A Portable Real-Time Test Bench for Dielectric Elastomer Actuators
Abstract
1. Introduction
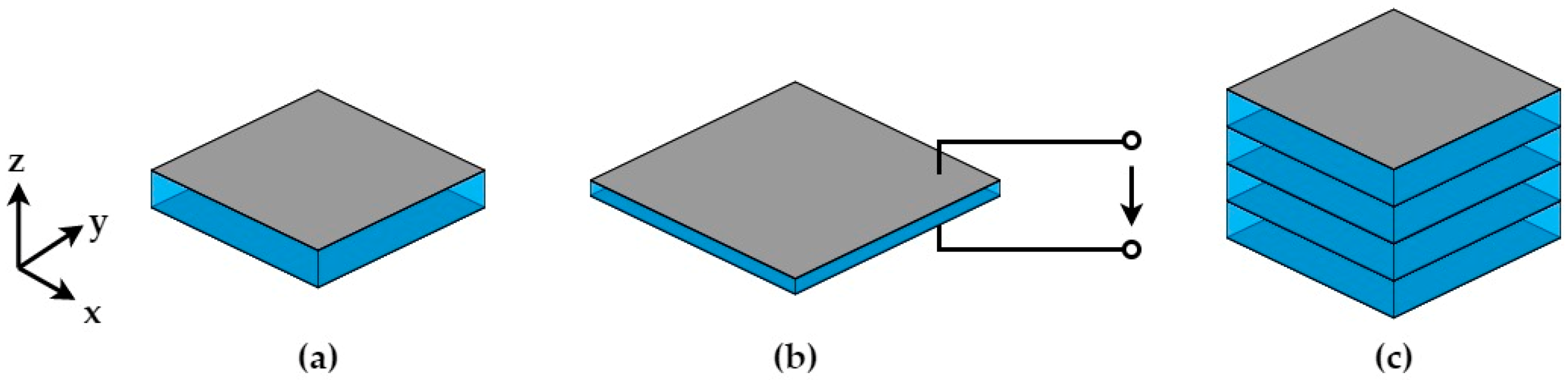
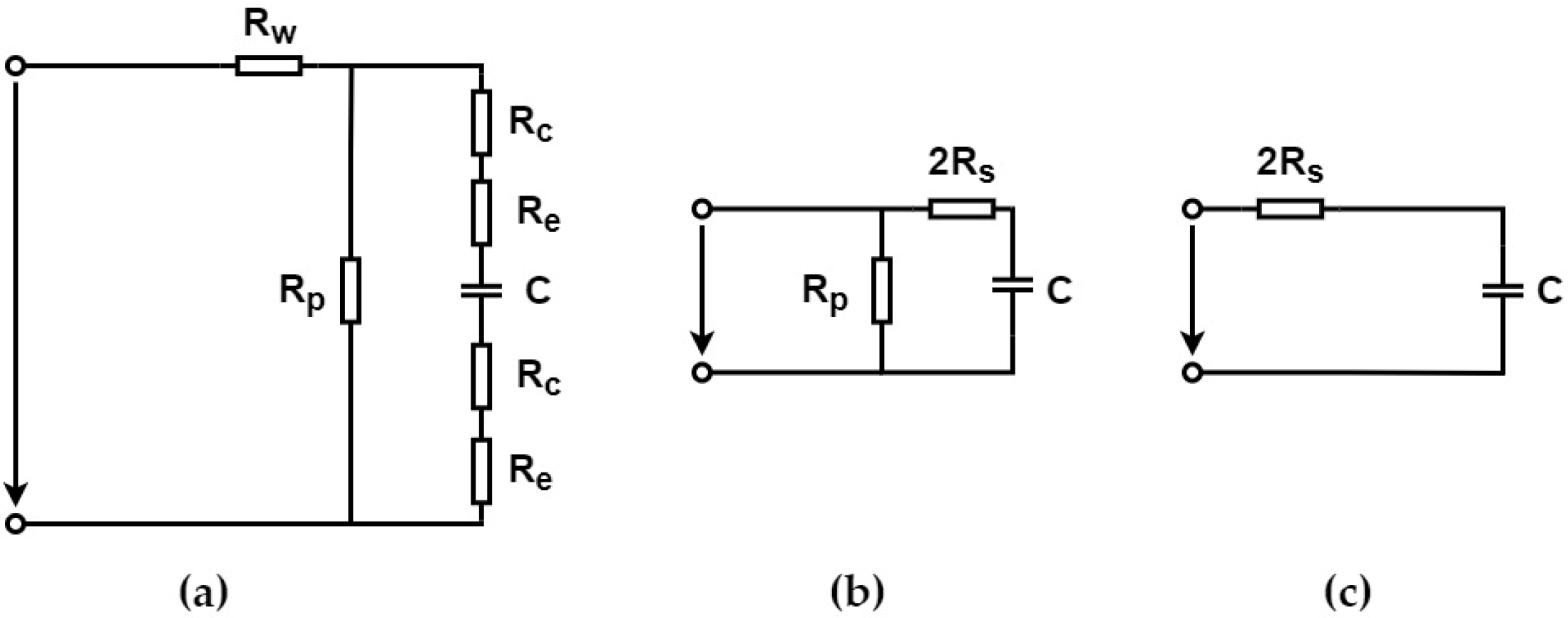
2. Dielectric Elastomer Actuators
3. Methods
4. Results
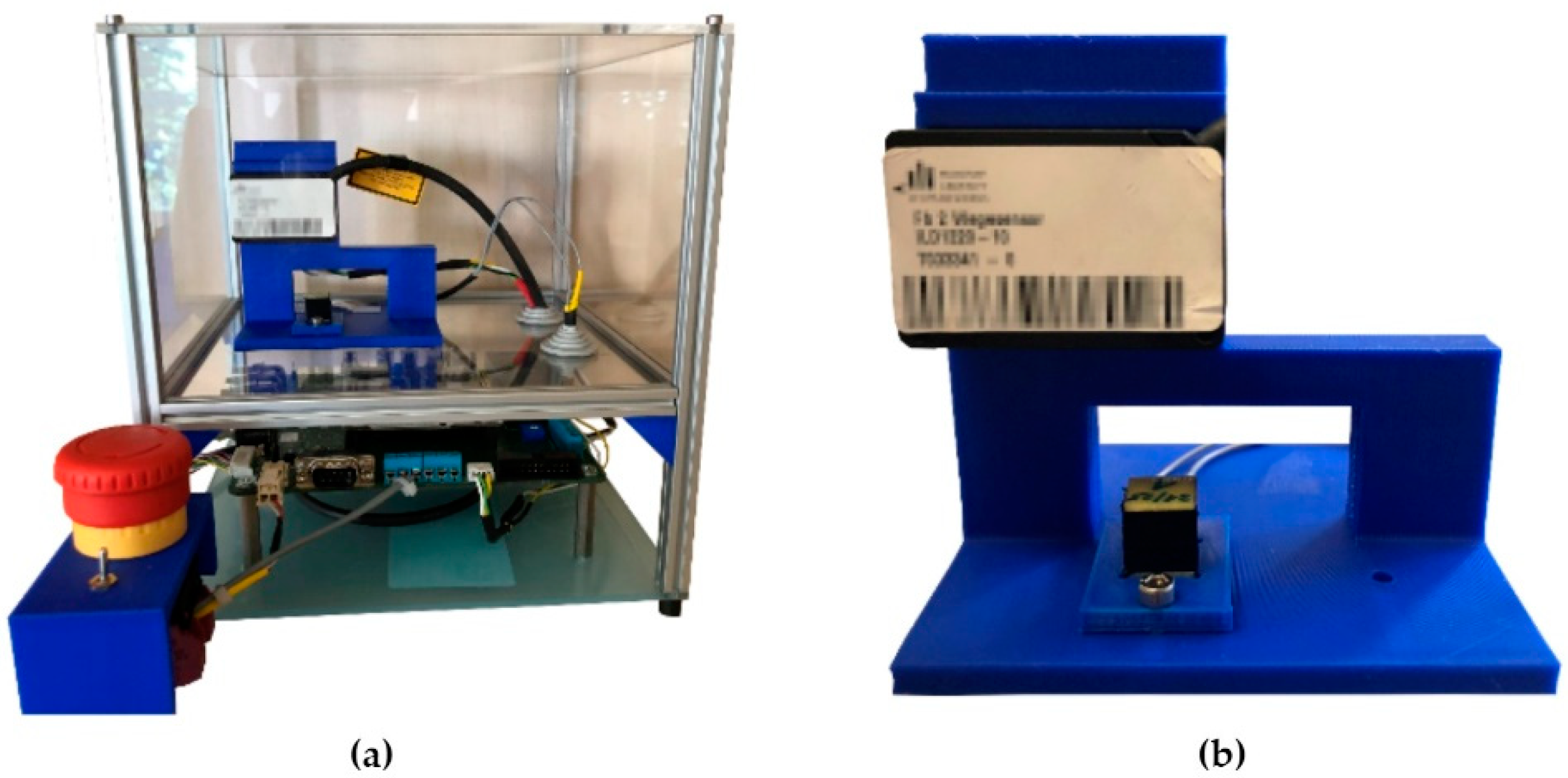
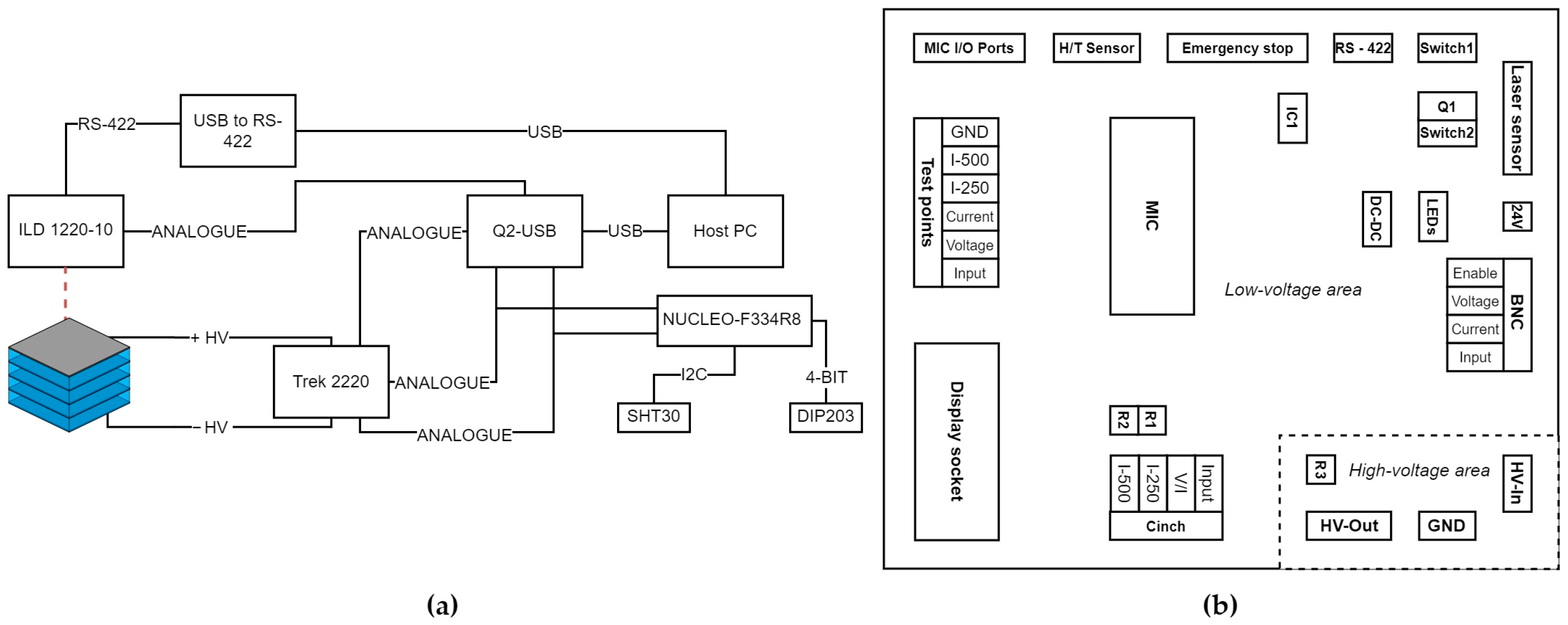
4.1. Printed Circuit Board
4.1.1. High-Voltage Area
4.1.2. Low-Voltage Area
4.1.3. Laser Sensor
4.1.4. Voltage and Current Monitors
4.1.5. Testing and Safety
4.2. Housing
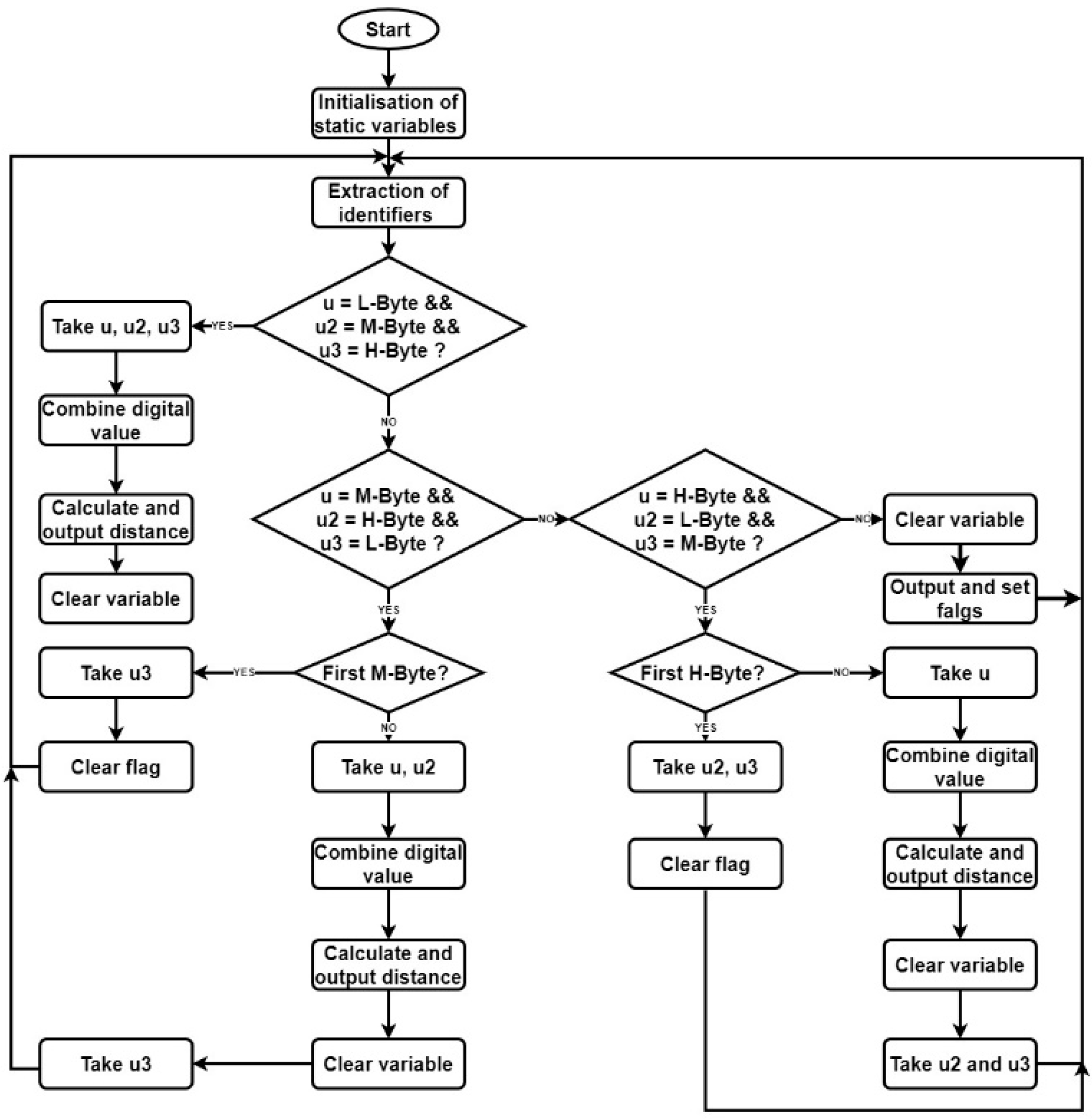
4.3. Software Implementation
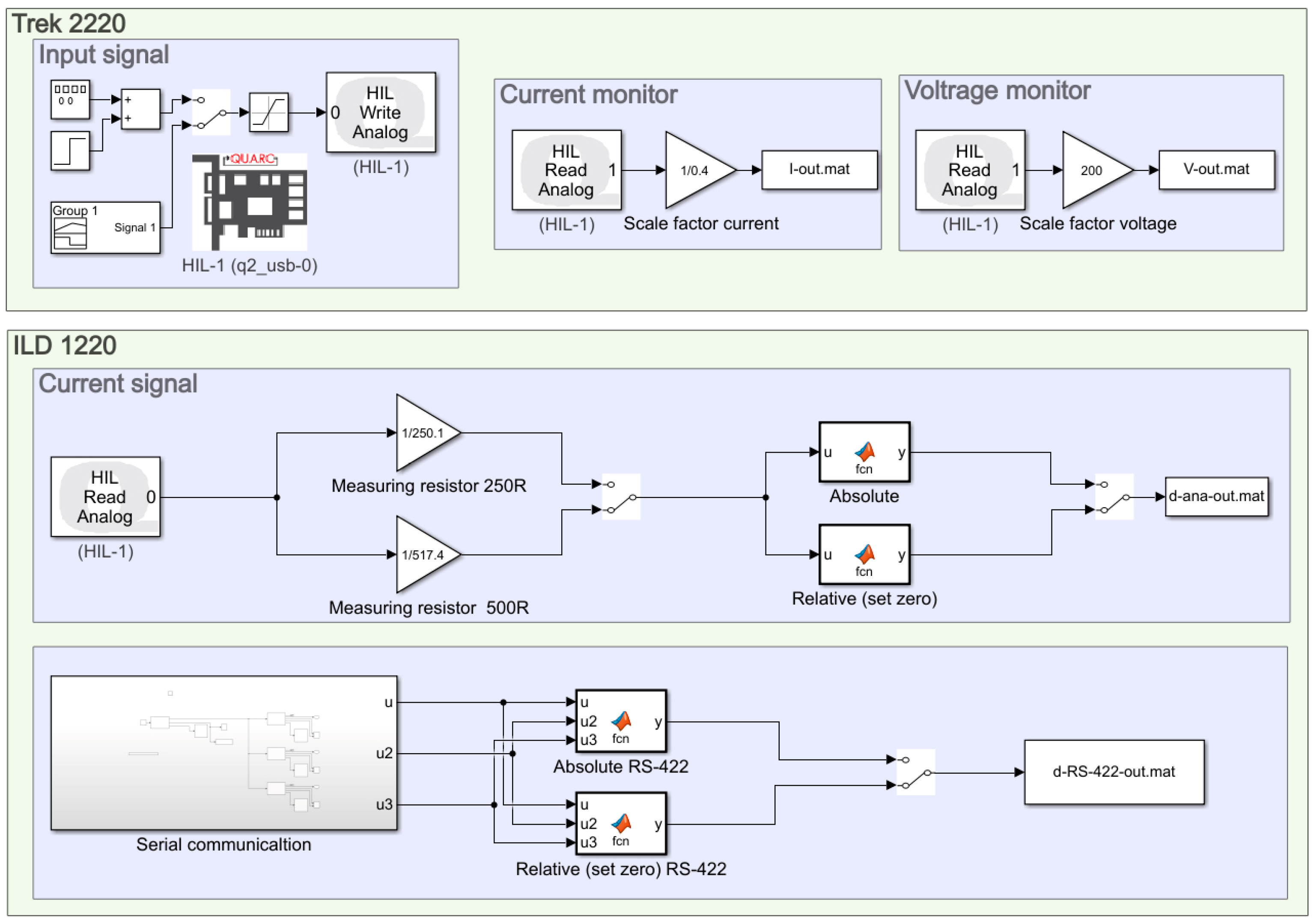
4.3.1. MATLAB/Simulink
4.3.2. NUCLEO-F334R8
4.3.3. Temperature and Humidity Measurement
4.3.4. Zeroing of the Laser Sensor
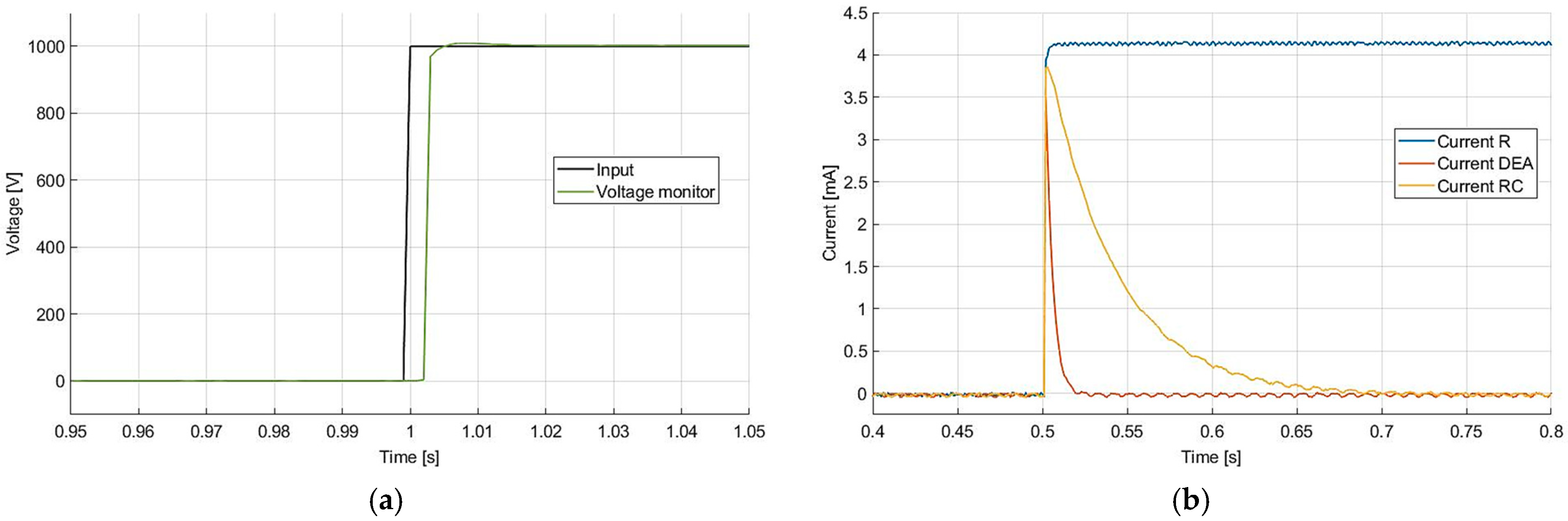
4.4. Measurements
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Nurzaman, S.G.; Iida, F. Soft-Material Robotics. ROB 2017, 5, 191–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, C.; Mazzolai, B.; Cianchetti, M. Soft robotics: Technologies and systems pushing the boundaries of robot abilities. Sci. Robot. 2016, 1, eaah3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verl, A.; Albu-Schäffer, A.; Brock, O.; Raatz, A. Soft Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gao, D.; Lee, P.S. Recent Progress in Artificial Muscles for Interactive Soft Robotics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 33, e2003088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaka, K.; Okuzaki, H. Soft