Abstract
In order to improve the plane quality of the workpiece shape accuracy, a correction abrasive finishing method is proposed. This method is used to achieve the effect of correcting the workpiece surface by changing the finishing conditions of different areas according to the profile of the initial surface, such as feed speed. In previous research, the feasibility and effectiveness of this method were proven. In this research, a theoretical analysis of this method was carried out and the extension of this method to the processing of larger planes was studied. Through a series of experiments on an aluminum plate (A5052), it was proven that the shape accuracy of the workpiece surface can be effectively corrected by accurately controlling the feed speed. The experimental results showed that the extreme difference of the workpiece can be reduced from 4.81 μm to 2.65 μm within the processed area of 30 mm by 10 mm.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of electronic technology, optical technology and aerospace technology, the requirements for workpiece surface accuracy in many fields are higher and higher. For these components, their surfaces are required to be smooth, have low roughness, and have high geometric accuracy. The magnetic abrasive finishing (MAF) process is an important non-traditional finishing process [1,2]. The MAF process uses magnetic particles to form a flexible brush structure under the action of a magnetic field, mixing abrasive particles with magnetic particles, and using the motor to drive the magnetic brush to rotate so as to drive the abrasive particles to move relative to the workpiece and to realize the finishing of the workpiece [3].
Shinmura et al. proposed and designed a plane MAF device, analyzed the process principle of plane MAF, and discussed the effect of the supply weight of finishing fluid and magnetic abrasion on the finishing depth and surface roughness [4]. Yamaguchi studied the use of magnetic grinding technology to process the inside of a round tube [5]. In order to solve the disadvantage of a weak magnetic force when processing thick tubes, Zou et al. proposed a processing method that could improve the magnetic force and made it possible to process the inside of thick non-ferromagnetic tubing [6]. Because the magnetic brush formed in the magnetic field has a certain flexibility and can conform to the shape of the workpiece, it is applied to the processing of various irregular shapes, such as the inner and outer surfaces of a tube, irregular surfaces, and so on. In order to improve processing efficiency, researchers combined MAF with other processing methods. Based on the MAF principles, additional ultrasonic vibration is used to achieve a high-quality workpiece surface [7,8]. Mulik et al. employed ultrasonic vibration in the horizontal direction of the workpiece using an ultrasonic power, a piezoelectric transducer, and a horn device [9]. A high-frequency electrical signal was generated by ultrasonic power and transformed into a horizontal mechanical vibration by the transducer. In order to further improve the processing efficiency of magnetic grinding, Zou et al. made different attempts and proposed a variety of processing methods. They proposed a processing method combining the MAF process with electrolytic technology [10,11,12] and a processing method that combined MAF with fixed abrasive polishing technology [13]. They analyzed the process mechanisms and finishing characteristics and proved that the purpose of improving processing efficiency can be achieved by these methods through experiments. They also proposed a MAF process using an alternating magnetic field. Compared with a static magnetic field, the MAF process using an alternating magnetic field can achieve higher finishing efficiency and surface quality [14,15,16].
With the continuous development and improvement of MAF technology, higher requirements for this technology are put forward. In order to make the magnetic field of finishing tools more uniform, a lot of research was carried out to change the shape of the magnetic pole, such as adding grooves, improving finishing tracks, and so on. Since the magnetic abrasive finishing process is a machining process using a magnetic brush with flexible machining behavior, the process can be used for finishing free-form surfaces and improving surface accuracy without destroying the profile of the workpiece [17,18,19]. However, because the magnetic brush is not a uniform finishing tool, further research is still needed to maintain the geometric accuracy of the workpiece or correct the geometry, which is also the research content of this subject. Zou et al. calculated the trajectory to elevate the surface quality of plane magnetic abrasive finishing. The finishing trajectory could be predicted by combining the revolution motion of the magnetic brush, the pole rotation motion, and the linear reciprocating motion of the workpiece to investigate the finishing results [20,21]. They conducted further studies on this method and proved that the revolution radius was an important factor affecting the surface flatness and proposed an effective method for evaluating the surface topography [22].
Through a series of experiments and theoretical analysis, this research uses magnetic abrasive finishing technology to realize the plane correction of the workpiece. In order to further solve the problem of uniformity of finishing, a method of forming a small magnetic brush with a small magnetic pole is proposed in this research. According to the initial profile of the surface, the finishing in different positions is controlled at different feed speeds. Through the analysis and finishing of the collected surface profile data, and according to the finishing characteristics of the magnetic brush, the feed speed distribution in the finishing process is planned to make the effective finishing time at different positions different, and finally to improve the surface flatness.
2. Processing Principle
2.1. Processing Principle of Magnetic Abrasive Finishing
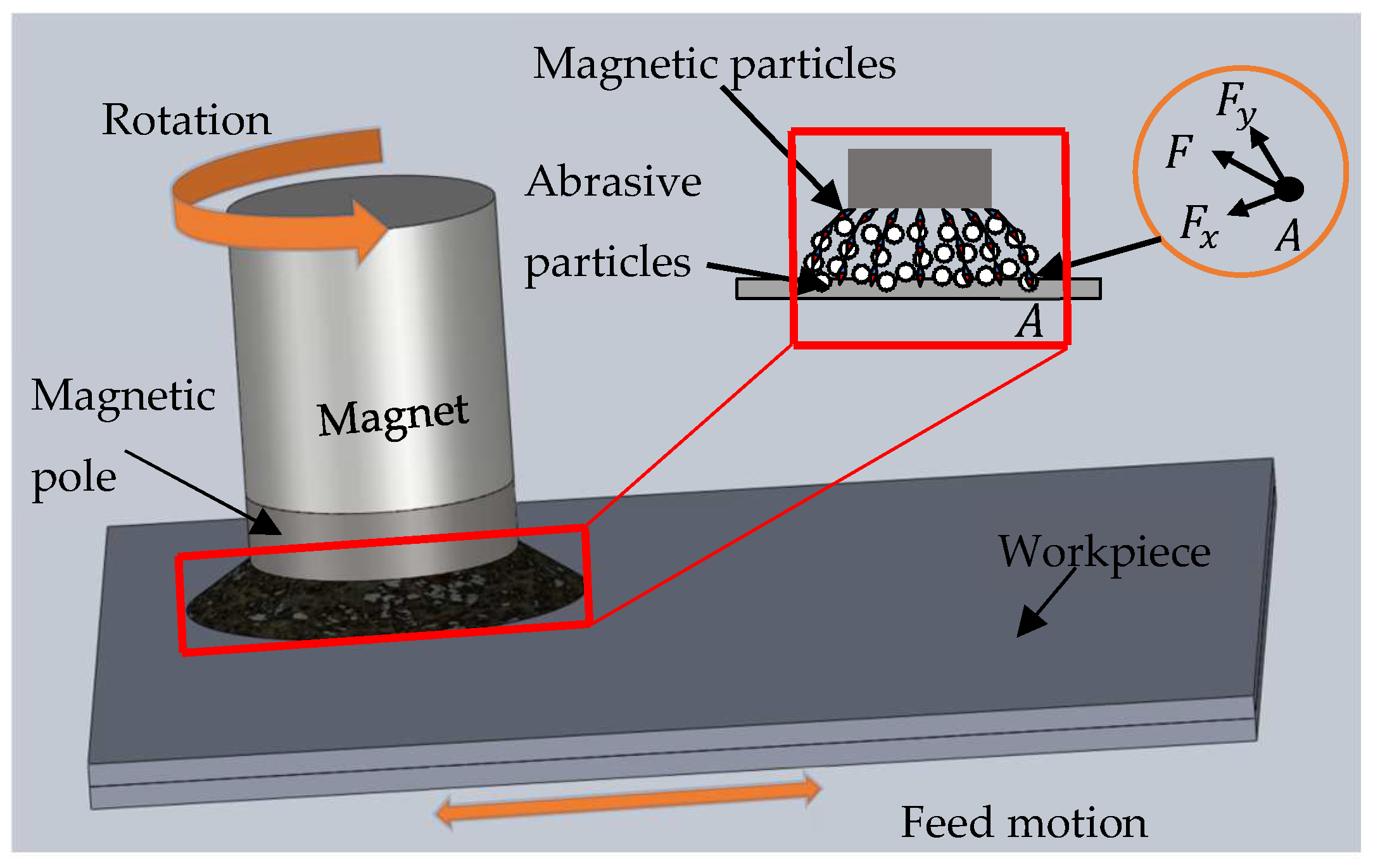
MAF is a precision finishing process, which realizes the finishing of the workpiece by driving the abrasive particles to move relative to the workpiece through a flexible magnetic brush formed by magnetic particles under the action of a magnetic field. Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the principle of the MAF process. The magnetic pole and magnetic particles are magnetized under the action of the magnet and the magnetic particles are arranged in order to form a brush-like structure. The abrasive particles are mixed within the brush-like structure and driven to rotate and to move relative to the workpiece, together with the magnet, magnetic pole, and magnetic brush, by the motor, so the workpiece can be finished.
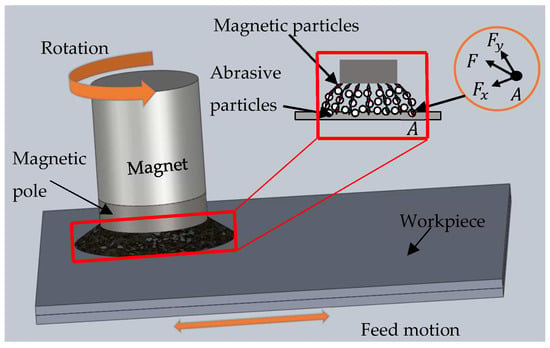
Figure 1.
Schematic of finishing principle.
Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram of the magnetic force acting on a magnetic particle at point A in a magnetic field. and can be calculated by Equations (1) and (2) [3,4].
where is the direction of the line of magnetic force, is the direction of the magnetic equipotential line, is the volume of magnetic particle, is the susceptibility of particles, is the permeability of vacuum, is the magnetic field intensity at point A, and are gradients of magnetic field intensity in and directions, respectively.
2.2. Processing Principle of Corrective Magnetic Abrasive Finishing
Based on Preston’s Law (Preston, 1927), the Integrated Material Removal Rate (IMRR) is proportional to the polishing tool pressure on the surface of the workpiece and the relative velocity between the tool and the workpiece [23]. The material removal amount satisfies the following formula:
where is the amount of material removal, is the removal factor, is the coordinate of a point on the plane. The is the pressure at the point , is the resultant velocity of the tool relative to the workpiece, and is the finishing time. When the magnetic field strength, the composition of the abrasion liquid and the working gap are constant, the amount of material removal is dependent on and [24].
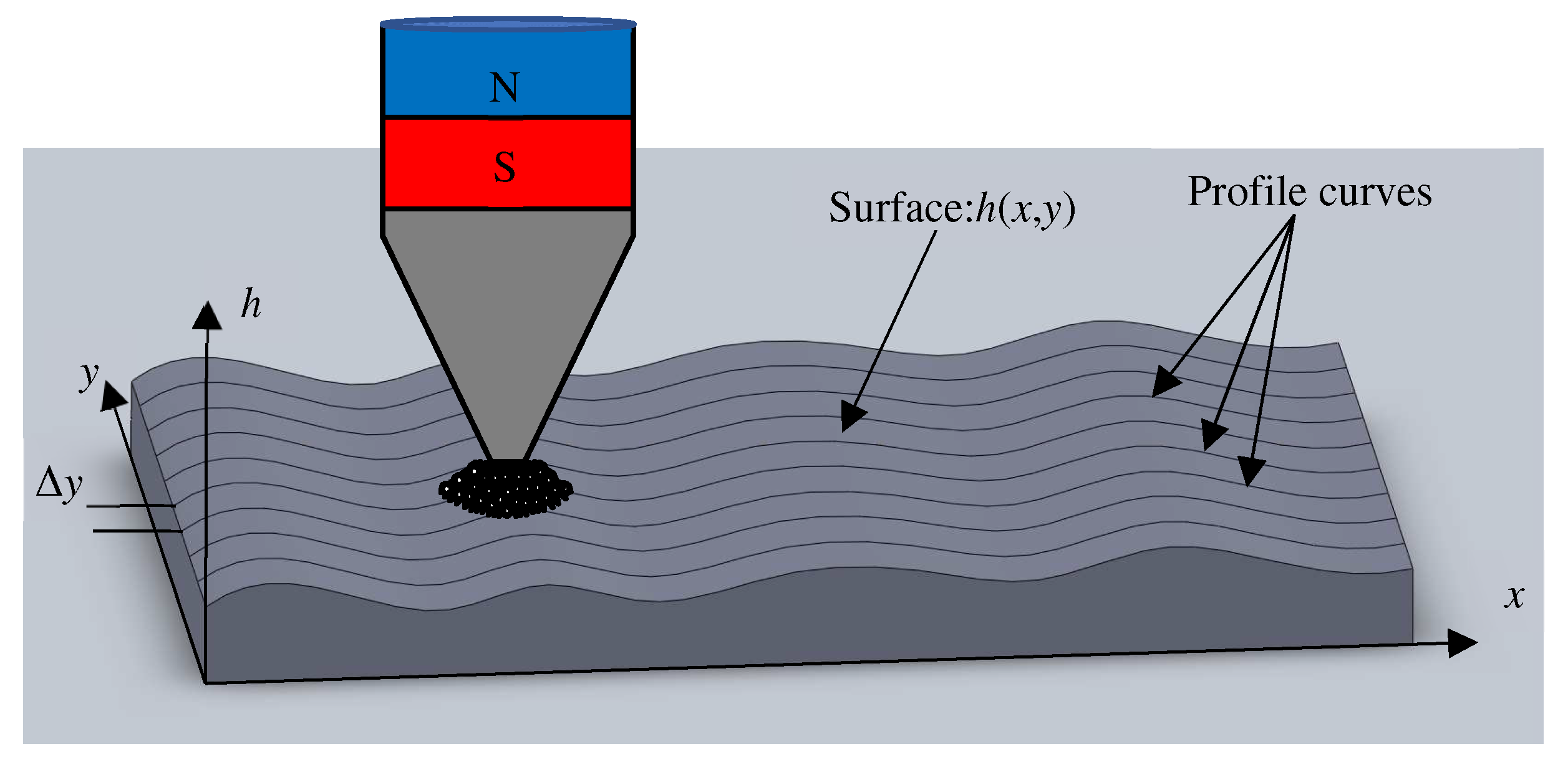
Previous studies have proven that the planar quality of the processed area can be improved by controlling the feed speed of the workpiece, but only a single track was finished [25]. Now the finishing area needs to be extended to a larger planar area. Assuming that the initial profile of the workpiece is shown in Figure 2, and its profile curves are shown as in the figure in the direction , due to the flexibility of the magnetic brush, the workpiece can be finished and its roughness can be reduced while maintaining the original profile of the workpiece. However, from another point of view, can magnetic abrasive finishing technology be used to reduce the height difference of the surface and improve its flatness? A simple method that is easy to think of is to change the processing time or feed speed at different positions. For example, where the surface is high, the feed speed is slower and the processing time is longer. On the contrary, where the surface is low, the feed speed is faster and the processing time is shorter. In other words, the purpose of correcting the plane can be realized by controlling the motion conditions during finishing.
