A Novel Experimental Method for Identifying the Flux Linkage Map of a High-Power Medium-Voltage Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine with Double Stator Winding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
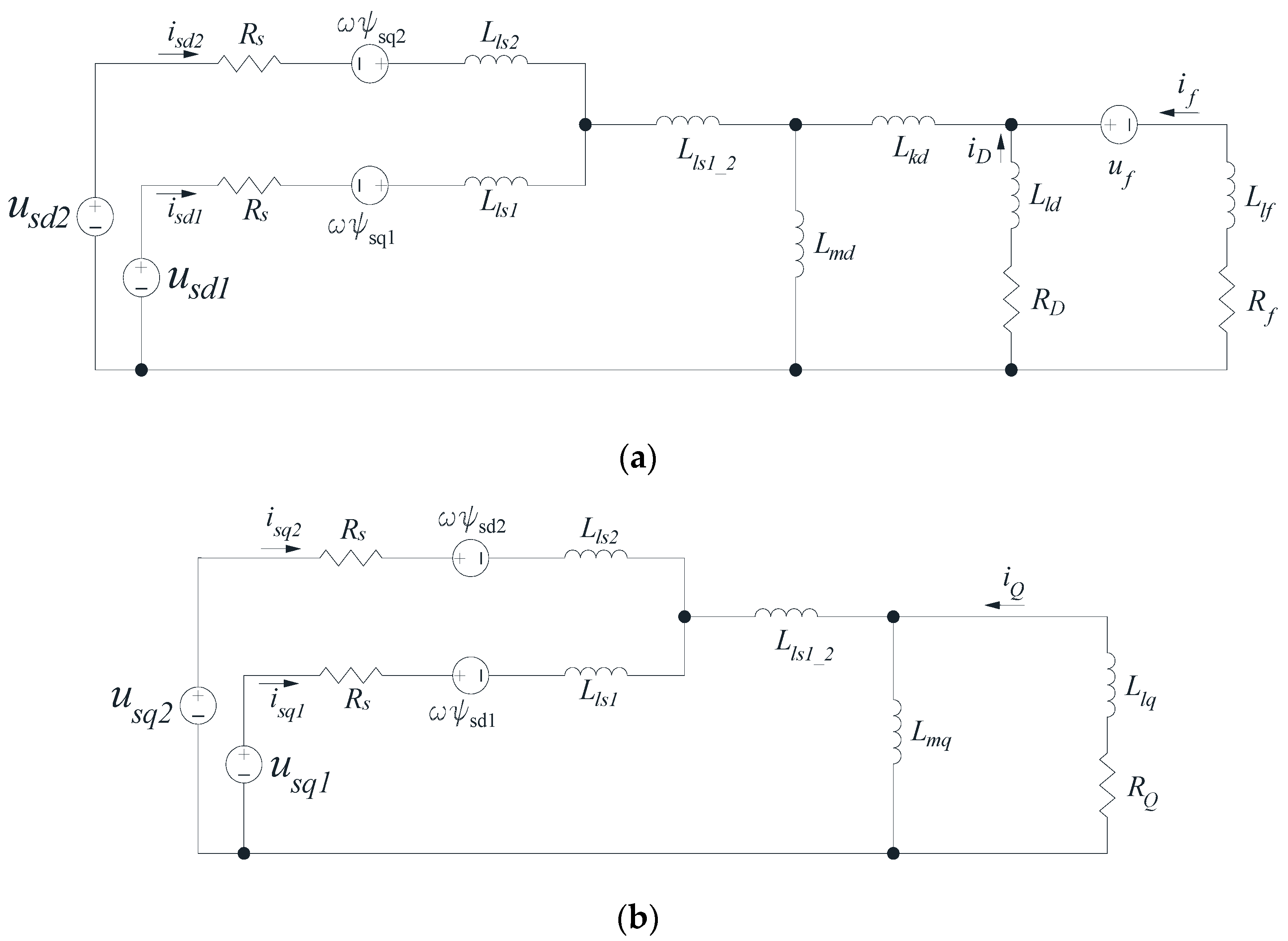
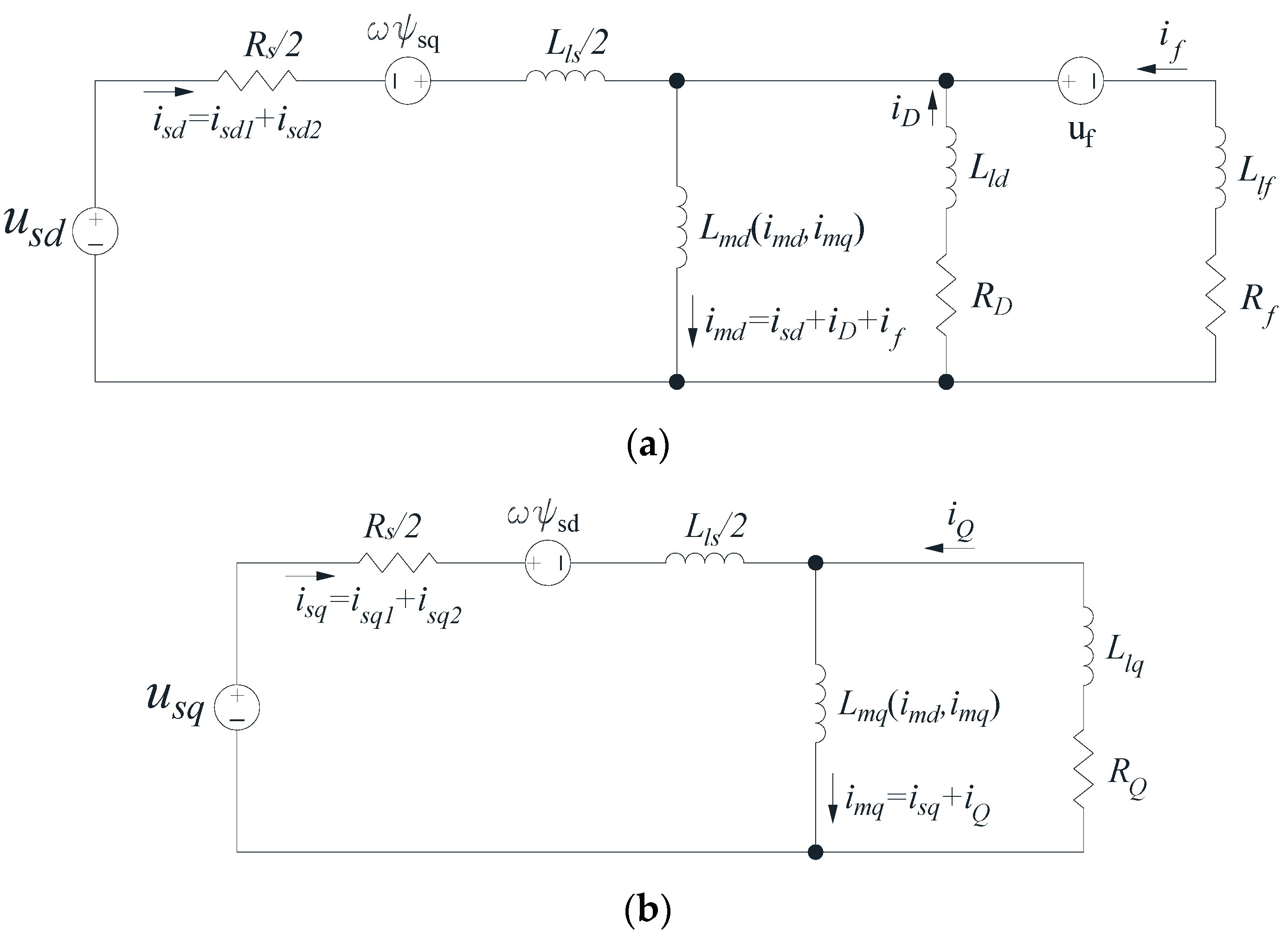
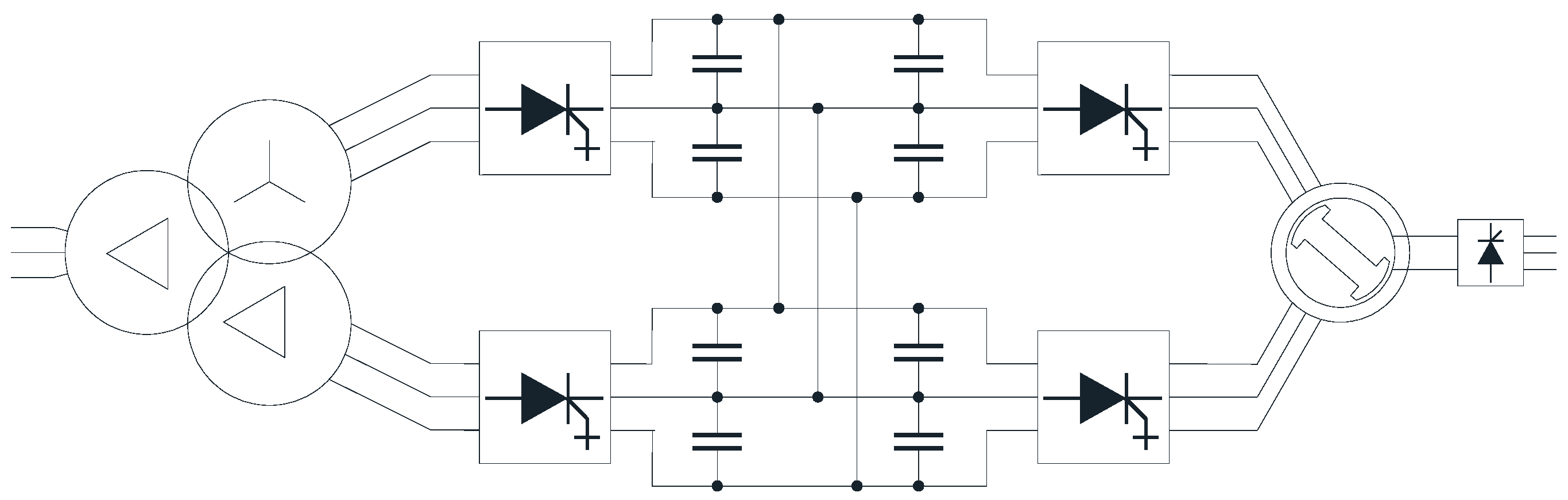
2. Mathematical Model of an EESM with Double Stator Winding
3. Analytical Methods for Determining the Flux Linkage Map
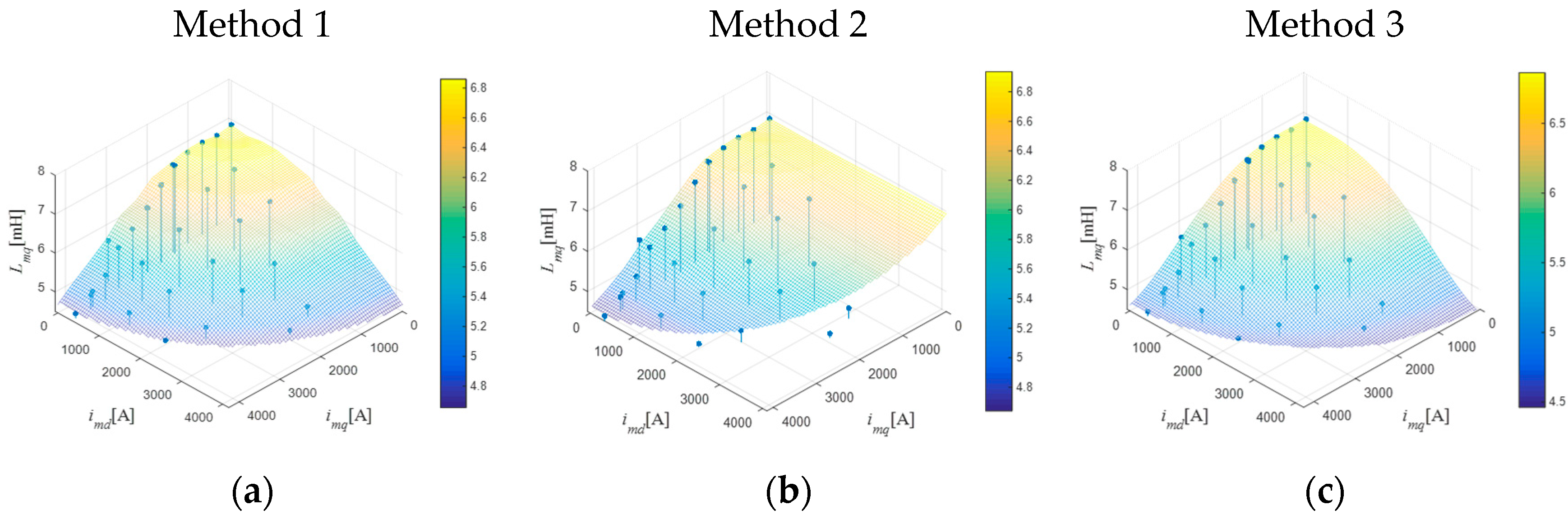
3.1. Method 1 (Levi)
3.2. Method 2 (Kaukonen)
3.3. Method 3 (El-Serafi & Wu)
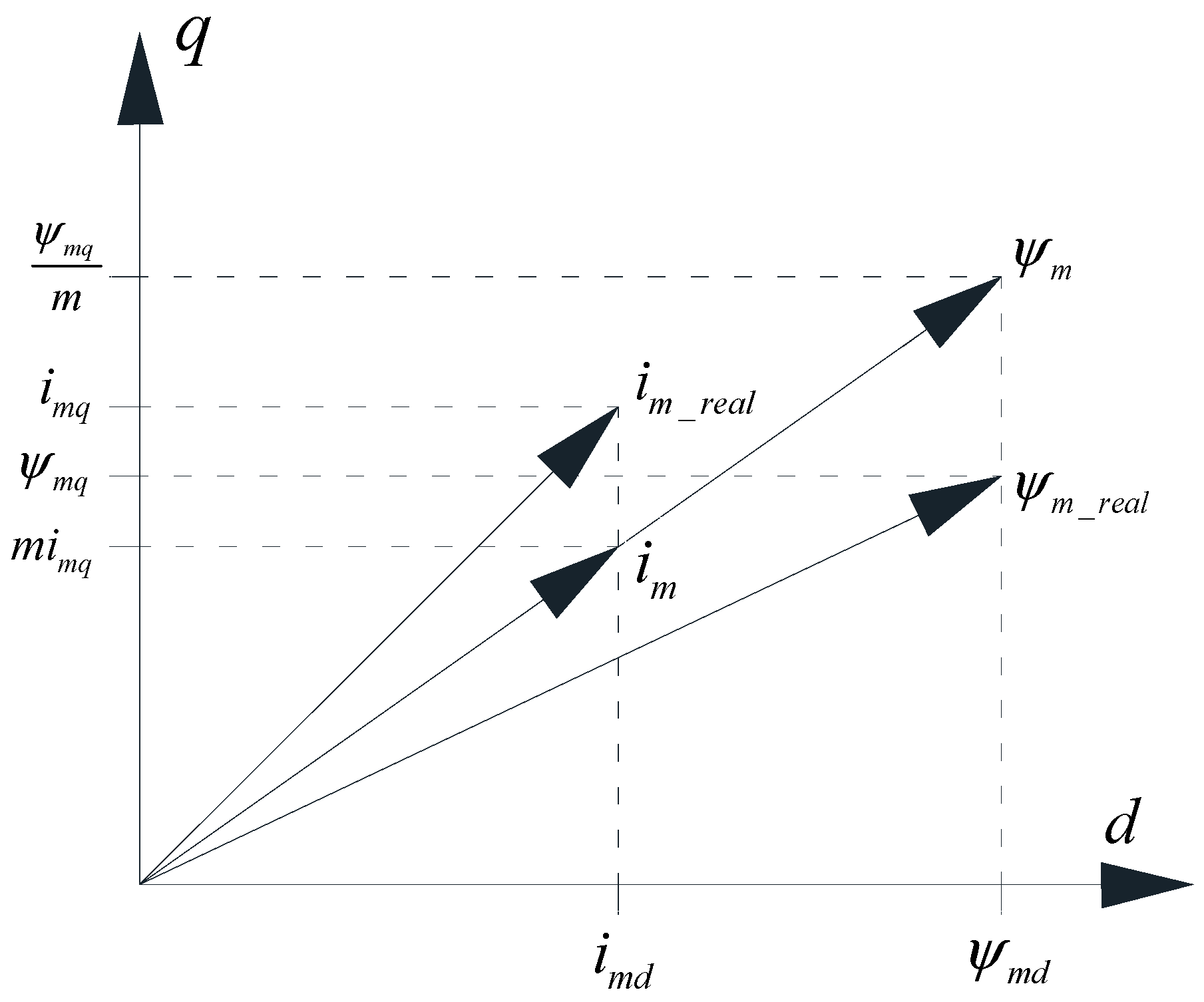
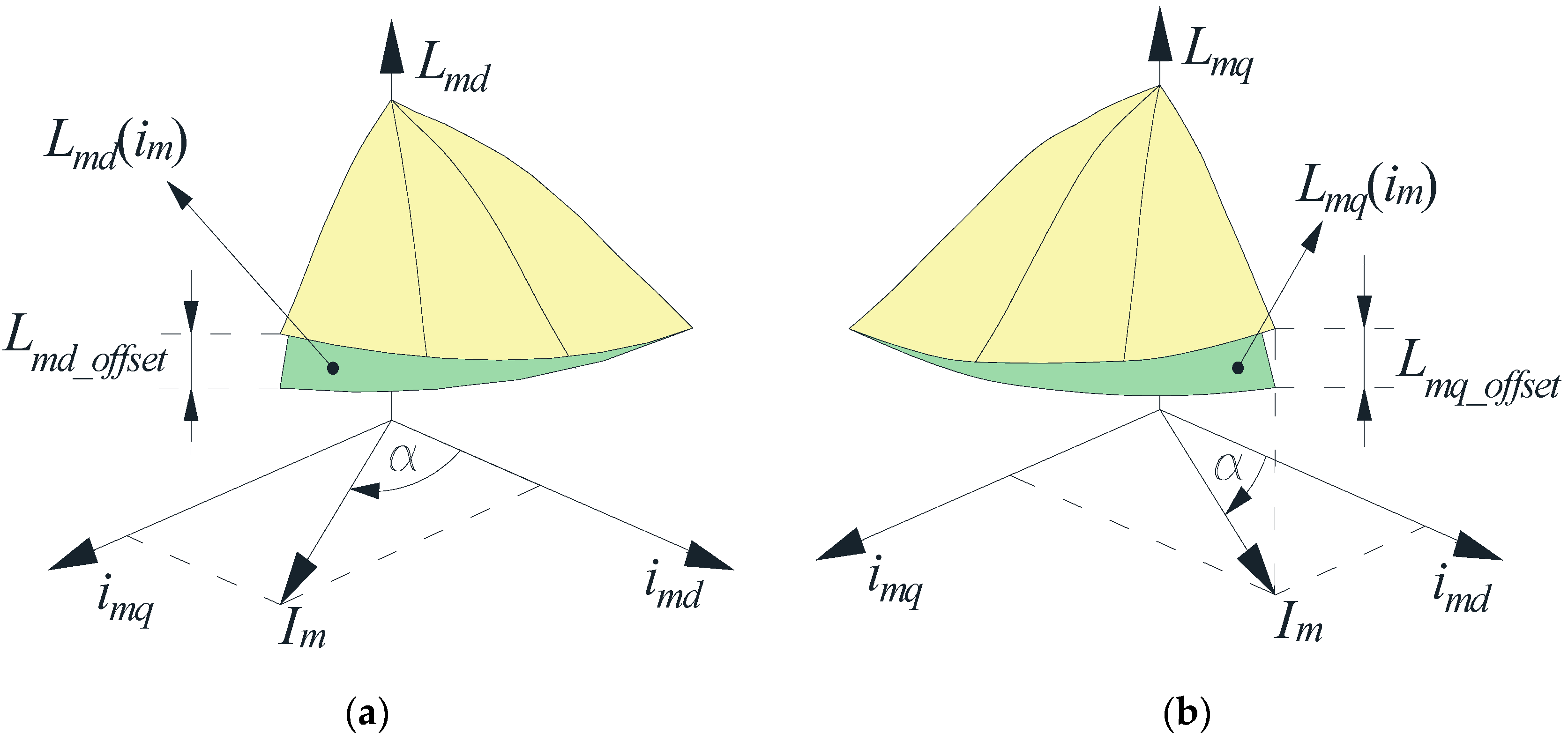
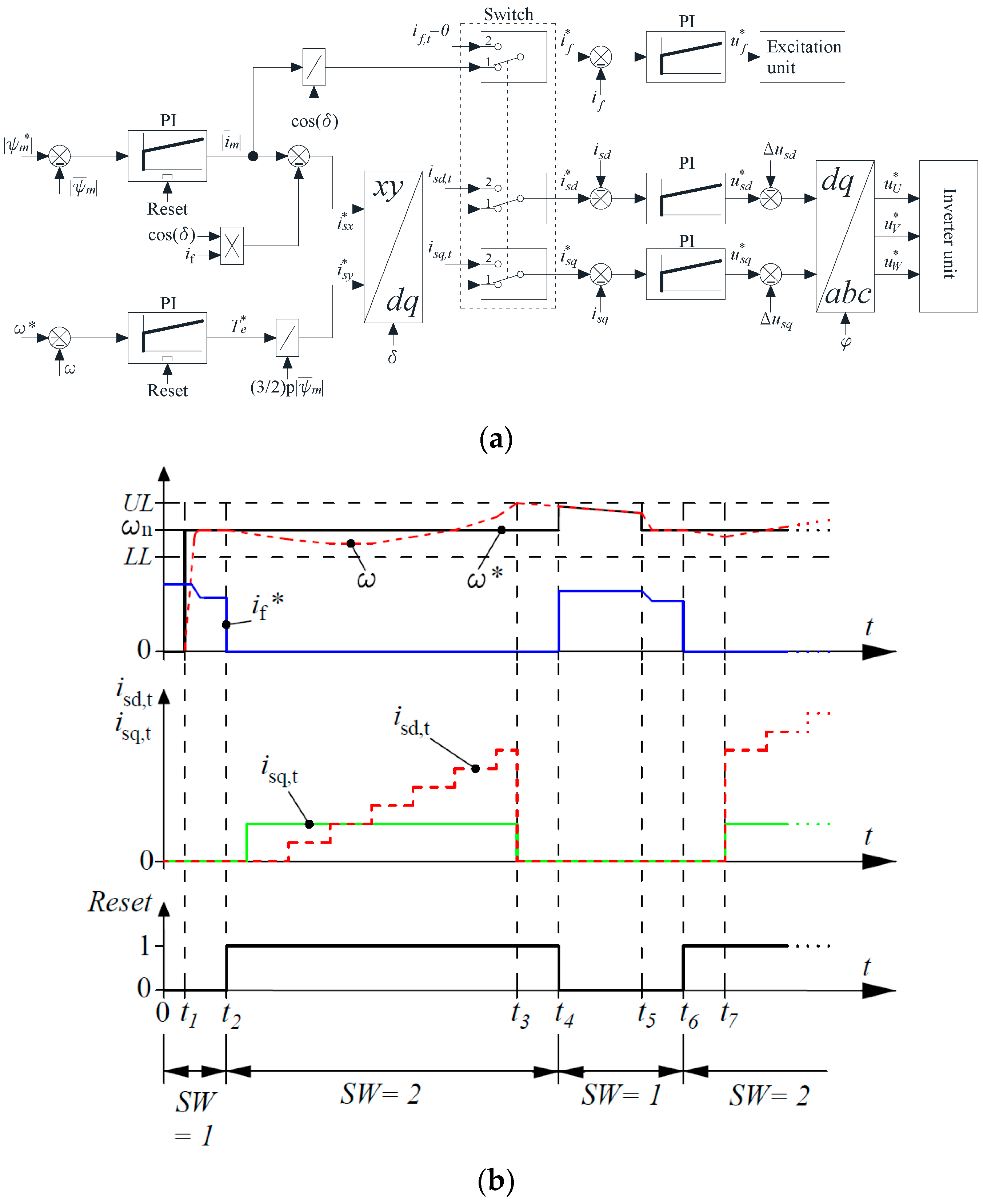
4. Description of the Proposed Experimental Method
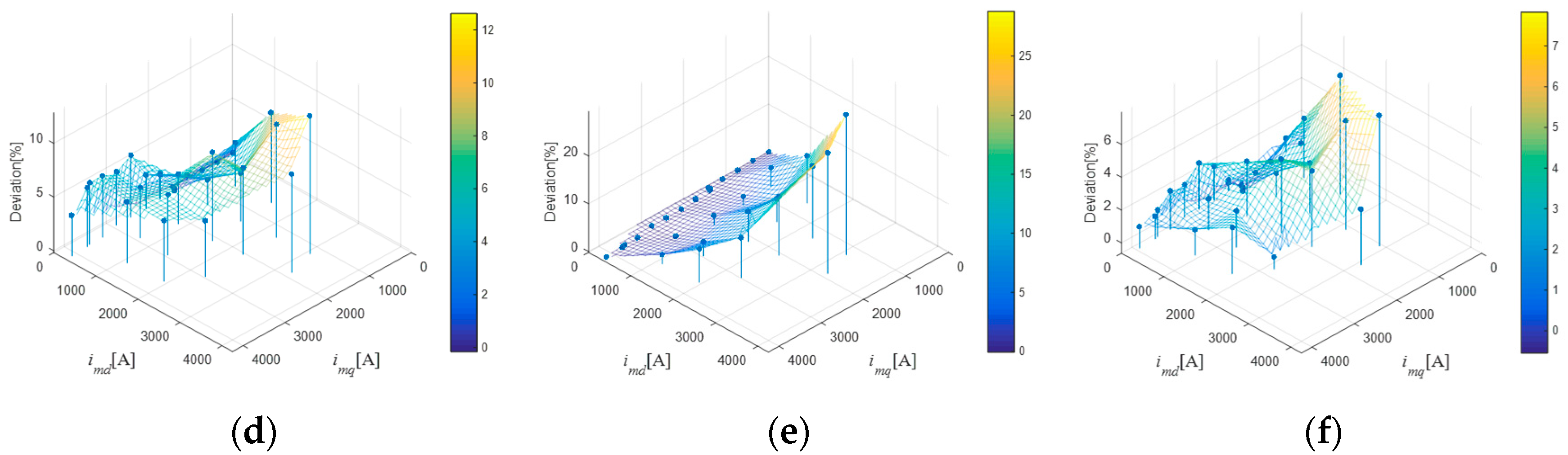
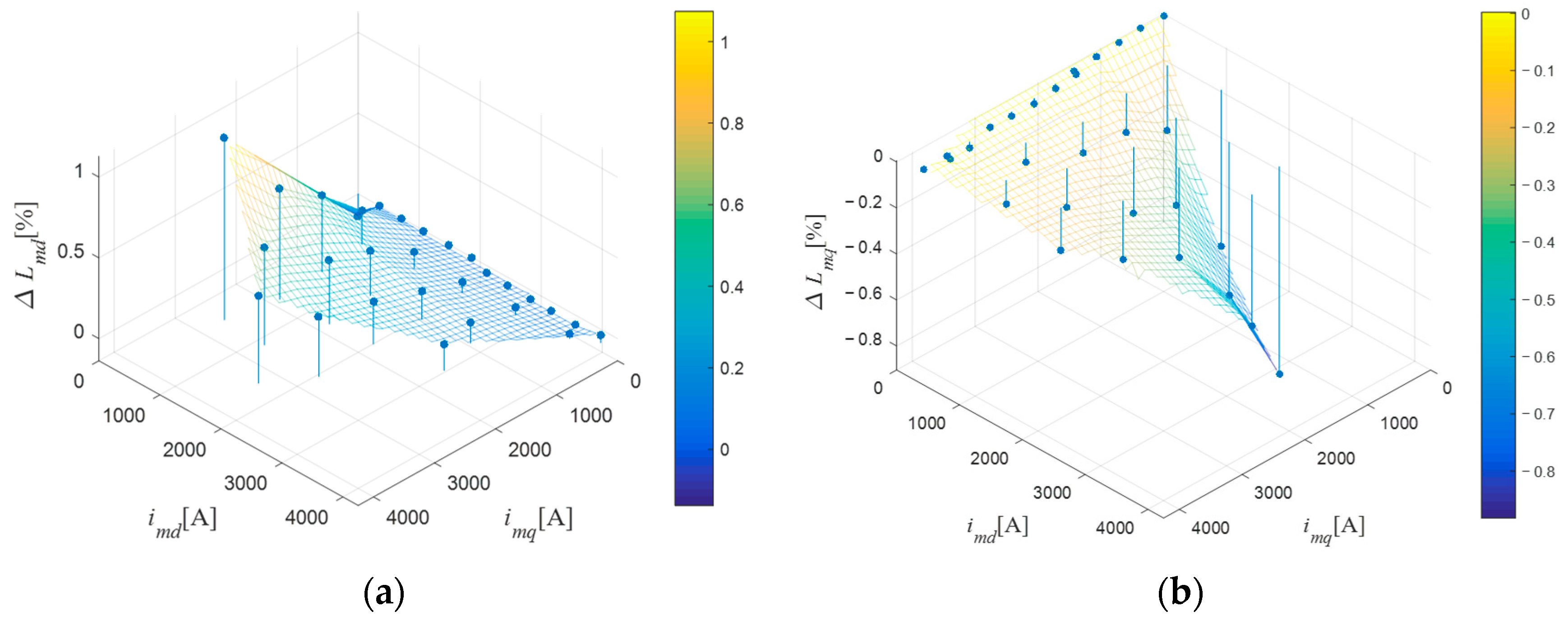
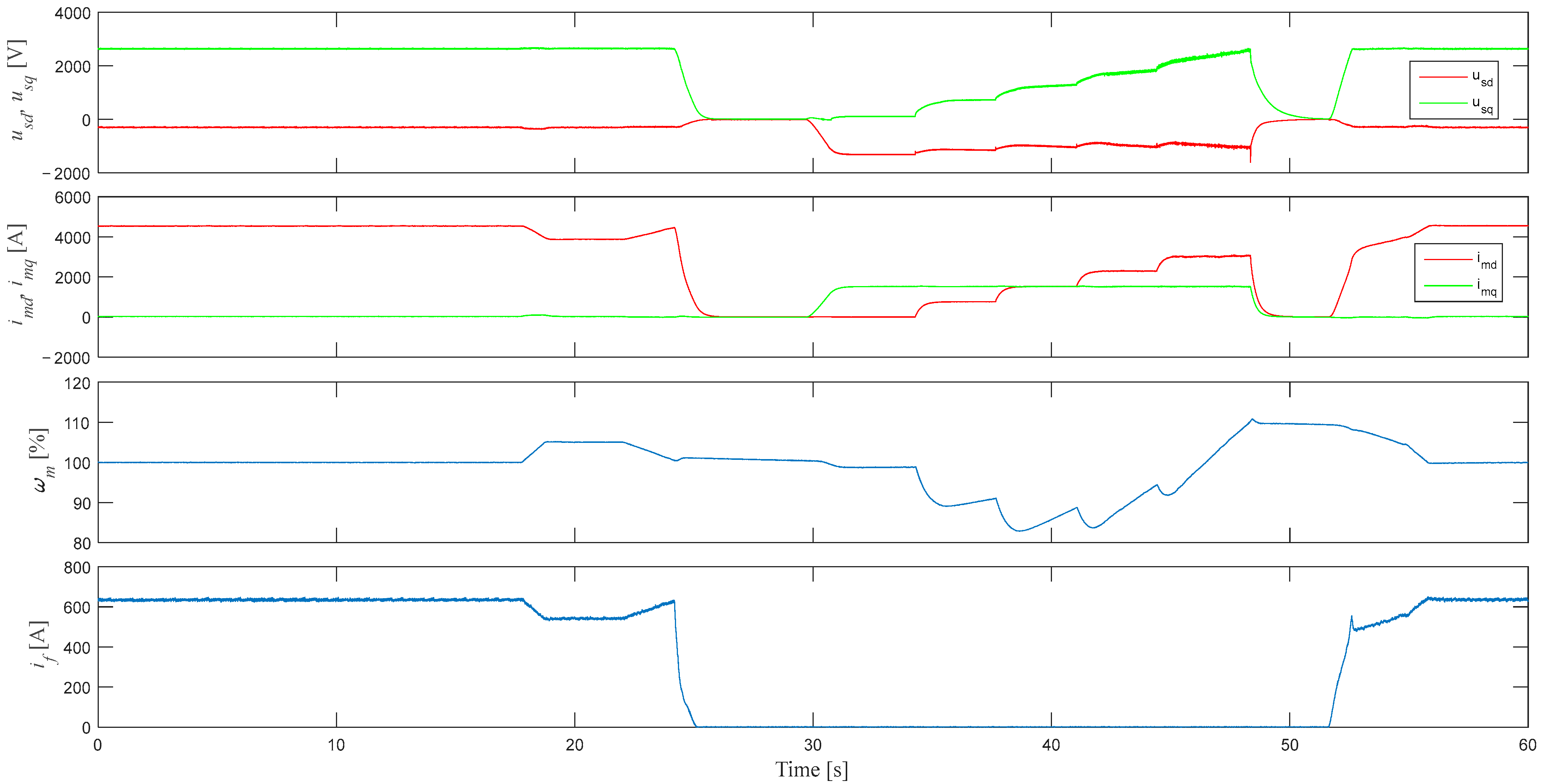
5. Experimental Verification of the Proposed Method
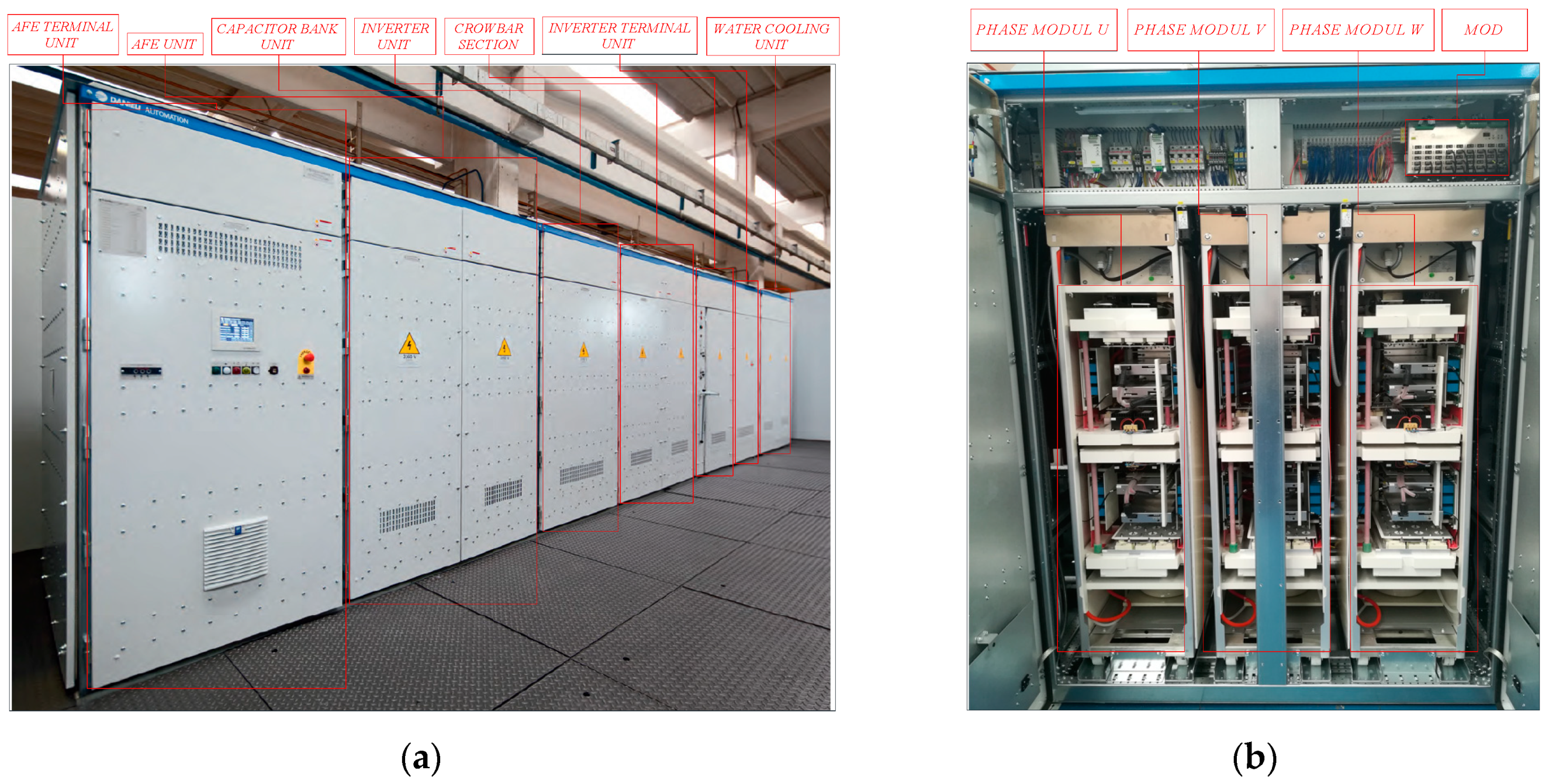
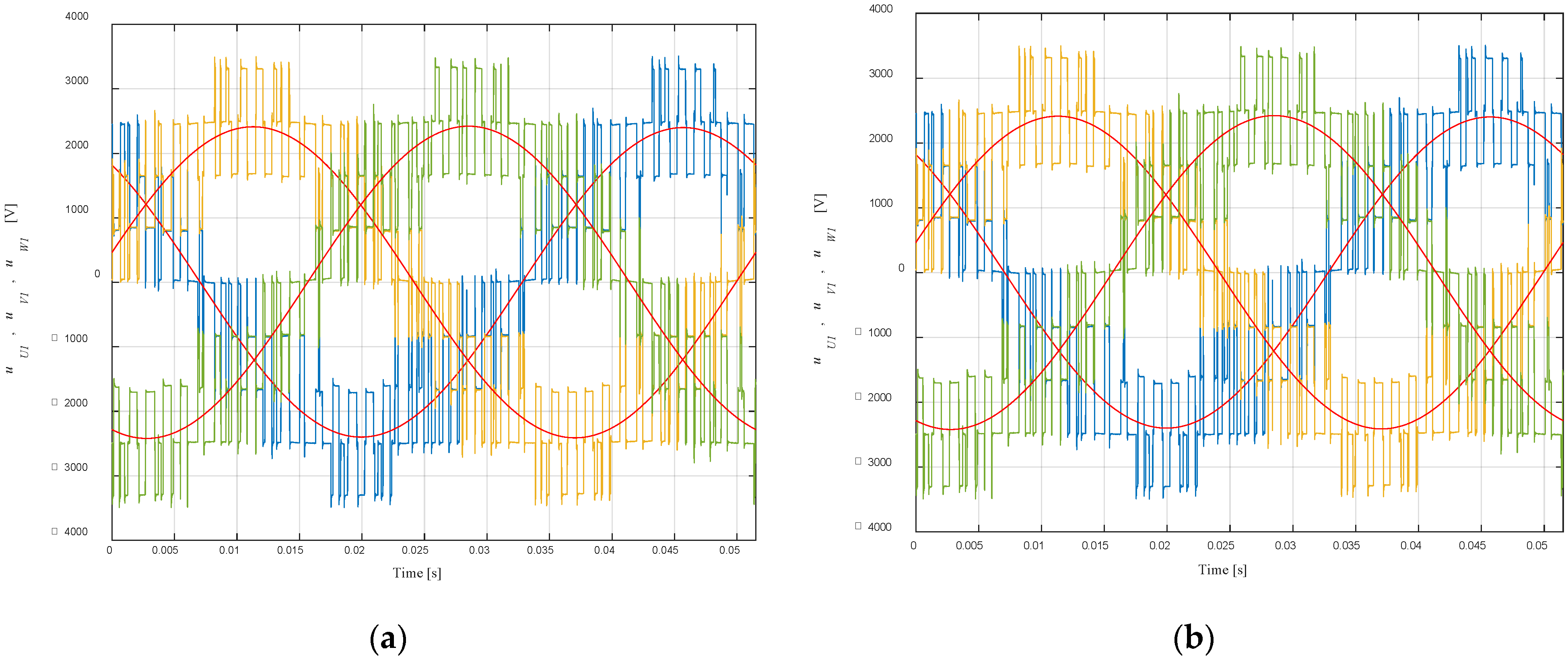
5.1. Experimental Setup
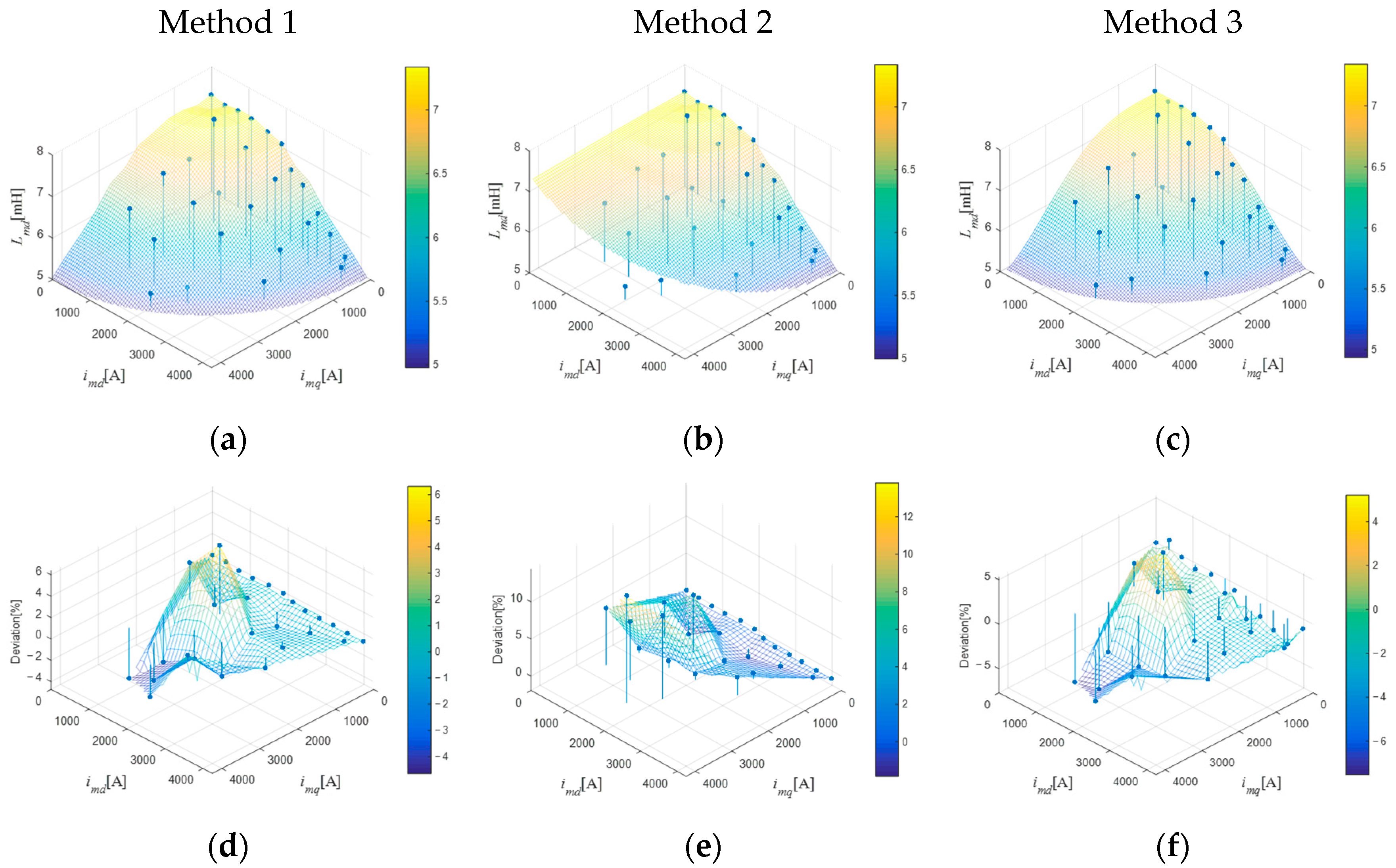
5.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Method 1 | Method 2 | Method 3 | Proposed Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nm. | ||||||
| 1. | 0 | 0 | 7.33 | 7.33 | 7.33 | 7.33 |
| 2. | 370 | 15 | 7.27 | 7.27 | 7.34 | 7.27 |
| 3. | 741 | 31 | 7.33 | 7.33 | 7.33 | 7.33 |
| 4. | 1110 | 42 | 7.32 | 7.32 | 7.23 | 7.32 |
| 5. | 1499 | 11 | 7.19 | 7.19 | 7.17 | 7.19 |
| 6. | 1874 | 7 | 7.08 | 7.08 | 6.97 | 7.08 |
| 7. | 2250 | 137 | 6.71 | 6.71 | 6.70 | 6.71 |
| 8. | 2606 | 168 | 6.53 | 6.53 | 6.37 | 6.53 |
| 9. | 3001 | 175 | 6.05 | 6.05 | 5.97 | 6.05 |
