Design and Optimization of a Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Exploiting the Fundamental and Third Harmonic
Abstract
1. Introduction
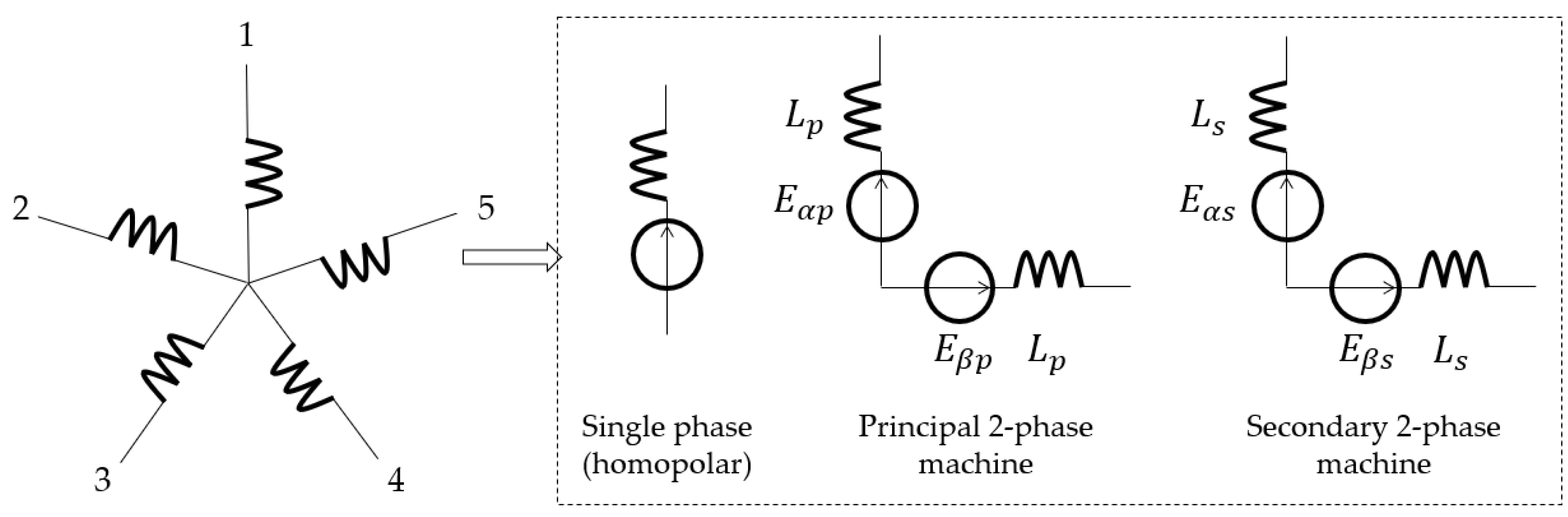
2. Analytical Modeling
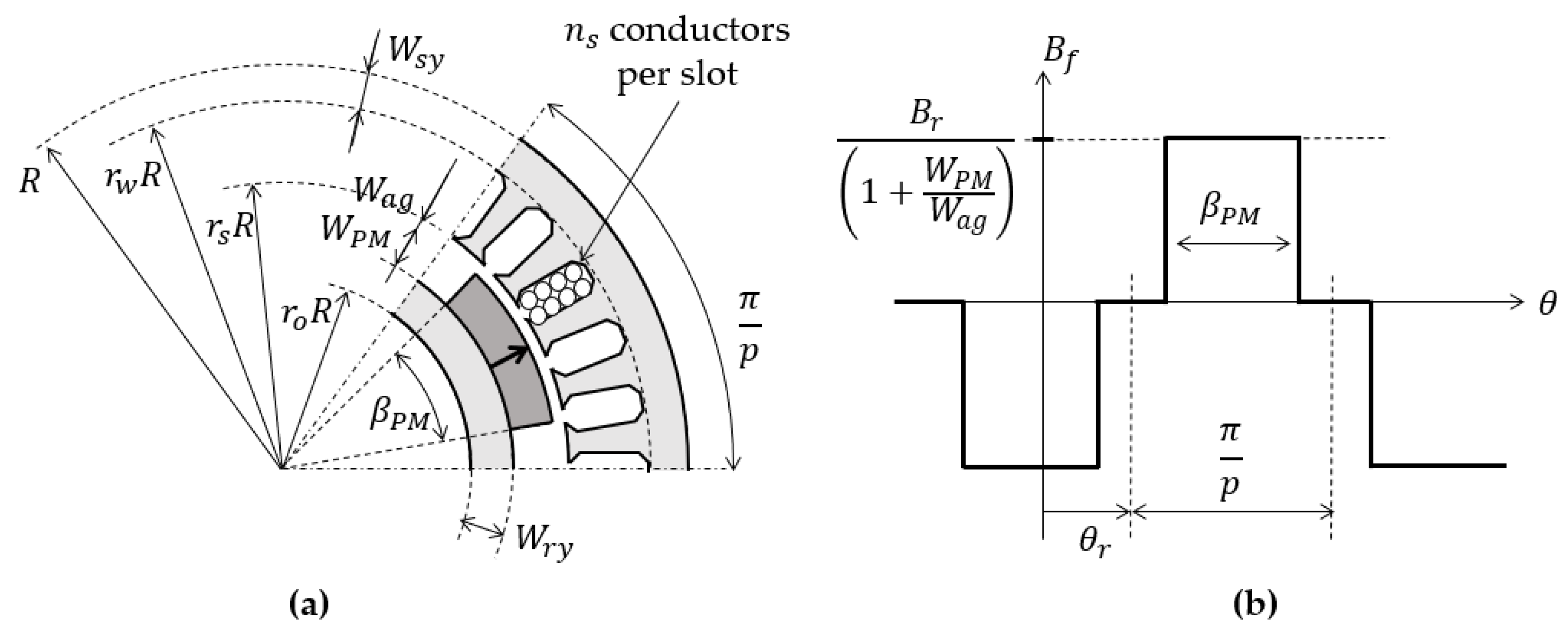
2.1. Magnetic Model of the PMSM
2.1.1. Flux Densities
2.1.2. Torque
2.2. Loss Model
2.2.1. Copper Losses
2.2.2. Iron Losses
2.3. Constraints
2.3.1. Mechanical Constraints
2.3.2. Electrical Constraints
2.3.3. Saturation Constraints
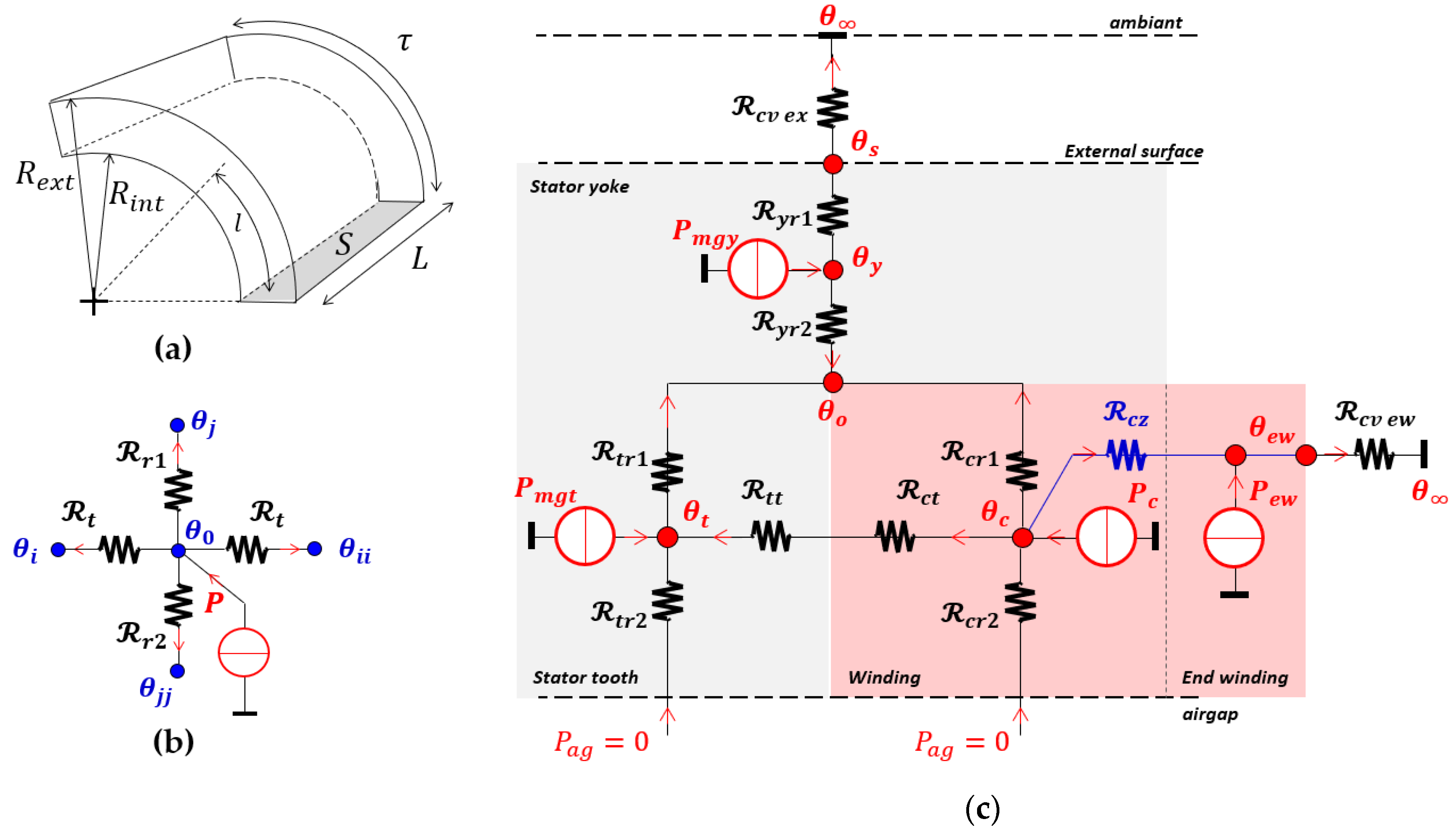
2.3.4. Thermal Constraints
3. Optimization
3.1. Constant Parameters
3.2. Results
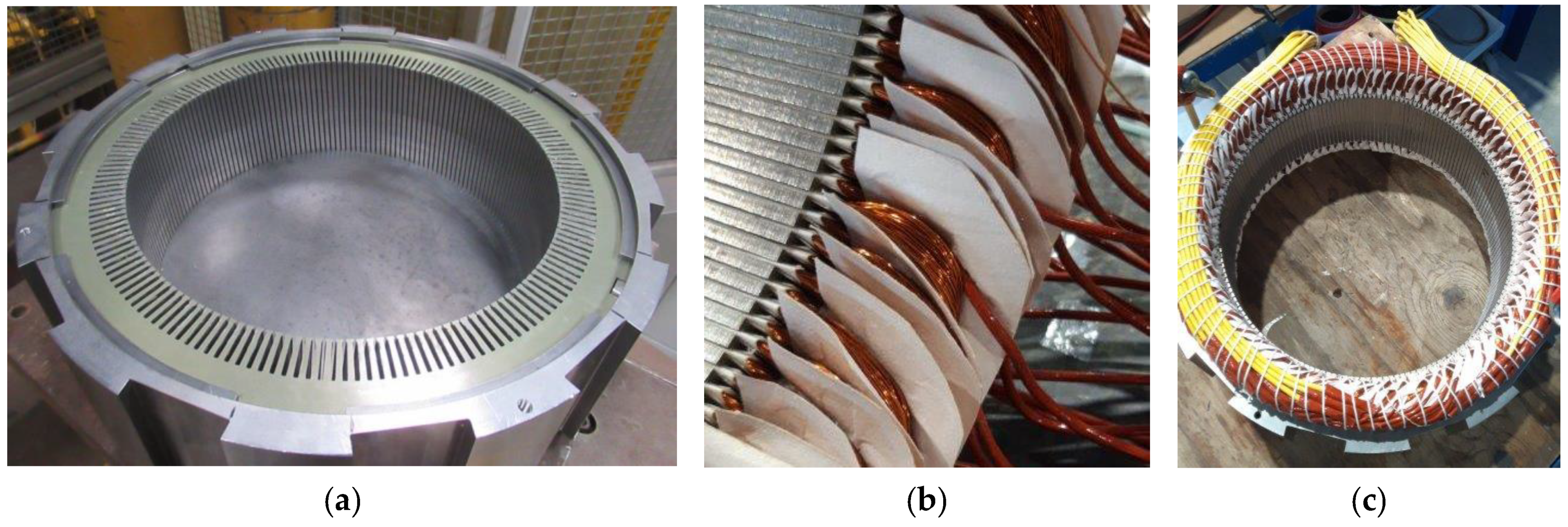
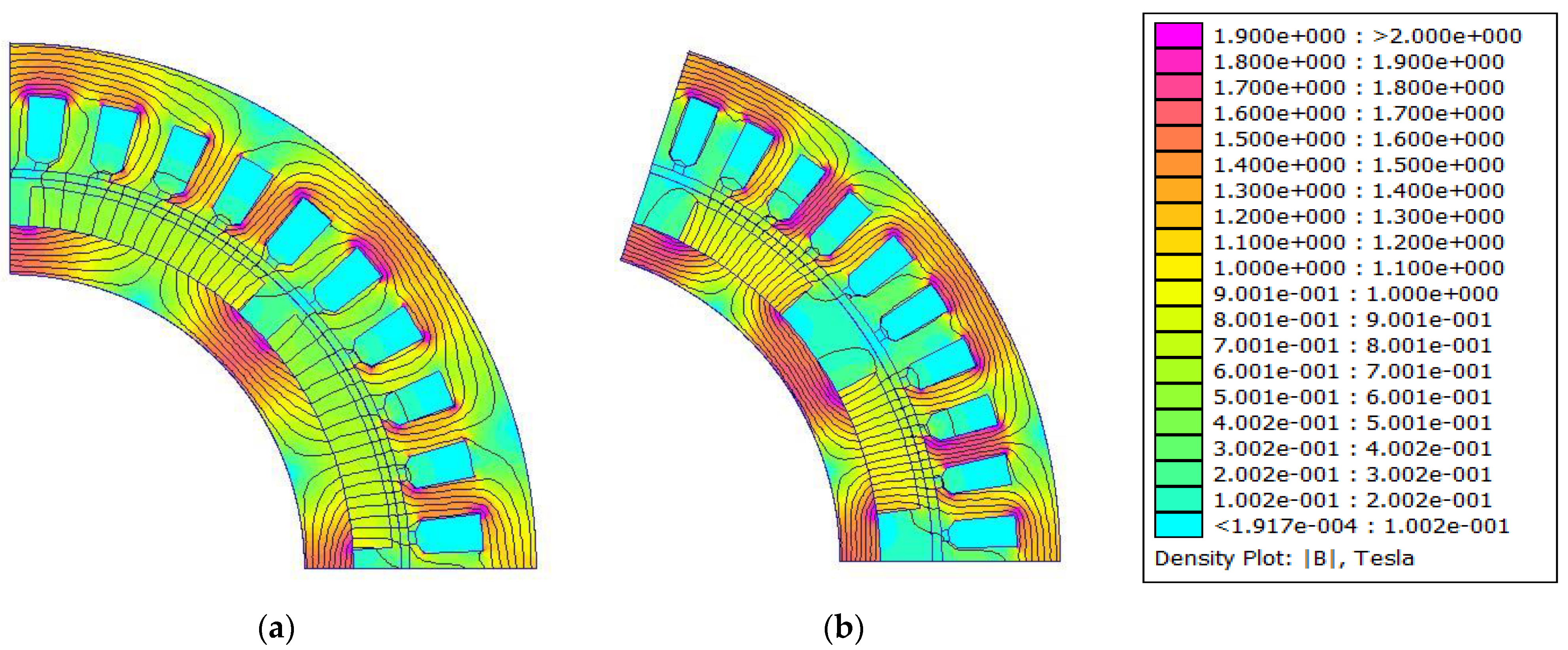
4. FE Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A | area of the cylinder [m2] |
| [deg] | |
| electromotive force of a phase k for an harmonic of rank h [V] | |
| electromotive force projected on the axis [V] | |
| electromotive force projected on the axis [V] | |
| electromotive force projected on the axis [V] | |
| electromotive force projected on the axis [V] | |
| frequency [Hz] | |
| distribution of the harmonic electro-magnetomotive force | |
| harmonic rank | |
| convection heat coefficient [W/m2K] | |
| additional iron loss coefficient | |
| tooth-opening-to--slot-pitch ratio | |
| coefficient for correcting the active length | |
| hysteresis specific loss coefficient | |
| active length [m] | |
| end-winding length [m] | |
| self-inductance [H] | |
| cyclic inductance of the main machine [H] | |
| cyclic inductance of the secondary machine [H] | |
| mass of the copper [kg] | |
| mass of permanent magnet [kg] | |
| mass of the rotor yoke [kg] | |
| mass of the stator teeth [kg] | |
| mass of the stator yoke [kg] | |
| copper losses [W] | |
| end-winding losses [W] | |
| iron losses in the stator teeth [W] | |