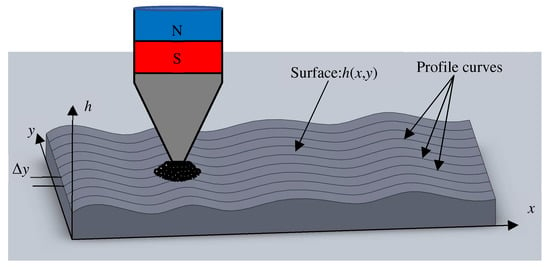
Figure 2.
The principle of corrective magnetic abrasive finishing.
However, for the magnetic brush, the processing efficiency of the point with different positions from the center point is different. There are many reasons, such as the different linear velocity of rotation, different magnetic field intensities and many other factors. Therefore, it is not an easy thing to plan the processing speed well. In order to prove the effectiveness of the corrective MAF method, theoretical analysis and experimental verification are carried out, and it was proved that the surface range can be reduced from 14.317 μm to 2.18 μm by the experiments [19]. However, only a single trajectory was carried out in the previous study, and further discussion and research are still needed if this finishing is to be extended to the larger plane range.
At present, the amount of material removal is usually described according to Preston’s Equation [26]. The Preston equation is related to the pressure, relative velocity and residence time in the contact area [27], as shown in Equation (3).
If the density of the workpiece is , the contact area between the workpiece and the magnetic brush is , and the removal depth of the material is . Then , which is substituted into Equation (3), meaning the following equation will be obtained:
where is the removal depth at on the workpiece surface at time. The material removal curve generated within dwell time t is expressed as:
In the finishing process, the movement of the particles consists of a circular motion and feed motion relative to the workpiece. When the feed speed is very small, the particle velocity can be approximately equal to the linear velocity of the circular motion. To simplify the model, in this research, it is considered that the velocity of the particle relative to the workpiece is approximately equal to . Where is the angular velocity of circular motion, is the distance between the particle and the axis of rotation, which is the radius of the circular motion. Therefore, when the angular velocity is constant, is almost unchanged. From Equation (5), it can be seen that the amount of material removal only depends on the finishing time . The processing time is inversely proportional to the feed speed , so the corrective finishing of the workpiece can be realized by controlling the feed speed. Then the key is how to calculate the feed speed according to the profile curves.
2.3. Calculation of Feed Speed Array
First of all, the initial profile data of the workpiece need to be measured. In this research, the initial height at position is obtained by Surftest (SV-624-3D, Mitutoyo, 2200 Shimogurimachi, Utsunomiya City, Tochigi Prefecture 321-0923). is the abscissa of the i-th sampling point in the x-direction. Then, it is necessary to calculate the feed speed at different positions. To facilitate the processing of data, the original data are filtered and is obtained after filtering with:
Here, the method of mean filtering is adopted. Where is the position of the i-th sampling point and is the width of the data to be filtered, which is the number of data to be averaged every time. Then, in order to calculate the processing time and feed speed, it is necessary to set the height of the target finishing line. Therefore removed height sequence at each position can be calculated according to:
Thereby, the processed height transformation sequence is obtained. Assuming the finishing efficiency is η μm min−1, then the finishing time for each position is:
Then, assuming that it needs loops to finish the workpiece, the displacement change is , the speed at each position is:
Because the composite velocity of the particles is the vector sum of the rotation speed and the feed speed, and the rotation speed is much faster than the feed speed, the influence of the feed speed on the composite velocity is ignored here. The feed speed only changes the finishing time. Then, at high places, the speed is slow, the time is long, and in low places, the speed is fast and the time is short. Reorganizing the above equations yields:
It can be seen that when the finishing parameters are unchanged, is a constant. Therefore, is inversely proportional to .
This is:
To facilitate the calculation, should be obtained first, and then all regional velocity arrays can be solved according to the above recurrence in Equation (12). It can be seen that the feed speed is inversely proportional to the initial height. Therefore, by controlling the feed speed, the profile characteristics of the surface can be improved.
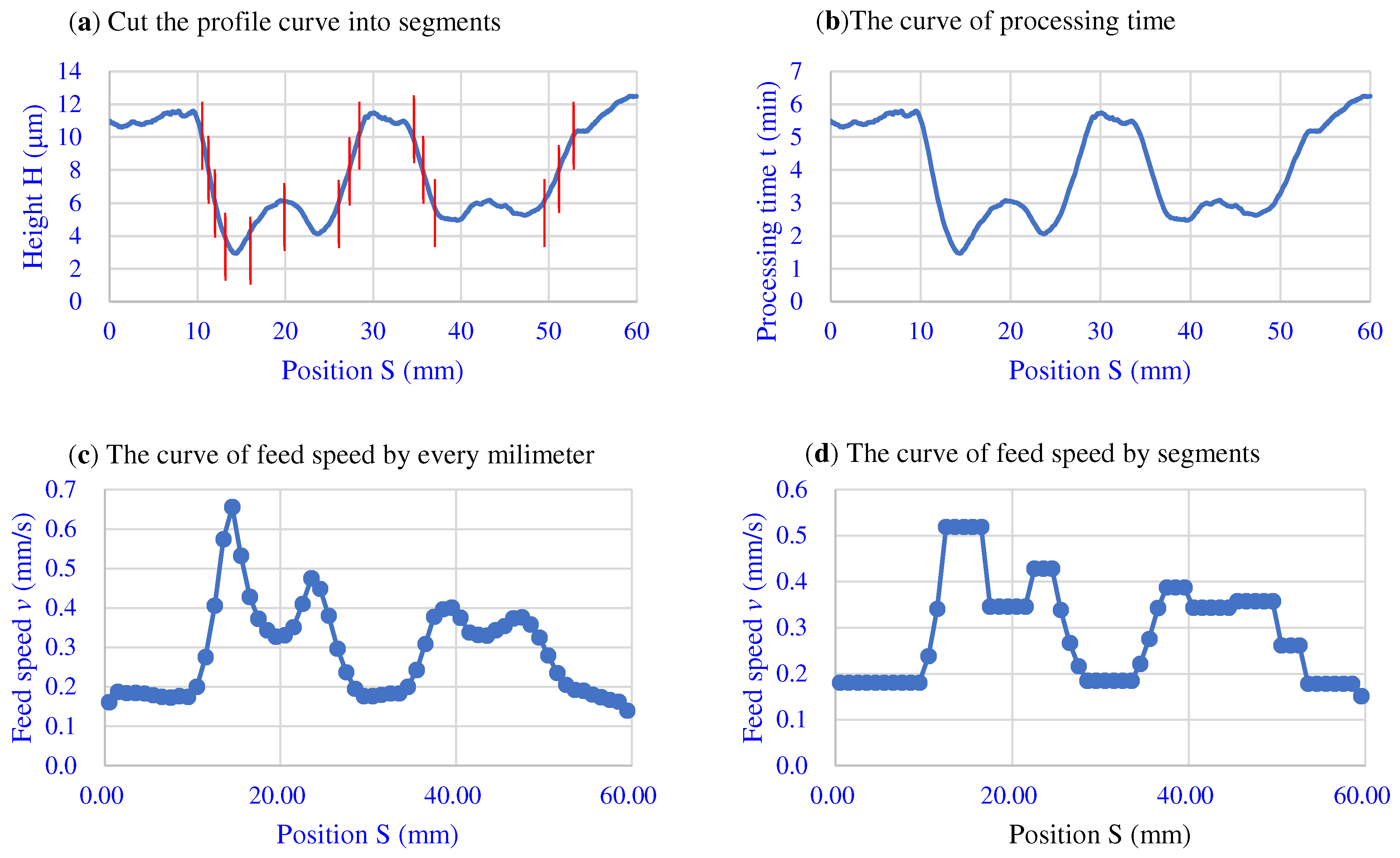
Figure 3a shows a profile curve after filtering. If the finishing efficiency η is known, the relationship between the processing time curve and the position can be calculated according to Equation (8), as shown in Figure 3b. Then, according to Equations (9) and (12), the speed sequence can be calculated, as shown in Figure 3c.
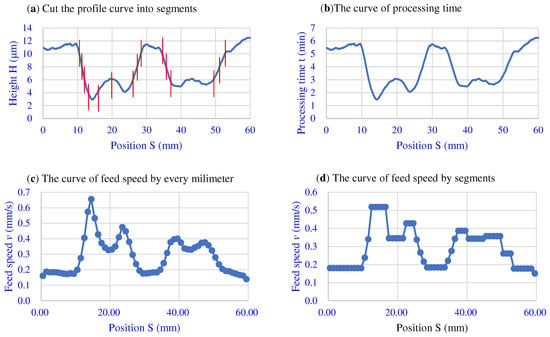
Figure 3.
The curves of dividing the height, time and speed into segments.
So now the key problem is how to make the control system control the motor to move according to the feed speed curve. The specific realization method is determined by the actual mechanical structure and motor control mode. One way to achieve this is to directly control the speed of the motor by using analog quantities, which can make the motor run according to the speed curve shown in Figure 3c. However, the curve of velocity versus the position needs to be converted to a curve of velocity versus time. In this way, due to the control error, it may not be able to accurately correspond to the displacement and velocity.
Another way is to control the position of the motor, dividing the speed curve into several segments, and calculating the average speed of each segment, as shown in Figure 3c, which is the speed curve segmented according to 1 mm for one segment. It can be seen that the velocity curve is basically the same as before the segmentation. In fact, the original velocity curve is also equivalent to the curve obtained by 0.01 mm in each section, because the data sampling interval is 0.01 mm. For this equidistant scheme, the smaller the distance of the partitions, the closer the resulting curve is to the target velocity curve.
But when the division is too small, the speed of the motor will change frequently, which requires high performance from the motor. Therefore, the standard of the segmentation curve can be changed according to the characteristics of the workpiece profile curve. In this study, the segments are divided according to the height variation range of the profile curve. A certain fixed height difference is used as the standard for dividing the area. When the height change is less than this value, it is regarded as an area. In order to facilitate the use of this area division method, it can be performed after filtering. A practical example of the division result is shown in Figure 3a. Here, is set to 2 μm.
The number of changes of the speed curve obtained is reduced according to the second method, which is convenient for control. After segmentation, the average height of each segment is calculated to obtain the approximate curve of the workpiece surface. Then, according to this curve, the processing time curve is calculated. Thus, the finishing speed curve after segmentation is calculated as shown in Figure 3d.
