Fusion Maximal Information Coefficient-Based Quality-Related Kernel Component Analysis: Mathematical Formulation and an Application for Nonlinear Fault Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel multivariate statistical methodology termed the FMIC-QRKCA method for quality-related fault detection in nonlinear industrial processes, explicitly addressing quality-related feature extraction to significantly enhance detection performance for quality-related faults.
- (2)
- Based on the information fusion and the MIC, a FMIC method is proposed to rigorously quantify the correlations between process variables and multivariate quality indicators, enabling targeted screening of quality-informative process variables through information fusion.
- (3)
- Building upon the fundamentals of FMIC and KPCA, a QRKCA method is developed, which advances traditional KPCA by incorporating quality relevance into principal component selection via statistical correlation analysis and cumulative information criteria.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Methodological Review
2.2. Problem Description
3. Main Results
3.1. Fusion Maximal Information Coefficient
3.2. Online Monitoring
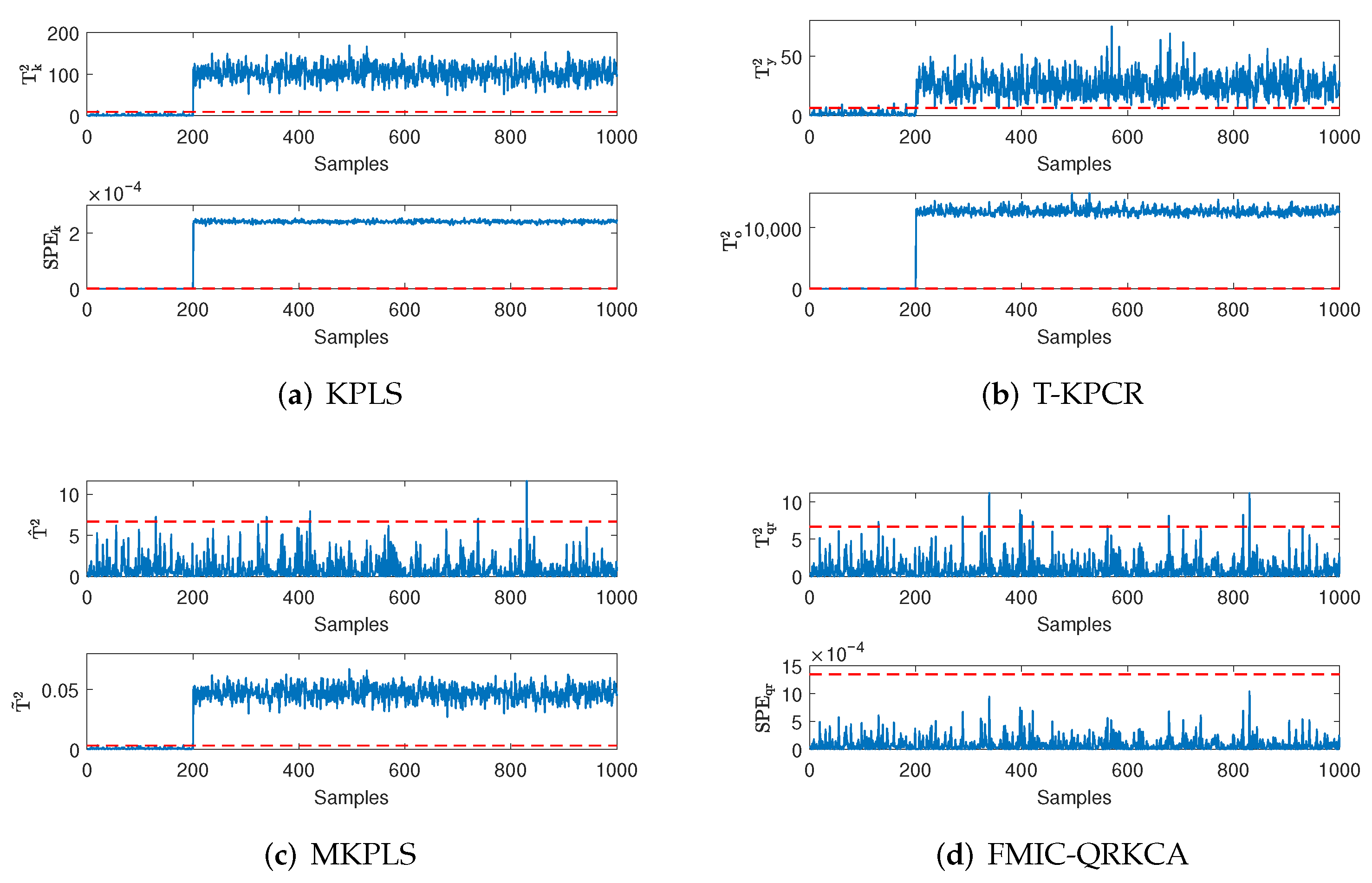
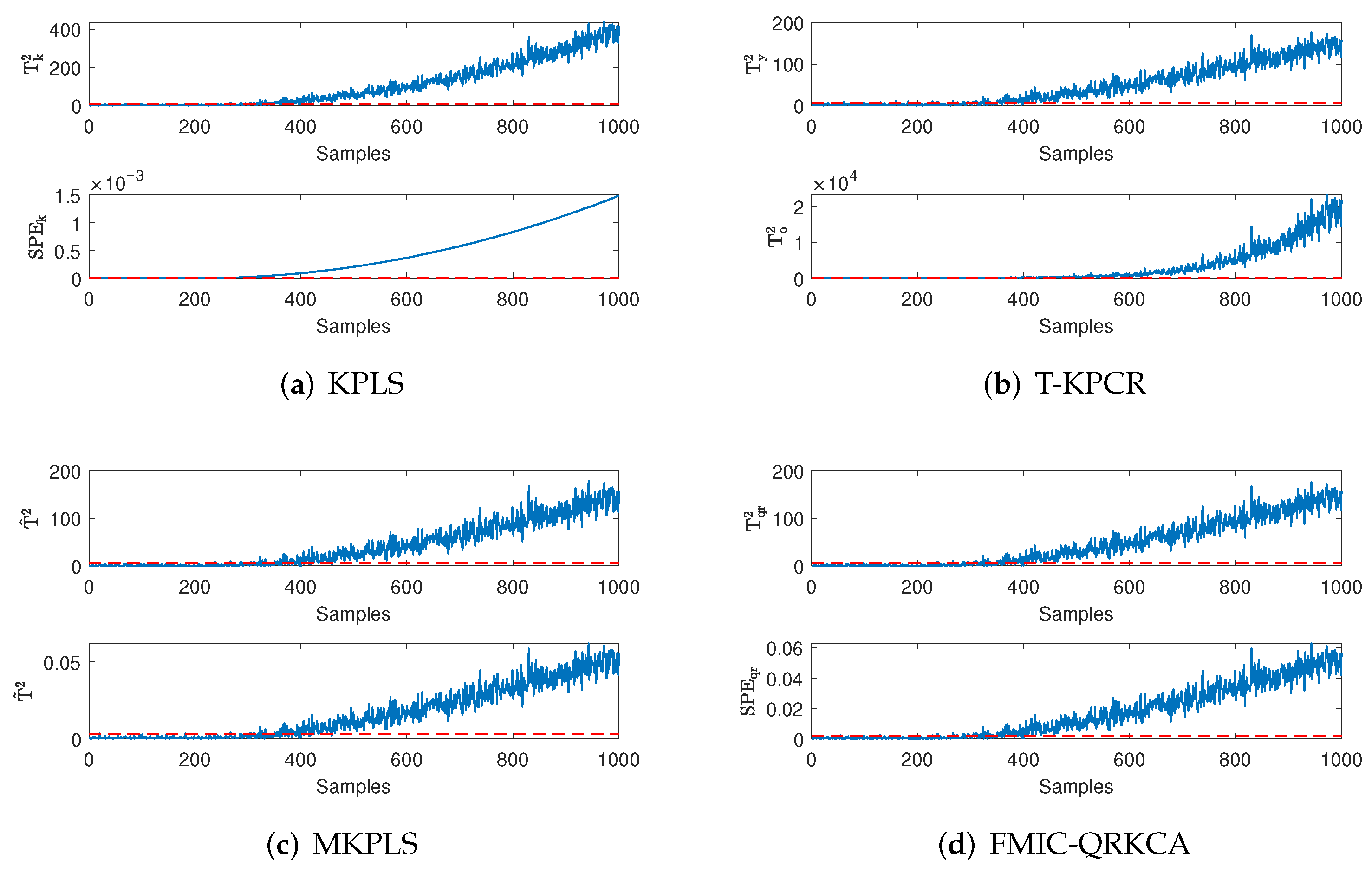
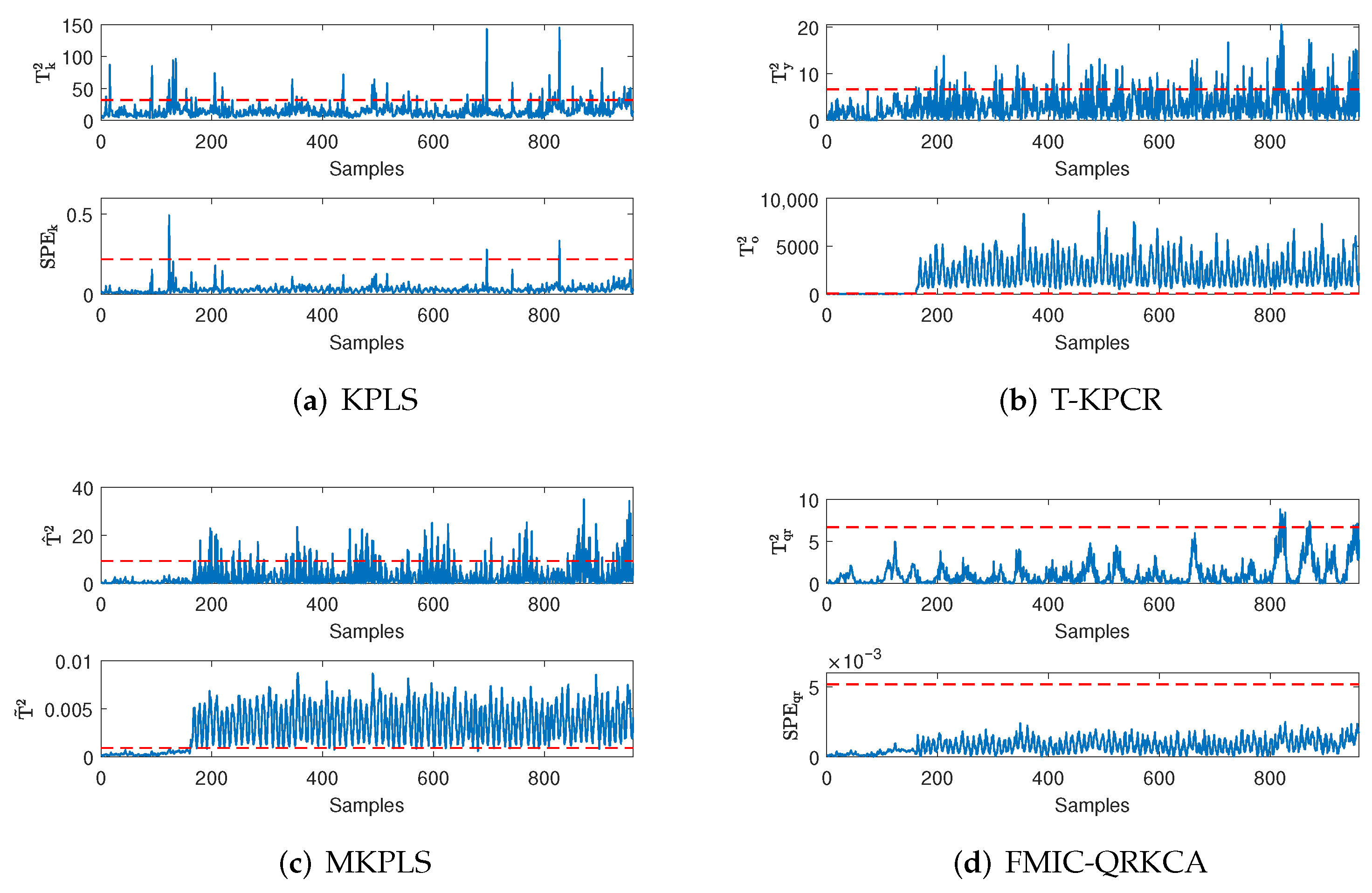
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Numerical Case
4.2. Industrial Case
4.3. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, S.; Song, Z. Quality-relevant modeling and monitoring of industrial cyber-physical systems: The semi-supervised dynamic latent variable models. IEEE Trans. Ind. Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2024, 3, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Peng, K.; Zhang, C.; Shahid, M.A. A cloud–edge collaboration based quality-related hierarchical fault detection framework for large-scale manufacturing processes. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 256, 124909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, S.X.; Li, L. On observer-based fault detection for nonlinear systems. Syst. Control Lett. 2015, 82, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhao, C.; Huang, B.; Xie, M. Intrinsic causality embedded concurrent quality and process monitoring strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 15111–15121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J. Dynamic