| iron losses in the stator yoke [W] | |
| total losses of the machine [W] | |
| outer stator radius [m] | |
| copper resistance [] | |
| end-winding resistance [] | |
| radial thermal resistance [m2K/W] | |
| orthoradial thermal resistance [m2K/W] | |
| axial thermal resistance [m2K/W] | |
| convection thermal resistance [m2K/W] | |
| external reduced radius | |
| internal reduced radius | |
| S | rectangular cross-section [m2] |
| slot cross-section [m2] | |
| voltage limit [V] | |
| [m] | |
| [m] | |
| [m] | |
| minimum width of the yoke [m] | |
| of slots | |
| [N/A2] | |
| conductivity of the material [S/m] | |
| [deg] | |
| machine mechanical angular velocity [rad/s] | |
| material conductivity [S/m] | |
| ambient temperature [°C] | |
| maximal permissible temperature [°C] | |
| cylinder angle [deg] | |
| ration between the third-harmonic current and the first-harmonic current |
References
- Bouyahia, O.; Yazidi, A.; Betin, F. Experimental Comparison of Robust Control Algorithms for Torque Ripple Reduction in Multiphase Induction Generators. Energies 2023, 16, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwly, M.Y.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Hamad, M.S.; Ahmed, S.; Elmalhy, N.A. Multiphase Stator Winding: New Perspectives, Advanced Topologies, and Futuristic Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 103241–103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, A.G.; Lopez, O.; Gonzalez-Prieto, I.; Duran, M.J.; Doval-Gandoy, J. A Comprehensive Survey on Fault Tolerance in Multiphase AC Drives, Part 1: General Overview Considering Multiple Fault Types. Machines 2022, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, A.G.; Gonzalez-Prieto, I.; Lopez, O.; Duran, M.J.; Doval-Gandoy, J. A Comprehensive Survey on Fault Tolerance in Multiphase AC Drives, Part 2: Phase and Switch Open-Circuit Faults. Machines 2022, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekri, F.; Ben Elghali, S.; Benbouzid, M.E.H. Fault-Tolerant Control Performance Comparison of Three- and Five-Phase PMSG for Marine Current Turbine Applications. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.; Samb, S.O.; Sadou, R.; Bernard, N. Bernard, Co-Design Optimization of Direct Drive PMSGs for Offshore Wind Turbines Based on Wind Speed Profile. Energies 2021, 14, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, B. Design and Analysis of a Five-Phase Fault-Tolerant Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Aerospace Starter-Generator System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 135040–135049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahr, H.; Semail, E.; Aslan, B.; Scuiller, F. Maximum Torque Per Ampere strategy for a biharmonic five-phase synchronous machine. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Capri, Italy, 22–24 June 2016; pp. 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuiller, F.; Semail, E.; Charpentier, J.-F.; Letellier, P. Multi-criteria-based design approach of multi-phase permanent magnet low-speed synchronous machines. Electric Power Applications. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2009, 3, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervone, A.; Slunjski, M.; Levi, E.; Brando, G. Optimal Third-Harmonic Current Injection for Asymmetrical Multiphase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2772–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajaku, A.; Gerling, D. Analysis of a Five Phase PMSM with Third Harmonic Injection. In Proceedings of the IECON 2023-49th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Singapore, 16–19 October 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, F.; Duran, M.J. Recent Advances in the Design, Modeling, and Control of Multiphase Machines—Part I. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, M.J.; Barrero, F. Recent Advances in the Design, Modeling, and Control of Multiphase Machines—Part II. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.; Martín, C.; González-Prieto, I.; Durán, M.J.; Arahal, M.R.; Barrero, F. Predictive current control in electrical drives: An illustrated review with case examples using a five-phase induction motor drive with distributed windings. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 1291–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, B.; Zhao, T.; Cheng, Y.; Cui, S. Third-Harmonic Current Injection Control of Five-Phase Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Third-Harmonic Current Reference Online Identification. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 41840–41847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zahr, H.; Semail, E.; Trabelsi, M.; Aslan, B.; Scuiller, F. Design Considerations of Five-Phase Machine With Double p/3p Polarity. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, N.; Dang, L.; Moreau, L.; Bourguet, S. A Pre-Sizing Method for Salient Pole Synchronous Reluctance Machines with Loss Minimization Control for a Small Urban Electrical Vehicle Considering the Driving Cycle. Energies 2022, 15, 9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semail, E.; Meibody-Tabar, F.; Benkhoris, M.F.; Razik, H.; Pietrzak-David, M.; Monmasson, E.; Bouscayrol, A.; Davat, B.; Delarue, P.; de Fornel, B.; et al. Machines polyphasées: De la modélisation multimachine à la commande. J3eA 2005, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semail, E.; Meibody-Tabar, F.; Benkhoris, M.F.; Razik, H.; Pietrzak-David, M.; Monmasson, E.; Bouscayrol, A.; Davat, B.; Delarue, P.; Hautier, J.P.; et al. Représentations systèmes multimachines (SMM) de machines polyphasées. Rev. Int. Génie Électr. 