Uncertainty Quantification of Herschel–Bulkley Fluids in Rectangular Ducts Due to Stochastic Parameters and Boundary Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Random Fields Representation and Solution
2.1. Spectral Decomposition Methods
2.2. Polynomial Chaos Expansion (PCE)
2.3. The Stochastic Finite Difference with Homogenous Chaos Approach
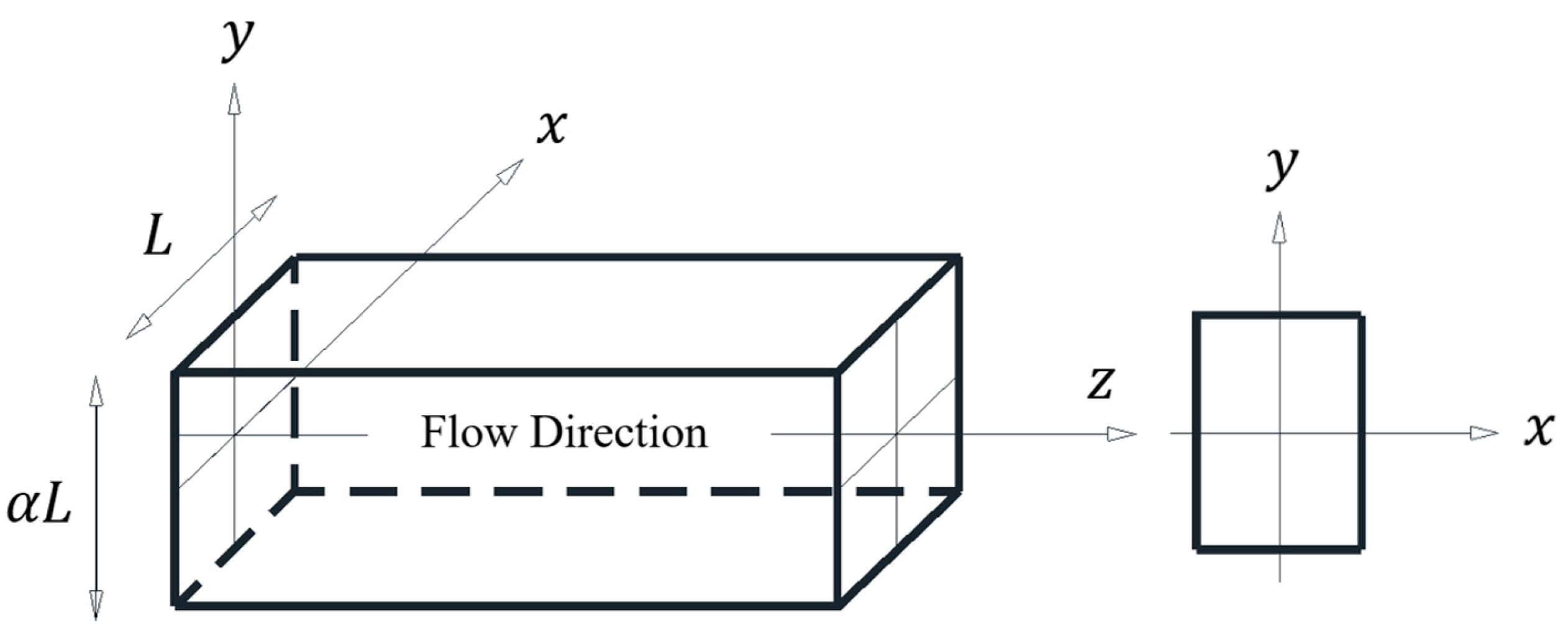
3. Formulation and Resolution of the Stochastic Model for Herschel–Bulkley Fluid
3.1. The Stochastic Model Formulation
3.2. Problem Solution Using SFDHC
4. Computational Implementation
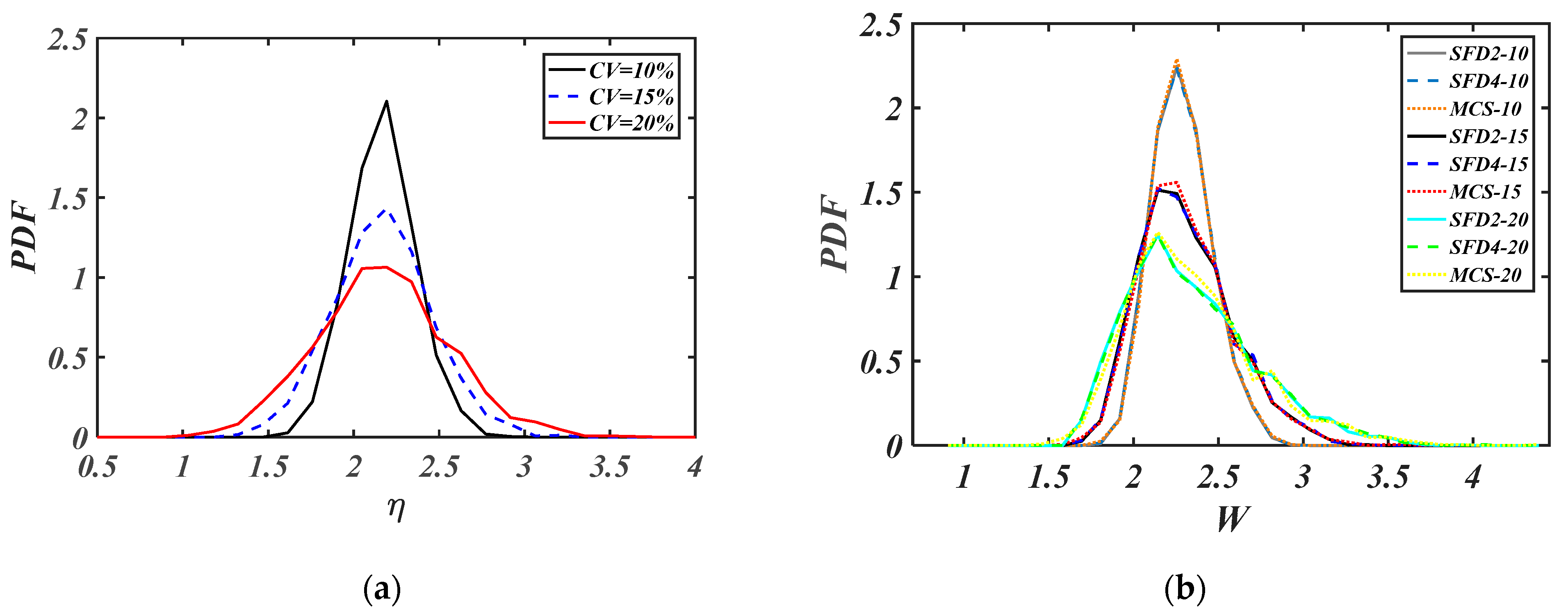
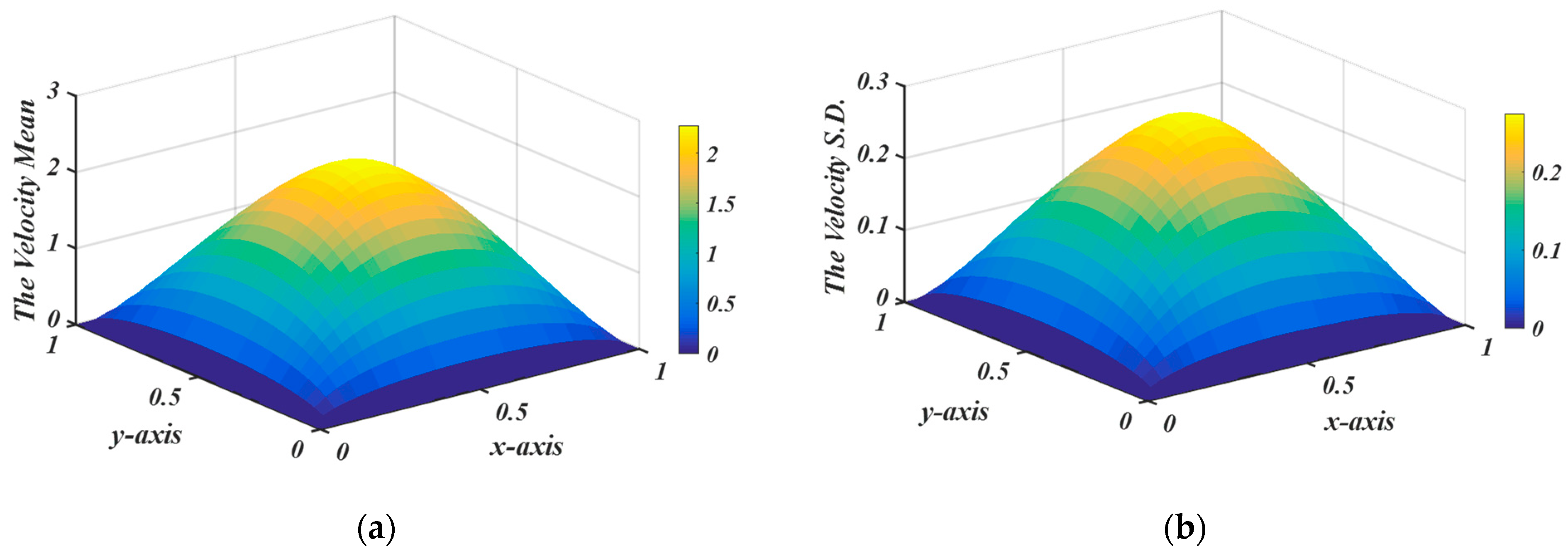
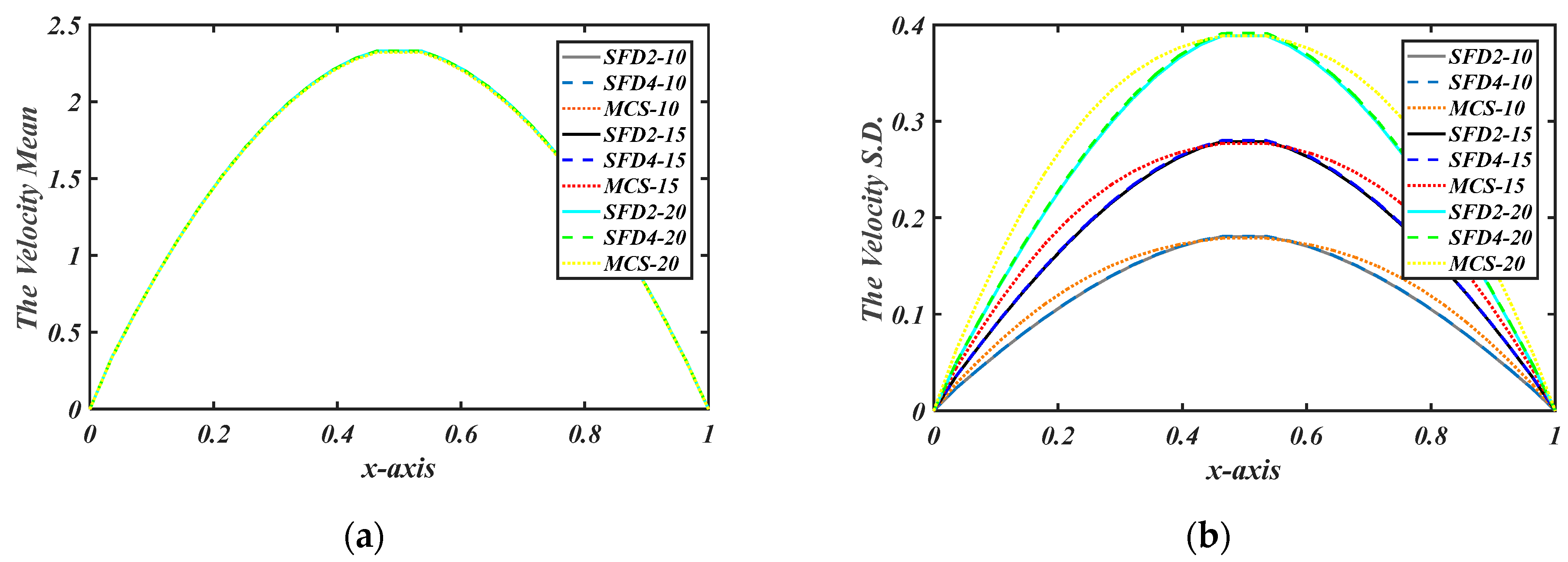
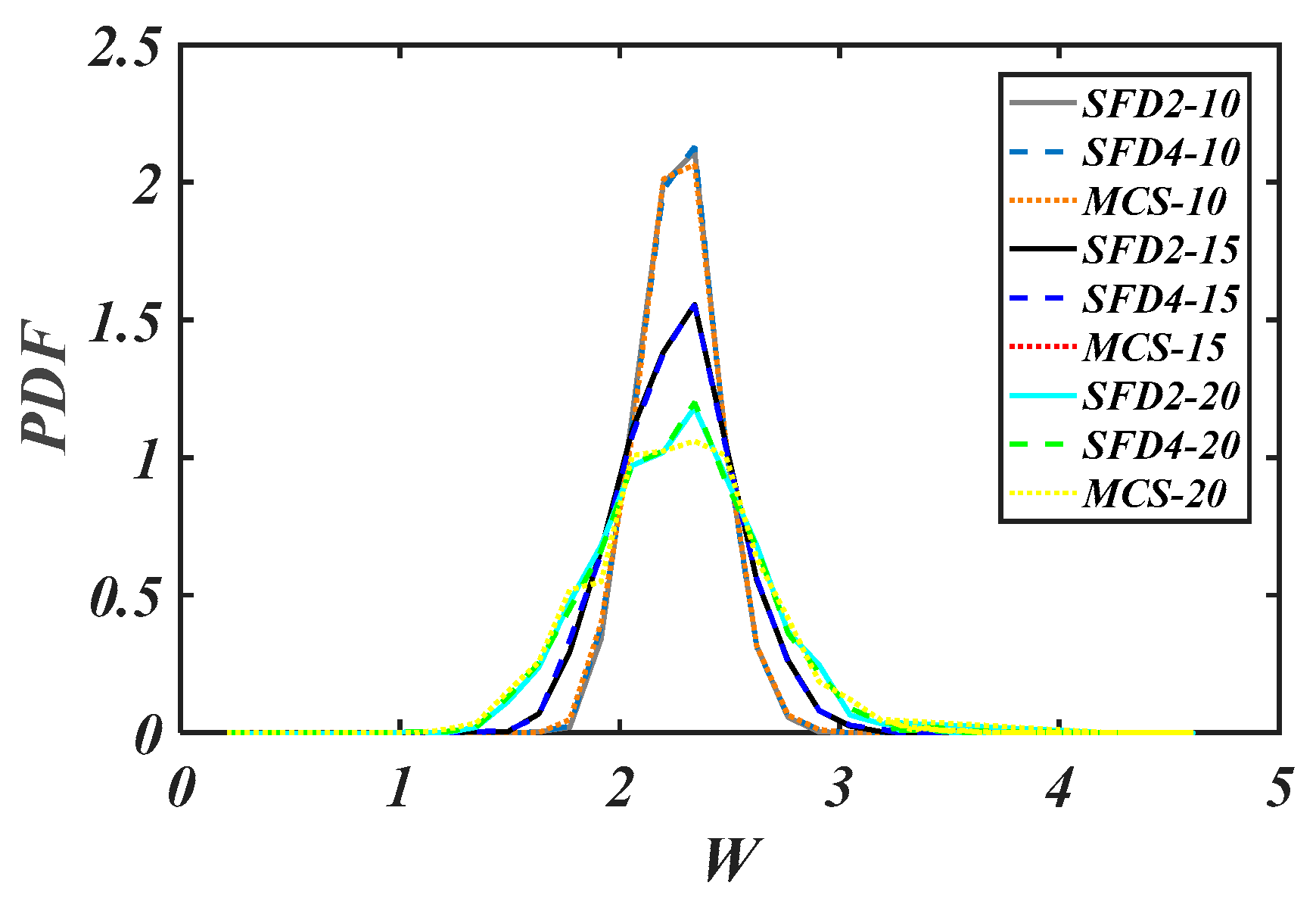
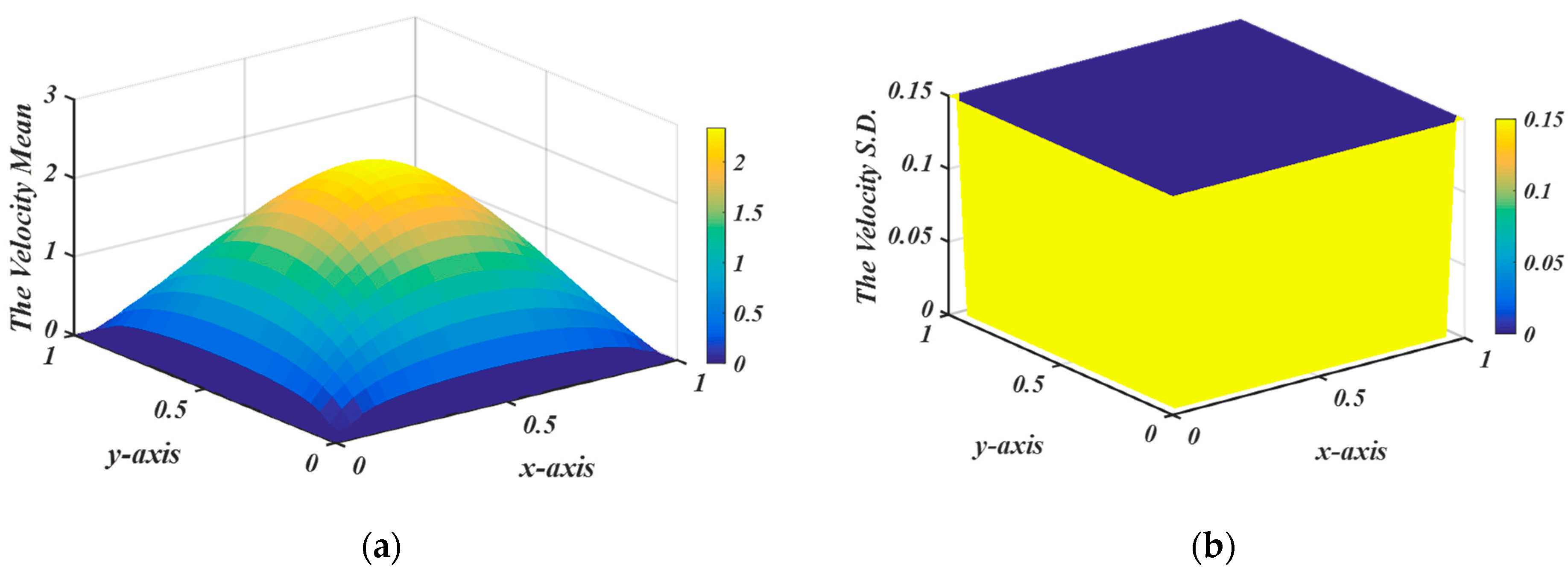
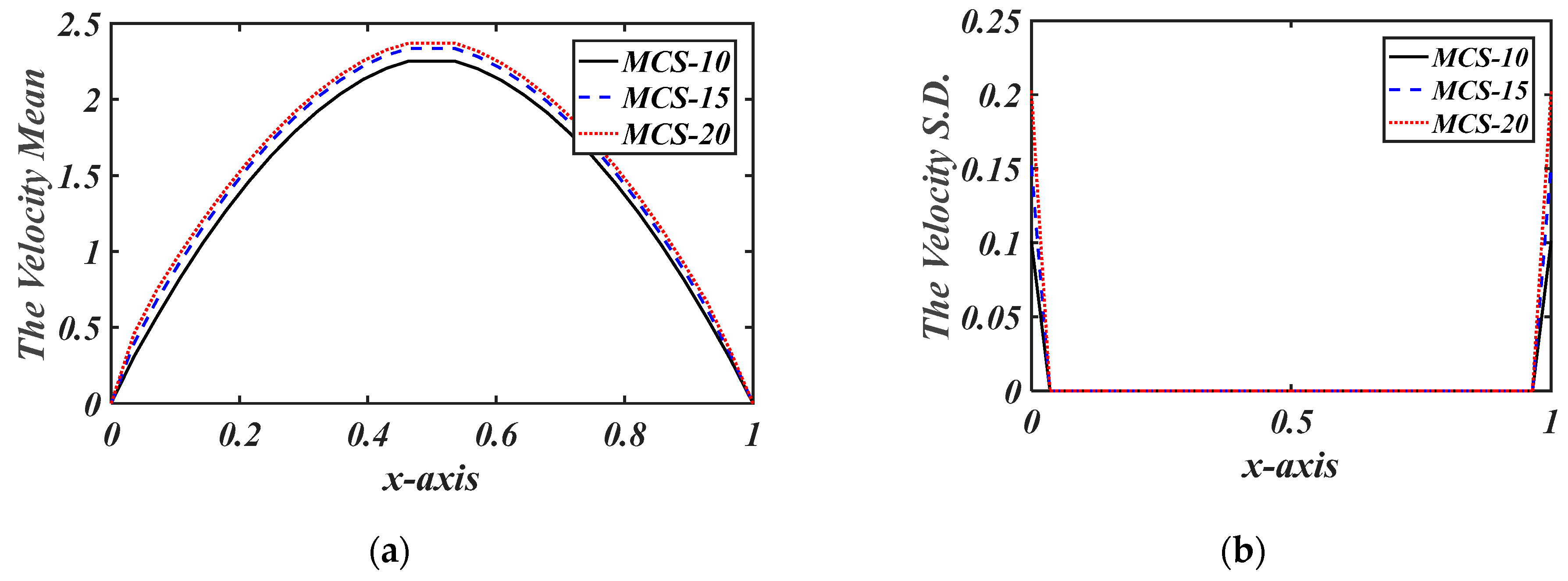
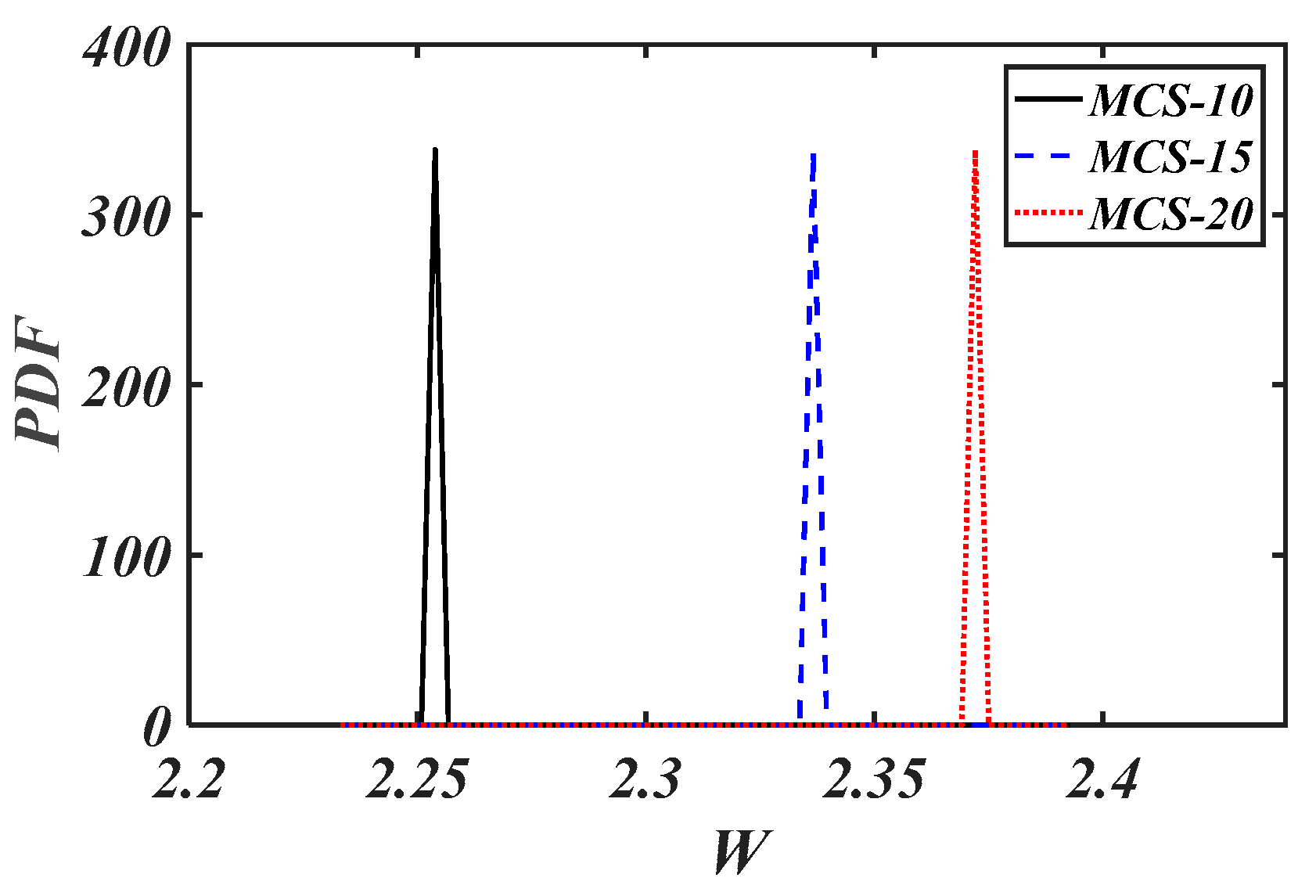
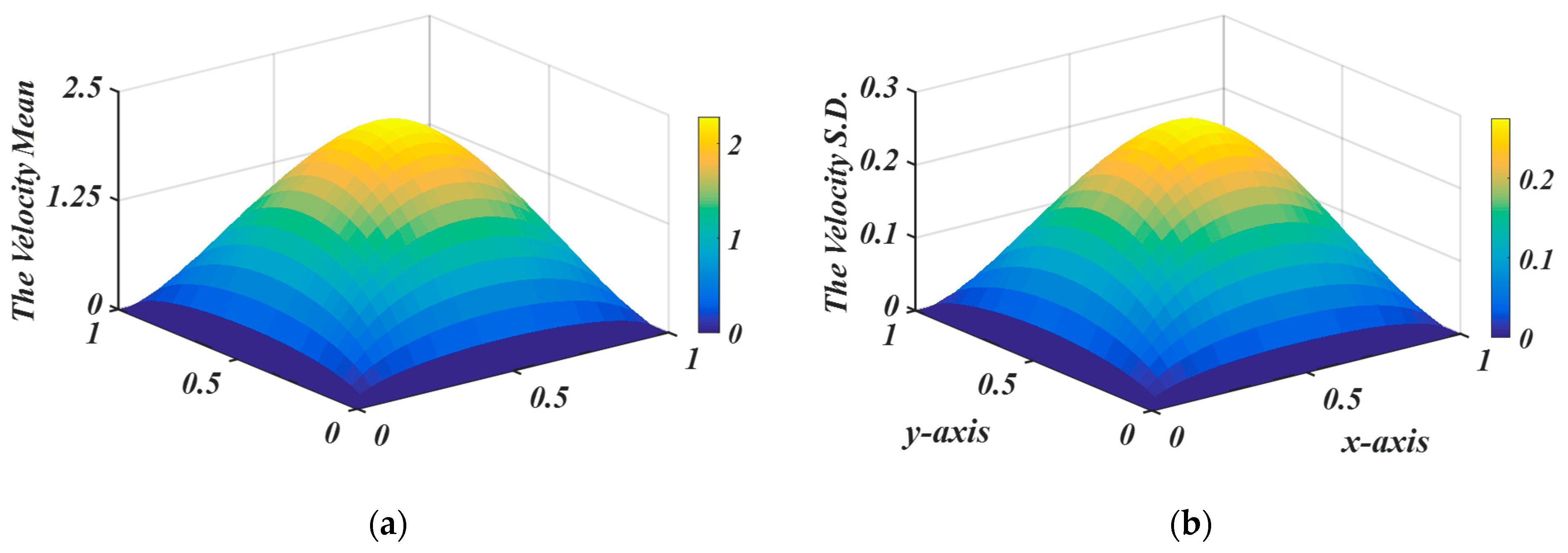
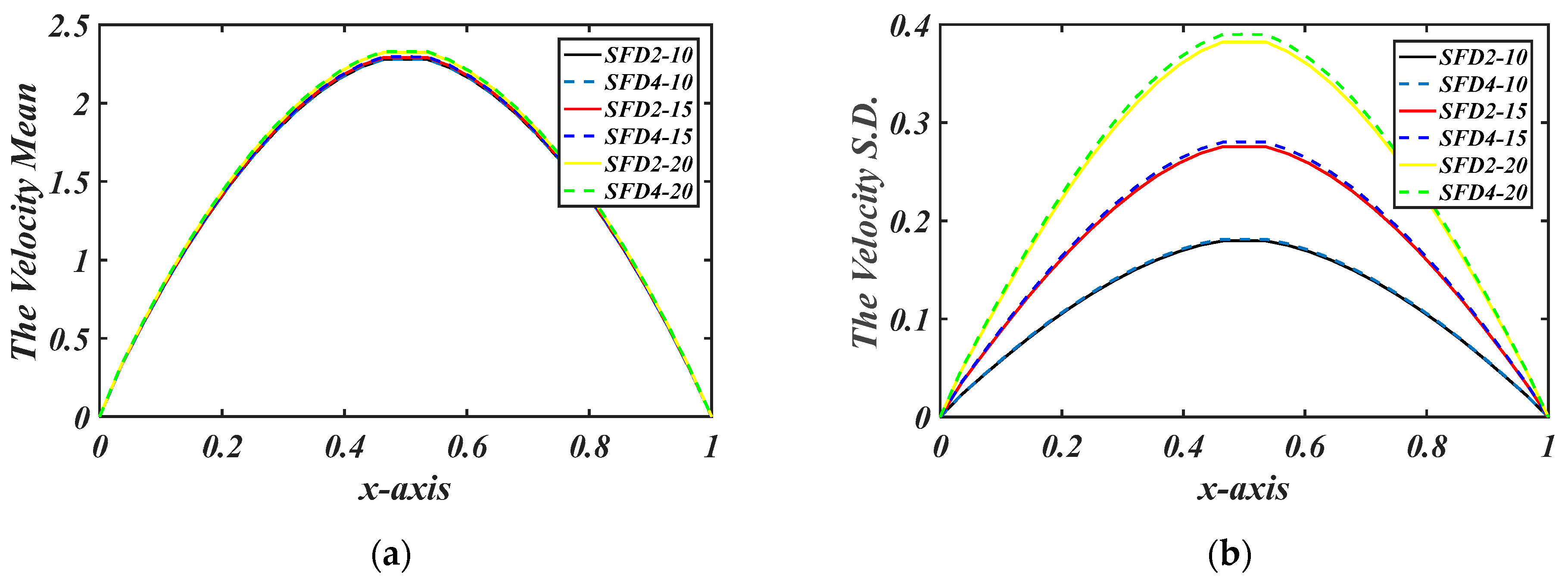
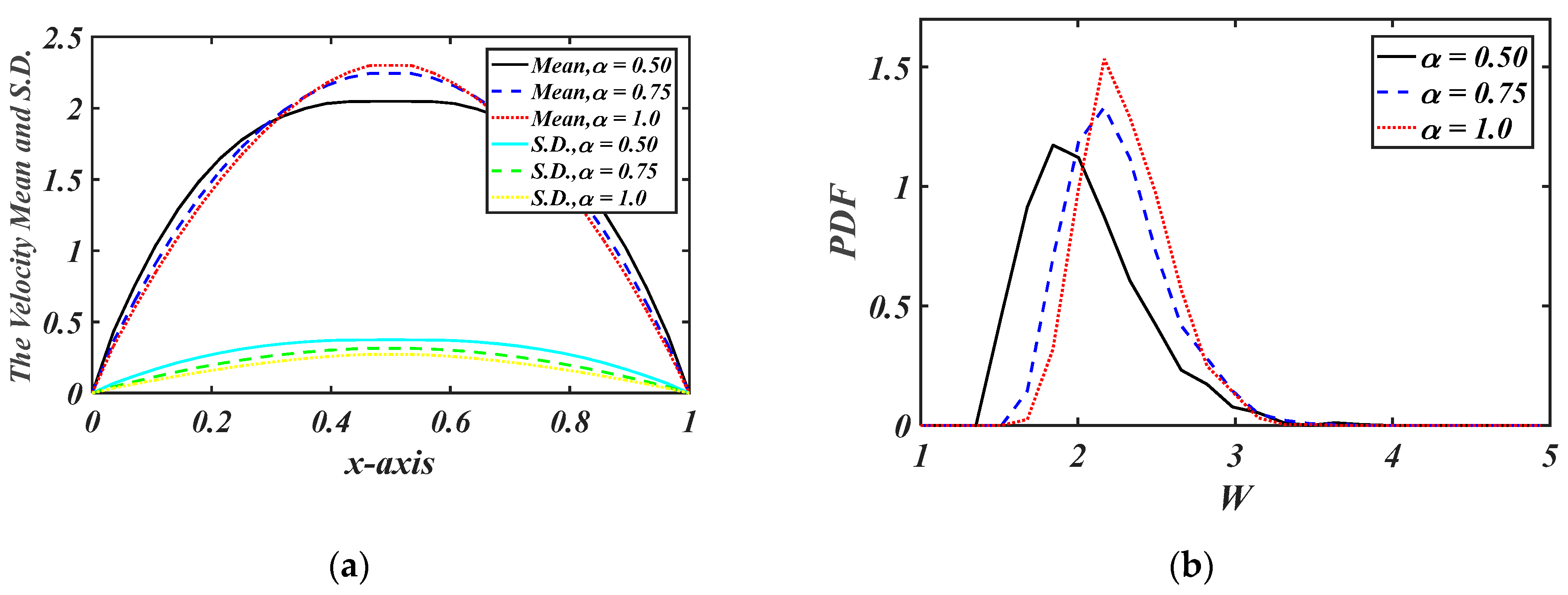
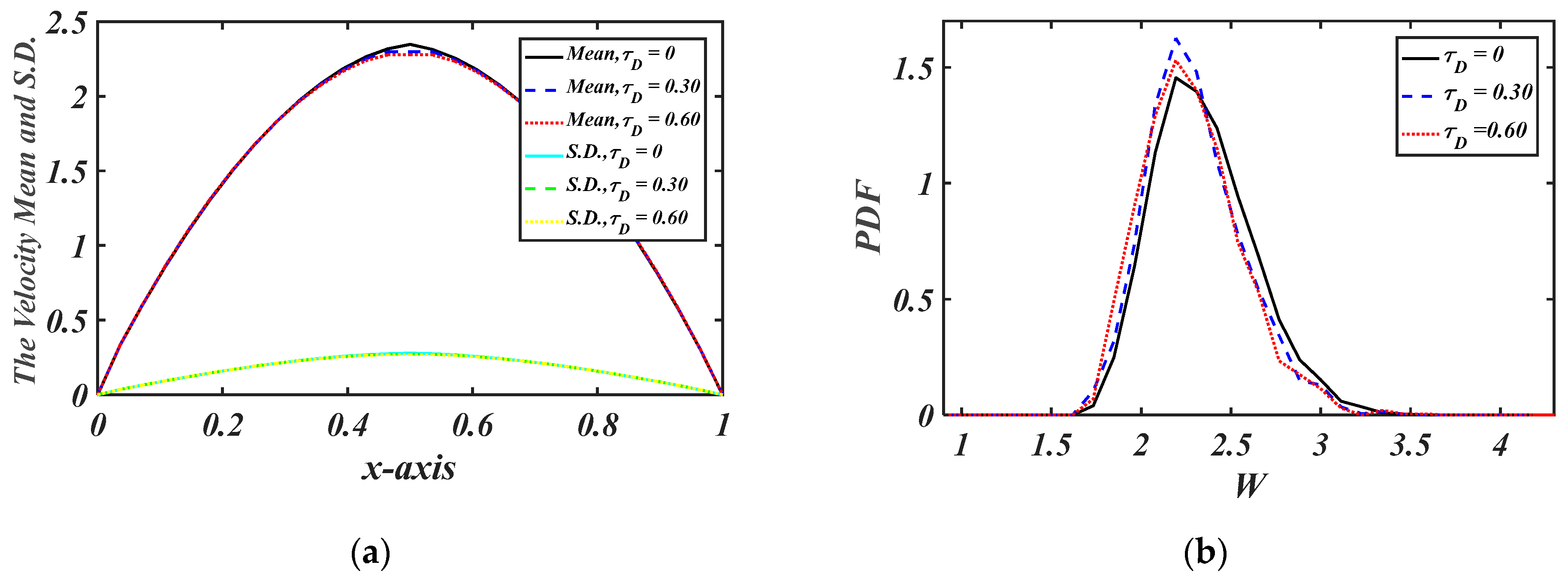
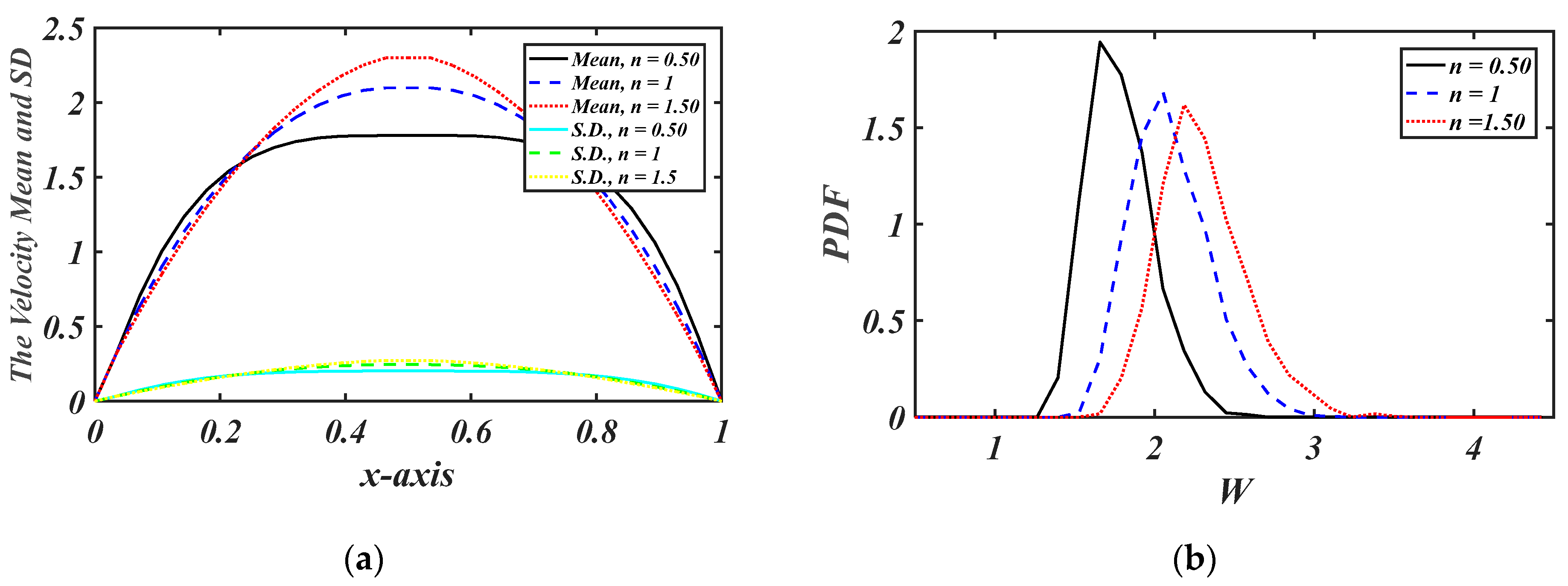
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herschel, W.H.; Bulkley, R. Konsistenzmessungen von Gummi-Benzollösungen. Kolloid-Zeitschrift 1926, 39, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Rémond, S.; Gallias, J.L.; Bigas, J.P.; Muller, P. Flow of Herschel-Bulkley fluids through the Marsh cone. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2006, 139, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed-Ahmed, M.E. Laminar heat transfer for thermally developing flow of a Herschel-Bulkley fluid in a square duct. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 27, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed-Ahmed, M.E.; Kishk, K.M. Heat transfer for Herschel-Bulkley fluids in the entrance region of a rectangular duct. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 35, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed-Ahmed, M.E.; Saif-Elyazal, A.; Iskander, L. Laminar flow and heat transfer of Herschel-Bulkley fluids in a rectangular duct; finite-element analysis. Tikrit J. Eng. Sci. 2009, 12, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Federico, V.; Pinardi, R.; Sgambati, M. Gravity-driven flow of Herschel-Bulkley fluid in a fracture and in a 2D porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 821, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajravelu, K.; Sreenadh, S.; Devaki, P.; Prasad, K.V. Mathematical model for a Herschel-Bulkley fluid flow in an elastic tube. Open Phys. 2011, 9, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.K. Mathematical modelling on blood flow under atherosclerotic condition. Am. J. Appl. Math. 2016, 4, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthi Prasad, K.; Radhakrishnamacharya, G. Flow of Herschel-Bulkley fluid through an inclined tube of non-uniform cross-section with multiple stenoses. Arch. Mech. 2008, 60, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Rajashekhar, C.; Manjunatha, G.; Basavarajappa, K.S. Peristaltic transport of two-layered blood flow using Herschel-Bulkley model. Cogent Eng. 2018, 5, 1495592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ding, Z.; Hu, K.X. Stabilities in plane Poiseuille flow of Herschel-Bulkley fluid. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2018, 251, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, R.; Gudekote, M.; Vaidya, H.; Prasad, K.V. Peristaltic flow of Herschel-Bulkley fluid in an elastic tube with slip at porous walls. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2018, 52, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadharshini, S.; Ponalagusamy, R. A numerical study on unsteady flow of Herschel-Bulkley nanofluid through an inclined artery with body acceleration and magnetic field. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberkampf, W.L.; DeLand, S.M.; Rutherford, B.M.; Diegert, K.V.; Alvin, K.F. Error and uncertainty in modeling and simulation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2002, 75, 333–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, H.P.; Petruccione, F. A stochastic approach to computational fluid dynamics. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 1992, 4, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulevicius, R.; Rozovskii, B. On equations of stochastic fluid mechanics. In Stochastics in Finite and Infinite Dimensions; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, R.A. Hermite polynomial chaos for uncertainty analysis in fluid flow modeling. J. Comput. Phys. 2009, 228, 2988–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, J.L. Stochastic particle level set simulations of buoyancy-driven droplets in non-Newtonian fluids. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2015, 226, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochi, T. Deterministic and stochastic algorithms for resolving the flow fields in ducts and networks using energy minimization. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2016, 27, 1650036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Kuipers, J.A.M.; Peters, E.A.J.F.; Padding, J.T. Viscoelastic flow simulations in random porous media. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2017, 248, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrossian, J.; Blumenthal, J.; Punshon-Smith, S. Lagrangian stochastic models with applications in turbulent transport. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 898, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagnini, A.; Porta, G.M.; Riva, M.; Bianchi Janetti, I. Quantification of uncertainties of fracture permeability via mud loss information and inverse stochastic modeling. In Proceedings of the 81st EAGE Conference and Exhibition, London, UK, 3–6 June 2019; EAGE: Houten, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, O.H. Stochastic velocity modeling of magneto-hydrodynamics non-Darcy flow between two stationary parallel plates. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 4191–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, O.H. Stochastic Velocity Assessment of Robertson-Stiff Fluids in Rectangular Ducts under Uncertain Parameters and Boundary Conditions. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkens, A.; Verhoosel, C.V.; Jaensson, N.O. Uncertainty quantification for the squeeze flow of generalized Newtonian fluids. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2023, 311, 105154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeiravesh, S.; Vinuesa, R.; Schlatter, P. An uncertainty-quantification framework for assessing accuracy, sensitivity, and robustness in computational fluid dynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 390, 114467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Jaberi, J.; Bageri, B.; Otain, W.; Alsaleem, A.; Adebayo, A.R. Fine-tuning filter cake sealing performance: The role of particle size in hematite weighted water-based drilling fluid. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 21845–21856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knio, O.M.; Le Maître, O.P. Uncertainty propagation in CFD using polynomial chaos decomposition. Fluid Dyn. Res. 2006, 38, 616–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunzburger, M.; Iliescu, T.; Mohebujjaman, M.; Schneier, M. An evolve-filter-relax stabilized reduced-order stochastic collocation method for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2019, 7, 1162–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Liu, Z. Enhancing performance of nanofluid mini-channel heat sinks through machine learning and multi-objective optimization of operating parameters. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 204, 124204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, O.H. A proposed stochastic finite difference approach based on homogeneous chaos expansion. J. Appl. Math. 2013, 2013, 950469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, R.G.; Spanos, P.D. Stochastic Finite Elements: A Spectral Approach; Courier Corporation: Mineola, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmforth, N.J.; Frigaard, I.A.; Ovarlez, G. Yielding to stress: Recent developments in viscoelastic fluid mechanics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.X.; Hartnett, J.P. Non-Newtonian fluid laminar flow and forced convection heat transfer in rectangular ducts. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1992, 19, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranovskii, E.S. The Stationary Navier–Stokes–Boussinesq System with a Regularized Dissipation Function. Math. Notes Acad. Sci. USSR 2024, 115, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks Inc. MATLAB Version: 9.13.0 (R2022b); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.mathworks.com (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Syrjala, S. Finite-element analysis of fully developed laminar flow of power-law non-Newtonian fluid in a rectangular duct. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1995, 22, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.V. (Ed.) Theory and Applications of Monte Carlo Simulations; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tehrani, A.; Cliffe, A.; Hodder, M.H.; Young, S.; Lee, J.; Stark, J.; Seale, S. Alternative drilling fluid weighting agents: A comprehensive study on ilmenite and hematite. In SPE/IADC Drilling Conference Proceedings; SPE: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadl, A.M.; Abdou, M.I.; El-Sayed Ahmed, H.; Wahab Gaber, M.A. Delaminated iron ore (hematite-Barite) as alternative weighting agent to Barite in petroleum drilling fluids engineering operations and mechanism study. Am. Shams Eng. J. 2020, 11, 1317–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| 0.5 | 0.75 | 1 | 1.5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syrjala [37] | 5.721 | 9.090 | 14.227 | 34.861 |
| Sayed-Ahmed [3] | 5.718 | 9.070 | 14.230 | 34.880 |
| Present Study | 5.775 | 9.095 | 14.228 | 34.629 |
| 1 | 0.5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| Syrjala [37] | 34.86093 | 14.22708 | 5.72140 | 39.71292 | 15.54806 | 5.99867 |
| Present Study | 34.62857 | 14.22832 | 5.77480 | 39.39822 | 15.55007 | 6.05751 |
| 0.6665% | 0.0087% | 0.9334% | 0.7924% | 0.0129% | 0.9809% | |