| 10. | 3352 | 179 | 5.73 | 5.73 | 5.61 | 5.73 |
| 11. | 3751 | 192 | 5.39 | 5.39 | 5.23 | 5.39 |
| 12. | 4174 | 198 | 4.98 | 4.98 | 4.96 | 4.98 |
| 13. | 771 | 710 | 7.32 | 7.33 | 7.30 | 7.47 |
| 14. | 1551 | 633 | 7.14 | 7.15 | 7.08 | 7.14 |
| 15. | 2299 | 596 | 6.65 | 6.67 | 6.59 | 6.74 |
| 16. | 3066 | 489 | 5.96 | 5.98 | 5.87 | 6.01 |
| 17. | 3859 | 391 | 5.26 | 5.27 | 5.14 | 5.28 |
| 18. | 845 | 1437 | 7.15 | 7.22 | 7.09 | 6.91 |
| 19. | 1592 | 1394 | 6.87 | 6.94 | 6.80 | 6.46 |
| 20. | 2363 | 1320 | 6.44 | 6.51 | 6.28 | 6.48 |
| 21. | 3112 | 1270 | 5.74 | 5.82 | 5.6 | 5.77 |
| 22. | 907 | 2193 | 6.68 | 7.02 | 6.59 | 6.98 |
| 23. | 1675 | 2148 | 6.46 | 6.70 | 6.26 | 6.64 |
| 24. | 2330 | 2081 | 5.98 | 6.23 | 5.85 | 6.19 |
| 25. | 3297 | 1890 | 5.37 | 5.55 | 5.2 | 5.43 |
| 26. | 753 | 2945 | 6.12 | 6.92 | 5.93 | 6.43 |
| 27. | 1451 | 2988 | 5.84 | 6.53 | 5.64 | 6.06 |
| 28. | 2360 | 3004 | 5.40 | 5.96 | 5.18 | 5.37 |
| 29. | 1964 | 3597 | 5.15 | 6.08 | 5.00 | 5.31 |
| Method 1 | Method 2 | Method 3 | Proposed Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nm. | ||||||
| 1. | 0 | 0 | 6.85 | 6.85 | 6.86 | 6.86 |
| 2. | 9 | 373 | 6.79 | 6.81 | 6.86 | 6.81 |
| 3. | 29 | 744 | 6.86 | 6.86 | 6.85 | 6.86 |
| 4. | 47 | 1120 | 6.85 | 6.82 | 6.81 | 6.82 |
| 5. | 63 | 1492 | 6.74 | 6.74 | 6.71 | 6.73 |
| 6. | 112 | 1498 | 6.74 | 6.74 | 6.71 | 6.75 |
| 7. | 146 | 1871 | 6.64 | 6.48 | 6.53 | 6.48 |
| 8. | 151 | 1870 | 6.64 | 6.49 | 6.53 | 6.50 |
| 9. | 186 | 2246 | 6.33 | 6.14 | 6.28 | 6.15 |
| 10. | 197 | 2615 | 6.14 | 5.81 | 5.97 | 5.81 |
| 11. | 194 | 2956 | 5.82 | 5.54 | 5.66 | 5.55 |
| 12. | 293 | 3382 | 5.42 | 5.12 | 5.24 | 5.13 |
