A Novel Methodology to Enhance the Smooth Running of the PM BLDC Motor Drive Using PWM-PWM Logic and Advance Angle Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Contributions
- Sliding mode controller is designed to identify the speed error in the BLDC motor.
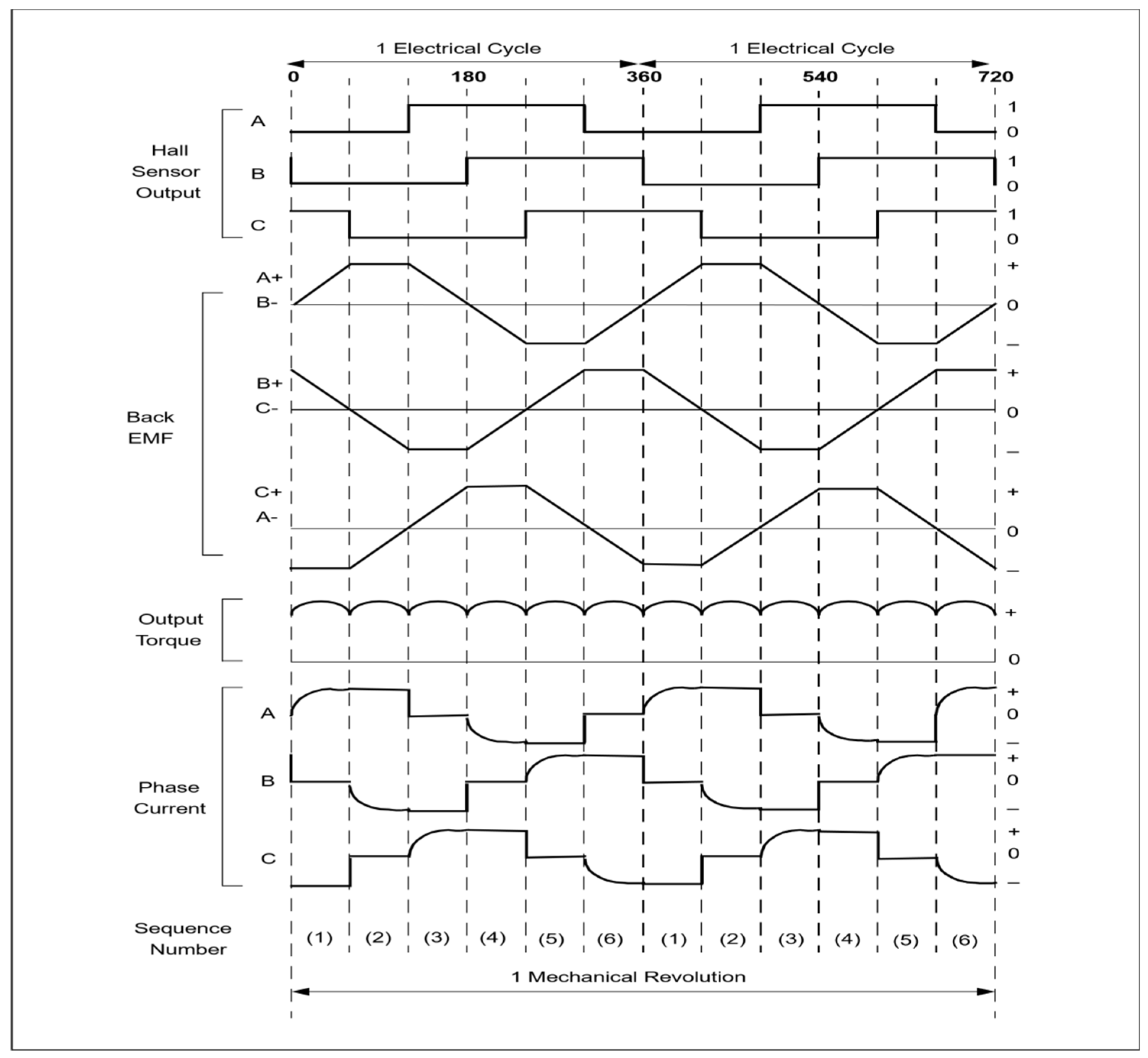
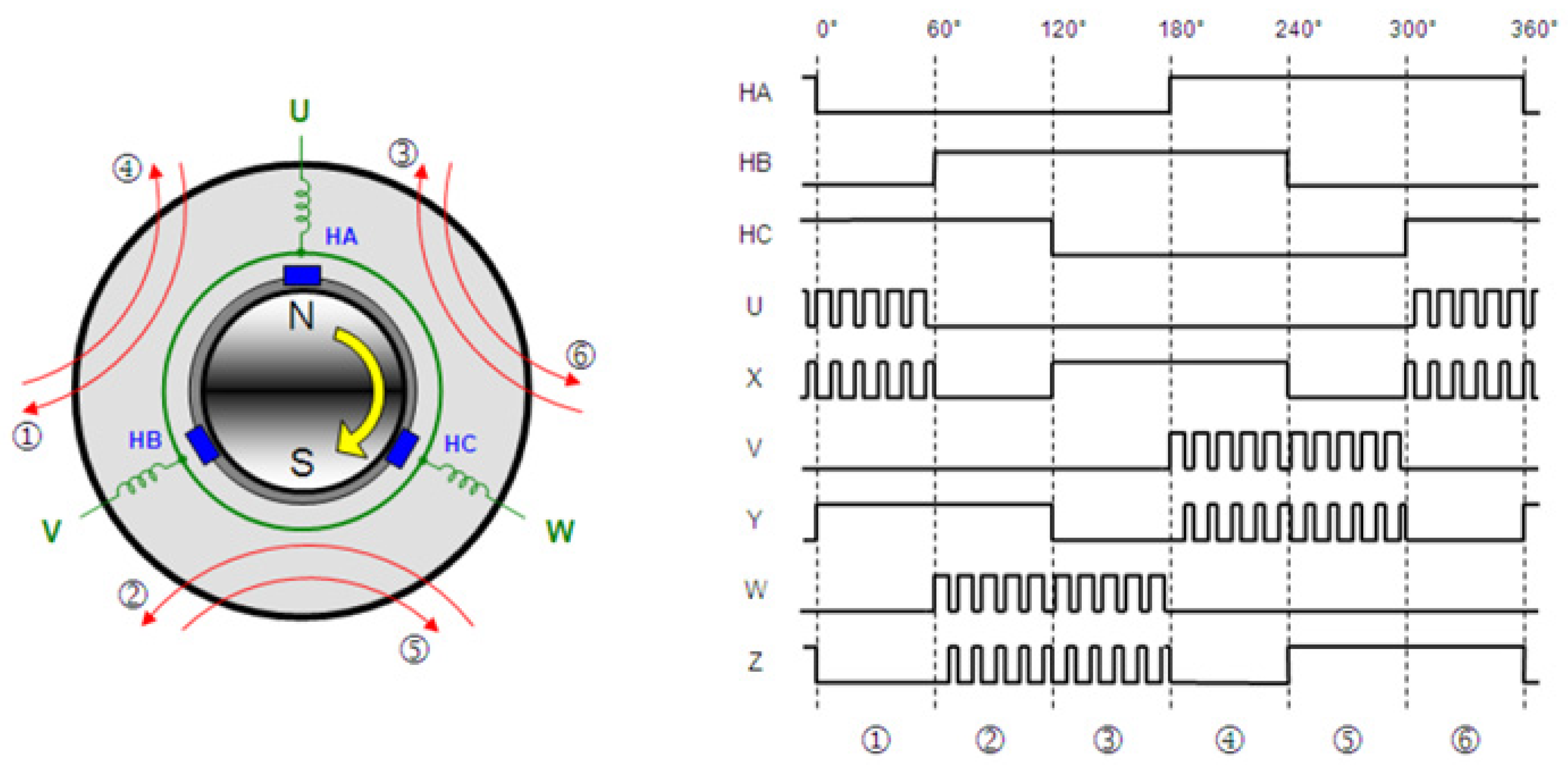
- Back-emf waveforms are generated using hall sensor signals.