| CV | Method of Solution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFD2-10 | 2.2848 | 1.0061 | 0.1757 | 0.078 | 1.8313 | 2.9501 | 1.1187 | |
| SFD4-10 | 2.2858 | 1.0066 | 0.1761 | 0.0781 | 1.8292 | 2.9512 | 1.1220 | |
| MCS-10 | 2.2905 | 1.0086 | 0.1742 | 0.0771 | 1.8058 | 2.9808 | 1.1749 | |
| SFD2-15 | 2.3029 | 1.0141 | 0.2718 | 0.1196 | 1.7129 | 3.4158 | 1.7029 | |
| SFD4-15 | 2.3054 | 1.0152 | 0.2729 | 0.1199 | 1.7115 | 3.4200 | 1.7085 | |
| MCS-15 | 2.3129 | 1.0185 | 0.2700 | 0.1183 | 1.6385 | 3.5453 | 1.9068 | |
| SFD2-20 | 2.3298 | 1.0259 | 0.3785 | 0.1647 | 1.6627 | 3.9906 | 2.3279 | |
| SFD4-20 | 2.3346 | 1.0281 | 0.3811 | 0.1654 | 1.6634 | 4.0018 | 2.3384 | |
| MCS-20 | 2.3454 | 1.0328 | 0.3785 | 0.1635 | 1.4998 | 4.3964 | 2.8966 |
| CV | Method of Solution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFD2-10 | 2.2709 | 1.0000 | 0.1758 | 0.0784 | 1.6814 | 2.8627 | 1.1813 | |
| SFD4-10 | 2.2709 | 1.0000 | 0.1778 | 0.0793 | 1.6831 | 2.8832 | 1.2000 | |
| MCS-10 | 2.2665 | 0.9981 | 0.1821 | 0.0814 | 1.7027 | 2.9077 | 1.2050 | |
| SFD2-15 | 2.2709 | 1.0000 | 0.2636 | 0.1177 | 1.3866 | 3.1586 | 1.7720 | |
| SFD4-15 | 2.2709 | 1.0000 | 0.2667 | 0.1190 | 1.3892 | 3.1893 | 1.8001 | |
| MCS-15 | 2.2644 | 0.9971 | 0.2732 | 0.1222 | 1.4186 | 3.2261 | 1.8075 | |
| SFD2-20 | 2.2709 | 1.0000 | 0.3515 | 0.1569 | 1.0919 | 3.4545 | 2.3626 | |
| SFD4-20 | 2.2709 | 1.0000 | 0.3555 | 0.1587 | 1.0954 | 3.4955 | 2.4001 | |
| MCS-20 | 2.2622 | 0.9962 | 0.3642 | 0.1632 | 1.1345 | 3.5445 | 2.4100 |
| CV | Method of Solution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCS-10 | 2.2524 | 0.9918 | 7.1519 × 10−14 | 3.2178 × 10−14 | 2.2524 | 2.2524 | 0 | |
| MCS-15 | 2.3354 | 1.0284 | 3.5093 × 10−14 | 1.5228 × 10−14 | 2.3354 | 2.3354 | 0 | |
