Efficient Modified Meta-Heuristic Technique for Unconstrained Optimization Problems
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Algorithm 1 The Basic SA Algorithm |
|
2. Simulated-Annealing Algorithm (SA)
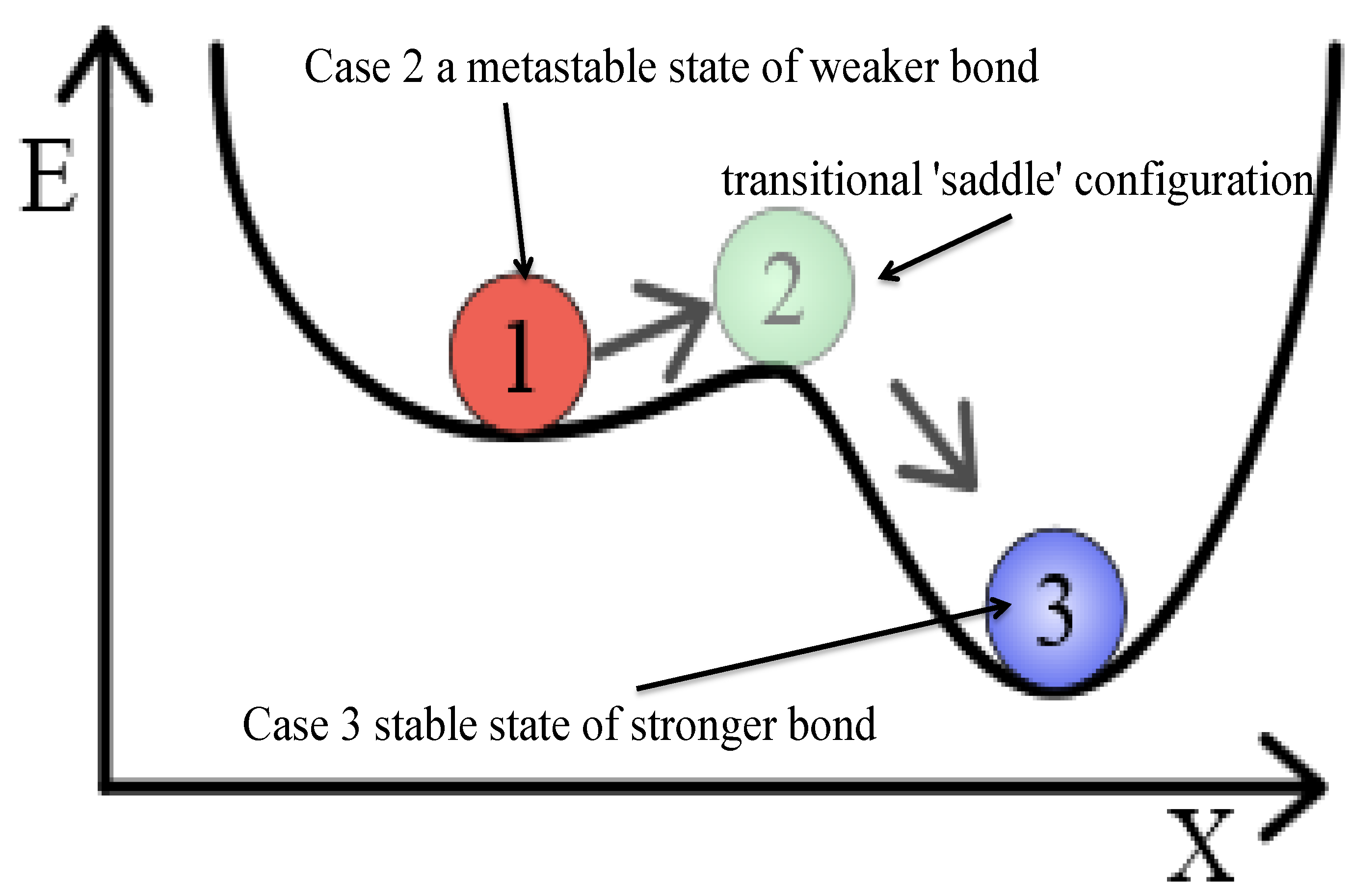
2.1. Metropolis Algorithm [32]
- Decrease carefully the temperature of the solid to reach a ground state (minimal energy state, crystalline structure.
- ∘
- In case 1, the matter is in its liquid state, where T is sufficiently high;
- ∘
- In case 2, the liquid will be frozen into a metastable state (in physics, metastability is a stable state of a dynamical system other than the system’s state of least energy [57]) (converts to a meta-stable state of weaker bond “at fast cooling”);
- ∘
- In case 3, the liquid will be frozen into the ground state (the ground state of a quantum mechanical system is its lowest-energy state; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system [58]) (at slow cooling).
