Design and Characterization of a Mckibben Pneumatic Muscle Prototype with an Embedded Capacitive Length Transducer
Abstract
1. Introduction
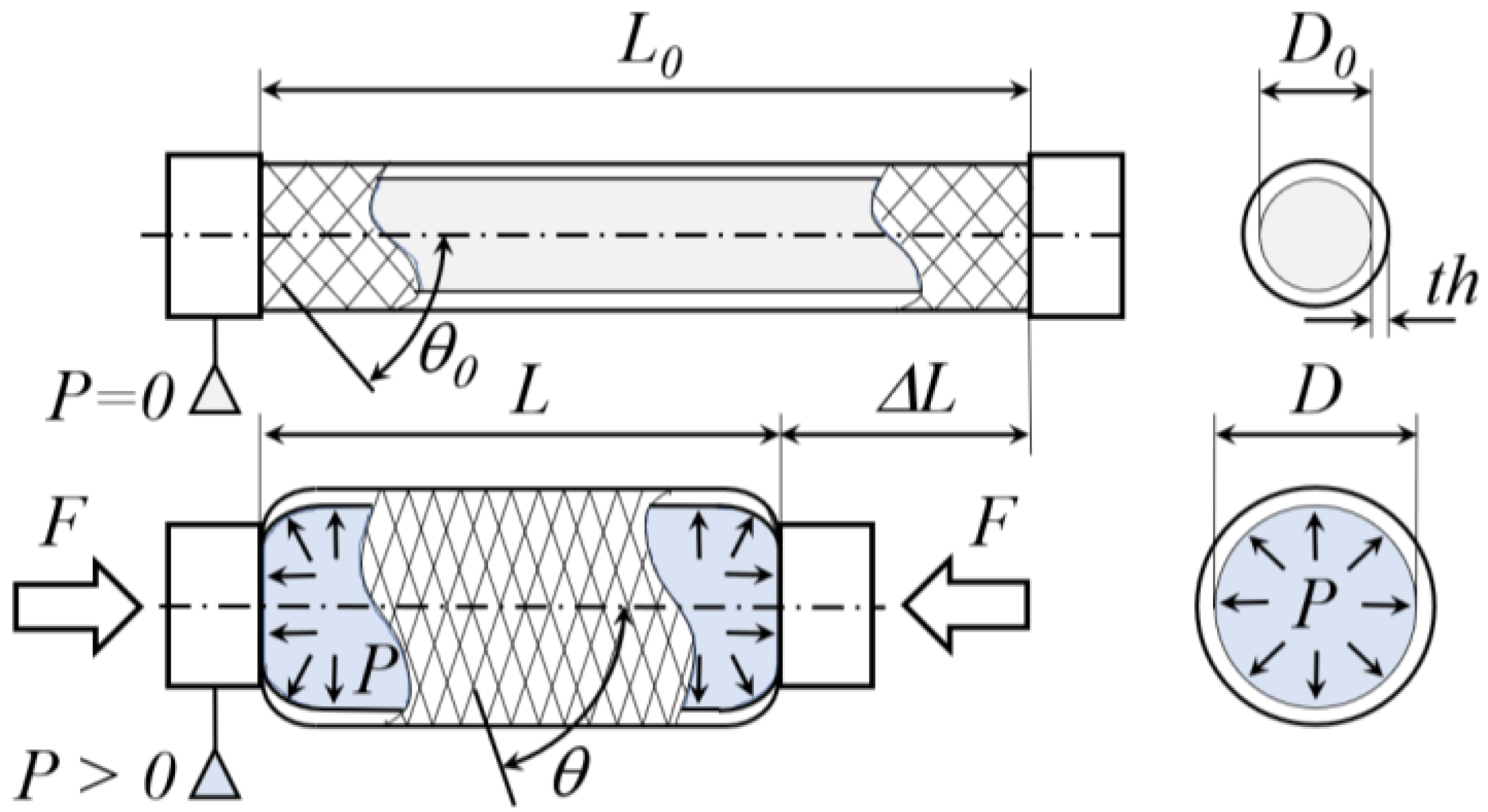
2. The Conceptual Idea
3. Fabrication and Experimental Characterization of the Capacitive Transducers
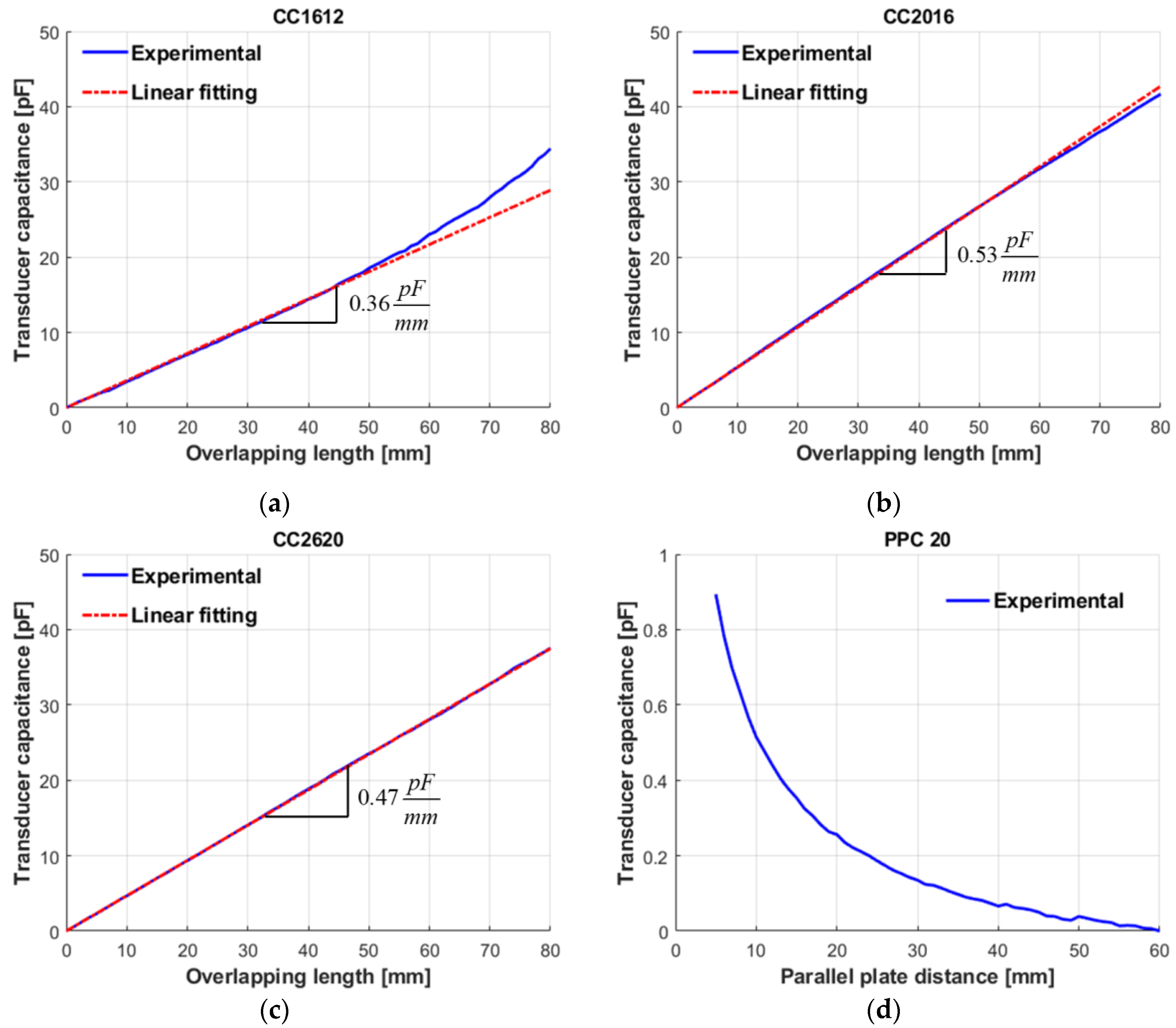
3.1. Capacitive Transducer Based on Cylindrical Capacitor Named CC1612
3.2. Capacitive Transducer Based on the Cylindrical Capacitors Named CC2016 and CC2620
3.3. Capacitive Transducer Based on the Parallel-Plate Capacitor Named PPC20
3.4. The Experimental Characterization
4. The Conceptual Idea
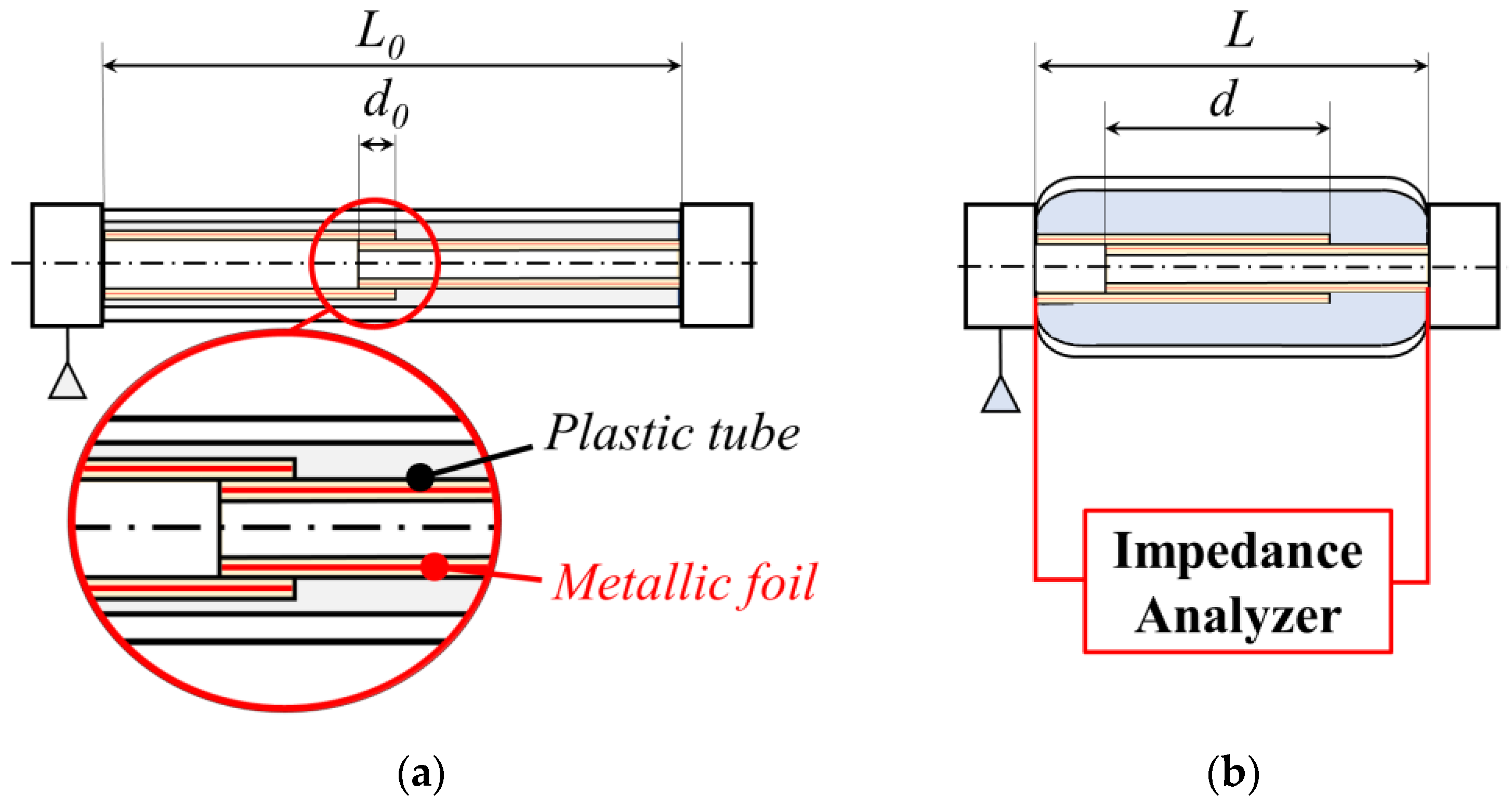
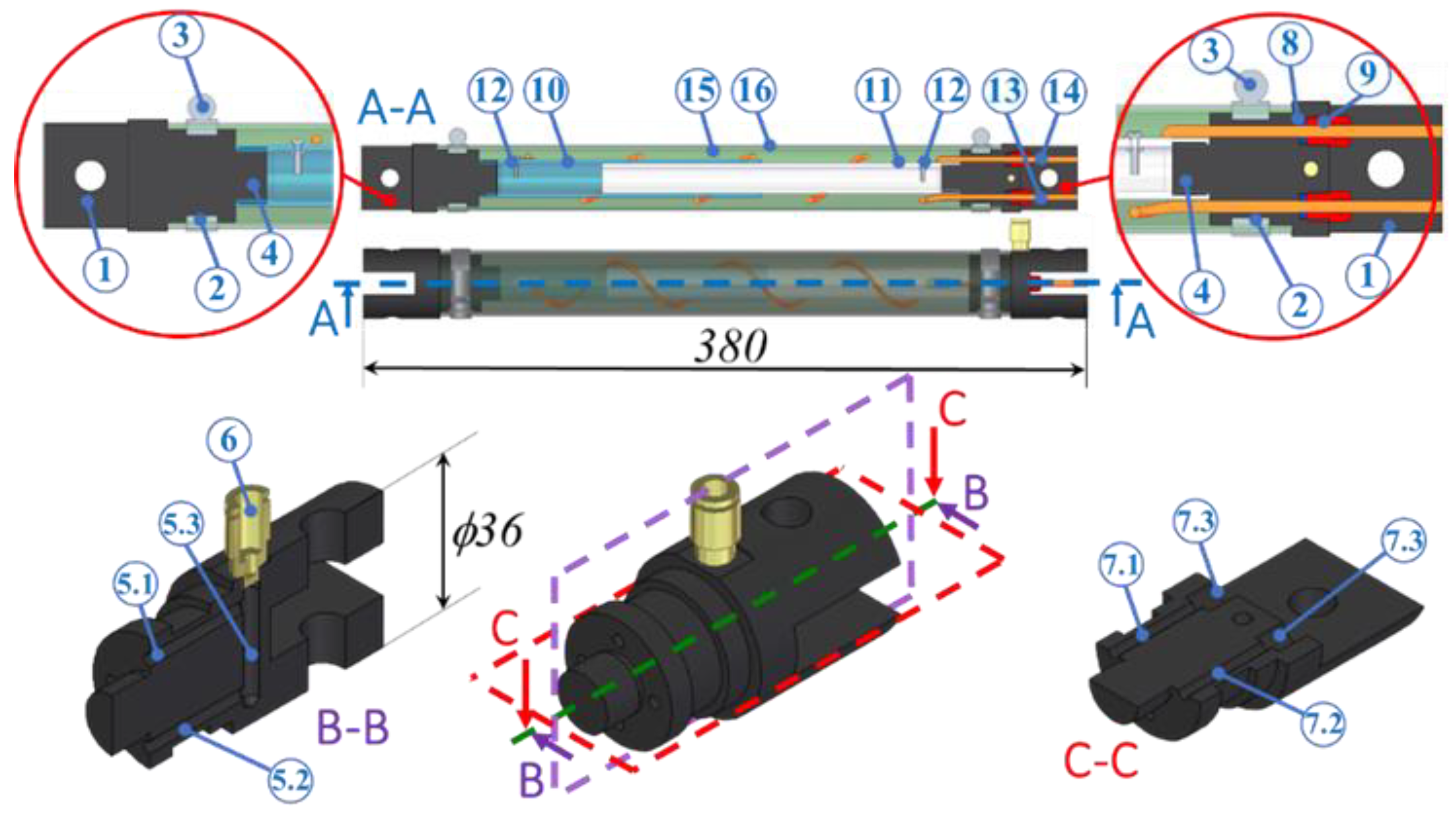
4.1. The Design of the MKM Based on the Cylindrical Capacitive Transducer
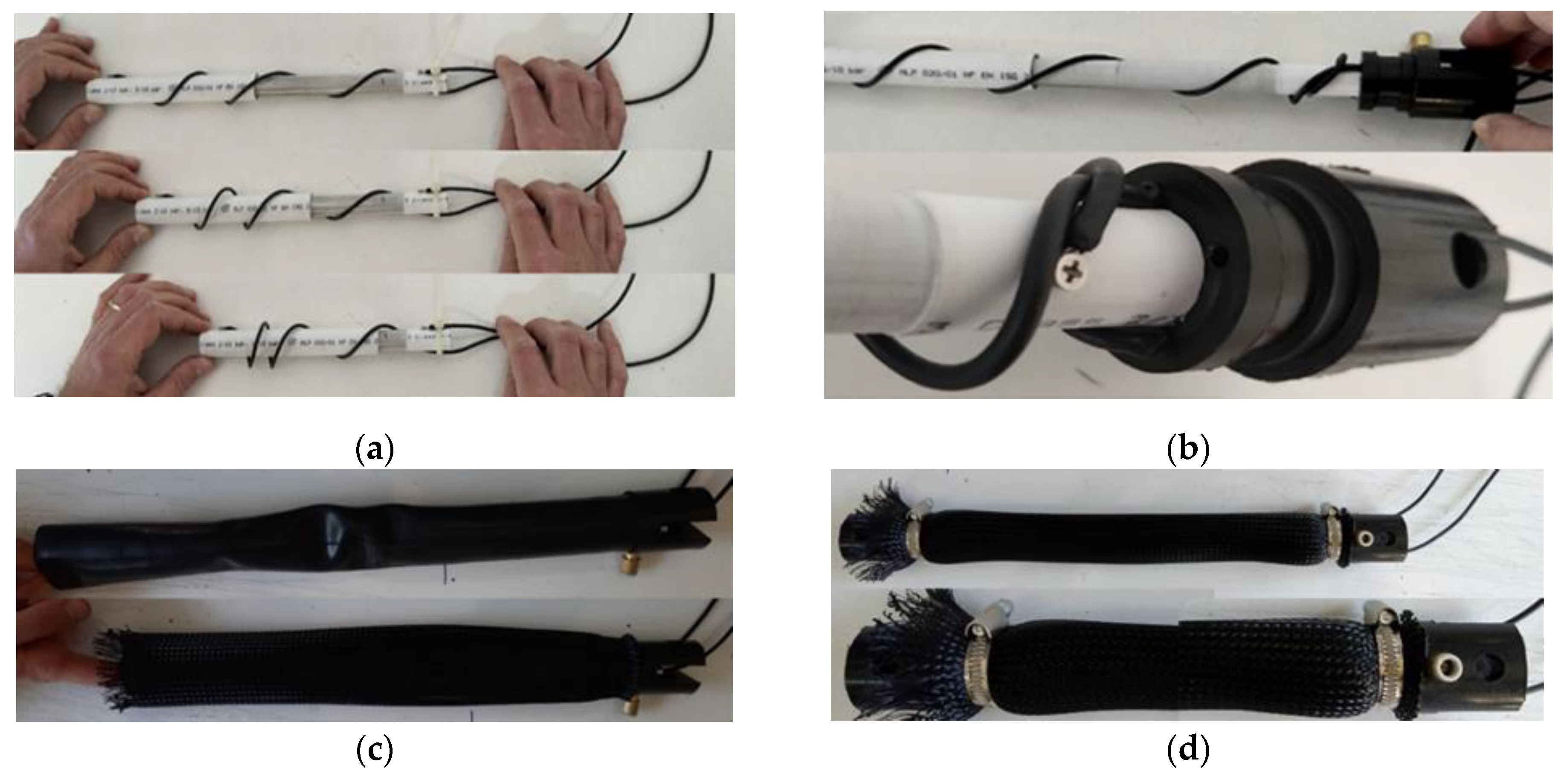
4.2. The MKM Protoype
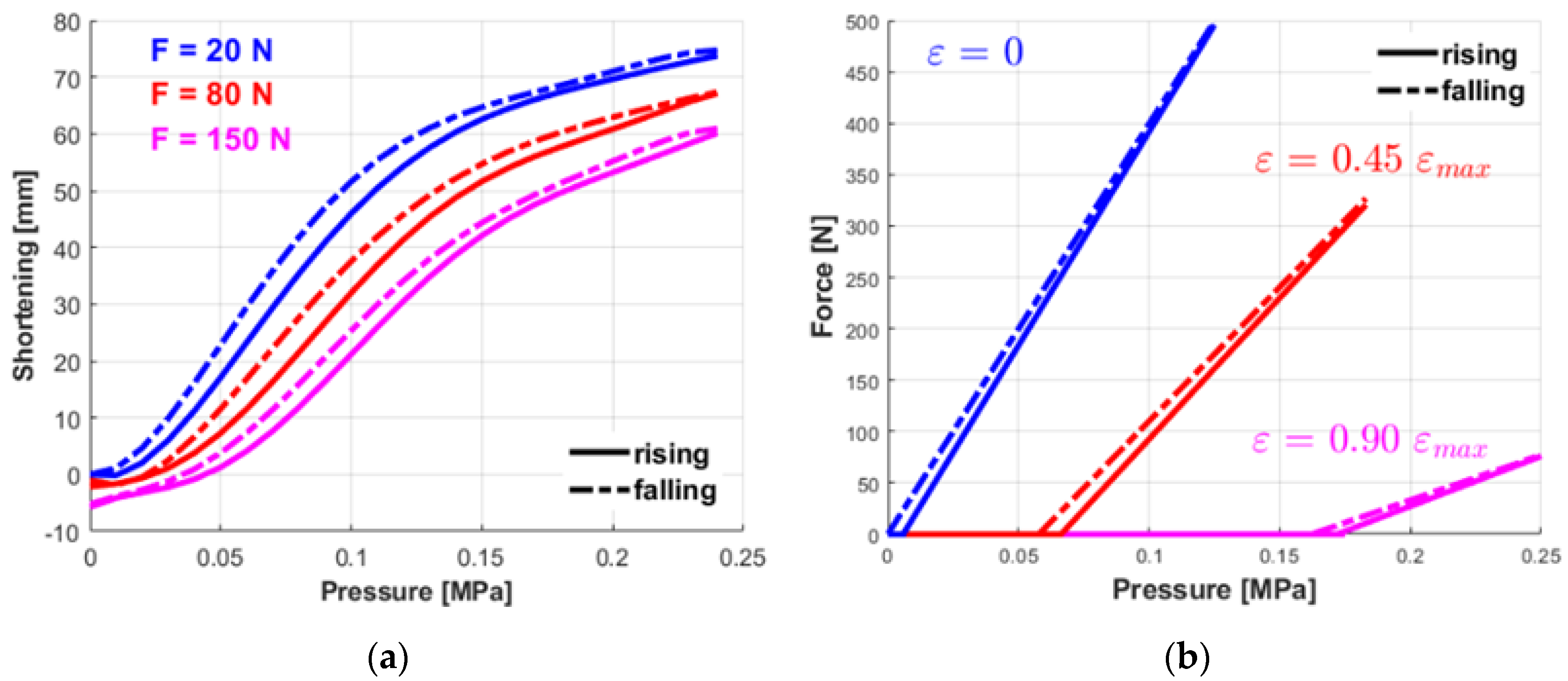
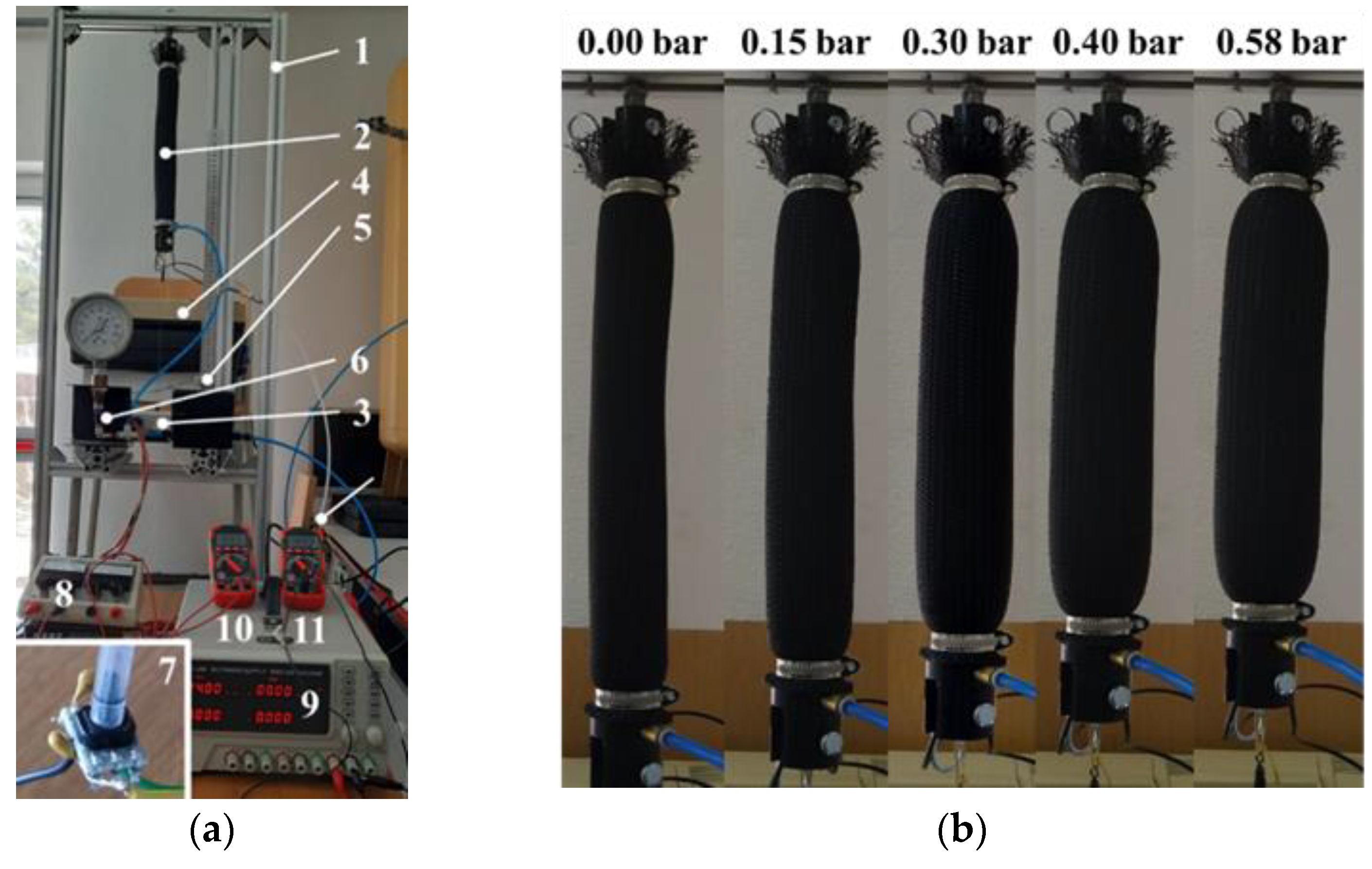
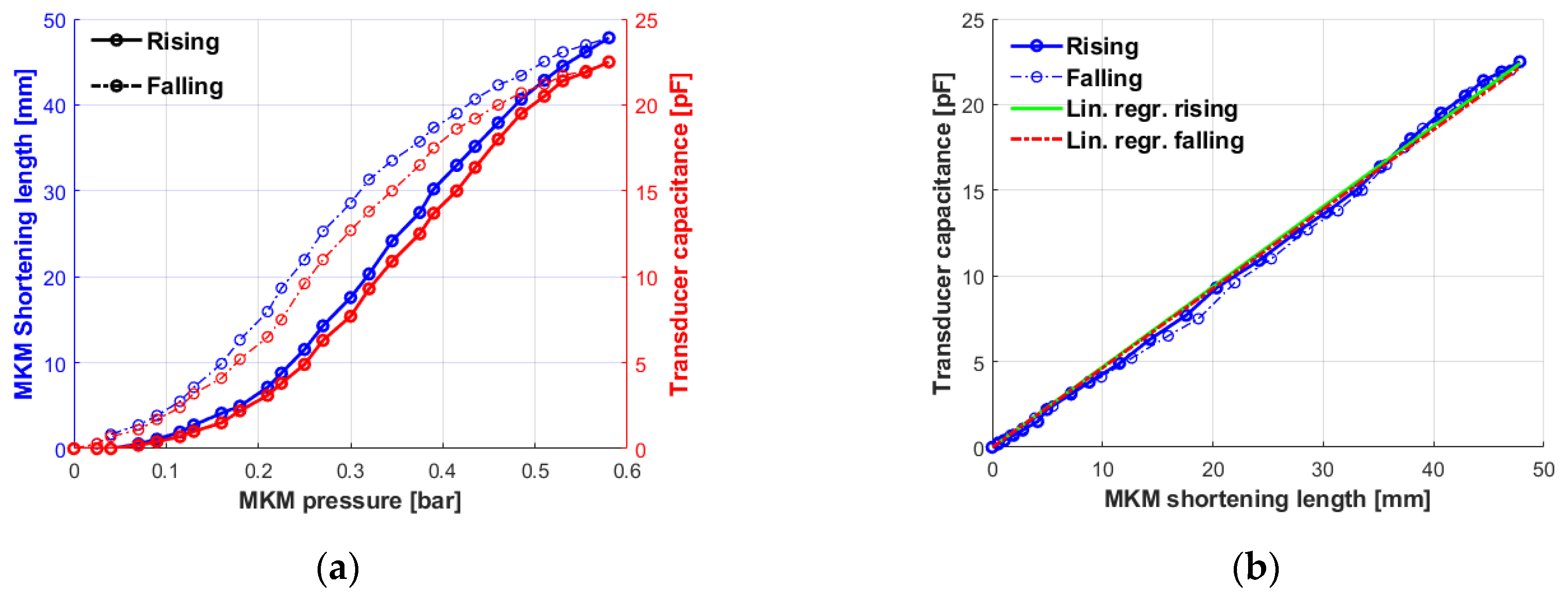
5. Experimental Characterization of the MKM
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daerden, F.; Lefeber, D. Pneumatic artificial muscles: Actuators for robotics and automation. Eur. J. Mech. Environ. Eng. 2002, 47, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Daerden, F.; Lefeber, D. The concept and design of pleated pneumatic artificial muscles. Int. J. Fluid Power 2001, 2, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, F.; Antonelli, M.G.; Beomonte Zobel, P.; Raparelli, T. Development of a straight fibers pneumatic muscle. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2018, 12, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Verma, M.S.; So, J.H.; Mosadegh, B.; Keplinger, C.; Lee, B.; Khashai, F.; Lossner, E.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. Buckling Pneumatic Linear Actuators Inspired by Muscle. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1600055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.G.; Beomonte Zobel, P.; Durante, F.; Gaj, F. Development and testing of a grasper for NOTES powered by variable stiffness pneumatic actuation. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2017, 13, e1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Rosario Carvalho, A.D.; Karanth, N.P.; Desai, V. Characterization of pneumatic muscle actuators and their implementation on an elbow exoskeleton with a novel hinge design. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Wang, T.; Zhao, L. Design and Modelling of Multi-DOF Manipulator Driven by Hysteresis-Attenuated Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2002, 7, 6447–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.G.; Beomonte Zobel, P.; D’Ambrogio, W.; Durante, F. Design methodology for a novel bending pneumatic soft actuator for kinematically mirroring the shape of objects. Actuators 2020, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Piccolo, M.V.; Muscolo, G.G.; Ferraresi, C. Use of Pneumatic Artificial Muscles in a Passive Upper Body Exoskeleton. Mech. Mach. Sci. 2002, 106, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Do Rosario Carvalho, A.D.; Karanth, N.P.; Desai, V. Design and characterization of a pneumatic muscle actuator with novel end-fittings for medical assistive applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 112877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.G.; D’Ambrogio, W.; Durante, F. Development of a pneumatic soft actuator as a hand finger for a collaborative robot. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Mechatronics Systems and Control Engineering, ICMSCE 2018, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 February 2018; pp. 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- De Volder, M.; Moers, A.J.M.; Reynaerts, D. Fabrication and control of miniature McKibben actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 166, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, H.F. The characteristic of the McKibben artificial muscle. In The Application of External Power in Prosthetics and Orthotics; National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council, Eds.; Publisher: Washington, DC, USA, 1962; Publication 874, Appendix H; pp. 94–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, C.P.; Hannaford, B. Measurement and modelling of McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondu, B. Modelling of the McKibben artificial muscle: A review. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2012, 23, 225–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosi, J.; Biro, I.; Nemeth, J.; Cveticanin, L. Dynamic modeling of a pneumatic muscle actuator with two-direction motion. Mech. Mach. Theory 2015, 85, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.G.; Beomonte Zobel, P.; D’Ambrogio, W.; Durante, F.; Raparelli, T. An analytical formula for designing McKibben pneumatic muscles. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 320–337. [Google Scholar]
- Antonelli, M.G.; Beomonte Zobel, P.; Durante, F.; Raparelli, T. Numerical modelling and experimental validation of a McKibben pneumatic muscle actuator. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, K.; Suzumori, K.; Wakimoto, S. A method of designing and fabricating McKibben muscles driven by 7MPa hydraulics. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2012, 6, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, T.; Noritsugu, Y. Motion analysis of McKibben type pneumatic rubber artificial muscle with finite element method. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2014, 8, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzedzickis, A.; Subačiuté-Žemaitié, J.; Šutinys, E.; Samukaité-Bubniené, U.; Bučinskas, V. Advanced Applications of Industrial Robotics: New Trends and Possibilities. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://sps.honeywell.com/it/it/products/advanced-sensing-technologies/healthcare-sensing/board-mount-pressure-sensors/basic-abp-series (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Available online: https://www.te.com/usa-en/product-CAT-FSE0006.html?q=FX29&source=header (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Tomori, H.; Hiyoshi, K. Control of Pneumatic Artificial Muscles Using Local Cyclic Inputs and Genetic Algorithm. Actuators 2018, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, F.; Beomonte Zobel, P.; Raparelli, T. Two-Dof Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot Driven by Straight Fibers Pneumatic Muscles. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takosoglu, J.E.; Laski, P.A.; Blasiak, S.; Bracha, G.; Pietrala, D. Determining the Static Characteristics of Pneumatic Muscles. Meas. Control 2016, 49, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumit, M.D.; Pardoel, S. Dynamic contraction behaviour of pneumatic artificial muscle. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 91, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Gai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Y. A contraction length feedback method for the McKibben pneumatic artificial muscle. Sens. Actuators A. Phys. 2022, 334, 113321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, S.; Ding, M.; Kurita, Y.; Ueda, J.; Ogasawara, T. Flexible Sensor for McKibben Pneumatic Artificial Muscle Actuator. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2009, 3, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T.; Fujimoto, S.; Akagi, T.; Kobayashi, W. Development of Outer Diameter Sensor for Position Control of McKibben Artificial Actuator Using Hall-effect Sensor. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2020, 9, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagia, T.; Dohtaa, S.; Kenmotsua, Y.; Zhaob, F.; Yonedac, M. Development of smart inner diameter sensor for position control of Mckibben artificial muscle. Procedia Eng. 2012, 41, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tiziani, L.O.; Hammond, F.L., III. Optical Sensor-Embedded Pneumatic Artificial Muscle for Position and Force Estimation. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felt, W.; Chin, K.Y.; Remy, C.D. Contraction Sensing with Smart Braid McKibben Muscles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erin, O.; Pol, N.; Valle, L.; Park, Y.L. Design of a bio-inspired pneumatic artificial muscle with self-Contained sensing. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 2115–2119. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, V.A.; Hirai, S. Measuring mcKibben actuator shrinkage using fiber sensor. In Proceedings of the 24th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Kobe, Japan, 31 August–4 September 2015; pp. 628–633. [Google Scholar]
- Felt, W.; Remy, C.D. Smart Braid: Air Muscles that Measure Force and Displacement. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2014), Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 2821–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, J.; Loenders, B.; Vos, A.; Schoevaerdts, L.; Poorten, E.V. Integrated Capacitance Sensing for Miniature Artificial Muscle Actuators. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, R.; Watanabe, S.; Shimizu, K.; Shintake, J. Self-Sensing McKibben Artificial Muscles Embedded with Dielectric Elastomer Sensor. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 6274–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.G.; Zobel, P.B.; Durante, F.; Zeer, M. Modeling-Based EMG Signal (MBES) Classifier for Robotic Remote-Control Purposes. Actuators 2022, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CC1612 | CC2016 | CC2620 | PPC20 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer tube | ||||
| External diameter | 16 | 20 | 26 | 28 |
| Thickness | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Length | 200 | 175 | 205 | 500 |
| Aluminum diameter | / | 18 | 24 | / |
| Disk diameter | / | / | / | 31 |
| Disk thickness | / | / | / | 2 |
| Inner tube | ||||
