Isogeometric Schwarz Preconditioners with Generalized B-Splines for the Biharmonic Problem †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. GB-Splines: Definition and Basic Properties
2.1. Generalized Polynomial Spaces
2.2. Univariate GB-Splines
- 1.
- Positivity: .
- 2.
- Compact support: if , .
- 3.
- Local partition of unity: , .
- 4.
- Local linear independence: are linearly independent on .
- 5.
- Smoothness: each has a continuous derivative of order at the knot , where is the multiplicity of in the knot vector .
- 6.
- Differentiation: The derivative of GB-splines is represented in terms of two consecutive GB-splines of a lower degree as
2.3. Multivariate GB-Splines
- ;
- ;
- ;
- and ;
- .
- Find such thatwith bilinear form .
3. The Overlapping Schwarz Preconditioners
3.1. Subdomains and Subspace Decomposition
4. A Condition Number Estimate
5. Numerical Results
5.1. Two-Dimensional Tests: OAS(2) Scalability in N and Optimality in
5.2. Two-Dimensional Tests: OAS Dependence on p and r
5.3. Three-Dimensional Tests: OAS(2) Scalability in N
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, T.J.R.; Cottrell, J.A.; Bazilevs, Y. Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry, and mesh refinement. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2005, 194, 4135–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, J.A.; Hughes, T.J.R.; Bazilevs, Y. Isogeometric Analysis. Towards Integration of CAD and FEA; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Piegl, L.; Tiller, W. The NURBS Book, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bracco, C.; Berdinsky, D.; Cho, D.; Oh, M.-J.; Kim, T.-W. Trigonometric generalized T-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 268, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, P.; Manni, C.; Pelosi, F.; Sampoli, M.L. Quasi-interpolation in isogeometric analysis based on generalized B-splines. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2010, 27, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasov, B.I.; Sattayatham, P. GB-splines of arbitrary order. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1999, 104, 63–88. [Google Scholar]
- Manni, C.; Pelosi, F.; Sampoli, M.L. Generalized B-splines as a tool in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, C.; Pelosi, F.; Sampoli, M.L. Isogeometric analysis in advection–diffusion problems: Tension splines approximation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 236, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, C.; Pelosi, F.; Speleers, H. Local hierarchical h-refinements in IgA based on generalized B-splines. In Mathematical Methods for Curves and Surfaces; Floater, M., Lyche, T., Mazure, M.L., Mørken, K., Schumaker, L.L., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 8177, pp. 341–363. [Google Scholar]
