Abstract
This paper presents hybrid sensorless speed tracking by an indirect field-oriented control (IFOC) for an induction motor (IM). The sensorless model is based on an improved virtual estimation topology model to predict the virtual speed and flux of the IM using stator current components. The hybrid sensorless model, defined as a modification of voltage with a rotor flux-oriented current model, was also implemented with proportional-integral (PI) control for comparison with the conventional voltage model (CVM). The suggested adaptive mechanism for PI control in the hybrid estimator was able to compensate for the back-EMF error from the rotor flux-oriented current model into the voltage model and change the air gap flux of the IM. An accurate rotor flux position was estimated and used to estimate the speed with low speed error. This IFOC model, with various speed change references, was tested in a simulation environment by using the MATLAB/Simulink program. The proposed hybrid estimator was tested in two different EV operations, which were reverse and forward operations. The effectiveness of the proposed estimator was analyzed for its transient and steady-state performances based on settling time, recovery time and the overshoot and speed error percentages. All the results were in good agreement in terms of the stability of the speed and current controller with minimum speed error obtained, where the average errors were 0.08% and 0.16% for high speed and lower speed, respectively.
1. Introduction
A high-performance induction motor (IM) requires various special characteristics, such as robustness against parameter variation, a stable system during operation, faster load disturbance rejection and also faster dynamic responses. The use of an IM in industrial applications is generally based on its main advantages, which are high reliability and a wide range of speed [1]. Due to its simple construction without magnets on its rotors, the trend of IM application will increase in the coming years because of its low cost.
The first electric vehicle (EV) was built in 1839, but the IM application in the transportation industry has been gaining acceptability in recent years [2]. EVs will be a major transportation mechanism due to the increase in concerns over global warming and due to energy efficiency plans that have led car manufacturers to deploy more IMs in EVs, compared with DC motors or permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs). IMs in the EV industry are used over other types of motors because of the possibility of regenerative braking in the four-quadrant operation [3].
A key condition toward a wider application of the IM is vector control, which is mostly used to control the IM in advance with a sensorless mode. The essential feature of vector control is the ability to have decoupled control between the flux and the torque generated by the stator currents with direct and indirect field-oriented control methods, which reflect the motor’s speed response [4]. Therefore, to realize the sensorless mode, an estimation technique could be used to estimate the speed of the IM, which would eliminate the use of a speed sensor and consequently reduce the maintenance cost, hence making the EV a smart system. Various estimation techniques have been developed to obtain the minimum speed error and reduce the computational burden in the estimating processes, such as the current model, voltage model, fuzzy logic and Kalman filter [5,6,7,8]. These techniques have excellent performance depending on how they are applied, but in some cases the speed estimation is still unsatisfactory due to the large speed error produced.
Vector control for motor operation is normally achieved by using a proportional-integral (PI) controller either for the speed or current control. As discussed in [9,10,11], a PI controller is used to control the speed with a single estimator of speed and without any adaptation mechanism. However, the weakness of a PI controller is that it cannot compromise with unknown motor parameters, such as stator resistance and inductance, if they are not being considered in the input parameters, which currently are obtained from the speed input sensor. These parameters vary during operation due to temperature changes and the magnetic saturation effect, which deteriorate the IM performance and make it operate at low efficiency [12]. The issue was resolved in [13,14,15], where a tuning method (PI tuner) was used to tune the controller’s response. The tuning process focused on the variable speed operation without considering the load disturbance rejection. This could harm the IM, where the cogging torque reduces the IM performance and makes it operate below the base speed [16]. Various tuning methods have been developed by introducing currently trending methods, such as fuzzy logic, Kalman filters, neural networks and neuro-fuzzy, in order to have good load disturbance rejection [17,18,19,20,21,22]. However, due to complexities, few have been applied in IM vector control. These complexities give a computational burden to the control system, which causes the overlapping loop problem between the controllers [23].
In this paper, an indirect field-oriented control (IFOC) was adopted with a sensorless model and with the PI speed and current controllers to control the speed and torque of the IM. Here, the sensorless model took the function of the speed sensor. The current and voltage coming to the IM became the inputs of the speed estimation model, which were based on the parameters of the IM. A pre-compensating method was introduced in the current controller to balance the control operation at a wide range of speed so that the ripples on the current response could be reduced. In order to resolve the load disturbance rejection, a hybrid topology based on the modified voltage model and the rotor flux-oriented current model was applied to estimate the feedback speed by the stator voltage and current components, which responded according to the load torque disturbances. The results obtained were analyzed for controller stability to seek the minimum speed error.
This paper is organized as follows: In Section 2 and Section 3, the dynamic modeling of the IM and the concept of field-oriented control (FOC) are described, respectively. In Section 4, the proposed hybrid estimator with the stator flux control as the adaptive mechanism is explained. In Section 5, the stability of the speed and current controllers are determined. In Section 6, the simulation results are analyzed, followed by the performance evaluation and conclusion.
2. Dynamic Modeling of Induction Motor
The space vector method presented in Figure 1 describes the mathematical modeling of the IM. Based on the vector method, s and r are stator and rotor circuits, respectively, and e refers to the synchronously rotating frame, while a, b and c are the axes of the phase system and d and q are direct and quadrature axes with respect to the stator components, respectively. The field angle θe is extracted from the time integral of the angular frequency ωe. By subtracting the slip frequency ωsl from the field angle, the rotor flux position θr can be calculated as:
θr = θe − θsl
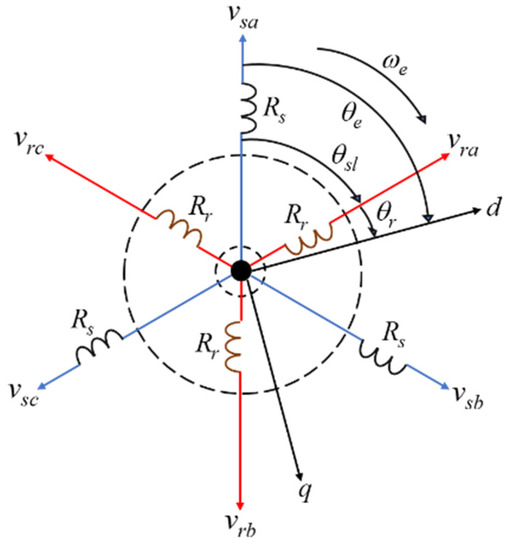
Figure 1.