event-triggered interval observer-based fault detection for a class of nonlinear cyber-physical systems with disturbance. Axioms 2025, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. Variational autoencoder based on knowledge sharing and correlation weighting for process-quality concurrent fault detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Qin, S.J.; Chai, T. Dynamic concurrent kernel cca for strip-thickness relevant fault diagnosis of continuous annealing processes. J. Process Control 2018, 67, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, N.; Lopes, A.M. Fault detection and identification with kernel principal component analysis and long short-term memory artificial neural network combined method. Axioms 2023, 12, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Cao, Y.; Ding, S.X.; Zhang, K.; Koenings, T.; Peng, T.; Yang, C.; Gui, W. A distributed canonical correlation analysis-based fault detection method for plant-wide process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 2710–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.Z.H.; Ahmed, Z.; Lisheng, H. Weighted linear local tangent space alignment via geometrically inspired weighted pca for fault detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Luo, J.; Kong, X.; Xu, Z. Orthogonal multi-block dynamic pls for quality-related process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 21, 3421–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shang, J.; Chen, M. Principal component analysis-based ensemble detector for incipient faults in dynamic processes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 5391–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Ding, S.X.; Peng, T.; Yang, C.; Gui, W.; Shardt, Y.A. A just-in-time-learning-aided canonical correlation analysis method for multimode process monitoring and fault detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 5259–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Qin, S.J. Regression on dynamic pls structures for supervised learning of dynamic data. J. Process Control 2018, 68, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, Y. Key-performance-indicator-related fault detection based on deep orthonormal subspace analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 7249–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jiao, J.; Yin, S. A kernel direct decomposition-based monitoring approach for nonlinear quality-related fault detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 13, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D. Key-performance-indicator-related process monitoring based on improved kernel partial least squares. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 2626–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhen, W.; Zhu, W.; Wang, G. Quality-related root cause diagnosis based on orthogonal kernel principal component regression and transfer entropy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 6347–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, J.; Qian, Y.; Han, J.; Jiao, J. Kpca-cca-based quality-related fault detection and diagnosis method for nonlinear process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 6492–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Yin, Y.; Kang, H.; Ma, H. A distributed principal component regression method for quality-related fault detection and diagnosis. Inf. Sci. 2022, 600, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y. Artificial neural correlation analysis for performance-indicator-related nonlinear process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, G.; Qin, S.J. Total projection to latent structures for process monitoring. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Zhang, K.; Li, G. Quality-related process monitoring based on total kernel PLS model and its industrial application. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 707953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Luo, H.; Peng, K. Quality-related fault detection using linear and nonlinear principal component regression. J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 2159–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhao, N.; Wang, G.; Yin, S. A nonlinear quality-related fault detection approach based on modified kernel partial least squares. ISA Trans. 2017, 66, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, M. Dynamic related component analysis for quality-related process monitoring with applications to thermal power plants. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 132, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, M.; Wang, M. Weighted part mutual information related component analysis for quality-related process monitoring. J. Process Control 2020, 88, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Shi, H.; Tan, S.; Tao, Y. Multisubspace orthogonal canonical correlation analysis for quality-related plant-wide process monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 6368–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, K.; Dong, J.; Zhang, X. Kpi-related operating performance assessment based on distributed imrmr-kocta for hot strip mill process. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshef, D.N.; Reshef, Y.A.; Finucane, H.K.; Grossman, S.R.; McVean, G.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Lander, E.S.; Mitzenmacher, M.; Sabeti, P.C. Detecting novel associations in large data sets. Science 2011, 334, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAvoy, T.J. A plant-wide industrial process control problem. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1993, 17, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Offline modeling: |
|
| Online detection: |
|
| Variable | Step Fault () | Ramp Fault () |
|---|---|---|
| Fault : | Fault : () | |
| Fault : | Fault : () | |
| Fault : | Fault : () | |
| Fault : | Fault : () |
| Fault Types | KPLS | T-KPCR | MKPLS | FMIC-QRKCA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| faut-free | 1.25 | 0.75 | 4.13 | 3.87 | 1.13 | 1.37 | 1.12 | 0 |
| Fault Types | KPLS | T-KPCR | MKPLS | FMIC-QRKCA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fault | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Fault | 100 | 100 | 99.25 | 100 | 0.5 | 100 | 1.12 | 0 |
| Fault | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.75 | 100 | 100 | 98.38 |
| Fault | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0.625 | 100 | 1.12 | 0 |
| Fault Types | KPLS | T-KPCR | MKPLS | FMIC-QRKCA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fault | 88.62 | 99.38 | 84.88 | 99.25 | 92.37 | 91 | 91.88 | 87.85 |
| Fault | 88.50 | 99.12 | 79.87 | 99.12 | 1 | 91.25 | 1 | 0 |
| Fault | 85.38 | 99.00 | 82.87 | 96.13 | 80.12 | 79.87 | 81.87 | 73.62 |
| Fault | 88.12 | 98.75 | 88.88 | 98.25 | 1 | 81.25 | 1.12 | 0.00 |
| Fault Types | KPLS | T-KPCR | MKPLS | FMIC-QRKCA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| faut-free | 1.16 | 0.55 | 9.5 | 17.37 | 1.25 | 11.37 | 6.12 | 0 |
| Fault | Definition | KPLS | T-KPCR | MKPLS | FMIC-QRKCA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| & | |||||