| 13. | 315 | 3764 | 5.12 | 4.85 | 4.92 | 4.85 |
| 14. | 328 | 4146 | 4.79 | 4.62 | 4.68 | 4.62 |
| 15. | 771 | 710 | 6.85 | 6.84 | 6.82 | 6.58 |
| 16. | 1551 | 633 | 6.68 | 6.76 | 6.61 | 6.16 |
| 17. | 111 | 1496 | 6.74 | 6.74 | 6.71 | 6.73 |
| 18. | 845 | 1438 | 6.69 | 6.65 | 6.63 | 6.53 |
| 19. | 1592 | 1394 | 6.43 | 6.45 | 6.34 | 6.15 |
| 20. | 2363 | 1320 | 6.02 | 6.27 | 5.81 | 5.45 |
| 21. | 3112 | 1270 | 5.37 | 6.15 | 5.13 | 4.75 |
| 22. | 187 | 2243 | 6.34 | 6.15 | 6.28 | 6.15 |
| 23. | 907 | 2193 | 6.24 | 6.06 | 6.17 | 5.97 |
| 24. | 1675 | 2148 | 6.04 | 5.93 | 5.84 | 5.58 |
| 25. | 2330 | 2081 | 5.60 | 5.82 | 5.42 | 5.18 |
| 26. | 3297 | 1890 | 5.02 | 5.77 | 4.76 | 4.6 |
| 27. | 753 | 2945 | 5.73 | 5.5 | 5.58 | 5.47 |
| 28. | 1451 | 2988 | 5.46 | 5.33 | 5.29 | 5.17 |
| 29. | 2360 | 3004 | 5.05 | 5.20 | 4.83 | 4.80 |
| 30. | 293 | 3691 | 5.18 | 4.90 | 4.97 | 4.90 |
| 31. | 1134 | 3640 | 5.08 | 4.90 | 4.88 | 4.80 |
| 32. | 1965 | 3597 | 4.82 | 4.88 | 4.69 | 4.56 |
References
- Niemelä, M. Position Sensorless Electrically Excited Synchronous Motor Drive for Industrial Use Based on Direct Flux Linkage and Torque Control. Ph.D. Thesis, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland, 16 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Boldea, I.; Nasar, S.A. Electric Drives, 3rd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.; Sun, J.; Tian, Z.; Huang, M.; Zha, X.; Gong, J. Speed-Sensorless and Motor Parameters-Free Starting Method for Large-Capacity Synchronous Machines Based on Virtual Synchronous Generator Technology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 