2.2. Improving the Performance of SA
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Research Direction and a Step Length
3.1.1. First Approach
| Algorithm 2 First approach for generating a direction and step length |
Step 1: Generate a random vector Step 2: Set , if , , otherwise . Step 3: Generate a random number Step 4: Compute . Step 5: Compute . Step 6: Compute . Step 7: Compute . |
3.1.2. Second Approach
| Algorithm 3 Second approach to generate a direction and step length |
Step 1: Set . Step 2: Compute Step 3: Generate a random vector . Step 4: Compute , where . Step 5: Set , if , , otherwise . Step 6: Compute . Step 7: Compute . Step 8: . Step 9: Repeat steps 2–8 until . |
3.2. Acceptance of Steps
| Algorithm 4 Efficient Modified Meta-Heuristic Technique “EMST” |
|
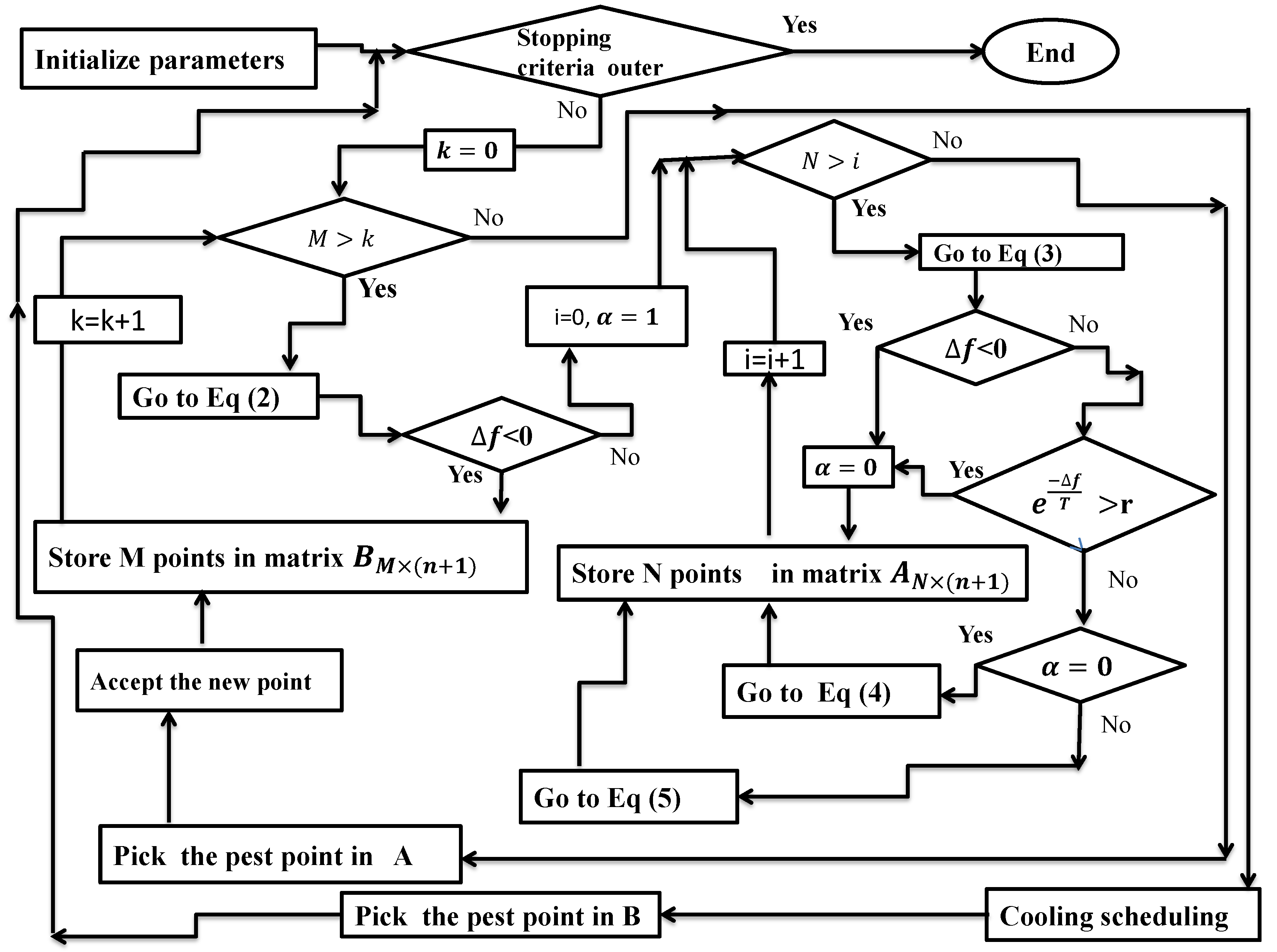
3.3. Cooling Schedule
3.4. Algorithm’s Loops
- The outer loop, which reduces the temperature T.
