An Analytic Method to Determine the Optimal Time for the Induction Phase of Anesthesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
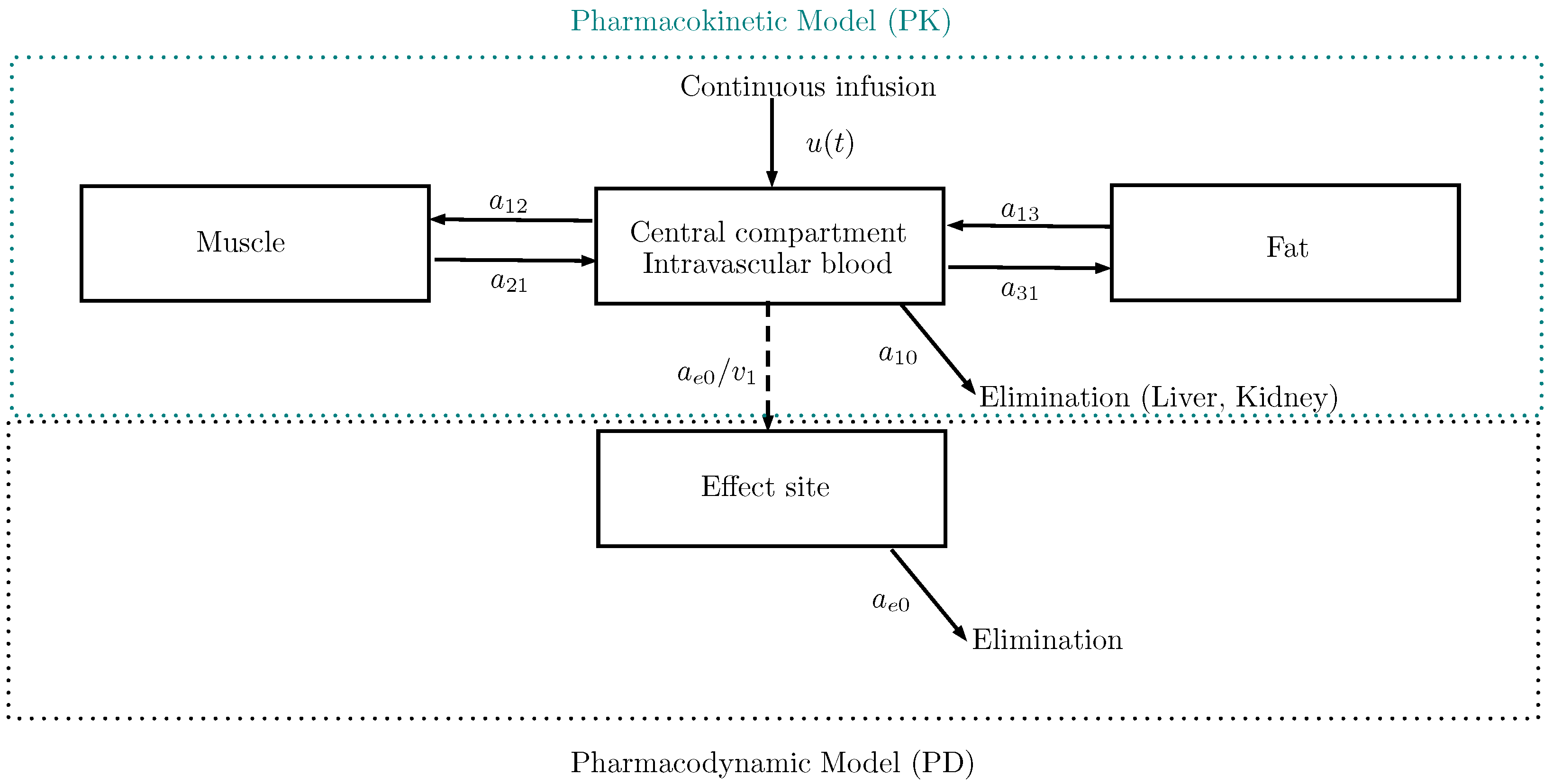
2. The PK/PD Model
2.1. Schnider’s Model
2.2. The Bispectral Index (BIS)
2.3. The Equilibrium Point
3. Time-Optimal Control Problem
3.1. Pontryagin Minimum Principle
3.2. Shooting Method
3.3. Analytical Method
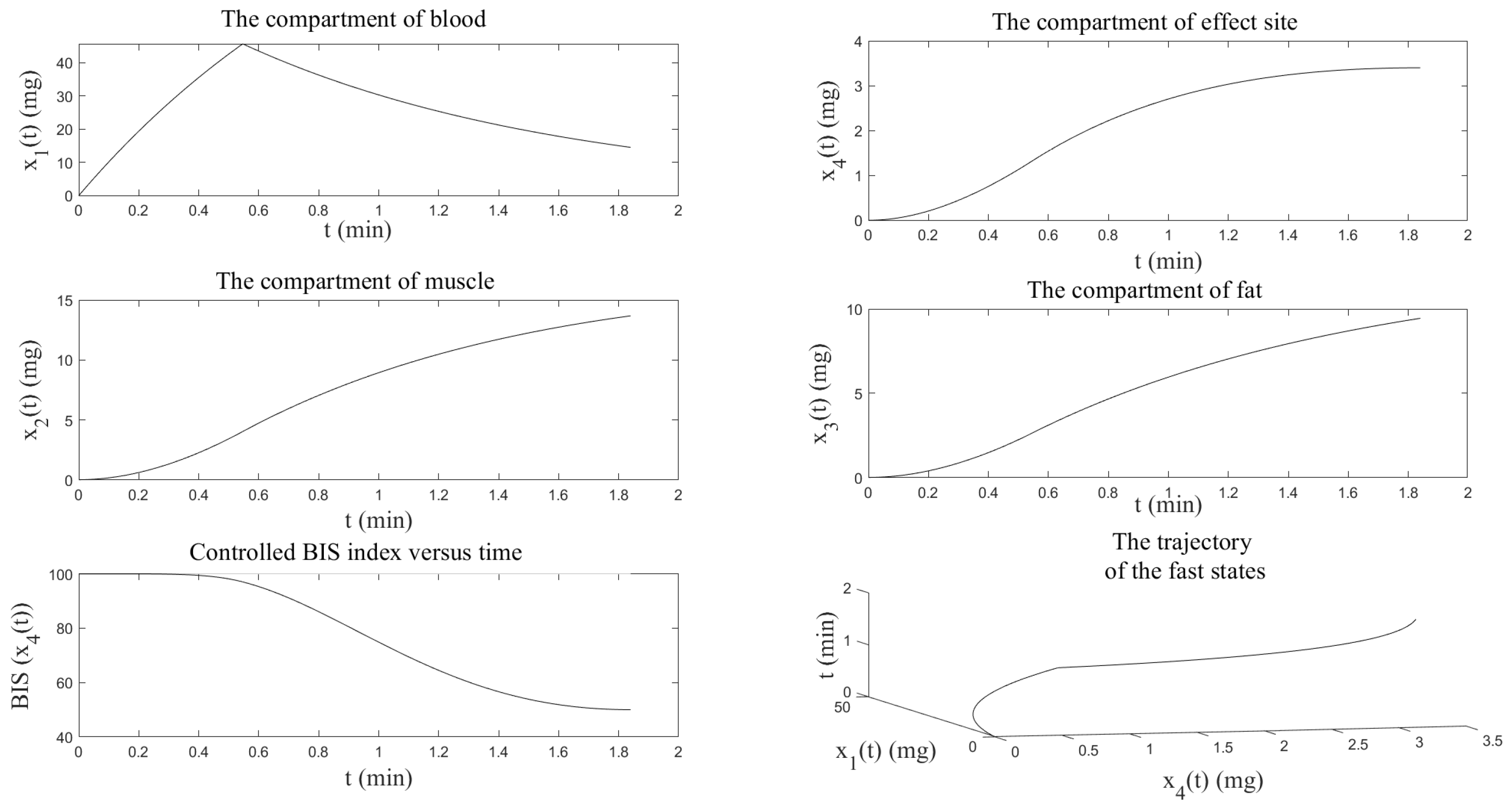
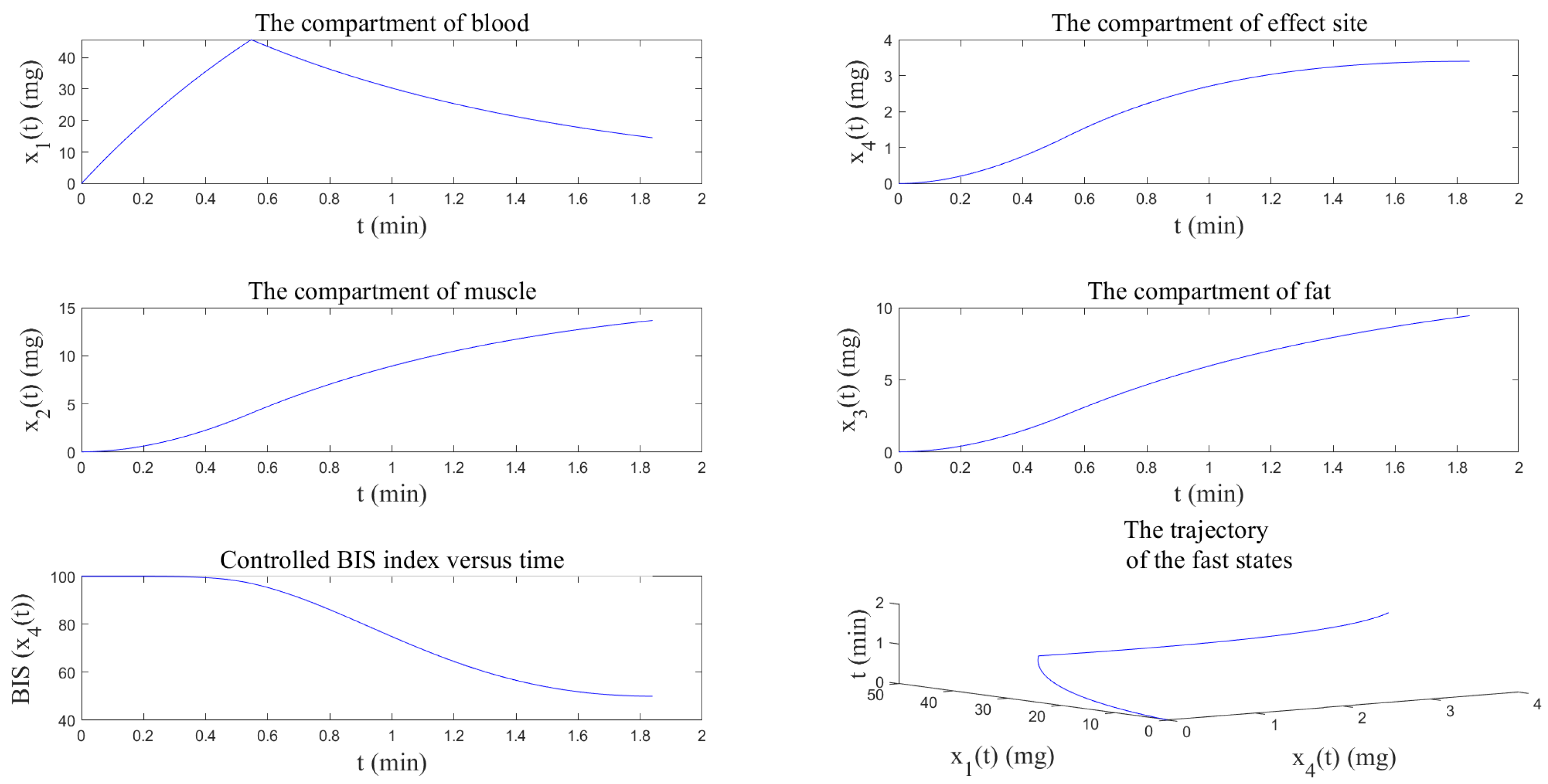
4. Numerical Example
4.1. Numerical Resolution by the Shooting Method
4.2. Numerical Resolution by the Analytical Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evers, A.S.; Maze, M.; Kharasch, E.D. Anesthetic Pharmacology: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Sidawy, A.N.; Dezee, K.; Neville, R.F.; Weiswasser, J.; Arora, S.; Aidinian, G.; Abularrage, C.; Adams, E.; Khuri, S.; et al. The effects of the type of anesthesia on outcomes of lower extremity infrainguinal bypass. J. Vasc. Surg. 2006, 44, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, A.F.; Mitchell, S.J. Complications of anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 2018, 73, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.L. Modeling and control of pharmacodynamics. Eur. J. Control 2015, 24, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meibohm, B.; Derendorf, H. Basic concepts of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modelling. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 35, 401–413. [Google Scholar]