3. Experimental Stage
3.1. Experimental Setup
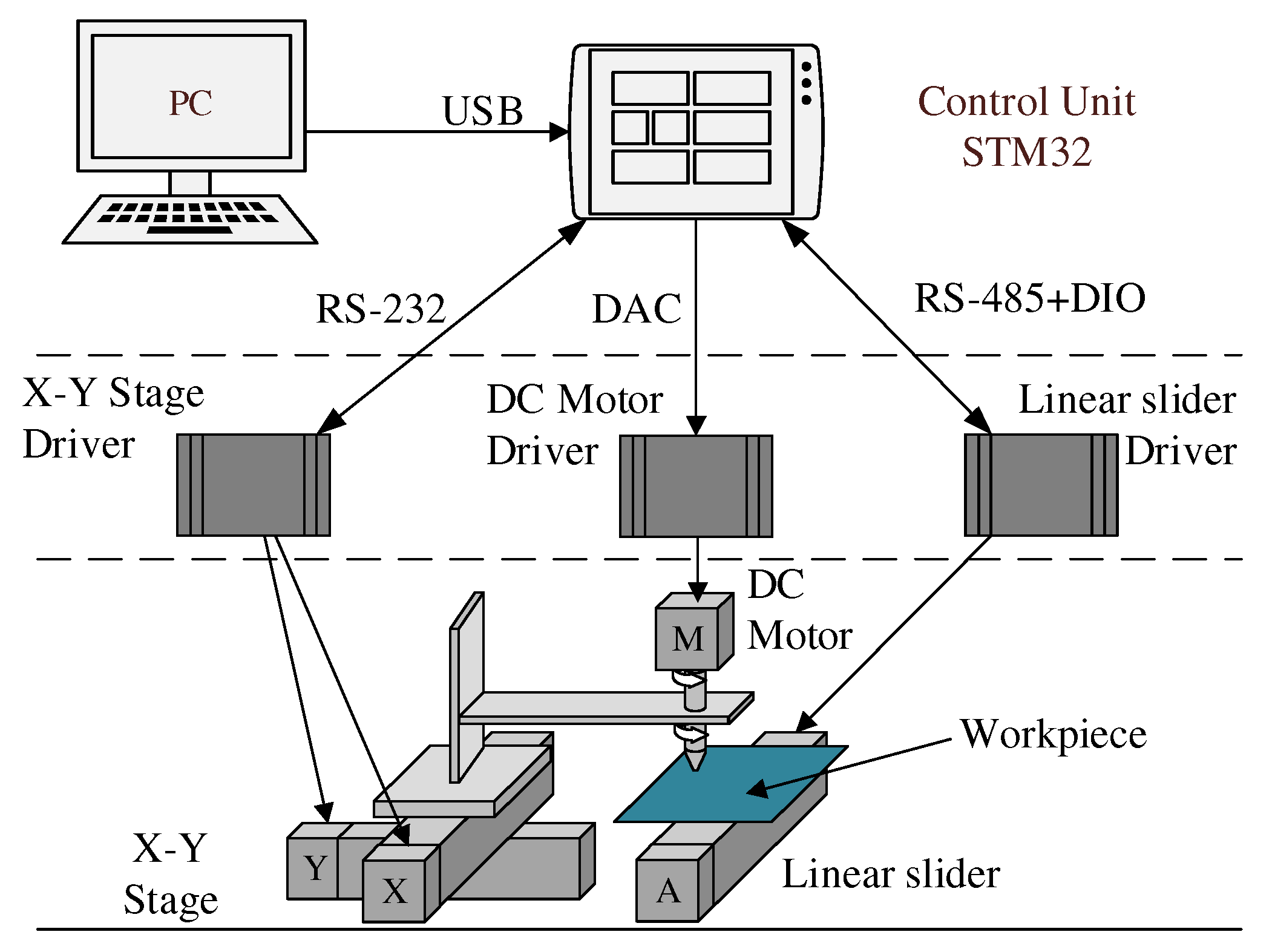
Figure 4 is the system structure diagram of the experimental setup. It includes debugging computer, motion control circuit board, X-Y stage driver, linear slide driver, and DC motor driver. The computer programs the STM32 circuit board by USB to control the processing position, feed speed and rotation speed. The STM32 control board communicates with the X-Y stage driver through the RS232 interface to control the processing position and trajectory. The STM32 control board communicates with the linear motor driver through the RS485 interface to realize the control of the feed speed. The STM32 control board uses DAC to directly output analog signals to control the speed of the DC motor.
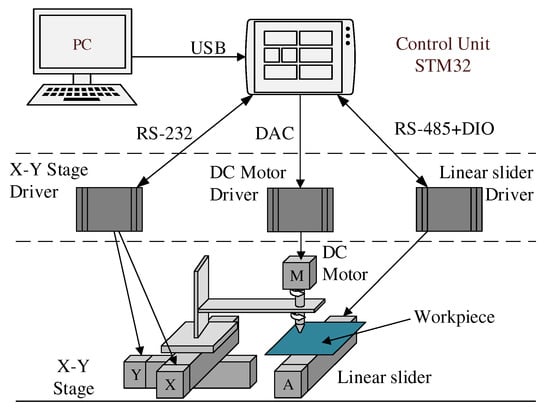
Figure 4.
Schematic of experimental setup.
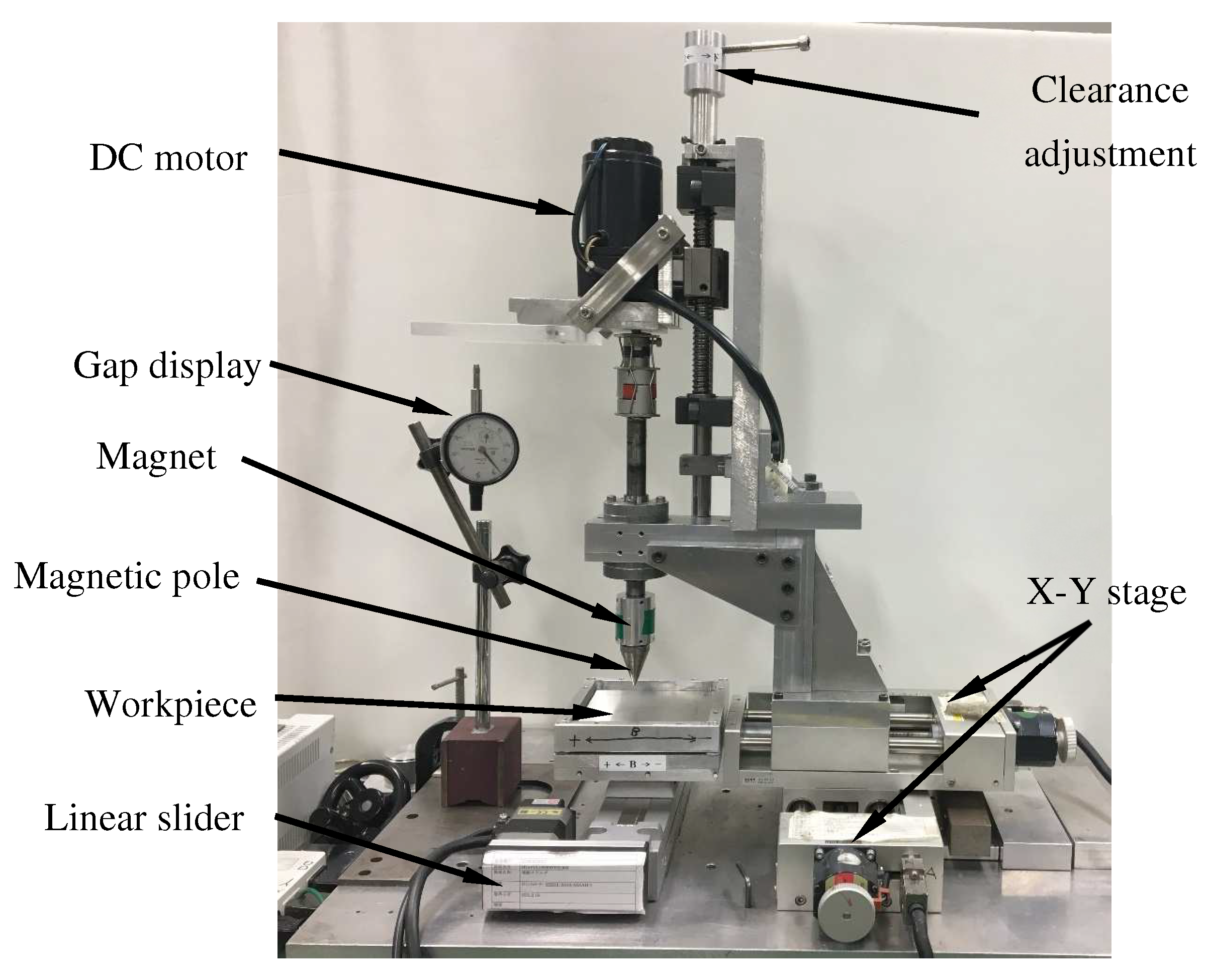
A photo of the experimental setup used in this research is shown in Figure 5. The X-Y stage is used to control the processing position of the workpiece. The DC motor drives the magnetic poles and the magnetic brush rotation to process the workpiece. The linear feed motor realizes the control of the feed speed by changing its speed to realize variable speed processing. The height adjustment device is used to adjust the processing gap, which can be accurate to 0.1 mm.
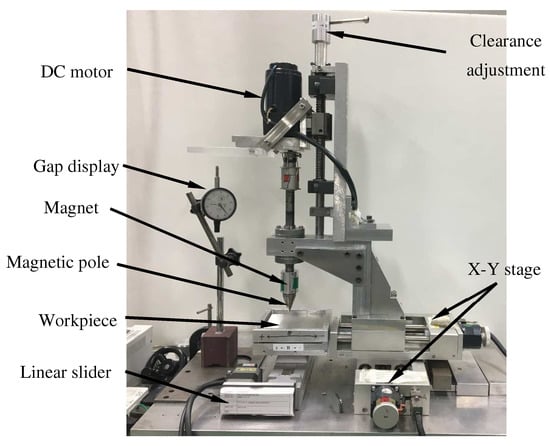
Figure 5.
Experimental setup.
3.2. Magnetic Field Analysis
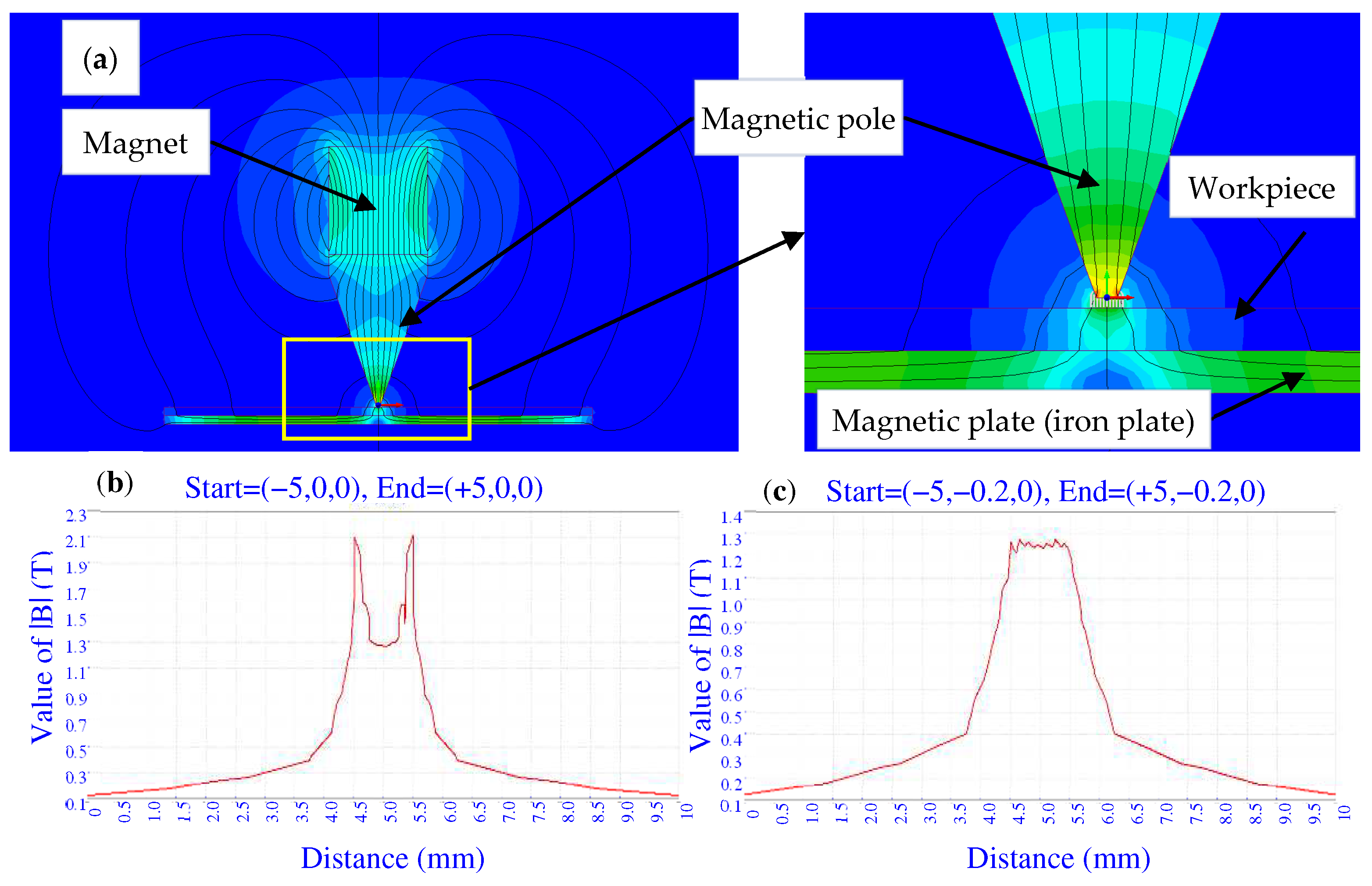
Figure 6 shows the simulation results of the magnetic field around the magnetic pole using Magnet 7 software. It can be seen from Figure 6a that the magnetic field at the lower end of the magnetic pole is stronger. In order to more specifically reflect the change of the magnetic field intensity, the curves of the magnetic field intensity were drawn respectively on a line segment with a length of 10 mm at a distance of 0 mm and 0.2 mm from the lower surface of the magnetic pole. It can be seen from Figure 6b that there is an obvious edge effect on the surface of the magnetic pole, and the magnetic field intensity in the center is much smaller than that at the edges. However, at a distance of 0.2 mm from the surface of the magnetic pole, as shown in Figure 6c, the magnetic field is relatively uniform. This is conducive to the uniform pressure of the magnetic brush.