- The inner loop, which has a finite number of iterations. Particularly from 1 to M, where M is a preconceived maximum number of iterations.
- In the second approach, we generate N trials to obtain N points at each iteration k.
3.5. Stopping Criteria
- Outer loop stopping criterion: the algorithm will be terminated if one of the following is satisfied: Either and or , where , denotes a value of function at a best point after “M” iterations as inner loop iterations, denotes a value of function at the starting point. The value of is computed, we set , and are sufficiently small with ().
- Inner loop stopping criterion: this loop continues until it reaches a pre-specified maximum number of inner iterations denoted by M.
4. Numerical Experiments
4.1. Setting Parameters
4.2. Testing Efficiency of Algorithm
- (1)
- The rate of success “RS”, which represents the rate of success for trials leading to the global minimum of a problem.
- (2)
- The average number of function evaluations “AFE”.
- (3)
- The quality of the final result (average error) “AE”.
4.3. Results
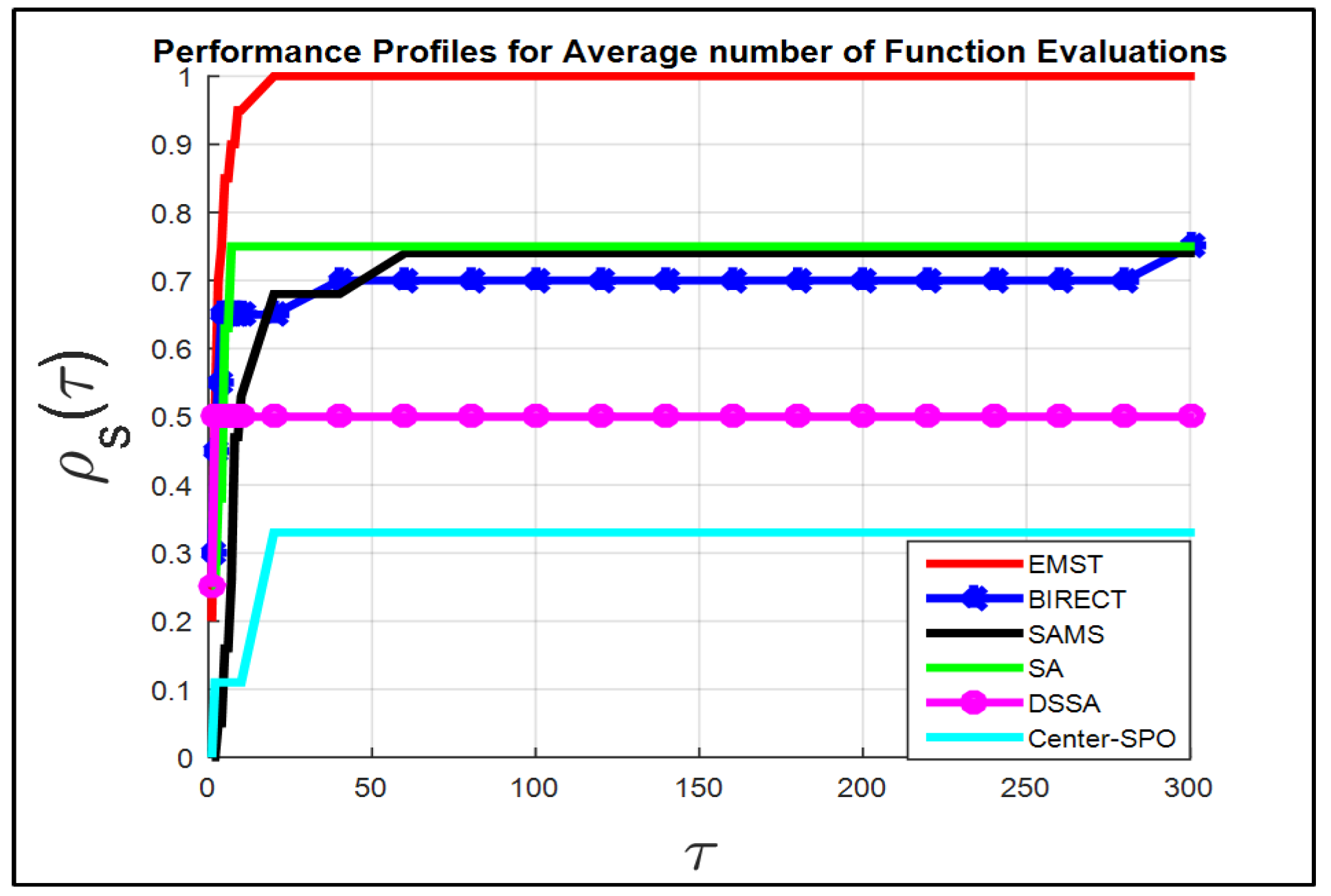
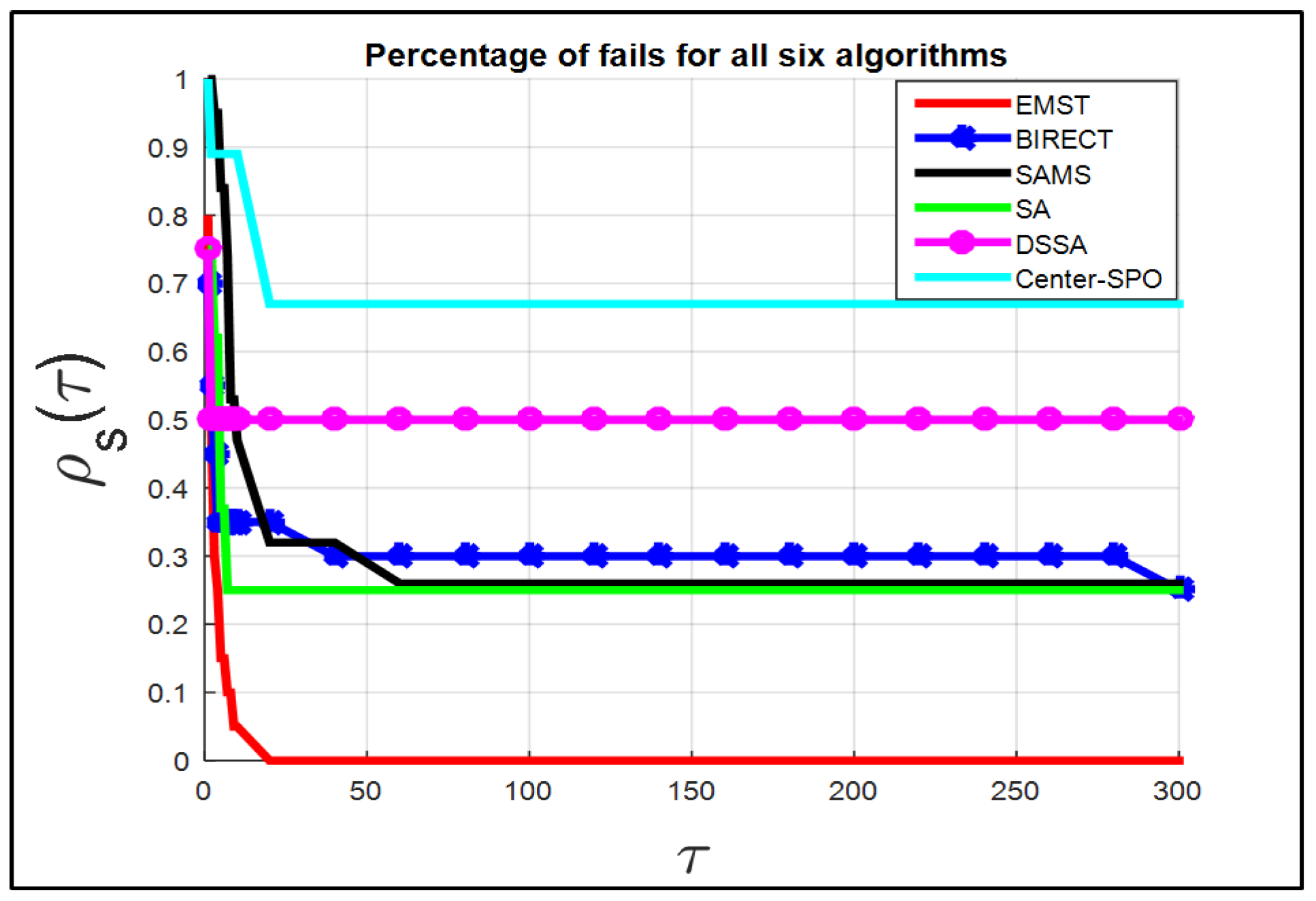
4.4. Performance Profiles
Performance Analysis of Algorithms Using Performance Files
5. Concluding Remark
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Baset, M.; Hezam, I. A Hybrid Flower Pollination Algorithm for Engineering Optimization Problems. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 140, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Ganesh, T.; Mohamed, A.W. A novel binary gaining–sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm for feature selection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 5989–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayumi, V.; Rere, L.; Fanany, M.I.; Arymurthy, A.M. Optimization of Convolutional Neural Network using Microcanonical Annealing Algorithm. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.02306. [Google Scholar]
- Lobato, F.S.; Steffen, V., Jr. Fish swarm optimization algorithm applied to engineering system design. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 11, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhoud, I.; Hadj-Hamou, K.; Bigeon, J.; Joyeux, P. Particle swarm optimization for solving engineering problems: A new constraint-handling mechanism. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.W.; Sabry, H.Z. Constrained optimization based on modified differential evolution algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2012, 194, 171–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.W.; Hadi, A.A.; Mohamed, A.K. Gaining-sharing knowledge based algorithm for solving optimization problems: A novel nature-inspired algorithm. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 1501–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rere, L.; Fanany, M.I.; Arymurthy, A.M. Metaheuristic Algorithms for Convolution Neural Network. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samora, I.; Franca, M.J.; Schleiss, A.J.; Ramos, H.M. Simulated annealing in optimization of energy production in a water supply network. WAter Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 1533–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y. Dynamics of an Impulsive Stochastic Predator–Prey System with the Beddington–DeAngelis Functional Response. Axioms 2021, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallepuga-Espinosa, J.; Cifuentes-Rodríguez, J.; Gutiérrez-Posada, V.; Ubero-Martínez, I. Thermomechanical Optimization of Three-Dimensional Low Heat Generation Microelectronic Packaging Using the Boundary Element Method. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.E., Jr.; Schnabel, R.B. Numerical Methods for Unconstrained Optimization and Nonlinear Equations; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Andrei, N. An unconstrained optimization test functions collection. Adv. Model. Optim 2008, 10, 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.K.S.; Zahara, E. A hybrid simplex search and particle swarm optimization for unconstrained optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 181, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedar, A.R.; Fukushima, M. Hybrid simulated annealing and direct search method for nonlinear unconstrained global optimization. Optim. Methods Softw. 2002, 17, 891–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parouha, R.P.; Verma, P. An innovative hybrid algorithm for bound-unconstrained optimization problems and applications. J. Intell. Manuf. 2022, 33, 1273–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y. Solving unconstrained global optimization problems via hybrid swarm intelligence approaches. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, C.; Roli, A. Metaheuristics in combinatorial optimization: Overview and conceptual comparison. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2003, 35, 268–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S. Numerical Optimization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Aarts, E.; Korst, J. Simulated Annealing and Boltzmann Machines: A Stochastic Approach to Combinatorial Optimization and Neural Computing; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, F.S.; Price, C.C. International Series in Operations Research & Management Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Laarhoven, P.J.V.; Aarts, E.H. Simulated Annealing: Theory and Applications; Springer-Science ++ Business Media, B.V.: Berlin, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, A.R.; Timmer, G. Stochastic methods for global optimization. Am. J. Math. Manag. Sci. 1984, 4, 7–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M. Some Modified Stochastic Global Optimization Algorithms with Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Desale, S.; Rasool, A.; Andhale, S.; Rane, P. Heuristic and meta-heuristic algorithms and their relevance to the real world: A survey. Int. J. Comp. Eng. Res. Trends 2015, 2, 296–304. [Google Scholar]
