Design and Analysis of a Novel Double-Stator Double-Rotor Motor Drive System for In-Wheel Direct Drive of Electric Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
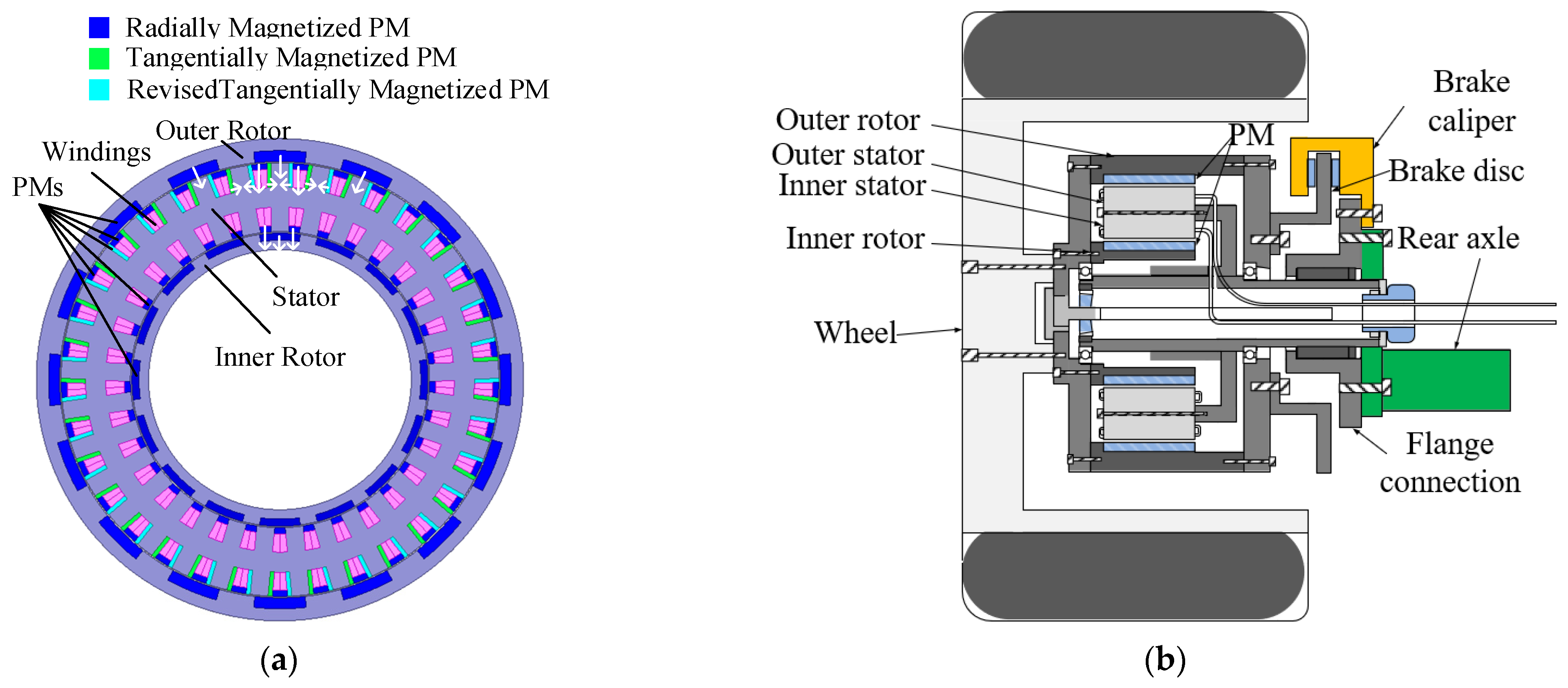
2. Basic Structure and Design Rules
2.1. Machine Topology Design of the DSDRM
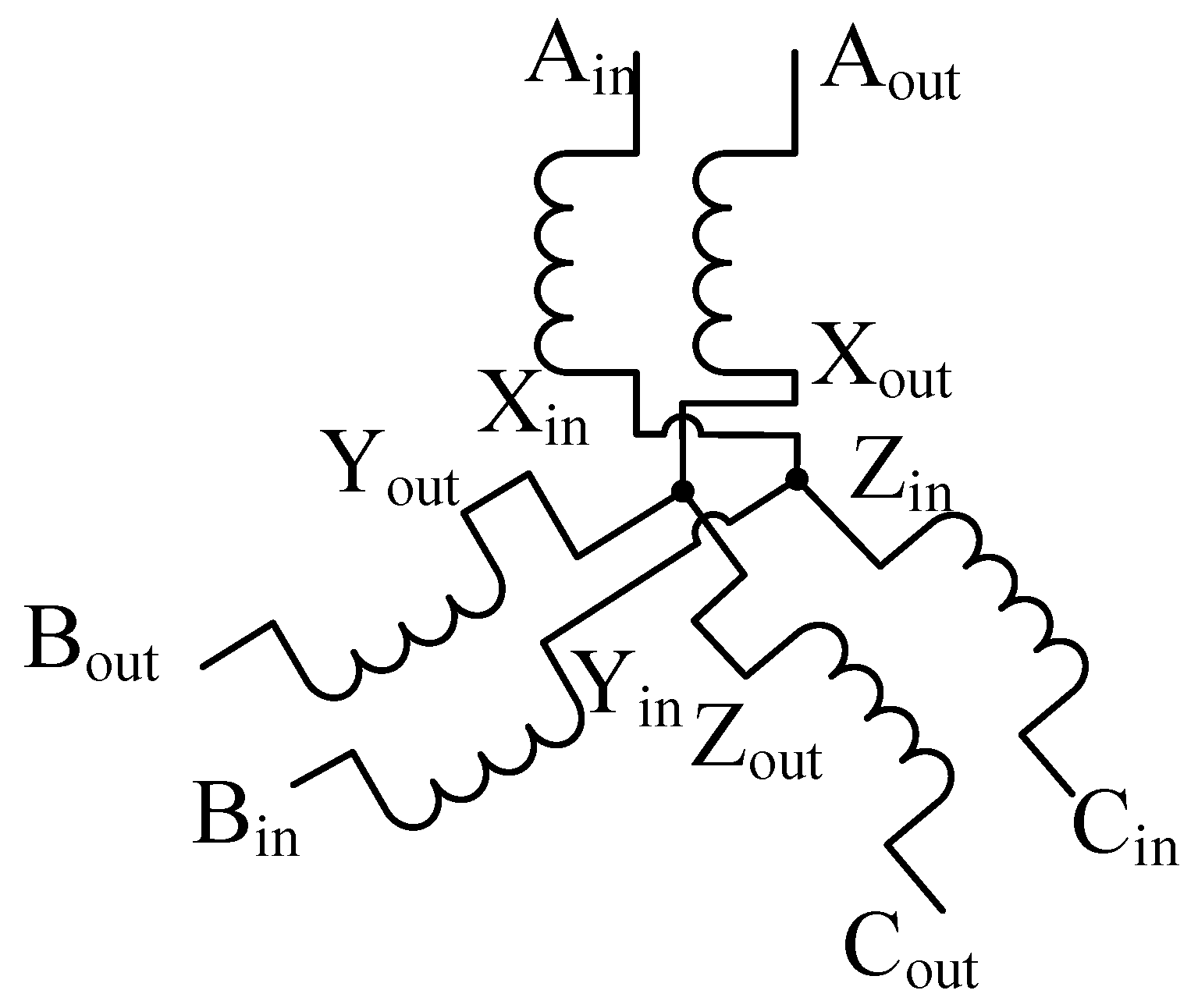
2.2. Operating Principle of the DSDRM
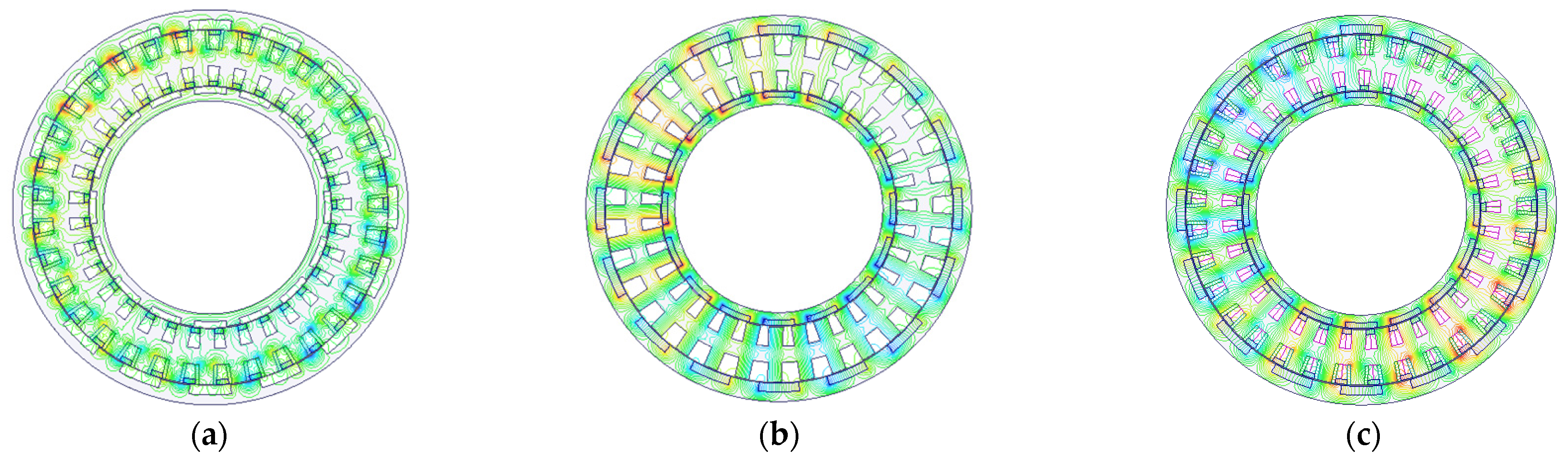
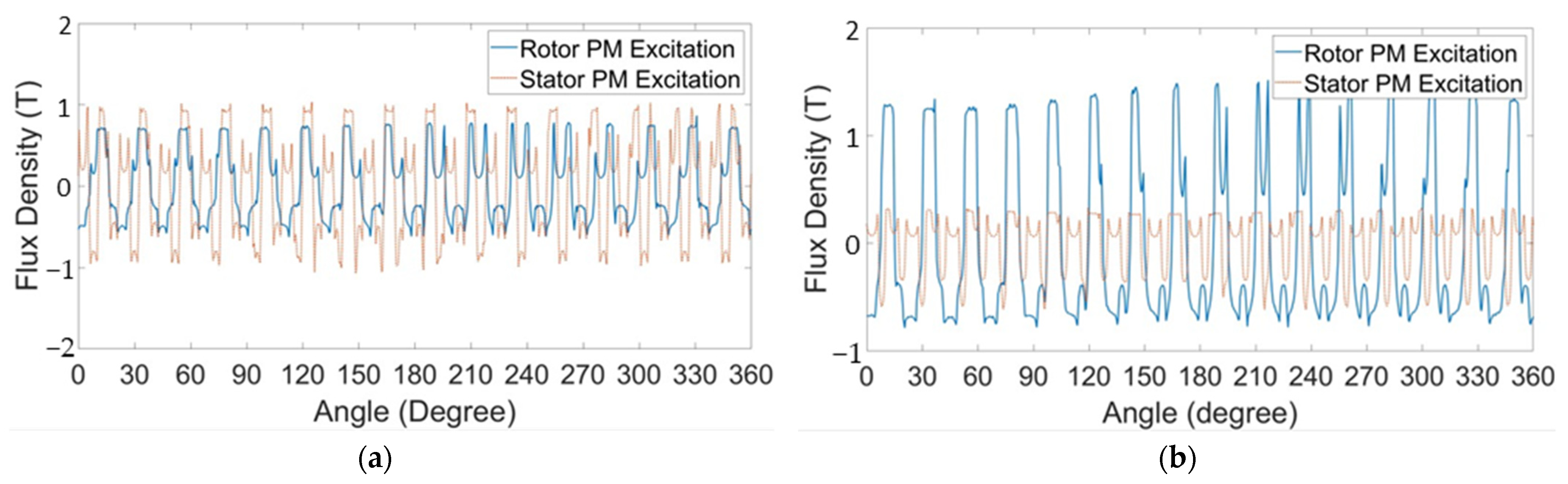
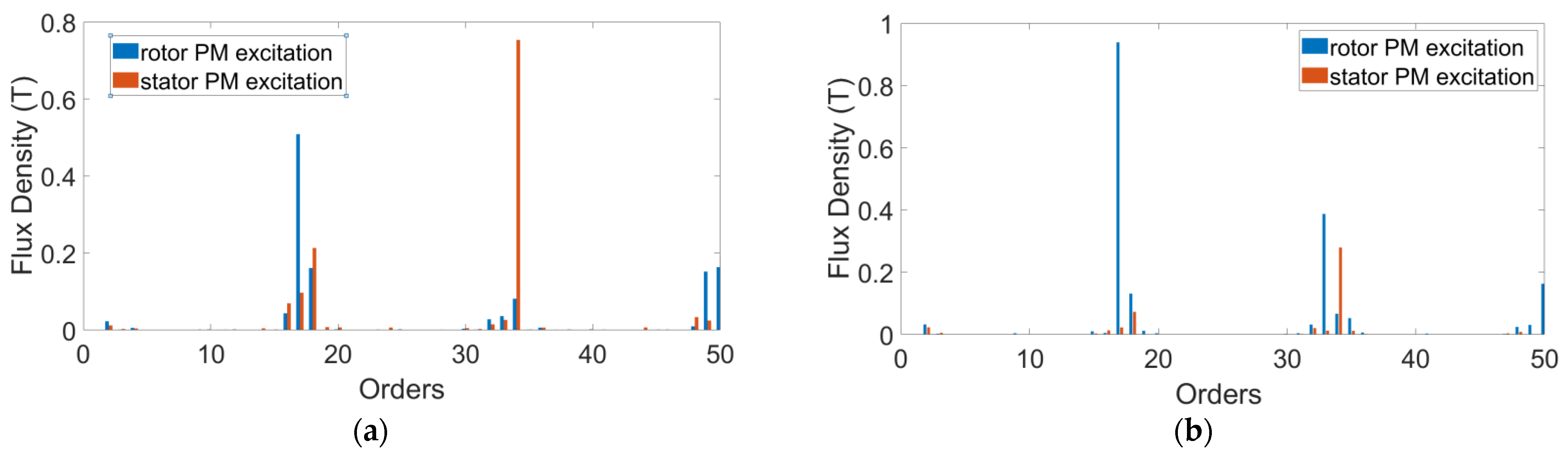
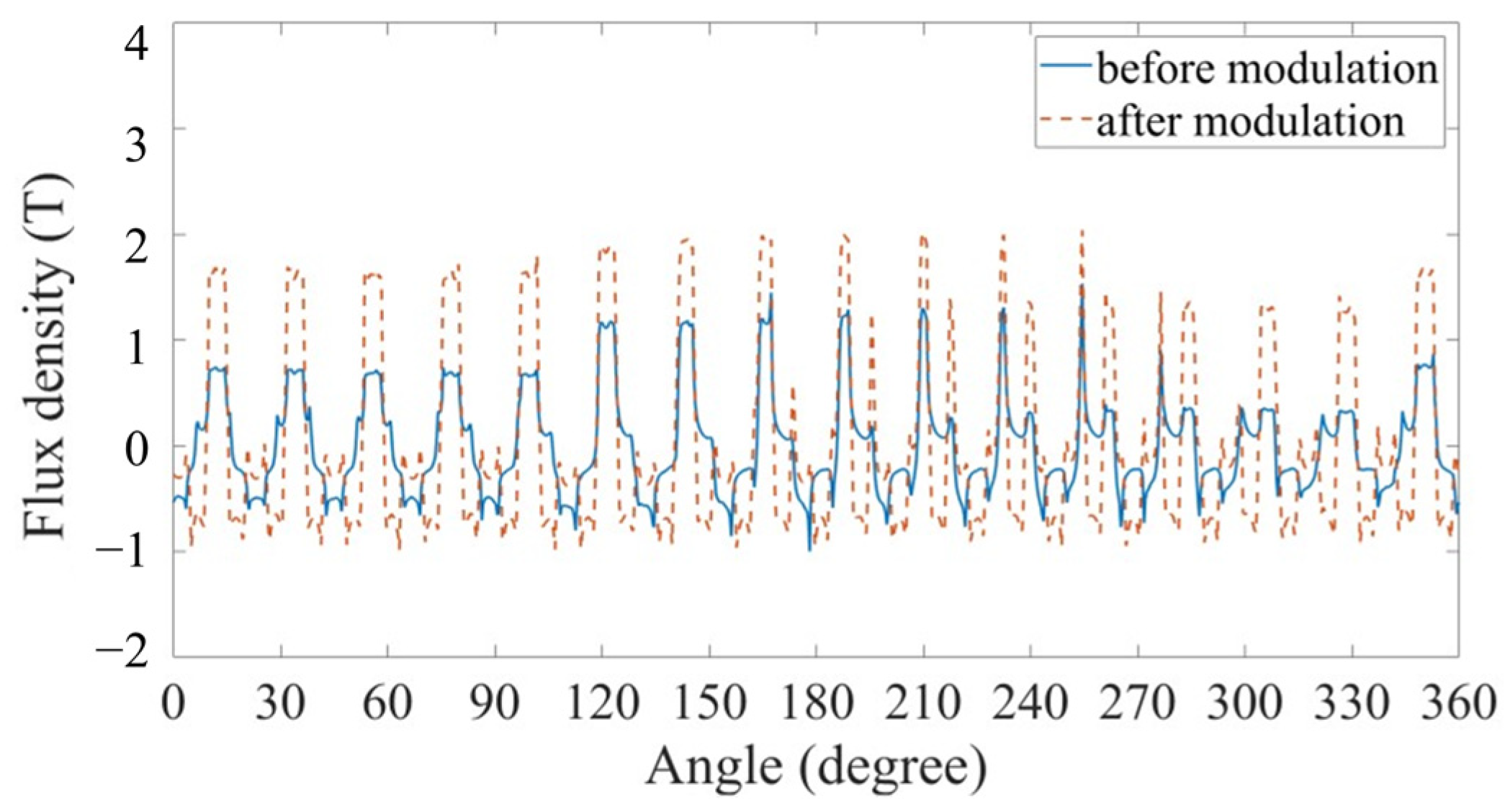
3. Simulations
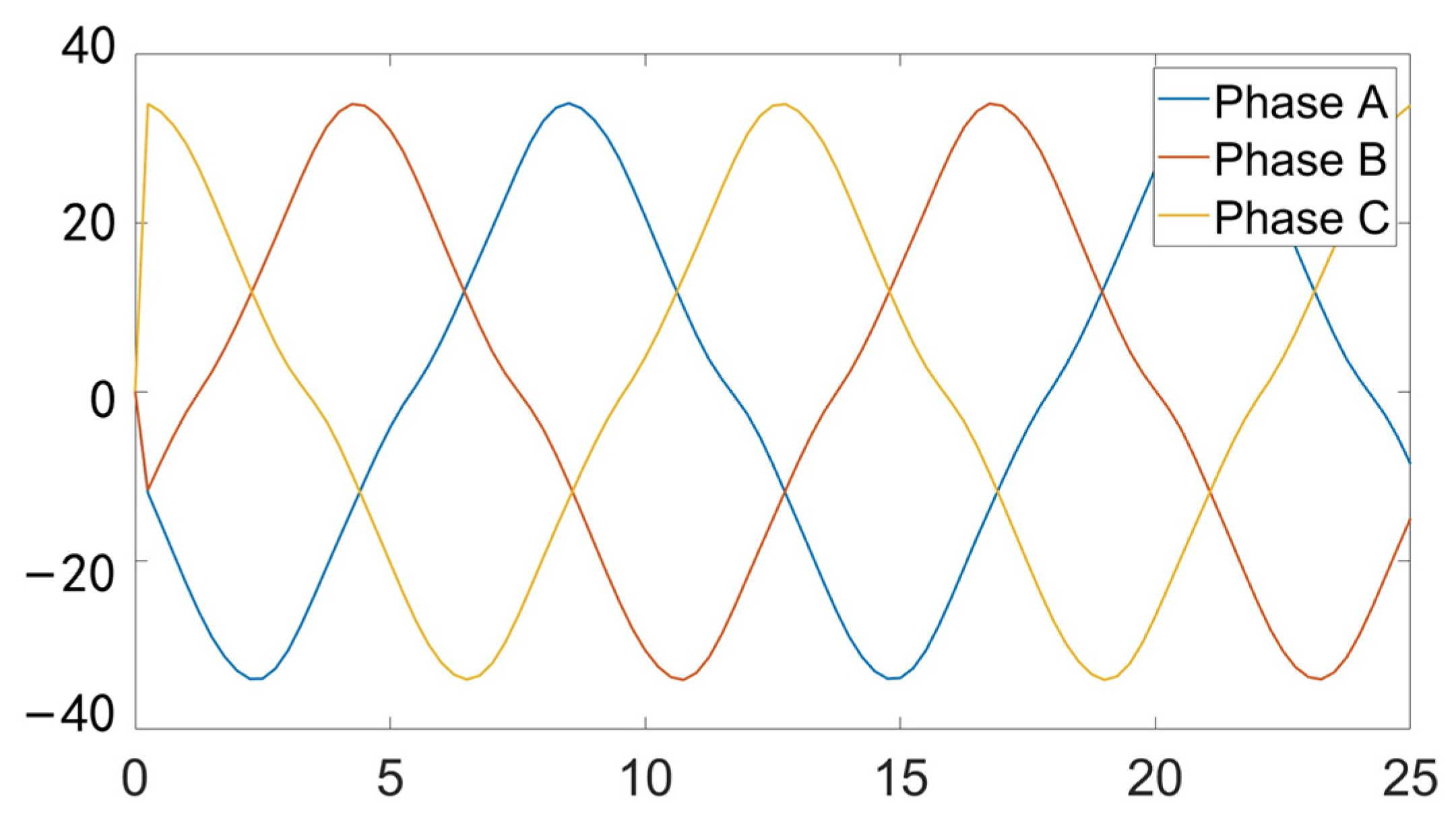
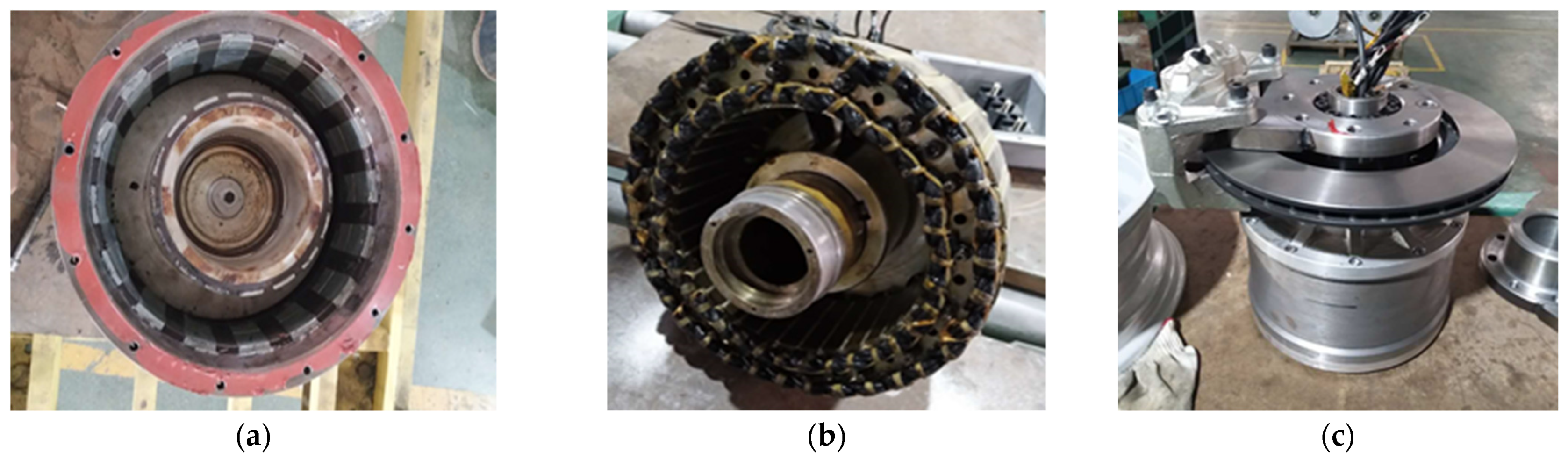
4. Experimental Verification
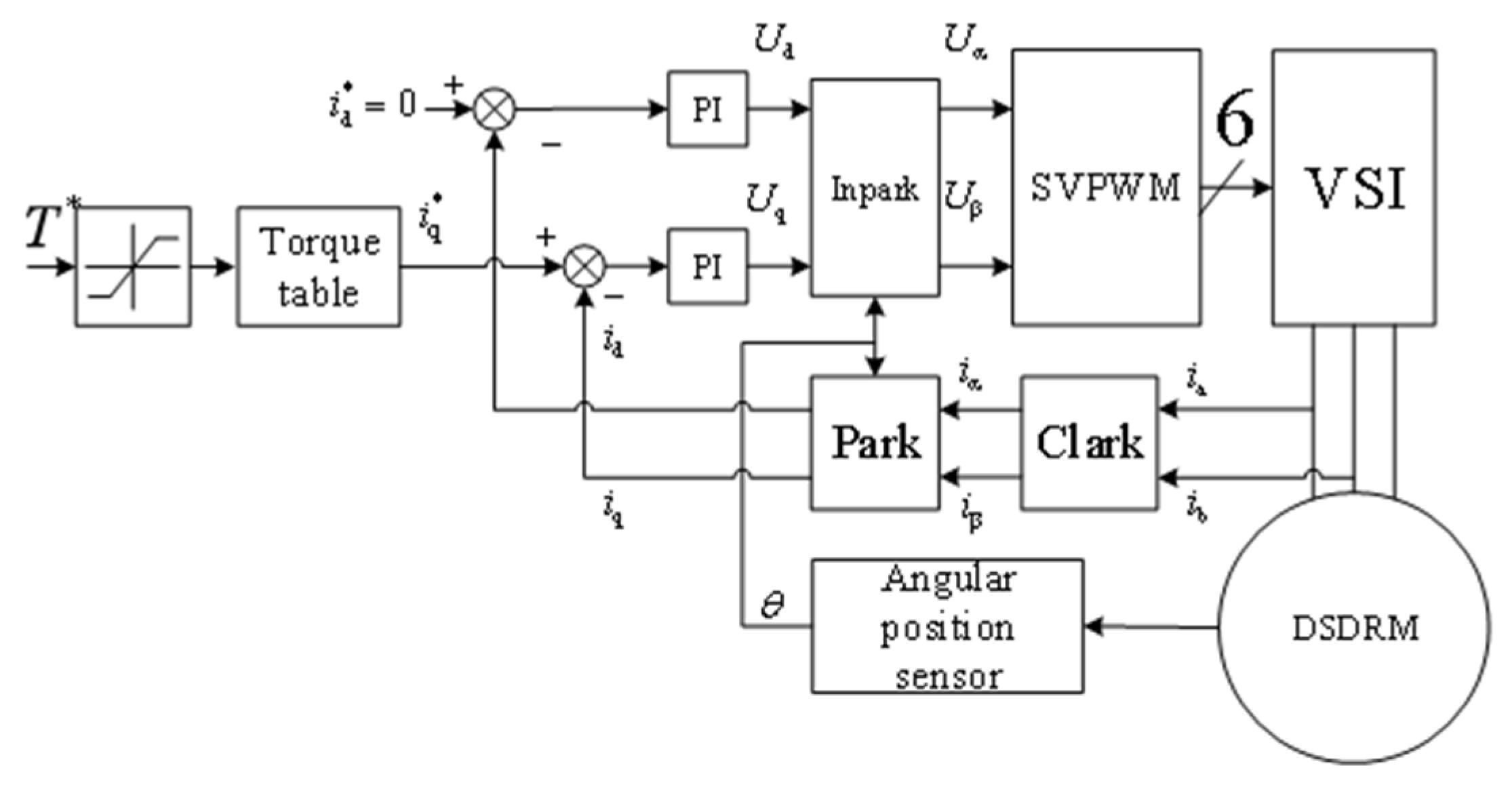
4.1. DSDRM Control System
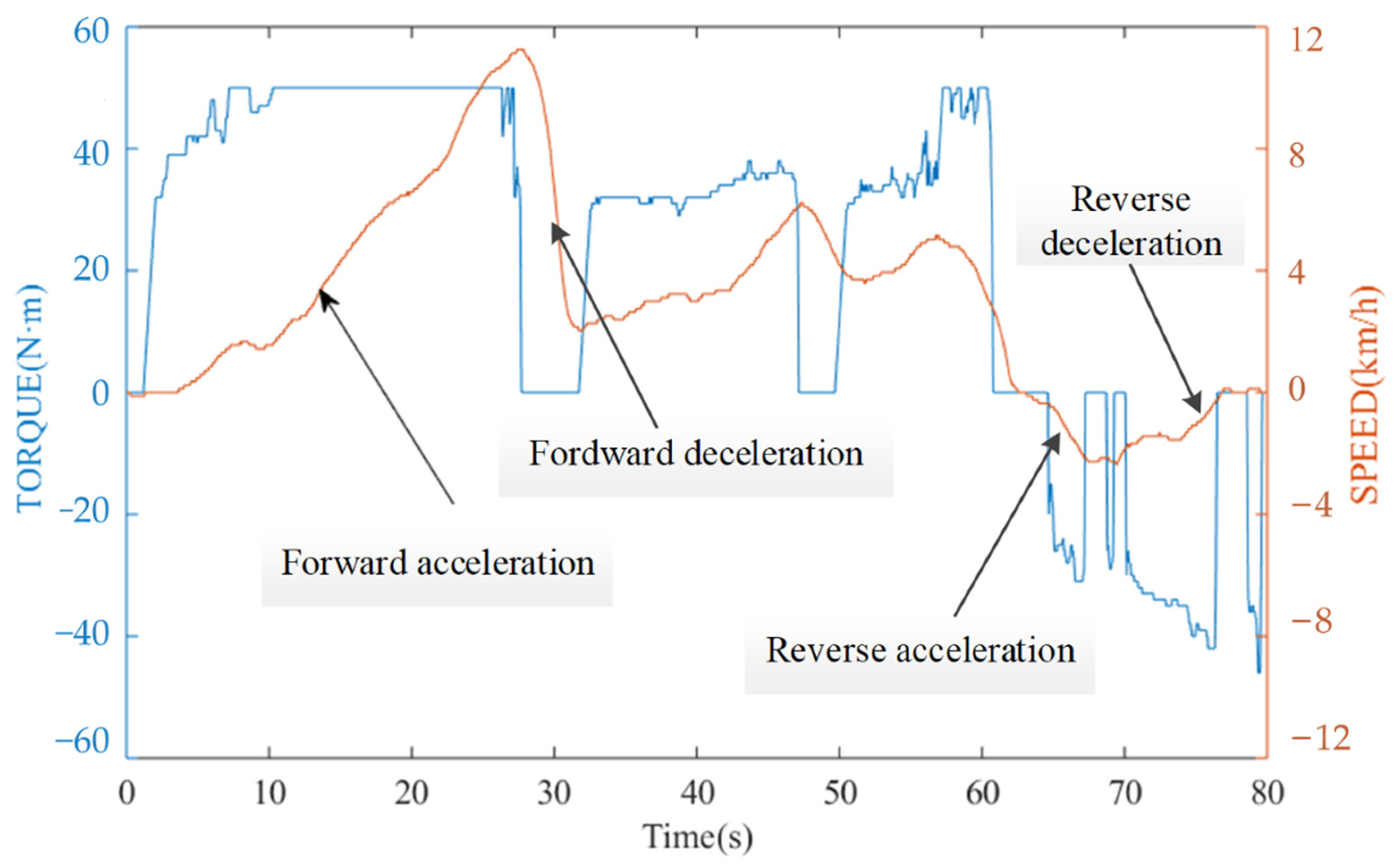
4.2. Vehicle Test with DSDRM
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, L.; Yu, Z. Control Allocation of Vehicle Dynamics Control for a 4 In-Wheel-Motored EV. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Power Electronics and Intelligent Transportation System, Shenzhen, China, 19–20 December 2009; pp. 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Liao, C.; Ouyang, A.; Li, X.; Xiao, Q. Research and development of in-wheel motor driving technology for electric vehicles. Int. J. Electr. Hybrid Veh. 2016, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthamoussou, F.A.; Pegueroles-Queralt, J.; Bianchi, F.D. Control of a Supercapacitor Energy Storage System for Microgrid Applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.B.; Ji, Q. Multi-perspective analysis of China’s energy supply security. Energy 2014, 64, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Z. Speed Regulation System of a Flux-Modulated Permanent-Magnet In-Wheel Motor Based on Sliding Mode Control and Adaptive Notch Filter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rui, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J. Modeling method for battery distribution path optimization of EV charging and swapping service network. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2015, 35, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, T. Temperature effects on torque production and efficiency of PM motors using NdFeB magnets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, S.; Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, P. Control of a Dual-Stator Flux-Modulated Motor for Electric Vehicles. Energies 2016, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chau, K.T.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Design of a Magnetic-Geared Outer-Rotor Permanent-Magnet Brushless Motor for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 2504–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, S.; Fu, W. Electrical-Continuously Variable Transmission System Based on Doubly Fed Flux-Bidirectional Modulation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2722–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, K.; Rens, J.; Mezani, S.; Hove, D. A