2005, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klingshirn, E.A. Harmonic Filters for Six-Phase and Other Multiphase Motors on Voltage Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1984, IA-21, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortescue, C.L. Method of Symmetrical Co-Ordinates Applied to the Solution of Polyphase Networks. In Proceedings of the Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 28 June 1918; Volume 37, pp. 1027–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samb, S.O.; Bernard, N.; Benkhoris, M.F.; Bui, H.K. Design Optimization of a Direct-Drive Electrically Excited Synchronous Generator for Tidal Wave Energy. Energies 2022, 15, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.; Slemon, G.; Bonert, R. Modeling of iron losses of permanentmagnet synchronous motor. Industry Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmyrek, Z.; Boglietti, A.; Cavagnino, A. Estimation of Iron Losses in Induction Motors: Calculation Method, Results, and Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, T.G.; Kwon, S.O.; Hong, J.P. Vibration analysis according to stator shape design in a PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 10–13 October 2010; pp. 1235–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Fall, O.; Charpentier, J.F.; Nguyen, N.K.; Letellier, P.; Semail, E.; Kestelyn, X. Variable speed Control under Voltage and Current Limits of a 5-phase PMSM drive in Healthy and Open-Circuited Modes. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 140, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, R.; Mellor, P.H. A General Cuboidal Element for Three-Dimensional Thermal Modelling. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 3197–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bilgin, B.; Kasprzak, M.; Nalakath, S.; Sadek, H.; Preindl, M.; Cotton, J.; Schofield, N.; Emadi, A. Thermal Management of Electric Machines. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2016, 7, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Barranco, A.; Lopez-De-Heredia, A.; Villar, I.; Briz, F. Modeling of End-Space Convection Heat-Transfer for Internal and External Rotor PMSMs With Fractional-Slot Concentrated Windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonna, V.; Walker, A.; Giangrande, P.; Serra, G.; Gerada, C.; Galea, M. Improved Thermal Management and Analysis for Stator End-Windings of Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5057–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. Evolutionary Computation. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB Code for Constrained NSGA II—Dr.S.Baskar, S. Tamilselvi and P.R.Varshini. Available online: https://fr.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/49806-matlab-code-for-constrained-nsga-ii-dr-s-baskar-s-tamilselvi-and-p-r-varshini (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Akay, A.; Lefley, P. Torque Ripple Reduction Method in a Multiphase PM Machine for No-Fault and Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Conditions. Energies 2021, 14, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Husain, I.; Fardoun, A.; McLaughlin, K. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Magnet Designs with Skewing for Torque Ripple and Cogging Torque Reduction. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Industry Applications Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–27 September 2007; pp. 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Ombach, G.; Chlebosz, W. Optimal rotor shape with third harmonic for maximizing torque and minimizing torque ripple in IPM motors. In Proceedings of the 2012 XXth International Conference on Electrical Machines, Marseille, France, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