- Manni, C.; Reali, A.; Speleers, H. Isogeometric collocation methods with generalized B-splines. Comput. Math. Appl. 2015, 70, 1659–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarlet, P.G. Volume II: Theory of Plates, Studies in Mathematics and its Applications vol 27. In Mathematical Elasticity; North-Holland Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Girault, V.; Raviart, P.-A. Finite Element Approximation of the Navier-Stokes Equations; Lecture Notes in Mathematics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 749. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, S.; Scott, R. The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.-C. Nonconforming finite element methods. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2002, 149, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarlet, P.G.; Raviart, P.-A. A mixed finite element method for the biharmonic equation. In Mathematical Aspects of Finite Elements in Partial Differential Equations, Proceedings of the Symposium Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA, 1–3 April 1974; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, D. Overlapping Schwarz methods for isogeometric analysis based on generalized B-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 372, 113430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão da Veiga, L.; Cho, D.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S. Overlapping Schwarz methods for Isogeometric Analysis. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2012, 50, 1394–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão da Veiga, L.; Cho, D.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S. Isogeometric Schwarz preconditioners for linear elasticity systems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 253, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão da Veiga, L.; Cho, D.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S. Overlapping Schwarz preconditioners for isogeometric collocation methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 278, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S. Overlapping additive Schwarz preconditioners for isogeometric collocation discretizations of linear elasticity. Comput. Math. Appl. 2021, 93, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão da Veiga, L.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S.; Widlund, O.B.; Zampini, S. Isogeometric BDDC preconditioners with deluxe scaling. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2014, 36, A1118–A1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirão da Veiga, L.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S.; Widlund, O.B.; Zampini, S. Adaptive selection of primal constraints for isogeometric BDDC deluxe preconditioners. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2017, 39, A281–A302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S.; Widlund, O.B.; Zampini, S. Isogeometric BDDC deluxe preconditioners for linear elasticity. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 2018, 28, 1337–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widlund, O.B.; Scacchi, S.; Pavarino, L.F. BDDC deluxe algorithms for two-dimensional H(curl) isogeometric analysis. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 44, A2349–A2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiss, S.K.; Pechstein, C.; Jüttler, B.; Tomar, S. IETI-Isogeometric Tearing and Interconnecting. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2012, 247–248, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S. Isogeometric block FETI-DP preconditioners for the Stokes and mixed linear elasticity systems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 310, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracco, C.; Cho, D.; Giannelli, C.; Vázquez, R. BPX preconditioners for isogeometric analysis using (truncated) hierarchical B-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 379, 113742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, A.; Harbrecht, H.; Kunoth, A.; Sangalli, G. BPX-preconditioning for isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 265, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatelli, M.; Garoni, C.; Manni, C.; Serra-Capizzano, S.; Speleers, H. Robust and optimal multi-iterative techniques for IgA Galerkin linear systems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 284, 230–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahalaut, K.; Kraus, J.; Tomar, S. Multigrid Methods for Isogeometric Discretization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 253, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofreither, C.; Takacs, S. Robust multigrid for isogeometric analysis based on stable splittings of spline spaces. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 2017, 55, 2004–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montardini, M.; Sangalli, G.; Tani, M. Robust isogeometric preconditioners for the Stokes system based on the Fast Diagonalization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 338, 162–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangalli, G.; Tani, M. Isogeometric preconditioners based on fast solvers for the Sylvester equation. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2016, 38, A3644–A3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, M. A preconditioning strategy for linear systems arising from nonsymmetric schemes in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Math. Appl. 2017, 74, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapl, M.; Buchegger, F.; Bercovier, M.; Jüttler, B. Isogeometric analysis with geometrically continuous functions on planar multi-patch geometries. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 316, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.E. Discontinuous Galerkin isogeometric analysis for the biharmonic equation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2018, 76, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Pavarino, L.F.; Scacchi, S. Isogeometric Schwarz preconditioners for the biharmonic problem. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 2018, 49, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyche, T.; Manni, C.; Speleers, H. Tchebycheffian B-splines revisited: An introductory exposition. In Advanced Methods for Geometric Modeling and Numerical Simulation; Springer INdAM Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 35, pp. 179–216. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, P.; Lyche, T.; Manni, C. On a class of weak Tchebycheff systems. Numer. Math. 2005, 101, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazure, M.-L. On a general new class of quasi-Chebyshevian splines. Numer. Algorithm 2011, 58, 399–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazure, M.-L. How to build all Chebyshevian spline spaces good for Geometric Design. Numer. Math. 2011, 119, 517–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, C.; Roman, F.; Speleers, H. Generalized B-splines in isogeometric analysis, Approximation theory XV: San Antonio 2016. Springer Proc. Math. Stat. 2017, 201, 239–267. [Google Scholar]
- de Boor, C. A Practical Guide to Splines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lyche, L. A recurrence relation for Chebyshevian B-splines. Constr. Approx. 1985, 1, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Fang, M. Unified and extended form of three types of splines. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2008, 216, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumaker, L.L. Spline Functions: Basic Theory, 3rd ed.; Cambridge Mathematical Library, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Toselli, A.; Widlund, O.B. Domain Decomposition Methods: Algorithms and Theory. In Computational Mathematics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- Dryja, M.; Widlund, O.B. Domain Decomposition Algorithms with Small Overlap. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1994, 15, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, C.D.; Reali, A.; Vazquez, R. GeoPDEs: A research tool for Isogeometric Analysis of PDEs. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2011, 42, 1020–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, R. A new design for the implementation of isogeometric analysis in Octave and Matlab: GeoPDEs 3.0. Comput. Math. Appl. 2016, 72, 523–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speleers, H. Algorithm 1020, Computation of multi-degree Tchebycheffian B-splines. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 2022, 48, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

