Computer Vision Method for In Situ Measuring Forming Accuracy of 3D Sand Mold Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Methods
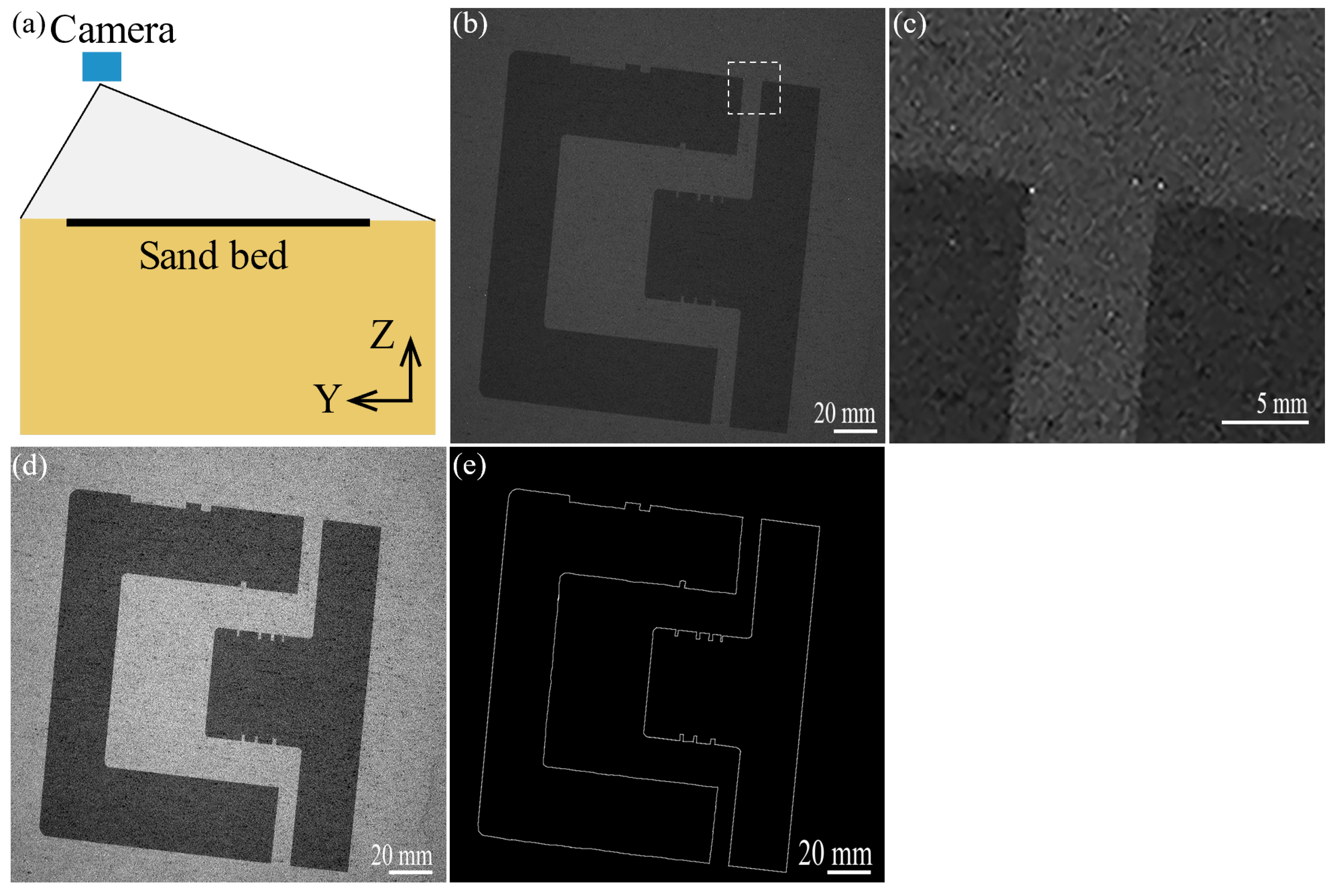
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Edge Extraction Method
3.2.1. Digital Image Processing
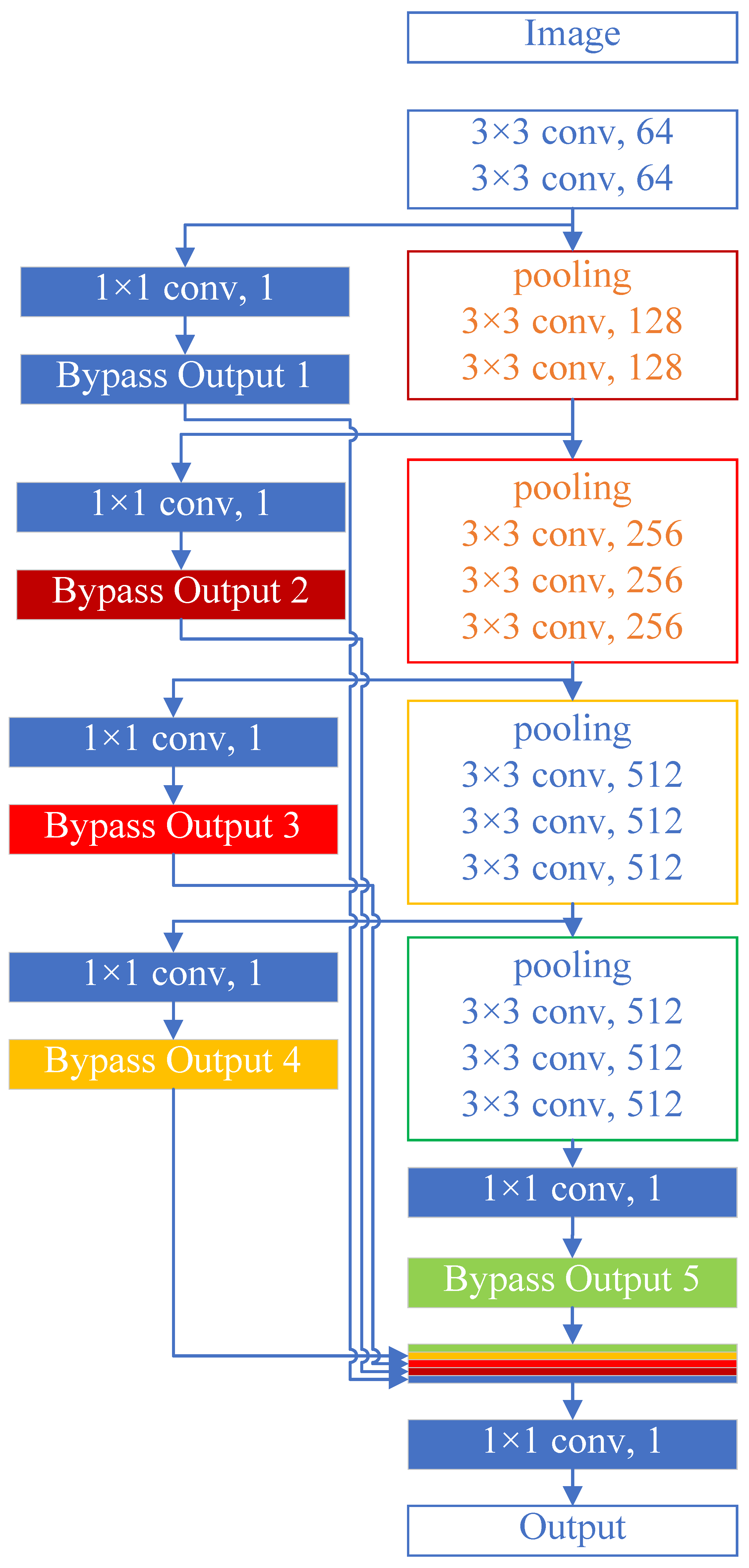
3.2.2. CNN Model and Train Procedure
3.2.3. Edge Thining
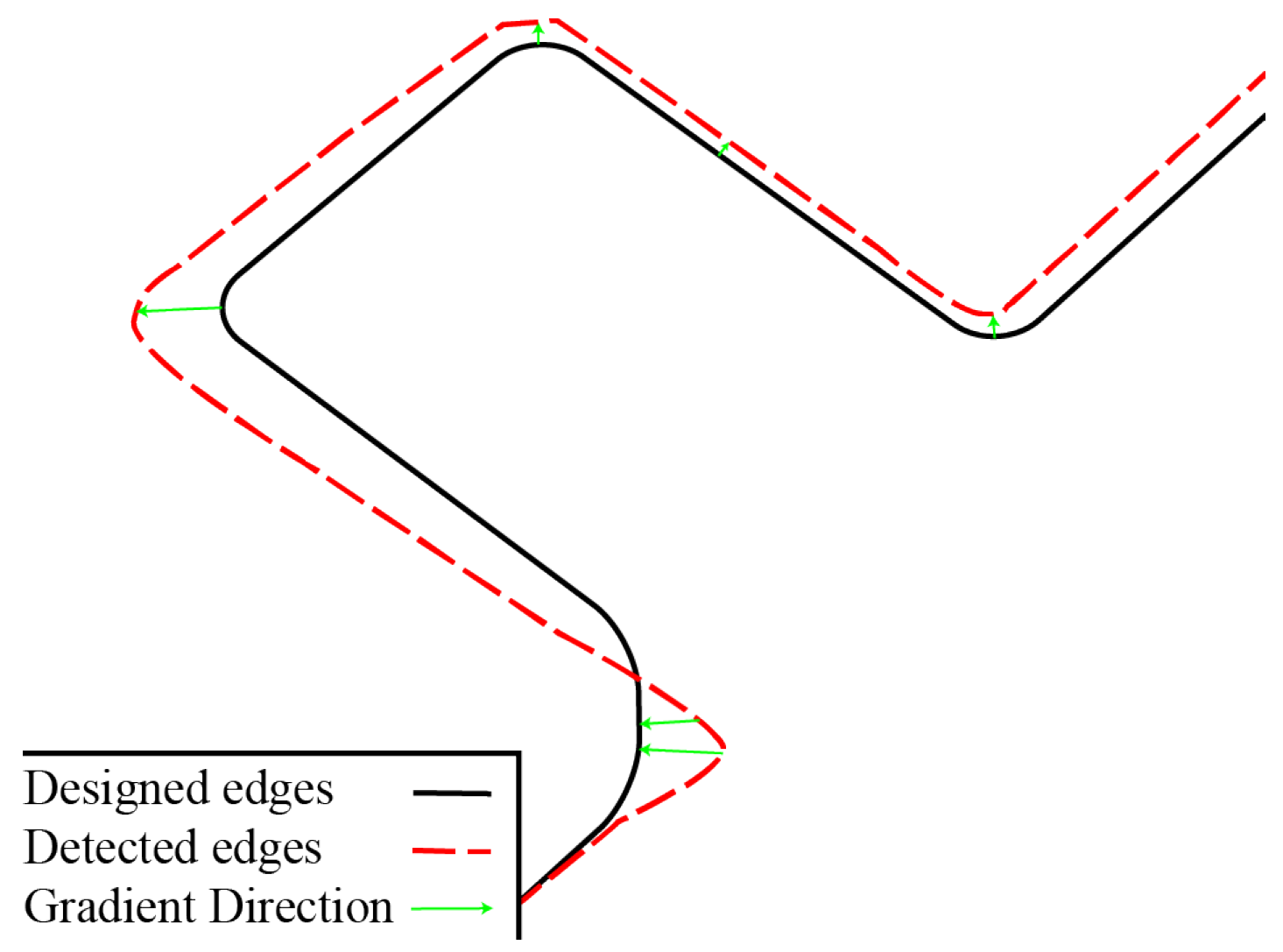
3.3. Accuracy Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
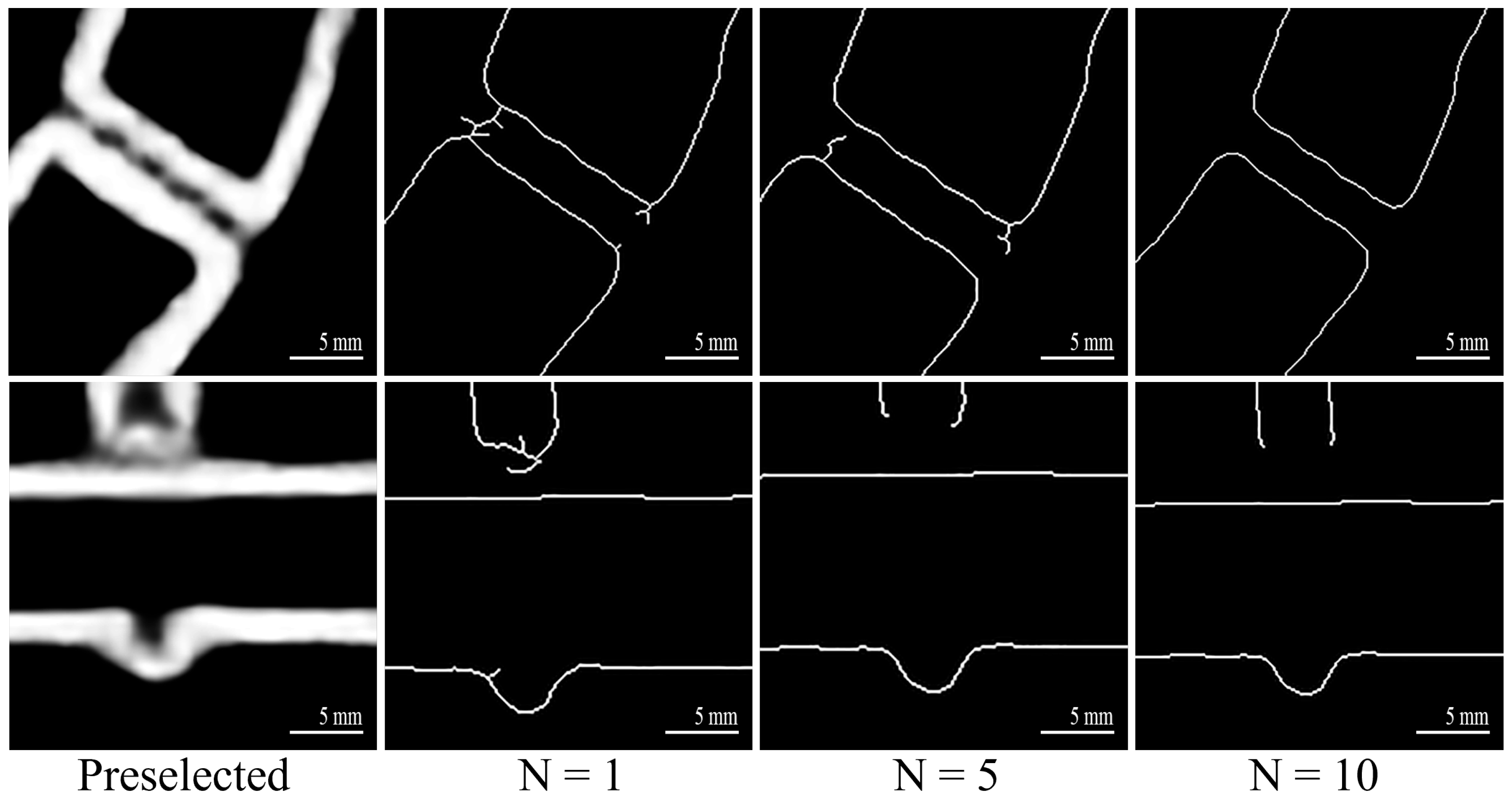
4.1. Performance of Edge Extraction
4.2. Performance of Measuring Accuracy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prasad, D.; Ratna, S. Decision Support Systems in the Metal Casting Industry: An Academic Review of Research Articles. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 1298–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarupan, T.; Balasubramani, N.; Saxena, P.; Nagarajan, D.; El Mansori, M.; Salonitis, K.; Jolly, M.; Dargusch, M.S. A Review on the Progress and Challenges of Binder Jet 3D Printing of Sand Moulds for Advanced Casting. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 40, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.; Sivarupan, T.; El Mansori, M. 3D Printing for Rapid Sand Casting—A Review. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 29, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sama, S.R. Investigation into Non-Conventional Mold Designs Using 3D Sand-Printing in Castings. Master’s Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sama, S.R.; Badamo, T.; Lynch, P.; Manogharan, G. Novel sprue designs in metal casting via 3D sand-printing. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbins, R.; King, P.; Manogharan, G. A Computational Study on Novel Runner Extension Designs via 3D Sand-Printing to Improve Casting Performance. In Proceedings of the MSEC2021, Online, 21–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Kang, J.; Shangguan, H.; Hu, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, Z. Effects of Hollow Structures in Sand Mold Manufactured Using 3D Printing Technology. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 255, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Rodríguez de Castro, A.; El Mansori, M. On the Rapid Manufacturing Process of Functional 3D Printed Sand Molds. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 42, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Chen, W.; Jin, T.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. A Review of Computer Vision-Based Structural Deformation Monitoring in Field Environments. Sensors 2022, 22, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.L.; Shen, S.S.; Yun, Y. Fatigue Crack Length Real Time Measurement Method Based on Camera Automatically Tracking and Positioning. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 130–134, 3111–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, J. Chisel Edge Wear Measurement of High-Speed Steel Twist Drills Based on Machine Vision. Comput. Ind. 2021, 128, 103436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, M.R. Image Analysis via the General Theory of Moments. Josa 1980, 70, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Ge, Z.; Su, X.; Guo, X.; Suo, T.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Q. Crack Length Measurement Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Image Processing. Sensors 2021, 21, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Tu, Z. Holistically-Nested Edge Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1395–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected Crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemian, A.; Khoshnevis, B. Real-Time Extrusion Quality Monitoring Techniques for Construction 3D Printing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, A.; Zhang, J.; Alfieri, V.; Caiazzo, F.; Gao, R.; Teti, R. Machine Learning-Based Image Processing for on-Line Defect Recognition in Additive Manufacturing. CIRP Ann. 2019, 68, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ziegert, J.; Farahi, F.; Davies, A. In Situ Surface Topography of Laser Powder Bed Fusion Using Fringe Projection. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 12, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, M.; Laguzza, V.; Semeraro, Q.; Colosimo, B.M. In-Process Monitoring of Selective Laser Melting: Spatial Detection of Defects Via Image Data Analysis. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2016, 139, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubenskaia, M.A.; Zhirnov, I.V.; Teleshevskiy, V.I.; Bertrand, P.; Smurov, I.Y. Determination of True Temperature in Selective Laser Melting of Metal Powder Using Infrared Camera. Mater. Sci. Forum 2015, 834, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubeck, A.; Van Gool, L. Efficient Non-Maximum Suppression. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; Volume 3, pp. 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, S.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Cao, H.; Xiang, D.; Dong, X. Computer Vision Method for In Situ Measuring Forming Accuracy of 3D Sand Mold Printing. Machines 2023, 11, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030330
Guo S, Li S, Wang L, Cao H, Xiang D, Dong X. Computer Vision Method for In Situ Measuring Forming Accuracy of 3D Sand Mold Printing. Machines. 2023; 11(3):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030330
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Shuren, Shang Li, Lanxiu Wang, Huatang Cao, Dong Xiang, and Xuanpu Dong. 2023. "Computer Vision Method for In Situ Measuring Forming Accuracy of 3D Sand Mold Printing" Machines 11, no. 3: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030330
APA StyleGuo, S., Li, S., Wang, L., Cao, H., Xiang, D., & Dong, X. (2023). Computer Vision Method for In Situ Measuring Forming Accuracy of 3D Sand Mold Printing. Machines, 11(3), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030330