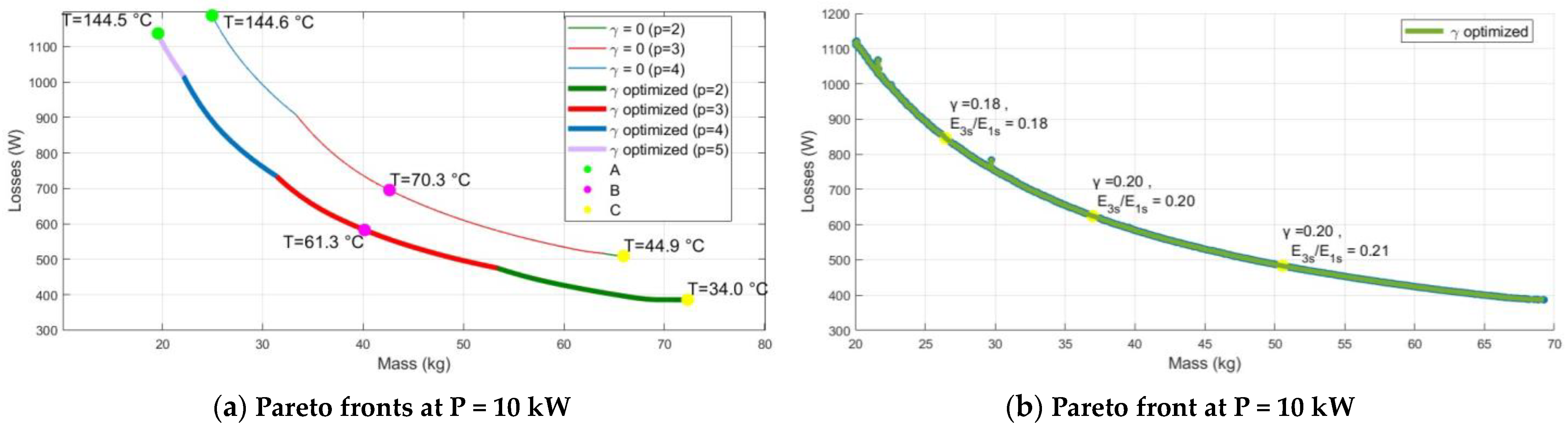
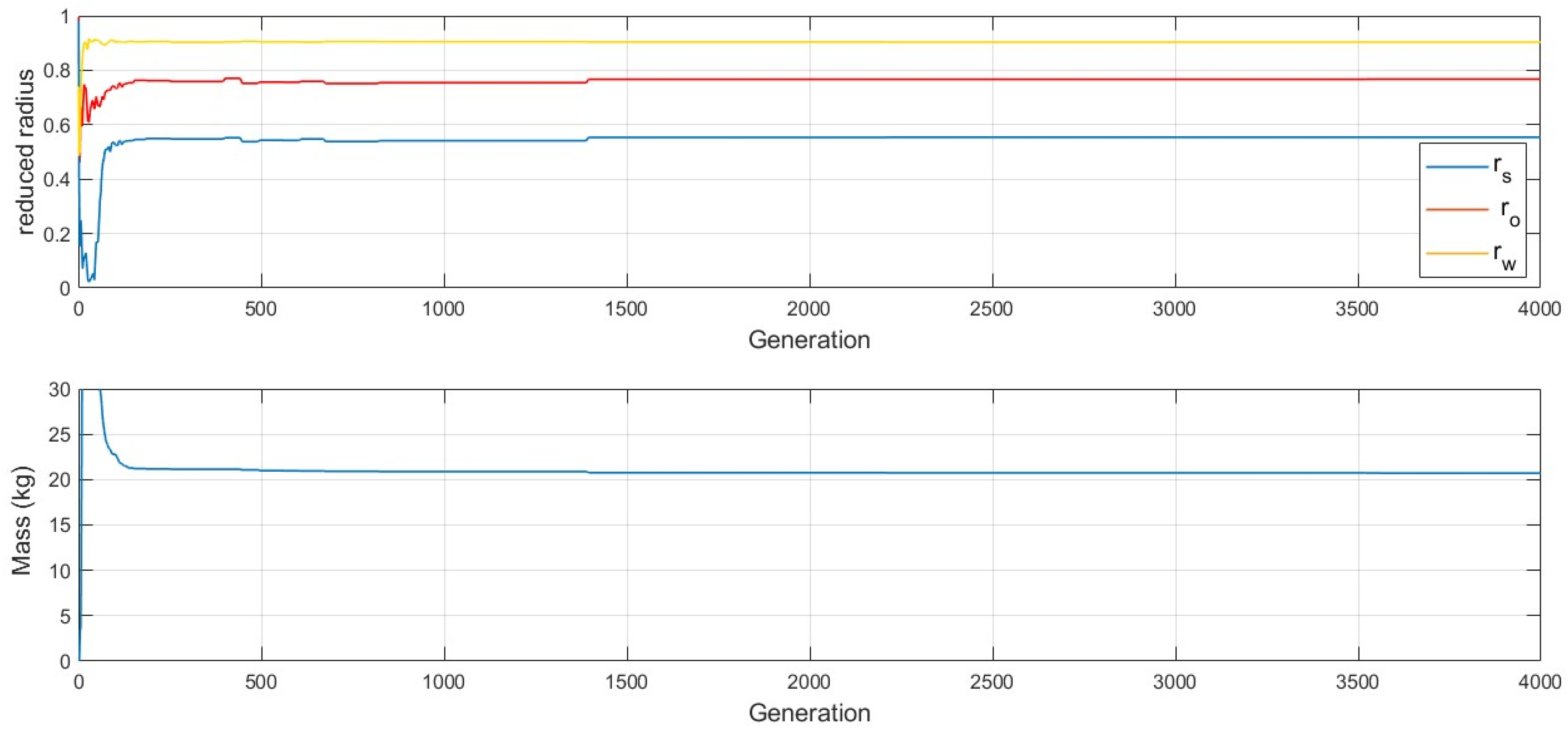
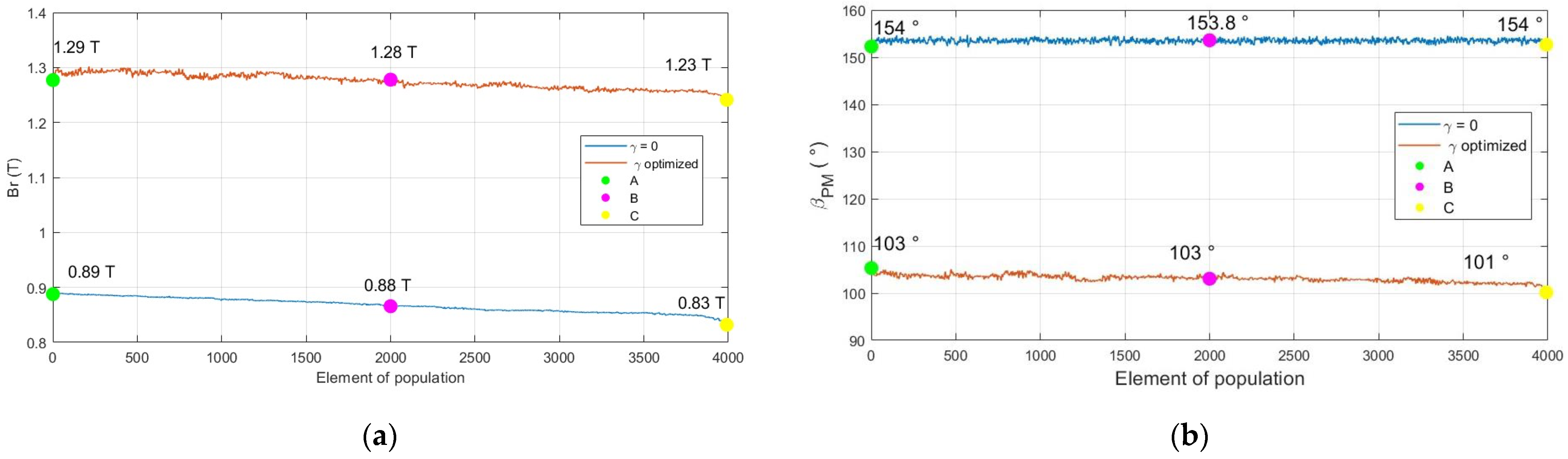
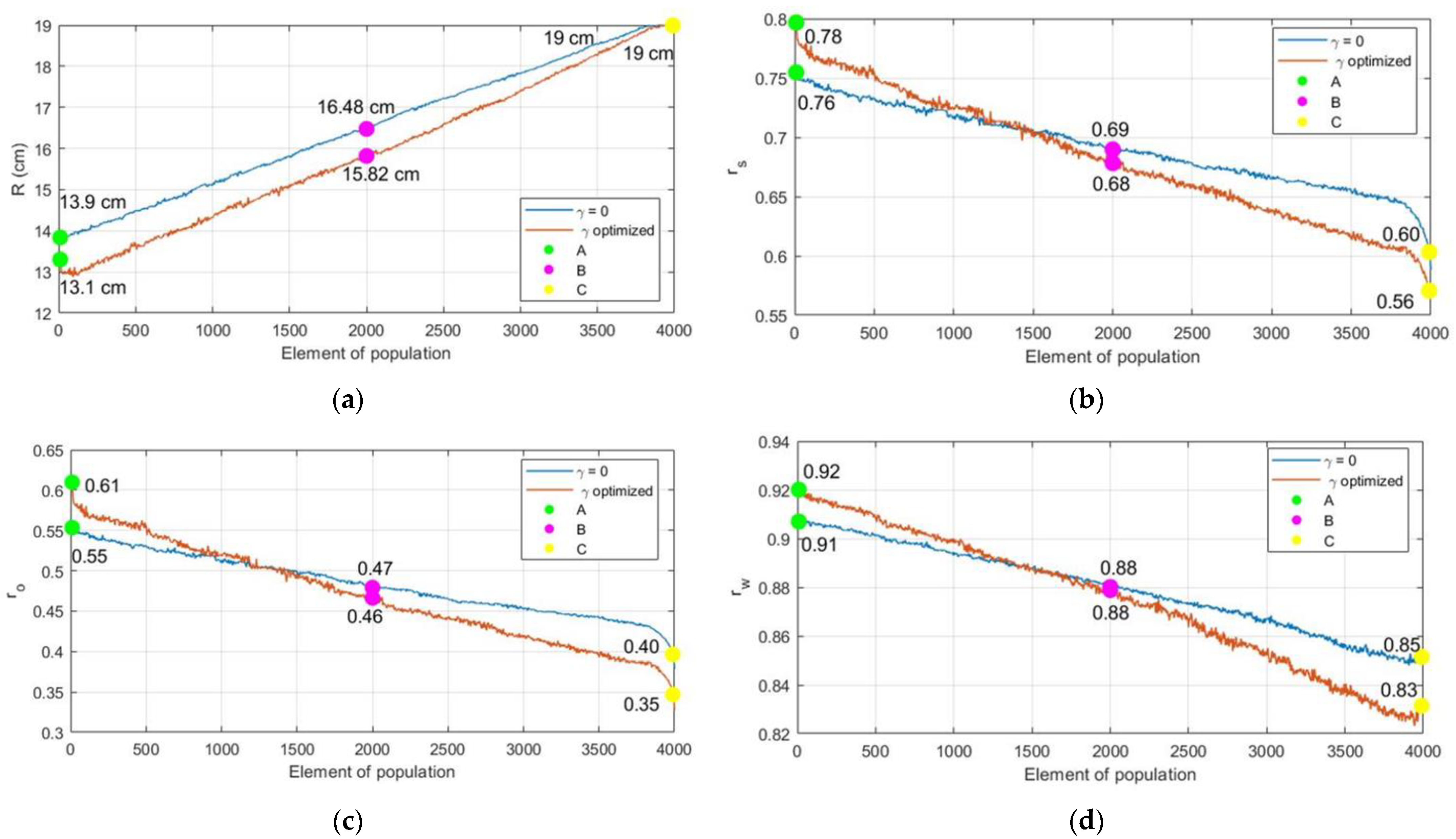
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| 3/7 | |
| 0.5 | |
| 9.5 cm | |
| 19 cm | |
| 400 tr/min | |
| 0.5 | |
| 8900 | |
| 7800 | |
| 7400 | |
| 59 × | |
| 1.2 | |
| 2 | |
| 0.0019 | |
| 8.33 × 10−7 | |
| 5 W/m K | |
| 25 W/m K | |
| 25 °C | |
| 100 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Population size | 4000 |
| Number of generations | 4000 |
| Distribution index for crossover | 20 |
| Distribution index for mutation | 50 |
| Mass Minimized | Loss Minimized | Combined Objectives | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal Parameters | ||||||
| p | 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | ||
| R (cm) | 13.9 | 13.1 | 19 | 19 | 16.5 | 15.8 |
| 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.6 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.68 | |
| 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 0.88 | |
| 0.61 | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.46 | |||
| (deg) | 103 | 154 | 101 | 103 | ||
| (mm) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| (T) | 0.89 | 1.29 | 0.83 | 1.23 | 0.88 | 1.28 |
| 0 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.21 | |
| Mass Minimized | Loss Minimized | Combined Objectives | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass (kg) | 20 | 66 | 67 | 34 | ||
| Total losses (kW) | 1.2 | 1.12 | 0.49 | 0.39 | 0.74 | 0.66 |
| Copper losses (kW) | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.49 | 0.44 |
| Iron losses (kW) | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.22 |
