End-of-Life Prediction for Milling Cutters Based on an Online Vibro-Acoustic System
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Indirect Methods for Measuring Tool Wear
Acoustic Emissions’ Monitoring
1.2. Aim of This Study
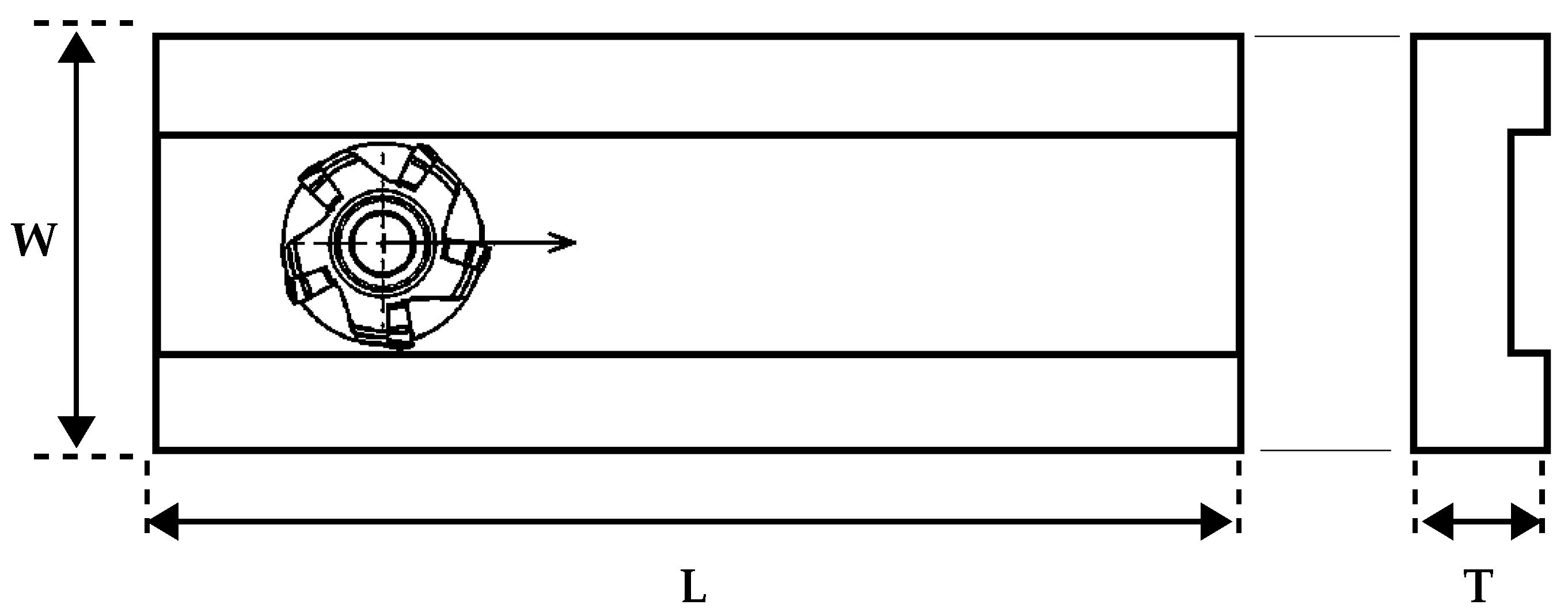
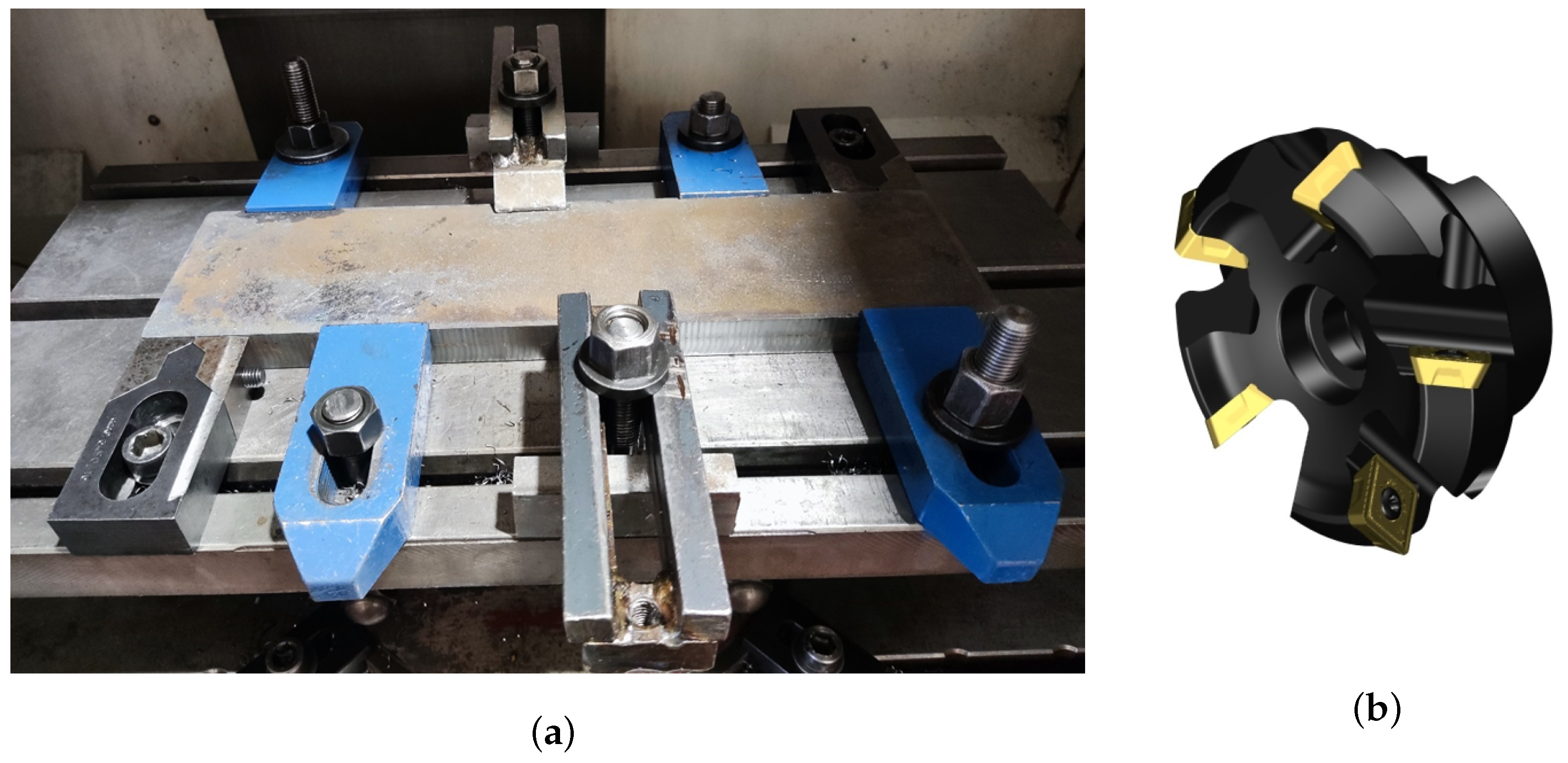
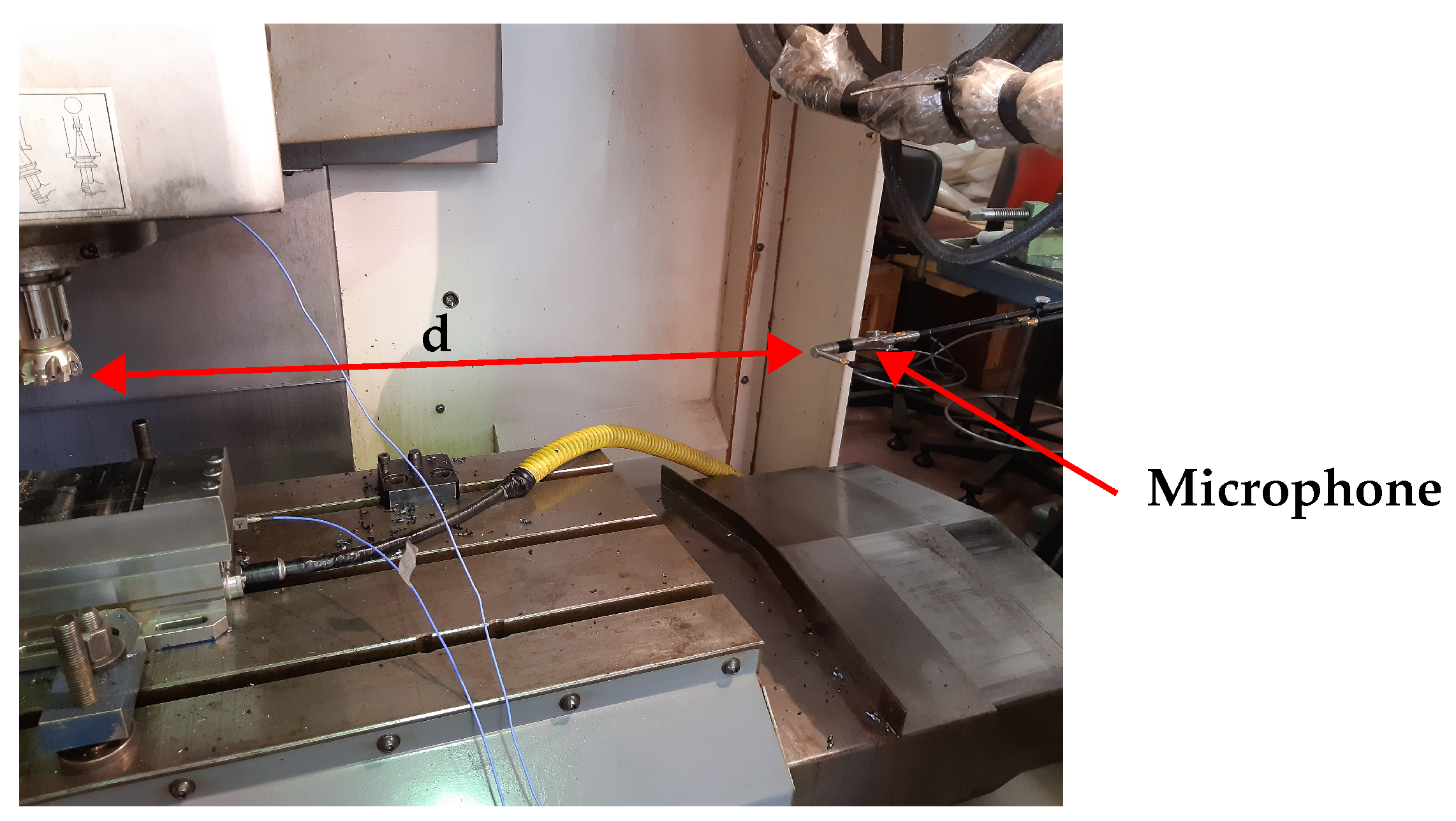
2. Methods
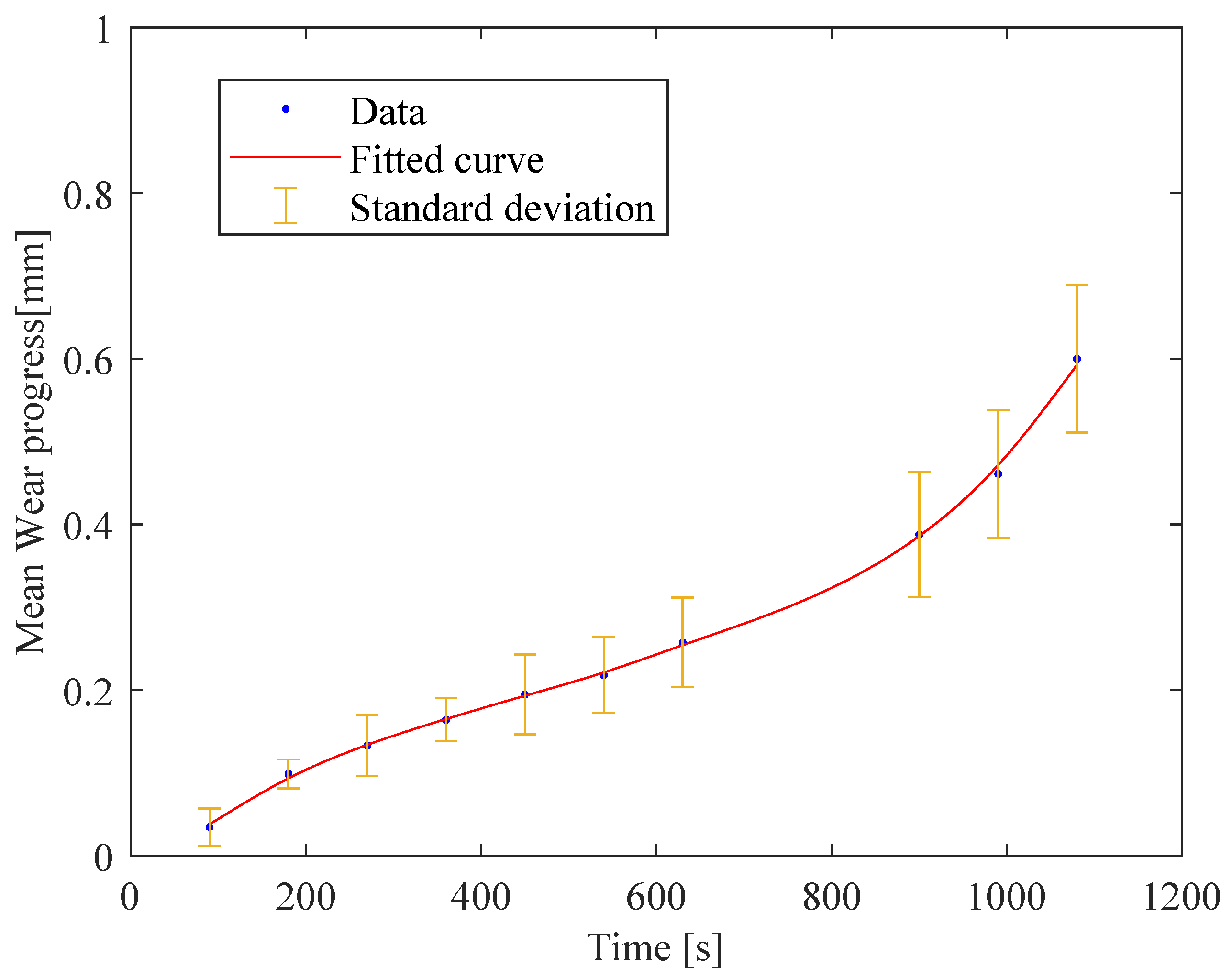
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alswede, F.A.J. Study of Vibration for CNC Machine at Difference Feed. Int. J. Adv. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Che, C.; Zan, T.; Gao, X.; Gao, P. Tool wear process monitoring by damping behavior of cutting vibration for milling process. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Mishra, D.; Awasthi, U.; Bollas, G.M.; Pattipati, K.R. Tool wear and remaining useful life estimation in precision machining using interacting multiple model. J. Manuf. Syst. 2024, 74, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirad, M.M.; Das, B. Machine learning coupled with acoustic emission signal features for tool wear estimation during ultrasonic machining of Inconel 718. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2024, 28, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Hiremath, S.S. Review on tools and tool wear in EDM. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2021, 25, 802–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenov, D.Y.; Kumar Gupta, M.; da Silva, L.R.; Kiran, M.; Khanna, N.; Krolczyk, G.M. Application of measurement systems in tool condition monitoring of Milling: A review of measurement science approach. Measurement 2022, 199, 111503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Outeiro, J.; Costes, J.P.; Karouni, H.; Dorlin, T.; Saoubi, R.M. 3D modeling of turning of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy using a constitutive model considering the state of stress. