Multiple Electromechanical-Failure Detection in Induction Motor Using Thermographic Intensity Profile and Artificial Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
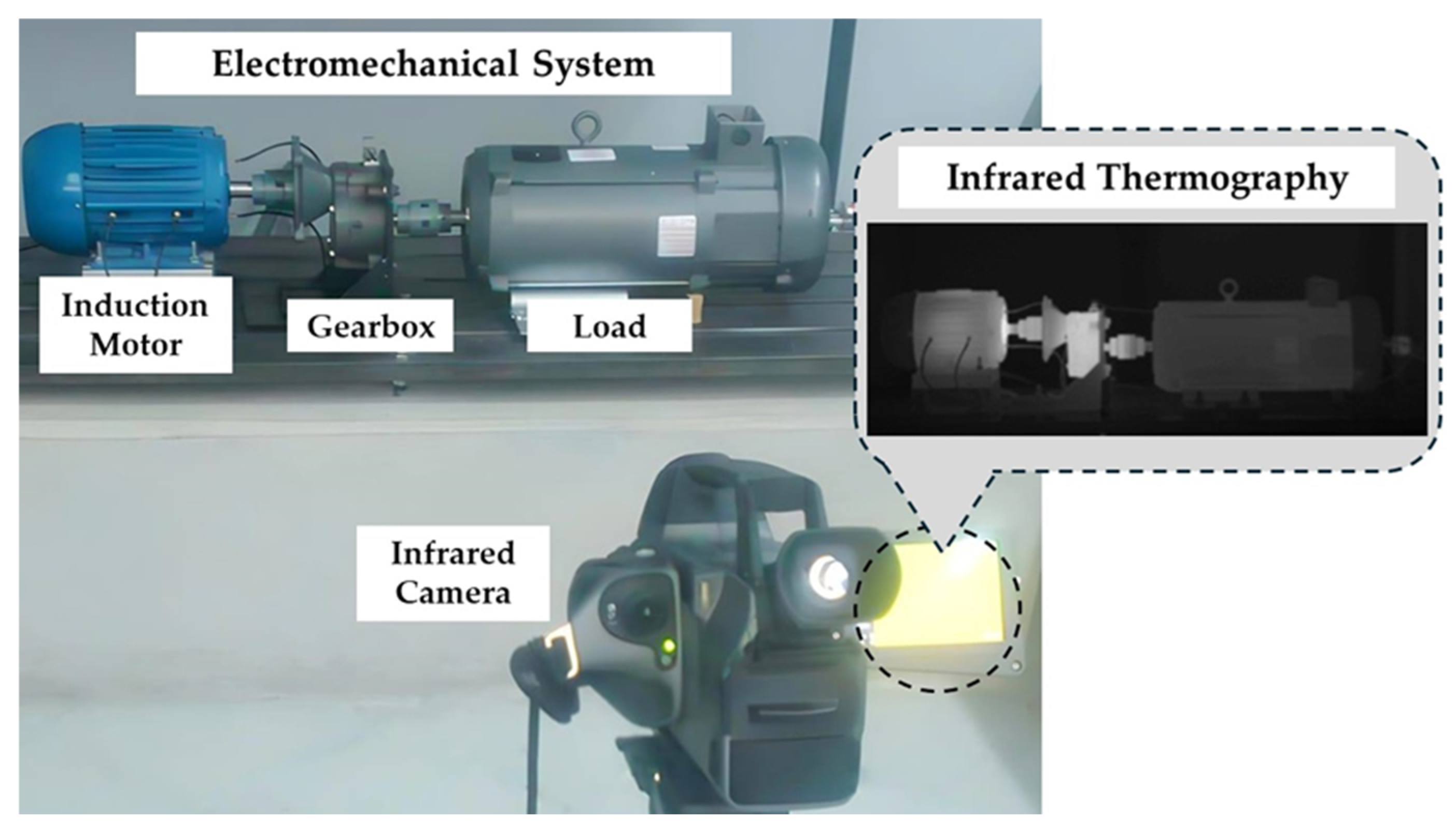
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. The Intensity Profile
2.3. Fast Fourier Transform
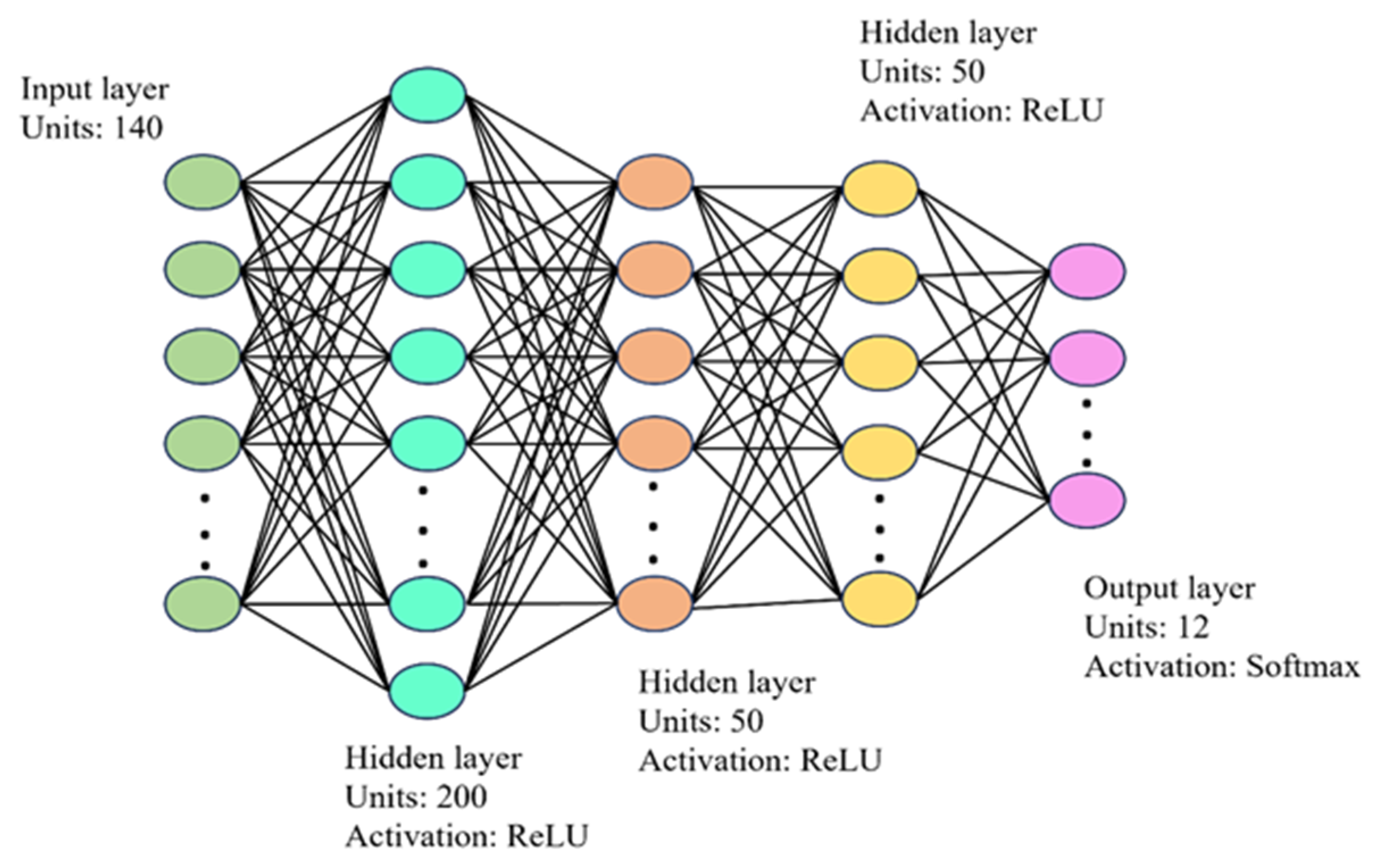
2.4. Multilayer Perceptron
2.5. Image Variations
3. Results
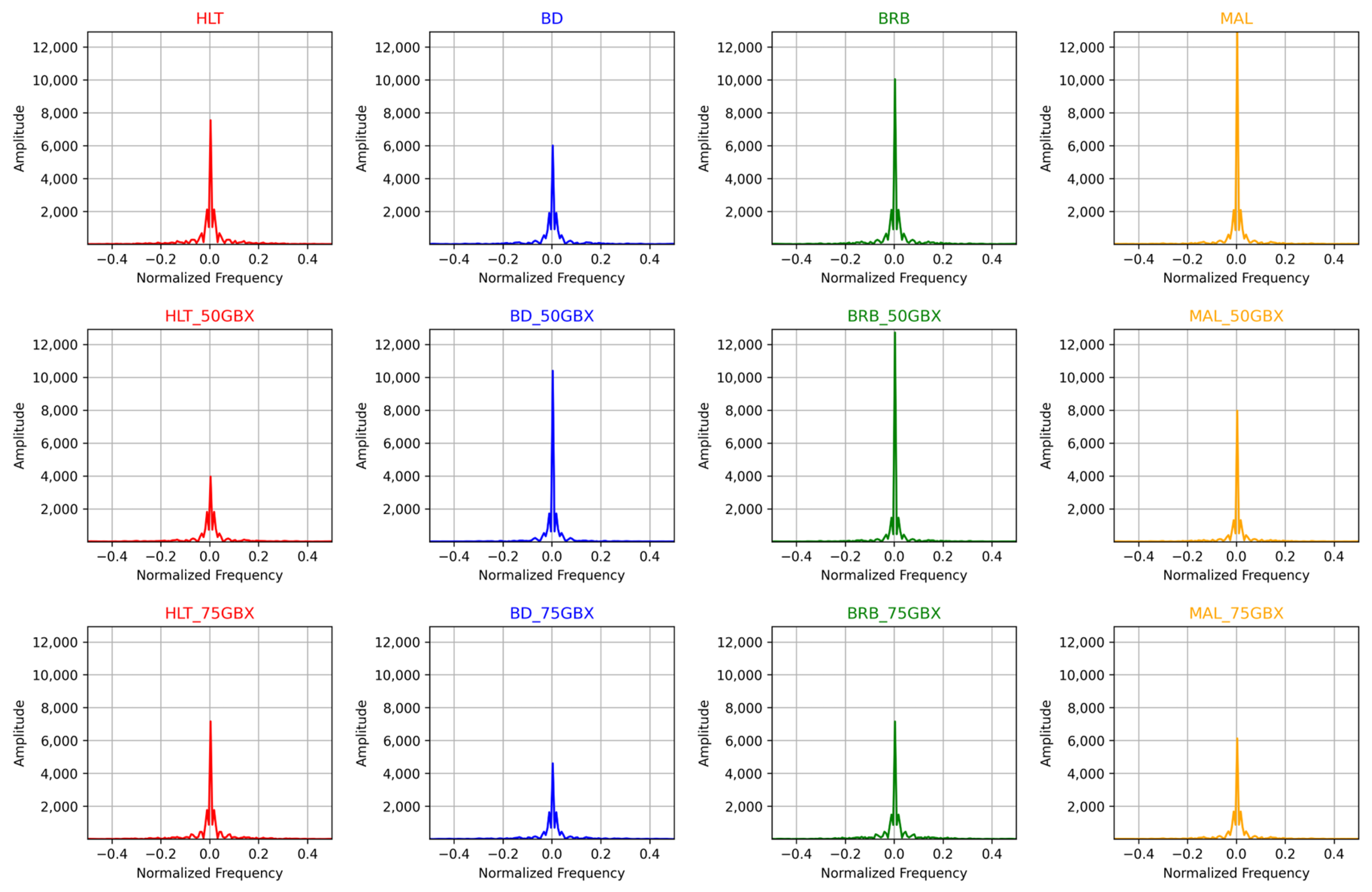
3.1. Application of Fast Fourier Transform to the Profile Intensity
3.2. Hyperparameter Tuning and Training Results
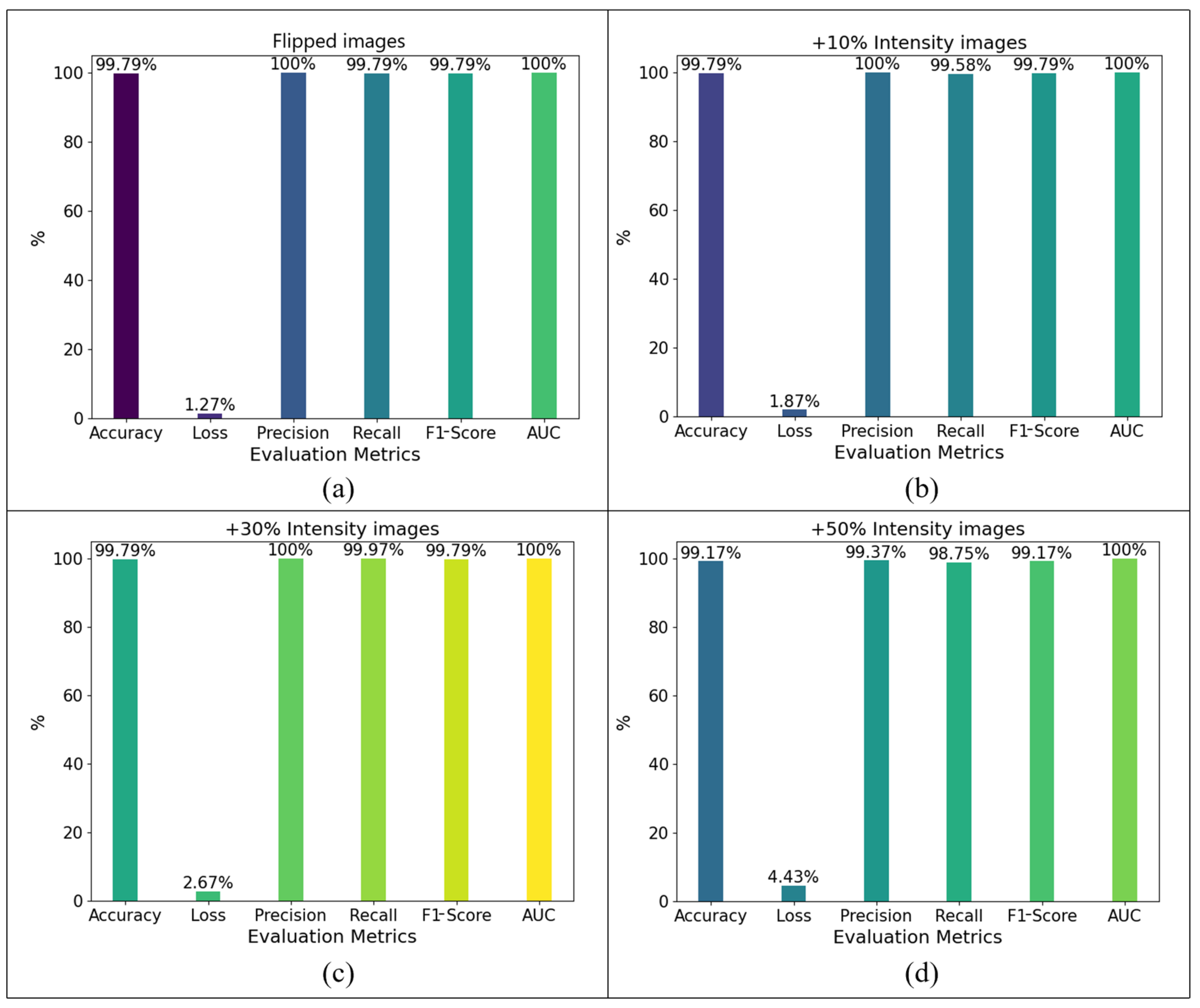
3.3. Robustness Evaluation
3.4. Compararisons Between Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, F. Reliability analysis of complex electromechanical systems: State, of the art, challenges, and prospects. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2022, 38, 3935–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Fatima, S.; Panigrahi, B.K. Multi-input CNN based vibro-acoustic fusion for accurate fault diagnosis of induction motor. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cui, L.; Liu, D. Bearing Weak Fault Feature Extraction Under Time-Varying Speed Conditions Based on Frequency Matching Demodulation Transform. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 28, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chu, F.; Peng, Z. Adaptive synchronous demodulation transforms with application to analyzing multicomponent signals for machinery fault diagnostics. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 191, 110208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhni, M.F.; Cauet, S.; Sakout, A.; Assoum, H.; Etien, E.; Rambault, L.; El-Gohary, M. Variable speed induction motors’ fault detection based on transient motor current signatures analysis: A review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 184, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaros, R.; Byrtus, R.; Dohnal, J.; Danys, L.; Baros, J.; Koziorek, J.; Zmij, P.; Martinek, R. Advanced Signal Processing Methods for Condition Monitoring. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Shakya, P.; Babureddy, P.; Vignesh, S.A. An approach to improve high-frequency resonance technique for bearing fault diagnosis. Measurement 2021, 178, 109318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhai, W. Data-driven adaptive chirp mode decomposition with application to machine fault diagnosis under non-stationary conditions. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2023, 188, 109997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasi, M.; Mostafavi, M.; Ojaghi, M. Motor Current Signature Analysis for Detecting Local Defects on Rolling Element Bearings of Induction Motors. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 14811–14822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Shokoohi, S.; Moshtagh, J. A Current Noise Cancellation Method Based on Integration of Stator Synchronized Currents for Bearing Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 73, 3504208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, N. Detection and analysis of shaft misalignment in application of production and logistics systems using motor current signature analysis. Exp. Syst. Appl. 2023, 217, 119463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Jalan, A.K.; Marathe, A. Condition Monitoring of Misaligned Rotor System Using Acoustic Sensor by Response Surface Methodology. ASME J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2023, 6, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahari-Nezhad, M.; Jafari, S.M. Comparison of MLP and RBF neural networks for bearing remaining useful life prediction based on acoustic emission. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. Eng. Tribol. 2023, 237, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Smart Sensor for Fault Detection in Induction Motors Based on the Combined Analysis of Stray-Flux and Current Signals: A Flexible, Robust Approach. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2022, 28, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamim Filho, P.C.M.; Rabelo Baccarini, L.M.; Batista, F.B.; Araújo, A.C. Orbit Analysis from a Stray Flux Full Spectrum for Induction Machine Fault Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 21, 16152–16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, H.; Benakcha, A.; Laib, I.; Chehaidia, S.E.; Menacer, A.; Soudan, B.; Olabi, A.G. Early detection and localization of stator inter-turn faults based on discrete wavelet energy ratio and neural networks in induction motor. Energy 2020, 212, 118684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanuel, T.; Ghirmay, A.; Ghebremeskel, H.; Ghebrehiwet, R.; Bahlibi, W. Comparative analysis of signal processing techniques for fault detection in three phase induction motor. J. Electron. 