| (T) | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.34 | 1.36 | 1.5 | 1.51 |
| 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | |
| (A) | 9.87 | 11.45 | 9.23 | 11.68 | 10.2 | 11.32 |
| (A) | 9.87 | 11.21 | 9.23 | 11.32 | 10.2 | 11.1 |
| (A) | 0 | 2.25 | 0 | 2.89 | 0 | 2.22 |
| 102 | 68 | 198 | 166 | 130 | 107 | |
| Cases | Quantity | Analytical Model | FE | Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 238 | 1.7% | |||
| (T) | 1.6 | 1.53 | 4.4% | |
| (T) | 1.6 | 1.54 | 3.7% | |
| Torque ripple (%) | - | 3.14 | - | |
| 238 | 3.3% | |||
| (T) | 1.6 | 1.57 | 1.2% | |
| (T) | 1.6 | 1.65 | 3.1% | |
| Torque ripple (%) | - | 3.2 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oukrid, M.; Bernard, N.; Benkhoris, M.-F.; Ziane, D. Design and Optimization of a Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Exploiting the Fundamental and Third Harmonic. Machines 2024, 12, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12020117
Oukrid M, Bernard N, Benkhoris M-F, Ziane D. Design and Optimization of a Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Exploiting the Fundamental and Third Harmonic. Machines. 2024; 12(2):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12020117
Chicago/Turabian StyleOukrid, Mouna, Nicolas Bernard, Mohamed-Fouad Benkhoris, and Djamel Ziane. 2024. "Design and Optimization of a Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Exploiting the Fundamental and Third Harmonic" Machines 12, no. 2: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12020117
APA StyleOukrid, M., Bernard, N., Benkhoris, M.-F., & Ziane, D. (2024). Design and Optimization of a Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Exploiting the Fundamental and Third Harmonic. Machines, 12(2), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12020117