- Alshamrani, A.M.; Alrasheedi, A.F.; Alnowibet, K.A.; Mahdi, S.; Mohamed, A.W. A Hybrid Stochastic Deterministic Algorithm for Solving Unconstrained Optimization Problems. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, S.; Sanyal, S. An Elitist Simulated Annealing Algorithm for Solving Multi Objective Optimization Problems in Internet of Things Design. Int. J. Adv. Netw. Appl. 2015, 7, 2784. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales, G.V.; dos Santos, E.D.; Emmendorfer, L.R.; Isoldi, L.A.; Rocha, L.A.O.; Estrada, E.d.S.D. A Comparative Study of Simulated Annealing with different Cooling Schedules for Geometric Optimization of a Heat Transfer Problem According to Constructal Design. Sci. Plena 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poorjafari, V.; Yue, W.L.; Holyoak, N. A Comparison between Genetic Algorithms and Simulated Annealing for Minimizing Transfer Waiting Time in Transit Systems. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, A.; Marchesi, M.; Martini, C.; Ridella, S. Minimizing multimodal functions of continuous variables with the simulated annealing algorithm. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1987, 13, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, A.; Aarts, E. Global optimization and simulated annealing. Math. Program. 1991, 50, 367–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Rosenbluth, A.W.; Rosenbluth, M.N.; Teller, A.H.; Teller, E. Equation of state calculations by fast computer machines. J. Chem. Phys 1953, 21, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Gelatt, C.D.; Vecchi, M.P. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 1983, 220, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D.; Louie, S.G. A Monte Carlo simulated-annealing algorithm approach to optimization over continuous variables. J. Comput. Phys. 1984, 56, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohachevsky, I.O.; Johnson, M.E.; Stein, M.L. Generalized simulated annealing for function optimization. Technometrics 1986, 28, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anily, S.; Federgruen, A. Simulated annealing methods with general acceptance probabilities. J. Appl. Probab. 1987, 24, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingber, L. Simulated Annealing: Practice versus Theory. Mathl. Comput. Model. 1993, 18, 29–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Tsitsiklis, J. Simulated annealing. Stat. Sci. 1993, 8, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffe, W.L.; Ferrier, G.D.; Rogers, J. Global optimization of statistical functions with simulated-annealing algorithm. J. Econom. 1994, 60, 65–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsallis, C.; Stariolo, D.A. Generalized Simulated Annealing. Physica A 1996, 233, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siarry, P.; Berthiau, G.; Durbin, F.; Haussy, J. Enhanced Simulated-Annealing Algorithm for Globally Minimizing Functions of Many Continuous Variables. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1997, 23, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouraniy, Y.; Andresenz, B. A comparison of simulated-annealing algorithm cooling strategies. J. Phys. A Math. Gen 1998, 31, 8373–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Machado, J.M.; Ni, G.; Ho, S.L.; Zhou, P. A self-learning simulated-annealing for global optimizations of electromagnetic devices. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2000, 36, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.M.; Torn, A.; Viitanen, S. A direct search variant of the simulated-annealing for optimization involving continuous variables. Comput. Oper. Res. 2002, 29, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouleimen, K.; Lecocq, H. A new efficient simulated annealing algorithm for the resource-constrained project scheduling problem and its multiple mode version. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 149, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Gabere, M. A simulated annealing driven multi-start algorithm for bound constrained global optimization. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2010, 233, 2661–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Guo, L.; Gandomi, A.H.; Alavi, A.H.; Duan, H. Simulated annealing-based krill herd algorithm for global optimization. In Proceedings of the Abstract and Applied Analysis; Hindawi Publishing Corporation, Hindawi: London, UK, 2013; Volume 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rere, L.R.; Fanany, M.I.; Arymurthy, A.M. Simulated annealing algorithm for deep learning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 72, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certa, A.; Lupo, T.; Passannanti, G. A New Innovative Cooling Law for Simulated Annealing Algorithms. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2015, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Sui, S.; Du, Z. Application of Hybrid Genetic Algorithm Based on Simulated Annealing in Function Optimization. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Int. J. Math. Comput. Phys. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2015, 9, 677–680. [Google Scholar]
- Guodong, Z.; Ying, Z.; Liya, S. Simulated Annealing Optimization Bat Algorithm in Service Migration Joining the Gauss Perturbation. Int. J. Hybrid Inf. Technol. 2015, 8, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisumrannukul, S. Network reconfiguration for reliability worth enhancement in distribution system by simulated annealing. In Simulated Annealing, Theory with Applications; InTech Open: London, UK, 2010; pp. 