Space vector of ideal three-phase induction motor.
The state-space modeling of the IM is given in a synchronous frame, such that:
where x, u and y are state vector, input vector and output vector, respectively. Meanwhile, A, B and C are the matrix system.
where i, v and Ψ are current, voltage and flux, respectively, on the d–q axes with respect to their frames.
where , , and . Meanwhile, Tr is rotor time constant and σ is leakage coefficient, while R and L are resistance and inductance, respectively, with respect to their frames and Lm is the magnetizing inductance. The state-space modeling of the IM creates ease in interpreting the stationary current and voltage transformation into the d–q axes. This was recreated based on the balanced condition represented by the space vector. Therefore, this model was necessary for modeling the sensorless model based on the voltage, current and motor parameters in order to create a virtual speed value.
3. Indirect Field-Oriented Control
Indirect field-oriented control is a vector control with high acceptability in a high-performance drive system. The principle is essentially based on the decoupling between flux and torque through controlling the stator current component, as shown in Figure 2.
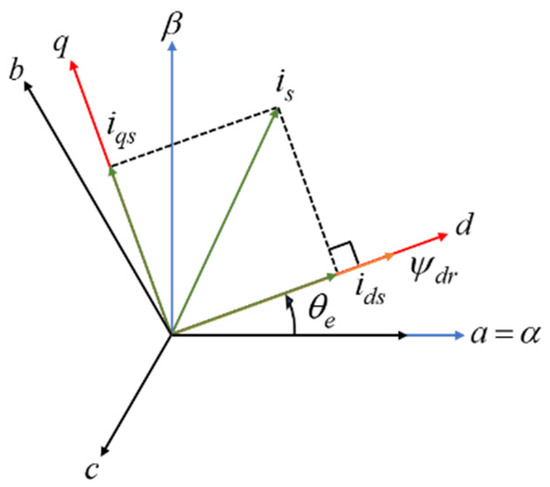
Figure 2.
Phasor diagram of FOC’s drive system.
Based on the dynamic model of the IM, the three phase quantities are transformed into two coordinates on the d–q axes, which are the flux and torque components aligned on the q–axis and d–axis, respectively. To realize this condition, the rotor flux on the axis is set to be zero, while the d–axis reaches the nominal value of the magnetizing flux. The behavior of the drive system subjected to the rotor flux-oriented control is depicted in Figure 3.
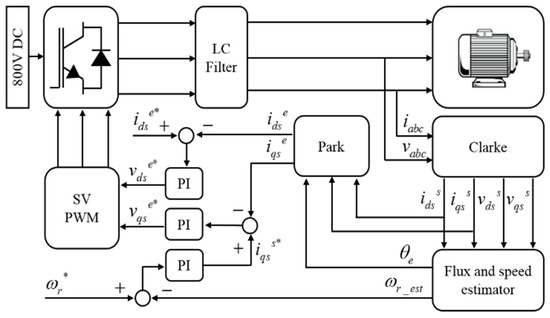
Figure 3.
Indirect field-oriented control of IM.
With zero flux on the q–axis, the electromagnetic torque reduces to:
where p is the number of poles. The angular frequency of the rotor flux is given by:
where the slip frequency is obtained from the q–axis stator current, such that:
The estimated rotor flux linkage can be calculated as:
Thus, based on Equation (1), the angular position is given by:
From Figure 3, the use of a conventional voltage model’s (CVM) estimator could give a large back-EMF error, since the frequency and magnitude could be different in phase. By forming the suggested hybrid model given in the next section, the phase shift could be reduced by compensating for the back-EMF error in the CVM so that a nearly zero back-EMF error can be achieved.
4. Proposed Hybrid Flux and Speed Estimator with Speed Controller
The proposed model of the hybrid sensorless estimator is illustrated in Figure 4, where it works together with the conventional PI speed controller based on the virtual speed generation shown in Figure 3 in order to gain the minimum rotor speed error. The combination between the modified voltage model and the rotor flux-oriented current model was to give the least back-EMF error in estimating the rotor position of the IM. An adaptive PI control mechanism was added into the flux estimator of the back EMF for error generation. In this mode, the voltage model acted as the reference model, while the rotor flux-oriented current model acted as the adjustable model, to form a new model reference in this adaptive system topology. This system formed a hybrid and interacted with the speed estimator to estimate the rotor speed feedback being fed to the speed controller.
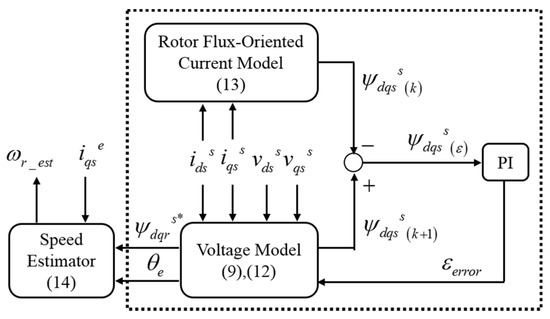
Figure 4.
Block diagram of flux and speed estimator.
