Reinforcement Learning-Based Dynamic Zone Placement Variable Speed Limit Control for Mixed Traffic Flows Using Speed Transition Matrices for State Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Proposal of an approach that utilizes the QL algorithm for VSL that computes speed limits and speed limit zone positions that are imposed on CAVs;
- Usage of STMs for environment state space approximation from the data collected from CAVs as an input to the QL algorithm that computes speed limits and speed limit zone positions;
- Analysis of scenarios with different penetration rates of CAVs on the simulated urban motorway by using the proposed STM-QL-DVSL approach.
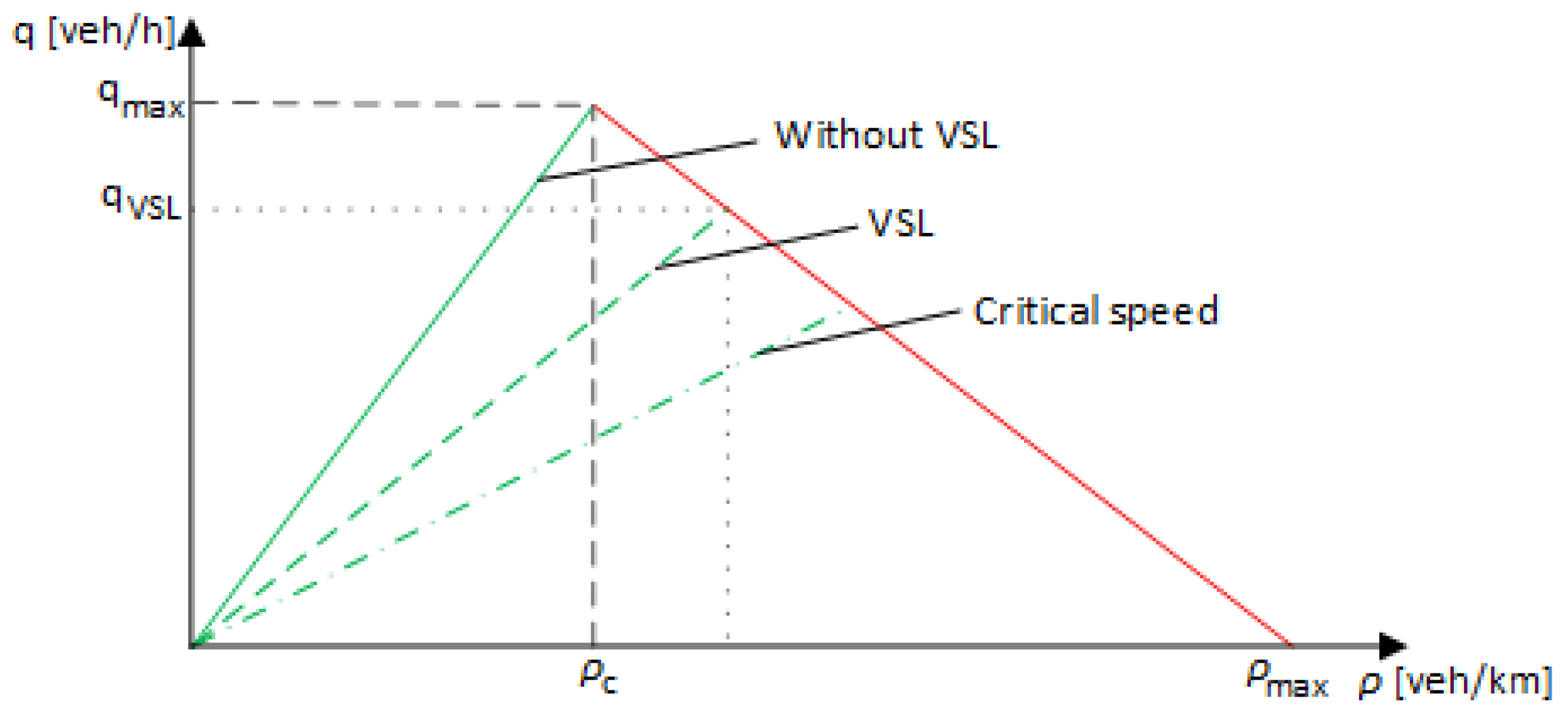
2. Variable Speed Limit
3. Variable Speed Limit Based on Q-Learning and Speed Transition Matrices
3.1. Q-Learning and Variable Speed Limit
3.2. State Space Representation Using Speed Transition Matrices
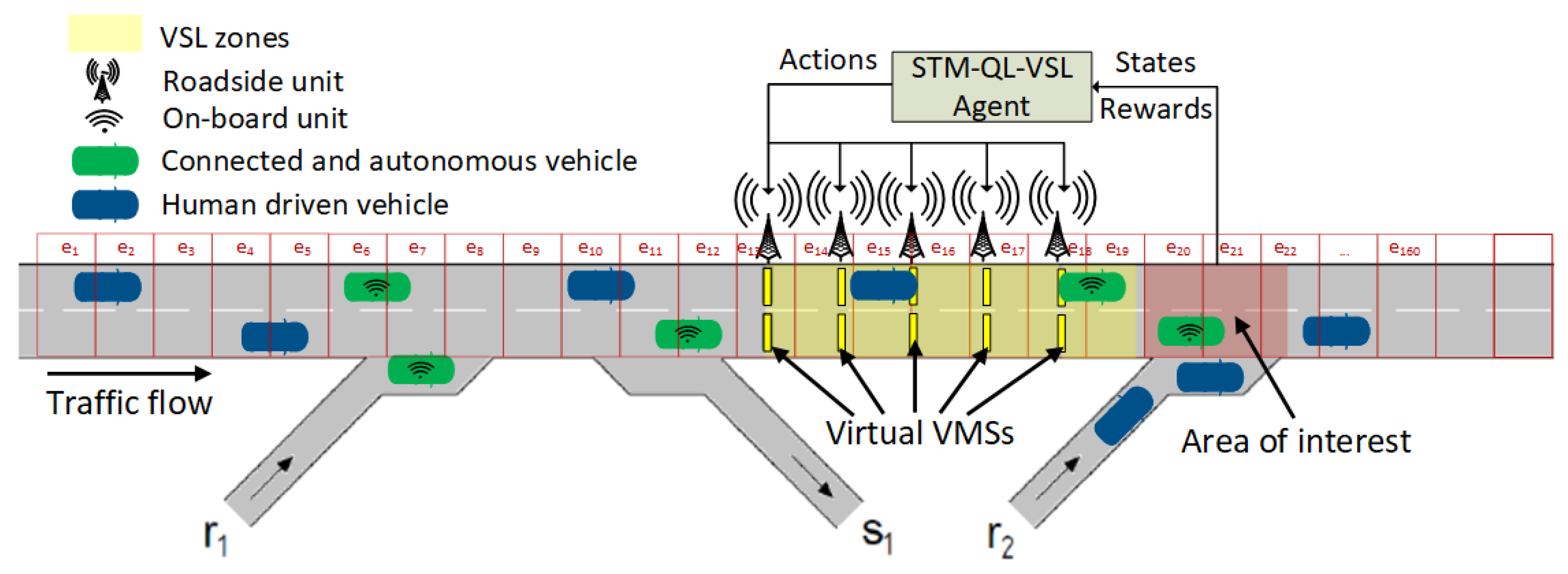
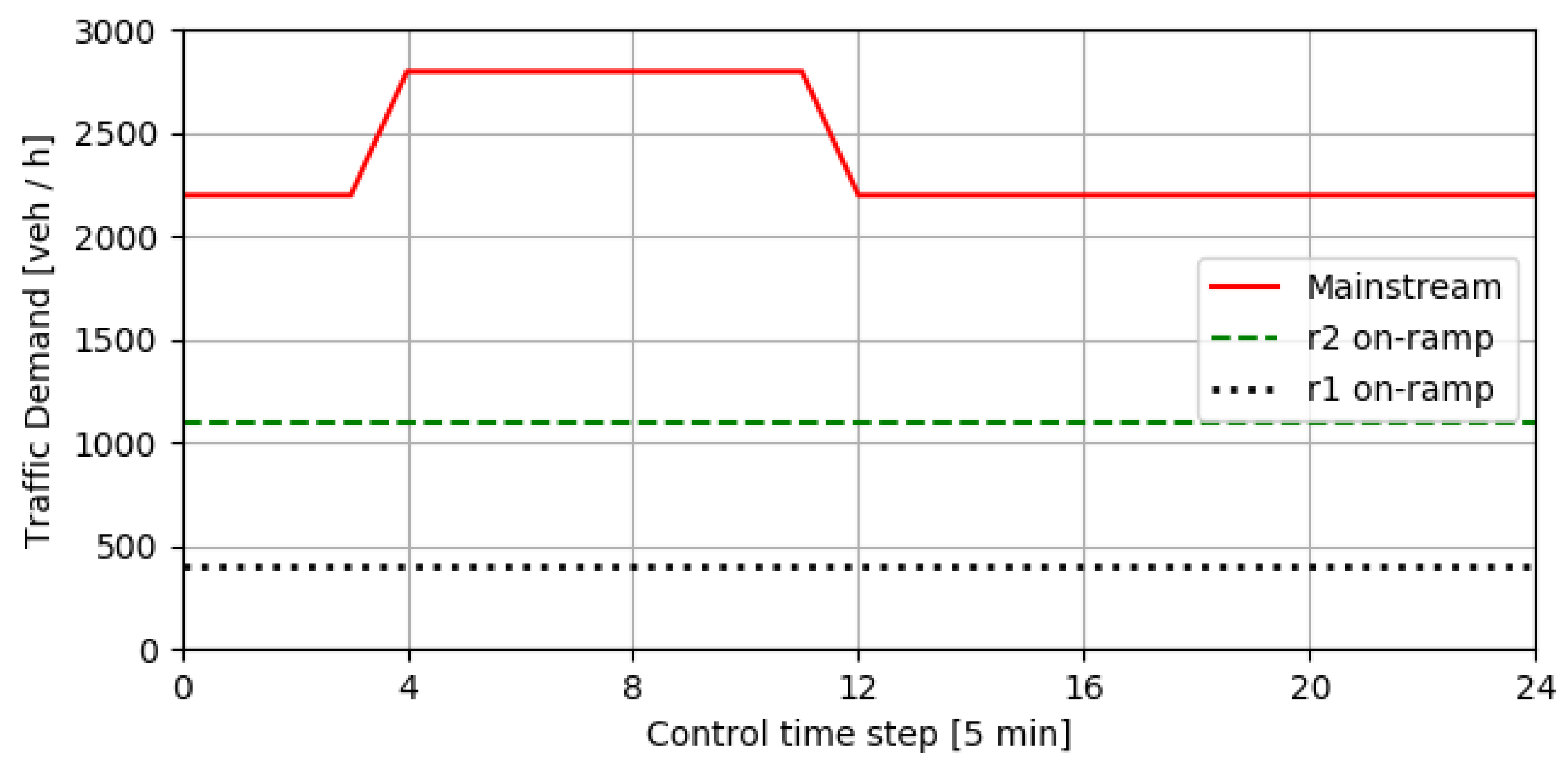
4. Simulation Framework
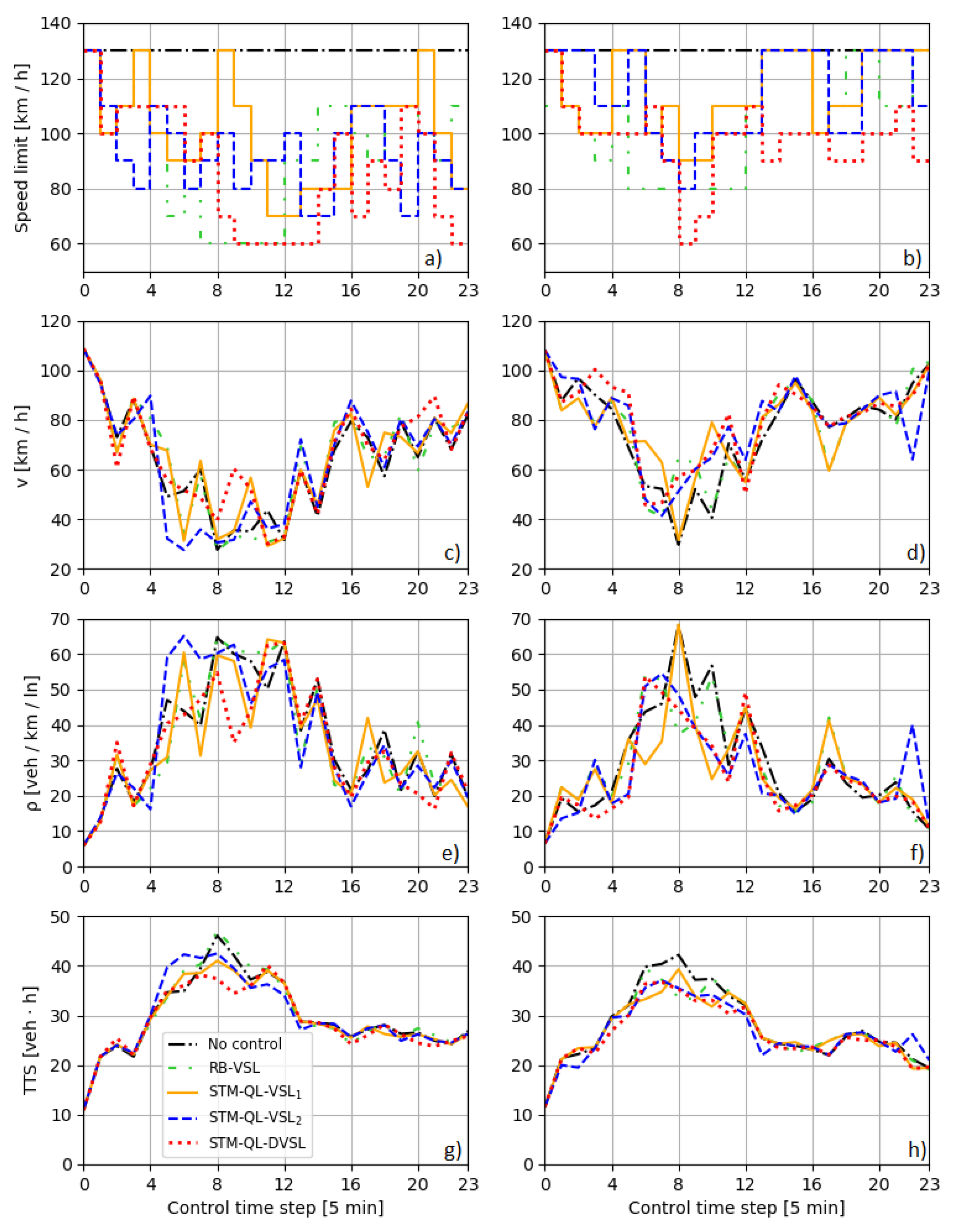
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AV | Autonomous Vehicle |
| CAV | Connected Autonomous Vehicle |
| FCA | Full Cellular Activity |
| HDV | Human-Driven Vehicle |
| HCM | Highway Capacity Manual |
| ITS | Intelligent Transportation Systems |
| MoE | Measure of Effectiveness |
| MTT | Mean Travel Time |
| OBU | On-Board Unit |
| QL | Q-Learning |
| QL-VSL | Q-Learning Variable Speed Limit |
| RB-VSL | Rule-Based Variable Speed Limit |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| RSU | Road Side Unit |