Novel “Pseudo” Direct-Drive Brushless Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 4349–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, W.N.; Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Fang, R. A Dual Permanent Magnet Machine for High-Torque Low-Speed Applications. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sydney, Australia, 11–14 August 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, L.; Chan, C.C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, G.; Gong, Y. A Novel Dual-Permanent-Magnet-Excited Machine for Low-Speed Large-Torque Applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 2381–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S.A. Novel Hybrid-Excited Dual-PM Machine with Bi-directional Flux Modulation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, Y.; Vido, L.; Gabsi, M.; Hoang, E.; Ben Ahmed, A.H.; Lecrivain, M. Hybrid Excitation Synchronous Machines: Energy-Efficient Solution for Vehicles Propulsion. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 2137–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.N.; Ho, S.L.A. Quantitative Comparative Analysis of a Novel Flux-Modulated Permanent-Magnet Motor for Low-Speed Drive. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 46, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Li, D.; Qu, R.; Gao, Y. A Novel Permanent Magnet Vernier Machine With Halbach Array Magnets in Stator Slot Opening. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 7207005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gu, J.; Li, J.; Lu, D. Design of the Control System for a Four-Wheel Driven Micro Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Dearborn, MI, USA, 7–10 September 2009; pp. 1813–1816. [Google Scholar]







| Symbol | Items | Value |
|---|---|---|
| r1 | Inner radius of inner rotor | 64.7 mm |
| r2 | Outer radius of inner rotor | 72.9 mm |