6607–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vas, P. Vector Control of AC Machines; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cikač, D.; Turk, N.; Bulić, N.; Barbanti, S. Flux Estimator for Salient Pole Synchronous Machines Driven by the Cycloconverter Based on Enhanced Current and Voltage Model of the Machine with Fuzzy Logic Transition. Machines 2021, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrhönen, J.; Hrabovcová, V.; Semken, R.S. Electrical Machine Drives Control, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kaukonen, J. Salient Pole Synchronous Machine Modelling in an Industrial Direct Torque Controlled Drive Application. Ph.D. Thesis, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland, 26 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Wu, X.; He, G.; Hu, Y.; Ni, K. Nonlinear Magnetic Field Vector Control with Dynamic-Variant Parameters for High-Power Electrically Excited Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 11053–11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Wu, M. Air-Gap Flux Oriented Vector Control Based on Reduced-Order Flux Observer for EESM. Energies 2021, 14, 5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, J.; Hahn, I. Improved accuracy of sensorless position estimation by combining resistance- and inductance-based saliency tracking. In Proceedings of the IECON 2015—41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Huang, S.; Luo, D.; Gao, J.; Fan, P. Dynamic DC-link Voltage Adjustment for Electric Vehicles Considering the Cross Saturation Effects. Energies 2018, 11, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, I.