Pipeline Corrosion Prediction Using the Grey Model and Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Exponentially transformed and dynamic coefficients are added to the traditional GM(1,1).
- (2)
- An improved version of the ABC algorithm, called the reformative artificial bee colony (RABC) algorithm, is proposed and its performance is verified by benchmark functions.
- (3)
- The exponentially transformed grey model (ETGM(1,1)) combined with RABC, called ETGM(1,1)-RABC, is proposed for the PCP.
- (4)
- The superiority of ETGM(1,1)-RABC is verified through experiments.
2. Related Theory
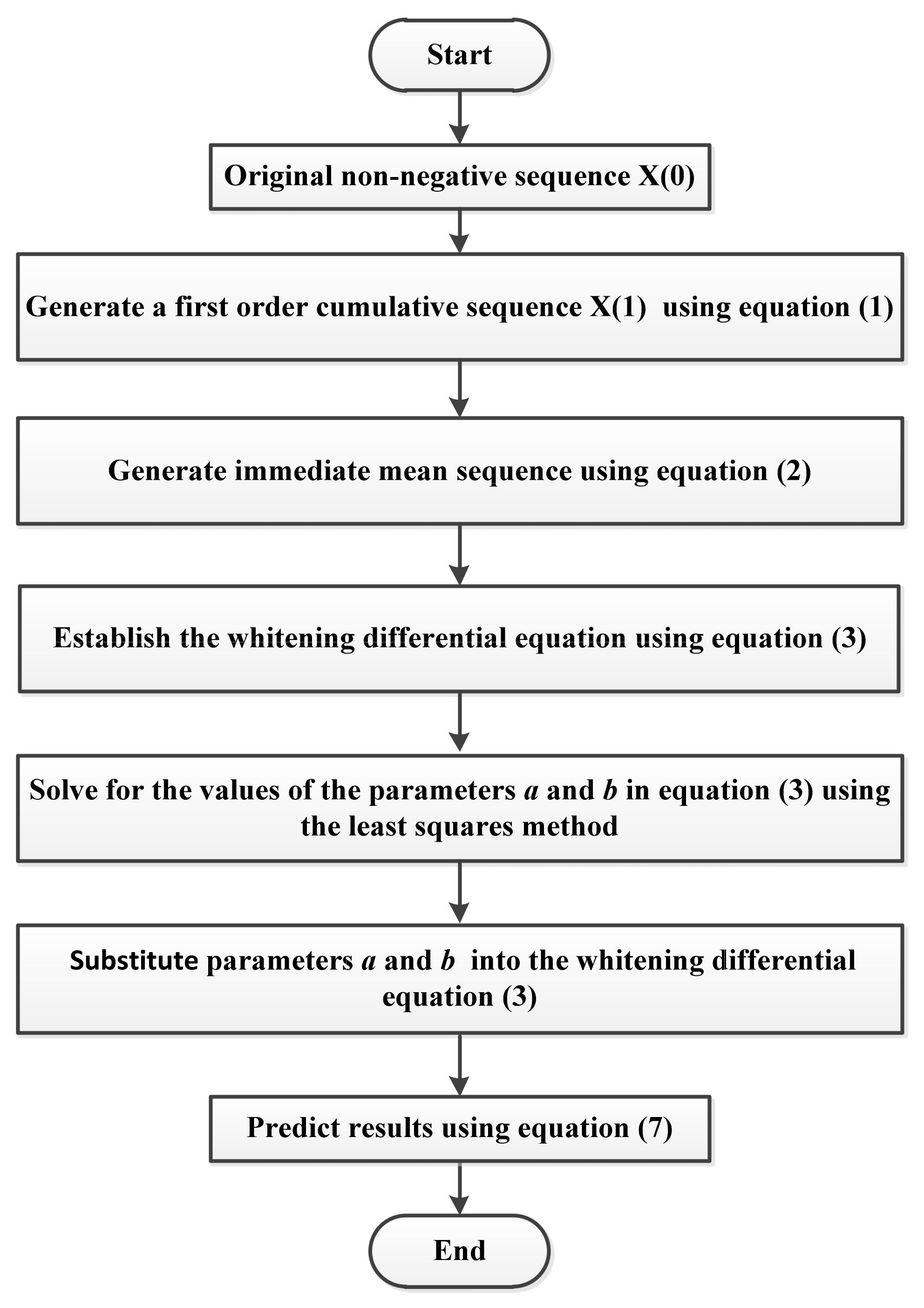
2.1. GM(1,1)
- (1)
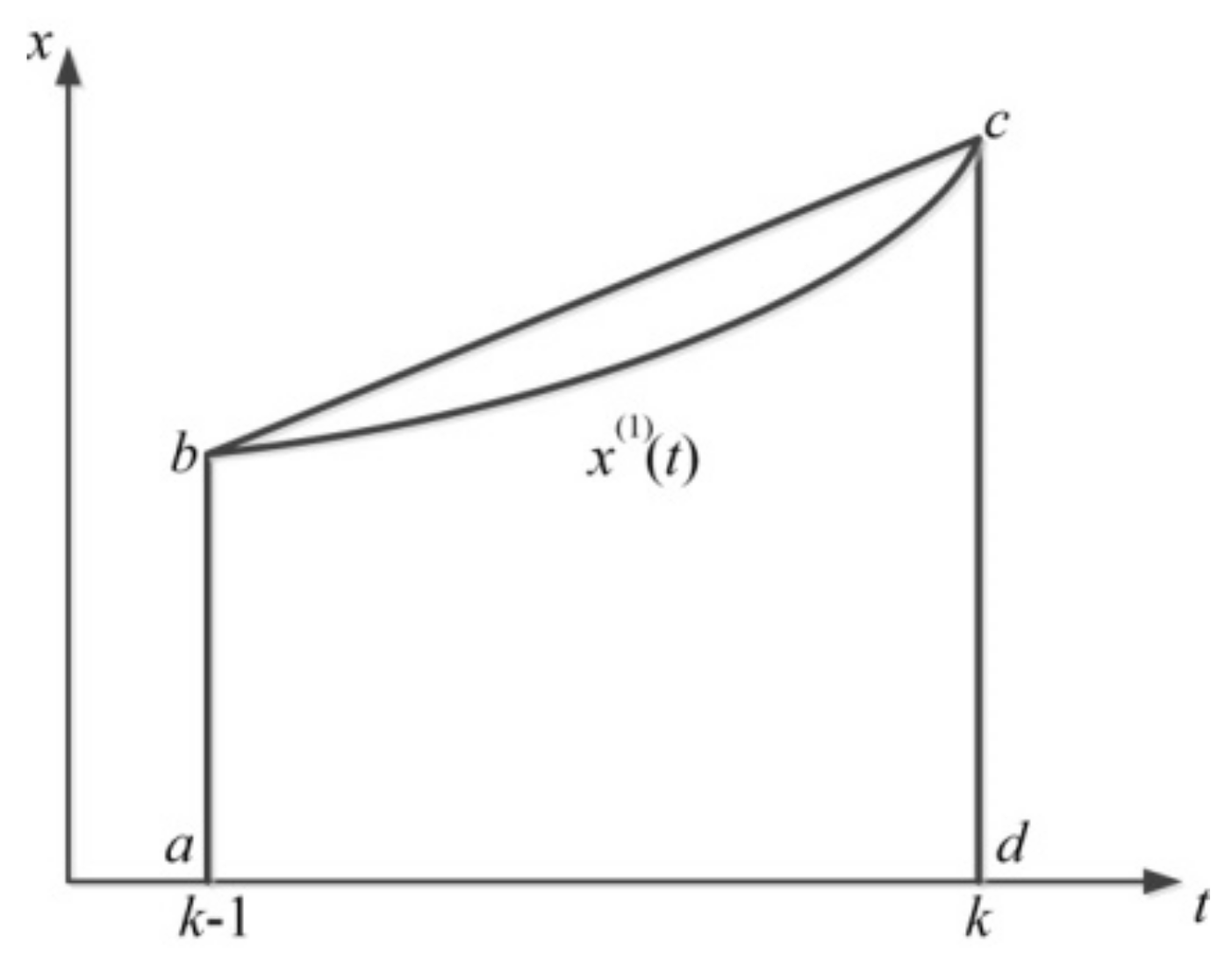