| r3 | Inner radius of outer rotor | 108.6 mm |
| r4 | Outer radius of outer rotor | 120 mm |
| h1 | Height of inner rotor yoke | 4.7 mm |
| h2 | Height of stator yoke | 10 mm |
| h3 | Height of outer rotor yoke | 6 mm |
| h4 | Height of inner rotor PMs | 3.5 mm |
| h5 | Height of outer rotor PMs | 5.4 mm |
| br1 | Bottom width of inner rotor PMs | 19.08 mm |
| br2 | Top width of inner rotor PMs | 20.04 mm |
| br3 | Bottom width of outer rotor PMs | 25.97 mm |
| br4 | Top width of outer rotor PMs | 24.74 mm |
| bs0 | Open width of inner stator PMs | 5.05 mm |
| bs1 | Top width of inner stator slots | 5.64 mm |
| bs2 | Bottom width of inner stator slots | 7.36 mm |
| bs3 | Open width of outer stator slots | 5.25 mm |
| bs4 | Top width of outer stator slots | 6.96 mm |
| bs5 | Top width of outer stator crosswise PMs | 7.54 mm |
| bs6 | Width of outer stator lengthways PMs | 2.08 mm |
| hp1 | Height of inner stator PMs | 3.11 mm |
| hp2 | Height of inner stator slots | 9 mm |