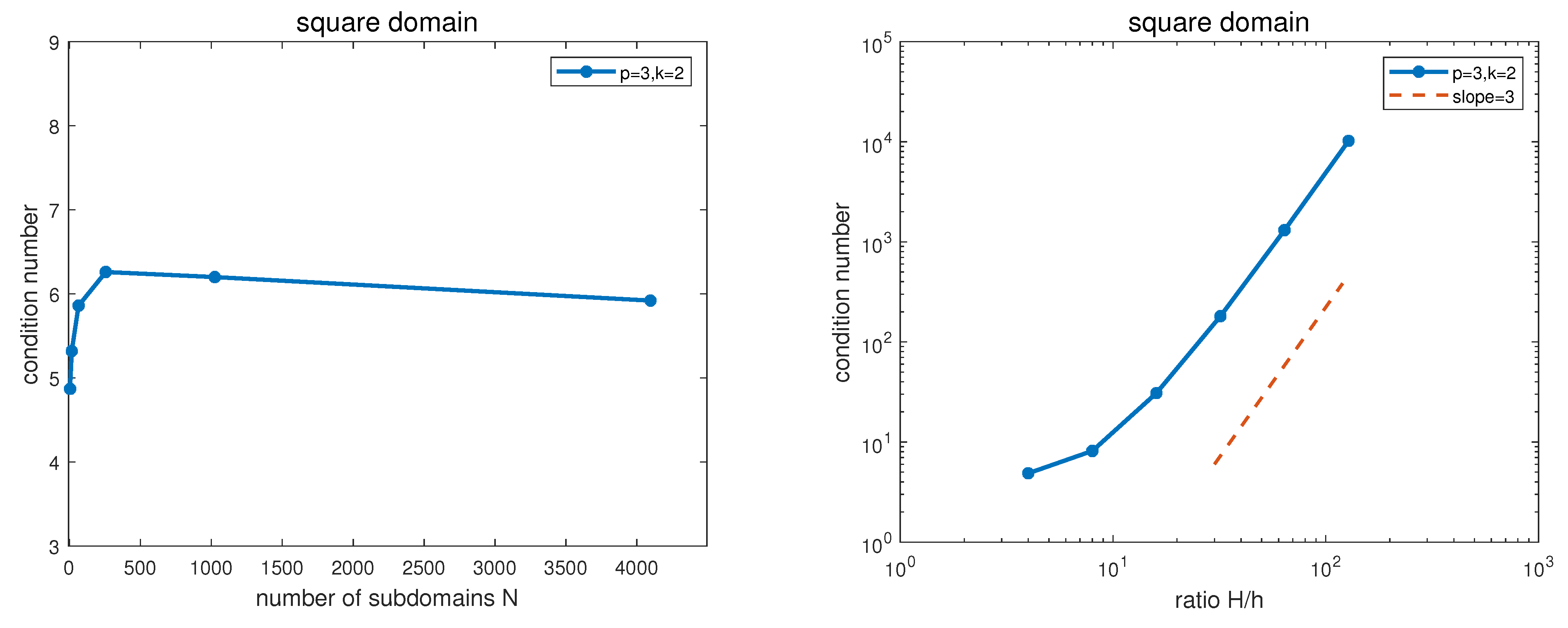
| OAS(1) Preconditioners with , GB-Splines, 2D Reference Square Domain | ||||||
| = 8 | = 16 | = 32 | = 64 | = 128 | = 256 | |
| N | (it.) | (it.) | (it.) | (it.) | (it.) | (it.) |
| 1.21 (9) | 5.86 (12) | 3.80 (17) | 2.84 (27) | 2.23 (51) | 1.78 (99) | |
| 8.50 (17) | 5.88 (28) | 4.46 (50) | 3.51 (96) | 2.79 (195) | ||
| 1.16 (36) | 8.86 (72) | 6.97 (155) | 5.55 (341) | |||
| 1.78 (96) | 1.40 (225) | 1.11 (534) | ||||
| 2.82 (305) | 2.23 (764) | |||||
| 4.51 (1077) | ||||||
| OAS(2) preconditioners with , GB-splines, 2D reference square domain | ||||||
| = 8 | = 16 | = 32 | = 64 | = 128 | = 256 | |
| N | (it.) | (it.) | (it.) | (it.) | (it.) | (it.) |
| 4.87 (8) | 8.15 (12) | 3.08 (16) | 1.81 (25) | 1.31 (47) | 1.02 (93) | |
| 5.32 (14) | 1.36 (20) | 6.25 (36) | 4.06 (75) | 3.06 (163) | ||
| 5.86 (16) | 1.96 (26) | 1.01 (53) | 6.86 (138) | |||
| 6.26 (17) | 2.39 (29) | 1.29 (66) | ||||
| 6.20 (16) | 2.48 (30) | |||||
| 5.92 (15) | ||||||
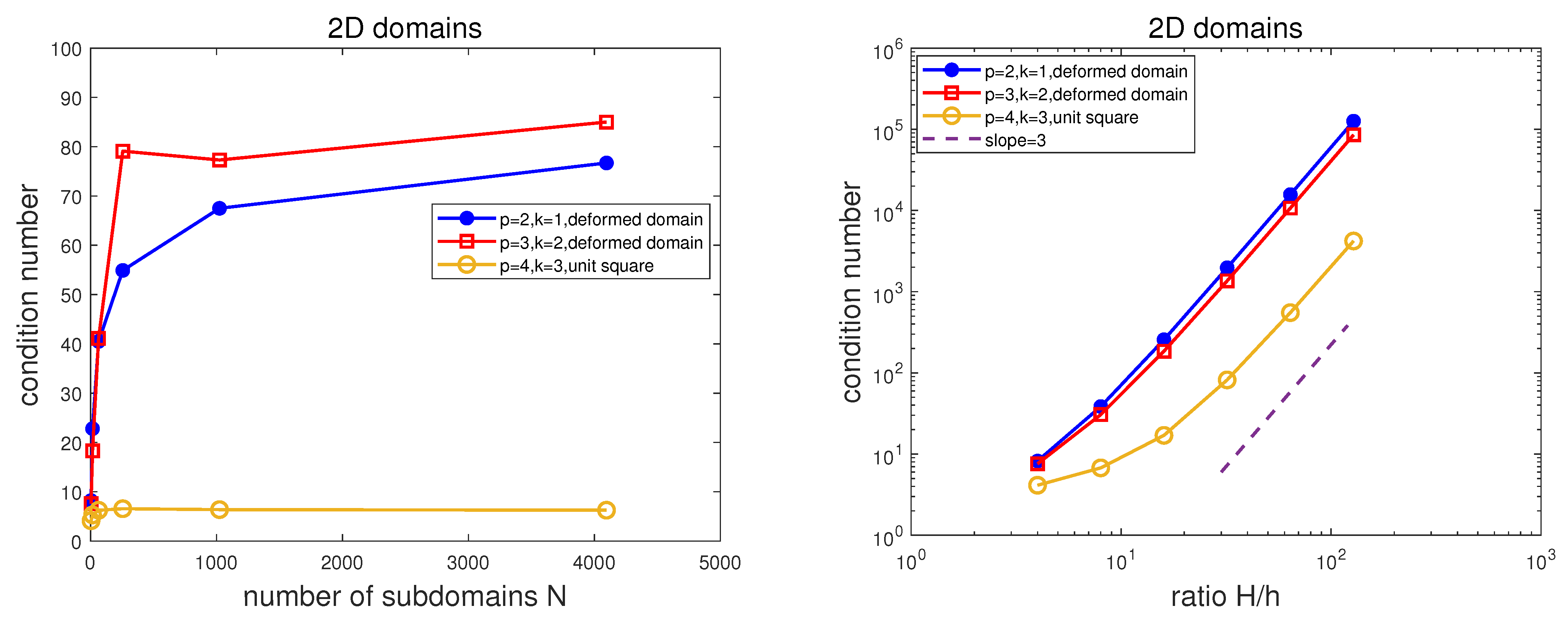
| OAS prec. with , 2D deformed domain | |||||||||||||
| = 8 | = 16 | = 32 | = 64 | = 128 | = 256 | ||||||||
| N | it. | it. | it. | it. | it. | it. | |||||||
| non-prec. | 1.09 | 19 | 2.02 | 105 | 3.53 | 460 | 5.96 | 1950 | 9.86 | 8175 | 1.61 | 33,502 | |
| 2-level OAS | 8.21 | 11 | 3.85 | 18 | 2.56 | 33 | 1.97 | 62 | 1.57 | 125 | 1.26 | 257 | |
| 2.28 | 24 | 1.56 | 50 | 1.22 | 123 | 9.84 | 315 | 7.96 | 723 | ||||
| 4.05 | 33 | 2.97 | 79 | 2.41 | 228 | 1.97 | 645 | ||||||
| 5.49 | 41 | 4.07 | 118 | 3.34 | 330 | ||||||||
| 6.75 | 48 | 5.02 | 133 | ||||||||||
| 7.67 | 53 | ||||||||||||
| OAS prec. with , 2D deformed domain | |||||||||||||
| non-prec. | 5.17 | 22 | 8.20 | 78 | 1.33 | 286 | 2.16 | 1159 | 3.49 | 4854 | 5.61 | 19,713 | |
| 2-level OAS | 7.59 | 13 | 3.06 | 18 | 1.85 | 33 | 1.36 | 65 | 1.07 | 138 | 8.54 | 313 | |
| 1.83 | 23 | 9.86 | 42 | 6.97 | 95 | 5.41 | 255 | 4.30 | 707 | ||||
| 4.11 | 32 | 2.49 | 69 | 1.95 | 177 | 1.54 | 509 | ||||||
| 7.91 | 41 | 3.66 | 80 | 4.08 | 258 | ||||||||
| 7.73 | 42 | 5.15 | 91 | ||||||||||
| 8.50 | 43 | ||||||||||||
| OAS prec. with , 2D reference domain (unit square) | |||||||||||||
| non-prec. | 2.77 | 10 | 3.81 | 27 | 5.88 | 66 | 9.32 | 211 | 1.49 | 772 | 2.38 | 6202 | |
| 2-level OAS | 4.13 | 8 | 6.76 | 11 | 1.70 | 14 | 8.19 | 21 | 5.52 | 36 | 4.21 | 116 | |
| 5.30 | 16 | 1.05 | 18 | 3.62 | 28 | 2.02 | 49 | 1.45 | 123 | ||||
| 6.25 | 16 | 1.73 | 24 | 7.60 | 44 | 4.71 | 97 | ||||||
| 6.56 | 16 | 2.27 | 26 | 1.18 | 55 | ||||||||
| 6.38 | 16 | 2.40 | 27 | ||||||||||
| 6.26 | 18 | ||||||||||||
| OAS prec. with , 2D deformed domain | |||||||||||||
| = 8 | = 16 | = 32 | = 64 | = 128 | = 256 | ||||||||
| N | it. | it. | it. | it. | it. | it. | |||||||