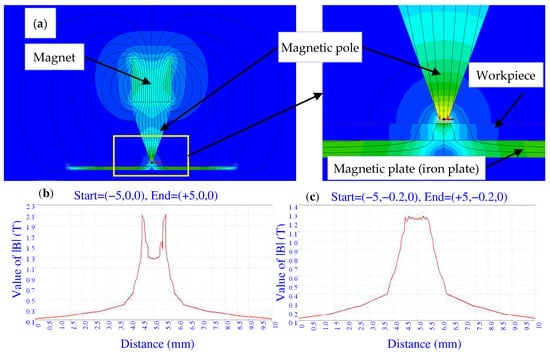
Figure 6.
The simulations with magnetic particles and with the magnetic plate under the workpiece. (a) The magnetic field distribution near the magnetic pole; (b) The magnetic field intensity |B| at a distance of 0 mm from the magnetic pole; (c) The magnetic field intensity |B| at a distance of 0.2 mm from the magnetic pole.
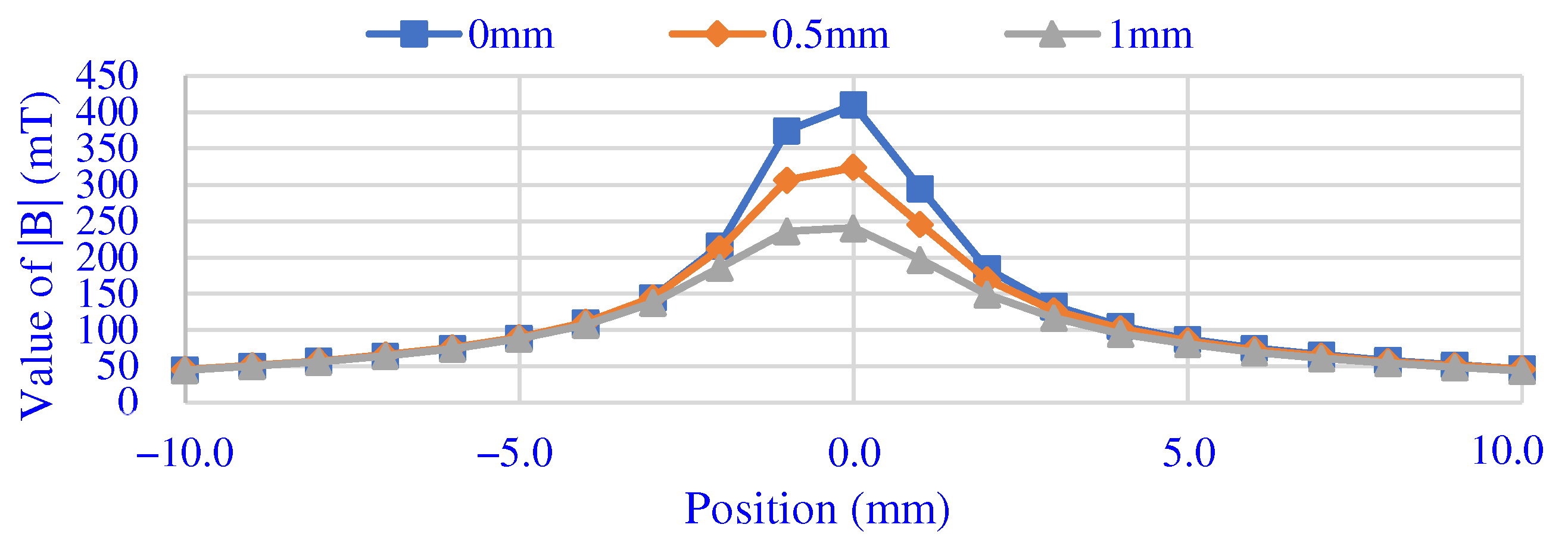
Figure 7 shows the results of measuring the magnetic field near the magnetic pole using the Tesla meter. Within 10 mm on both sides of the magnetic pole, the distances between the sensor and the surface of the magnetic pole are set to 0 mm, 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. It can be seen from the measurement results that as the distance increases, the magnetic field strength becomes weaker and weaker. However, due to the small magnetic pole diameter, the edge effect of magnetic field strength is weakened.
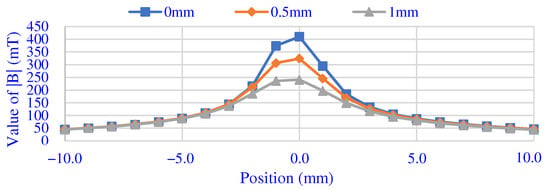
Figure 7.
The measured results of magnetic field.
3.3. Force Analysis
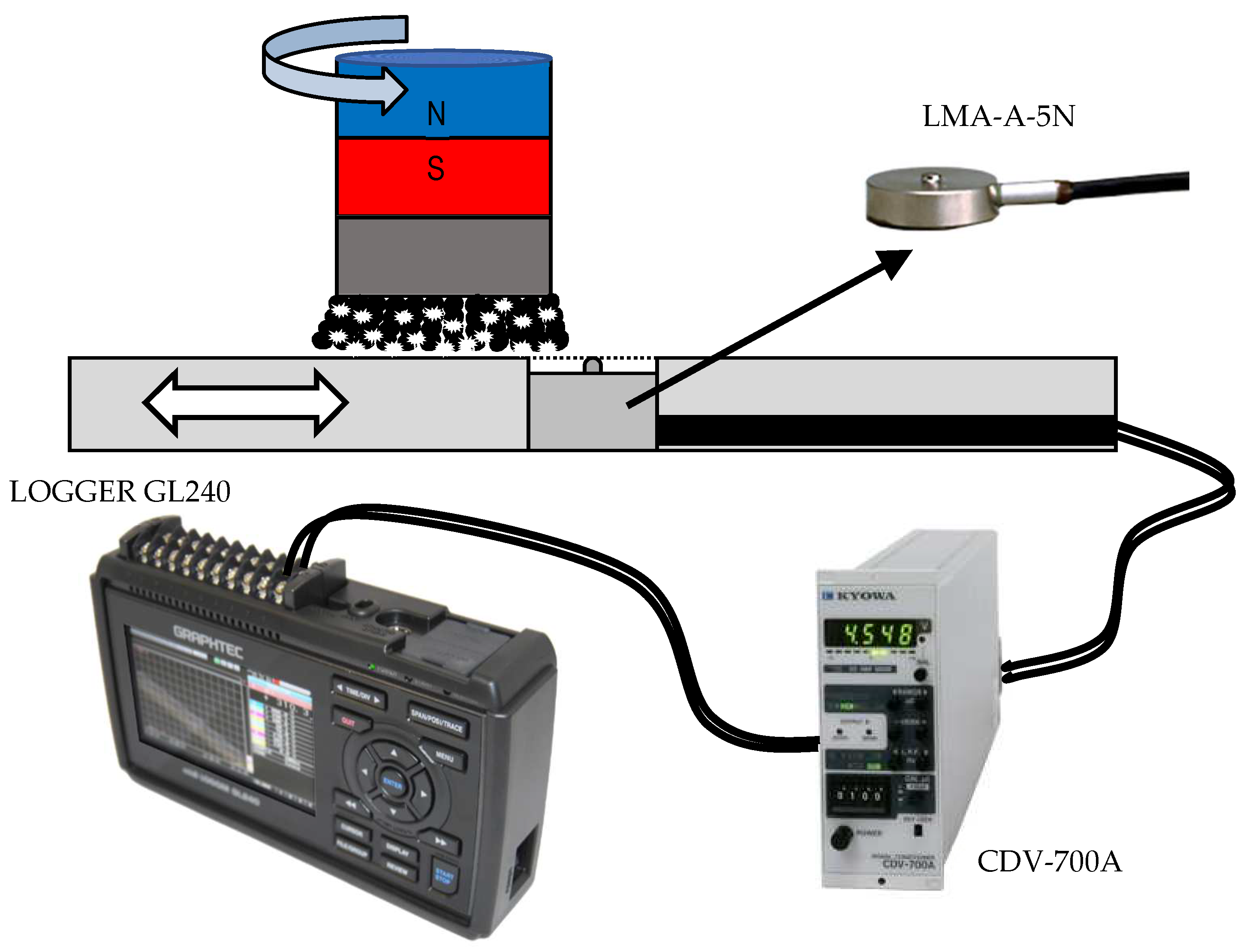
In order to better analyze the characteristics of the magnetic pole, a device is designed to measure the pressure distribution of the magnetic brush during processing. The measurement method is shown in Figure 8. The pressure sensor used here is the LMA-A-5N small pressure sensor from KYOWA. The pressure can be converted into an electrical signal by the sensor, which is amplified by an amplifier and sends the data to a recording instrument. In this research, the amplifier used is the CDV-700A (KYOWA, Chofugaoka 3-5-1, Chofu, Tokyo, 182-8520), and the data logging instrument is the LOGGER GL240 (Graphtec Corporation, 58/3-5 4th Floor, Sukhumvit 63 (Ekkamai) Rd., Phra Khanong-Nuea, Wattana, Bangkok 10110, Thailand).
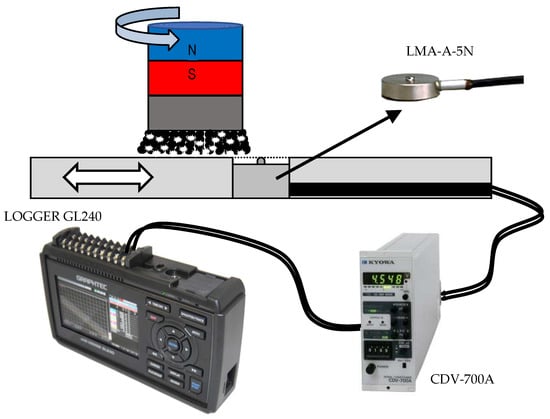
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of pressure measuring device structure.
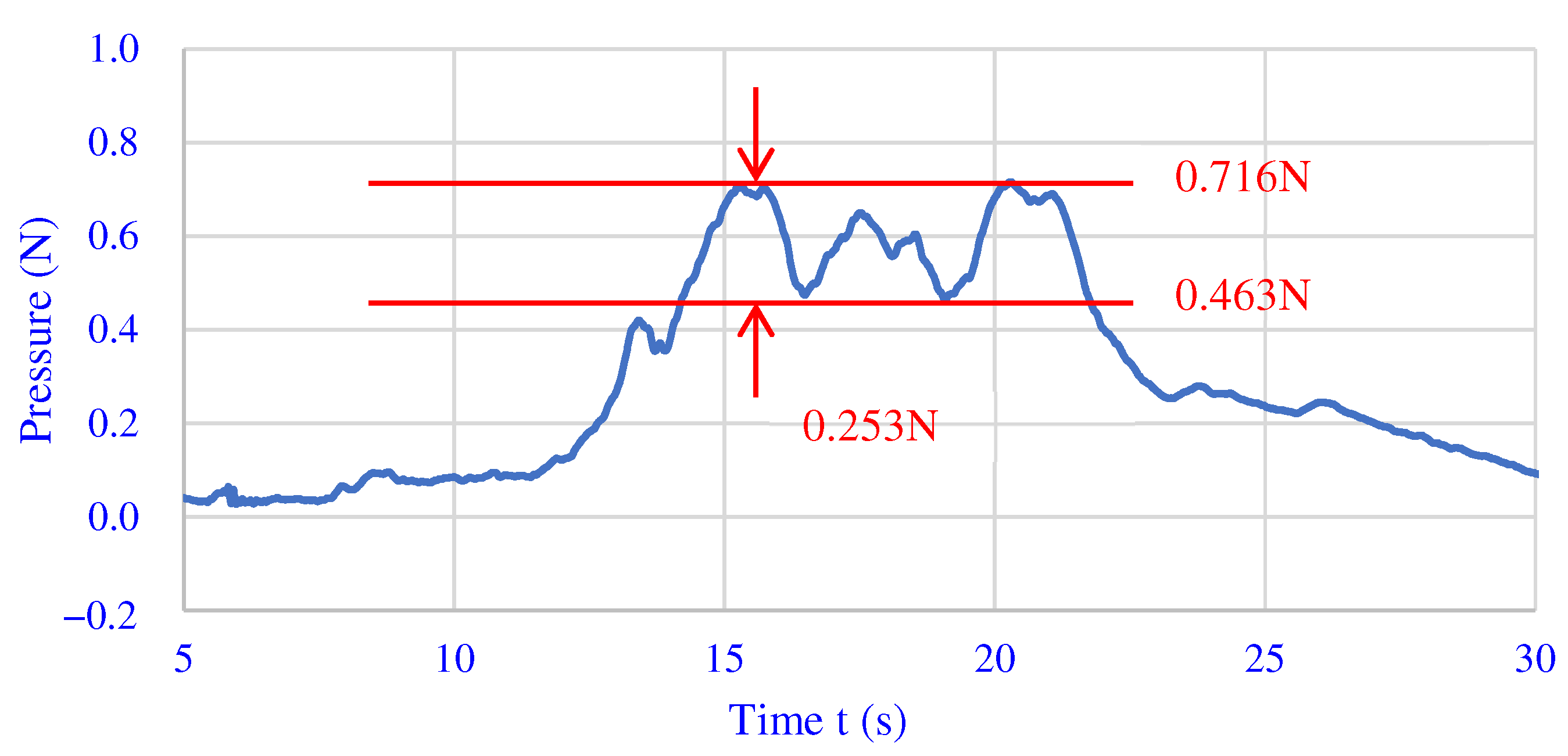
Figure 9 shows the measurement results of the pressure exerted by the magnetic brush on the workpiece. When the gap is 0.2 mm, the pressure near the magnetic brush is between 0.463 N and 0.716 N.