| STM | Speed Transition Matrix |
| STM-QL-VSL | Speed Transition Matrices-based Q-Learning Variable Speed Limit |
| STM-QL-DVSL | Speed Transition Matrices-based Q-Learning Dynamic Variable Speed Limit |
| SUMO | Simulation of Urban Mobility |
| TTS | Total Time Spent |
| TTT | Total Travel Time |
| VMS | Variable Message Sign |
| VSL | Variable Speed Limit |
References
- Müller, E.; Carlson, R.; Kraus, W.J.; Papageorgiou, M. Microsimulation analysis of practical aspects of traffic control with variable speed limits. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 16, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kušić, K.; Ivanjko, E.; Gregurić, M. A Comparison of Different State Representations for Reinforcement Learning Based Variable Speed Limit Control. In Proceedings of the MED 2018—26th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Zadar, Croatia, 19–22 June 2018; pp. 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kušić, K.; Ivanjko, E.; Gregurić, M.; Miletić, M. An Overview of Reinforcement Learning Methods for Variable Speed Limit Control. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kušić, K.; Ivanjko, E.; Vrbanić, F.; Gregurić, M.; Dusparic, I. Spatial-Temporal Traffic Flow Control on Motorways Using Distributed Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. Mathematics 2021, 9, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbanić, F.; Ivanjko, E.; Mandžuka, S.; Miletić, M. Reinforcement Learning Based Variable Speed Limit Control for Mixed Traffic Flows. In Proceedings of the 2021 29th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Puglia, Italy, 22–25 June 2021; pp. 