| IDV(1) | A/C feed ratio, B composition constant (Stream 4) | 95.13 | 65.75 | 91.75 | 99.88 |
| IDV(2) | B composition A/C ration constant (Streams 4) | 96.13 | 95.50 | 55.88 | 98.88 |
| IDV(5) | Condenser cooling water inlet temperature | 34.88 | 29.75 | 10.37 | 30.12 |
| IDV(6) | Reactor feed rate | 99.38 | 99.62 | 96.12 | 99.50 |
| IDV(7) | Reactor cooling water inlet temperature | 50.25 | 70.37 | 20.63 | 100 |
| IDV(8) | A, B, C feed composition (Stream 4) | 94.50 | 90.62 | 65.00 | 98.25 |
| IDV(12) | Condenser cooling water inlet temperature | 93.00 | 94.00 | 62.50 | 99.00 |
| IDV(13) | Reaction kinetics | 95.00 | 90.75 | 78.50 | 95.50 |
| Fault | Definition | KPLS | T-KPCR | MKPLS | FMIC-QRKCA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| & | |||||
| IDV(3) | D feed temperature (Stream 2) | 17 | 10.37 | 0.63 | 6.75 |
| IDV(4) | Reactor cooling water inlet temperature | 15 | 13.50 | 0.75 | 6.88 |
| IDV(9) | D Feed temperature | 14.25 | 9.25 | 0.75 | 4.50 |
| IDV(11) | Reactor cooling water inletting water inlet temperature | 18.12 | 15.50 | 2.75 | 10.62 |
| IDV(14) | Reactor cooling water inlet temperature | 6.38 | 16.63 | 13.63 | 1.38 |
| IDV(15) | Condenser cooling water valve | 17.25 | 14.50 | 5.5 | 10.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y. Fusion Maximal Information Coefficient-Based Quality-Related Kernel Component Analysis: Mathematical Formulation and an Application for Nonlinear Fault Detection. Axioms 2025, 14, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14100745
Yuan J, Ma H, Wang Y. Fusion Maximal Information Coefficient-Based Quality-Related Kernel Component Analysis: Mathematical Formulation and an Application for Nonlinear Fault Detection. Axioms. 2025; 14(10):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14100745
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Jie, Hao Ma, and Yan Wang. 2025. "Fusion Maximal Information Coefficient-Based Quality-Related Kernel Component Analysis: Mathematical Formulation and an Application for Nonlinear Fault Detection" Axioms 14, no. 10: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14100745
APA StyleYuan, J., Ma, H., & Wang, Y. (2025). Fusion Maximal Information Coefficient-Based Quality-Related Kernel Component Analysis: Mathematical Formulation and an Application for Nonlinear Fault Detection. Axioms, 14(10), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14100745






