Asymptotical Behavior of Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rates and Proportional Impulsive Vaccination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Asymptotical Stability of the Exact Solution
3. ILIEM for Impulsive SIR
3.1. Advantages of ILIEM
3.2. Asymptotical Stability of ILIEM
4. Numerical Experiments
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. Roy. Soc. 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Infectious Diseases of Humans: Dynamics and Control; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.E.; Zhou, Y.C.; Wu, J.H. Modeling and Dynamics of Infectious Diseases; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brauer, F.; Chavez, C.C.; Feng, Z.L. Mathematical Models in Epidemiology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Agur, Z.; Cojocaru, L.; Mazor, G.; Anderson, R.M.; Danon, Y.L. Pulse mass measles vaccination across age cohorts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11698–11702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulgin, B.; Stone, L.; Agur, Z. Pulse vaccination strategy in the SIR epidemic model. Bull. Math. Biol. 1998, 60, 1123–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, L.; Shulgin, B.; Agur, Z. Theoretical examination of the pulse vaccination policy in the SIR epidemic model. Math. Comput. Model. 2000, 31, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.Y.; Xiao, Y.N.; Clancy, D. New modelling approach concerning integrated disease control and cost-effectivity. Nonlinear Anal. 2005, 63, 439–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.J.; Chen, L.S.; Nieto, J.J.; Torres, A. Analysis of a delayed epidemic model with pulse vaccination and saturation incidence. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6037–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.J.; Teng, Z.D.; Xie, D.H. Analysis of a delayed SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 40, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Huo, H.F.; Sun, X.K.; Fu, Q. The differential susceptibility SIR epidemic model with time delay and pulse vaccination. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 34, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Smith, H.L.; Wang, L. Global dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with vertical transmission. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2001, 62, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chontita, R.; Inthira, C. A mathematical model for predicting and controlling COVID-19 transmission with impulsive vaccination. AIMS Math. 2024, 9, 6281–6304. [Google Scholar]
- João, P.S.M.C.; Rodrigues, A.A. Pulse vaccination in a SIR model: Global dynamics, bifurcations and seasonality. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2024, 139, 108272. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Chen, L.K.; Liu, S.S. Impulsive linearly implicit Euler method for the SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination strategy. Axioms 2024, 13, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, M.; Milner, F.A.; Pugliese, A. Analytical and numerical results for the age structured SIS epidemic model with mixed inter-intracohort transmission. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1992, 23, 662–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.W.; Zuo, T.Q.; Chen, Z.J. Numerical analysis of linearly implicit Euler–Riemann method for nonlinear Gurtin-MacCamy model. Appl. Numer. Math. 2021, 163, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Z.; Yang, Z.W.; Liu, S.Q. Numerical threshold of linearly implicit Euler method for nonlinear infection-age SIR models. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 2023, 28, 70–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.X.; Chen, Z.J.; Yang, Z.W. Numerical representations of global epidemic threshold for nonlinear infection-age SIR models. Math. Comput. Simul. 2023, 204, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.Z.; Chen, L.S. Complexity and asymptotical behavior of a SIRS epidemic model with proportional impulsive vaccination. Adv. Complex Syst. 2005, 8, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.E.; Zhou, Y.C.; Li, C.Z. Qualitative and Stability Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hairer, E.; Nørsett, S.P.; Wanner, G. Solving Ordinary Differential Equations I; Nonstiff Problems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L. Convergence, consistency and zero stability of impulsive one-step numerical methods. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 423, 127017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchia, M.; Ishiwata, E. Dynamics of a discretized SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination and time delay. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 236, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaydi, S. An Introduction to Difference Equations; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Liu, M.Z.; Song, M.H. Extinction and permanence of the numerical solution of a two-prey one predator system with impulsive effect. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2011, 88, 1305–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.H.; Wu, K.N.; Liu, M.Z. The Euler scheme and its convergence for impulsive delay differential equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 216, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.N.; Ding, X.H. Convergence and stability of Euler method for impulsive stochastic delay differential equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 229, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
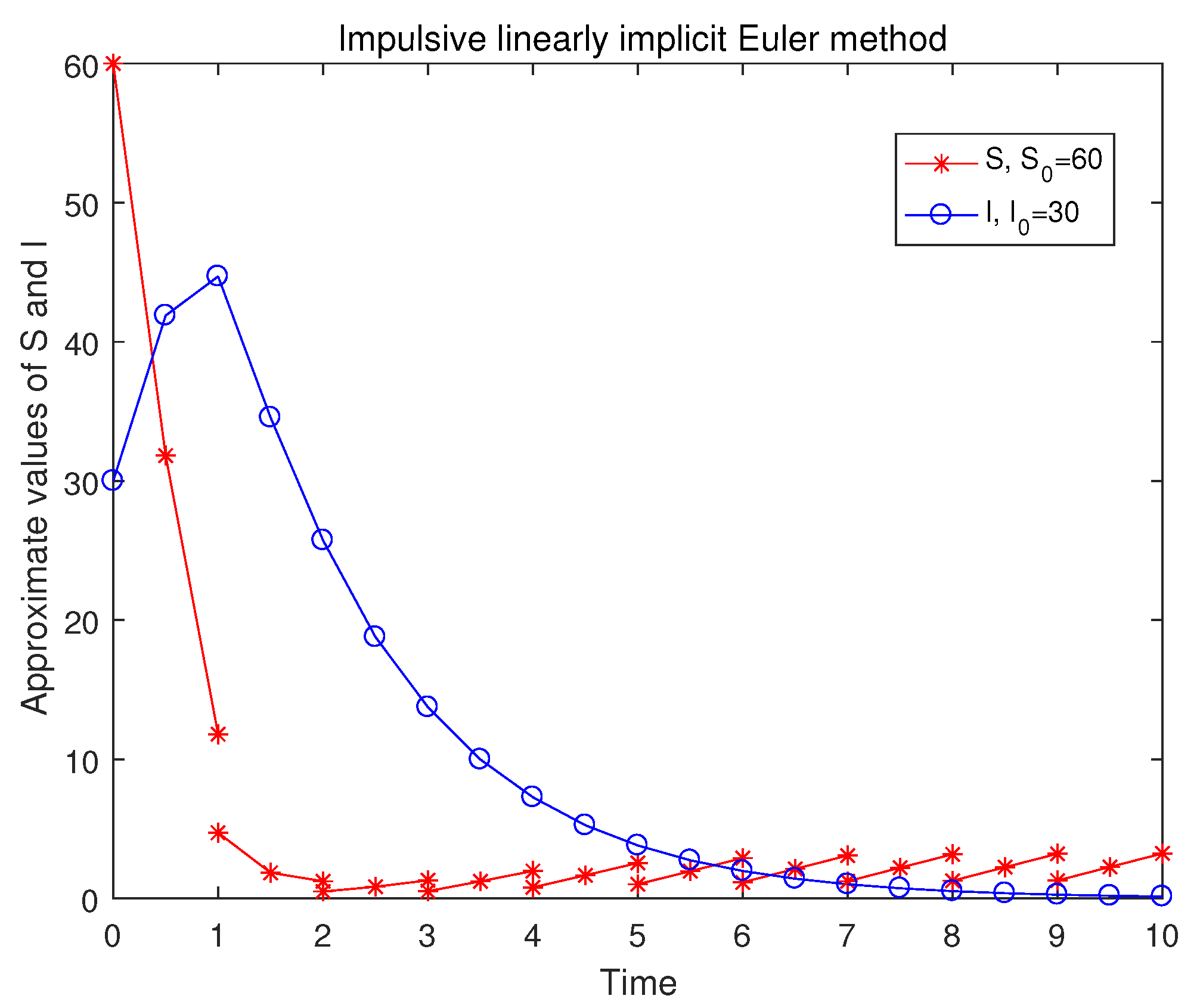
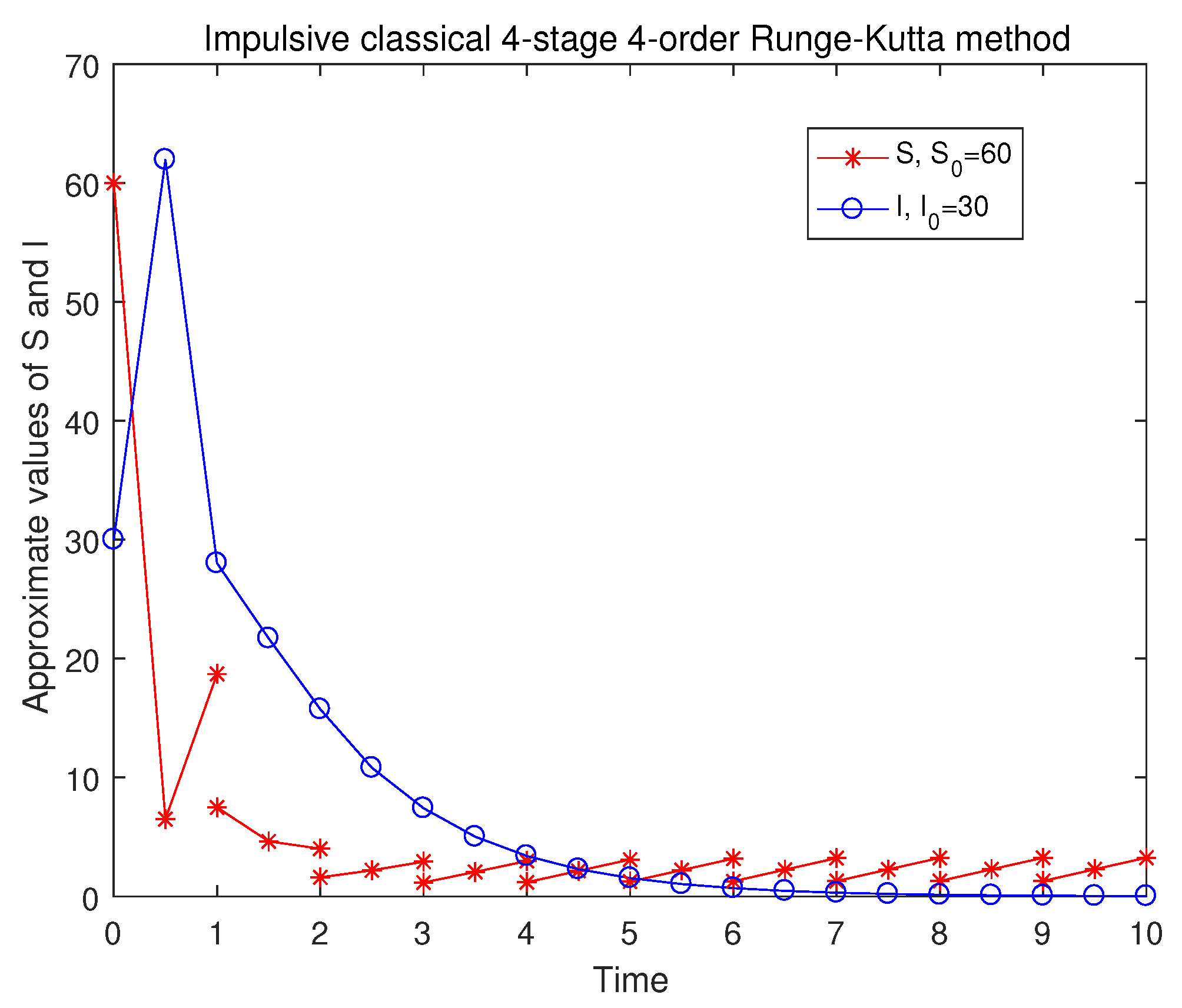
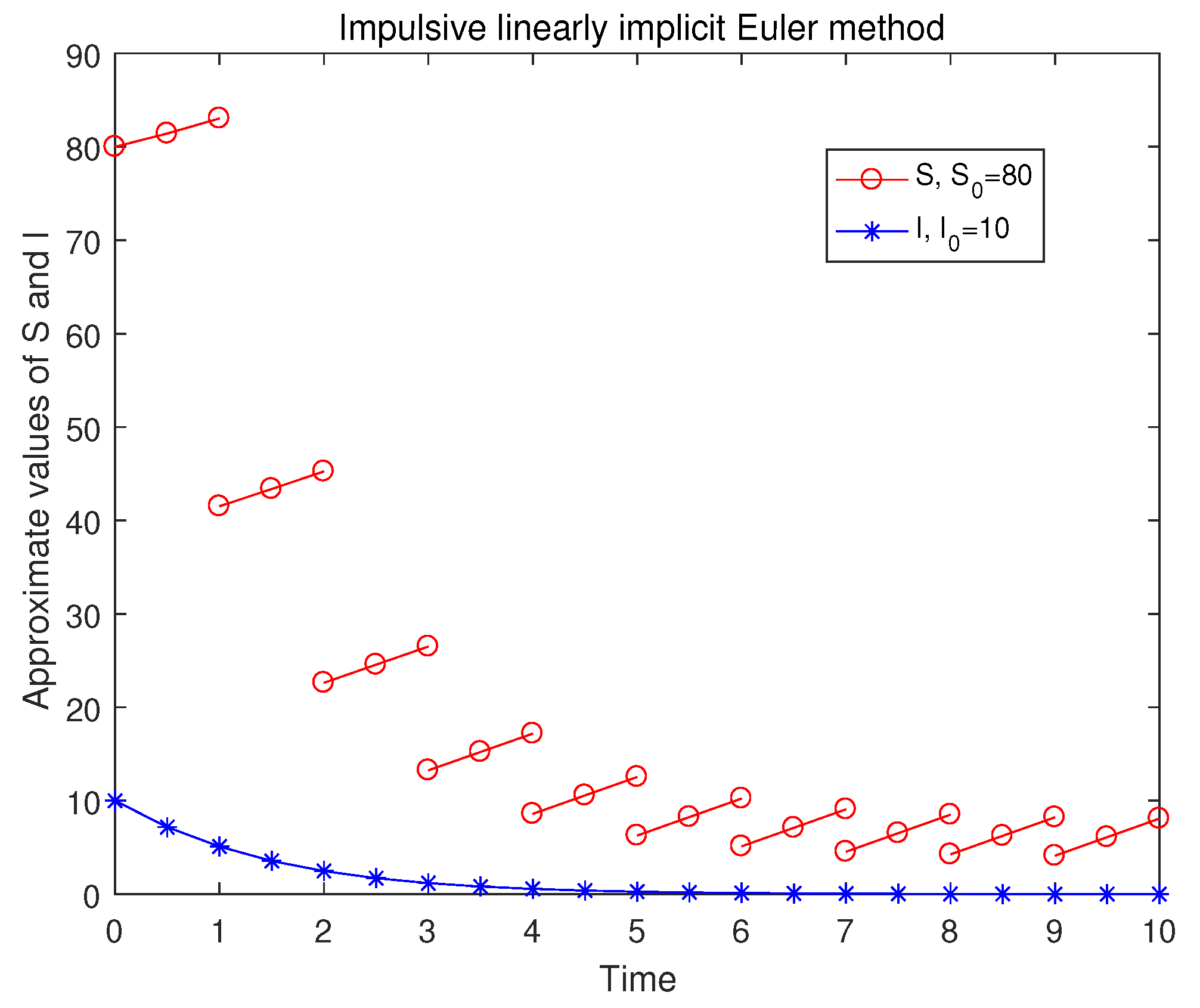
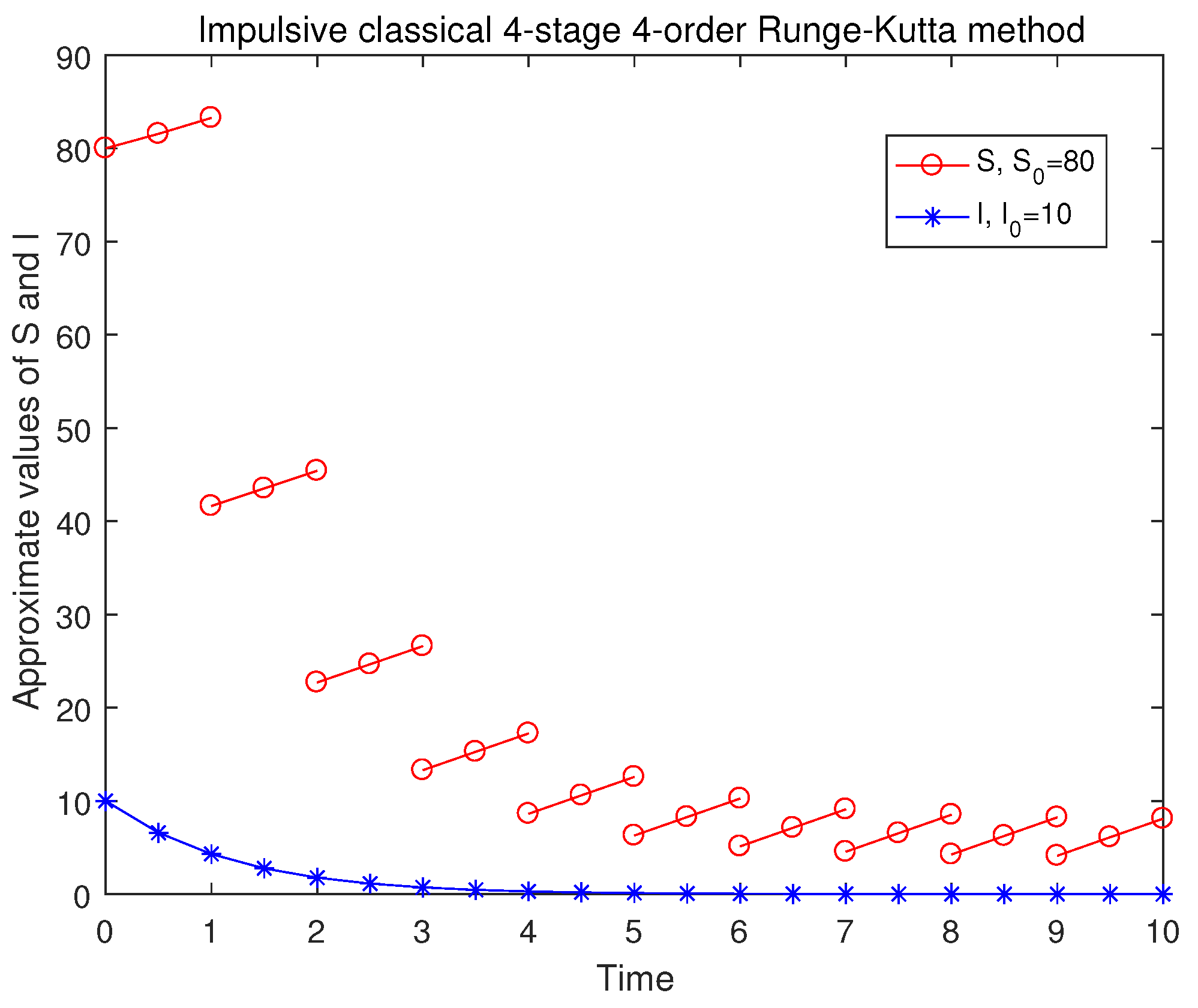
| m | ILIEM | IEEM | IHM | ICRKM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 0.013948 | 0.032256 | 3.796751 × 10−10 | 2.135055 × 10−4 |
| 2000 | 0.006978 | 0.016134 | 4.013805 × 10−11 | 1.238906 × 10−5 |
| 4000 | 0.003490 | 0.008045 | 2.039033 × 10−12 | 7.846188 × 10−7 |
| 8000 | 0.001745 | 0.004014 | 2.548791 × 10−13 | 4.961802 × 10−8 |