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbanić, F.; Ivanjko, E.; Kušić, K.; Cakija, D. Variable Speed Limit and Ramp Metering for Mixed Traffic Flows: A Review and Open Questions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbanić, F.; Miletić, M.; Tišljarić, L.; Ivanjko, E. Influence of Variable Speed Limit Control on Fuel and Electric Energy Consumption, and Exhaust Gas Emissions in Mixed Traffic Flows. Sustainability 2022, 14, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbanić, F.; Tišljarić, L.; Majstorović, Ž.; Ivanjko, E. Reinforcement Learning Based Variable Speed Limit Control for Mixed Traffic Flows Using Speed Transition Matrices for State Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 30th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Vouliagmeni, Greece, 28 June–1 July 2022; pp. 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, P.; Ding, F.; Li, Q.; Ran, B. A Feature-Based Approach to Large-Scale Freeway Congestion Detection Using Full Cellular Activity Data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tišljarić, L.; Carić, T.; Abramović, B.; Fratrović, T. Traffic State Estimation and Classification on Citywide Scale Using Speed Transition Matrices. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elefteriadou, L.A. (Ed.) Highway Capacity Manual 6th Edition: A Guide for Multimodal Mobility Analysis; Transportation Research Board, The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Kosmatopoulos, E.; Papamichail, I. Effects of Variable Speed Limits on Motorway Traffic Flow. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2008, 2047, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Hellinga, B.; Saccomanno, F. Evaluation of variable speed limits to improve traffic safety. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2006, 14, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, M. Der Verkehrsfluss auf Schnellstrassen: Modelle, Überwachung, Regelung; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.C.; Papamichail, I.; Papageorgiou, M.; Messmer, A. Optimal Motorway Traffic Flow Control Involving Variable Speed Limits and Ramp Metering. Transp. Sci. 2010, 44, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yamamoto, T. Evaluating the impact of connected and autonomous vehicles on traffic safety. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 526, 121009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olia, A.; Razavi, S.; Abdulhai, B.; Abdelgawad, H. Traffic capacity implications of automated vehicles mixed with regular vehicles. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. Technol. Plan. Oper. 2018, 22, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Li, L. Effect of connected automated driving on traffic capacity. In Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, C.J.C.H.; Dayan, P. Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walraven, E.; Spaan, M.T.; Bakker, B. Traffic flow optimization: A reinforcement learning approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2016, 52, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Ran, B. A New Solution for Freeway Congestion: Cooperative Speed Limit Control Using Distributed Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 41947–41957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Xu, C.; Duan, H.; Wang, W. Reinforcement Learning-Based Variable Speed Limit Control Strategy to Reduce Traffic Congestion at Freeway Recurrent Bottlenecks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 3204–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tišljarić, L.; Fernandes, S.; Carić, T.; Gama, J. Spatiotemporal Road Traffic Anomaly Detection: A Tensor-Based Approach. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tišljarić, L.; Vrbanić, F.; Ivanjko, E.; Carić, T. Motorway Bottleneck Probability Estimation in Connected Vehicles Environment Using Speed Transition Matrices. Sensors 2022, 22, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, P.A.; Behrisch, M.; Bieker-Walz, L.; Erdmann, J.; Flötteröd, Y.P.; Hilbrich, R.; Lücken, L.; Rummel, J.; Wagner, P.; Wiessner, E. Microscopic Traffic Simulation using SUMO. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wagner, P. A novel approach for mixed manual/connected automated freeway traffic management. Sensors 2020, 20, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Tettamanti, T. Impacts of autonomous vehicles on the urban fundamental diagram. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Road and Rail Infrastructure, CETRA 2018, Zadar, Croatia, 17–19 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majstorović, Ž.; Miletić, M.; Čakija, D.; Dusparić, I.; Ivanjko, E.; Carić, T. Impact of the Connected Vehicles Penetration Rate on the Speed Transition Matrices Accuracy. Transp. Res. Procedia 2022, 64, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

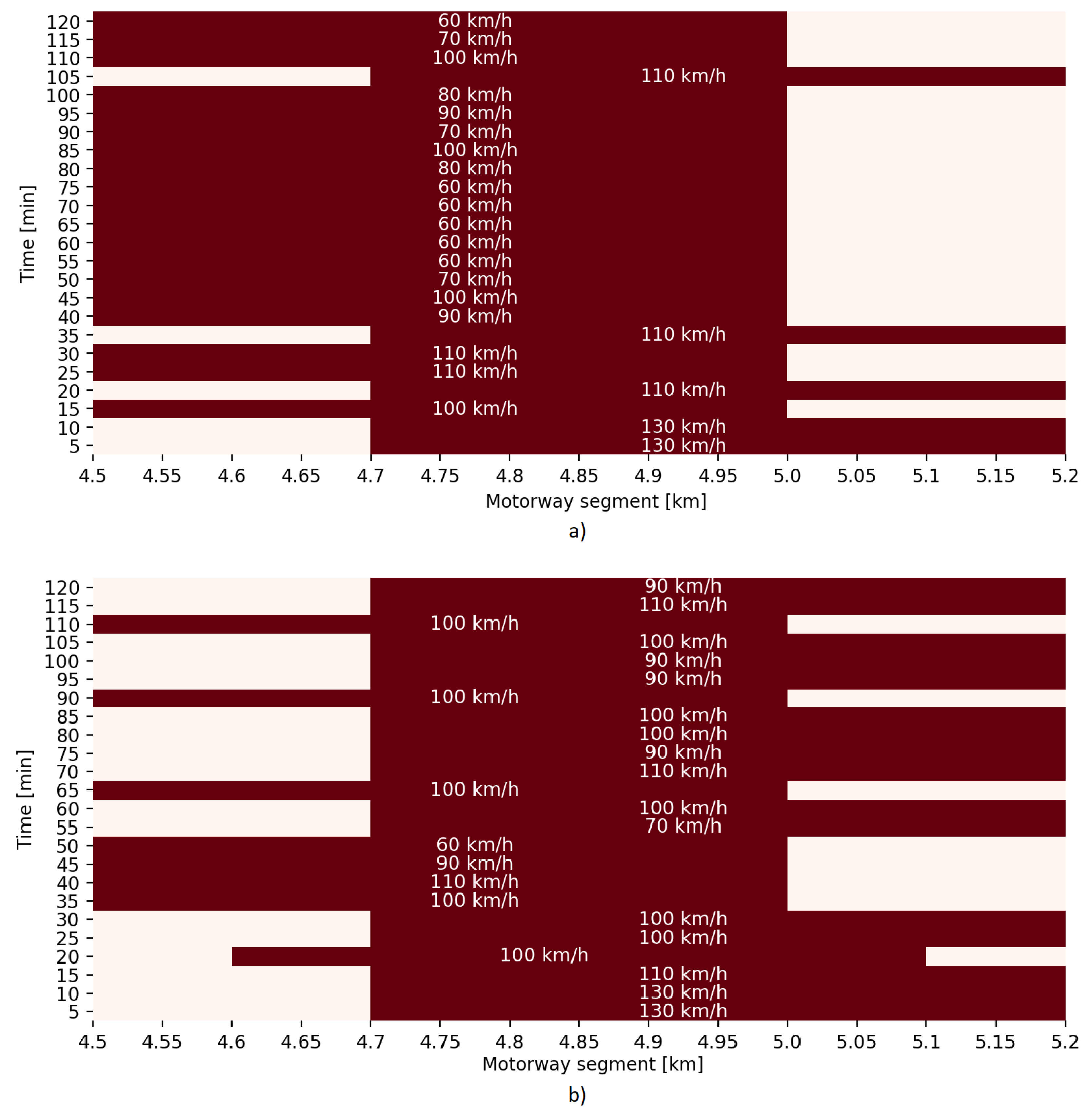
| Scenario | Results | Improvement | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motorway Segment | Area of Interest | Motorway Segment | Area of Interest | |||||||
| Number |
CAV Penetration Rate |
Control Strategy |
TTS [veh·h] |
MTT [s] |
Mean
v
[km/h] |
Mean [veh/km/ln] |
TTS [%] |
MTT [%] |
Mean
v
[%] |
Mean [%] |
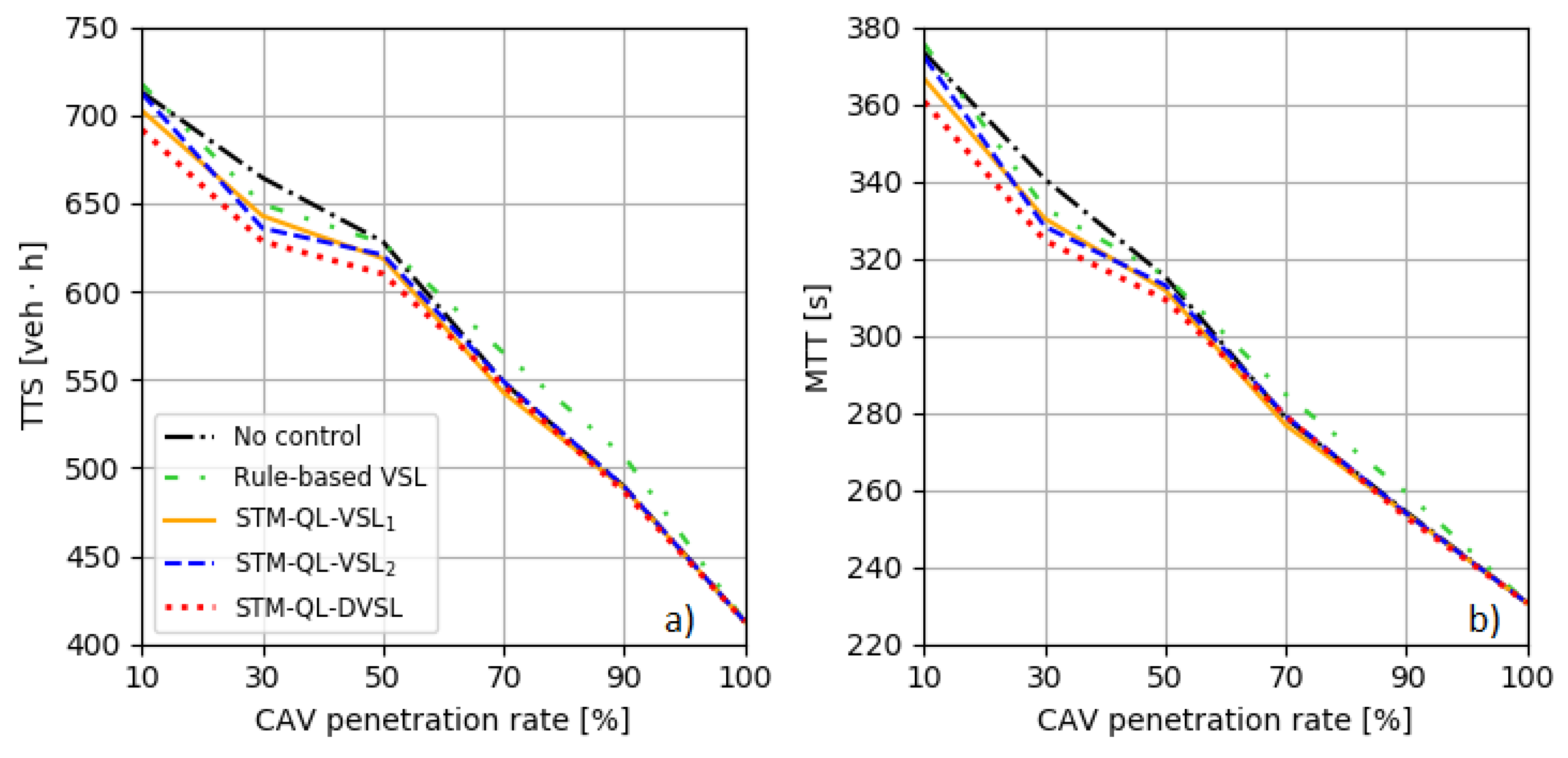
| 1 | 10% | No control | 713.0 | 373.3 | 61.5 | 36.9 | - | - | - | - |
| RB-VSL | 717.4 | 375.6 | 62.3 | 36.5 | −0.6 | −0.6 | 1.3 | 1.1 | ||
| STM-QL-VSL | 702.4 | 366.5 | 62.8 | 35.3 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 4.3 | ||
| STM-QL-VSL | 712.2 | 372.2 | 61.4 | 36.9 | 0.1 | 0.3 | −0.2 | 0.0 | ||
| STM-QL-DVSL | 691.6 | 360.6 | 64.2 | 34.8 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 4.4 | 5.7 | ||
| 2 | No control | 664.4 | 340.5 | 75.1 | 29.5 | - | - | - | - | |
| RB-VSL | 649.3 | 333.0 | 75.7 | 29.2 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 0.7 | ||
| 30% | STM-QL-VSL | 642.8 | 330.3 | 76.7 | 27.9 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.1 | 5.4 | |
| STM-QL-VSL | 635.8 | 328.2 | 77.9 | 27.4 | 4.3 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 7.1 | ||
