A Novel Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring Method Based on Reliable Life Consumption Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Based on the aircraft structure’s full-scale fatigue life test, the aircraft structure’s P-S-N curve, i.e., the relationship curve between the aircraft structure’s life (N) and fatigue load (S) under a certain probability (P), is established. By doing so, the lower confidence limit of the aircraft structure’s reliable life under any fatigue loads can be evaluated with the required confidence and reliability. This is the premise of reliable life consumption assessment.
- Based on the established P-S-N curve and the monitored service loads or flight missions of individual aircraft, the reliable life consumption percentage and remaining reliable life percentage of each aircraft can be assessed in real time. By doing so, individual aircraft life monitoring and online life management can be conveniently achieved.
- By this method, the aircraft structure’s full-scale fatigue test, reliable life determination, individual life monitoring, and reliable life extension (or other life management work) can be strung together. The disconnection between individual aircraft life monitoring and reliable life determination and extension is solved.
2. Small-Sample Assessment Method for the Aircraft Structure’s Reliable Life
2.1. Reliable Life Assessment under Test Load Spectrum
2.2. P-S-N Curve Determination and Reliable Life Assessment under Service Load
3. Reliable Life Consumption Assessment Method for the Aircraft Structure
3.1. Reliable Damage and Damage Threshold


3.2. Reliable Life Consumption Percentage and Its Confidence Limit
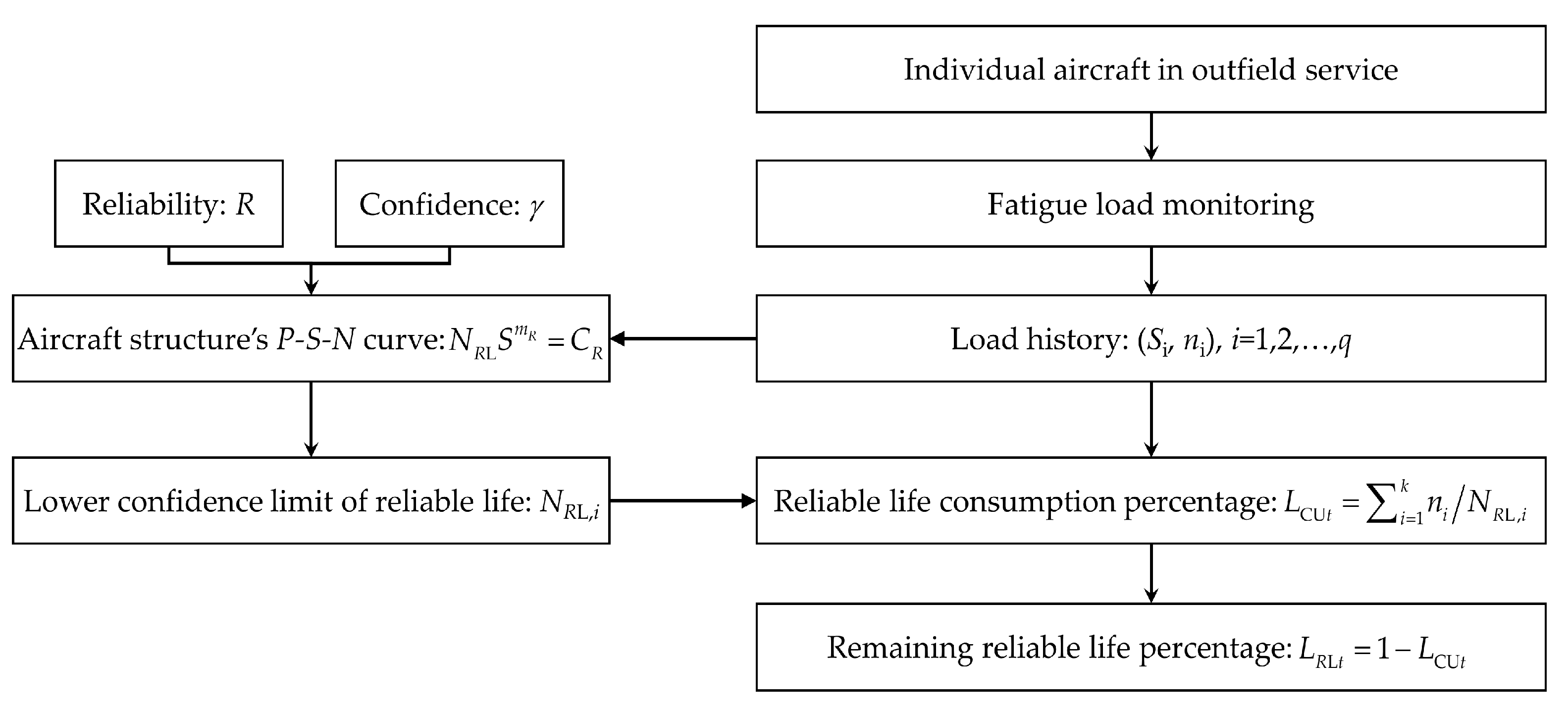
4. Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring Method
4.1. Load-Based Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring
4.2. Mission-Based Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring

4.3. Online Aircraft Life Management
5. Example and Discussion
5.1. Reliable Life Determination under Test Load Spectrum
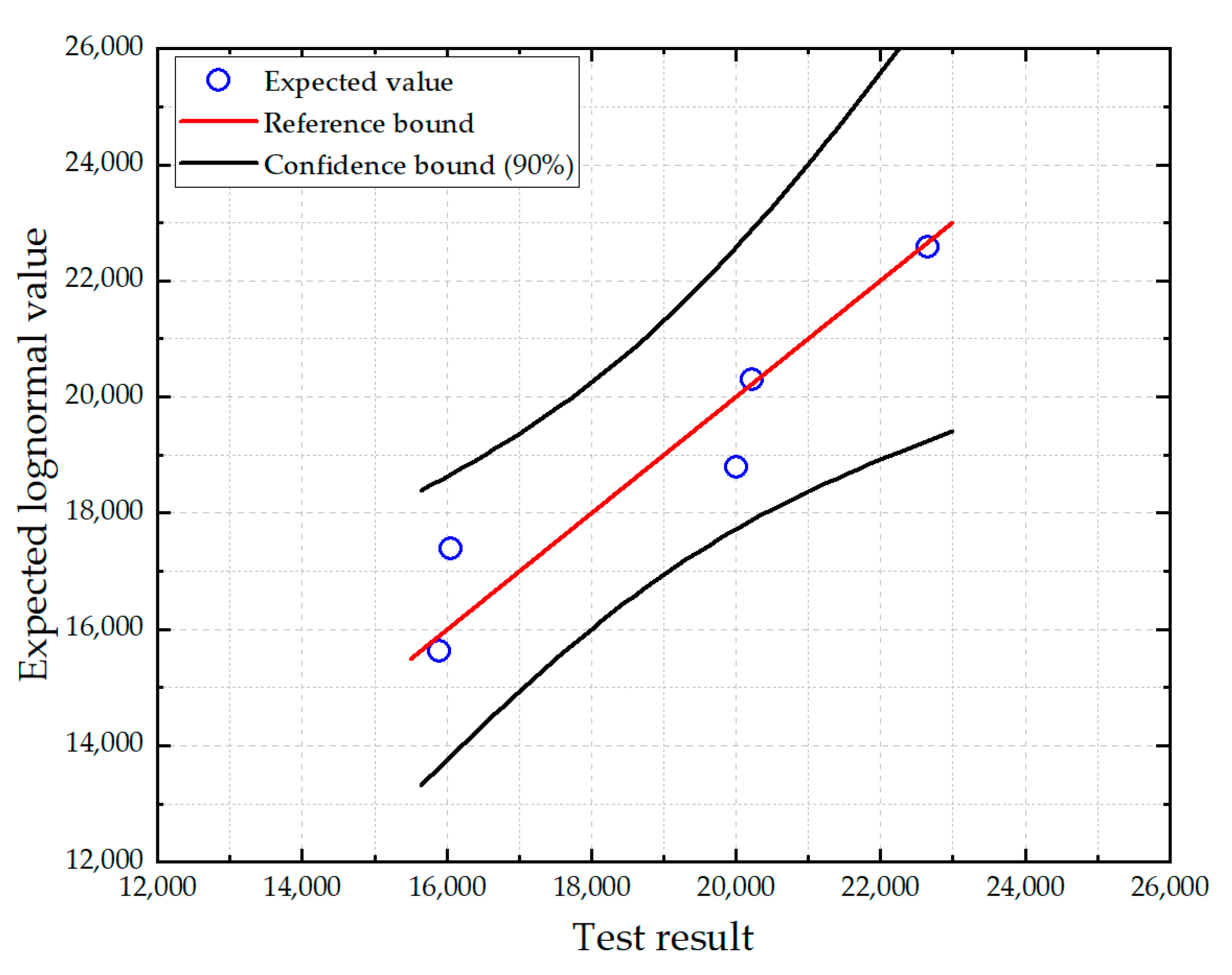
5.2. P-S-N Curve Assessment
5.3. Verification of Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring under Test Load Spectrum
- (1)
- Individual aircraft life monitoring is conducted based on reliable life consumption with high reliability and high confidence, while the same reliability values are required in the aircraft’s reliable life determination.