| Ratio | 0.500168 | 0.499246 | 0.093839 | 0.061429 |
| m | ILIEM | IEEM | IHM | ICRKM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 0.168657 | 3.408964 × 10−4 | 2.235798 × 10−6 | 1.983242 × 10−8 |
| 2000 | 0.084532 | 1.856005 × 10−4 | 2.815079 × 10−7 | 1.110038 × 10−9 |
| 4000 | 0.042318 | 9.799084 × 10−5 | 3.520072 × 10−8 | 6.243786 × 10−11 |
| 8000 | 0.021172 | 5.044188 × 10−5 | 4.285831 × 10−9 | 3.902366 × 10−12 |
| Ratio | 0.500709 | 0.528780 | 0.124210 | 0.058089 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.-W.; Zhang, G.-L. Asymptotical Behavior of Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rates and Proportional Impulsive Vaccination. Axioms 2025, 14, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14060470
Xu Z-W, Zhang G-L. Asymptotical Behavior of Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rates and Proportional Impulsive Vaccination. Axioms. 2025; 14(6):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14060470
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhi-Wei, and Gui-Lai Zhang. 2025. "Asymptotical Behavior of Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rates and Proportional Impulsive Vaccination" Axioms 14, no. 6: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14060470
APA StyleXu, Z.-W., & Zhang, G.-L. (2025). Asymptotical Behavior of Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rates and Proportional Impulsive Vaccination. Axioms, 14(6), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14060470