| non-prec. | 1.09 | 19 | 2.02 | 105 | 3.53 | 460 | 5.96 | 1950 | 9.86 | 8175 | 1.61 | 33,502 | |
| 2-level OAS | 4.36 | 9 | 1.42 | 15 | 7.90 | 24 | 5.69 | 43 | 4.48 | 84 | 3.59 | 172 | |
| 1.15 | 20 | 4.78 | 32 | 3.48 | 73 | 2.78 | 188 | 2.25 | 448 | ||||
| 2.03 | 27 | 8.79 | 51 | 6.76 | 132 | 5.53 | 357 | ||||||
| 2.74 | 31 | 1.20 | 66 | 9.33 | 180 | ||||||||
| 3.35 | 33 | 1.48 | 75 | ||||||||||
| 3.81 | 38 | ||||||||||||
| OAS prec. with , 2D deformed domain | |||||||||||||
| non-prec. | 5.17 | 22 | 8.20 | 78 | 1.33 | 286 | 2.16 | 1159 | 3.49 | 4854 | 5.61 | 19,713 | |
| 2-level OAS | 5.04 | 11 | 1.08 | 15 | 4.98 | 23 | 3.30 | 43 | 2.52 | 84 | 2.00 | 180 | |
| 7.85 | 17 | 2.81 | 28 | 1.73 | 55 | 1.28 | 137 | 1.01 | 361 | ||||
| 1.58 | 23 | 6.76 | 42 | 4.61 | 94 | 3.63 | 263 | ||||||
| 3.01 | 30 | 1.34 | 54 | 9.65 | 133 | ||||||||
| 3.51 | 32 | 1.32 | 56 | ||||||||||
| 3.44 | 32 | ||||||||||||
| p | , 2D Deformed Domain | , Unit Square | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Prec. | 2-Level OAS | Non-Prec. | 2-Level OAS | |||||||
| 2 | 5.96 | 1.97 | 2.43 | 7.70 | 2.43 | 2.07 | 1.70 | 2.18 | 7.14 | 2.18 |
| 3 | 2.16 | 1.36 | 1.34 | 4.22 | 6.95 | 7.08 | 1.81 | 2.34 | 9.83 | 1.41 |
| 4 | 2.88 | 5.03 | 8.58 | 3.22 | 3.22 | 9.32 | 8.19 | 1.91 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Two-Level OAS, 3D Cubic Domain | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| it. | it. | ||||
| 11.06 = 8.00/0.72 | 9 | 7.66 = 8.00/1.04 | 7 | ||
| 22.30 = 8.10/0.36 | 18 | 9.43 = 9.43/1.00 | 18 | ||
| 25.86 = 8.09/0.31 | 22 | 14.28 = 11.52/0.81 | 22 | ||
| 24.54 = 8.08/0.33 | 26 | 17.08 = 11.25/0.66 | 23 | ||
| 23.24 = 8.07/0.35 | 28 | 17.95 = 11.45/0.64 | 25 | ||
| 22.52 = 8.07/0.36 | 29 | 17.28 = 11.38/0.66 | 26 | ||
| 13.20 = 8.05/0.61 | 14 | 8.86 = 8.30/0.94 | 13 | ||
| 14.09 = 8.01/0.57 | 18 | 9.37 = 8.32/0.89 | 20 | ||
| 14.91 = 8.09/0.54 | 22 | 10.00 = 8.76/0.88 | 22 | ||
| 15.85 = 8.03/0.51 | 23 | 10.08 = 8.77/0.87 | 23 | ||
| 16.84 = 8.09/0.48 | 24 | 10.06 = 8.79/0.87 | 23 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, D. Isogeometric Schwarz Preconditioners with Generalized B-Splines for the Biharmonic Problem. Axioms 2023, 12, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050452
Cho D. Isogeometric Schwarz Preconditioners with Generalized B-Splines for the Biharmonic Problem. Axioms. 2023; 12(5):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050452
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Durkbin. 2023. "Isogeometric Schwarz Preconditioners with Generalized B-Splines for the Biharmonic Problem" Axioms 12, no. 5: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050452
APA StyleCho, D. (2023). Isogeometric Schwarz Preconditioners with Generalized B-Splines for the Biharmonic Problem. Axioms, 12(5), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12050452