| hp3 | Height of outer stator slots | 9 mm |
| hp4 | Height of outer stator crosswise PMs | 3.02 mm |
| a0 | Inner air-gap length | 0.75 mm |
| a1 | Outer air-gap length | 0.75 mm |
| Content | Material | Density (g/cm3) | Weight (kg) |
| Motor Case | Aluminum | 2.7 | 21.136 |
| Steel | 7.85 | 5.435 | |
| Magnetic | Sintered Nd-Fe-B | 6.0 | 2.608 |
| Winding | Refined copper | 8.9 | 2.183 |
| Screw | Iron | 7.86 | 0.242 |
| Total | 31.604 |
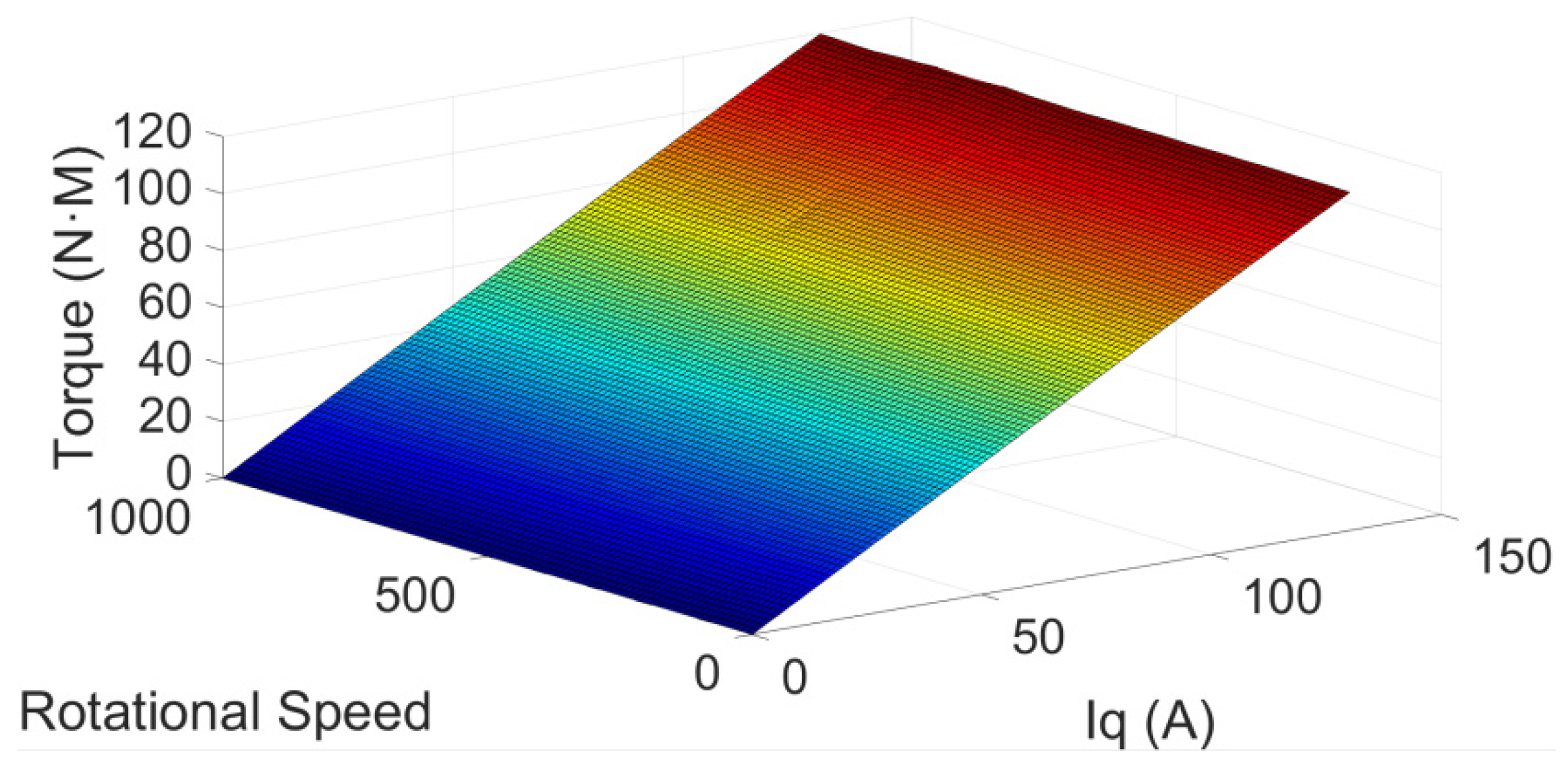
| Rotational Speed (r/min) | iq(A) | Torque (N·m) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 100 | 10 | 9.6 |
| 100 | 20 | 22.3 |
| 100 | 30 | 38.7 |
| 100 | 40 | 53.2 |
| 100 | 50 | 69.1 |
| 100 | 60 | 79.3 |
| 100 | 70 | 99.9 |
| 100 | 80 | 109.3 |
| 100 | 90 | 128.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Guo, X.; Fu, J.; Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, R.; Li, Z. Design and Analysis of a Novel Double-Stator Double-Rotor Motor Drive System for In-Wheel Direct Drive of Electric Vehicles. Machines 2022, 10, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10010027
Li C, Guo X, Fu J, Fu W, Liu Y, Chen H, Wang R, Li Z. Design and Analysis of a Novel Double-Stator Double-Rotor Motor Drive System for In-Wheel Direct Drive of Electric Vehicles. Machines. 2022; 10(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chunzhen, Xinhua Guo, Jinyuan Fu, Weinong Fu, Yulong Liu, Hao Chen, Rongkun Wang, and Zhongshen Li. 2022. "Design and Analysis of a Novel Double-Stator Double-Rotor Motor Drive System for In-Wheel Direct Drive of Electric Vehicles" Machines 10, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10010027
APA StyleLi, C., Guo, X., Fu, J., Fu, W., Liu, Y., Chen, H., Wang, R., & Li, Z. (2022). Design and Analysis of a Novel Double-Stator Double-Rotor Motor Drive System for In-Wheel Direct Drive of Electric Vehicles. Machines, 10(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10010027









