Development of a Rotary Damper Integrated with Magnetorheological Bearings toward Extremely High Torque–Volume Ratio
Abstract
1. Introduction
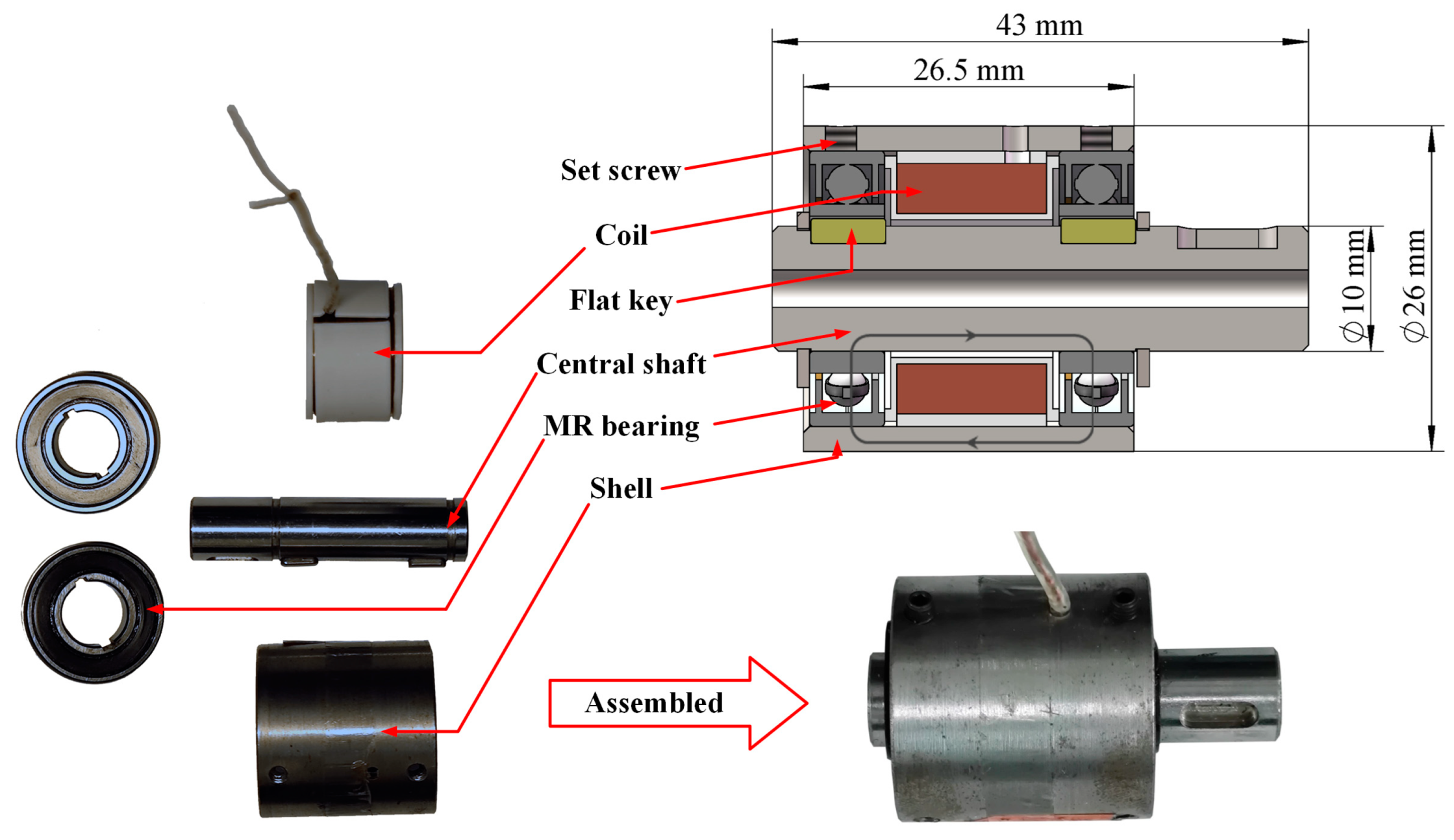
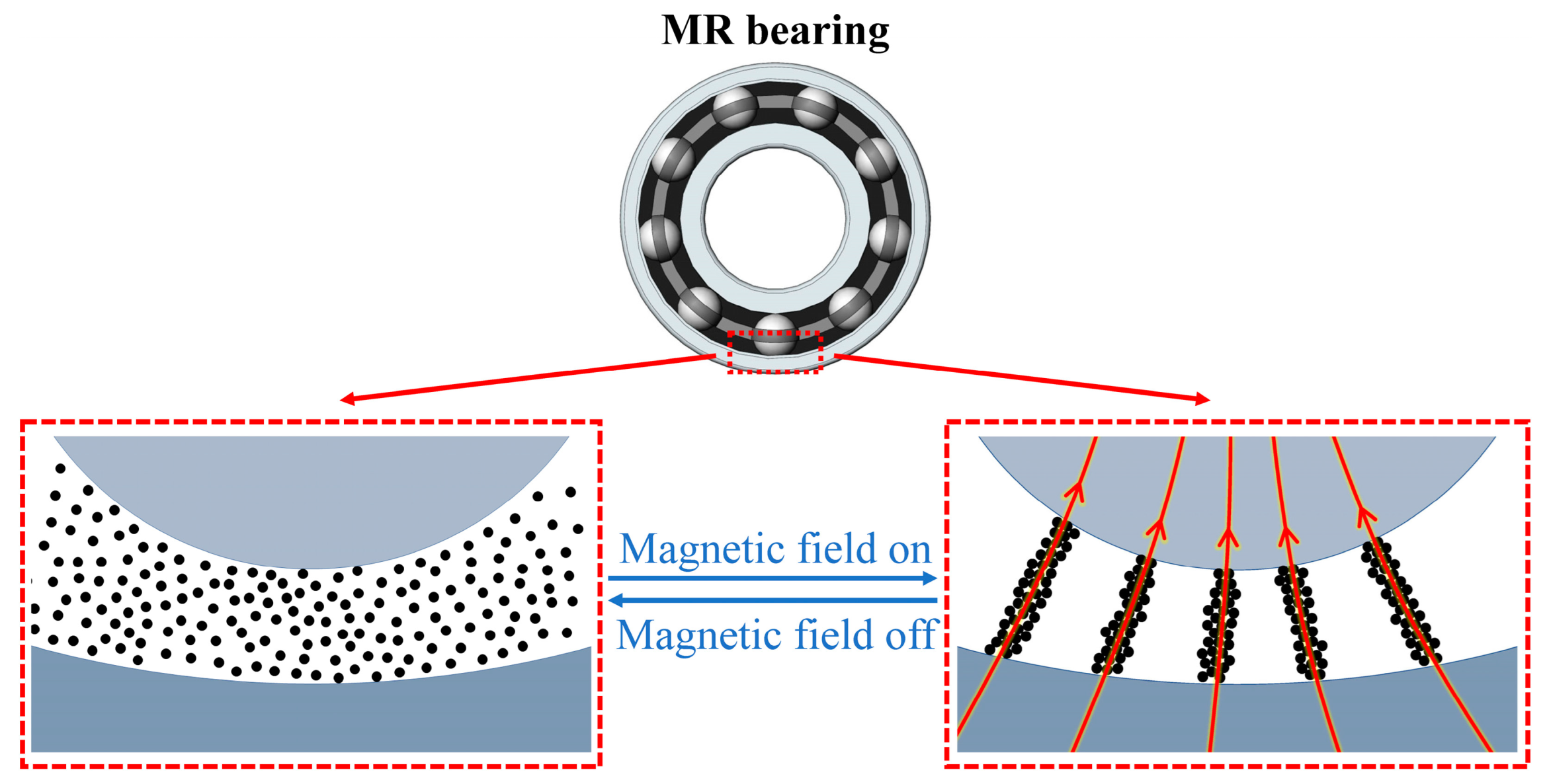
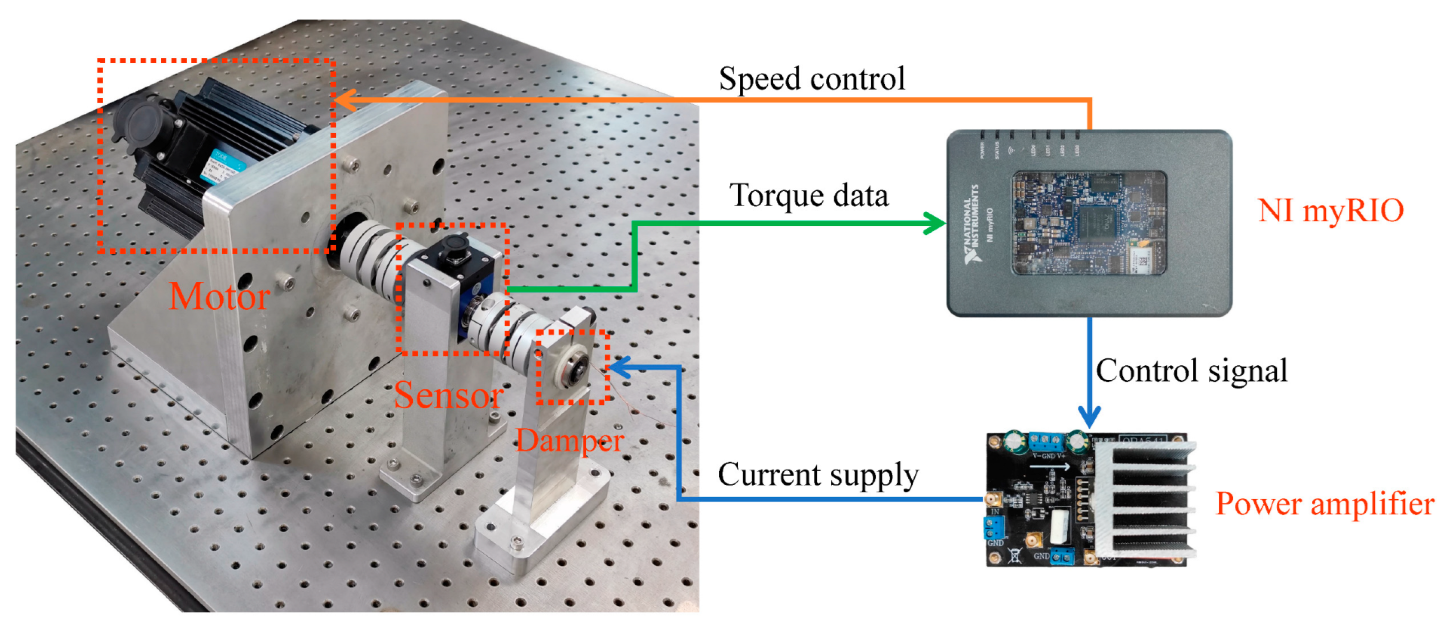
2. Structural Design and Prototype of the MR Damper
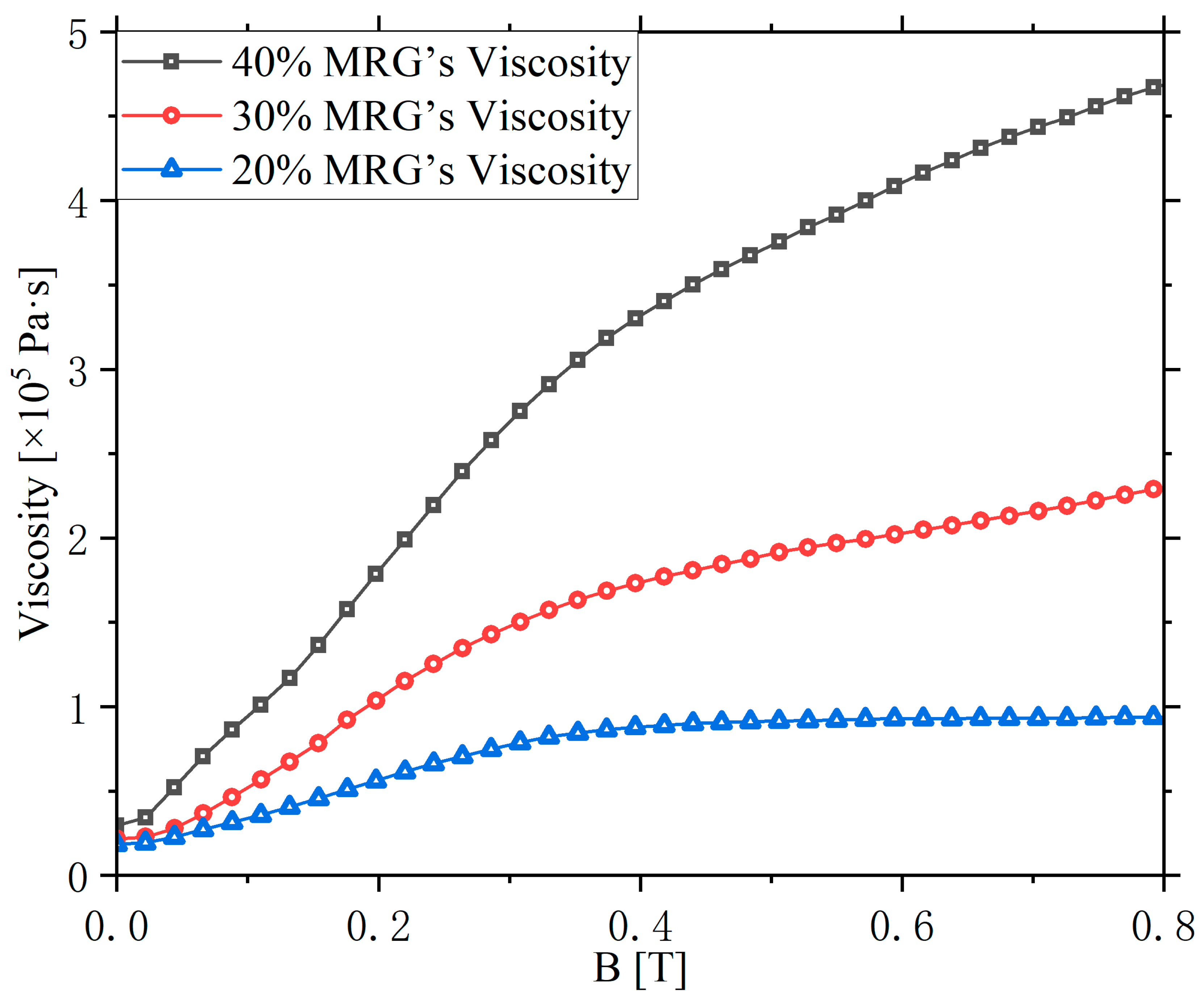
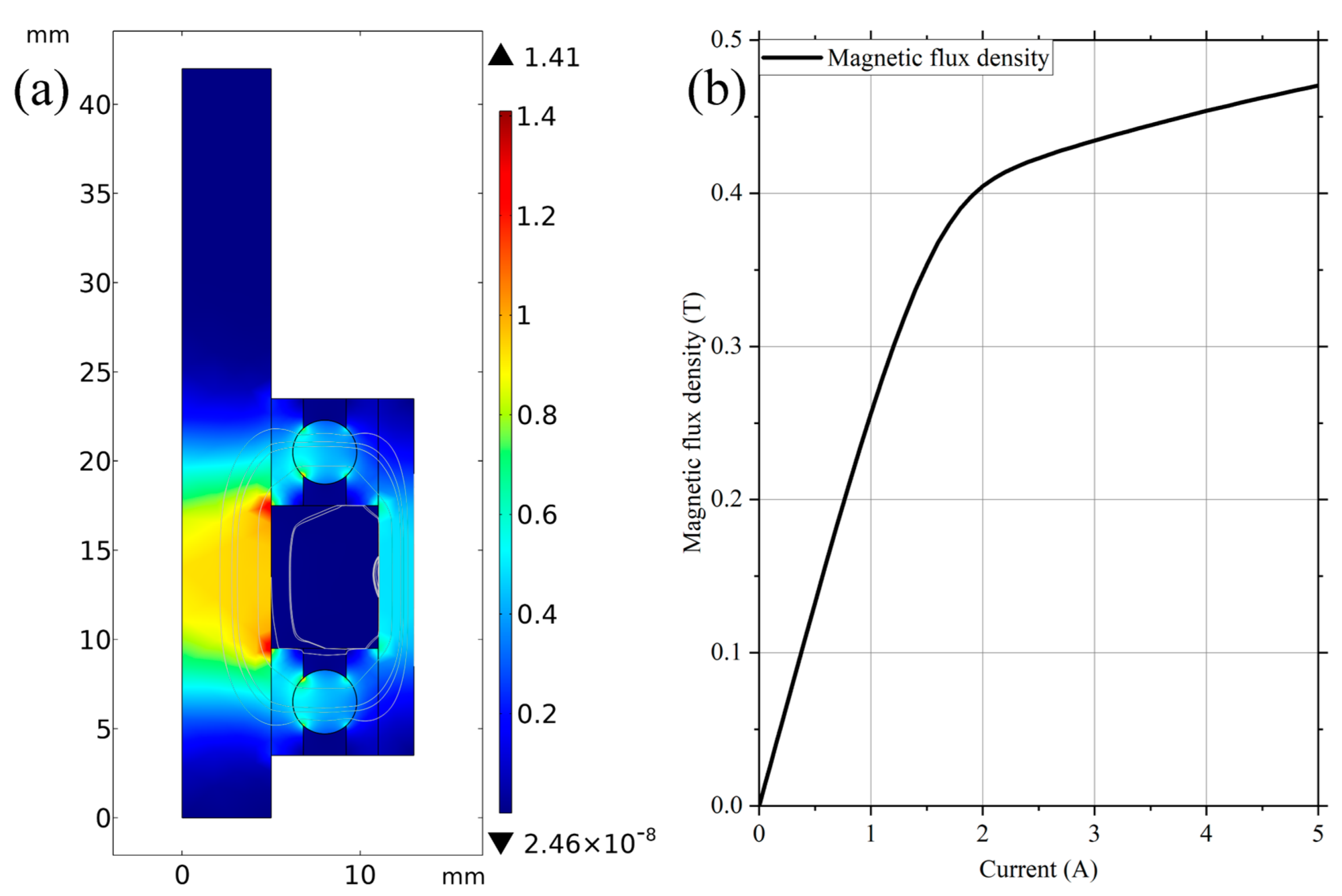
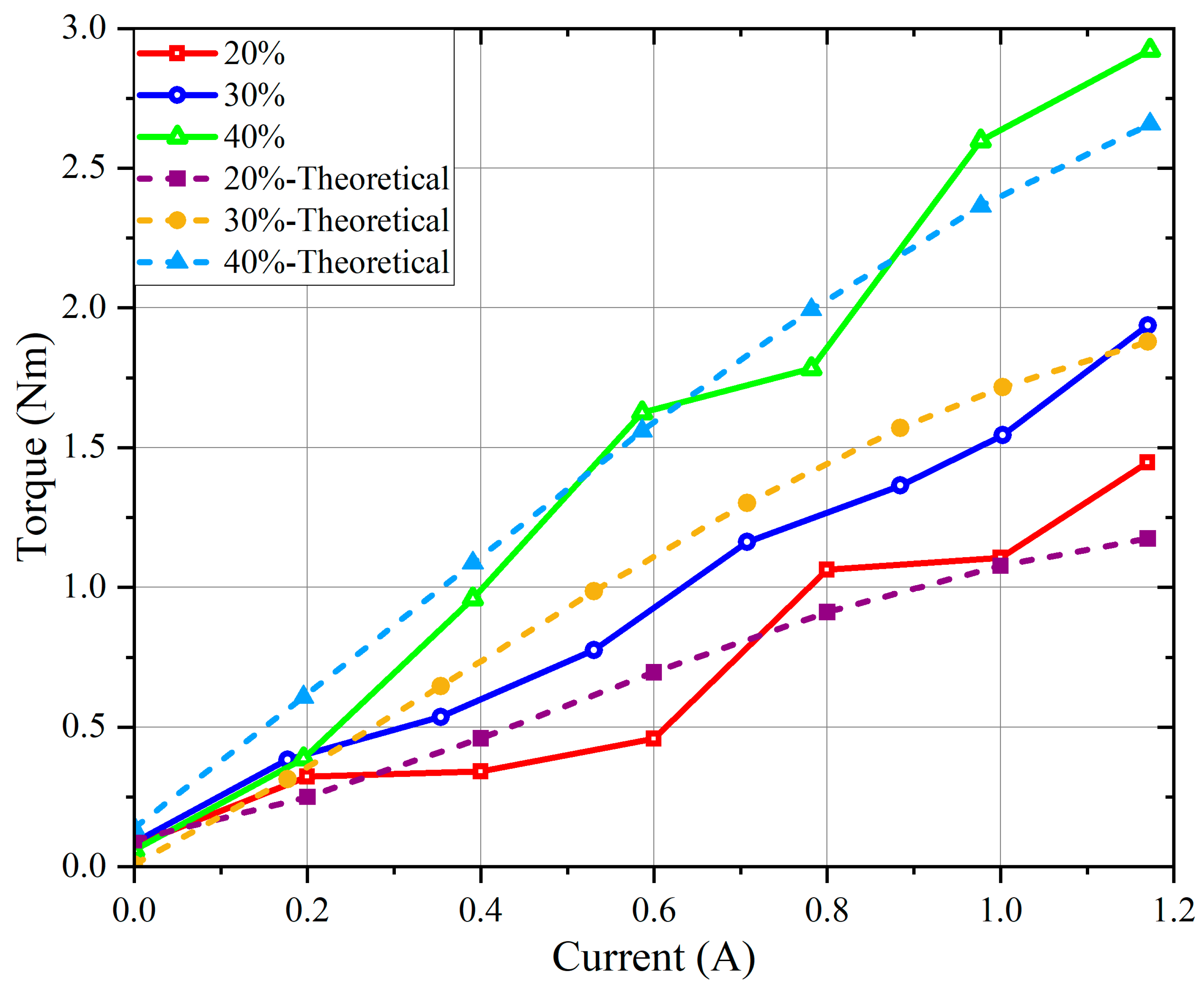
3. Theoretical Analysis of the Torque of the MR Damper
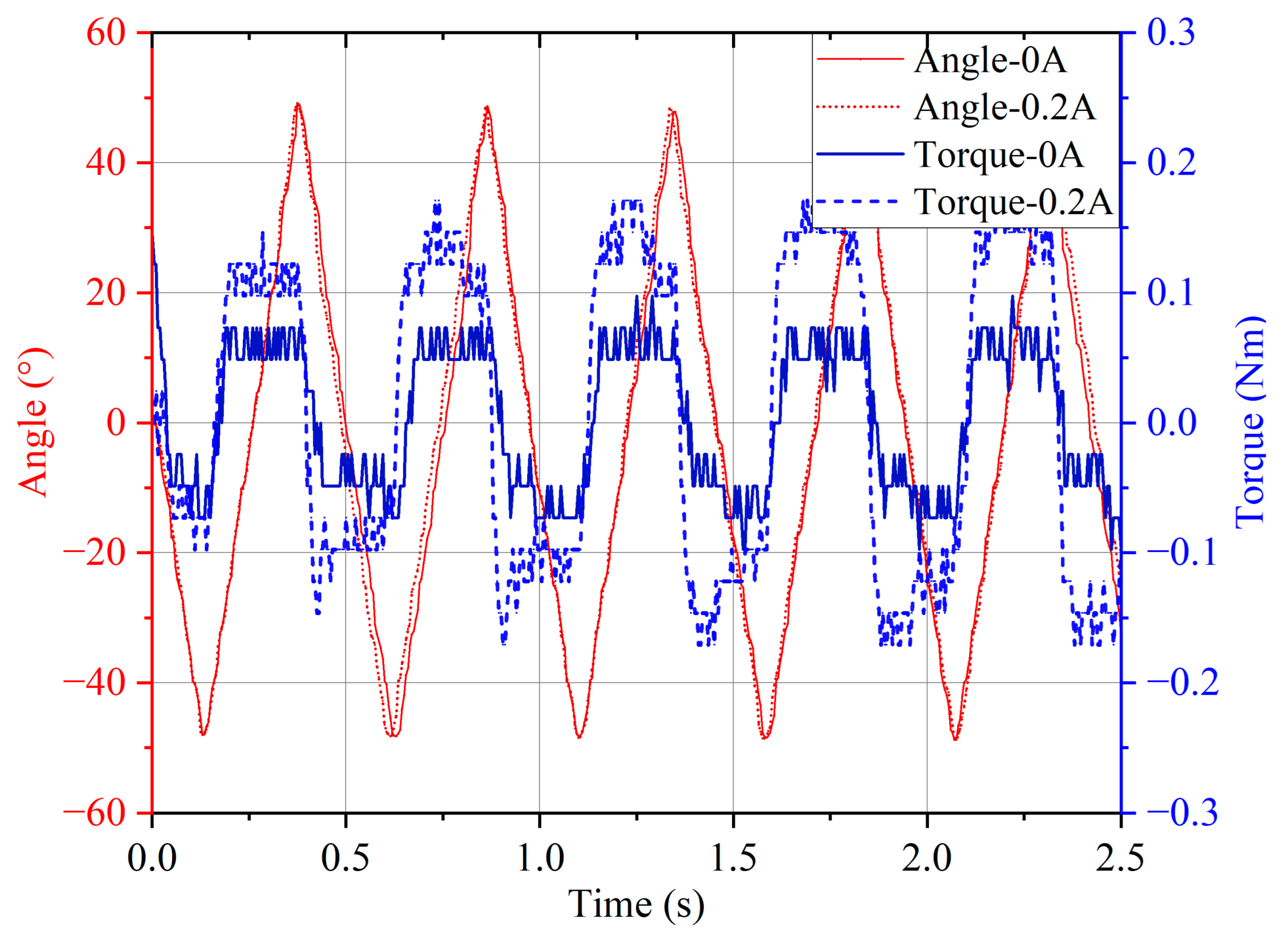
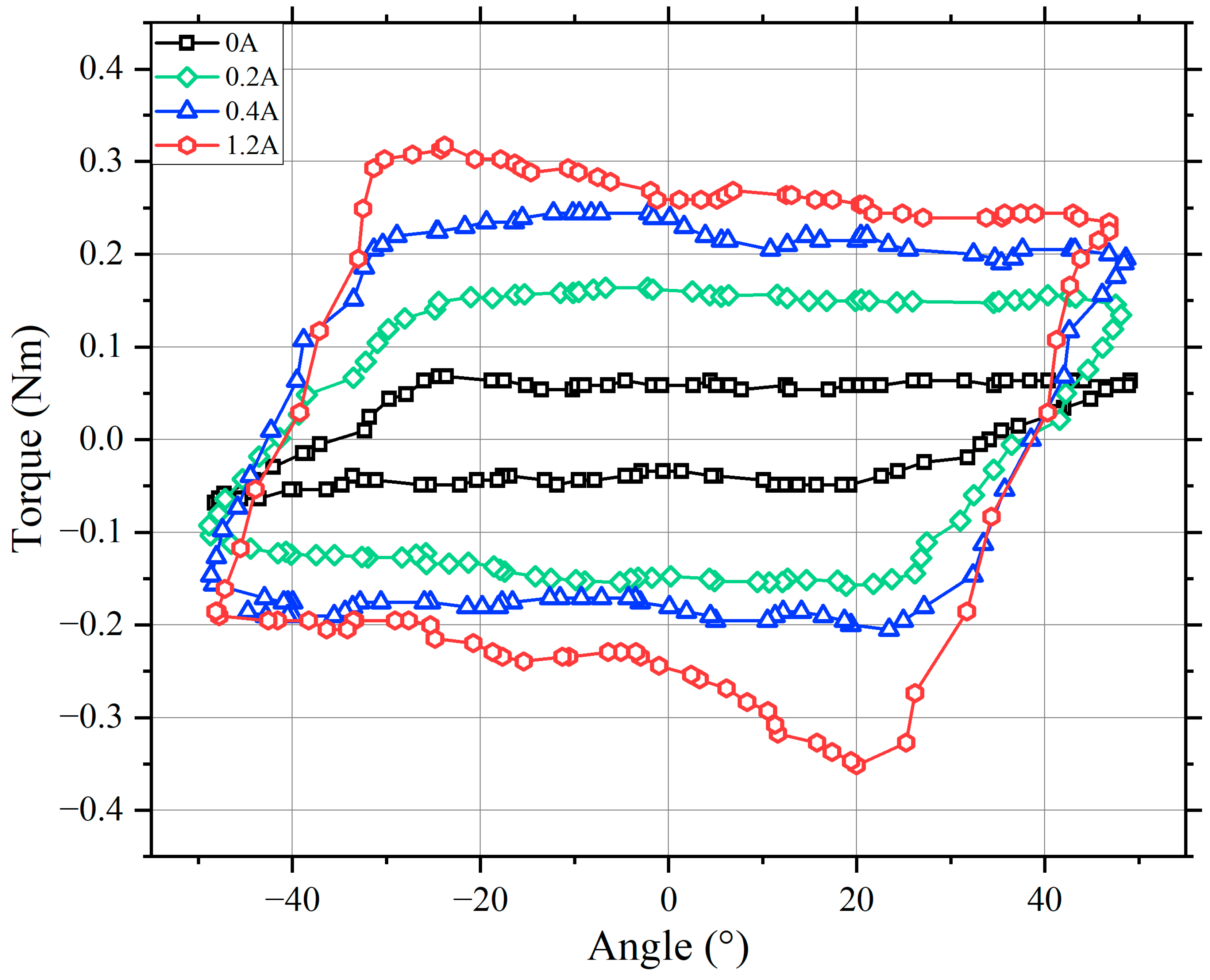
4. Performance Test of the MR Damper
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, B.J.; Fang, F.F.; Choi, H.J. Magnetorheology: Materials and application. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 5246–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancati, R.; Di Massa, G.; Pagano, S. Investigation on the Mechanical Properties of MRE Compounds. Machines 2019, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vicente, J.; Klingenberg, D.J.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. Magnetorheological fluids: A review. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3701–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Du, H. A state-of-the-art review on magnetorheological elastomer devices. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Ju, B.; Fu, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q. Influence of composition of carbonyl iron particles on dynamic mechanical properties of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Xuan, S.; Ding, L.; Gong, X. Stretchable and magneto-sensitive strain sensor based on silver nanowire-polyurethane sponge enhanced magnetorheological elastomer. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Mazlan, S.A.; Choi, S.B.; Nordin, M.F.M. The Field-Dependent Rheological Properties of Magnetorheological Grease Based on Carbonyl-Iron-Particles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 095043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Yang, S.; Pan, C. Dynamic Modeling of Magnetorheological Damper Behaviors. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2006, 17, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.-X.; Hu, W.; Wereley, N.M. Magnetorheological Damper Utilizing an Inner Bypass for Ground Vehicle Suspensions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3422–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.-H.; Choi, S.-B. Optimal design of a vehicle magnetorheological damper considering the damping force and dynamic range. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 18, 015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Shang, H.; Wei, X. Design and Performance Analysis of a Double-Outlet-Rod Magnetorheological Damper for Impact Load. Machines 2022, 10, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaduddin, F.; Mazlan, S.A.; Zamzuri, H. A design and modelling review of rotary magnetorheological damper. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piantini, S.; Giorgetti, A.; Baldanzini, N.; Monti, C.; Pierini, M. Design of a Motorcycle Steering Damper for a Safer Ride. Machines 2020, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Han, C.; Ahn, D.; Lee, J.K.; Park, S.-H.; Park, S. Design and Performance Evaluation of a Rotary Magnetorheological Damper for Unmanned Vehicle Suspension Systems. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.S.T.; Chandramohan, S.; Sujatha, S.; Kumar, H. Design of bypass rotary vane magnetorheological damper for prosthetic knee application. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2021, 32, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y. A rotary magnetorheological fluid damper for pathological tremor suppression. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Chengdu, China, 5–8 August 2012; pp. 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, P. A novel scissor-type magnetorheological seat suspension system with self-sustainability. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 30, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Du, H. Design and Experimental Evaluation of a Magnetorheological Brake. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2003, 21, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Stoikov, D.; Falcao Da Luz, L.; Suleman, A. A performance evaluation of an automotive magnetorheological brake design with a sliding mode controller. Mechatronics 2006, 16, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y. Analysis and design of a cylindrical magneto-rheological fluid brake. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 129, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, W. Prototype and test of a novel rotary magnetorheological damper based on helical flow. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossa, C.; Jaegy, A.; Micaelli, A.; Lozada, J. Development of a multilayered wide-ranged torque magnetorheological brake. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 025028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dong, X.; Su, X.; Qi, S. Development and characterization of a novel rotary magnetorheological fluid damper with variable damping and stiffness. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 165, 108320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Arevalo, J.C.; Muñoz, G.; Gonzalez-De-Santos, P. On the Biomimetic Design of Agile-Robot Legs. Sensors 2011, 11, 11305–11334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zi, B.; Cao, Z.; Ding, H. Development of an active and passive finger rehabilitation robot using pneumatic muscle and magnetorheological damper. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 147, 103762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Oh, J.-H. Development of an above knee prosthesis using MR damper and leg simulator. In Proceedings of the 2001 ICRA. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 01CH37164), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 21–26 May 2001; pp. 3686–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhu, A.; Song, J.; Dang, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. A novel magnetorheological damper combing multi-disc and multi-drum structures. In Proceedings of the 2022 19th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 4–6 July 2022; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, K.H.; Jónsdóttir, F.; Thorsteinsson, F. A geometrical optimization of a magneto-rheological rotary brake in a prosthetic knee. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 035023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gordaninejad, F. Flow analysis of field-controllable, electro-and magneto-rheological fluids using Herschel-Bulkley model. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1999, 10, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Lee, S.-K.; Parkb, Y.P. A hysteresis model for the field-dependent damping force of a magnetorheological damper. J. Sound Vib. 2001, 245, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wereley, N.M.; Pang, L.; Kamath, G.M. Idealized hysteresis modeling of electrorheological and magnetorheological dampers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1998, 9, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liao, C.R.; Chen, W.M.; Huang, S.L. Study on MR Semi-active Suspension System and its Road Testing. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2006, 17, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, W.; Ying, Q.; Long, C.; Fu, X. Forecasting the cumulative number of COVID-19 deaths in China: A Boltzmann function-based modeling study. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassow, F. Despin bearing technology and applications for communications satellites. In Proceedings of the 3rd Communications Satellite Systems Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–8 April 1970; p. 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.D.; Leroy, D.F.; Holzheimer, J.C.; Prindle, D.R.; Marjoram, R.H. Controllable Brake. U.S. Patents US5842547A, 1 December 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Senkal, D.; Gurocak, H. Serpentine flux path for high torque MRF brakes in haptics applications. Mechatronics 2010, 20, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, W.H.; Kosasih, P.B.; Zhang, X.Z. Development of an MR-brake-based haptic device. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liao, W.-H. Optimization of a multifunctional actuator utilizing magnetorheological fluids. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Budapest, Hungary, 3–7 July 2011; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, Y.-J.; Moon, Y.-J.; Park, M.-K. Performance Improvement of a Rotary MR Fluid Actuator Based on Electromagnetic Design. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2007, 19, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| α | A1(α) | A2(α) | x0(α) | dx(α) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 8153 | 93,555 | 0.17559 | 0.08557 |
| 30% | −19,297 | 2.0005 × 105 | 0.17565 | 0.10752 |
| 40% | −60,749 | 4.1824 × 105 | 0.19812 | 0.13147 |
| Parameters | Unit | Designed Damper in This Study | Carlos Rossa et al. [22] | Lord Corp. RD-2078-1 [35] | Senkal and Gurocak [36] | Liu et al. [37] | Guo and Liao [38] | Nam et al. [39] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max torque | Nm | 2.92 | 5.3 | 4 | 10.9 | 7 | 0.48 | 4.2 |
| Length | mm | 43 | 39 | 35.7 | 89.7 | 21 | 18 | 38 |
| Radius | mm | 13 | 30 | 96.6 | 31.75 | 78 | 25 | 60 |
| Power | W | 10.9 | 19 | 15 | 20 | — | — | 52 |
| Torque/vol. | kN·m−2 | 190 | 48.1 | 12.5 | 38.3 | 17.4 | 13.6 | 9.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Gong, N.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Gong, X.; Li, W.; Sun, S. Development of a Rotary Damper Integrated with Magnetorheological Bearings toward Extremely High Torque–Volume Ratio. Machines 2023, 11, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030368
Zhu S, Gong N, Yang J, Zhang S, Gong X, Li W, Sun S. Development of a Rotary Damper Integrated with Magnetorheological Bearings toward Extremely High Torque–Volume Ratio. Machines. 2023; 11(3):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030368
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Shengfeng, Ning Gong, Jian Yang, Shiwu Zhang, Xinglong Gong, Weihua Li, and Shuaishuai Sun. 2023. "Development of a Rotary Damper Integrated with Magnetorheological Bearings toward Extremely High Torque–Volume Ratio" Machines 11, no. 3: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030368
APA StyleZhu, S., Gong, N., Yang, J., Zhang, S., Gong, X., Li, W., & Sun, S. (2023). Development of a Rotary Damper Integrated with Magnetorheological Bearings toward Extremely High Torque–Volume Ratio. Machines, 11(3), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030368