| STM-QL-DVSL | 628.3 | 324.6 | 79.5 | 26.2 | 5.4 | 4.7 | 5.9 | 11.2 | ||
| 3 | No control | 628.1 | 315.2 | 81.0 | 27.3 | - | - | - | - | |
| RB-VSL | 627.4 | 315.5 | 81.3 | 26.6 | 0.1 | −0.1 | 0.4 | 2.6 | ||
| 50% | STM-QL-VSL | 618.6 | 311.7 | 83.0 | 25.3 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 7.3 | |
| STM-QL-VSL | 620.7 | 313.0 | 83.3 | 25.3 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 2.8 | 7.3 | ||
| STM-QL-DVSL | 609.9 | 309.4 | 85.7 | 24.1 | 2.9 | 1.8 | 5.8 | 11.7 | ||
| 4 | No control | 548.4 | 278.6 | 95.4 | 19 | - | - | - | - | |
| RB-VSL | 565.1 | 284.7 | 92.7 | 21.5 | −3.0 | −2.2 | −2.8 | −13.2 | ||
| 70% | STM-QL-VSL | 542.6 | 276.7 | 96.3 | 18.3 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 3.7 | |
| STM-QL-VSL | 548.9 | 279.1 | 95.4 | 19.2 | −0.1 | −0.2 | 0.0 | −1.1 | ||
| STM-QL-DVSL | 546.5 | 279 | 95.9 | 19.4 | 0.4 | −0.1 | 0.5 | −2.1 | ||
| 5 | No control | 489.2 | 254.2 | 103.4 | 16.8 | - | - | - | - | |
| RB-VSL | 506.5 | 259.2 | 100.2 | 18.9 | −3.5 | −2.0 | −3.1 | −12.5 | ||
| 90% | STM-QL-VSL | 488.5 | 253.7 | 103.4 | 16.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 2.4 | |
| STM-QL-VSL | 489.2 | 253.8 | 103.6 | 16.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 3.6 | ||
| STM-QL-DVSL | 486.4 | 252.9 | 104.2 | 15.9 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 5.4 | ||
| 6 | No control | 412.9 | 230.7 | 112.5 | 12.3 | - | - | - | - | |
