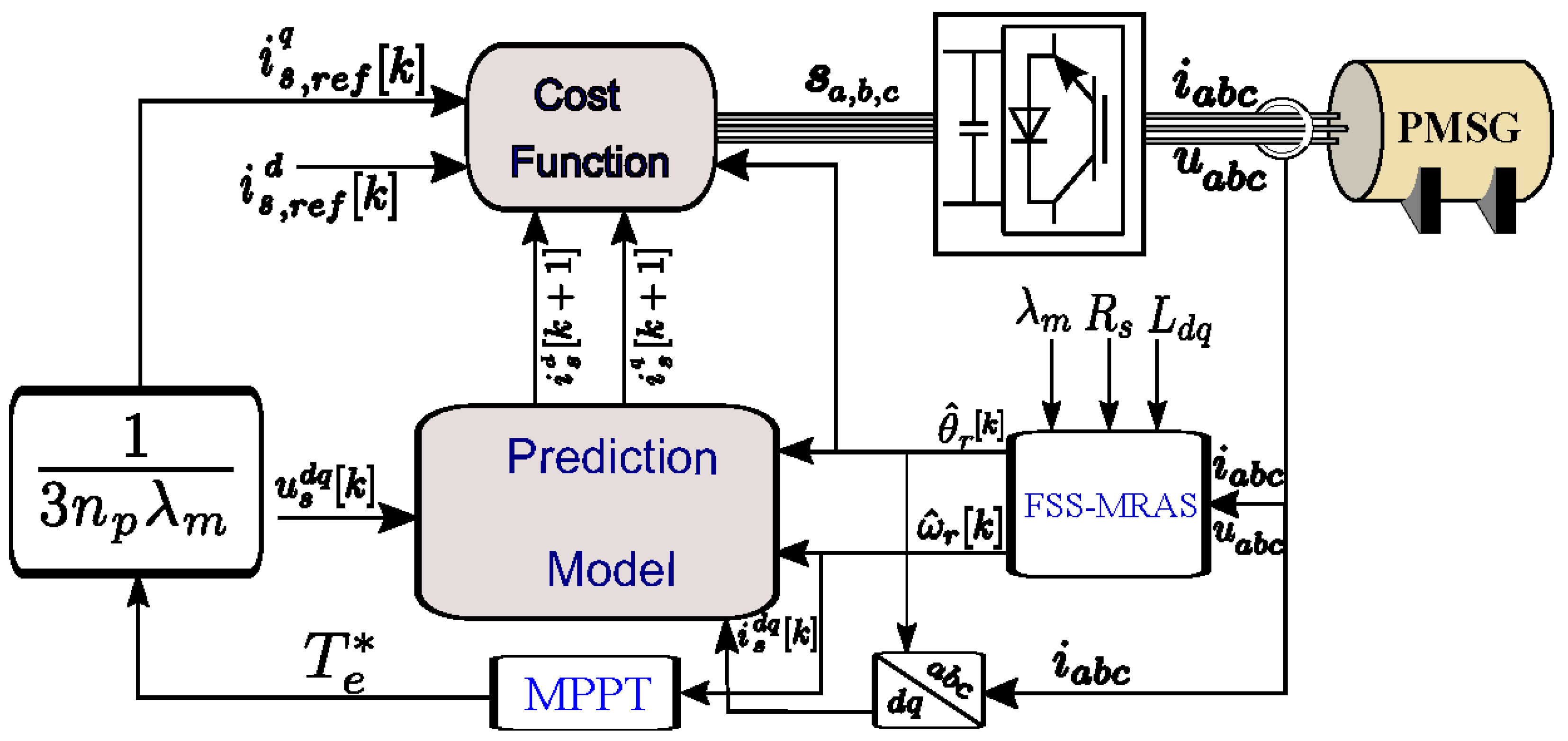
3. Current Predictive Control Finite Set of PMSG
4. Proposed and Traditional Observers
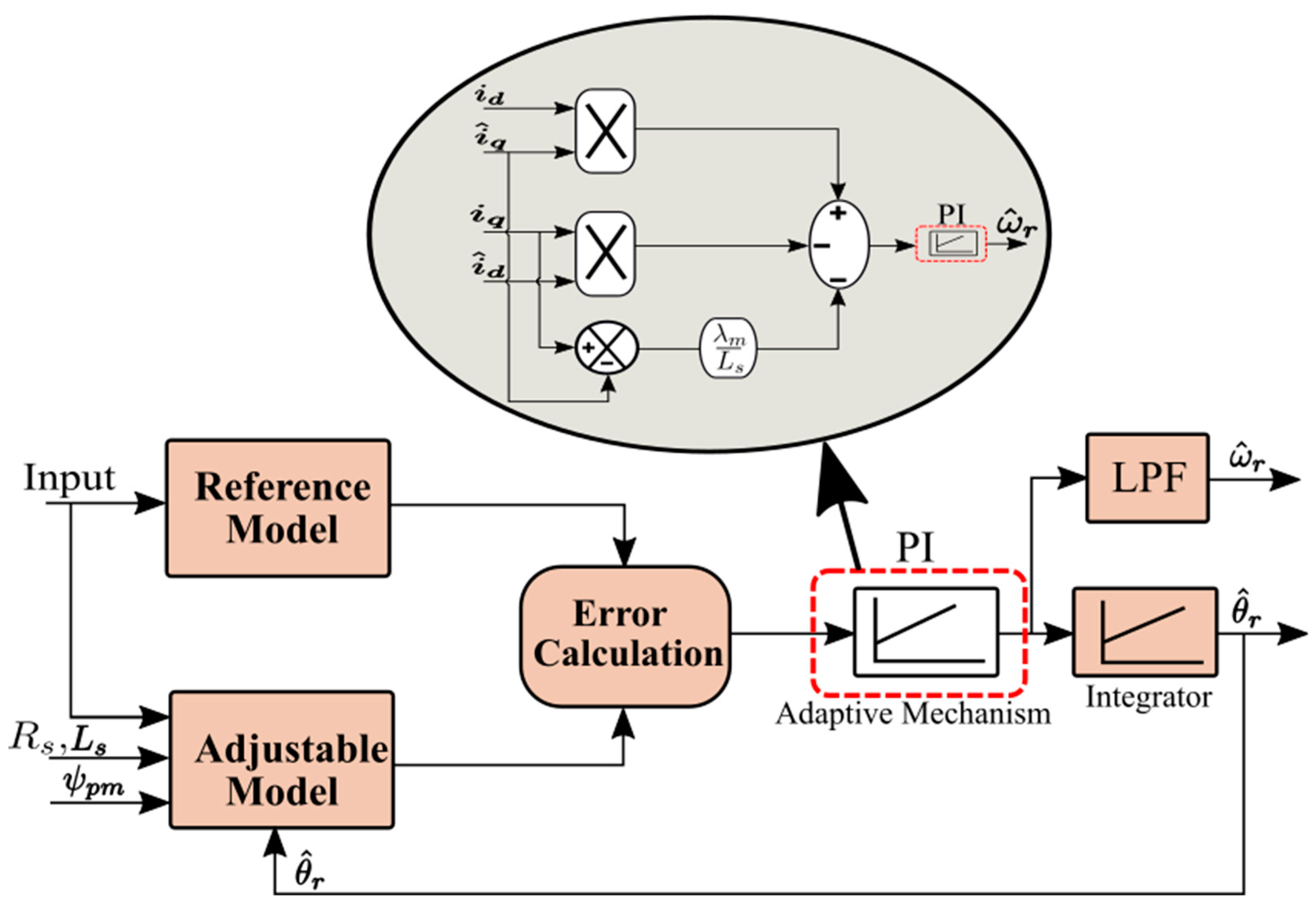
4.1. Traditional MRAS for PMSGs
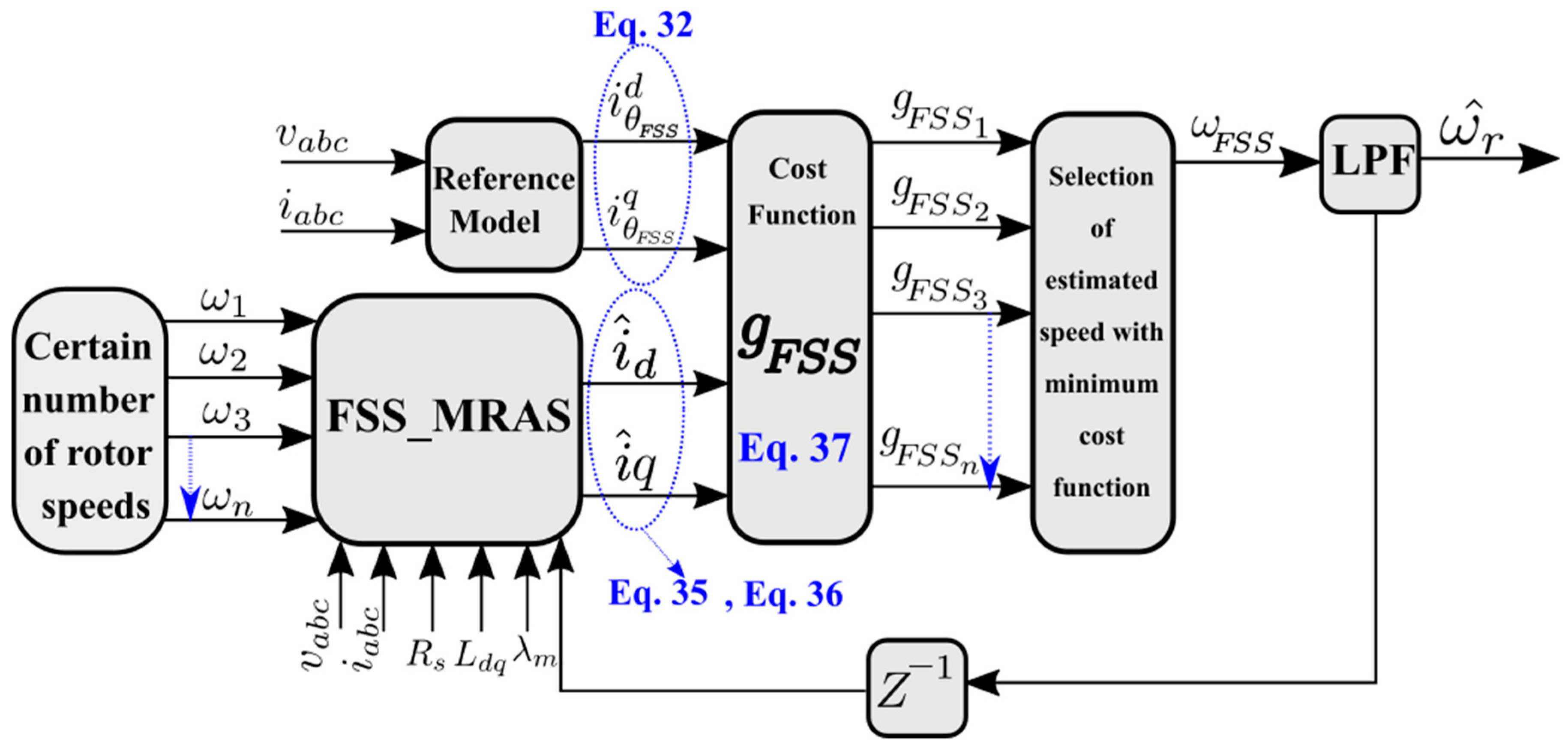
4.2. Proposed Finite Speed-Set MRAS (FSS-MRAS) of PMSGs
| Algorithm 1. Algorithm of the proposed FSS-MRAS | |
| Step 1 | Read |
| Step 2 | Transform to and using Equations (31) and (33) |
| Step 3 | Define the speed change direction (increasing or decreasing) Calculate the predicted position from Equation (30) Calculate from Equation (32) for both and Calculate from Equation (34) for both and Calculate from Equations (35) and (36) for both and Calculate the cost functions and from Equation (37) for both and respectively. Note: if then the right direction is increasing, else the right direction is decreasing. |
| Step 4 | If then Define the finite speed-set starting from the old speed in positive direction. For ( is the rated electrical angular speed) Calculate the predicted position from Equation (30) Calculate , from Equation (32) for Calculate , from Equation (34) for Calculate , from Equations (35) and (36) for If End If < accepted tolerance Break End End |
| elseif then Define the finite speed-set starting from the old speed in negative direction For Calculate the predicted position from Equation (30) Calculate , from Equation (32) for Calculate , from Equation (34) for Calculate , from Equations (35) and (36) for If End If accepted tolerance Break End End End | |
5. Simulation Results
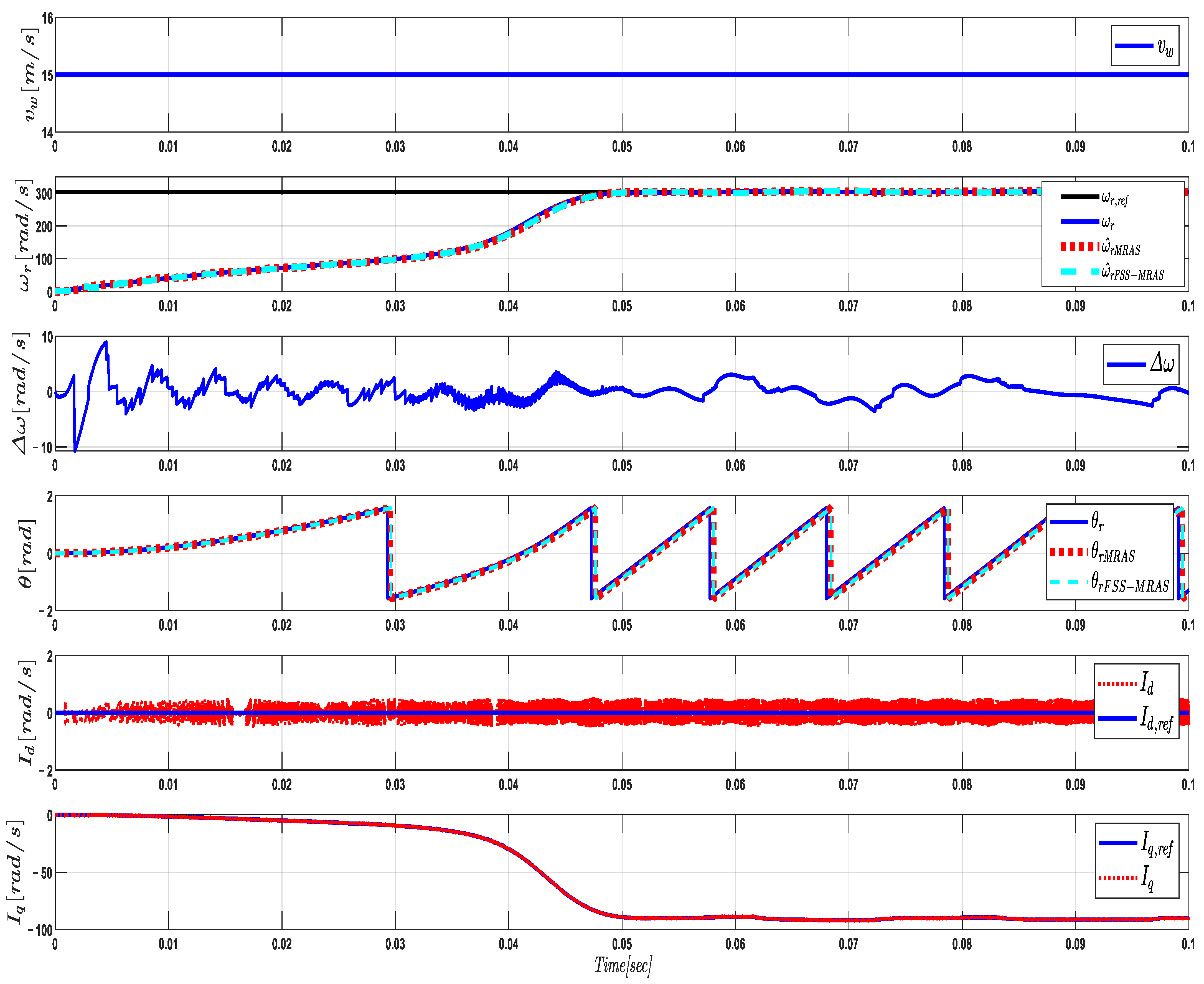
5.1. Response of the Proposed FSS-MRAS at Rated Wind Speed
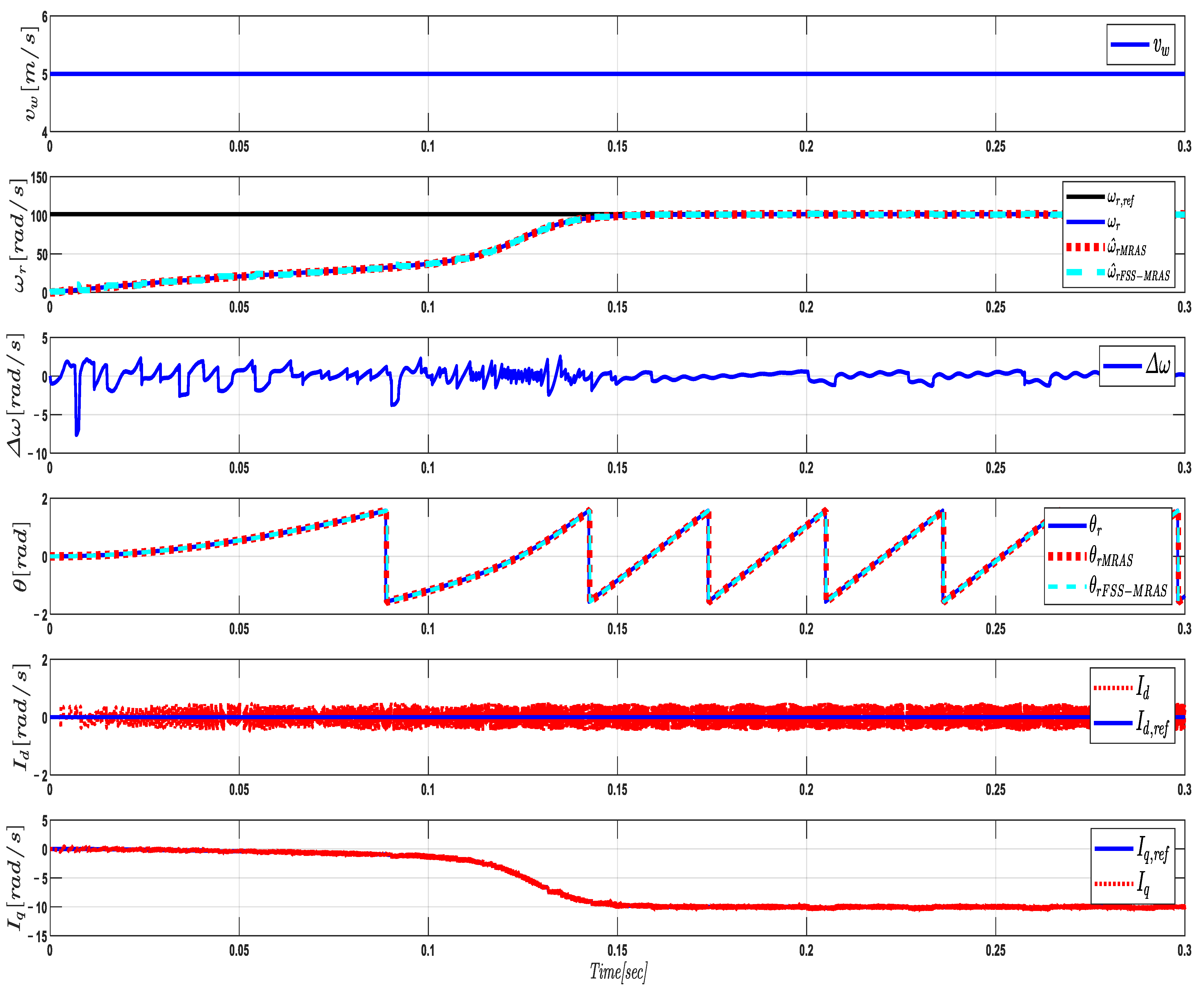