- Advanced angle method (AS voltage method) is implemented to adjust the lead angle.
- PWM-PWM commutation technique is developed to drive the BLDC motor.
- The toque ripples are minimized for the dynamic load.
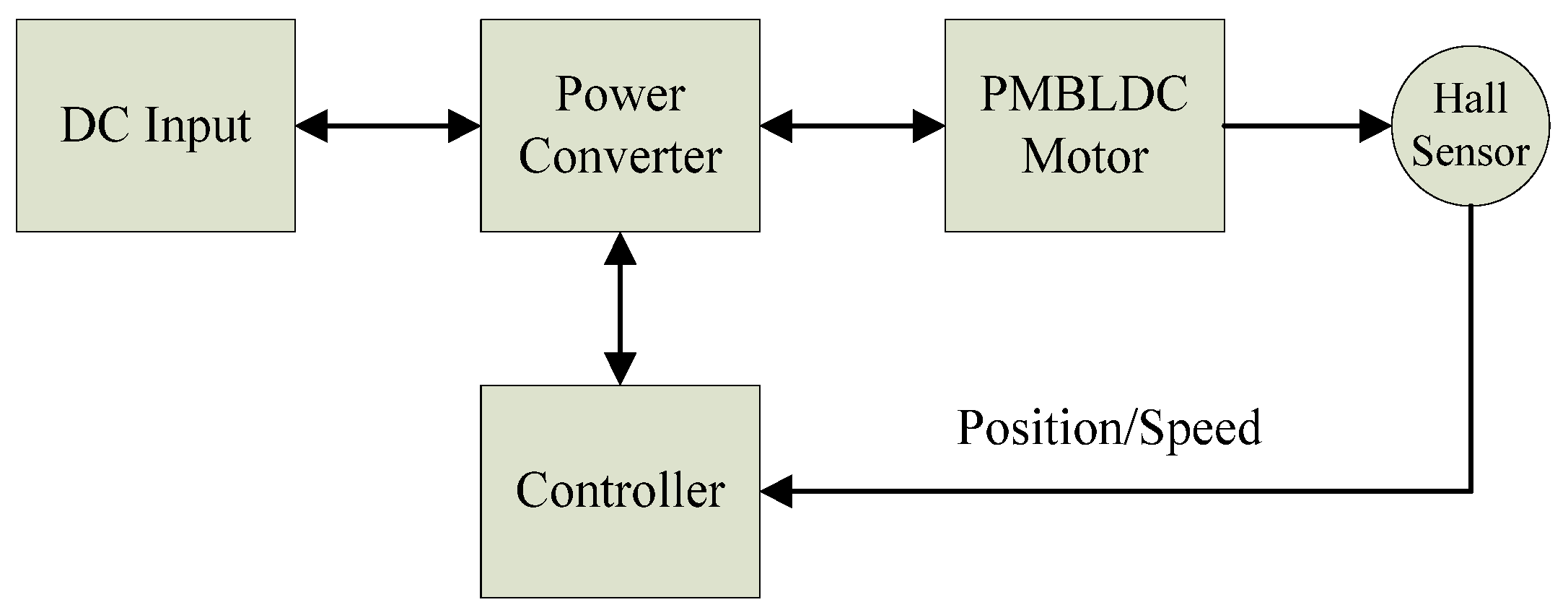
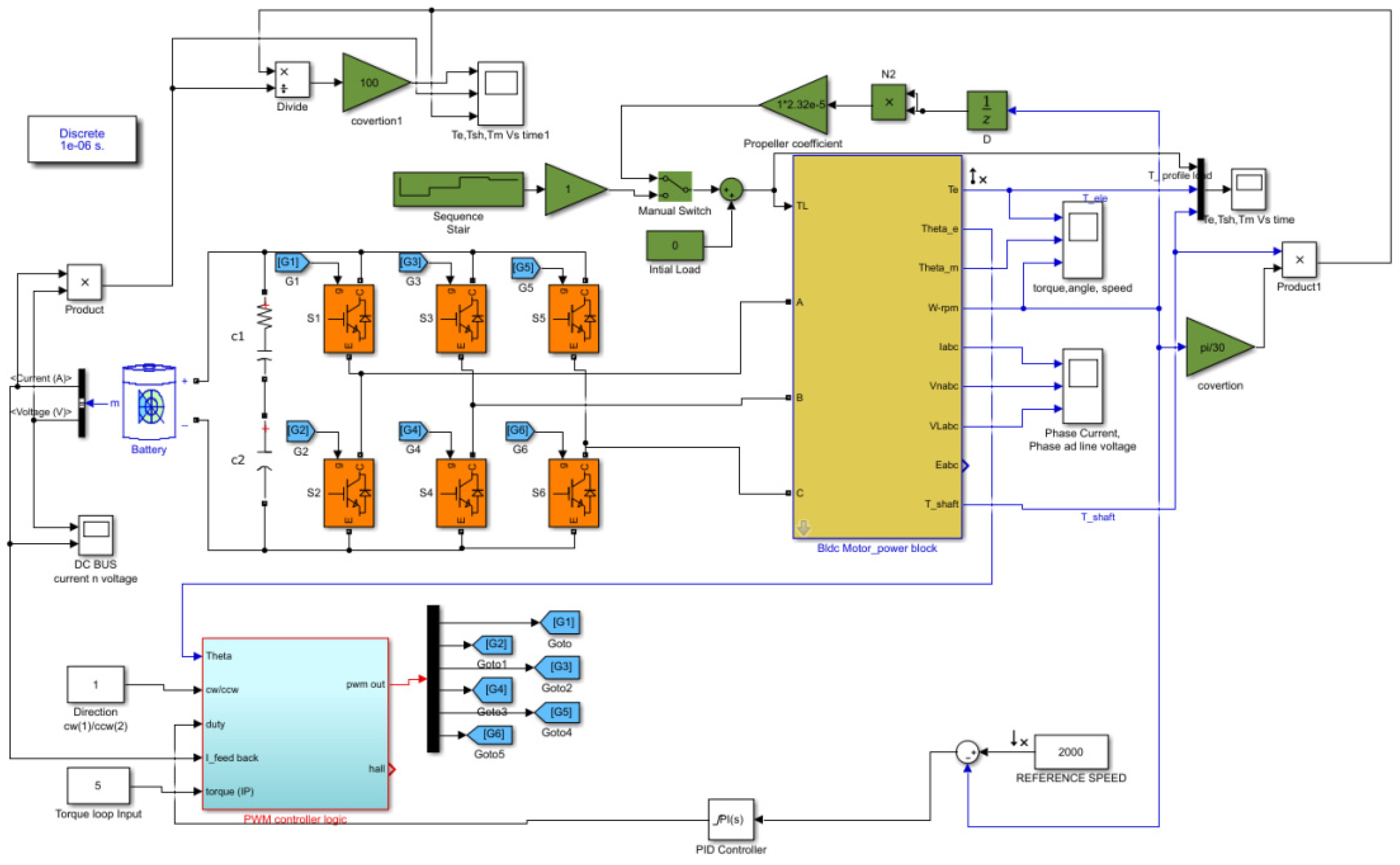
2. Materials of the BLDC Motor and Controllers
2.1. Machine Model and Power Control Theory
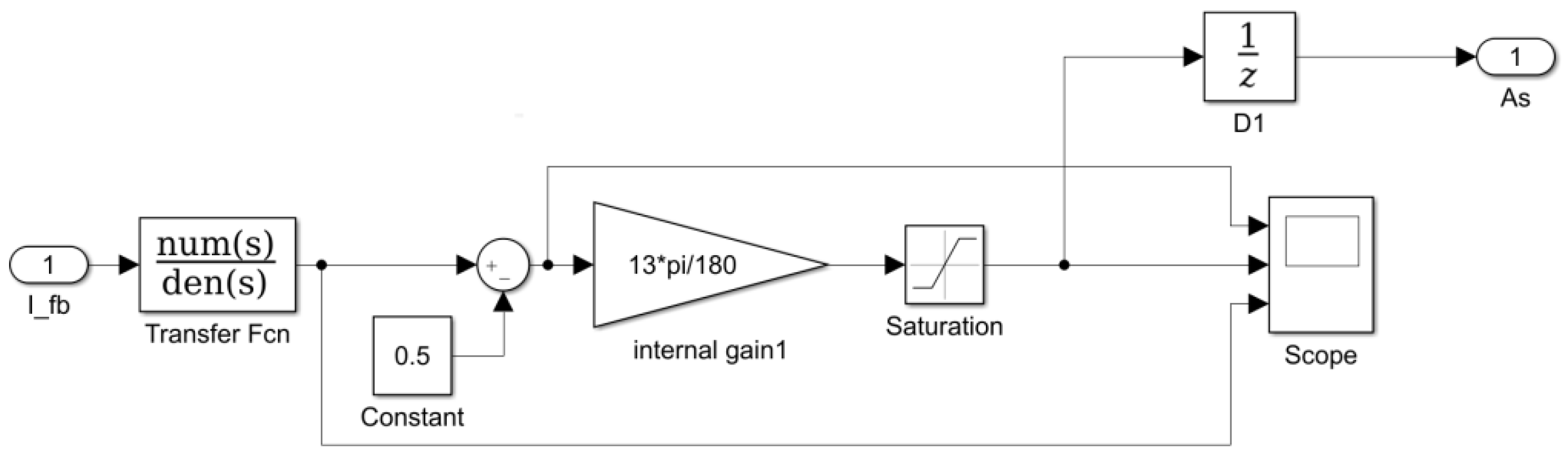
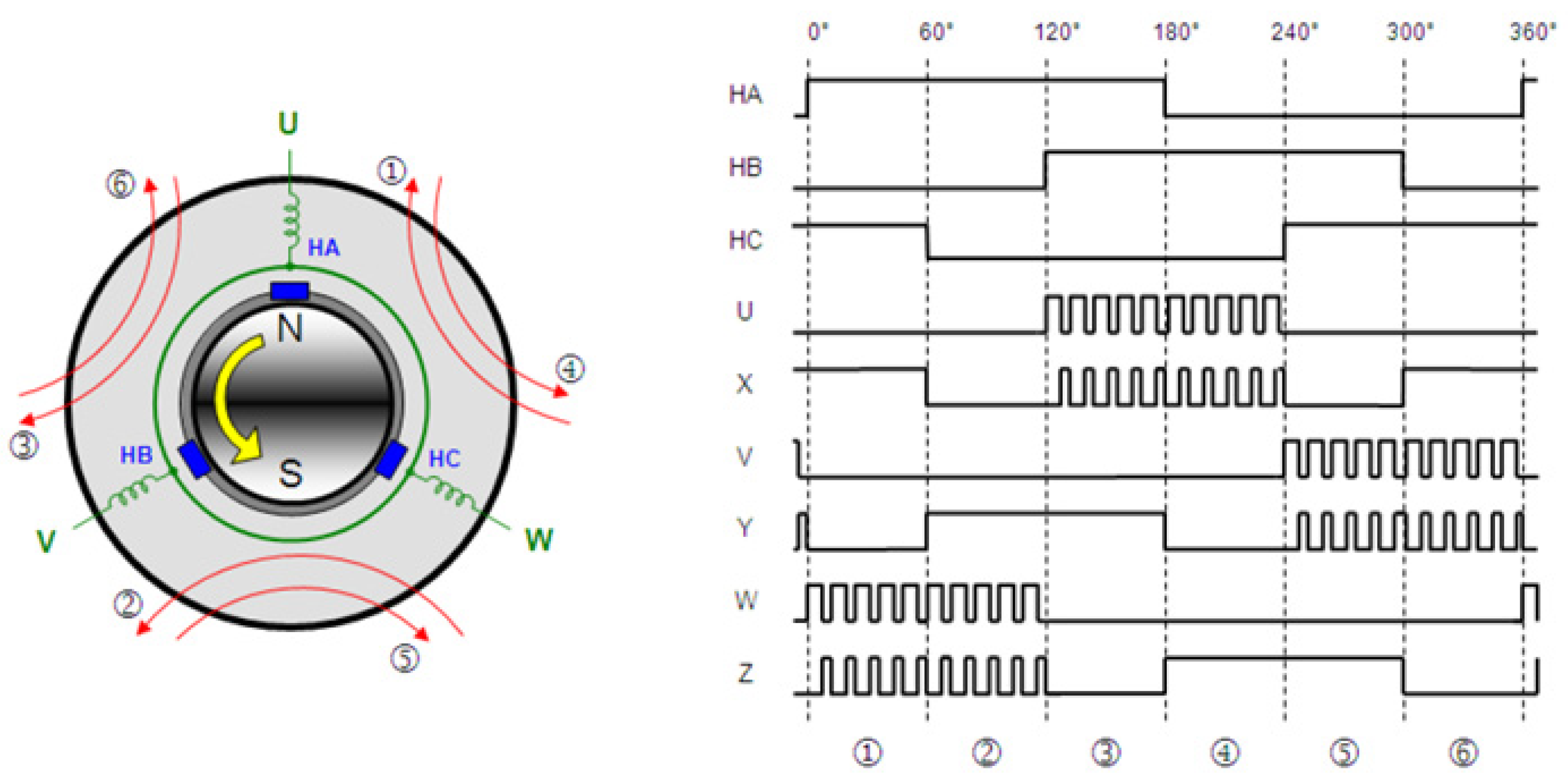
2.2. Advance Angle Method
2.3. Pulse Width Modulation
3. Methodology for Minimization of Torque Ripples in the BLDC Motor
3.1. Advance Angle Adjustment
3.2. Pulse Width Modulation Scheme
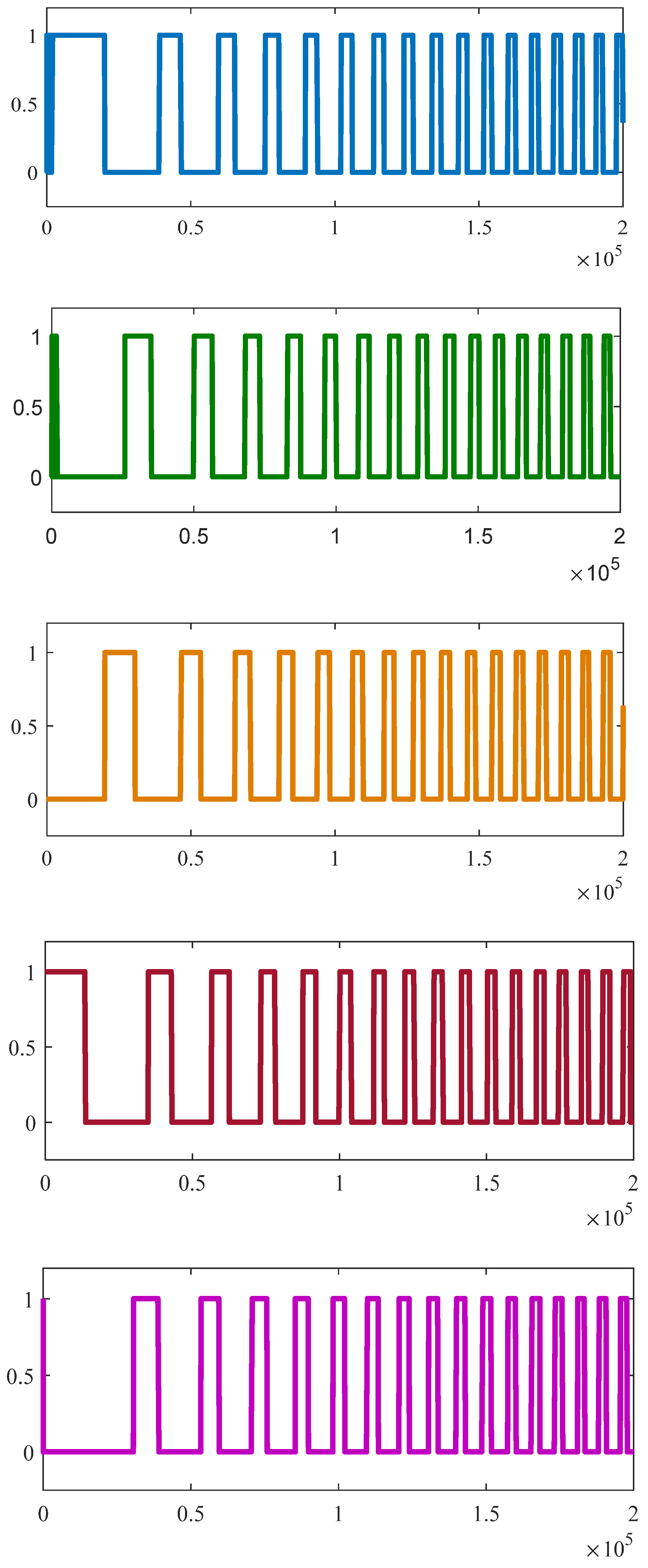
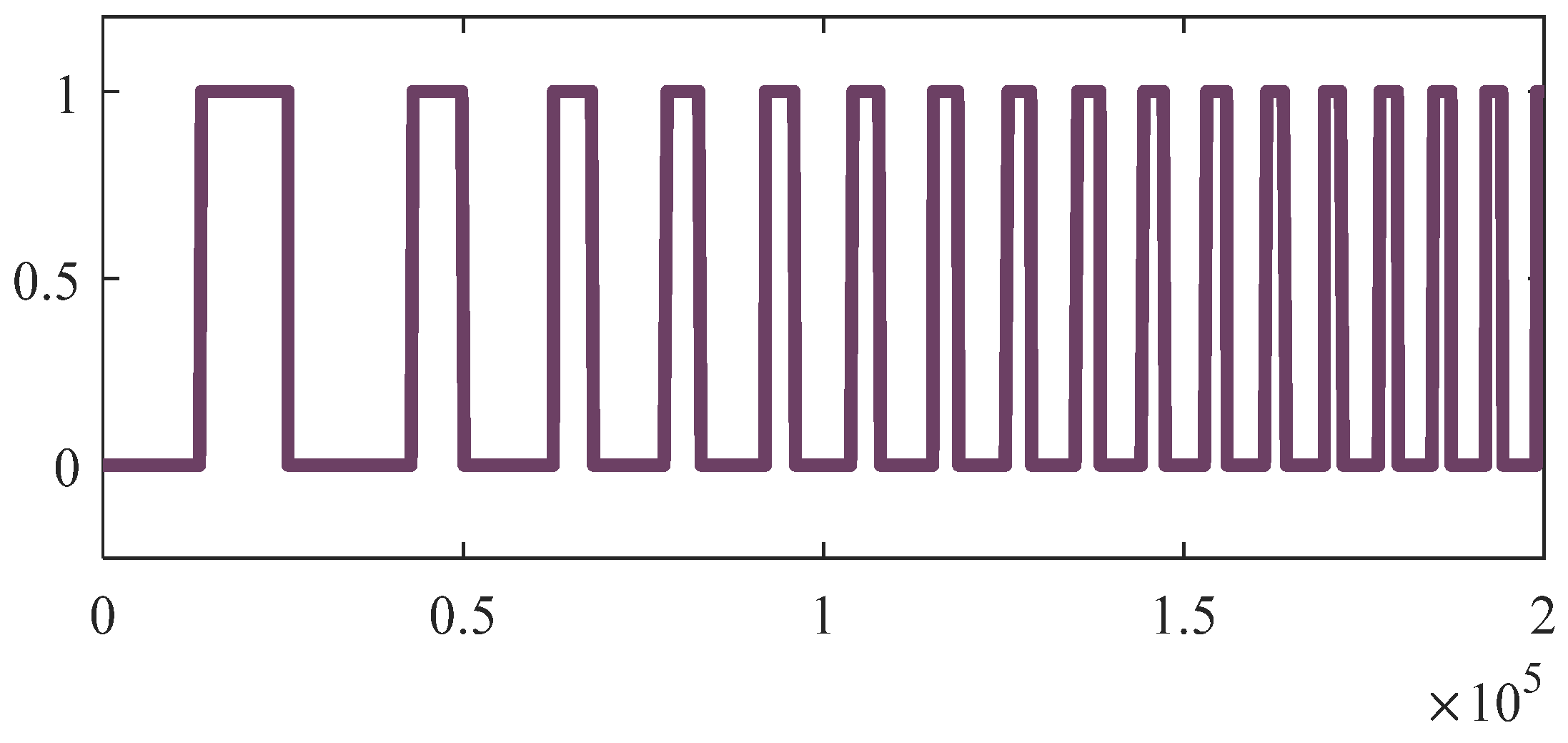
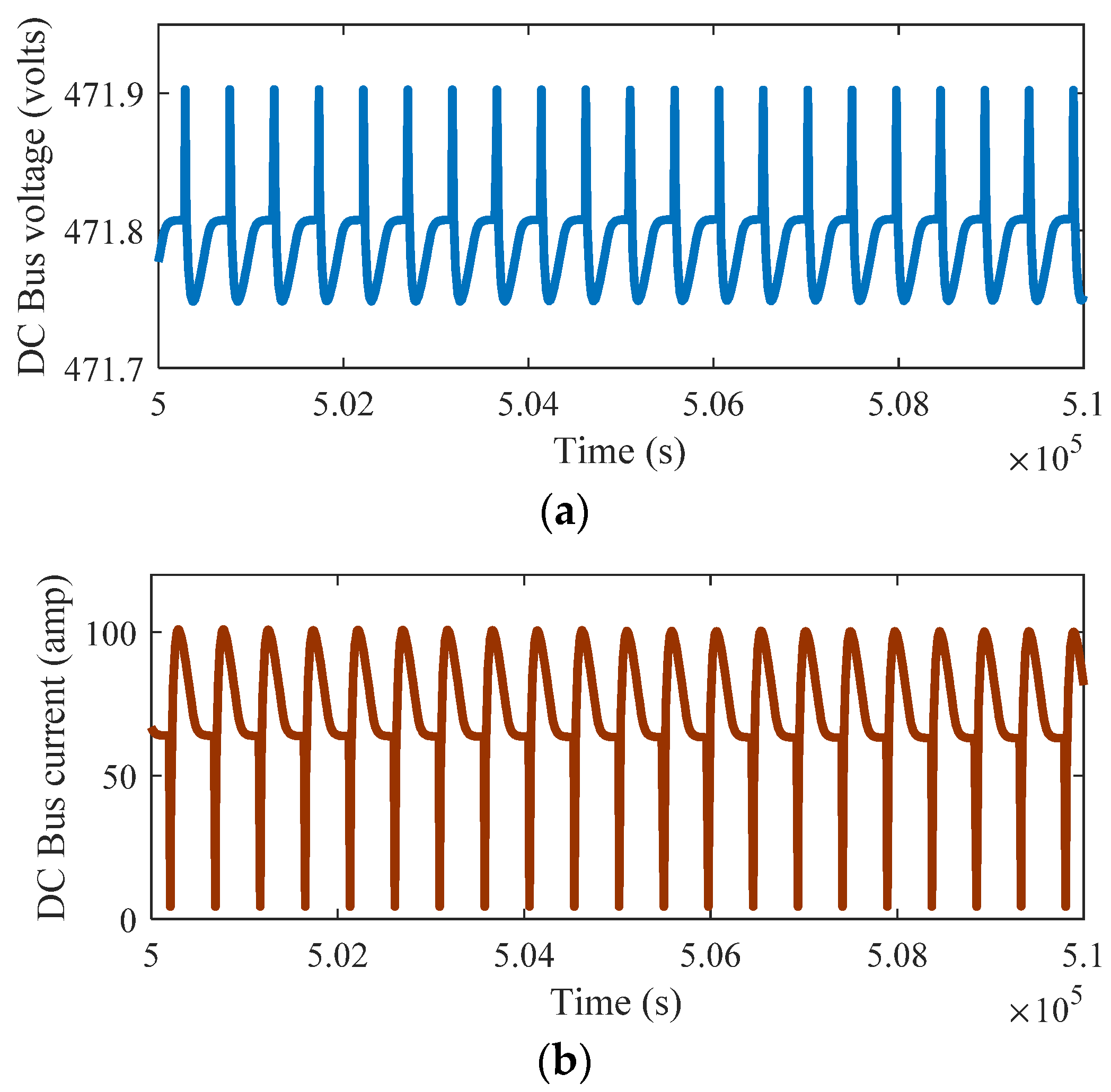
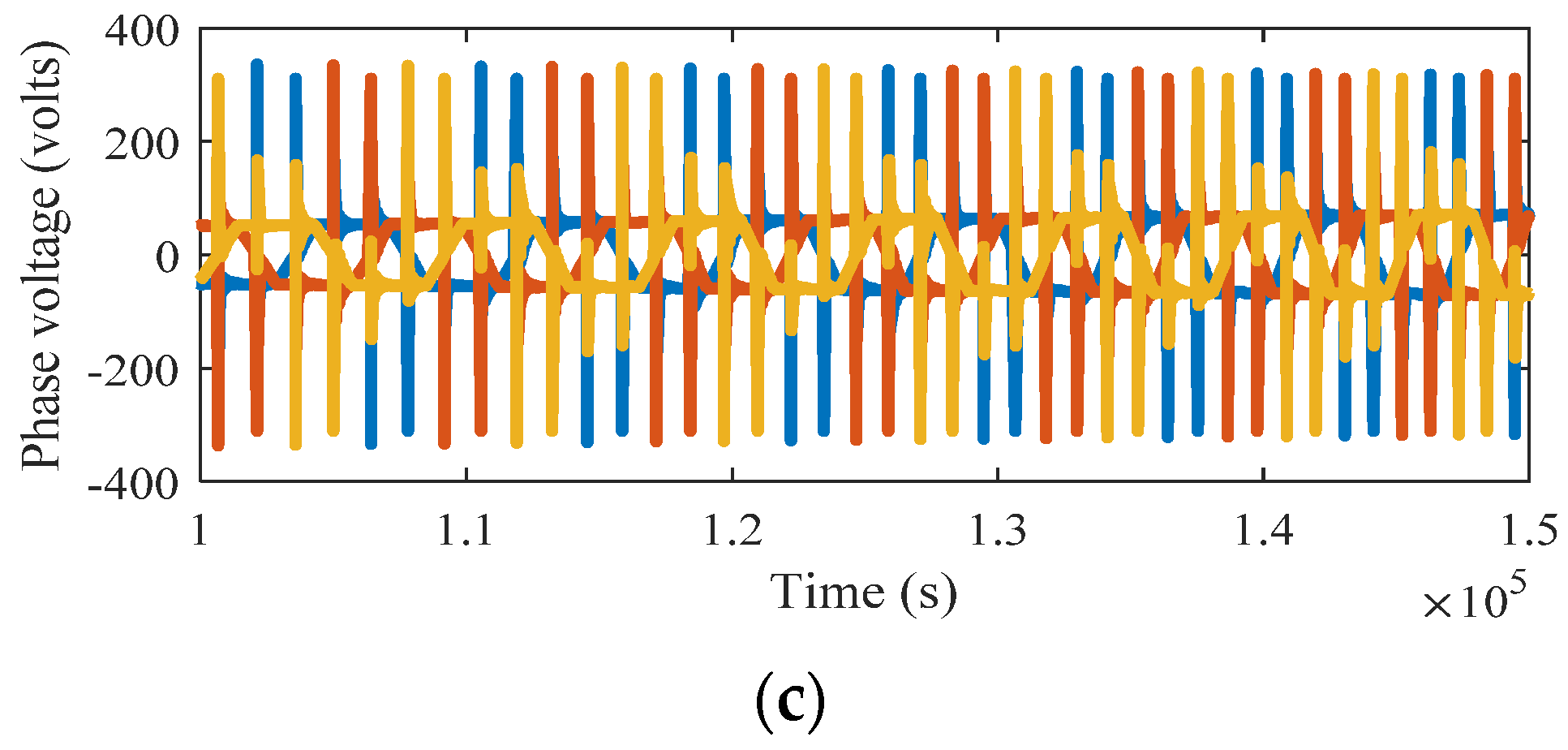
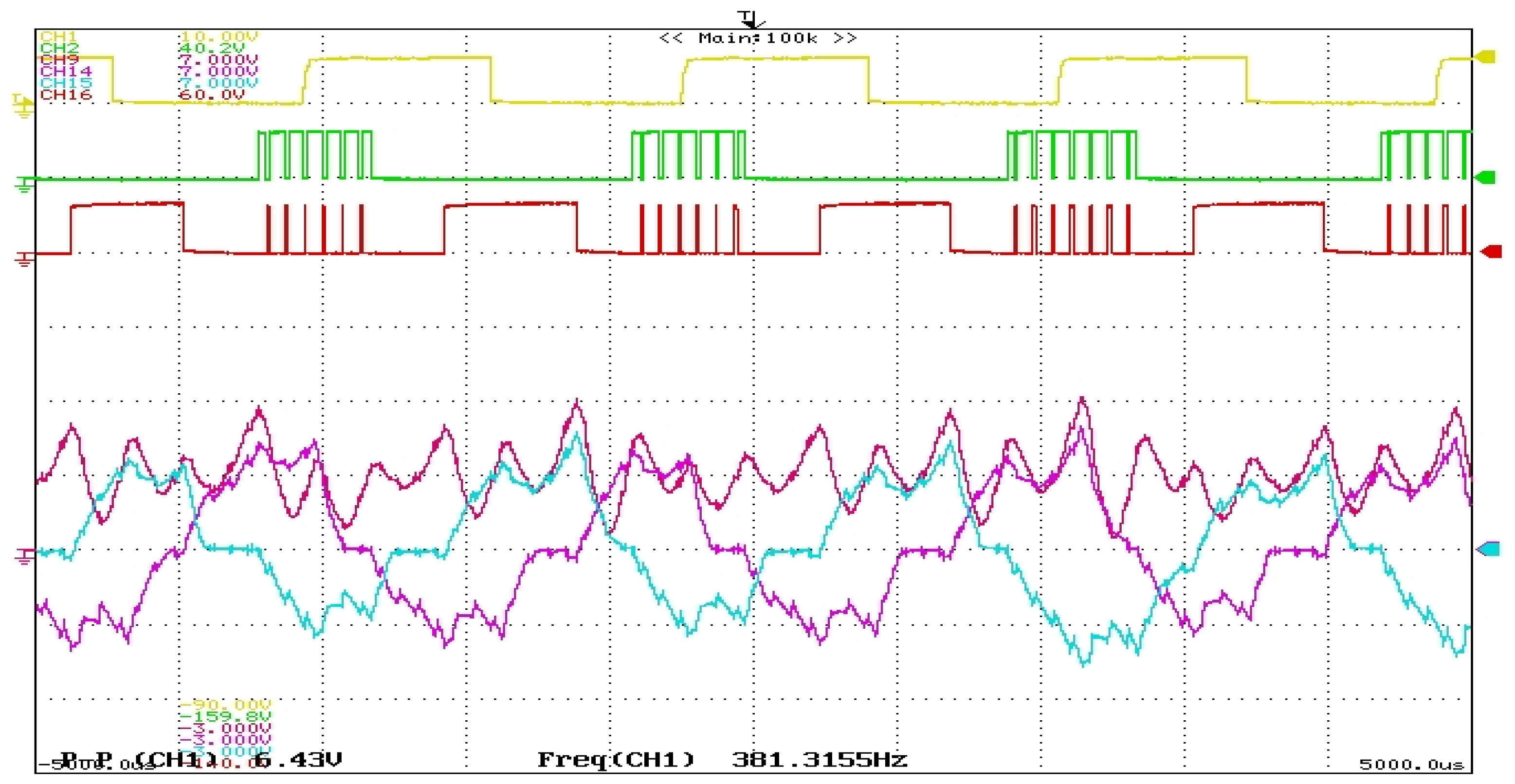
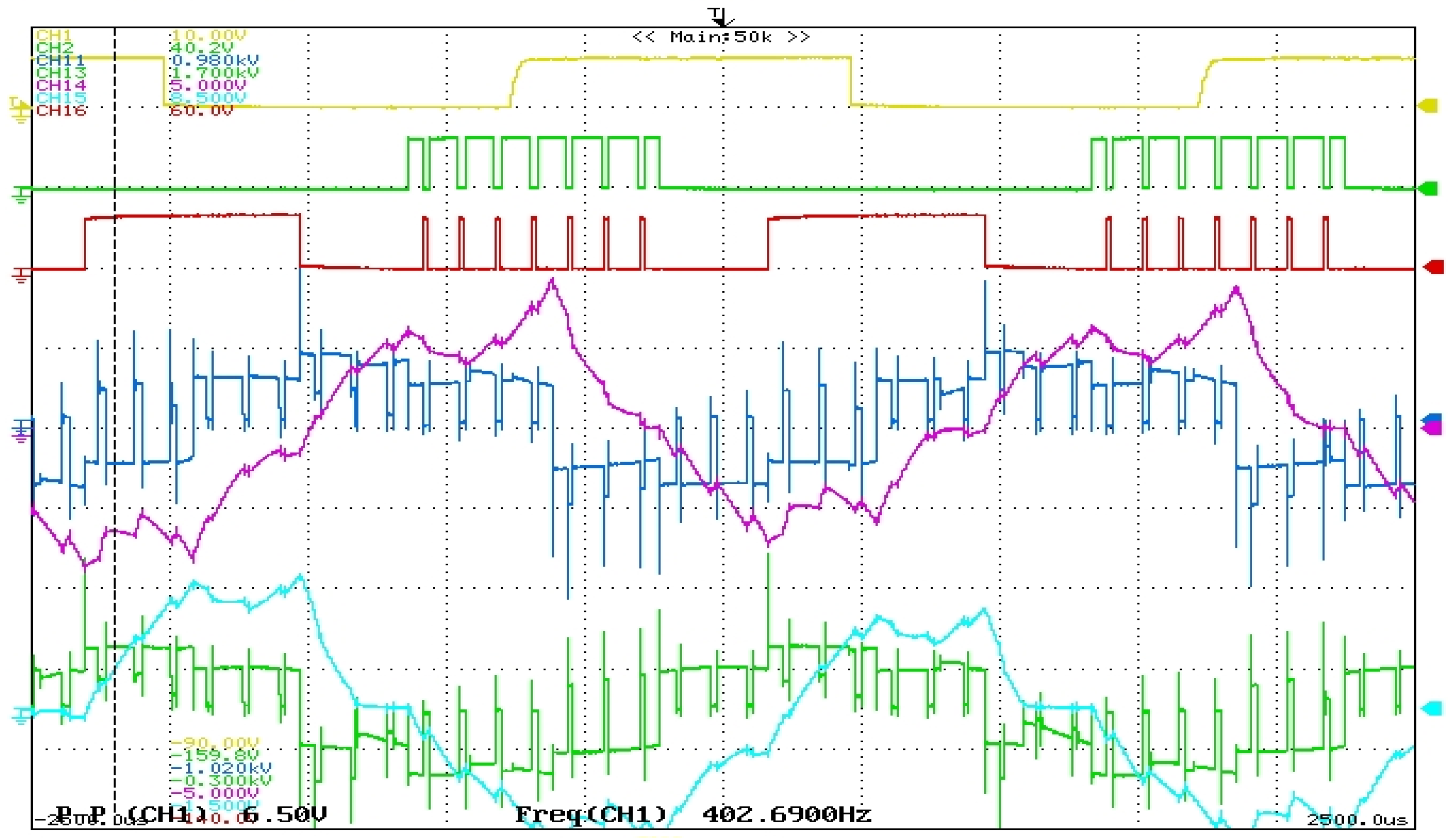
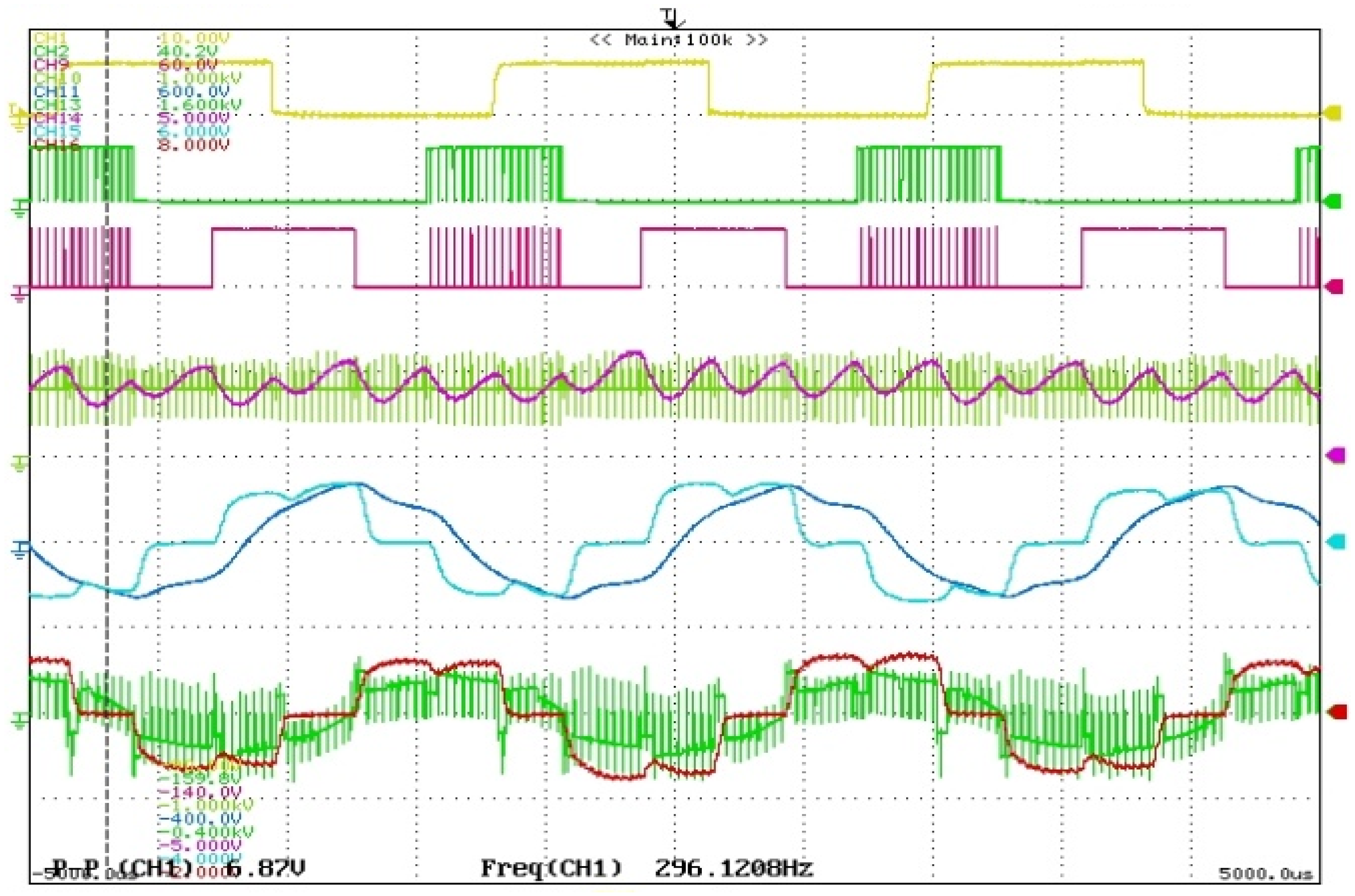
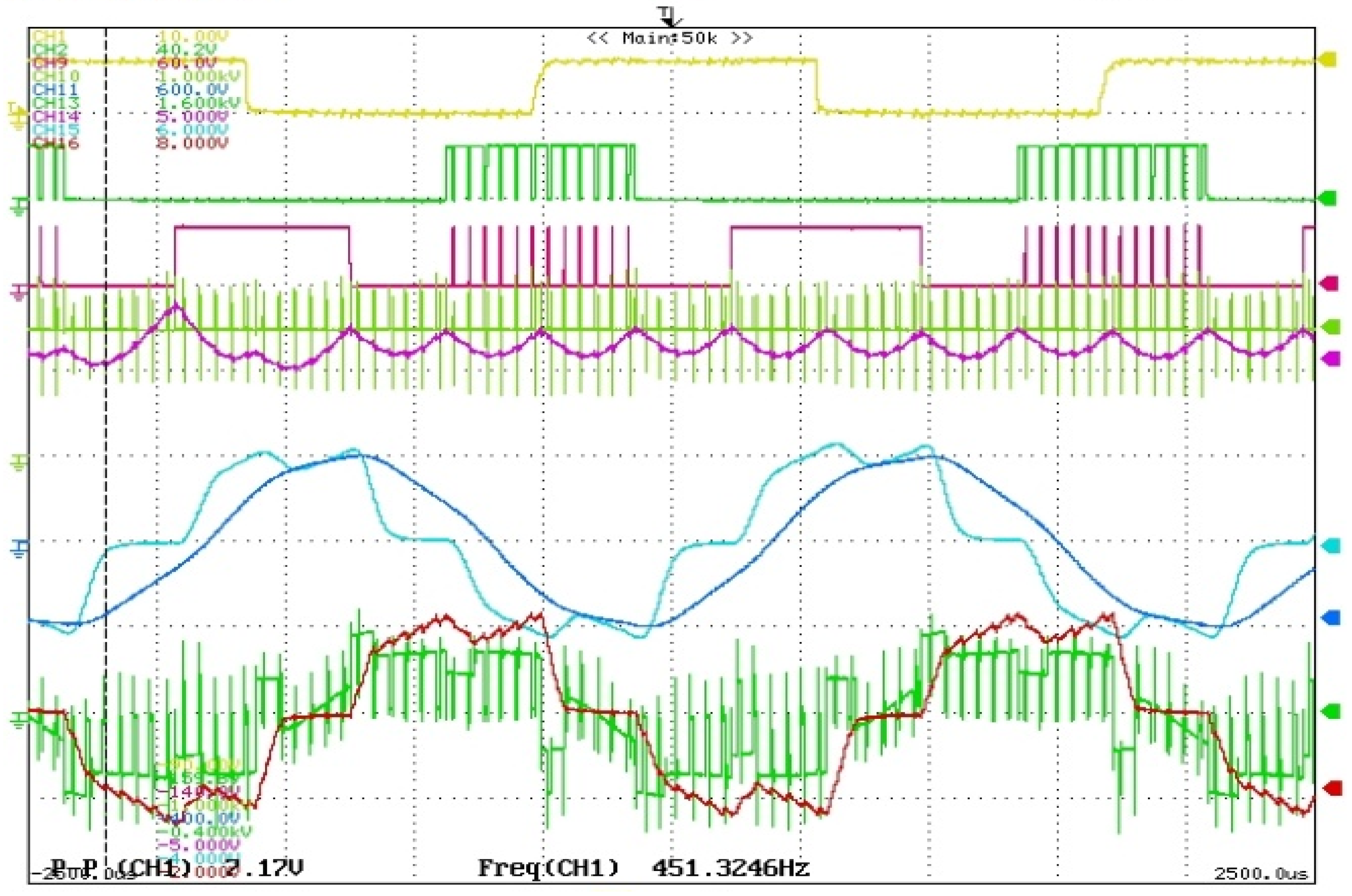
4. Results and Discussions
Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.-T.; Liou, Y.-K.; Liang, R.-H. Axial Magnetic Force Analysis and Optimized Design for Single-Phase BLDC Slim Fan Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 6840–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Rajpurohit, B.S. Modeling and Classification of Stator Inter-Turn Fault and Demagnetization Effects in BLDC Motor Using Rotor Back-EMF