4.1. Sensorless Flux Estimator
The integration of the back EMF into the flux estimator was to estimate in advance the rotor flux with respect to the synchronously rotating frame for rotor position production. Two blocks, which were the voltage model and the rotor flux-oriented current model, were used to synthesize the rotor flux with respect to the stationary frame for the back-EMF error compensation. The plant was depicted as the flux estimator and can be expressed as:
where , and k = rotor flux at time kth.
The stator flux is obtained by the stator reference current and voltage, such that:
The back-EMF error in Equation (9) is given as:
where G is a positive constant of proportional gain kp and integral gain ki. Thus, the adaptation mechanism law becomes:
The extraction of rotor flux from the stator flux is by using:
As in the rotor flux-oriented current model, the stator flux is obtained by the stator current reference, and (6) can be expressed as:
where T and T−1 are Park and inverse Park transformations, respectively. The stator flux in (13) acts as the feedback to the stator flux controller, which gives the compensated back-EMF error at a reduced level.
4.2. Sensorless Speed Estimator
The speed estimator in Figure 4 is another key building block of the proposed scheme. Angular frequency was used to determine the estimated speed. By subtracting slip frequency from angular frequency, as in Equation (4), the rotor speed can be determined. In the case of a pole machine, the slip speed as seen from the rotor frame is equal to and the rotor speed can be expressed as:
The slip speed in (14) is taken into account to reduce the rotor losses in the air gap space. Through this consideration, the IM can give a high output of mechanical power. Thus, the efficiency of the IM is increased directly proportional to the input power.
5. Controller’s Stability on Proposed Hybrid Estimator for IFOC
In a conventional control method, a closed-loop system is where the output speed of the IM is fed back to the speed controller in order to obtain the transfer function. However, for this stability test, the closed-loop system used a current control, which was included for the transfer function derivation. Both stability analyses were tested when the new plant of the controllers was embedded with the hybrid estimator system for checking the new locations of the pole and zero.
5.1. Inner Loop Current Control
It was important to ensure that the rotor flux remained constant so that a linear structure could be achieved. The inner loop of the plant system needed to be considered to fulfill the closed-loop transfer function. Therefore, the block diagram in Figure 5 was obtained after several calculations based on the IM circuit analysis with respect to the d–axis of the current controller.
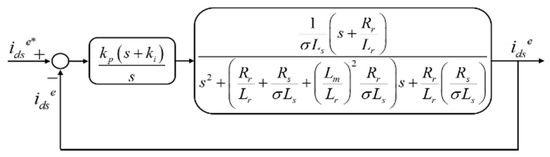
Figure 5.
Simplified block diagram of d–axis current controller.
A better understanding can be obtained based on Figure 6, where the closed-loop transfer function was interpreted into the pole-zero map plot. The closed-loop transfer function consisted of two poles, labeled as “X”, and one zero, labeled as “O”, that were plotted on the left-hand side of the pole-zero map. This validated that the closed-loop transfer function of the d–axis current controller was in a stable system.
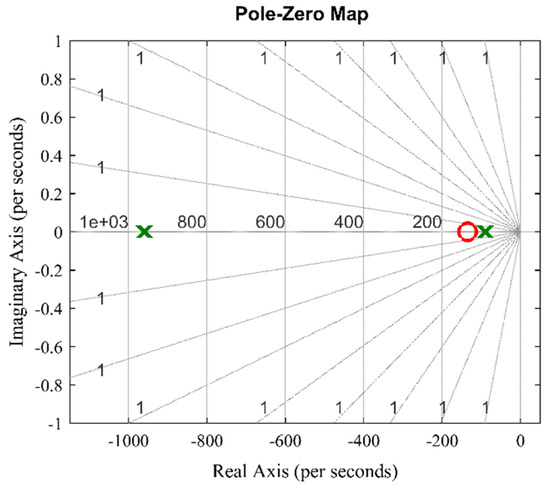
Figure 6.
Pole-zero plot of closed-loop transfer function of d–axis current controller.
The same implementation was also applied on the axis, where the slip was held at a value that ensured that the q–axis rotor flux was zero. The closed-loop transfer function for the axis current controller is shown in Figure 7.
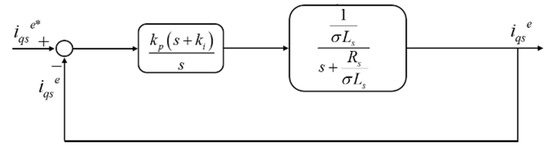
Figure 7.
Simplified block diagram of q–axis current controller.
The obtained closed-loop transfer function stability is shown in Figure 8. As observed, there were two poles and one zero on the left-hand side of the pole-zero map. This confirmed that the controller fulfilled the stability criterion, which meant that it was in a stable system.
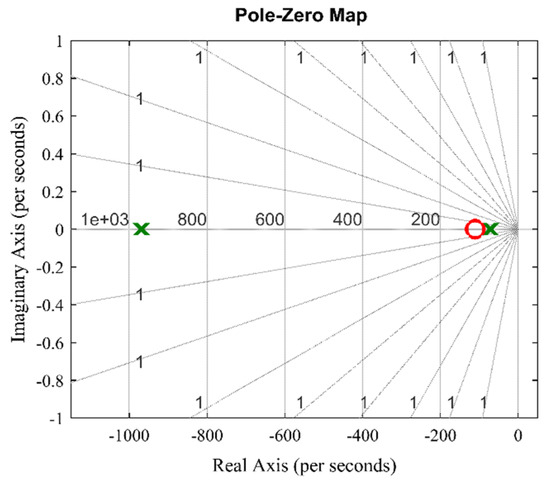
Figure 8.
Pole-zero plot of closed-loop transfer function of q–axis current controller.
5.2. Outer Loop Speed Control
A current controller with a closed-loop time constant is ten times smaller than with a rotor or mechanical time constant. Under this condition, the current controller acts so rapidly that it can be neglected for practical purposes. The speed controller is designed based on a separately excited DC motor.
