Energy Absorption of Square Tubes Filled by Modularized Honeycombs with Multiple Gradients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Square Tube Filled with Modularized Honeycomb
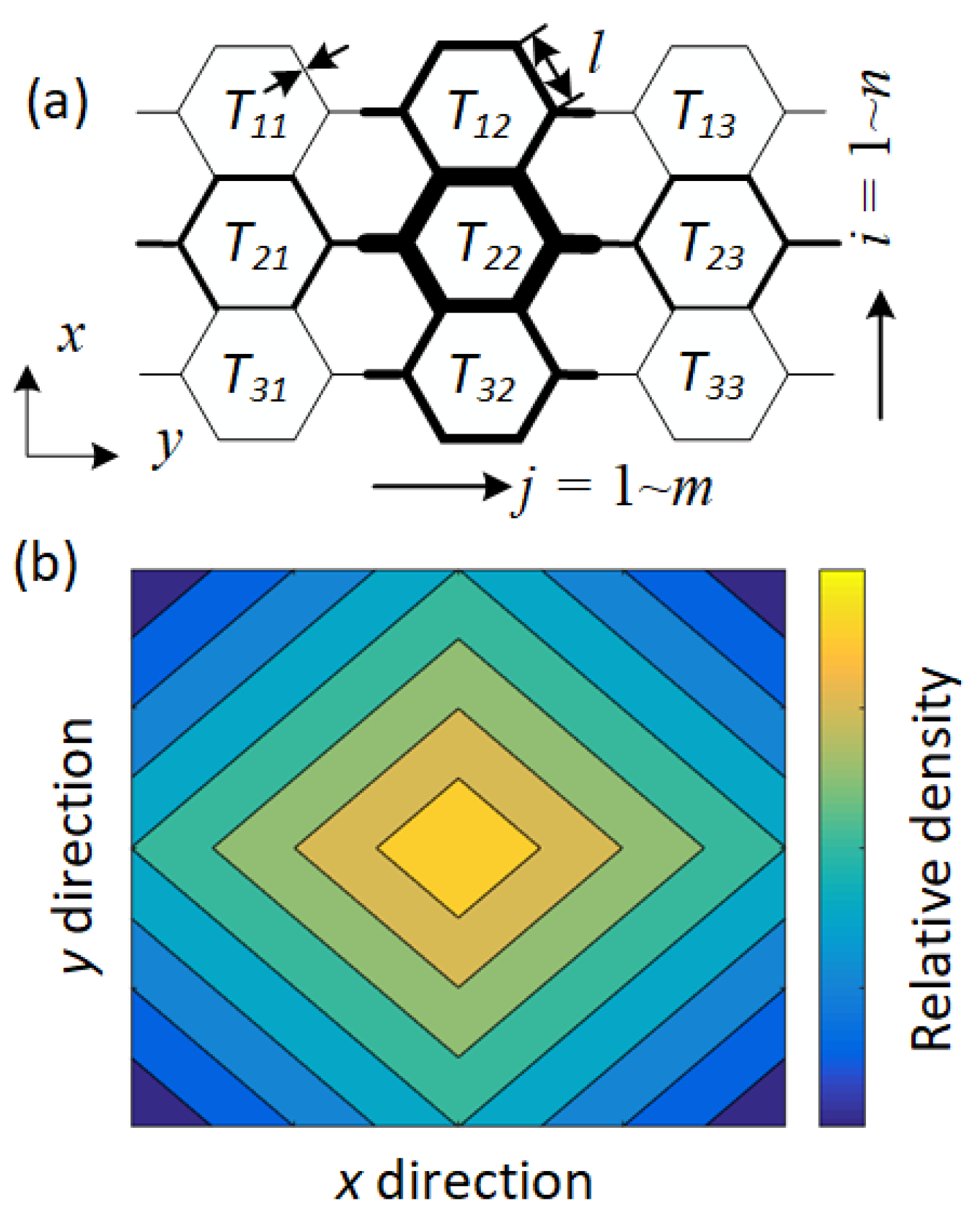
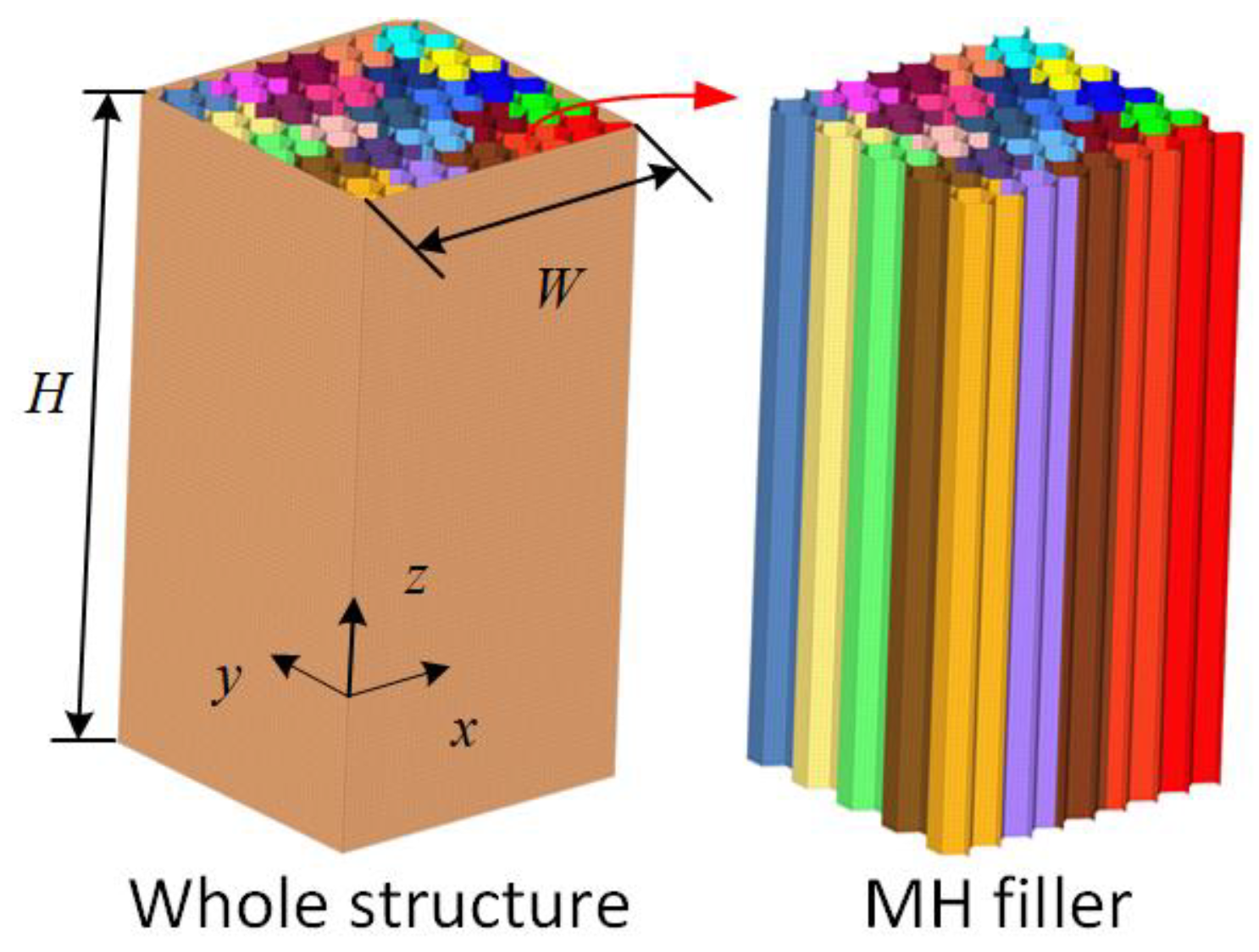
2.1. Model Description
2.2. Finite Element Model
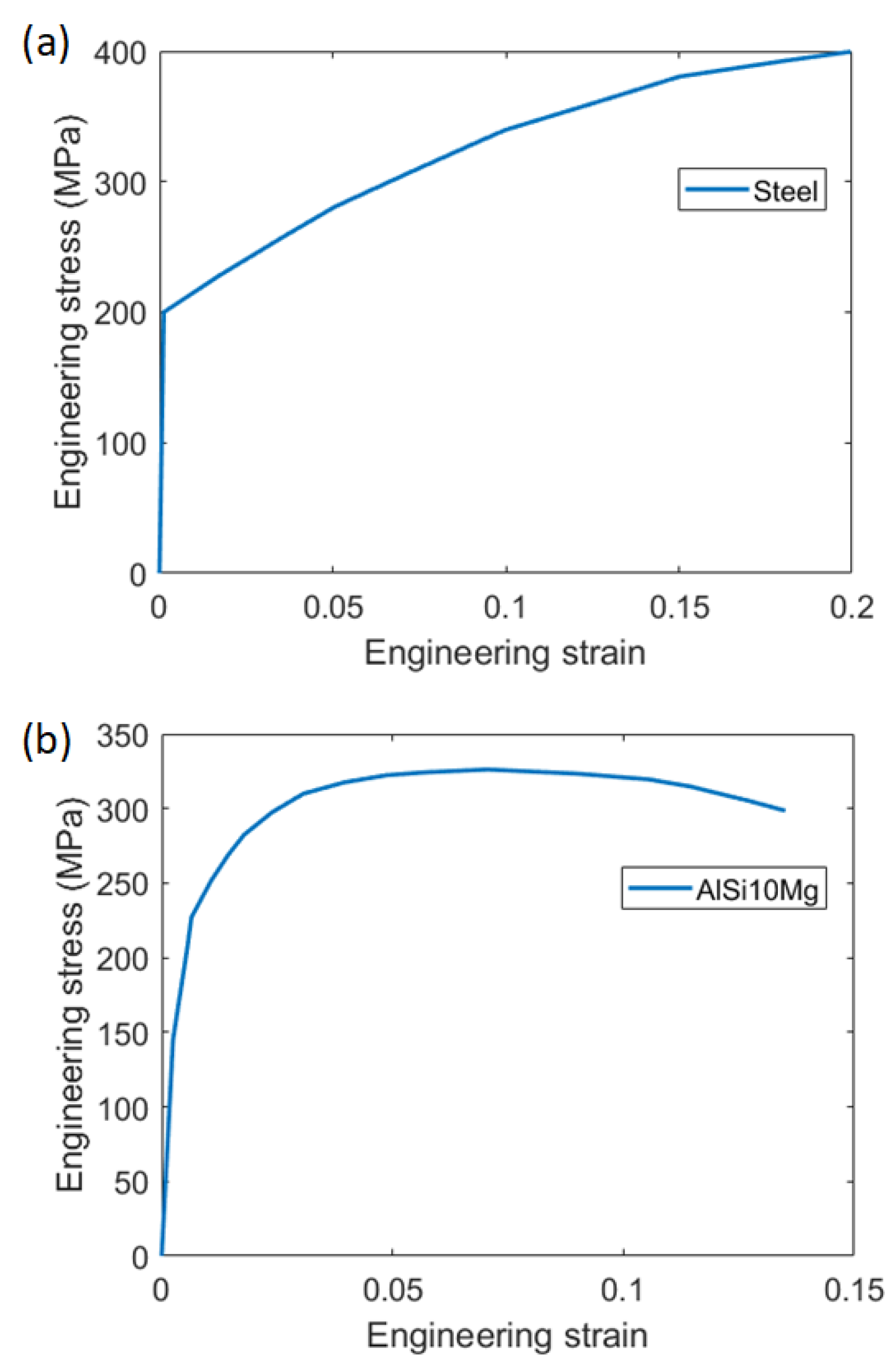
2.3. Material Properties
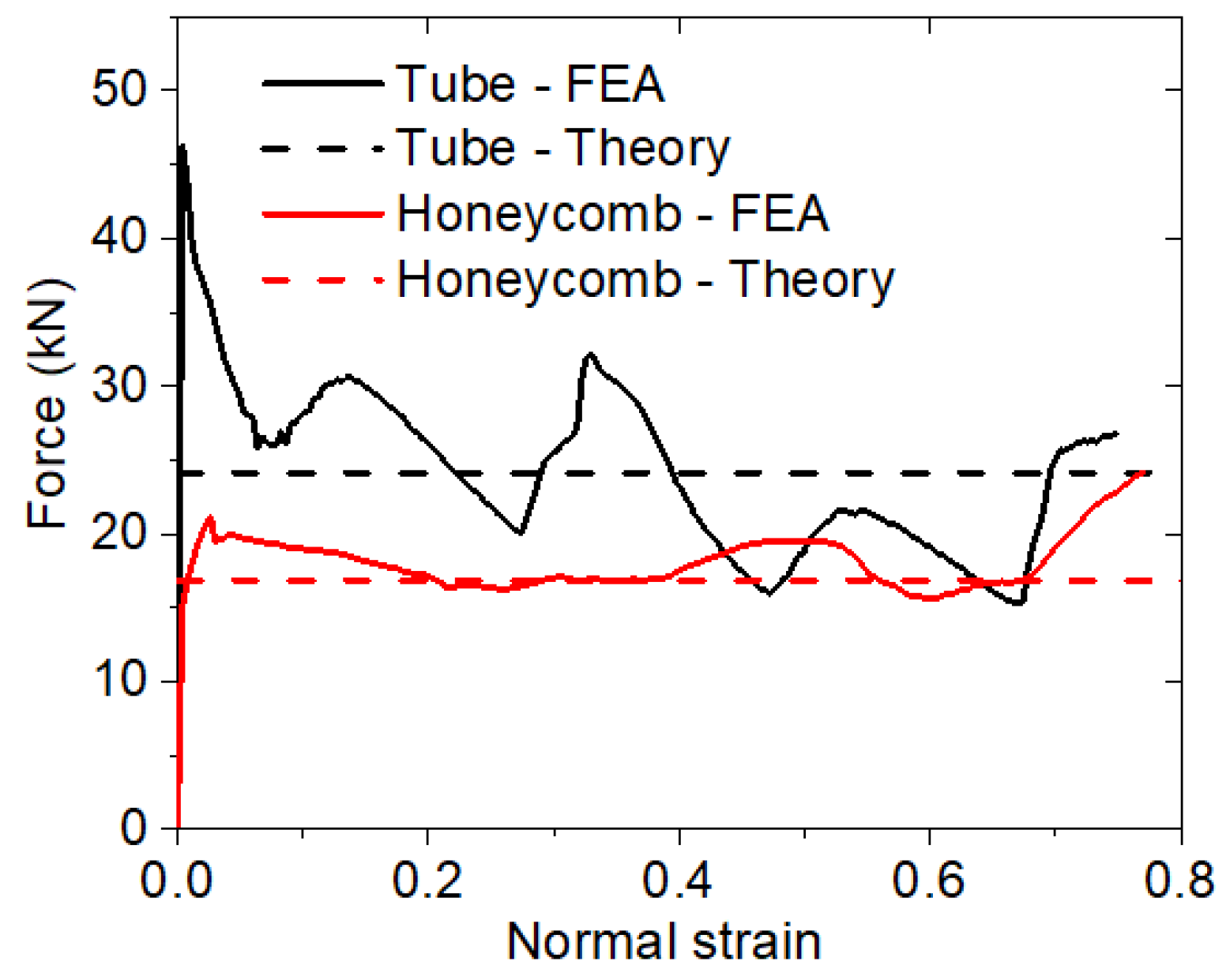
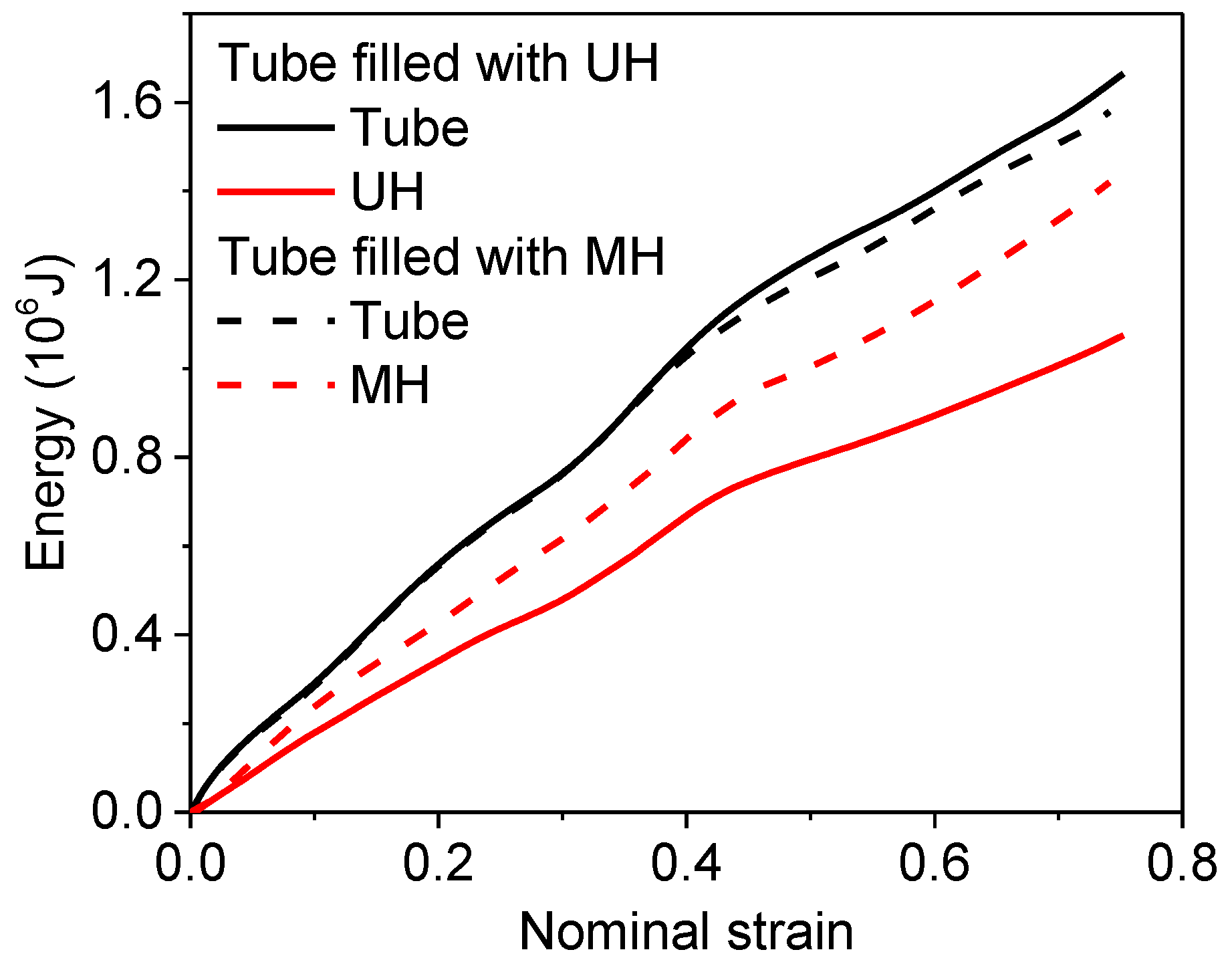
2.4. Model Validation
3. Energy Absorption of Modularized Honeycomb-Filled Square Tube
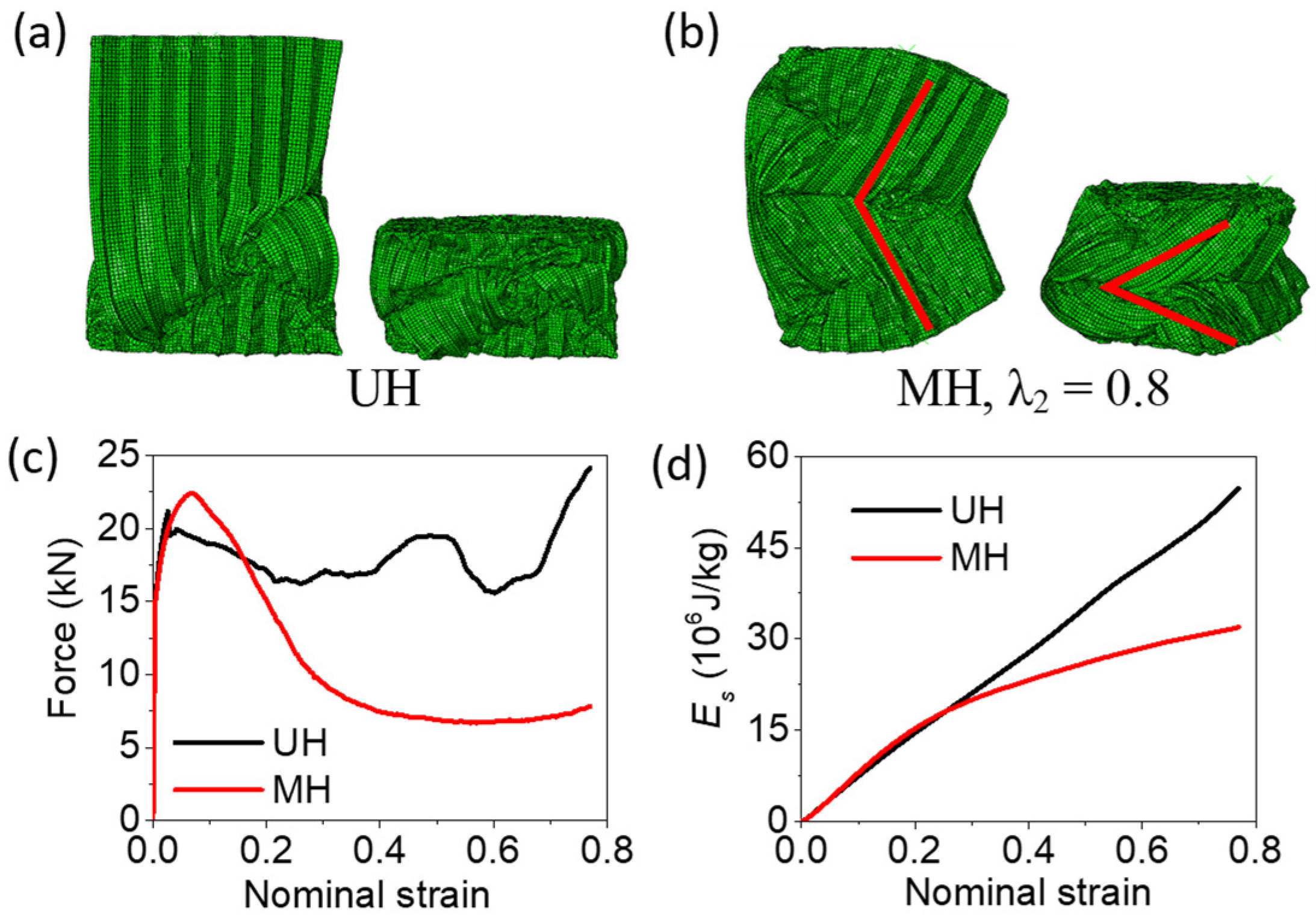
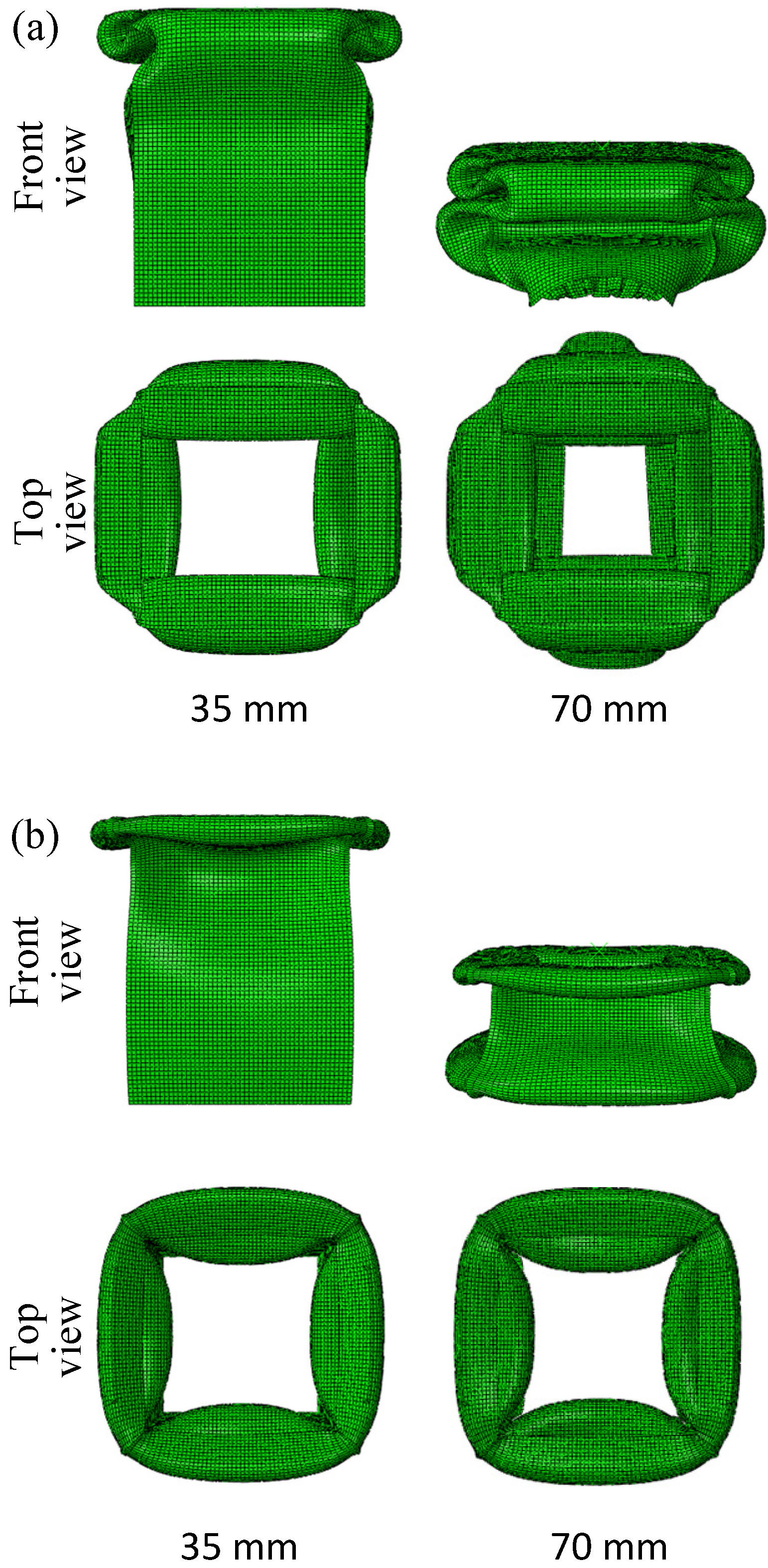
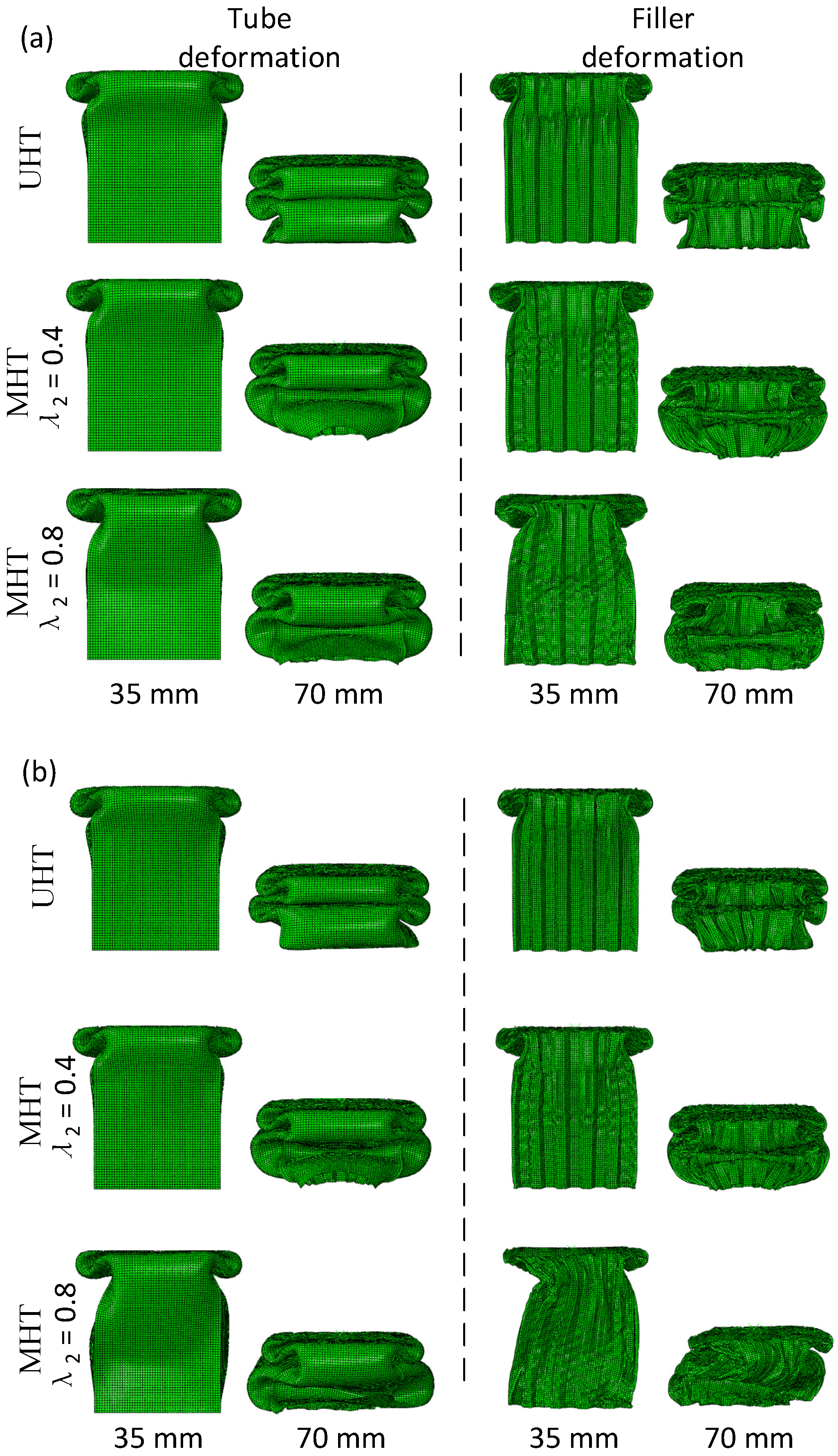
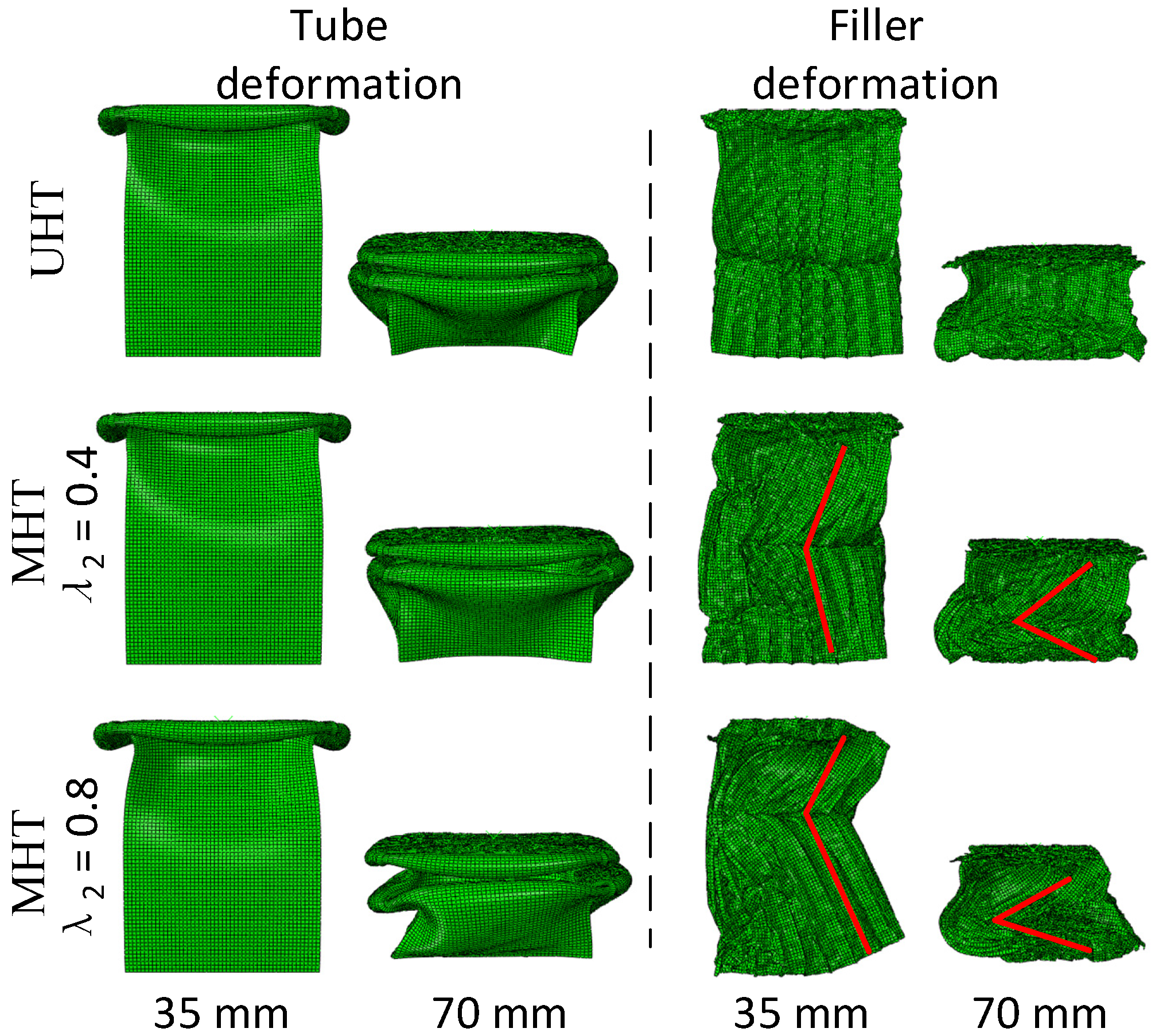
3.1. Deformation Stability of Honeycomb Filler
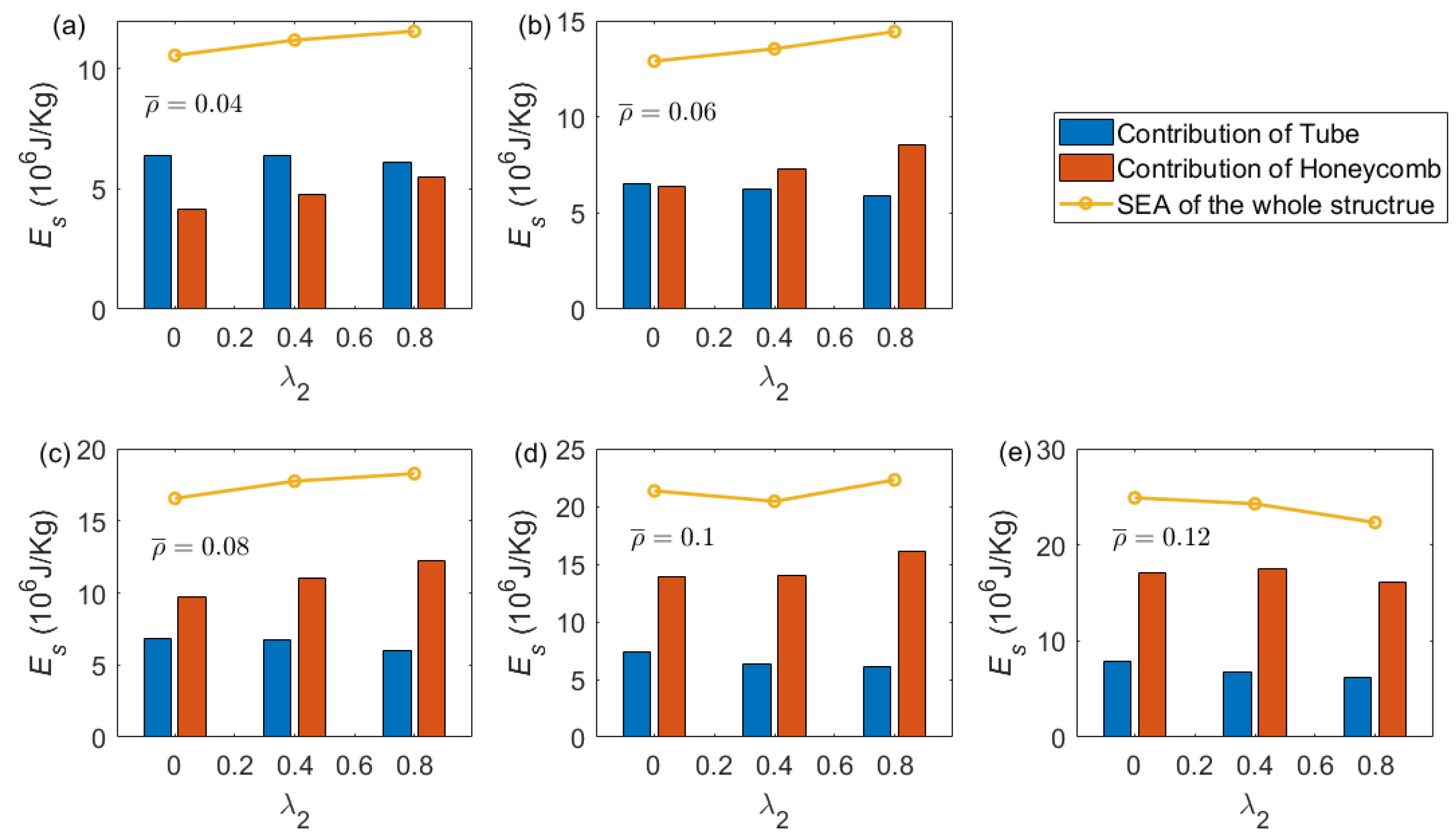
3.2. Effects of Honeycomb Design Parameters
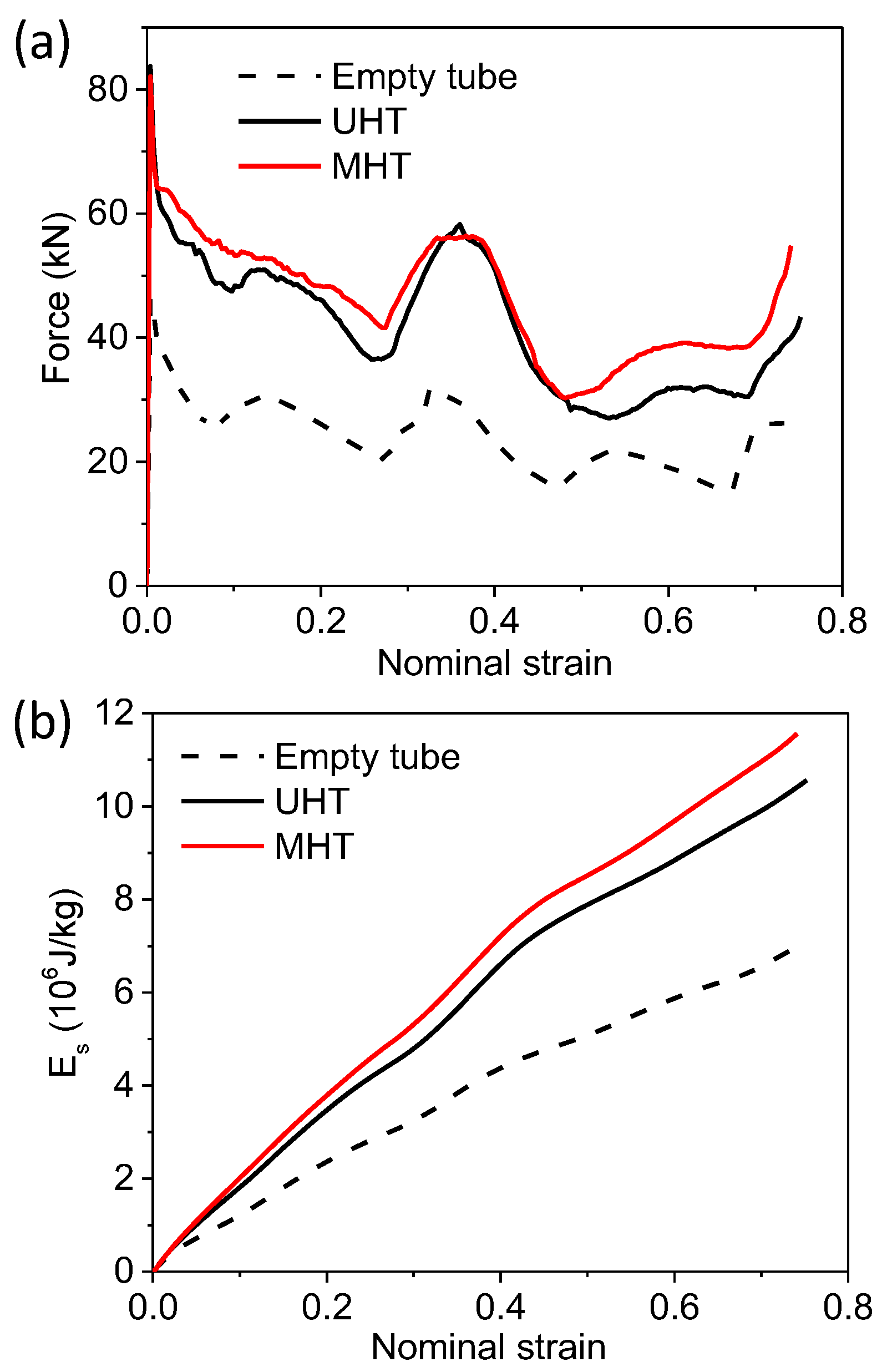
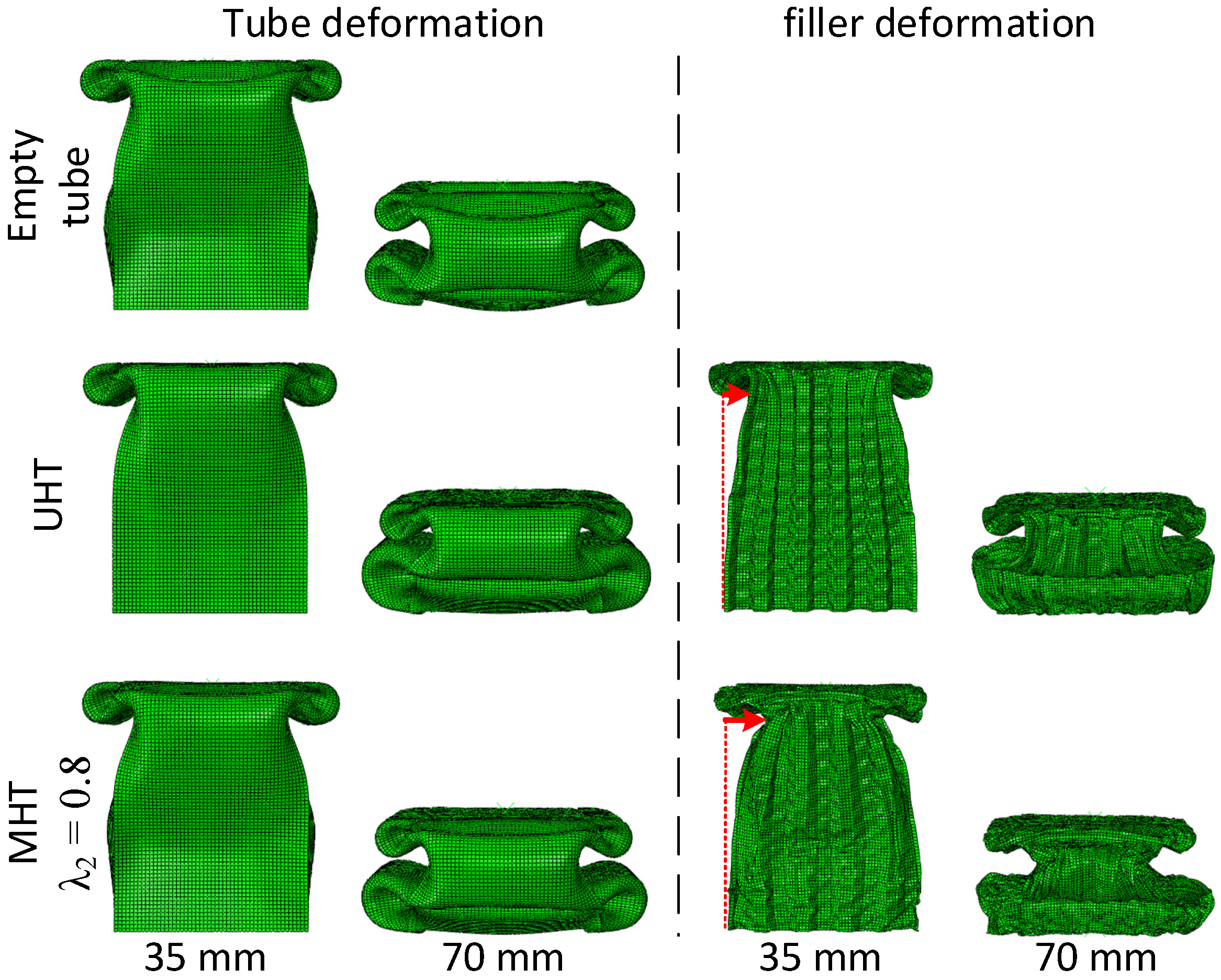
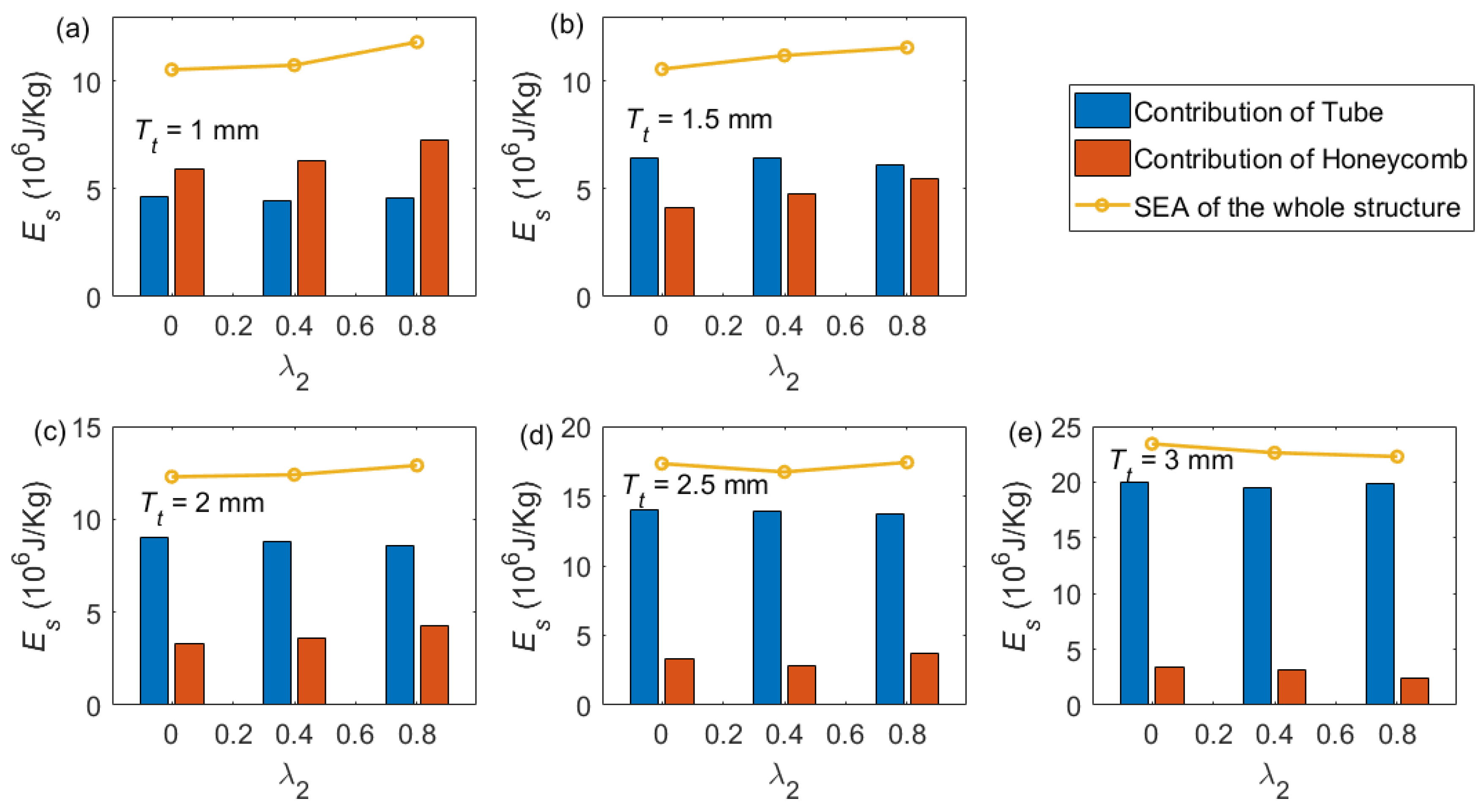
3.3. Effects of Tube Thickness
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Gao, Q.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Tang, J. Comparative study of the in-plane uniaxial and biaxial crushing of hexagonal, re-entrant, and mixed honeycombs. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2019, 21, 1991–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.C.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang X., Y.; Zhang X., G.; Luo, C.; Cheng, X.; Xie, Y. Mechanical properties of foam-filled hexagonal and re-entrant honeycombs under uniaxial compression. Compos. Struct. 2022, 280, 114922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, D. Design-oriented crushing analysis of hexagonal honeycomb core under in-plane compression. Compos. Struct. 