and Radial Magnetic Flux Analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 118030–118049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.S.; Keshri, R.K. Evaluation of Predictive Current Control Techniques for PM BLDC Motor in Stationary Plane. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 46217–46228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Rajpurohit, B.S. Comprehensive Analysis of Demagnetization Faults in BLDC Motors Using Novel Hybrid Electrical Equivalent Circuit and Numerical Based Approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147542–147552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Sun, W.; Shen, J.-X. Flux Observer Model for Sensorless Control of PM BLDC Motor with a Damper Cage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 55, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. A New Method to Minimize Overall Torque Ripple in the Presence of Phase Current Shift Error for Three-Phase BLDC Motor Drive. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019, 42, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan, T.; Atiq, S.; Kwon, B.-I.; Baloch, N.; Kwon, J.-W. Two Phase Dual-Stator Axial-Flux PM BLDC Motor with Ironless Rotor Using Only-Pull Drive Technique. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 82144–82153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.-T.; Shin, H.-S.; Lee, Y.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, J.-Y. Optimal Design of a BLDC Motor Considering Three-Dimensional Structures Using the Response Surface Methodology. Energies 2022, 15, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-M. Precision control of a sensorless PM BLDC motor using PLL control algorithm. Electr. Eng. 2017, 100, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuja, T.A.; Doss, M.A.N. Asymmetrical Magnets in Rotor Structure of a Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor for Cogging Torque Minimization. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, V.; Singh, N.J.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, V. Position Control of PMBLDC Motor Using SVR- and ANFIS-Based Controllers. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2021, 45, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, Z.; Li, T. Bipolar modulation of brushless DC motor with integrated control of motoring and regenerative braking. J. Power Electron. 2022, 22, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Hu, H.; Lu, X.; Zhao, S. An adaptive fuzzy PID controller for speed control of brushless direct current motor. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H. A Fast Commutation Error Correction Method for Sensorless BLDC Motor Considering Rapidly Varying Rotor Speed. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 3938–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kong, K. Fourier-Series-Based Phase Delay Compensation of Brushless DC Motor Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, G.; Zhu, L. Sensorless Startup Strategy for a 315-kW High-Speed Brushless DC Motor with Small Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, D.-H. Simple Commutation Torque Ripple Reduction Using PWM With Compensation Voltage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransara, H.K.S.; Madawala, U.K. A Torque Ripple Compensation Technique for a Low-Cost Brushless DC Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6171–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, P.M.; Valle, R.L.; Barbosa, P.G.; Montagner, V.F.; Cuk, V.; Ribeiro, P.F. Robust Control of a Variable-Speed BLDC Motor Drive. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2020, 2, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Bhaskar, D.V.; Behera, R.K.; Muduli, U.R. A Modified torque ripple minimization technique for BLDC motor drive using synthesized current phase compensation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Tech-nology (ICIT), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, T.; Suh, Y. Comparison of fault-tolerant control methods reducing torque ripple of multi-phase BLDC motor drive system under open-phase fault. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), virtual, 10–14 October 2021; pp. 4987–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Thabet, A.M.; Mahgoub, O.A. Brushless DC motor drive with minimum torque ripple. In Proceedings of the 2016 Eighteenth International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, 27–29 December 2016; pp. 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Hong, J.-P.; Jang, W.-K. Characteristics comparison of BLDC motor according to the lead angles. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 9–12 October 2012; pp. 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.B.; Rao, P.M. Adaptive sliding mode control of BLDC motor using cuckoo search algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 January 2018; pp. 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, T.; Wu, H. A Radial-flux Permanent Magnet Micromotor with 3D Solenoid Iron-core MEMS In-chip Coils of High Aspect Ratio. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2020, 41, 1090–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Shin, K.H.; Jang, G.H.; Cho, S.K.; Jung, K.H.; Choi, J.Y. Experimental Verification and 2D Equivalent Analysis Techniques of BLDC Motor with Permanent Magnet Overhang and Housing Integrated Rotor Core. EEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2020, 30, 5201805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L. Investigation of a Stator-Ironless Brushless DC Motor with Non-Ideal Back-EMF. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 28044–28054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Gu, C.; Sun, Q.; Peng, C.; Pang, G. Reduction of Rotor Harmonic Eddy-Current Loss of High-Speed PM BLDC Motors by Using a Split-Phase Winding Method. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashidhar, S.; Reddy, V.G.P.; Fernandes, B.G. A Single-Stage Sensorless Control of a PV-Based Bore-Well Submersible BLDC Motor. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 7, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yin, M.; Hua, W.; Ma, Z.; Lin, M.; Kong, Y. Design and Analysis of Halbach Ironless Flywheel BLDC Motor/Generators. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8109305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FCM8201 Three-Phase Sine-Wave BLDC Motor Controller. Available online: www.bdtic.com/DataSheet/FAIRCHILD/AN-8201.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Deng, Z. A PLL-Based Novel Commutation Correction Strategy for a High-Speed Brushless DC Motor Sensorless Drive System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 3752–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, M.; Reddy, A.S.; Kumar, M.V. Modified Luo converter based FOPID controller for torque ripple minimization in BLDC drive system. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Symbol | Quantity | Value of Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| J | Moment of inertia | 0.155 kg m2 |
| B | Friction coefficient | 0.0031575 kg/ms |
| Kb | Back-emf constant | 0.07 volt/rad/sec |
| L | Inductance | 0.0000462 H |
| P | Number of pole pairs | 9 |
| R | Resistance per phase | 0.0127 ohms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Surakasi, B.; Satish, R.; Pydi, B.; Kotb, H.; Shouran, M.; Abdul Samad, B. A Novel Methodology to Enhance the Smooth Running of the PM BLDC Motor Drive Using PWM-PWM Logic and Advance Angle Method. Machines 2023, 11, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11010041
Surakasi B, Satish R, Pydi B, Kotb H, Shouran M, Abdul Samad B. A Novel Methodology to Enhance the Smooth Running of the PM BLDC Motor Drive Using PWM-PWM Logic and Advance Angle Method. Machines. 2023; 11(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleSurakasi, Balamurali, Raavi Satish, Balamurali Pydi, Hossam Kotb, Mokhtar Shouran, and Bdereddin Abdul Samad. 2023. "A Novel Methodology to Enhance the Smooth Running of the PM BLDC Motor Drive Using PWM-PWM Logic and Advance Angle Method" Machines 11, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11010041
APA StyleSurakasi, B., Satish, R., Pydi, B., Kotb, H., Shouran, M., & Abdul Samad, B. (2023). A Novel Methodology to Enhance the Smooth Running of the PM BLDC Motor Drive Using PWM-PWM Logic and Advance Angle Method. Machines, 11(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11010041