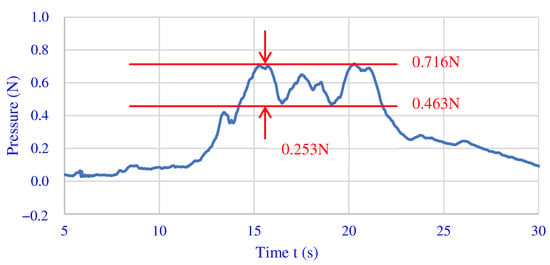
Figure 9.
The measured results of pressure at 0.2 mm from magnetic pole.
4. Experiment and Discussion
According to previous studies, it is possible to effectively improve the surface profile of the workpiece and to correct the profile of the surface by controlling the feed speed during the processing. So can this kind of processing be extended to a larger plane range? Therefore, the following experiments were designed.
The experimental steps are as follows:
- (1)
- First, it is necessary to design experiments to calculate the processing efficiency of the magnetic brush, and to obtain the value of ;
- (2)
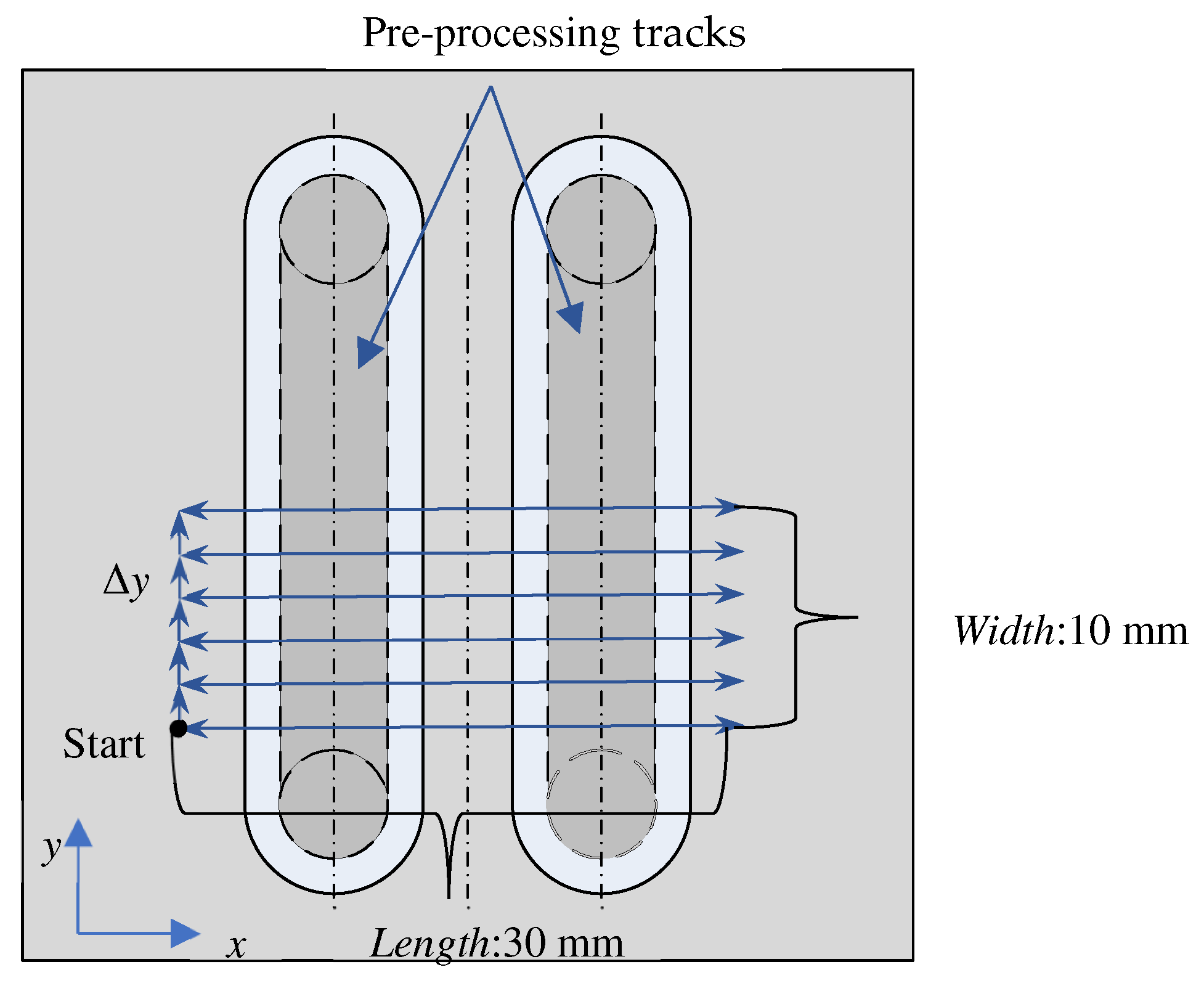
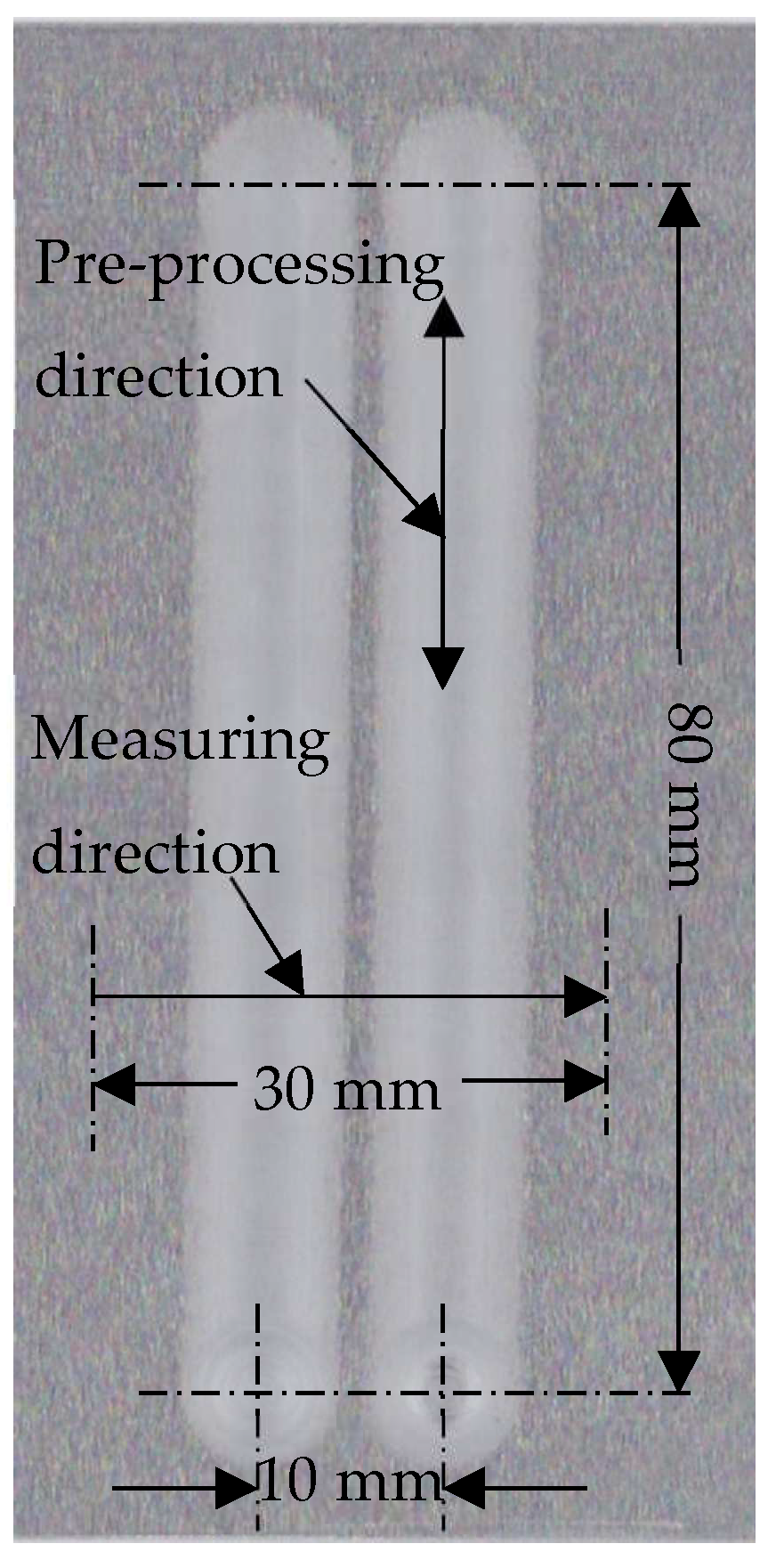
- For Pre-processing, two tracks are processed with a magnetic pole with an end diameter of 3 mm to produce a surface with fluctuation in the x-direction, as shown in Figure 10;
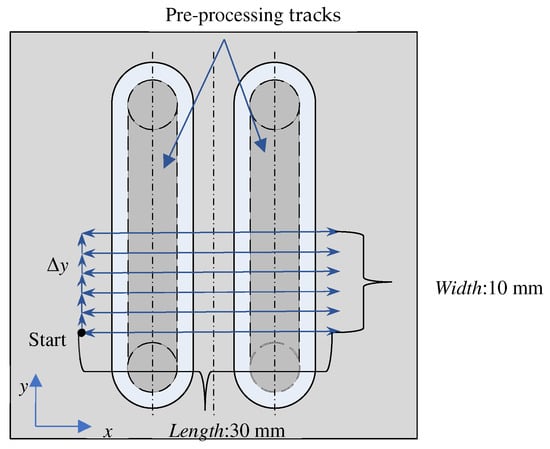 Figure 10. Schematic diagram of processing position.
Figure 10. Schematic diagram of processing position. - (3)
- Measuring the profile curves of the workpiece along the x-direction, analyzing and processing the measured data according to the previous method, and obtaining the feed speed curves data during corrective processing;
- (4)
- Corrective processing of the workpiece surface with an area of 30 mm 10 mm ( is 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm, 1.5 mm and 2.0 mm, respectively);
- (5)
- The experimental results are measured and analyzed.
The results of each step of the experiments will be described in detail below.