- Absalom, A.R.; Mani, V.; Smet, T.D.; Struys, M.M.R.F. Pharmacokinetic models for propofol—Defining and illuminating the devil in the detail. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 103, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enlund, M. TCI: Target Controlled Infusion, or Totally Confused Infusion? Call for an Optimised Population Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Propofol. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2008, 113, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshin, T.A. Exploratory mathematical frameworks and design of control systems for the automation of propofol anesthesia. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2022, 10, 1858–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, J. An analytical approach of one-compartmental pharmacokinetic models with sigmoidal Hill elimination. Bull. Math. Biol. 2022, 84, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanditha, C.K.; Rajan, M.P. An adaptive pharmacokinetic optimal control approach in chemotherapy for heterogeneous tumor. J. Biol. Syst. 2022, 30, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.J. Operating room scheduling for non-operating room anesthesia with emergency uncertainty. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 321, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnider, T.W.; Minto, C.F.; Gambus, P.L.; Andresen, C.; Goodale, D.B.; Shafer, S.L.; Youngs, E.J. The influence of method of administration and covariates on the pharmacokinetics of propofol in adult volunteers. Anesthesiology 1998, 88, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, B.; White, M.; Morton, N.; Kenny, G.N. Pharmacokinetic model driven infusion of propofol in children. Br. J. Anaesth. 1991, 67, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabi, S.; Queinnec, I.; Tarbouriech, S.; Garcia, G.; Mazerolles, M. New approach for the control of anesthesia based on dynamics decoupling. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabi, S.; Queinnec, I.; Garcia, G.; Mazerolles, M. Time-optimal control for the induction phase of anesthesia. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 12197–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, M.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.A.; Xie, W.; Riaz, R.A.; Khan, Y. Observer design estimating the propofol concentration in PKPD model with feedback control of anesthesia administration. Arch. Control Sci. 2022, 32, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.G.; Plitt, K.J. A Multiple shooting algorithm for direct solution of optimal control problems. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1984, 17, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontryagin, L.S.; Boltyanskii, V.G.; Gamkrelidze, R.V.; Mishchenko, E.F. The Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes; Trirogoff, K.N., Neustadt, L.W., Eds.; Interscience Publishers John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, J.M.; Haddad, W.M. Drug dosing control in clinical pharmacology. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2005, 25, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, W.P.T. Research on obesity: A report of the DHSS/MRC Group. Nutr. Bull. 1977, 4, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, W.M.; Chellaboina, V.; Hui, Q. Nonnegative and Compartmental Dynamical Systems; Princeton Univ. Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitri, M.A.; Bibi, M.O.; Bentobache, M. A hybrid direction algorithm for solving optimal control problems. Cogent Math. Stat. 2019, 6, 1612614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuflhard, P. Newton Methods for Nonlinear Problems; Springer Series in Computational Mathematics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 35. [Google Scholar]
- Elsisi, M.; Soliman, M. Optimal design of robust resilient automatic voltage regulators. ISA Trans. 2021, 108, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.E.; Mohamed, S.M.R.; Saied, E.M.M.; Elsisi, M.; Su, C.-L.; Hadi, H.A. Optimal energy management solutions using artificial intelligence techniques for photovoltaic empowered water desalination plants under cost function uncertainties. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 93646–93658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Delgado, V.F.; Taneco-Hernández, M.A.; Vargas-De-León, C.; Gómez-Aguilar, J.F. Exact solutions to fractional pharmacokinetic models using multivariate Mittag-Leffler functions. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 168, 113164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
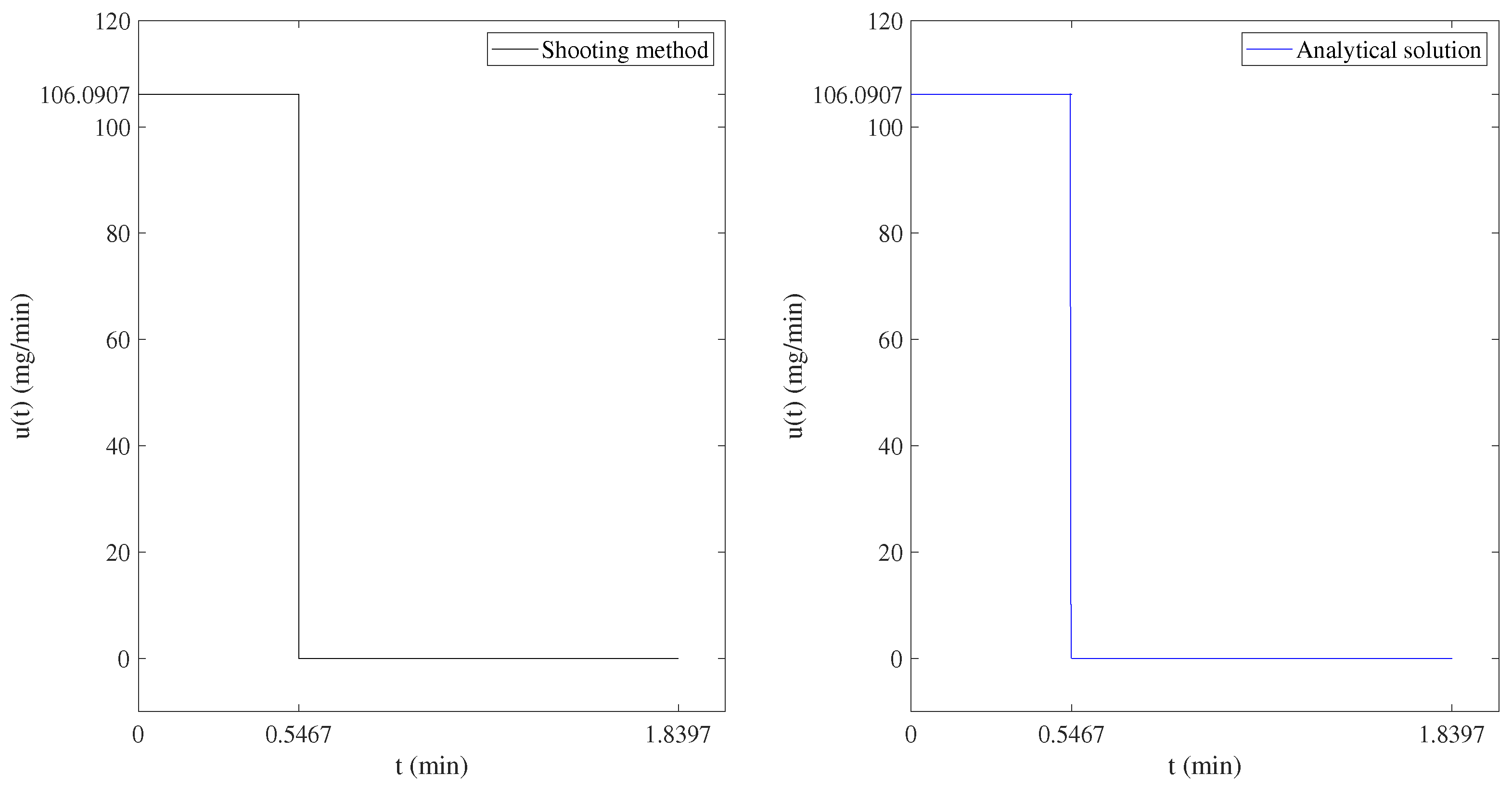
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaitri, M.A.; Silva, C.J.; Torres, D.F.M. An Analytic Method to Determine the Optimal Time for the Induction Phase of Anesthesia. Axioms 2023, 12, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090867
Zaitri MA, Silva CJ, Torres DFM. An Analytic Method to Determine the Optimal Time for the Induction Phase of Anesthesia. Axioms. 2023; 12(9):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090867
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaitri, Mohamed A., Cristiana J. Silva, and Delfim F. M. Torres. 2023. "An Analytic Method to Determine the Optimal Time for the Induction Phase of Anesthesia" Axioms 12, no. 9: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090867
APA StyleZaitri, M. A., Silva, C. J., & Torres, D. F. M. (2023). An Analytic Method to Determine the Optimal Time for the Induction Phase of Anesthesia. Axioms, 12(9), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090867