The control structure of the IM is shown in Figure 9 with the load torque, motor inertia and friction factors. All these parameters could affect the PI’s speed control response. Initially, the load torque was assumed to be zero. Therefore, the general closed-loop transfer function for the speed controller can be realized with the aid of the second-order system, as in [24], such that:
where is the natural frequency and ξ is the damping ratio. The overshoot percentage of the system is given as:
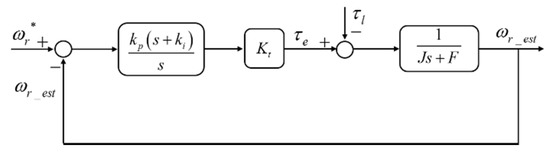
Figure 9.
Simplified block diagram of speed controller.
In order to have an overshoot between 2% and 5% of the speed response, the value of ξ and must be greater than 0.7 and 1.8 rad/s, respectively. Based on Equation (16), ξ can be calculated as:
It can be defined that the settling is almost 98% of the final response value and the duration is approximately four times the time constant of the signal. When the time constant of the second-order control system is , the steady-state settling time can be given as:
Referring to the response of the closed-loop IM model under normal condition testing, the values of settling time and overshoot are 0.278 s and 0.025%, respectively. Substituting into (17), the value of ξ is 0.9352. Then, the value of is obtained based on (18) at 15.3861 rad/s.
Substituting the values of ξ and into (15), the general closed-loop transfer function for the speed controller can be expressed as:
Based on the second-order closed-loop transfer function above, the stability of the system can be analyzed by solving the poles of the transfer function. It consists of two poles, labeled as “X”, which are −14.3891 + 5.4485i and −14.3891 − 5.4485i, with a negative real part and no positive pole, as shown in Figure 10.
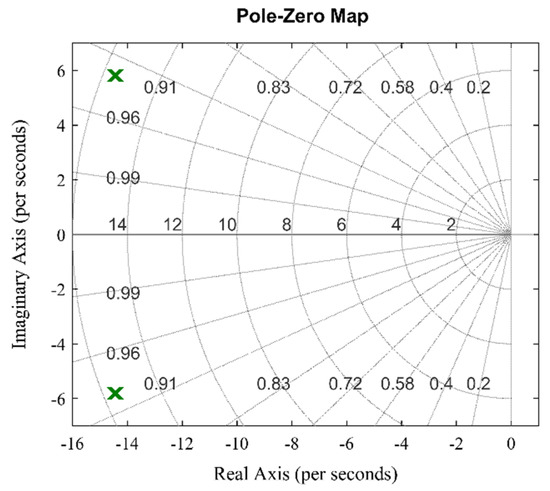
Figure 10.
Pole-zero plot of closed-loop transfer function of speed controller.
6. Simulation Results
6.1. IM Performance under Parameter Variation
6.1.1. Rotor Resistance Variation
The block diagram of the estimator, depicted in Figure 4, consists of the stator flux control obtained from the rotor position by compensating the back-EMF error. Since rotor position is related to speed, which is affected by rotor time constant, it depends on rotor resistance, which varies according to temperature during the operation. To test the drive performance of the stator flux control in the suggested hybrid estimator, rotor resistance was varied by 50% of the nominal value with an increment of 25%. Figure 11a,b show the effect of rotor resistance variation on the rotor speed of two different estimators in two different modes. Both HYB and CVM estimators showed consistent performance in forward and reverse operations, with the results obtained confirming the estimator’s functions. The speed characteristics of the two estimators are summarized in Table 1. The two estimators without parameter uncertainty produced similar performances. However, compared with these two estimators, the conventional voltage model, which is not discussed here, took a longer time to track the reference rotor speed (blue line). When the hybrid estimator was applied, there was a shorter tracking time, but it was not remarkable.
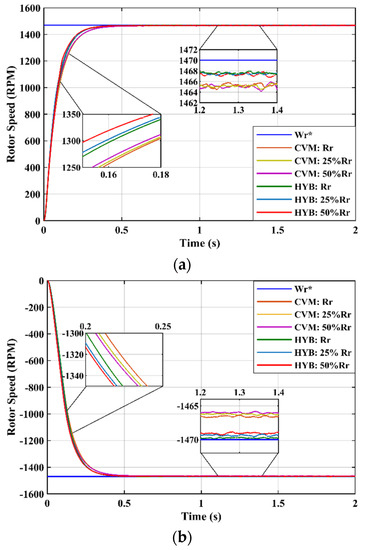
Figure 11.
Rotor speed response against rotor resistance variation: (a) in forward operation and (b) in reverse operation.

Table 1.
Rotor speed performance under rotor resistance variation.
Based on the rotor speed obtained for the proposed hybrid sensorless estimator, the stability response of the rotor flux against rotor resistance variation is shown in forward operation in Figure 12. As can be observed, the rotor flux response consisted of a few overshoots at the beginning due to the variation of 25% Rr and 50% Rr. However, the value was in an acceptable range of <20% overshoot with a 0.46 damping ratio. This confirms that the proposed hybrid estimation possesses a good dynamic response against parameter variation during its operation.
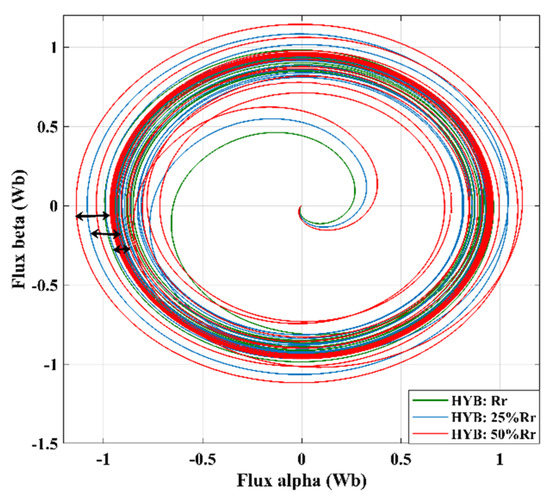
Figure 12.