Actuators; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 978-981-13-6849-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mirvakili, S.M.; Hunter, I.W. Artificial Muscles: Mechanisms, Applications, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randazzo, M. Multilayer Dielectric Elastomer Actuators; University of Genoa: Genova, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Behboodi, A.; Lee, S. Benchmarking of a Commercially Available Stacked Dielectric Elastomer as an Alternative Actuator for Rehabilitation Robotic Exoskeletons. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 499–505, ISBN 978-1-7281-2755-2. [Google Scholar]
- CTsystems AG. CTstack: The Transducer Technology. Available online: https://ct-systems.ch/technology/ctstack-the-transducer-technology/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Zuo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J. Humidity Effect on Dynamic Electromechanical Properties of Polyacrylic Dielectric Elastomer: An Experimental Study. Polymers 2021, 13, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, S.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wissler, M.; Löwe, C.; Kovacs, G. A comparison between silicone and acrylic elastomers as dielectric materials in electroactive polymer actuators. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.D.; Assaf, T.; Pearson, M.J.; Rossiter, J.M.; Anderson, S.R.; Porrill, J.; Dean, P. Cerebellar-inspired algorithm for adaptive control of nonlinear dielectric elastomer-based artificial muscle. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20160547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Liang, W.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Q. Control of a muscle-like soft actuator via a bioinspired approach. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2018, 13, 66005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Cao, J.; Ren, Q.; Xu, J.-X. Control of Dielectric Elastomer Soft Actuators Using Antagonistic Pairs. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 2862–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lee, H.P.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Q. Control of a Soft Inchworm Robot With Environment Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 3809–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, S.; O’Brien, B.M.; Gisby, T.; Xu, D.; Shea, H.R.; Anderson, I.A. Self-sensing dielectric elastomer actuators in closed-loop operation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 104018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Qin, L.; Cao, J.; Kankanhalli, M.S.; Zhu, J. Deep Reinforcement Learning in Soft Viscoelastic Actuator of Dielectric Elastomer. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2094–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.-H.; Jeong, S.M.; Hwang, G.; Kim, H.; Hyeon, K.; Park, J.; Kyung, K.-U. Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Soft Robotics Applications and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.-Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, L.-M.; Zhu, X. A survey on dielectric elastomer actuators for soft robots. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2017, 12, 11003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Tadokoro, S. Electroactive Polymers for Robotic Applications: Artificial Muscles and Sensors; Springer: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hau, S. High-Performance Dielectric Elastomer Actuators; Universität des Saarlandes: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pelrine, R.E.; Kornbluh, R.D.; Joseph, J.P. Electrostriction of polymer dielectrics with compliant electrodes as a means of actuation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 64, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, P. Dielektrische Elastomerstapelaktoren für ein Peristaltisches Fluidfördersystem; Technischen Universität Darmstadt: Darmstadt, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- El Atrache Ceballos, A. Dynamic Modeling of Soft Robotic Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Ph.D. Thesis, Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, Daytona Beach, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J. Mechanics of dielectric elastomers: Materials, structures, and devices. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2016, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haus, H.; Matysek, M.; Mößinger, H.; Schlaak, H.F. Modelling and characterization of dielectric elastomer stack actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 104009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanser. QUARC Real-Time Control Software-Quanser. Available online: https://www.quanser.com/products/quarc-real-time-control-software/ (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Advanced Energy Industries, Inc. Trek 2200 Series|Piezo Drivers|Advanced Energy. Available online: https://www.advancedenergy.com/products/high-voltage-products/high-voltage-amplifiers/piezo-drivers/trek-2200-series/ (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Giousouf, M.; Kovacs, G. Dielectric elastomer actuators used for pneumatic valve technology. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanser. Q2-USB Data Acquisition Device-Quanser. Available online: https://www.quanser.com/products/q2-usb-data-acquisition-device/ (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Micro-Epsilon Messtechnik. Kompakter Laser-Wegsensor für OEM und Serieneinsatz. Available online: https://www.micro-epsilon.de/displacement-position-sensors/laser-sensor/optoNCDT_1220/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Keferstein, C.P.; Marxer, M. Fertigungsmesstechnik: Praxisorientierte Grundlagen, moderne Messverfahren, 8th ed.; Springer Fachmedien: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2015; ISBN 3-8348-2583-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sensirion. Home. Available