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Nam, K. Extended MTPA with cross coupling inductances for electrically excited synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Denver, CO, USA, 15–19 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Liu, Y. Design and Experimental Verification of a 48 V 20 kW Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine for Mild Hybrid Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Nam, K. Copper-Loss-Minimizing Field Current Control Scheme for Wound Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.; Gu, B.G.; Kim, J.; Nam, K.; Kim, Y. Inductance Estimation of Electrically Excited Synchronous Motor via Polynomial Approximations by Least Square Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koteich, M. Flux estimation algorithms for electric drives: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Renewable Energies for Developing Countries (REDEC), Zouk Mosbeh, Lebanon, 13–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, T.; Bhattacharya, A.; Ahmed, H. Transient and steady-state study of a speed sensorless IPMSM drive with an advanced integrator-based stator flux estimator. IET Power Electron. 2021, 14, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.; Quan, J. Drift- and parameter-compensated flux estimator for persistent zero-stator-frequency operation of sensor-less-controlled induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasic, V.; Vukosavic, S.N.; Levi, E. A stator resistance estimation scheme for speed sensorless rotor flux oriented induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2003, 18, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-S.; Sul, S.-K.; Yoo, H.; Oh, J. Distortion-Minimizing Flux Observer for IPMSM Based on Frequency-Adaptive Observers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldea, I.; Agarlita, S.C. The active flux concept for motion-sensorless unified AC drives: A review. In Proceedings of the International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics and Electromotion (ACEMP), Istanbul, Turkey, 8–10 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Lu, K.; Rasmussen, P.O. Improved Closed-Loop Flux Observer Based Sensorless Control Against System Oscillation for Synchronous Reluctance Machine Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 4593–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, G.-J.; Choi, J.-W. Gopinath Model-Based Voltage Model Flux Observer Design for Field-Oriented Control of Induction Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 4581–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armando, E.G.; Bojoi, I.R.; Guglielmi, P.; Pellegrino, G.; Pastorelli, M.A. Experimental Identification of the Magnetic Model of Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.M.; Hiti, S.S. Identification of machine parameters of a synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the 38th IAS Annual Meeting on Conference Record of the Industry Applications Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 12–16 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino, G.; Boazzo, B.B.; Jahns, T.M. Magnetic Model Self-Identification for PM Synchronous Machine Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Feng, J.; Guo, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, Z.