| MCS-20 | 2.3706 | 1.0439 | 4.6643 × 10−14 | 1.9939 × 10−14 | 2.3706 | 2.3706 | 0 |
| CV | Method of Solution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFD2-10 | 2.2863 | 1.0068 | 0.1897 | 0.0830 | 1.6603 | 3.0717 | 1.4114 | |
| SFD4-10 | 2.2871 | 1.0071 | 0.1921 | 0.0840 | 1.6451 | 3.0806 | 1.4355 | |
| SFD2-15 | 2.3104 | 1.0174 | 0.2923 | 0.1265 | 1.5267 | 3.5353 | 2.0086 | |
| SFD4-15 | 2.3112 | 1.0177 | 0.2951 | 0.1277 | 1.5135 | 3.5391 | 2.0256 | |
| SFD2-20 | 2.3317 | 1.0268 | 0.4064 | 0.1743 | 1.4113 | 4.4151 | 3.0038 | |
| SFD4-20 | 2.3348 | 1.0281 | 0.4103 | 0.1757 | 1.3872 | 4.5317 | 3.1445 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galal, O.H.; Alruwaili, E. Uncertainty Quantification of Herschel–Bulkley Fluids in Rectangular Ducts Due to Stochastic Parameters and Boundary Conditions. Axioms 2025, 14, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14070492
Galal OH, Alruwaili E. Uncertainty Quantification of Herschel–Bulkley Fluids in Rectangular Ducts Due to Stochastic Parameters and Boundary Conditions. Axioms. 2025; 14(7):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14070492
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalal, Osama Hussein, and Eman Alruwaili. 2025. "Uncertainty Quantification of Herschel–Bulkley Fluids in Rectangular Ducts Due to Stochastic Parameters and Boundary Conditions" Axioms 14, no. 7: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14070492
APA StyleGalal, O. H., & Alruwaili, E. (2025). Uncertainty Quantification of Herschel–Bulkley Fluids in Rectangular Ducts Due to Stochastic Parameters and Boundary Conditions. Axioms, 14(7), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14070492