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2023, 27, 422–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururaja, S.; Singh, K.K. Development of smart manufacturing framework for micromilling of thin-walled Ti6Al4V. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2024, 28, 459–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, Y.; Yacout, S.; Balazinski, M.; Jemielniak, K. Cutting tool wear detection using multiclass logical analysis of data. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2017, 21, 526–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, T.; Shankar, S.; Rajasekar, R.; Sakthivel, N.; Pramanik, A. Tool condition monitoring techniques in milling process—A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash, P.M.; Chakradhar, D. Performance monitoring and failure prediction system for wire electric discharge machining process through multiple sensor signals. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2022, 26, 245–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudana, C.; Kumar, H.; Narendranath, S. Condition monitoring of face milling tool using K-star algorithm and histogram features of vibration signal. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbestawi, M.; Papazafiriou, T.; Du, R. In-process monitoring of tool wear in milling using cutting force signature. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1991, 31, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagavathiappan, S.; Lahiri, B.B.; Suresh, S.; Philip, J.; Jayakumar, T. Online monitoring of cutting tool temperature during micro-end milling using infrared thermography. Insight Non-Destr. Test. Cond. Monit. 2015, 57, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, W. Tool Wear Condition Monitoring in Milling Process Based on Current Sensors. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 95491–95502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekita, M.; Takaya, Y. Tool condition monitoring for form milling of large parts by combining spindle motor current and acoustic emission signals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Lin, R. Tool wear monitoring in face milling using force signals. Wear 1996, 198, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Mohanraj, T.; Rajasekar, R. Prediction of cutting tool wear during milling process using artificial intelligence techniques. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2019, 32, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagavathiappan, S.; Lahiri, B.; Saravanan, T.; Philip, J.; Jayakumar, T. Infrared thermography for condition monitoring—A review. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2013, 60, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauro, C.; Brandão, L.; Ribeiro Filho, S.L. Monitoring the temperature of the milling process using infrared camera. Sci. Res. Essays 2013, 8, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xue, J.; Lu, M.; Gai, X.; Guan, R. Research on tool wear prediction based on the random forest optimized by NGO algorithm. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2024, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilyurt, I.; Ozturk, H. Tool condition monitoring in milling using vibration analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 1013–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.; Salgado, D. Analysis of the structure of vibration signals for tool wear detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2008, 22, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q. Vibration sensor based tool condition monitoring using support vector machine and locality preserving projection. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 209, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Wang, P.; Cheng, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y. Machining dynamics and chatters in micro-milling: A critical review on the state-of-the-art and future perspectives. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Yeh, S.S. Integration of cutting force control and chatter suppression control into automatic cutting feed adjustment system design. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2020, 24, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, D.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Song, X. Cutting tool wear monitoring based on a smart toolholder with embedded force and vibration sensors and an improved residual network. Measurement 2022, 199, 111520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyżycki, J.; Twardowski, P.; Felusiak-Czyryca, A.; Tabaszewski, M.; Wiciak, M. Monitoring and forecasting of tool wear based on measurements of vibration accelerations during cast iron milling. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 95, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, K.; Balaji, A. Tool condition monitoring of PCB milling machine based on vibration analysis. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 3386–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesser, D.F.; Markert, B. Tool wear monitoring of a retrofitted CNC milling machine using artificial neural networks. Manuf. Lett. 2019, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Guo, K.; Sun, J. An integrated wireless vibration sensing tool holder for milling tool condition monitoring with singularity analysis. Measurement 2021, 174, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zou, Y.; Chen, N. Study on tool wear state recognition algorithm based on spindle vibration signals collected by homemade tool condition monitoring ring. Measurement 2023, 223, 113787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, V.; Dibaji, S.; Alaswad, K.; Cool, J. Tool wear monitoring by ensemble learning and sensor fusion using power, sound, vibration, and AE signals. Manuf. Lett. 2021, 30, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Sun, J.; Yang, B. Multisensory based tool wear monitoring for practical applications in milling of titanium alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Huo, D. Tool condition monitoring in micro milling of brittle materials. Precis. Eng. 2024, 87, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntoğlu, M.; Sağlam, H. ANOVA and fuzzy rule based evaluation and estimation of flank wear, temperature and acoustic emission in turning. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liang, S.Y. Analytical modeling of acoustic emission for monitoring of peripheral milling process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1991, 31, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.; Senthilkumar, P.; Kumaravel, A.; Manoharan, N. Study of flank wear in single point cutting tool using acoustic emission sensor techniques. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2008, 3, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, Q.; Shao, H. Cutting sound signal processing for tool breakage detection in face milling based on empirical mode decomposition and independent component analysis. J. Vib. Control 2015, 21, 3348–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrisi, S.; Zangara, G.; Izquierdo, D.R.; Lofaro, D.; Guido, R.; Conforti, D.; Ambrogio, G. Tool Condition Monitoring for milling process using Convolutional Neural Networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 232, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Hey, A.; D’Attelis, C.; Ruzzante, J. Assessment of Cutting Tool Condition by Acoustic Emission. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2012, 1, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nawrocki, W.; Stryjski, R.; Kostrzewski, M.; Woźniak, W.; Jachowicz, T. Application of the vibro-acoustic signal to evaluate wear in the spindle bearings of machining centres. In-service diagnostics in the automotive industry. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 92, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, C. A recurrent neural network approach for remaining useful life prediction utilizing a novel trend features construction method. Measurement 2019, 146, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kwon, S.; Ryu, S.; Lee, S.; Jeong, J.; Chung, J. Noise Identification for an Automotive Wheel