4.1. Magnetic Brush Processing Efficiency Experiments
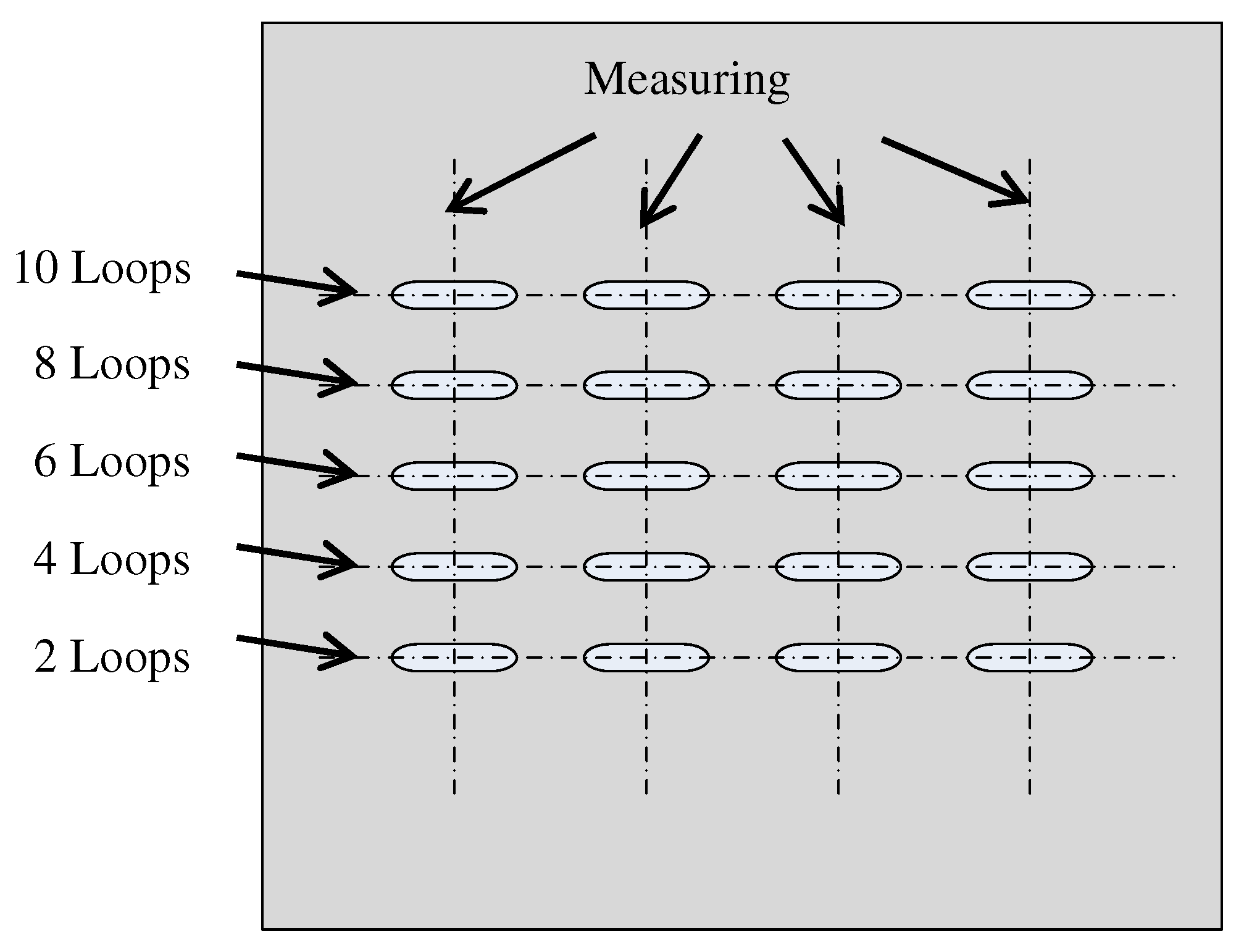
To reasonably control the feed speed during finishing, it is necessary to measure the finishing efficiency of the magnetic pole. The finishing object selected is a 100 mm × 100 mm × 2 mm A5052 plate in this research. The calculation method of the finishing efficiency is the processing of five tracks with a length of 6 mm on the same workpiece, and each track is processed with 2-4-6-8-10 loops, respectively, as shown in Figure 11. Then the cross-section curve is measured to calculate the finishing depth, and the average of four times is used as the average finishing efficiency. The experiment conditions are shown in Table 1. The feed speed of the workpiece is 0.2 mms−1, and the rotation speed of the magnetic pole is 400 rmin−1. The abrasive liquid is composed of 0.5 mL of oil (Honilo 988) and 1 g of #4000 WA particles, and the magnetic brush was soaked in the abrasive liquid for processing each time.
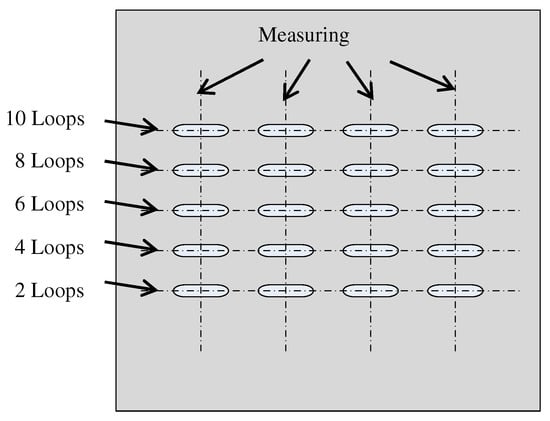
Figure 11.
Evaluation of finishing efficiency.

Table 1.
Experimental conditions of evaluating finishing efficiency.
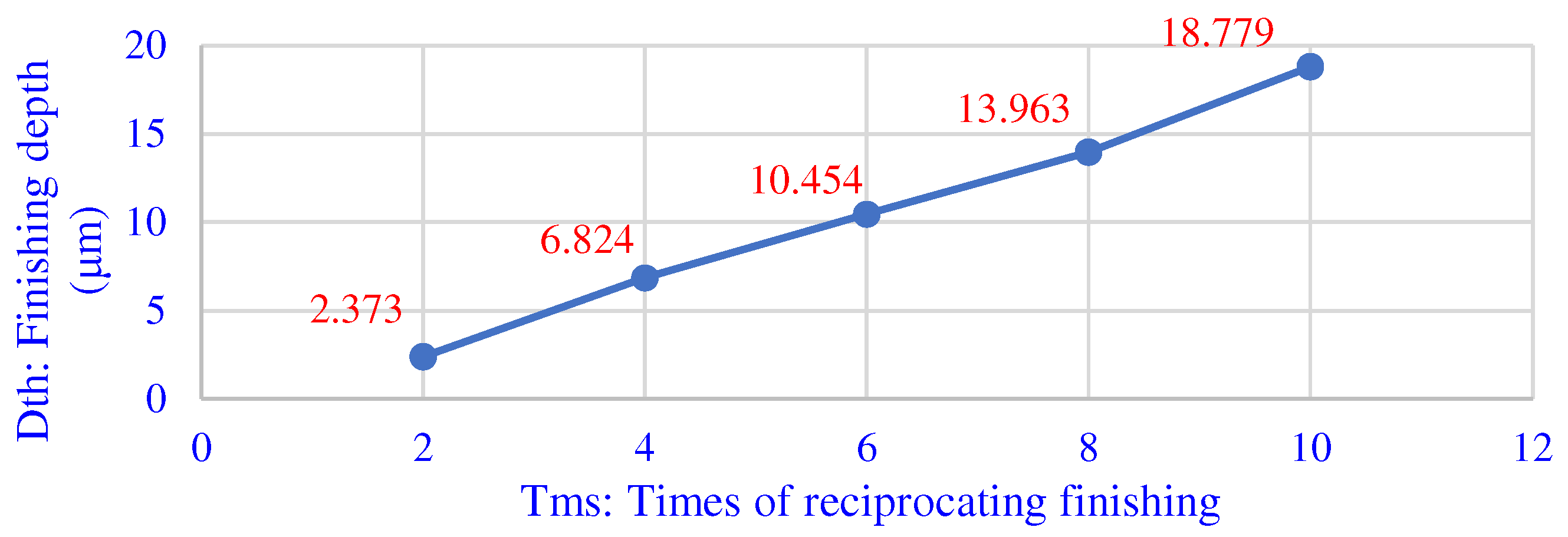
Figure 12 is the average value of the finishing depth of each group according to the finishing method described above. As the times of reciprocating finishing increase, the finishing depth becomes deeper. Moreover, the finishing depth has a linear relationship with the number of reciprocations. After calculation, the average height reduction of the one loop process is about 1.88 μm.
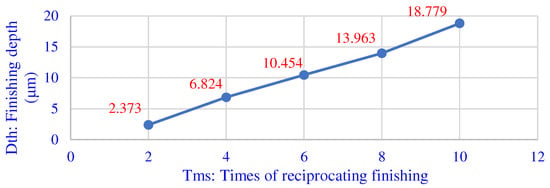
Figure 12.
The relationship between reciprocating times and processing depth.
4.2. Pre-Processing Experiment
Pre-processing is processing two traces using a magnetic pole with an end face diameter of 3 mm. Figure 13 shows a photo of the workpiece after pre-processing. Then, the profile of the workpiece is measured along the direction perpendicular to the preprocessing. Many curves are measured at an interval of 1 mm by Surftest (SV-624-3D). The data obtained are used to calculate the speed curves of the correction finishing. The preprocessing conditions of the experiments are shown in Table 2.
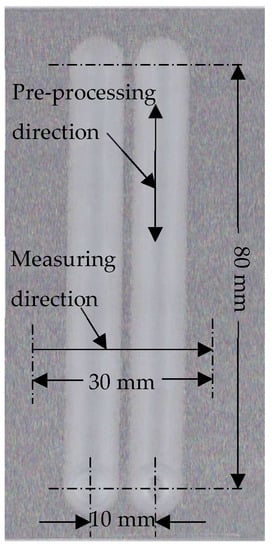
Figure 13.
The workpiece after pre-processing.

Table 2.
Experimental conditions of preparation finishing.
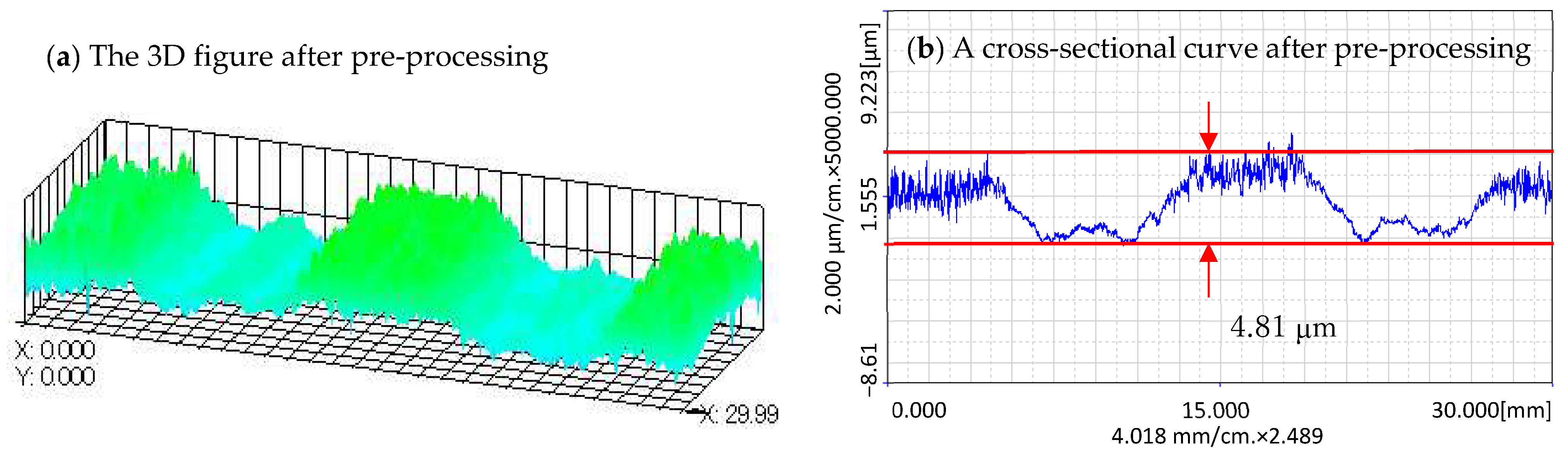
Figure 14a shows the 3D figure and Figure 14b shows a cross-sectional curve of the surface profile of the workpiece after pre-processing. Since the pre-processing is processed by using a uniform feed speed, the cross-sectional curves at different positions are almost the same.
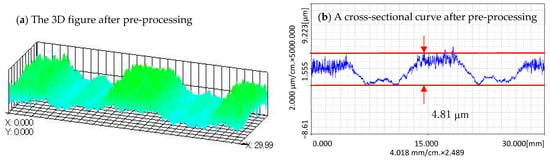
Figure 14.
The measurement result of the workpiece surface after pre-processing: (a) The 3D figure after pre-processing; (b) A cross-sectional curve after pre-processing.