Alpha-beta rotor flux response against rotor resistance variation.
For more details, Table 2 summarizes the rotor flux response. It can be seen that the response is more superior without rotor resistance variation. Hence, with the proposed stator flux control as an adaptive mechanism, the response can be stable against rotor resistance variation with optimum overshoot and high capability of tracking rotor speed.

Table 2.
Rotor flux performance under rotor resistance variation.
As recorded (Table 1), it can be concluded from the values of speed error that the hybrid estimator improved motor speed performance by compensating the back-EMF error into the CVM via controlling the stator flux of the IM. A minimum error was achieved with respect to reference speed with no oscillations.
6.1.2. Stator Resistance Variation
The voltage model consists of back-EMF error compensation, as in (9), and it is indicated that stator resistance variation should be taken into account in the study case. As mentioned above, the resistance varies due to temperature during motor operation. It could result in back-EMF error changes, consequently changing the speed’s estimated value. So, stator resistance was varied as with rotor resistance in Section 6.1.1 previously. As shown in Figure 13a,b, the speed estimation response operated at minimum error for both forward and reverse operations. The proposed estimator also gave excellent dynamic performance under stator resistance variation with a shorter time to track the reference rotor speed, as tabulated in Table 3. Clearly, the speed estimation efficiently tracked the reference with a speed error range of below 10 rpm and an acceptable range of <20% overshoot. Stator resistance variation had the least effect on IM response compared with rotor resistance variation due to the exact amount of back-EMF error compensation by the adaptation mechanism of stator flux control at the stator side.
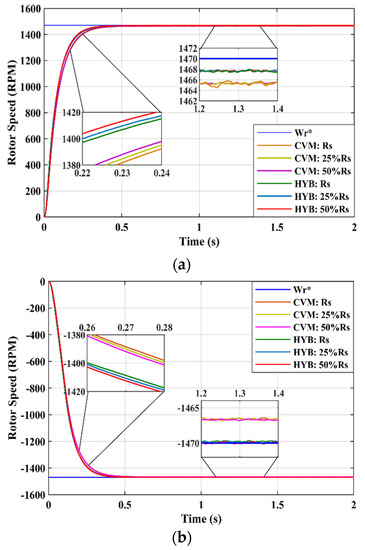
Figure 13.
Rotor speed response against stator resistance variation: (a) in forward operation and (b) in reverse operation.

Table 3.
Rotor speed performance under stator resistance variation.
6.1.3. Mutual Inductance Variation
When involving temperature, the mutual inductance parameter was also taken into account in this study case. The values of stator and rotor inductance parameters in this research were the same. The variation in inductance also affect the mutual inductance of the IM. Several studies on inductance against temperature have been conducted, such as in [25], which concluded that inductance remains functional in a high temperature and there is no temperature dependence. However, [26] stated that a 1% change in resistance produced by 2.54 °C corresponds to a 0.0076% increase in inductance. In this research, mutual inductance was varied by 25% and 50% of the nominal value. This means that the temperature was very high during motor operation. As shown in Figure 14a,b, the effect of mutual inductance gave almost the same speed response in both forward and reverse operations either for the CVM or the HYB. Referring to Table 4, the HYB estimator could improve the dynamic performance of the IM compared with the CVM, as the average speed error was below 0.16%. This proves that the proposed estimator works effectively against parameter variation.
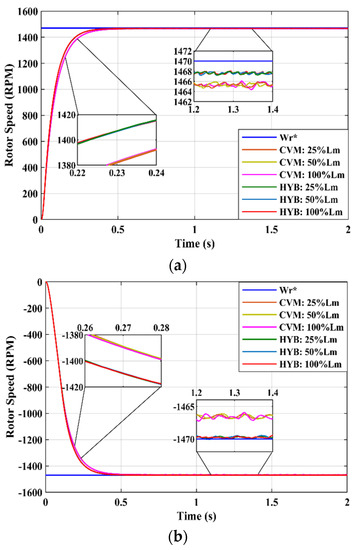
Figure 14.
Rotor speed response against mutual inductance variation: (a) in forward operation and (b) in reverse operation.

Table 4.
Rotor speed performance under mutual inductance variation.
6.2. IM Performance under Variable Speed Trajectory
The derivative of rotor position with time was then applied to determine the rotor speed during driving, since the feedback of the speed estimator to the reference speed determines the speed error of the control system. Figure 15a,b show the speed tracking response with respect to the speed reference in order to seek the speed tracking capability. The reference speed was given in the trapezoidal signal input with a constant value during the motor’s starting operation in order to see the transient behavior. The variable speed trajectory was applied in forward and reverse motoring operations with the proposed hybrid estimator of the stator flux control.
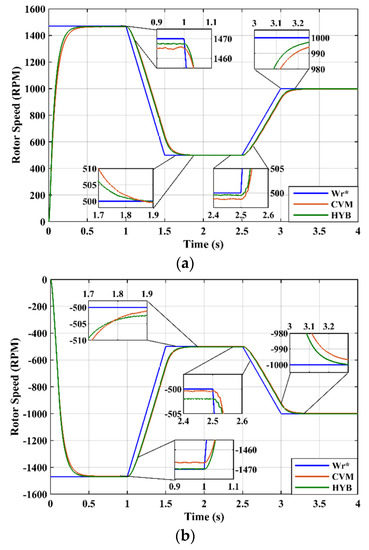
Figure 15.
Rotor speed response under variable speed trajectory: (a) in forward operation and (b) in reverse operation.