2021, 3, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resendiz-Ochoa, E.; Saucedo-Dorantes, J.J.; Benitez-Rangel, J.P.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A. Novel methodology for condition monitoring of gear wear using supervised learning and infrared thermography. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Ren, M.; Wang, B.; Dong, M.; Xu, G.; Xie, J.; Zhang, C. Infrared thermography-based diagnostics on power equipment: State-of-the-art. High Volt. 2021, 6, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.K.; Yaw, C.T.; Koh, S.P.; Abedin, T.; Raj, A.A.; Tiong, S.K.; Chen, C.P. A review of infrared thermography for condition-based monitoring in electrical energy: Applications and recommendations. Energies 2022, 15, 6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charitha, B.V.; Ananthan, T. Machine Learning Based Fault Detection in Induction Motor using Thermal Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 17–19 August 2022; pp. 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Goyal, D.; Letha, S.S. Infrared thermography-based fault diagnosis of induction motor bearings using machine learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Goyal, D.; Shimi, S.L.; Akula, A. Condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of induction motors: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Lu, H.; Sadoughi, M.; Hu, C.; Nemani, V.; Thelen, A.; Webster, K.; Darr, M.; Sidon, J.; Kenny, S. A physics-informed deep learning approach for bearing fault detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 103, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, A.; Taheri-Garavand, A.; Omid, M.; Carlomagno, G.M. Intelligent fault diagnosis of cooling radiator based on deep learning analysis of infrared thermal images. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 163, 114410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, O.; Van de Walle, R.; Loccufier, M.; Van Hoecke, S. Deep learning for infrared thermal image based machine health monitoring. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 23, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, X.; Si, S. Industrial gearbox fault diagnosis based on multi-scale convolutional neural networks and thermal imaging. ISA Trans. 2022, 129, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Du, X.; Wan, F.; Wang, X.; Yu, H. Rotating machinery fault diagnosis based on convolutional neural network and infrared thermal imaging. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Xia, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J. Intelligent fault diagnosis of rotor-bearing system under varying working conditions with modified transfer convolutional neural network and thermal images. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 3488–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacz, A. Thermographic fault diagnosis of shaft of BLDC motor. Sensors 2022, 22, 8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Goyal, D.; Kanda, R. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Bearings based on Convolutional Neural Network using Infrared Thermography. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2022, 236, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Hernandez, A.I.; Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Jaen-Cuellar, A.Y.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Donderis-Quiles, V.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Infrared Thermography Smart Sensor for the Condition Monitoring of Gearbox and Bearings Faults in Induction Motors. Sensors 2022, 22, 6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resendiz-Ochoa, E.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Benitez-Rangel, J.P.; Romero-Troncoso, R.D.J.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A. Induction motor failure analysis: An automatic methodology based on infrared imaging. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 76993–77003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, O.; Sarhan, H.; Alomour, B. Thermal performance analysis of induction motor. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2012, 30, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Picazo-Rodenas, M.J.; Antonino-Daviu, J.; Climente-Alarcon, V.; Royo-Pastor, R.; Mota-Villar, A. Combination of noninvasive approaches for general assessment of induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milford, M.J.; Wyeth, G.F. Single Camera Vision-only SLAM on a Suburban Road Network. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 3684–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbes, G.; Sakar, B.E.; Gulcur, H.O.; Aydin, N. An emboli detection system based on Dual Tree Complex Wavelet Transform and ensemble learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 37, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Troncoso, R.J. Multirate signal processing to improve FFT-based analysis for detecting faults in induction motors. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform. 2017, 13, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Andriollo, M.; Cirrincione, G.; Cirrincione, M.; Tortella, A. A Comprehensive Review of Conventional and Intelligence-Based Approaches for the Fault Diagnosis and Condition Monitoring of Induction Motors. Energies 2022, 15, 8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P. Probabilistic Machine Learning: Advanced Topics; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, W. Bearing fault diagnosis method based on stacked autoencoder and softmax regression. In Proceeding of the 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference, Hangzhou, China, 28–30 July 2015; pp. 6331–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Pack, J.H.; Lee, I.S. Fault diagnosis of induction motor using convolutional neural network. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, R.; Wu, Q. MPCE: A maximum probability based cross entropy loss function for neural network classification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146331–146341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Huang, Y.; Qin, C.; Shi, H.; Li, Y. Fault diagnosis of induction motors using recurrence quantification analysis and LSTM with weighted BN. Shock. Vib. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sarkar, S.; Pradhan, C. Malaria disease detection using cnn technique with sgd, rmsprop and adam optimizers. In Deep Learning Techniques for Biomedical and Health Informatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowron, M.; Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Wolkiewicz, M.; Kowalski, C.T. Convolutional neural network-based stator current data-driven incipient stator fault diagnosis of inverter-fed induction motor. Energies 2020, 13, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, A.N.; Taib, S. Application of infrared thermography for predictive/preventive maintenance of thermal defect in electrical equipment. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 61, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Prieto, M.; Carino-Corrales, J.A.; Saucedo-Dorantes, J.J.; de Jesus Romero-Troncoso, R.; Osornio-Rios, R.A. Thermography-based methodology for multifault diagnosis on kinematic chain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 5553–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahami, A.; Rahmoune, C.; Bettahar, T.; Benazzouz, D. Induction motor condition monitoring using infrared thermography imaging and ensemble learning techniques. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2021, 13, 168781402110609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.R.; Shabbir, Z.; Asghar, F.; Amjad, W.; Mahmood, F.; Khan, M.O.; Virk, U.S.; Waleed, A.; Haider, Z.M. An efficient fault detection method for induction motors using thermal imaging and Machine Vision. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.; Ezoji, M. Electrical fault detection in three-phase induction motor using deep network-based features of thermograms. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2021, 173, 108622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Jaen-Cuellar, A.Y.; Alvarado-Hernandez, A.I.; Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Cruz-Albarran, I.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Fault detection and classification in kinematic chains by means of PCA extraction-reduction of features from thermographic images. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2022, 197, 111340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Chavez, O.; Cruz-Albarran, I.A.; Resendiz-Ochoa, E.; Salinas-Aguilar, A.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A.; Basurto-Hurtado, J.A.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A. A CNN-based methodology for identifying mechanical faults in induction motors using thermography. Machines 2023, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmer dos Santos, L.F.; dos Santos Canuto, J.L.; Thom de Souza, R.C.; Aylon, L.B.R. Thermographic image-based diagnosis of failures in electrical motors using deep transfer learning. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-Y.; Wong, P.-K.; Vong, C.-M.; Fei, K.; Chan, I.-N. A novel electric motor fault diagnosis by using a convolutional neural network, normalized thermal images and few-shot learning. Electronics 2023, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variations | Orientation | Intensity lvl.1 | Intensity lvl.2 | Intensity lvl.3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | Specular | +10% | +30% | +50% |
| MLP (Optimizer: Adam, lr: 0.01) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hidden Layers | Neurons in the Hidden Layer | Batch Size | Epochs | Accuracy |