4.3. Corrective Finishing Experiments
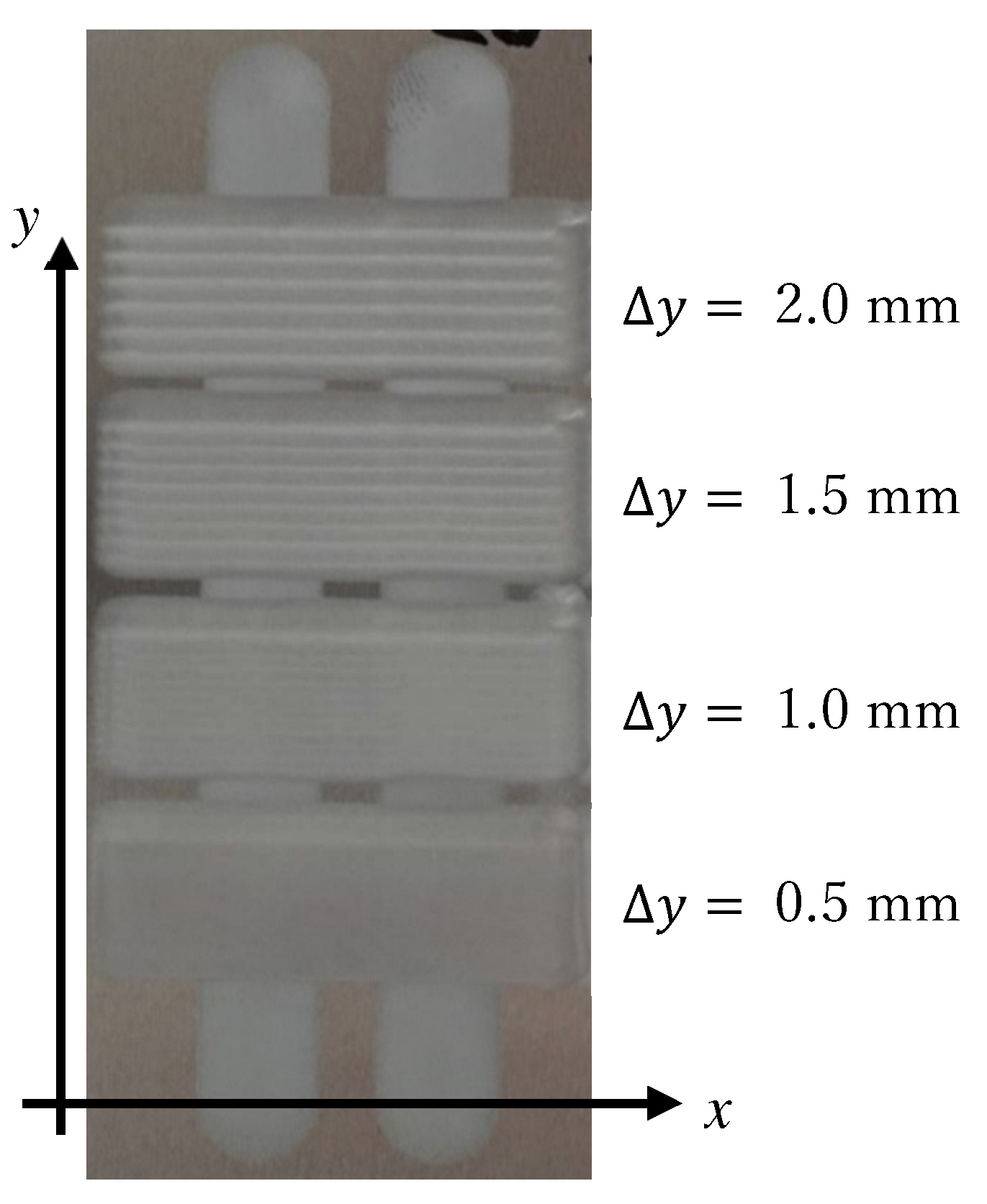
A photo of the processed workpiece is shown in Figure 15. It can be seen from the picture that as the step size of ∆y decreases, the surface becomes more uniform. The traces of the transition between the two processing tracks are also reduced. When Δy is 0.5 mm or 1.0 mm, the traces of this transition are not obvious. When Δy is 0.5 mm, the traces of this transition are almost indistinguishable with the naked eye. However, in terms of processing time, a long processing time is required at 0.5 mm spacing, so the efficiency is slightly lower. The measurement results will be compared below.
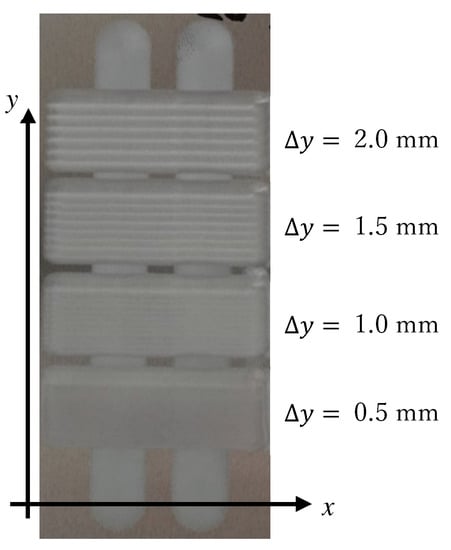
Figure 15.
The photograph of the surface of the workpiece after processing.
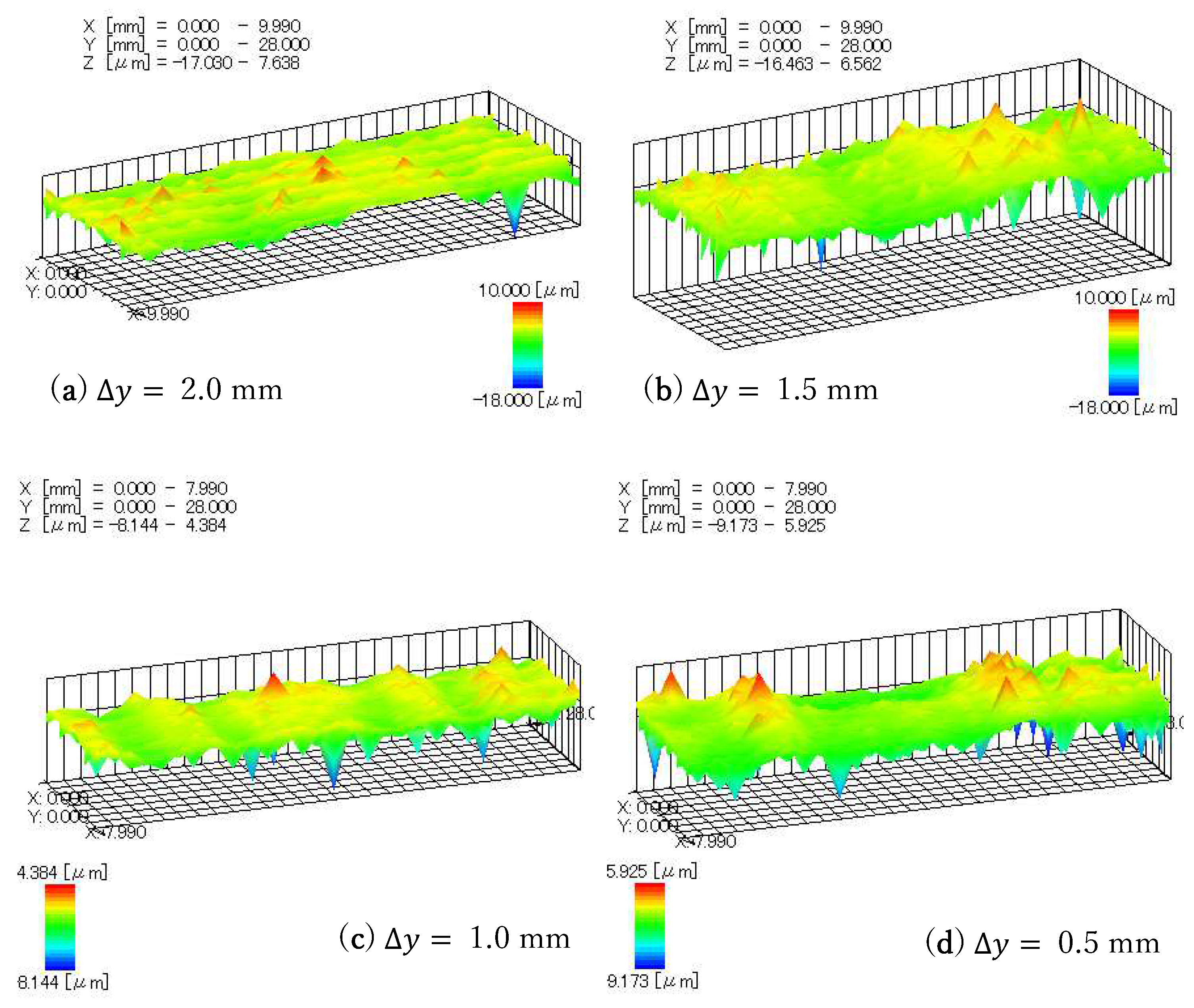
Figure 16 is a 3D figure of the processed workpiece surface measured by a roughness measuring instrument (Surftest: SV-624-3D). The measurement method is to measure a group of section curves at 0.5 mm intervals to draw 3D figures. It can be seen from the figure that when ∆y is 2 mm and 1.5 mm, there are obvious transition traces. When the spacing is 1 mm and 0.5 mm, the traces are not very obvious and the two traces produced by the pre-processing are no longer obvious. The surface was processed to be smooth.
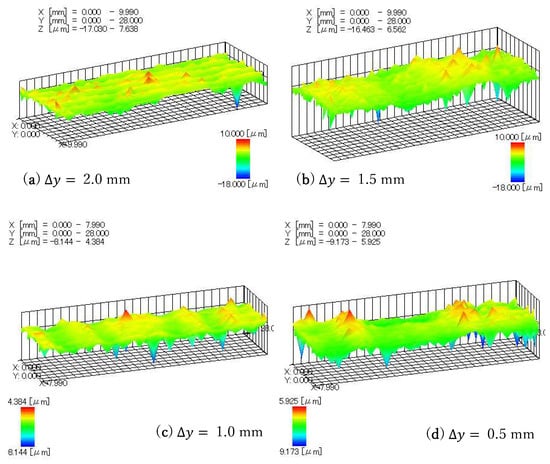
Figure 16.
Three-dimensional figures of the processed surface: (a) The 3D figure after processing at ∆y = 2.0 mm; (b) The 3D figure after processing at ∆y = 1.5 mm; (c) The 3D figure after processing at ∆y = 1.0 mm; (d) The 3D figure after processing at ∆y = 0.5 mm.