Using accurate rotor position tracking, the speed error was minimized nearly to zero. A good tracking capability was obtained in both reverse and forward operations with no overshoots at the starting of the IM. As can be seen between 1.5 and 3 s, the speed errors were recorded in Table 5 from the reference values at 0.082% and 0.132%, respectively. Meanwhile, in the existing voltage model estimator, it contributed about 0.243% and 0.285% errors for both speed trajectories. With the 0.161% and 0.153% margin errors, the hybrid estimator has shown an excellent performance in estimating speeds using the stator flux control under a variable speed trajectory. This shows that the back-EMF error was completely compensated into the voltage model in order to create the correct position of the rotor.

Table 5.
Rotor speed performance under variable speed trajectory.
The stability of the speed controller’s response can be seen in Figure 16a–c, which present the forward motoring operation. In Figure 16a, the spiral graph shows a highly stable response during full-speed operation without any ripples. Meanwhile, as shown in Figure 16b, at a minimum low speed of 500 rpm, the current faced a few ripples with a stable response. This happened due to the integration of very small signals of angular frequency that made the rotor position shifted a few degrees. When reaching 1000 rpm, as shown in Figure 16c, the spiral response of the current had fewer ripples compared with the response at a lower speed. However, the speed estimation response was within the boundary of the speed reference’s range and a high speed-tracking capability was obtained with accurate rotor position estimation.
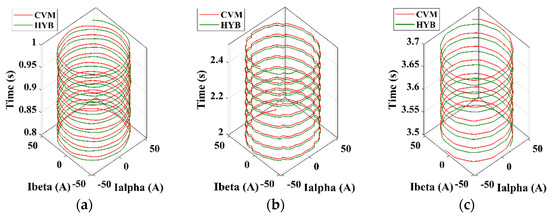
Figure 16.
Alpha-beta stator current response: (a) at 1470 rpm, (b) at 500 rpm and (c) at 1000 rpm.
6.3. IM Performance at Very Low Speed under Regenerative Braking and Zero-Speed Conditions
In order to behave like in a real EV operation, the four-quadrant operation needed to be fulfilled. In the above section, forward and reverse motoring had been discussed, and is not repeated here. Forward braking and reverse braking are under the regenerative mode and could be realized by slowing down the reference speed or applying a mechanical load to the IM to reduce the speed to 0 rpm. In this research, a mechanical load was applied at τ = 20 Nm to show the IM braking and operating at a very low speed. In addition, a mechanical load was also applied at τ = 40 Nm to show the IM braking until the steady-state zero-speed condition. Figure 17a,b show the response of braking in two different operations. As can be seen, the IM operated at a very low speed by following the reference speed at 100 rpm. At time τ = 1.5 s, a mechanical load was applied to show the braking system slowing down the IM until the extra-low speed of 50 rpm and zero-speed condition at 0 rpm. As shown in Table 6, the speed error obtained was less than 1 rpm for the proposed HYB estimator compared with the speed error for the CVM, which was more than 1 rpm at zero speed. This shows that the speed tracking capability successfully reduced speed estimation errors. This confirms that the proposed HYB is able to improve speed tracking capability and operate the IM under very-low-speed conditions.
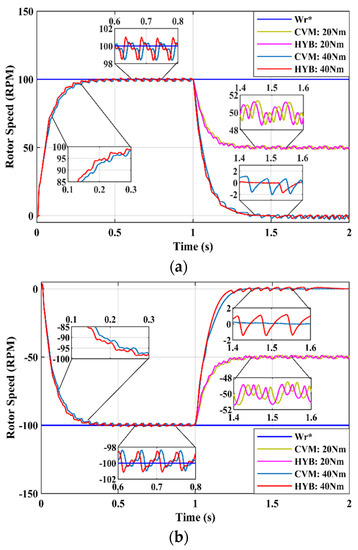
Figure 17.
Rotor speed response at very low speed in regenerative braking: (a) in forward operation and (b) in reverse operation.

Table 6.
Rotor speed performance at very low speed in regenerative braking.
This also indicates that the HYB estimator was able to operate under zero-speed conditions, where its speed estimation had the least mismatch compared with the CVM in tracking the actual zero speed. Figure 18 shows the speed estimation by the HYB, as well as the speed estimation error of under 2 rpm, approaching zero with accurate flux estimation. Furthermore, the results confirmed that the rotor flux position was at accurate reference speed, while not losing stability in very-low-speed operation. This satisfies the supremacy of the HYB’s flux estimation in extracting accurate speed estimation under very-low-speed and zero-speed conditions.
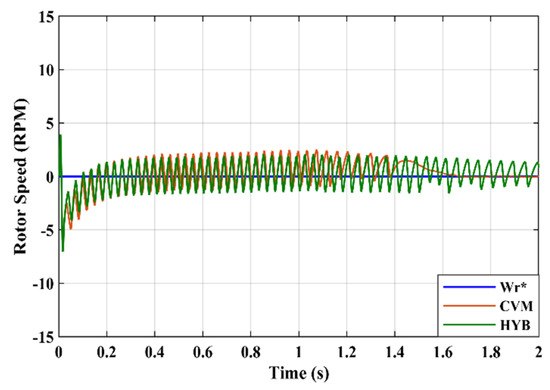
Figure 18.
Rotor speed response at zero speed condition.
6.4. IM Performance under Load Torque Disturbances
Since speed and torque are related to each other, a justification can be made under the load torque disturbances, as presented in Figure 19a and 19b for the forward and reverse operations, respectively, that torque does not give any effect to the controller. Torque disturbances were set up at times t = 0.7 s, 1.3 s and 2 s with torque values of 50 Nm, 75 Nm and 100 Nm, respectively. As depicted in Figure 19, there was a quick convergence in the speed response after the load disturbances were rejected. The quality of estimation also can be seen in the speed errors, which were relatively low as expected. The speed estimation response tracked the constant reference speed in spite of load torque disturbances both in forward and reverse operations. In addition, the dynamics of the IM was still maintained with no overshoots and oscillations during the starting of the IM.