| 2 | 300,100 | 32 | 30 | 99% |
| 64 | 60 | 99% | ||
| 128 | 120 | 99% | ||
| 200,50 | 32 | 60 | 99% | |
| 64 | 90 | 99% | ||
| 128 | 90 | 99% | ||
| 150,20 | 32 | 120 | 62% | |
| 64 | 80 | 99% | ||
| 128 | 120 | 79% | ||
| 3 | 300,100,50 | 32 | 50 | 99% |
| 64 | 120 | 99% | ||
| 128 | 120 | 98% | ||
| 200,50,50 | 32 | 90 | 100% | |
| 64 | 60 | 99% | ||
| 128 | 100 | 99% | ||
| 150,50,20 | 32 | 70 | 99% | |
| 64 | 120 | 66% | ||
| 128 | 120 | 60% | ||
| MLP+FFT (Optimizer: Adam, lr: 0.01) | ||||
| Hidden Layers | Neurons in the Hidden Layer | Batch Size | Epochs | Accuracy |
| 2 | 300,100 | 32 | 75 | 100% |
| 64 | 60 | 100% | ||
| 128 | 70 | 98% | ||
| 200,50 | 32 | 100 | 99% | |
| 64 | 90 | 99% | ||
| 128 | 90 | 99% | ||
| 150,20 | 32 | 120 | 20% | |
| 64 | 120 | 11% | ||
| 128 | 120 | 10% | ||
| 3 | 300,100,50 | 32 | 70 | 100% |
| 64 | 75 | 99% | ||
| 128 | 85 | 99% | ||
| 200,50,50 | 32 | 100 | 100% | |
| 64 | 90 | 99% | ||
| 128 | 100 | 99% | ||
| 150,50,20 | 32 | 120 | 70% | |
| 64 | 120 | 96% | ||
| 128 | 120 | 16% | ||
| Database | Accuracy | Precision | F1-Score | AUC | Recall | Time of Training (s) | Time of Inference (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | 600 | 100% | 100% | 99.81% | 100% | 99.79% | 22.48 | 0.0017 |
| PIF | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 29.17 | 0.0073 | |
| PI | 480 | 99.22% | 99.74% | 99.22% | 100% | 98.96 | 22.29 | 0.0119 |
| PIF | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 25.53 | 0.0116 | |
| PI | 360 | 99.31% | 99.65% | 99.31% | 100% | 98.61% | 24.52 | 0.0024 |
| PIF | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 35.23 | 0.0090 | |
| PI | 240 | 98.44% | 100% | 99.48% | 100% | 97.92% | 16.94 | 0.0101 |
| PIF | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 22.14 | 0.0090 | |
| PI | 120 | 98.96% | 100% | 98.95% | 99.96% | 90.62% | 12.58 | 0.0306 |
| PIF | 98.96% | 98.96% | 98.96% | 100% | 98.96% | 23.47 | 0.0169 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 93.00% | 94.00% | 92.500% | 92.70% |
| RF | 93.00% | 95.32% | 93.33% | 92.95% |
| LR | 99.00% | 99.30% | 99.16% | 99.19% |
| ANN (proposed) | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Reference | Classification Method | Images/ Camera | Fault (Number) | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [48] | Self-organizing maps | 240/FLIR GF320 | Healthy, unbalance, misalignment, bearing (4) | 84.4–99.7% |