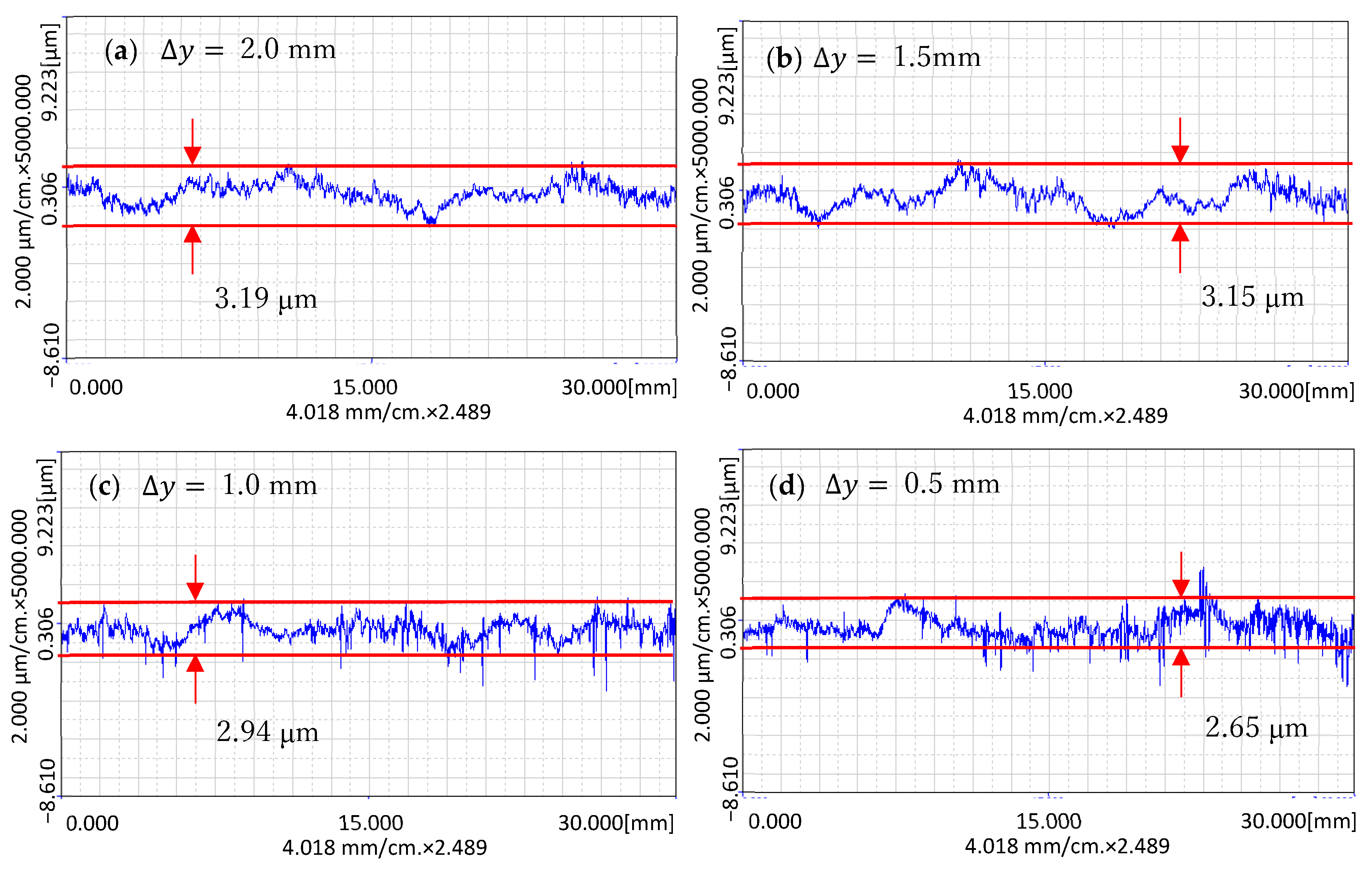
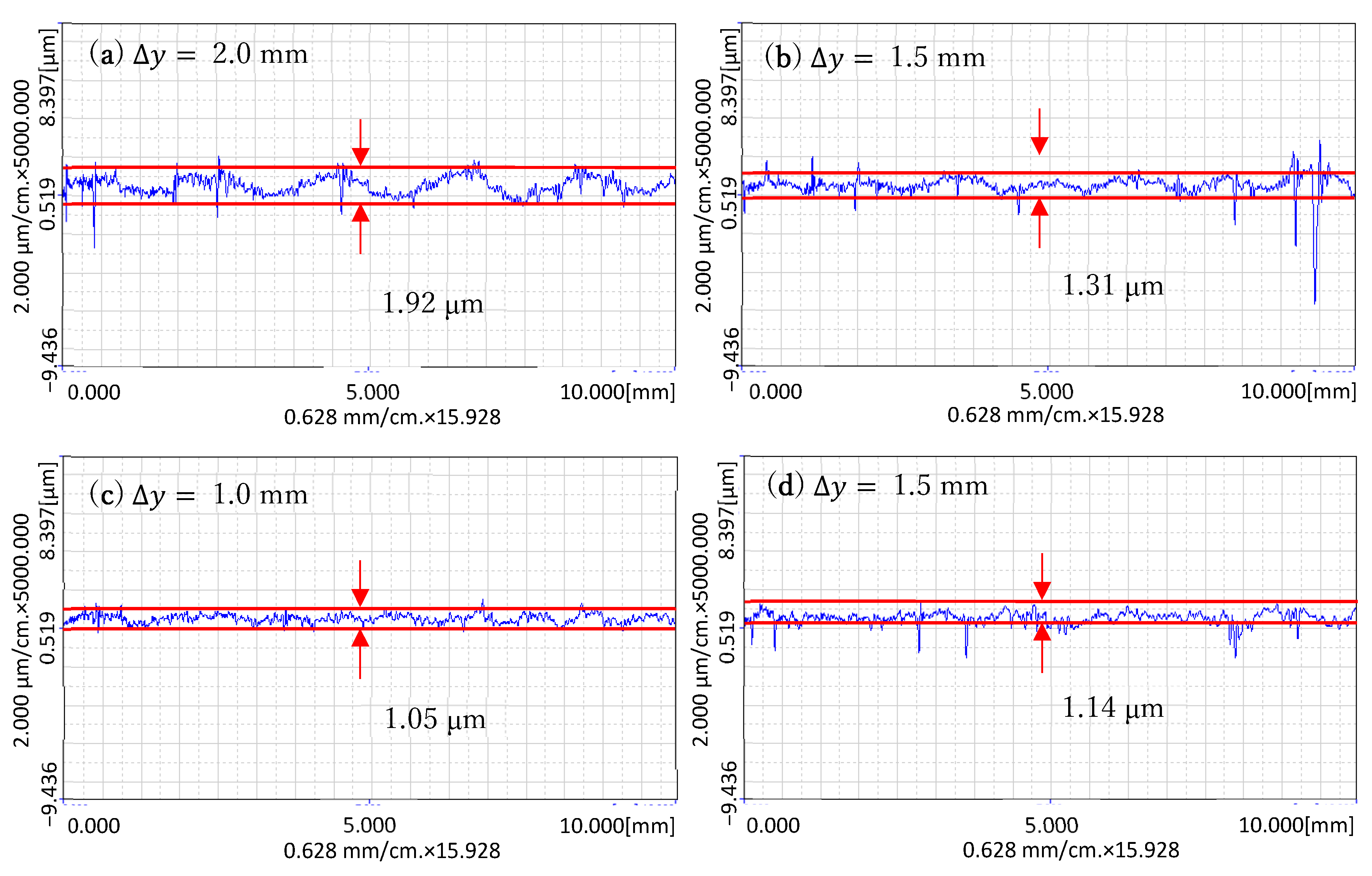
In order to be able to see the difference in experimental results more clearly, the cross-sections of the processing area were measured along the x and y directions. The measurement results are shown in Figure 17 and Figure 18.
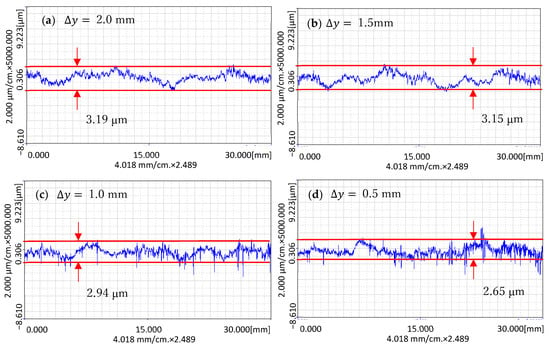
Figure 17.
The cross-section curves of the surface along the x-direction after processing: (a) The cross-section curves at ∆y = 2.0 mm; (b) The cross-section curves at ∆y = 1.5 mm; (c) The cross-section curves at ∆y = 1.0 mm; (d) The cross-section curves at ∆y = 0.5 mm.
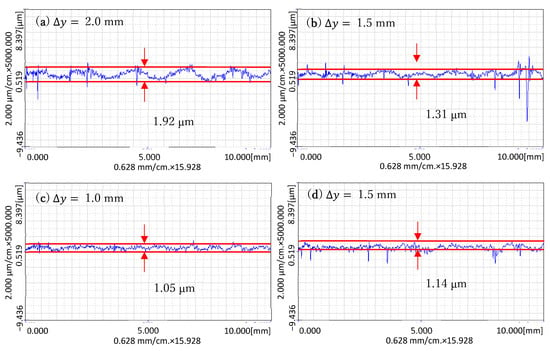
Figure 18.
The cross-section curves of the surface along the y-direction after processing: (a) The cross-section curves at ∆y = 2.0 mm; (b) The cross-section curves at ∆y = 1.5 mm; (c) The cross-section curves at ∆y = 1.0 mm; (d) The cross-section curves at ∆y = 0.5 mm.
As shown in Figure 17, the x-direction is the direction measured along the processing feed direction. It can be seen that the surface was significantly improved compared with before processing, and the surface of Δy = 1.0 mm and 0.5 mm is relatively flat. This is because when ∆y is equal to 1.0 mm and 0.5 mm, the processing time is relatively long, and when ∆y is equal to 1.5 mm and 2.0 mm, the processing time is relatively short.
The y-direction is the direction measured along the translation direction of the trajectory, as shown in Figure 18. In this direction, the transition of the processing track during translation can be clearly seen. For example, when Δy = 2.0 mm, there are five obvious transition intervals. When Δy = 1.5 mm, there are six obvious transition intervals. When Δy = 1.0 mm and 0.5 mm, the transition becomes inconspicuous. With the decrease in Δy, the transition is no longer obvious, and the surface is almost flat. This shows that the smaller Δy is, the better the processing effect is. However, when Δy decreases, the time of the processing becomes longer. For example, when Δy = 2.0 mm, six lines need to be processed. The processing time of each line is about 1 min, so the processing time is 6 min. When Δy = 1.0 mm, 11 lines need to be processed, so the processing time is 11 min. When Δy = 0.5 mm, 21 lines need to be processed, so the processing time is 21 min.
5. Conclusions
In this research, a surface corrective processing method is proposed and can be summarized as follows:
- (1)
- In the feed direction (-direction), variable speed finishing has an obvious effect on the surface correction. However, when decreases, the processing time becomes longer, so the correction effect is better.
- (2)
- When correcting the surface of the workpiece through speed control, the smaller the step length of the processing track, the smaller the trace of surface transition, but it takes a longer processing time. This experiment proves that the processing effect at 1.0 mm is almost the same as that at 0.5 mm, but the processing time is reduced by half. In variable speed correction finishing, there is a certain correction effect under different conditions, but when is large, it will produce transition traces to the profile in the -direction. When drops to 1.0 mm, the transition traces are almost gone.
- (3)
- The experimental results show that the speed control method can be used to correct the surface profile of the workpiece. The extreme difference can be reduced from 4.81 μm to 2.65 μm within a processed area of 30 mm by 10 mm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. (Yulong Zhang) and Y.Z. (Yanhua Zou); Data curation, Y.Z. (Yulong Zhang); Formal analysis, Y.Z. (Yulong Zhang); Funding acquisition, Y.Z. (Yanhua Zou); Investigation, Y.Z. (Yulong Zhang) and Y.Z. (Yanhua Zou); Methodology, Y.Z. (Yulong Zhang) and Y.Z. (Yanhua Zou); Project administration, Y.Z. (Yanhua Zou); Validation, Y.Z. (Yulong Zhang) and Y.Z. (Yanhua Zou); Writing—original draft, Y.Z. (Yulong Zhang) and Y.Z. (Yanhua Zou); Writing—review & editing, Y.Z. (Yulong Zhang) and Y.Z. (Yanhua Zou). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Patil, M.G.; Chandra, K.; Misra, P.S. Magnetic abrasive finishing–A Review. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 418, pp. 1577–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Fan, Z.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, J. A review on magnetic abrasive finishing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 112, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinmura, T.; Takazawa, K.; Hatano, E.; Matsunaga, M.; Matsuo, T. Study on magnetic abrasive finishing. CIRP Ann. 1990, 39, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinmura, T.; Aizawa, T. Study on magnetic abrasive finishing process-development of plane finishing apparatus using a stationary type electromagnet. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng. 1989, 23, 236–239. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Shinmura, T. Study of an internal magnetic abrasive finishing using a pole rotation system: Discussion of the characteristic abrasive behavior. Precis. Eng. 2000, 24, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.H. A new internal magnetic deburring process using a magnetic machining jig-Precise deburring of a drilled hole on the inside of a SUS304 stainless steel tube. J. Jpn. Soc. Abras. Technol. 2007, 51, 696. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, A.; Pandey, P.M.; Dixit, U.S. Modeling of material removal in ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 131, 853–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Zhao, J. Material removal profile prediction and experimental validation for obliquely axial ultrasonic vibration-assisted polishing of K9 optical glass. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33106–33119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulik, R.S.; Pandey, P.M. Ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing of hardened AISI 52100 steel using unbonded SiC abrasive. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zou, Y.H. Development of magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process for finishing SUS304 stainless steel plane. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 3373–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.H.; Xing, B.J.; Sun, X. Study on the magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process—Investigation of machining mechanism. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.J.; Zou, Y.H. Investigation of finishing aluminum alloy A5052 using the magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process. Machines 2020, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.H.; Satou, R.; Yamazaki, O.; Xie, H.J. Development of a New Finishing Process Combining a Fixed Abrasive Polishing with Magnetic Abrasive Finishing Process. Machines 2021, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Z.; Zou, Y.H.; Sugiyama, H. Study on finishing characteristics of magnetic abrasive finishing process using low-frequency alternating magnetic field. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.H.; Xie, H.J.; Dong, C.; Wu, J. Study on complex micro surface finishing of alumina ceramic by the magnetic abrasive finishing process using alternating magnetic field. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.J.; Zou, Y.H.; Dong, C.W.; Wu, J.Z. Study on the magnetic abrasive finishing process using alternating magnetic field: Investigation of mechanism and applied to aluminum alloy plate. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.T.; Yang, L.D.; Chow, H.M. Study of magnetic abrasive finishing in free-form surface operations using the Taguchi method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 34, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.D.; Lv, M.; Chen, H.L. Theoretical research on polishing free-form surface with magnetic abrasive finishing. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 392, pp. 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Maksarov, V.V.; Keksin, A.I. Technology of magnetic-abrasive finishing of geometrically-complex products. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 327, p. 042068. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.H.; Jiao, A.Y.; Toshio, A. Study on plane magnetic abrasive finishing process-experimental and theoretical analysis on polishing trajectory. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 126, pp. 1023–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, A.Y.; Quan, H.J.; Li, Z.Z.; Zou, Y.H. Study on improving the trajectory to elevate the surface quality of plane magnetic abrasive finishing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 80, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.H.; Xie, H.J.; Zhang, Y.L. Study on surface quality improvement of the plane magnetic abrasive finishing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 109, 1825–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, F.W. The Theory and Design of Plate Glass Polishing Machines. J. Soc. Glass Technol. 1927, 11, 214–256. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Prediction of surface roughness in magnetic abrasive finishing using acoustic emission and force sensor data fusion. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2011, 225, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zou, Y.H. Study of corrective abrasive finishing for plane surfaces using magnetic abrasive finishing processes. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2021, 4, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.W. Static tool influence function for fabrication simulation of hexagonal mirror segments for extremely large telescopes. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michaeli, W.; Heßner, S.; Klaiber, F.; Forster, J. Geometrical accuracy and optical performance of injection moulded and injection-compression moulded plastic parts. CIRP Ann. 2007, 56, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).