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fradkin, E. Field Theories of Condensed Matter Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Downarowicz, T. Entropy structure. J. d’Analyse Math. 2005, 96, 57–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, E.H.; Yngvason, J. The physics and mathematics of the second law of thermodynamics. Phys. Rep. 1999, 310, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, I. Dynamical entropy for Markov operators. J. Dyn. Control. Syst. 2000, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debenedetti, P.G. Metastable Liquids: Concepts and Principles; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Contributors, W. Metastability. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Boussaïd, I.; Lepagnot, J.; Siarry, P. A survey on optimization metaheuristics. Inf. Sci. 2013, 237, 82–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Y.; Cao, W.; Chung, T.S.; Morris, J. Applied Numerical Methods Using MATLAB; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bessaou, M.; Siarry, P. A genetic algorithm with real-value coding to optimize multimodal continuous functions. Struct. Multidisc Optim. 2001, 23, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelouah, R.; Siarry, P. Tabu search applied to global optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 123, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoulos, I.G.; Stavrakoudis, A. Enhancing PSO methods for global optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 216, 2988–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulavičius, R.; Chiter, L.; Žilinskas, J. Global optimization based on bisection of rectangles, function values at diagonals, and a set of Lipschitz constants. J. Glob. Optim. 2018, 71, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Khompatraporn, C.; Zabinsky, Z.B. A numerical evaluation of several stochastic algorithms on selected continuous global optimization test problems. J. Glob. Optim. 2005, 31, 635–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.M.; Fateen, S.E.K.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A. MAKHA-A New Hybrid Swarm Intelligence Global Optimization Algorithm. Algorithms 2015, 8, 336–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, H.J.; Bernardino, H.S.; Barreto, A.M. Using performance profiles to analyze the results of the 2006 CEC constrained optimization competition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, E.D.; Moré, J.J. Benchmarking optimization software with performance profiles. Math. Program. 2002, 91, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moré, J.J.; Wild, S.M. Benchmarking derivative-free optimization algorithms. SIAM J. Optim. 2009, 20, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, A.I.F.; Vicente, L.N. A particle swarm pattern search method for bound constrained global optimization. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 39, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
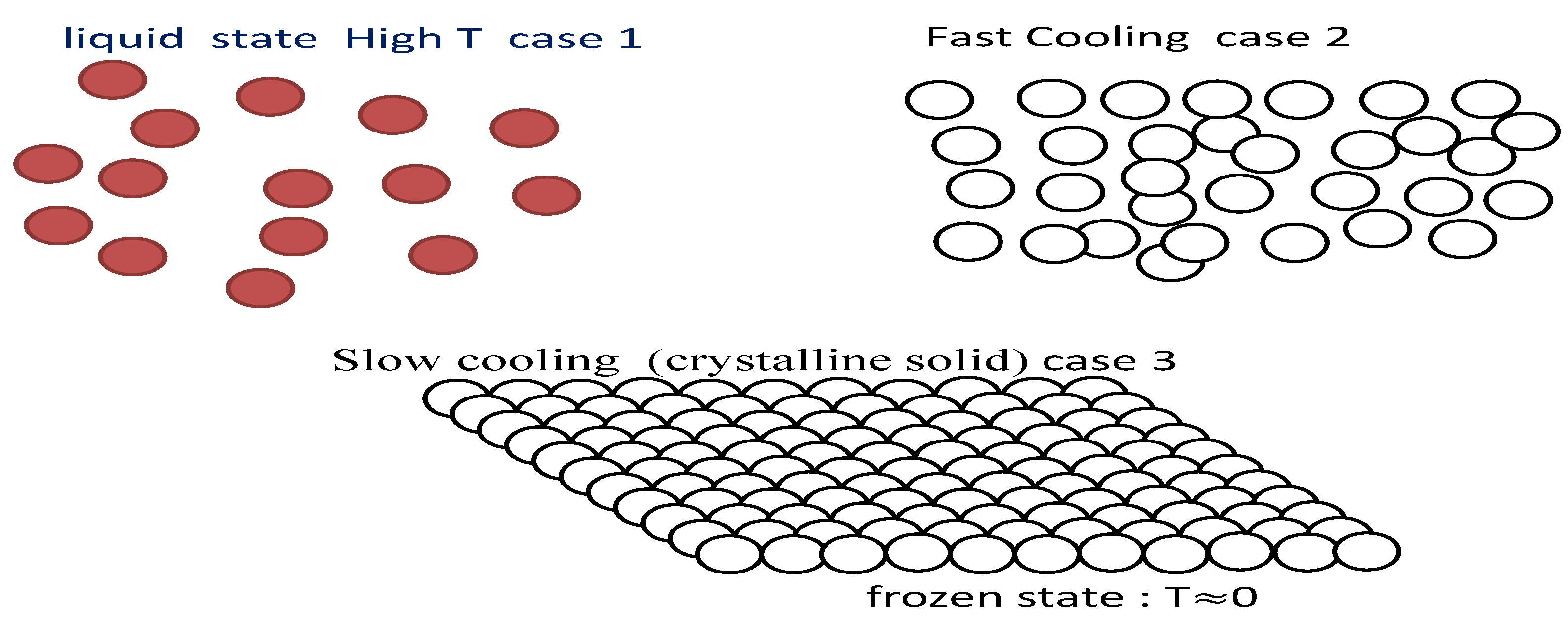
| Thermodynamic Simulation | Optimization Problem |
|---|---|
| States of system i | Solutions |
| Energy of a state | Cost of a solution |
| Change of a state | Neighbor of a solution |
| Temperature T | Control parameter T |
| Minimum energy E | Minimum cost |
| Ground-state energy | Global minimizer |