| External diameter | 12 | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| Thickness | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1.5 |
| Length | 188 | 218 | 122 | 550 |
| Aluminum diameter | / | 15 | 19 | / |
| Disk diameter | / | / | / | 20 |
| Disk thickness | / | / | / | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonelli, M.G.; Beomonte Zobel, P.; De Marcellis, A.; Palange, E. Design and Characterization of a Mckibben Pneumatic Muscle Prototype with an Embedded Capacitive Length Transducer. Machines 2022, 10, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121156
Antonelli MG, Beomonte Zobel P, De Marcellis A, Palange E. Design and Characterization of a Mckibben Pneumatic Muscle Prototype with an Embedded Capacitive Length Transducer. Machines. 2022; 10(12):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121156
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonelli, Michele Gabrio, Pierluigi Beomonte Zobel, Andrea De Marcellis, and Elia Palange. 2022. "Design and Characterization of a Mckibben Pneumatic Muscle Prototype with an Embedded Capacitive Length Transducer" Machines 10, no. 12: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121156
APA StyleAntonelli, M. G., Beomonte Zobel, P., De Marcellis, A., & Palange, E. (2022). Design and Characterization of a Mckibben Pneumatic Muscle Prototype with an Embedded Capacitive Length Transducer. Machines, 10(12), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121156