Bearing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klocke, F.; Döbbeler, B.; Pullen, T.; Bergs, T. Acoustic emission signal source separation for a flank wear estimation of drilling tools. Procedia CIRP 2019, 79, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, K. Acoustic emission based tool condition monitoring system in drilling. Proc. World Congr. Eng. 2011, 3, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, S.; Wang, Z.; Min, T.; Dai, Z.; Chen, G. Detection of Tool Wear in Drilling CFRP/TC4 Stacks by Acoustic Emission. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2020, 8, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.H.; Choudhury, I.A.; Nukman, Y. Tool Condition Monitoring using Acoustic Emission and Vibration Signature in Turning. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 4–6 July 2012; Volume III. [Google Scholar]
- Denkena, B.; Klemme, H.; Stiehl, T.H. Multivariate time series data of milling processes with varying tool wear and machine tools. Data Brief 2023, 50, 109574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perrelli, M.; Conte, R.; Zangara, G.; Gagliardi, F. End-of-Life Prediction for Milling Cutters Based on an Online Vibro-Acoustic System. Machines 2024, 12, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12100703
Perrelli M, Conte R, Zangara G, Gagliardi F. End-of-Life Prediction for Milling Cutters Based on an Online Vibro-Acoustic System. Machines. 2024; 12(10):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12100703
Chicago/Turabian StylePerrelli, Michele, Romina Conte, Gabriele Zangara, and Francesco Gagliardi. 2024. "End-of-Life Prediction for Milling Cutters Based on an Online Vibro-Acoustic System" Machines 12, no. 10: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12100703
APA StylePerrelli, M., Conte, R., Zangara, G., & Gagliardi, F. (2024). End-of-Life Prediction for Milling Cutters Based on an Online Vibro-Acoustic System. Machines, 12(10), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12100703