| Algorithm Name | Algorithm | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Global Optimization and Simulated Annealing | “SA” | [31] |
| 2 | Direct Search Simulated Annealing | DSSA | [15] |
| 3 | Enhancing PSO Methods for Global Optimization | “Center-PSO” | [63] |
| 4 | Simulated Annealing Driven multi-Start | “SAMS” | [46] |
| 5 | A new DIRECT type Algorithm | BIRECT | [64] |
| 6 | Efficient Modified Stochastic Technique | “EMST” | This work |
| f | n | Reference | f | n | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.397887 | [31,63] | 2 | 24776.51 | [31] | ||
| 2 | −1 | [61,62,63,65] | 10 | 0 | [65] | ||
| 2 | 3 | [31,41,61,62,65] | 3 | 0 | [31] | ||
| 2 | −2 | [63] | 2 | −1.0316285 | [63,65] | ||
| 2 | −186.7309 | [31,61,62,65] | 4 | 0 | [65] | ||
| 3 | −3.86278 | [31,41,61,62,63,65] | 3 | 0 | [61,62] | ||
| 4 | −10.1532 | [31,41,61,62,63,65,66] | 2 | 0 | [65] | ||
| 4 | −10.4029 | [31,41,61,62,63,65,66] | 5 | 0 | [31] | ||
| 4 | −10.5364 | [31,41,61,62,63,65,66] | 6,10 | 0 | [65] | ||
| 6 | −3.32237 | [31,41,61,62,63,65] | 2 | 0 | [65] | ||
| 10 | 0 | [65] | 4 | 0 | [65] | ||
| 2–10 | 0 | [61,62,65] | 10 | 0 | [65] | ||
| 4 | 0.4 | [65] | 2 | 1.29695 | [65] | ||
| 10 | 0 | [65] |
| f | f | f | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.6 | 456 | 7.3 | 541 | 1.1 | 501 | |||
| 1.1 | 456 | 0 | 13,232 | 0 | 506 | |||
| 4.6 | 456 | 6.8 | 506 | 2.5 | 736 | |||
| 6.9 | 729 | 2.1 | 722 | 4 | 6700 | |||
| 1.4 | 1486 | 3.9 | 1486 | 9.6 | 1486 | |||
| 1.3 | 1838 | 1.68 | 2172 | 0 | 13,636 | |||
| 4.1 | 11,100 | 1.21 | 456 | 2.26 | 6288 | |||
| 2.56 | 8133 | 9.48 | 13,771 | 1.0 | 16,756 | |||
| 1.36 | 426 | 7.7 | 430 | 2.53 | 10,976 | |||
| 2.86 | 5609 | 2.58 | 13,030 | 2.4 | 1495 | |||
| 4.05 | 501 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alnowibet, K.A.; Alshamrani, A.M.; Alrasheedi, A.F.; Mahdi, S.; El-Alem, M.; Aboutahoun, A.; Mohamed, A.W. Efficient Modified Meta-Heuristic Technique for Unconstrained Optimization Problems. Axioms 2022, 11, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11090483
Alnowibet KA, Alshamrani AM, Alrasheedi AF, Mahdi S, El-Alem M, Aboutahoun A, Mohamed AW. Efficient Modified Meta-Heuristic Technique for Unconstrained Optimization Problems. Axioms. 2022; 11(9):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11090483
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlnowibet, Khalid Abdulaziz, Ahmad M. Alshamrani, Adel Fahad Alrasheedi, Salem Mahdi, Mahmoud El-Alem, Abdallah Aboutahoun, and Ali Wagdy Mohamed. 2022. "Efficient Modified Meta-Heuristic Technique for Unconstrained Optimization Problems" Axioms 11, no. 9: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11090483
APA StyleAlnowibet, K. A., Alshamrani, A. M., Alrasheedi, A. F., Mahdi, S., El-Alem, M., Aboutahoun, A., & Mohamed, A. W. (2022). Efficient Modified Meta-Heuristic Technique for Unconstrained Optimization Problems. Axioms, 11(9), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11090483