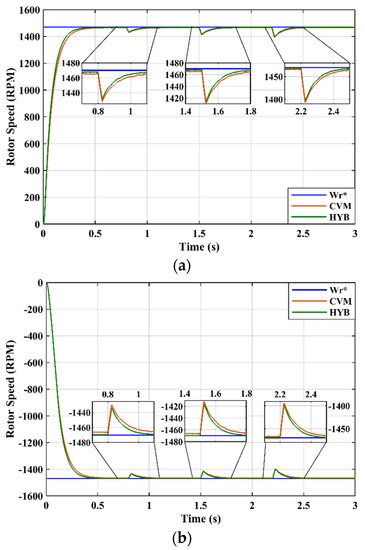
Figure 19.
Rotor speed response under load torque disturbances: (a) in forward operation and (b) in reverse operation.
Table 7 shows the summary of the torque load effect on the two estimators. Clearly, there were smaller speed drops in the hybrid (HYB) estimator compared with the CVM due to the compensated EMF error that changed the stator flux response. A faster recovery time was noticed in the proposed HYB estimator with an average of 0.078 s, which gave the IM an excellent performance. Additionally, there were no ripples on the speed response, which meant that the IM did not suffer from torque cogging.

Table 7.
Rotor speed performance under load torque disturbances.
7. Performance Evaluation Comparison
Based on the presented simulation result, the good dynamic performance of the IM was successfully achieved by the suggested model. The HYB estimator was effectively more robust than the CVM. The results demonstrate that the system exhibits good speed estimation accuracy under different conditions. This is supported by the stability effect given in Figure 16 for speed and current controllers, which are responsible for controlling the torque and speed of the IM. An evaluation table (Table 8) is provided to compare with the findings from previous research works, as examined in [27], to clarify the improvements that have been achieved with the suggested model.

Table 8.
Comparison table of FOC scheme with different estimation methods.
8. Conclusions
This paper presents a hybrid estimator model, along with the accuracy analysis of speed and torque tracking of an IFOC in estimating rotor flux position and speed to control the speed of the IM. The parameters of the IM are listed in the Appendix A, Table A1. In order to enhance speed control, a new model of hybrid estimator was proposed with stator flux control as the adaptation mechanism. The proposed estimator was investigated under four cases: (1) parameter sensitivity against rotor and stator resistance and mutual inductance variation, (2) variable speed trajectory, (3) very low speed in regenerative mode and zero-speed conditions and (4) variable load torque disturbances. The analyses showed that the three controllers were confirmed in a stable operation, as evidenced by the pole-zero maps.
All results proved that parameter sensitivity did not affect speed response. All speed responses also showed good tracking capability under variable speed trajectories and had faster recovery time under torque disturbances by using the hybrid estimator as compared with the conventional model. The proposed control scheme was successfully validated in various cases. The stability analysis and reported results showed excellent performance of the IM in both forward and reverse operations at a steady state and during transients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A.Z.; Data curation, M.S.S.; Formal analysis, M.S.S., S.A.Z. and S.Y.S.; Investigation, M.S.S., S.A.Z. and S.Y.S.; Methodology, S.A.Z. and S.Y.S.; Software, M.S.S., S.A.Z. and S.Y.S.; Supervision, S.A.Z., S.Y.S., H.-J.C. and M.Z.C.W.; Writing—original draft, M.S.S.; Writing—review and editing, S.A.Z., H.-J.C. and M.Z.C.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work was supported by Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM) and the UTHM Publisher’s Office via Publication Fund E15216, and Electronics Lab of Taiwan via Publication Fund 99AA6419.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their deepest appreciation to all those who provided them with the possibility of completing this paper. A special gratitude to the Advance Control on Power Converter Team at Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, who provided support in conducting this research. A special gratitude is also to the Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, as communication of this research is made possible through monetary assistance by Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia and the UTHM Publisher’s Office via Publication Fund E15216. A big thanks to the Power Electronic Lab Team at the National Taiwan University of Science and Technology (NTUST) and Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data (AIBIG) at Universiti Malaysia Kelantan (UMK) for the great collaboration in guiding this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Parameters of induction motor.
Table A1.