| RB-VSL | 412.9 | 230.7 | 112.5 | 12.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| 100% | STM-QL-VSL | 412.9 | 230.7 | 112.5 | 12.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| STM-QL-VSL | 412.9 | 230.7 | 112.5 | 12.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| STM-QL-DVSL | 412.9 | 230.7 | 112.5 | 12.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrbanić, F.; Tišljarić, L.; Majstorović, Ž.; Ivanjko, E. Reinforcement Learning-Based Dynamic Zone Placement Variable Speed Limit Control for Mixed Traffic Flows Using Speed Transition Matrices for State Estimation. Machines 2023, 11, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11040479
Vrbanić F, Tišljarić L, Majstorović Ž, Ivanjko E. Reinforcement Learning-Based Dynamic Zone Placement Variable Speed Limit Control for Mixed Traffic Flows Using Speed Transition Matrices for State Estimation. Machines. 2023; 11(4):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11040479
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrbanić, Filip, Leo Tišljarić, Željko Majstorović, and Edouard Ivanjko. 2023. "Reinforcement Learning-Based Dynamic Zone Placement Variable Speed Limit Control for Mixed Traffic Flows Using Speed Transition Matrices for State Estimation" Machines 11, no. 4: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11040479
APA StyleVrbanić, F., Tišljarić, L., Majstorović, Ž., & Ivanjko, E. (2023). Reinforcement Learning-Based Dynamic Zone Placement Variable Speed Limit Control for Mixed Traffic Flows Using Speed Transition Matrices for State Estimation. Machines, 11(4), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11040479