5.2. Response of the Proposed FSS-MRAS at Low Wind Speed
5.3. Response of the Proposed FSS-MRAS at Variant Wind Speeds
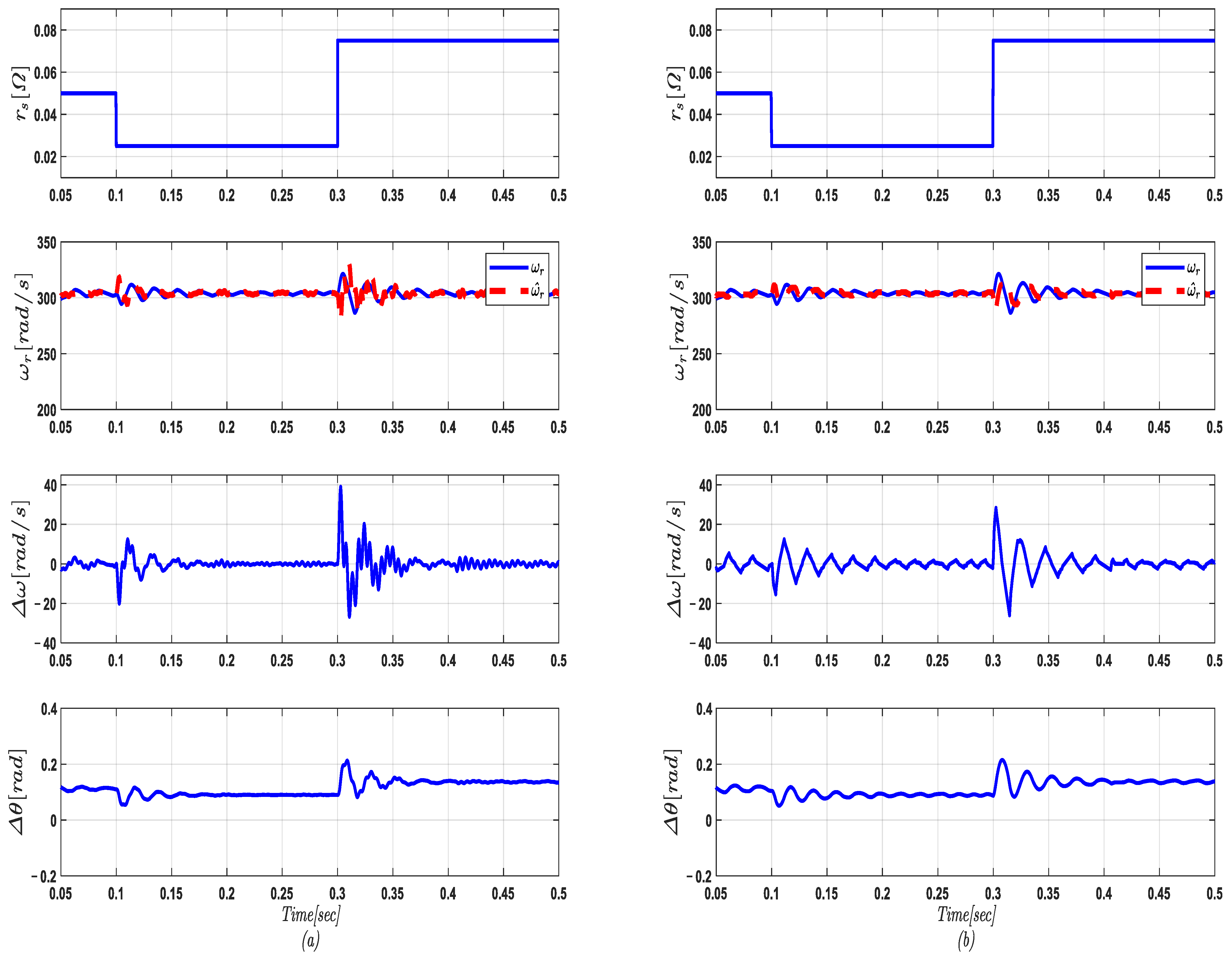
5.4. Response of the Proposed FSS-MRAS at Variations of PMSG Resistance
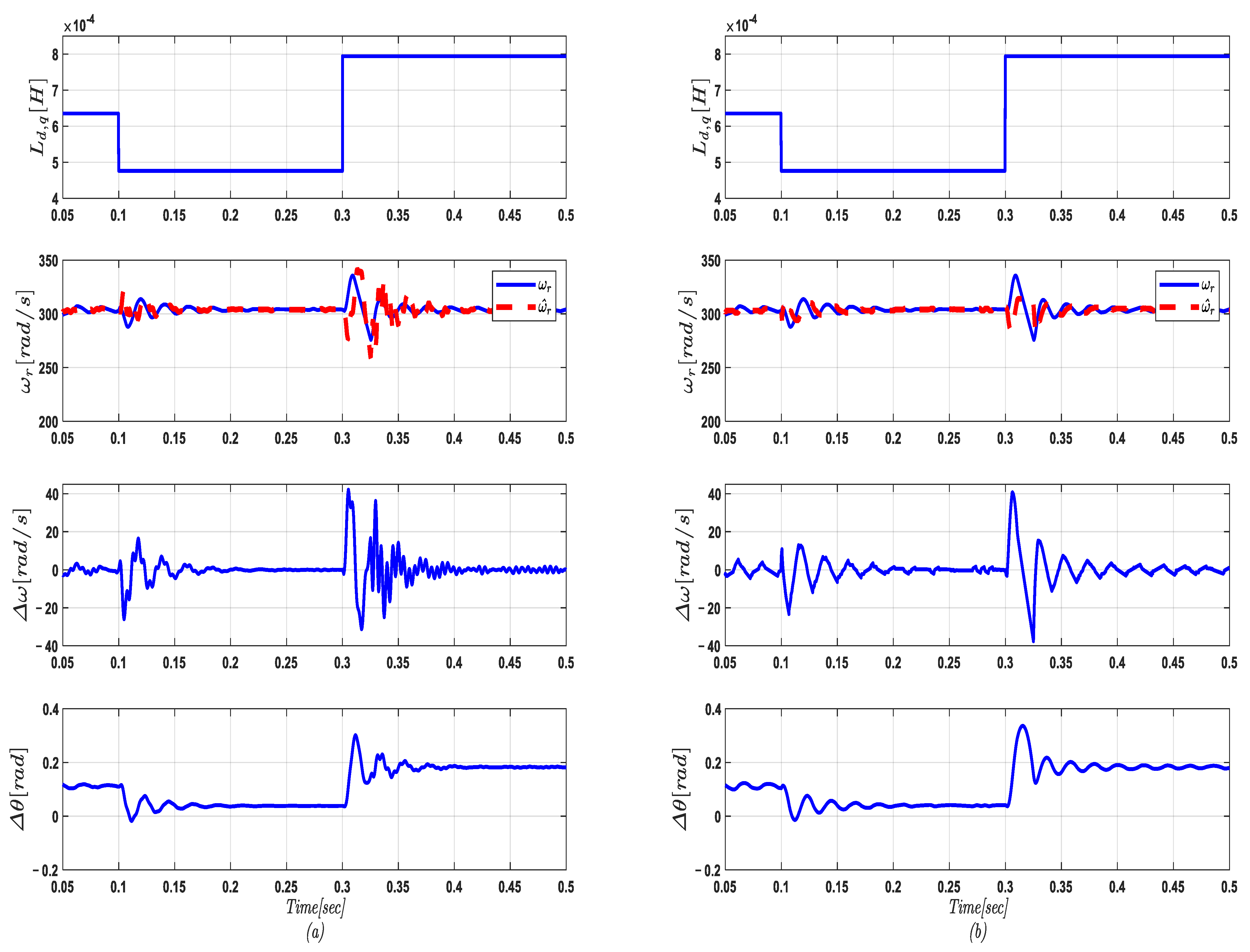
5.5. Response of the Proposed FSS-MRAS at Variations of PMSG Inductance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| PMSG | Permanent magnet synchronous generator |
| CPC | Current predictive control |
| MPC | Model predictive control |
| DFIG | Doubly fed induction generator |
| WES | Wind energy system |
| FOC | Field oriented control |
| PMSG | Permanent magnet synchronous generator |
| CS-MPC | Continuous-set model predictive control |
| FS-MPC | Finite-set model predictive control |
| EKF | Extended Kalman filter |
| SMO | Sliding mode observer |
| PLL | Phase locked loop |
| MRAS | Model reference adaptive system |
| FSS-MRAS | Finite speed-set model reference adaptive system |
References
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R. Model Predictive Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generators in Variable-Speed Wind Turbine Systems. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Student Summit (PESS 2016), Aachen, Germany, 19–20 January 2016; pp. 19–20. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:58979165 (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Datta, R.; Ranganathan, V.T. Variable-Speed Wind Power Generation Using Doubly Fed Wound Rotor Induction Machine-a Comparison with Alternative Schemes. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2002, 17, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Z. Overview of Different Wind Generator Systems and Their Comparisons. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2008, 2, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.; Nguyen, V.L.; Hossain, M.J.; To, A.N.; Tran, H.T.; Phan, T.N. Transient Responses of the Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Wind Turbine under Grid Fault Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Applications (ACOMP), Can Tho City, Vietnam, 23–25 November 2016; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zarei, M.E.; Ramirez, D.; Prodanovic, M.; Arana, G.M. Model Predictive Control for PMSG-Based Wind Turbines with Overmodulation and Adjustable Dynamic Response Time. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir Uddin, M.; Patel, N. Maximum Power Point Tracking Control of IPMSG Incorporating Loss Minimization and Speed Sensorless Schemes for Wind Energy System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.A.M. Testing the Performance of a Resolution-Level MPPT Controller for PMG-Based Wind Energy Conversion Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, D.; Tricarico, G.; Brescia, E.; Cascella, G.L.; Monopoli, V.G.; Cupertino, F. Variable Structure Control of a Small Ducted Wind Turbine in the Whole Wind Speed Range Using a Luenberger Observer. Energies 2020, 13, 4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.R.; Farhangi, S.; Rodriguez, J. Model Predictive Control of a Multilevel CHB STATCOM in Wind Farm Application Using Diophantine Equations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanakos, P.; Geyer, T. Guidelines for the Design of Finite Control Set Model Predictive Controllers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 7434–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zou, X.; Li, J. Sensorless Control Strategy of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Fuzzy Sliding Mode Observer. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 36743–36752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Nie, J.; Wei, H.-L.; Chen, L.; Li, X.-H.; Lv, M.-Y. Switched PI Control Based MRAS for Sensorless Control of PMSM Drives Using Fuzzy-Logic-Controller. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2022, 3, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.A.E.M.; Adel, M.M.; Taha, M.; Saleh, A.A. PSO Technique Applied to Sensorless Field-Oriented Control PMSM Drive with Discretized RL-Fractional Integral. Alexandria Eng. J. 2021, 60, 4029–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyong, Y.; Peie, Y.; Zhenguo, C.; Zhigang, C.; Zhengxi, L. A Novel Control Strategy of Power Converter Used to Direct Driven Permanent Magnet Wind Power Generation System. In Proceedings of the 2009 2nd International Conference on Power Electronics and Intelligent Transportation System (PEITS), Shenzhen, China, 19–20 December 2009; Volume 1, pp. 456–459. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, P.; Chang, Z. A Novel Fuzzy Logic and Anti-Windup PI Controller for a Rectifier with Direct Driven Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator. In Proceedings of the 2009 2nd International Conference on Power Electronics and Intelligent Transportation System (PEITS), Shenzhen, China, 19–20 December 2009; Volume 2, pp. 422–426. [Google Scholar]
- Shariatpanah, H.; Fadaeinedjad, R.; Rashidinejad, M. A New Model for PMSG-Based Wind Turbine with Yaw Control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, M.L.; Ippoliti, G.; Orlando, G. Robust Control of Variable-Speed Wind Turbines Based on an Aerodynamic Torque Observer. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benadja, M.; Chandra, A. Adaptive Sensorless Control of PMSGs-Based Offshore Wind Farm and VSC-HVdc Stations. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Kennel, R. Finite Position Set-Phase Locked Loop for Sensorless Control of Direct-Driven Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 3097–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Kennel, R.; Rodriguez, J. Computationally Efficient Finite-Position-Set-Phase-Locked Loop for Sensorless Control of PMSGs in Wind Turbine Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 3007–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Farhan, A.; Kennel, R. Finite-Set MRAS Observer for Encoderless Control of PMSGs in Wind Turbine Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Power Electronics and Renewable Energy (CPERE), Aswan City, Egypt, 23–25 October 2019; pp. 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R. Model Reference Adaptive System with Finite-Set for Encoderless Control of PMSGs in Micro-Grid Systems. Energies 2020, 13, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Kennel, R. Limited-Position Set Model-Reference Adaptive Observer for Control of DFIGs without Mechanical Sensors. Machines 2020, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeji, O.; Hannachi, M.; Benhamed, M.; Sbita, L. Artificial Neural Network—Based Sensorless Control of Wind Energy Conversion System Driving a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator. Wind Eng. 2021, 45, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Lang, Y.; Zargari, N.; Kouro, S. Power Conversion and Control of Wind Energy Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 76. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R. Robust Predictive Control Scheme for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generators Based Modern Wind Turbines. Electronics 2021, 10, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Dou, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, L. Model Predictive Virtual Synchronous Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator-Based Wind Power System. Energies 2020, 13, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.; Kennel, R.; Rodriguez, J. Sensorless Predictive Speed Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generators in Wind Turbine Applications. In Proceedings of the PCIM Europe 2019; International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nuremberg, Germany, 7–9 May 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Farhan, A.; Abdelrahem, M.; Saleh, A.; Shaltout, A.; Kennel, R. Simplified Sensorless Current Predictive Control of Synchronous Reluctance Motor Using Online Parameter Estimation. Energies 2020, 13, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Kennel, R.; Shaltout, A.; Saleh, A. Advanced Strategy of Speed Predictive Control for Nonlinear Synchronous Reluctance Motors. Machines 2020, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Abdelrahem, M.; Saleh, A.; Shaltout, A.; Kennel, R. Robust Sensorless Direct Speed Predictive Control of Synchronous Reluctance Motor. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 29th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Delft, The Netherlands, 17–19 June 2020; pp. 1541–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Farhan, A.; Abdelrahem, M.; Shaltout, A.; Kennel, R.; Saleh, A. Encoderless Current Predictive Control of Synchronous Reluctance Motor by Extended Kalman Filter Based State Estimation. In Proceedings of the PCIM Europe Digital Days 2020; International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nuremburg, Germany, 7–8 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Farhan, A.; Saleh, A.; Abdelrahem, M.; Kennel, R.; Shaltout, A. High-Precision Sensorless Predictive Control of Salient-Pole Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based-on Extended Kalman Filter. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, 17–19 December 2019; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, R. Speed-Sensorless Predictive Current Controlled PMSM Drive with Adaptive Filtering-Based MRAS Speed Estimators. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 2577–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, M.M.; Saleh, A.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Kennel, R.; Farhan, A. Efficient Sensorless Speed Predictive Control Without Weighting Factors for PMSM Drive Based on MRAS Estimator. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2024, 27, 3697–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Machine Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Wind turbine radius (m) | 1.6 |
| Rated wind speed (m/s) | 15 |
| Air density (kg/m3) | 1.22 |
| 8.11 | |
| ) | 0.48 |
| 0 | |
| Magnetic pole pairs | 4 |
| Rated speed (rpm) | 3000 |
| Inertia J (kg·m2) | 0.011 |