Parameters of induction motor.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| DC voltage | 800 V |
| Inverter frequency | 5 kHz |
| Rated power | 20 hp |
| Rated speed | 1500 rpm |
| Rated voltage | 400 V |
| Frequency | 50 Hz |
| Stator resistance | 0.6 Ω |
| Rotor resistance | 1.15 Ω |
| Stator inductance | 19.561 mH |
| Rotor inductance | 19.561 mH |
| Magnetizing inductance | 18.82 mH |
| Inertia | 0.2 kg.m2 |
| Number of pole pairs | 2 |
References
- Quintero-Manriquez, E.; Sanchez, E.N.; Felix, R.A. Real-time direct field-oriented and second order sliding mode controllers of induction motor for electric vehicles applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th System of Systems Engineering Conference (SoSE), San Antonio, TX, USA, 17–20 May 2015; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.C. The Rise & Fall of Electric Vehicles in 1828–1930: Lessons Learned [Scanning Our Past]. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarescu, N.-V.; Weinmann, M.; Zeh, S.; Musuroi, S.; Sorandaru, C. Optimum torque control algorithm for wide speed range and four quadrant operation of stator flux oriented induction machine drive without regenerative unit. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 September 2011; pp. 1773–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhano, S.A.; Bojoi, R.; Boglietti, A.; Rosu, S.G.; Griva, G. Maximum Efficiency per Torque Direct Flux Vector Control of Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 4415–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, D.; Stumper, J.-F.; Kennel, R. Sensorless Control of Synchronous Machines Based on Direct Speed and Position Estimation in Polar Stator-Current Coordinates. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 2503–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Stone, D.A. Parameter Estimation for Condition Monitoring of PMSM Stator Winding and Rotor Permanent Magnets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5902–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoussi, Z.; Boulghasoul, Z.; Elbacha, A.; Tajer, A. Fuzzy sliding mode observer based sensorless Indirect FOC for IM drives. In Proceedings of the 2015 Third World Conference on Complex Systems (WCCS), Marrakech, Morocco, 23–25 November 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonge, F.; D’Ippolito, F.; Sferlazza, A. Sensorless Control of Induction-Motor Drive Based on Robust Kalman Filter and Adaptive Speed Estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnefors, L.; Saarakkala, S.E.; Hinkkanen, M. Speed Control of Electrical Drives Using Classical Control Methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yi, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, T. Robust PI speed tracking control for PMSM system based on convex optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control Conference, Nanjing, China, 28–30 July 2014; pp. 4294–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, M.S. A stable adaptive flux observer for a very low speed-sensorless induction motor drives insensitive to stator resistance variations. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2011, 2, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsofyani, I.M.; Idris, N. A review on sensorless techniques for sustainable reliablity and efficient variable frequency drives of induction motors. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, M.; Gao, S. Fractional order PI speed control for permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. In Proceedings of the 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Shenyang, China, 29 June–4 July 2014; pp. 4681–4685. [Google Scholar]
- Sariyildiz, E.; Yu, H.; Ohnishi, K. A Practical Tuning Method for the Robust PID Controller with Velocity Feed-Back. Machines 2015, 3, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemmit, A.; Messalti, S.; Harrag, A. A new improved DTC of doubly fed induction machine using GA-based PI controller. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Orellana, A.; Juliet, J.; Cardenas, R. Model Predictive Torque Control for Torque Ripple Compensation in Variable-Speed PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4584–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shang, W.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Zeng, Y. Simulation of PMSM vector control based on a self-tuning fuzzy PI controller. In Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics (BMEI), Shenyang, China, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, O.; Omer, U. EKF-based self-regulation of an adaptive nonlinear PI speed controller for a DC motor. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 25, 4131–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lftisi, F.; George, G.; Aktaibi, A.; Butt, C.; Rahman, M.A. Artificial neural network based speed controller for induction motors. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016–42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016; pp. 2708–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Singh, S. Speed Control of DC Motor Using Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System Based PID Controller. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Power Energy, Environment and Intelligent Control (PEEIC), Greater Noida, India, 18–19 October 2019; pp. 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areed, F.G.; Haikal, A.Y.; Mohammed, R.H. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy control of an induction motor. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2010, 1, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Taher, S.A.; Munuz, D.V. Neural network-based sensorless direct power control of permanent magnet synchronous motor. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2016, 7, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepeeh, M.S.; Zulkifli, S.A.; Sim, S.Y.; Pathan, E. A Comprehensive Review of Field-Oriented Control in Sensorless Control Techniques for Electric Vehicle. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. (IREE) 2018, 13, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, N.; Talib, M.H.N.; Shah, N.S.M.; Abdullah, Q.; Ibrahim, Z.; Lazi, J.B.M.; Jidin, A. A Novel Self-Tuning Fuzzy Logic Controller Based Induction Motor Drive System: An Experimental Approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 68172–68184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumit, N.; Danoumbé, B.; Capraro, S.; Chatelon, J.-P.; Blanc-Mignon, M.-F.; Rousseau, J.-J. Temperature impact on inductance and resistance values of a coreless inductor (Cu/Al2O3). Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 72, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, S.; Ansari, M.A.; Saxena, A.K. Determination and comparison of temperature coefficients of standard inductors using different methods. In Proceedings of the 2012 Conference on Precision electromagnetic Measurements, Washington, DC, USA, 1–6 July 2012; pp. 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepeeh, M.S.; Zulkifli, S.A.; Sim, S.Y. A Simulation on Hybrid Speed and Flux Estimation-Based Back EMF Integration with Rotor Flux-Oriented Current Model. Int. Rev. Model. Simul. (IREMOS) 2020, 13, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Dybkowski, M. Stator-Current-Based MRAS Estimator for a Wide Range Speed-Sensorless Induction-Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xu, D.; Yu, Y.; Chen, W. Improved rotor flux estimation based on voltage model for sensorless field-oriented controlled induction motor drives. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 15–19 June 2008; pp. 1887–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.M.; Daya, J.F. MRAS speed estimator with fuzzy and PI stator resistance adaptation for sensorless induction motor drives using RT-lab. Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farasat, M.; Trzynadlowski, A.M.; Fadali, M.S. Efficiency improved sensorless control scheme for electric vehicle induction motors. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2014, 4, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Kumar, R.; Das, S. Sensorless Speed Control of Induction Motor Driven Electric Vehicle Using Model Reference Adaptive Controller. In Proceedings of the Energy Procedia 5th International Conference on Advances in Energy Research, (ICAER 2015), Mumbai, India, 15–17 December 2015; pp. 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, C.-M.; Uchida, T.; Hori, Y. MRAS-based speed sensorless control for induction motor drives using instantaneous reactive power. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON’01), Denver, CO, USA, 29 November–2 December 2001; pp. 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yujie, L.; Shaozhong, C. Model reference adaptive control system simulation of permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 19–20 December 2015; pp. 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhifu, W.; Jun, F.; Zhijian, S.; Qiang, S. Study on Speed Sensor-less Vector Control of Induction Motors Based on AMEsim-Matlab/Simulink Simulation. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Applied Energy (ICAE2016), Beijing, China, 8–11 October 2016; pp. 2378–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensiali, N.; Etien, E.; Benalia, N. Convergence analysis of back-EMF MRAS observers used in sensorless control of induction motor drives. Math. Comput. Simul. 2015, 115, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).