2018, 187, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Jiang, F.; Yang, S. Advanced honeycomb designs for improving mechanical properties: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 227, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Ha, N.; Lu, G. Thin-walled corrugated structures: A review of crashworthiness designs and energy absorption characteristics. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 157, 106995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutada, S.; Goel, M.D. Crashworthiness parameters and their improvement using tubes as an energy absorbing structure: An overview. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2021, 27, 1569–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Hulbert, G. Crashworthiness analysis and collaborative optimization design for a novel crash-box with re-entrant auxetic core. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2020, 62, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, S.; Wierzbicki, T. Crash behavior of box columns filled with aluminum honeycomb or foam. Comput. Struct. 1998, 68, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids: Structures and Properties, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, W.; Liu, D. In-plane crushing behaviors of piecewise linear graded honeycombs. Compos. Struct. 2019, 207, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; You, F.; Yu, T. Effect of cell-wall angle on the in-plane crushing behaviour of hexagonal honeycombs. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; You, F.; Yu, T. Analyses on the dynamic strength of honeycombs under the y -directional crushing. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, S.; Lu, Z.; Hui, D.; Feo, L. Matching effect of honeycomb-filled thin-walled square tube—Experiment and simulation. Compos. Struct. 2016, 157, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T. Dynamic crushing behavior of functionally graded honeycomb structures with random defects. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 107, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Lu, Q.; He, C.W.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Xiao, D. Impact energy absorption of functionally graded chiral honeycomb structures. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2019, 32, 100568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Meng, J.; Ma, G.; Ren, S.; Fang, L.; Cao, X.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Xiao, D. Insight into the negative Poisson’s ratio effect of the gradient auxetic reentrant honeycombs. Compos. Struct. 2021, 274, 114366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Dong, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Fang, D. Compression behavior of the graded metallic auxetic reentrant honeycomb: Experiment and finite element analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 758, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousanezhad, D.; Ghosh, R.; Ajdari, A.; Hamouda, A.; Nayeb-Hashemi, H.; Vaziri, A. Impact resistance and energy absorption of regular and functionally graded hexagonal honeycombs with cell wall material strain hardening. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2014, 89, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Duan, S.; Wen, W.; Pei, Y.; Fang, D. Enhanced out-of-plane crushing strength and energy absorption of in-plane graded honeycombs. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 118, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Tao, Y.; Lei, H.; Wen, W.; Liang, J.; Fang, D. Enhanced out-of-plane compressive strength and energy absorption of 3D printed square and hexagonal honeycombs with variable-thickness cell edges. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2018, 18, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, L. Enhanced strength and weakened dynamic sensitivity of honeycombs by parallel design. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 151, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, P.; Fang, J.; Li, W. Energy absorption of additively manufactured functionally bi-graded thickness honeycombs subjected to axial loads. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 164, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Su, X. Modularizing honeycombs for enhancement of strength and energy absorption. Compos. Struct. 2022, 279, 114744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.R.; Reddy, T.Y.; Gray, M.D. Static and dynamic axial crushing of foam-filled sheet metal tubes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1986, 28, 295–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, H.R.; Kröger, M. Crashworthiness optimization of empty and filled aluminum crash boxes. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2007, 12, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.D.; Ruan, D.; Lu, G.; Guillow, S.; Yoon, J. Crushing response of square aluminium tubes filled with polyurethane foam and aluminium honeycomb. Thin-Walled Struct. 2017, 110, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z.; Hu, D. Mechanical behavior of composited structure filled with tandem honeycombs. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 114, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.; Kazancı, Z. Crushing investigation of crash boxes filled with honeycomb and re-entrant (auxetic) lattices. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 150, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liao, W.H.; Wang, L.; Huang, C. Crashworthiness optimization of cylindrical negative Poisson’s ratio structures with inner liner tubes. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 64, 4271–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.Z.; Zou, S.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y. Structure design and multi-objective optimization of a novel crash box based on biomimetic structure. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 138, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, H.H.; Raza, S. Impact energy absorption of bio-inspired tubular sections with structural hierarchy. Compos. Struct. 2018, 195, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Duan, L.; Chen, T.; Hu, Z. Crashworthiness analysis and multi-objective design optimization of a novel lotus root filled tube (LFT). Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2018, 57, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, Y.; Wan, S.; Li, X.; Su, Q.; Li, M. How does bio-inspired graded honeycomb filler affect energy absorption characteristics? Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 144, 106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liao, W.H.; Huang, C. Theoretical predictions of dynamic responses of cylindrical sandwich filled with auxetic structures under impact loading. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 107, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ge, P.; Lu, M.; Lai, X. Crashworthiness study for multi-cell composite filling structures. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2018, 23, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wen, G.; Hou, S.; Chen, K. Crushing analysis and multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of honeycomb-filled single and bitubular polygonal tubes. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4449–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Lu, M.; Hu, Z.; Ge, P. Enhance crashworthiness of composite structures using gradient honeycomb material. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2018, 23, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Xiao, X.; Xu, P.; Qu, Q.; Che, Q. The impact performance of honeycomb-filled structures under eccentric loading for subway vehicles. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 123, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liao, W.H. Energy absorption of thin walled tube filled with gradient auxetic structures-theory and simulation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 201, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Du, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, P. Crashworthiness of Nomex® honeycomb-filled anti-climbing energy absorbing devices. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2021, 26, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, P.; Yang, C.; Xiao, X.; Che, Q. Crashing performance and multi-objective optimization of honeycomb-filled thin-walled energy absorber with axisymmetric thickness. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Yan, P.; Wang, Q.; Dai, S.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Y. Optimal design of a novel crash box with functional gradient negative Poisson’s ratio structure. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2022, 236, 3309–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, S.; Sun, G.; Li, G.; Li, Q. On design of graded honeycomb filler and tubal wall thickness for multiple load cases. Thin-Walled Struct. 2016, 109, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Gao, Y.; An, X.; Sun, G.; Chen, J.; Li, Q. Design of transversely-graded foam and wall thickness structures for crashworthiness criteria. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 92, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Dai, J.; Wen, G.; Tian, W.; Wu, Q. Multi-objective optimization design of functionally graded foam-filled graded-thickness tube under lateral impact. Int. J. Comput. Methods 2019, 16, 1850088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zang, M.; Li, Z. Effects of aluminum honeycomb filler on crashworthiness of CFRP thin-walled beams under dynamic impact. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2021, 27, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, L.; Fu, K. Progressive failure of CFRP tubes reinforced with composite sandwich panels: Numerical analysis and energy absorption. Compos. Struct. 2021, 263, 113674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; You, Z. Energy absorption of thin-walled beams with a pre-folded origami pattern. Thin-Walled Struct. 2013, 73, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, A.G.; Langseth, M.; Hopperstad, O.S. Static and dynamic crushing of circular aluminium extrusions with aluminium foam filler. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2000, 24, 475–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, T. Crushing analysis of metal honeycombs. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1983, 1, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| λ2 | Tt (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | ||
| 0.04 | 0 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 0.4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 0.6 | √ | √ | √ | × | × | |
| 0.8 | √ | √ | √ | × | × | |
| 0.06 | 0 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 0.4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 0.6 | √ | √ | √ | × | × | |
| 0.8 | √ | √ | √ | × | × | |
| 0.08 | 0 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 0.4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 0.6 | √ | √ | √ | × | × | |
| 0.8 | × | √ | √ | × | × | |
| 0.1 | 0 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 0.4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 0.6 | √ | √ | √ | √ | × | |
| 0.8 | × | √ | √ | × | × | |
| 0.12 | 0 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 0.4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 0.6 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 0.8 | × | × | √ | × | × | |
| Es (106 J/Kg) | Es (106 J/Kg) | Difference with That of | Es (106 J/Kg) | Difference with That of | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.04 | 10.56 | 11.19 | 5.97 | 11.56 | 9.47 |
| 0.06 | 12.90 | 13.54 | 4.96 | 14.44 | 11.94 |
| 0.08 | 16.56 | 17.75 | 7.19 | 18.27 | 10.33 |
| 0.1 | 21.34 | 20.44 | −4.22 | 22.30 | 4.50 |
| 0.12 | 24.89 | 24.27 | −2.49 | 22.33 | −10.29 |
| Tt (mm) | λ2 = 0 | λ2 = 0.4 | λ2 = 0.8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Es (106 J/Kg) | Es (106 J/Kg) | Difference with That of | Es (106 J/Kg) | Difference with That of | |
| 1 | 10.54 | 10.74 | 1.90 | 11.82 | 12.14 |
| 1.5 | 10.56 | 11.19 | 5.97 | 11.56 | 9.47 |
| 2 | 12.29 | 12.40 | 0.90 | 12.90 | 4.96 |
| 2.5 | 17.33 | 16.73 | −3.46 | 17.42 | 0.52 |
| 3 | 19.72 | 19.05 | −3.40 | 18.76 | −4.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Kang, Z.; Su, X. Energy Absorption of Square Tubes Filled by Modularized Honeycombs with Multiple Gradients. Machines 2023, 11, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020294
Li Z, Kang Z, Su X. Energy Absorption of Square Tubes Filled by Modularized Honeycombs with Multiple Gradients. Machines. 2023; 11(2):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020294
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhen, Zhengyang Kang, and Xiaoping Su. 2023. "Energy Absorption of Square Tubes Filled by Modularized Honeycombs with Multiple Gradients" Machines 11, no. 2: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020294
APA StyleLi, Z., Kang, Z., & Su, X. (2023). Energy Absorption of Square Tubes Filled by Modularized Honeycombs with Multiple Gradients. Machines, 11(2), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020294