| Viscous damping coefficient B (N·m·s/rad) | 0.001889 |
| Stator resistance rs (Ω) | 0.05 |
| flux linkage Ψf (wb) | 0.192 |
| Stator inductance (Ld = Lq) (H) | 0.000635 |
| Traditional MRAS | FSS-MRAS | |
|---|---|---|
| Tracking Response | accurate | Accurate |
| Speed steady state error | zero | Zero |
| change | Accurate (low ripples) 10% overshoot | more accurate (lower ripples) (7% overshoot) |
| change | Accurate (low ripples) 11% overshoot | more accurate (lower ripples) (9% overshoot) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, M.A.; Adel, M.M.; Farhan, A.; Saleh, A.A. Finite Speed-Set Model Reference Adaptive System Based on Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generators for Wind Turbines. Machines 2024, 12, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12070429
Hassan MA, Adel MM, Farhan A, Saleh AA. Finite Speed-Set Model Reference Adaptive System Based on Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generators for Wind Turbines. Machines. 2024; 12(7):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12070429
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Mohammed A., Mahmoud M. Adel, Ahmed Farhan, and Amr A. Saleh. 2024. "Finite Speed-Set Model Reference Adaptive System Based on Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generators for Wind Turbines" Machines 12, no. 7: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12070429
APA StyleHassan, M. A., Adel, M. M., Farhan, A., & Saleh, A. A. (2024). Finite Speed-Set Model Reference Adaptive System Based on Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generators for Wind Turbines. Machines, 12(7), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12070429