- (2)
- The P-S-N curve used for reliable life consumption is obtained based on the aircraft structure’s full-scale life test, while the aircraft structure’s life determination is also conducted through the full-scale life test.
| Aircraft fleet management method | Proposed individual aircraft monitoring method | Conventional life-consumption-based individual aircraft monitoring method |
| Work is not allowed after 7252 blocks | Work is not allowed after 7252 blocks | Work is allowed after 7252 blocks |
5.4. Comparision of Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring and Aircraft Fleet Management under Service Load
| i | /(MPa) | /(Cycles) | Lower Confidence Limit of Reliable Life /(Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 625 | 0.20 | 2.06 × 104 |
| 2 | 588 | 1.08 | 3.11 × 104 |
| 3 | 562 | 2.26 | 4.99 × 104 |
| 4 | 393 | 3.53 | 8.41 × 104 |
| 5 | 326 | 6.07 | 2.34 × 105 |
| 6 | 299 | 5.96 | 5.31 × 105 |
| 7 | 245 | 5.09 | 8.62 × 105 |
| 8 | 208 | 18.03 | 1.53 × 106 |
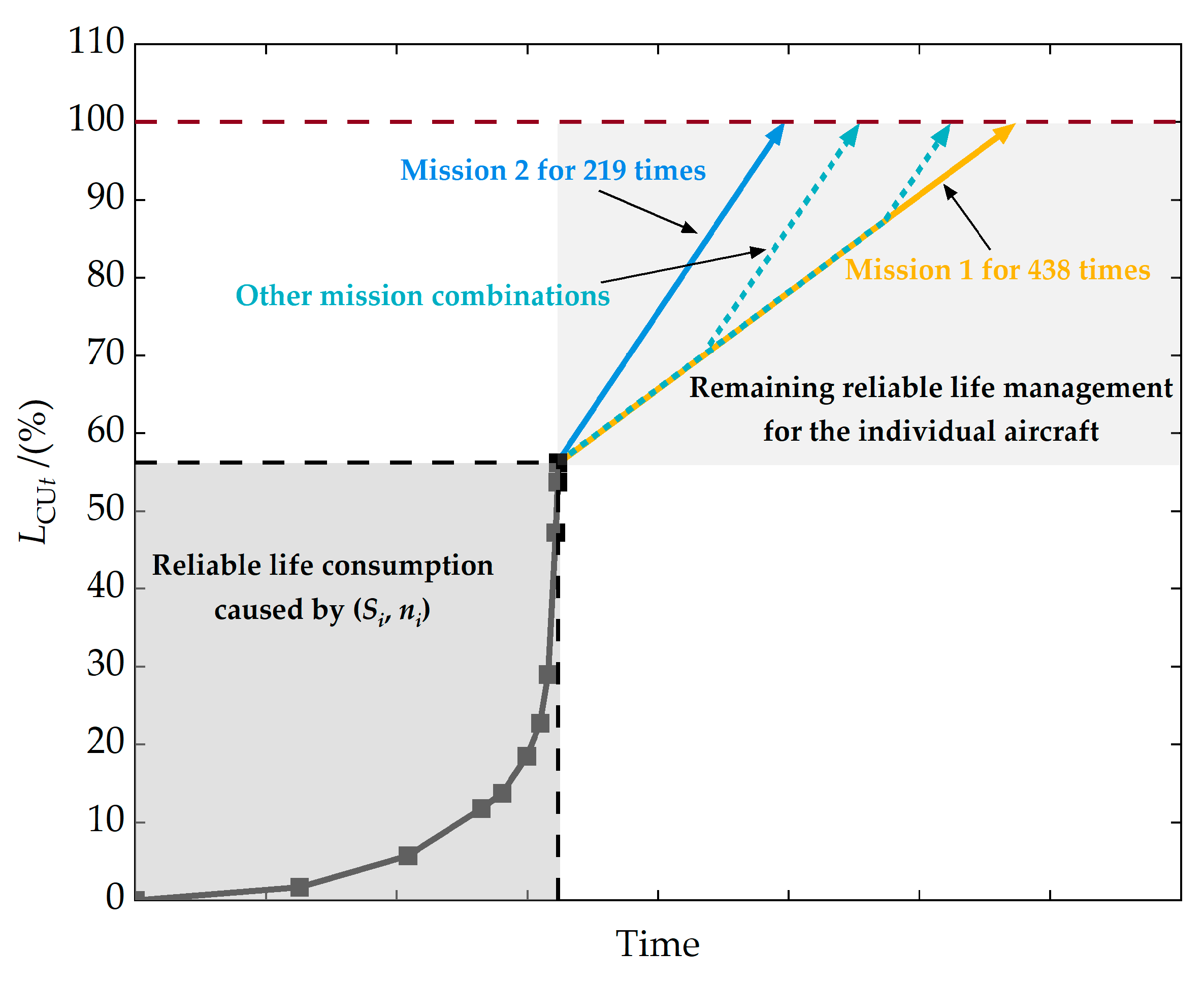
5.5. Online Life Management of Individual Aircraft
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molent, L.; Aktepe, B. Review of Fatigue Monitoring of Agile Military Aircraft. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2000, 23, 767–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, K.; Soutis, C. Structural Health Monitoring Techniques for Aircraft Composite Structures. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2010, 46, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfingstl, S.; Steinweg, D.; Zimmermann, M.; Hornung, M. On the Potential of Extending Aircraft Service Time Using Load Monitoring. J. Aircr. 2022, 59, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cho, H.; Park, S. Review of the F-16 Individual Aircraft Tracking Program. J. Aircr. 2012, 49, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R.; He, X.F.; Li, Y.H. Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring: An Engineering Approach for Fatigue Damage Evaluation. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, B.T.; Ning, Y.; Xue, H.F.; Lei, X.X. Study on Health Monitoring and Fatigue Life Prediction of Aircraft Structures. Materials 2022, 15, 8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, P.C. Fleet Management Issues and Technology Needs. Int. J. Fatigue 2009, 31, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, M.J.; Sullivan, R.W.; Richards, W.L. Large Scale Applications Using FBG Sensors: Determination of In-Flight Loads and Shape of a Composite Aircraft Wing. Aerospace 2016, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Cao, S.C.; Wang, B.T.; Yin, Z.P. A Flight Parameter-Based Aircraft Structural Load Monitoring Method Using a Genetic Algorithm Enhanced Extreme Learning Machine. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, M.; Lemmens, Y.; Cooper, J.E. Parametric Reduced Order Model Approach for Rapid Dynamic Loads Prediction. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candon, M.; Esposito, M.; Fayek, H.; Levinski, O.; Koschel, S.; Joseph, N.; Carrese, R.; Marzocca, P. Advanced Multi-Input System Identification for next Generation Aircraft Loads Monitoring Using Linear Regression, Neural Networks and Deep Learning. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2022, 171, 108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, W.; Wang, Y.Y. A Study of the Method for Calculating Fatigue Damage of Aircraft by Using Recorded Load Factors. In Proceedings of the Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences, Nice, France, 19 September 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Park, S.; Kim, H. Estimation of Aircraft Structural Fatigue Life Using the Crack Severity Index Methodology. J. Aircr. 2010, 47, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.; Mongru, D.; Molent, L. A Crack Growth-Based Individual Aircraft Monitoring Method Utilising a Damage Metric. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 17, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molent, L.; Barter, S.; Foster, W. Verification of an Individual Aircraft Fatigue Monitoring System. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 43, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyyer, N.; Sarkar, S.; Merrill, R.; Phan, N. Aircraft Life Management Using Crack Initiation and Crack Growth Models—P-3C Aircraft Experience. Int. J. Fatigue 2007, 29, 1584–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.; Infante, V.; Sousa, L.; Fonseca, A.; Antunes, P.J.; Moura, A.M.; Serrano, B. Numerical and Experimental Study of Aircraft Structural Health. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 132, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, B.; Molent, L.; Singh, R.; Barter, S. Fatigue Crack Growth Lessons from Thirty-Five Years of the Royal Australian Air Force F/A-18 A/B Hornet Aircraft Structural Integrity Program. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 133, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templalexis, I.; Lionis, I.; Christou, N. Comparative Study of a Powerplant Life Consumption Rate When Installed in Two Different Aircraft Variants. Aerospace 2021, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaras, Z.; Lukosevicius, V. Statistical Assessment of Low-Cycle Fatigue Durability. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.L.; Liu, K.G. Theory of Economic Life Prediction and Reliability Assessment of Aircraft Structures. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2011, 24, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.F.; Zhai, B.; Dong, Y.M.; Liu, W.T. Safe-Life Analysis Accounting for the Loading Spectra Variability. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2010, 17, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buderath, M.; McFeat, J.; Azzam, H. The Need for Guidance on Integrating Structural Health Monitoring within Military Aircraft Systems. Struct. Health Monit. 2014, 13, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Takagi, T.; Wada, K.; Matsunaga, H. Essential Structure of S-N Curve: Prediction of Fatigue Life and Fatigue Limit of Defective Materials and Nature of Scatter. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 146, 106138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohabeddine, A.; Correia, J.; Aires Montenegro, P.; De Jesus, A.; Miguel Castro, J.; Berto, F. Probabilistic S-N Curves for CFRP Retrofitted Steel Details. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 148, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.F.; Xie, L.Y. Fatigue Reliability Evaluation Method of a Gear Transmission System Under Variable Amplitude Loading. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2019, 68, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.M.; Fu, Y.S.; Wen, X.L. Methods for reliable life consumption assessment and life management. Dev. Innov. Mach. Electr. Prod. 2020, 33, 4–7. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.S.; Fu, H.M.; Wu, Q. A Reliable Life Consumption Assessment and Individual Life Monitoring Method for Rolling Bearings. Machines 2023, 11, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, F.C.; Liu, W.T. Study on the technique of developing constant amplitude load spectrum for aircraft fatigue test. J. Mech. Strength 2008, 30, 266–269. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Individual Aircraft Monitoring | Aircraft Fleet Management | |
|---|---|---|
| Load | Service load of individual aircraft | Typical load or load spectrum of the aircraft fleet |
| Reliability | Lack of consideration | High reliability (e.g., 0.999) and high confidence (e.g., 0.9) |
| Restrictions | Damage less than the threshold | Service time is less than the determined reliable life |
| i | /(MPa) | /(Cycles) | i | /(MPa) | /(Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 650 | 0.16 | 6 | 282 | 5.55 |
| 2 | 585 | 0.62 | 7 | 249 | 4.22 |
| 3 | 518 | 1.57 | 8 | 215 | 14.72 |
| 4 | 453 | 2.37 | 9 | 175 | 30.67 |
| 5 | 348 | 3.02 | 10 | 132 | 37.10 |
| i | /(MPa) | Lower Confidence Limit of Reliable Life /(Cycles) | Point Estimate of Median Life /(Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 650 | 2.06 × 104 | 5.35 × 104 |
| 2 | 585 | 3.11 × 104 | 8.07 × 104 |
| 3 | 518 | 4.99 × 104 | 1.29 × 105 |
| 4 | 453 | 8.41 × 104 | 2.18 × 105 |
| 5 | 348 | 2.34 × 105 | 6.04 × 105 |
| 6 | 282 | 5.31 × 105 | 1.38 × 106 |
| 7 | 249 | 8.62 × 105 | 2.22 × 106 |
| 8 | 215 | 1.53 × 106 | 3.93 × 106 |
| 9 | 175 | 3.40 × 106 | 8.83 × 106 |
| 10 | 132 | 1.02 × 107 | 2.65 × 107 |
| i | /(MPa) | /(Cycles) | Lower Confidence Limit of Reliable Life /(Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 589 | 0.15 | 3.03 × 104 |
| 2 | 531 | 0.58 | 4.53 × 104 |
| 3 | 502 | 2.01 | 5.64 × 104 |
| 4 | 376 | 2.13 | 1.74 × 105 |
| 5 | 297 | 3.59 | 4.34 × 105 |
| 6 | 261 | 6.65 | 7.18 × 105 |
| 7 | 217 | 5.58 | 1.47 × 106 |
| 8 | 210 | 19.82 | 1.67 × 106 |
| 9 | 171 | 29.34 | 3.72 × 106 |
| 10 | 123 | 44.29 | 1.34 × 107 |
| Aircraft fleet management method | Proposed individual aircraft monitoring method |
| 70.6% of reliable life has been consumed | 56.2% of reliable life has been consumed |
| Aircraft fleet management method | Proposed individual aircraft monitoring method |
| 70.6% of reliable life has been consumed | 92.5% of reliable life has been consumed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Fu, H. A Novel Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring Method Based on Reliable Life Consumption Assessment. Machines 2023, 11, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11111016
Fu Y, Fu H. A Novel Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring Method Based on Reliable Life Consumption Assessment. Machines. 2023; 11(11):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11111016
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yueshuai, and Huimin Fu. 2023. "A Novel Individual Aircraft Life Monitoring Method Based on Reliable Life Consumption Assessment" Machines 11, no. 11: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11111016