-Q. Identification of Flux Linkage Map of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Under Uncertain Circuit Resistance and Inverter Nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 14, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhano, S.A.; Bojoi, R.; Rosu, S.G.; Tenconi, A. Identification of the magnetic model of permanent magnet synchronous machines using DC-biased low frequency AC signal injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumberger, B.; Dolinar, D.; Hamler, A.; Trlep, M. Evaluation of saturation and cross-magnetization effects in interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serafi, A.M.; Kar, N.C. Methods for determining the intermediate-axis saturation Characteristics of salient-pole synchro-nous Machines from the measured D-axis Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, E. Saturation modelling in d-q axis models of salient pole synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serafi, A.M.; Wu, J. A new method for determining the saturation curves in the intermediate axes of salient-pole synchro-nous machines. Electr. Mach. Power Syst. 1993, 21, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzanowska, H.; Sario, P.; Stulz, C.A.; Joerg, P. Redundant Drive with Direct Torque Control (DTC) and dual-star synchro-nous machine, simulations and verification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Aalborg, Denmark, 2–5 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Boashash, B. Time-Frequency Signal Analysis and Processing: A Comprehensive Reference, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Value |
| Nominal voltage | 3050 V |
| Nominal current | 2 × 1348 A |
| Nominal frequency | 20 Hz |
| Nominal speed | 200 rpm |
| Pole pair number | 6 |
| Nominal power | 14 MW |
| Nominal field current | 805 A |
| Method 1 | Method 2 | Method 3 | |
| 11.9 | 23.3 | 19.2 | |
| 31.1 | 46.8 | 17.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turk, N.; Cikač, D.; Bulić, N.; Barbanti, S. A Novel Experimental Method for Identifying the Flux Linkage Map of a High-Power Medium-Voltage Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine with Double Stator Winding. Machines 2022, 10, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10030187
Turk N, Cikač D, Bulić N, Barbanti S. A Novel Experimental Method for Identifying the Flux Linkage Map of a High-Power Medium-Voltage Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine with Double Stator Winding. Machines. 2022; 10(3):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10030187
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurk, Nikola, Dominik Cikač, Neven Bulić, and Stefano Barbanti. 2022. "A Novel Experimental Method for Identifying the Flux Linkage Map of a High-Power Medium-Voltage Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine with Double Stator Winding" Machines 10, no. 3: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10030187
APA StyleTurk, N., Cikač, D., Bulić, N., & Barbanti, S. (2022). A Novel Experimental Method for Identifying the Flux Linkage Map of a High-Power Medium-Voltage Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine with Double Stator Winding. Machines, 10(3), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10030187