- Cumulative generation. Let X(0) = (x(0) (1), x(0) (2),…, x(0) (n)) be the original non-negative sequence; then let X(1) = (x(1) (1), x(1) (2),…, x(1) (n)) be the first-order cumulative sequence of X(0); here, x(1) (k) can be expressed as
- (2)
- Modeling solution. Let x(0) (k) + az (1) (k) = b be the grey differential equation for the GM(1,1), then the whitening differential equation can be expressed as
- (3)
- Accumulation reduction. Thus, the corresponding predicted values are obtained as follows
2.2. Basic ABC Algorithm
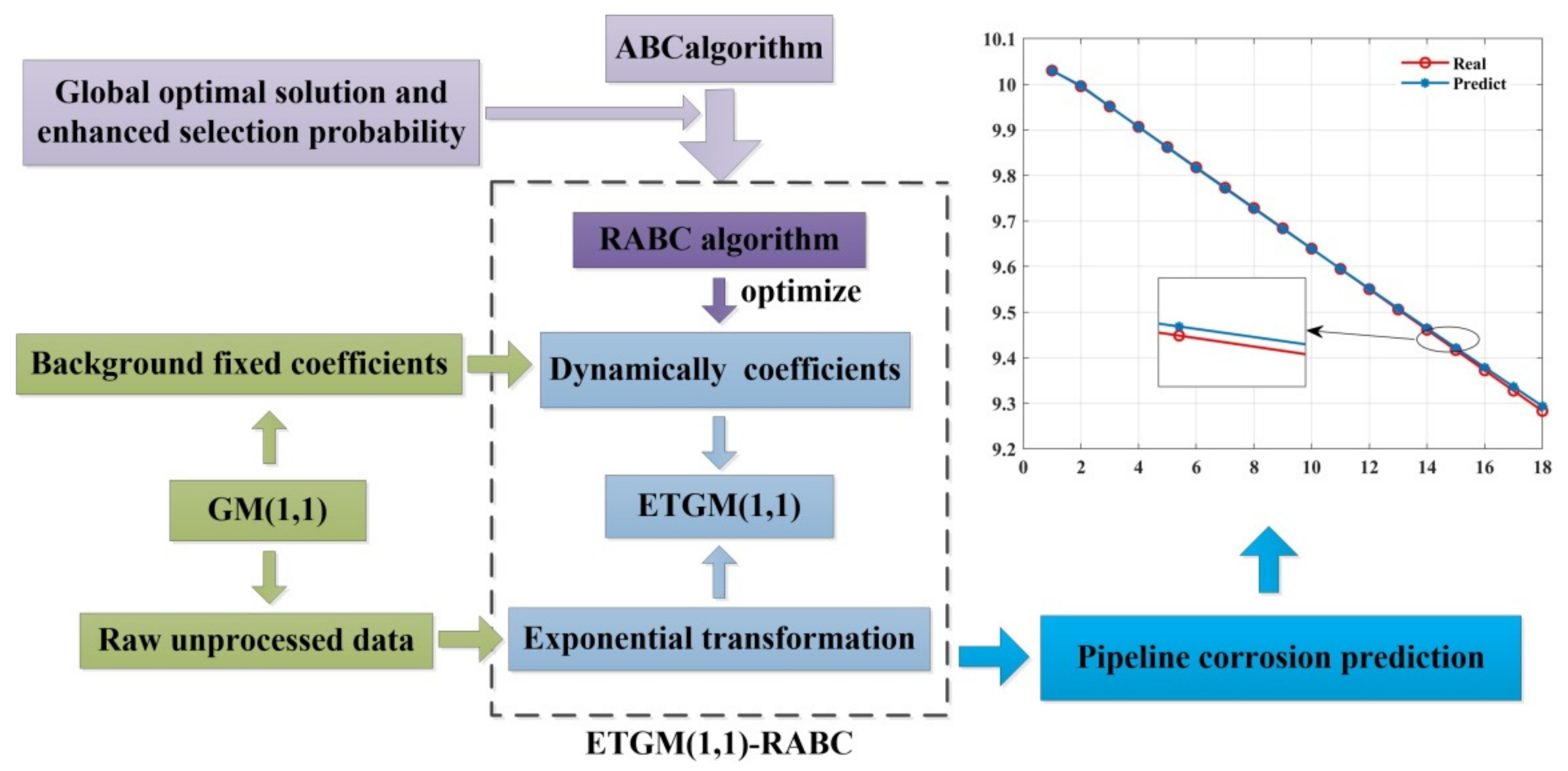
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Exponential Transformation (ET) for the Raw Data