online: https://sensirion.com/de/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- STMicroelectronics. STM32F334R8-STMicroelectronics. Available online: https://www.st.com/en/microcontrollers-microprocessors/stm32f334r8.html (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- FSnD Ltd. LCD Displays für Platinenmontage. Available online: https://www.lcd-module.de/produkte/dip.html (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- Multicomp Pro. Multicomp Pro|The Engineer’s Choice. Available online: http://www.multicomp-pro.com/ (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Quanser. QUARC Serial Interfacing Binary Demo: QUARC Demos. Available online: http://quanser-update.azurewebsites.net/quarc/documentation/quarc_serial_interfacing_binary_demo.html (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Flittner, K. Dielektrische Elastomerstapelaktoren für Mikroventile; Technischen Universität Darmstadt: Darmstadt, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Effinger, V.M. Finite Nichtlinear Viskoelastische Modellierung Offenzelliger Polymerschäume; Institut für Baustatik und Baudynamik, Universität Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-00-054033-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lotz, P.; Matysek, M.; Flittner, K.; Schlaak, H.F. Modeling of non ideal dielectric elastomer stack actuators. In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD) 2010; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; pp. 330–338. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, K.; Kitazaki, Y.; Kondo, K. A Simple Dynamic Characterization Method for Thin Stacked Dielectric Elastomer Actuators by Suspending a Weight in Air and Electrical Excitation. Actuators 2021, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat, J.; Gajewski, P.; Kołota, J.; Marcinkowska, A. Review of Soft Actuators Controlled with Electrical Stimuli: IPMC, DEAP, and MRE. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohlbach, L.; Bhatta, S.; Perez-Peña, F.; Schmidt, K. A Portable Real-Time Test Bench for Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Machines 2023, 11, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030380
Sohlbach L, Bhatta S, Perez-Peña F, Schmidt K. A Portable Real-Time Test Bench for Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Machines. 2023; 11(3):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030380
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohlbach, Lukas, Sushil Bhatta, Fernando Perez-Peña, and Karsten Schmidt. 2023. "A Portable Real-Time Test Bench for Dielectric Elastomer Actuators" Machines 11, no. 3: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030380
APA StyleSohlbach, L., Bhatta, S., Perez-Peña, F., & Schmidt, K. (2023). A Portable Real-Time Test Bench for Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Machines, 11(3), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030380