| [49] | Extremely randomized tree | -/Dali-tech T4/T8 | Healthy, short circuit faults in the stator windings (9) | 100% |
| [50] | SVM | 36/- | Healthy, overload, fault (3) | 97% |
| [51] | K-means + SVM | 394/Dali-tech T8 | Healthy, blocked rotor, blocked fan, short circuit at different levels in one, two or three phases of stator (11) | 100% |
| [52] | PCA—ANN | 2160/FLIR LEPTON 3 | Healthy, misalignment, unbalance, broken bars, rolling bearing fault, wear and tear in the gearbox (12) | 96.8% |
| [53] | CNN | 200/FLIR GF320 | Healthy, ball bearing damage, broken rotor bar, misalignment (4) | 95–99.6% |
| [54] | CNN (RegNetX002) | 369/Dali-tech T4/T8 | Healthy, cooling, rotor, and stator-1, 2 or 3 phases (11) | 98.18% |
| [55] | CNN | 2820/UTi260B | Three motors: healthy, bearing fault, coil fault, fan fault (11) | 91.8–98.9% |
| Intensity profile + ANN (Proposed) | 600/FLIR GF320 | Healthy, bearing defect, broken rotor bar, misalignment, 50 % and 75 % gear wear in gearbox (12) | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Resendiz-Ochoa, E.; Calderon-Uribe, S.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A.; Cruz-Albarran, I.A. Multiple Electromechanical-Failure Detection in Induction Motor Using Thermographic Intensity Profile and Artificial Neural Network. Machines 2024, 12, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120928
Resendiz-Ochoa E, Calderon-Uribe S, Morales-Hernandez LA, Perez-Ramirez CA, Cruz-Albarran IA. Multiple Electromechanical-Failure Detection in Induction Motor Using Thermographic Intensity Profile and Artificial Neural Network. Machines. 2024; 12(12):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120928
Chicago/Turabian StyleResendiz-Ochoa, Emmanuel, Salvador Calderon-Uribe, Luis A. Morales-Hernandez, Carlos A. Perez-Ramirez, and Irving A. Cruz-Albarran. 2024. "Multiple Electromechanical-Failure Detection in Induction Motor Using Thermographic Intensity Profile and Artificial Neural Network" Machines 12, no. 12: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120928
APA StyleResendiz-Ochoa, E., Calderon-Uribe, S., Morales-Hernandez, L. A., Perez-Ramirez, C. A., & Cruz-Albarran, I. A. (2024). Multiple Electromechanical-Failure Detection in Induction Motor Using Thermographic Intensity Profile and Artificial Neural Network. Machines, 12(12), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120928