3.2. Introducing Dynamic Coefficients
3.3. RABC Algorithm
3.4. Verification for RABC Algorithm
4. PCP Based on ETGM(1,1)-RABC
4.1. Pipeline Data
4.2. Objective Function
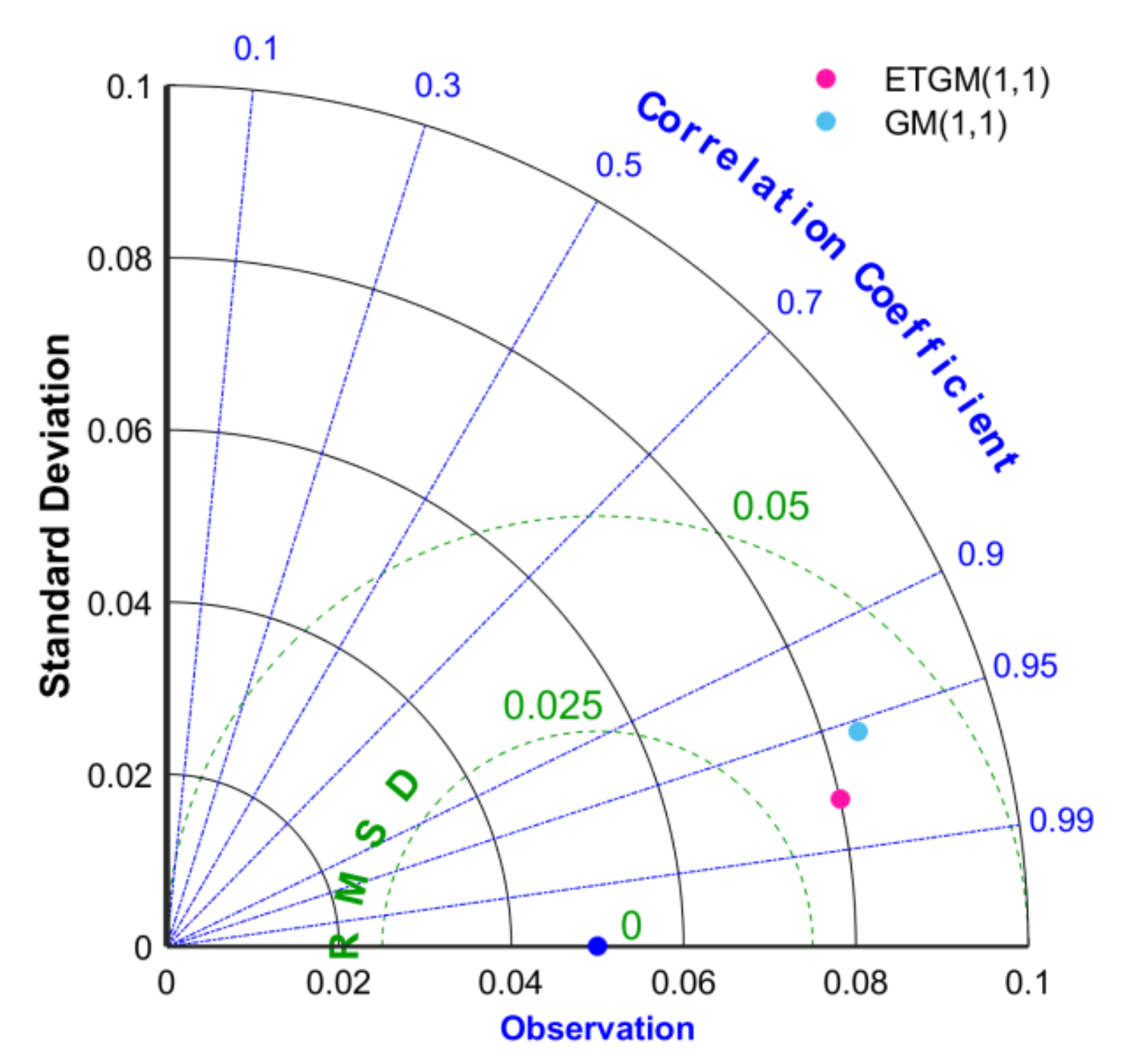
4.3. Evaluation Tool
4.4. Predicted Results
4.4.1. Comparison of GM(1,1) and ETGM(1,1)
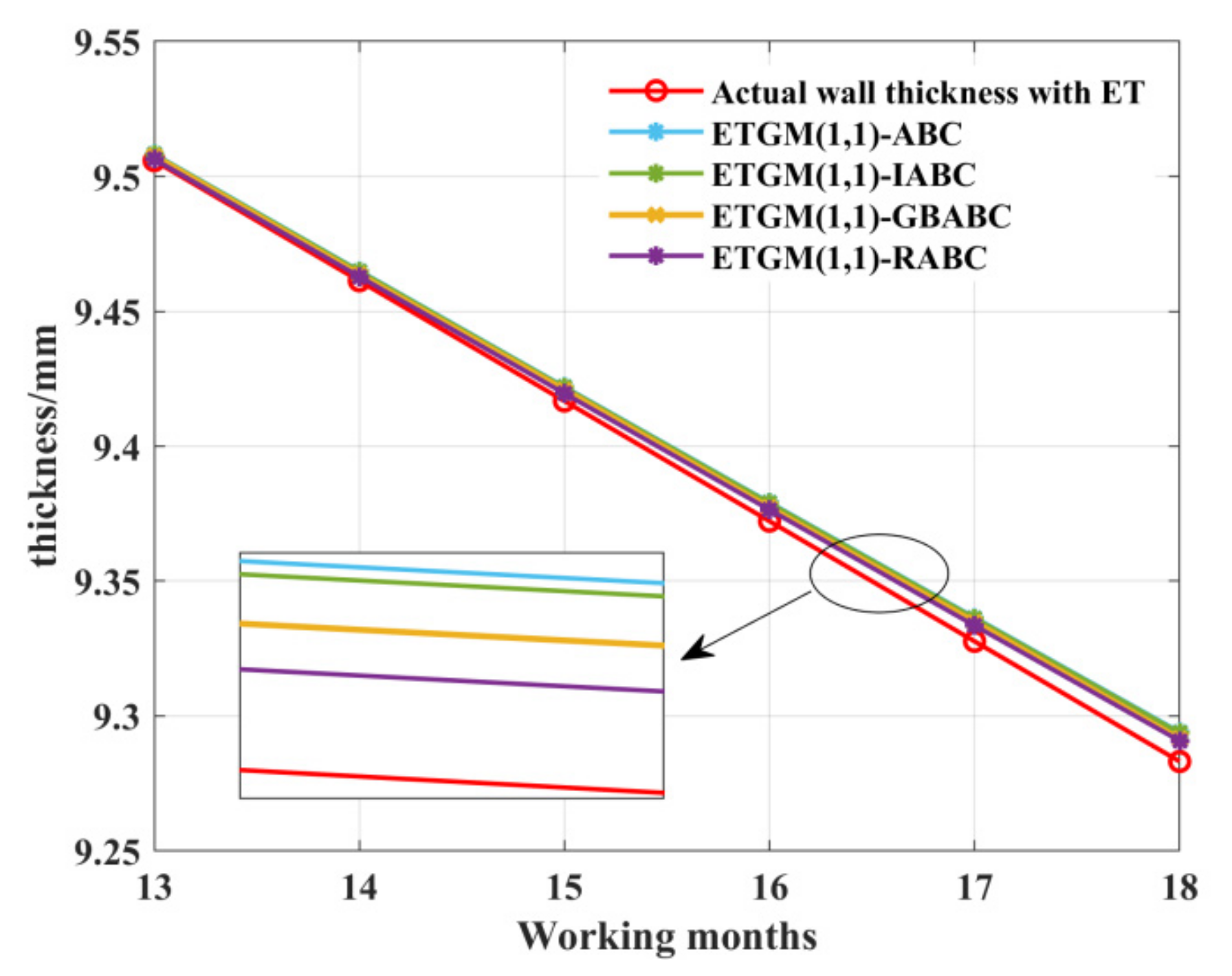
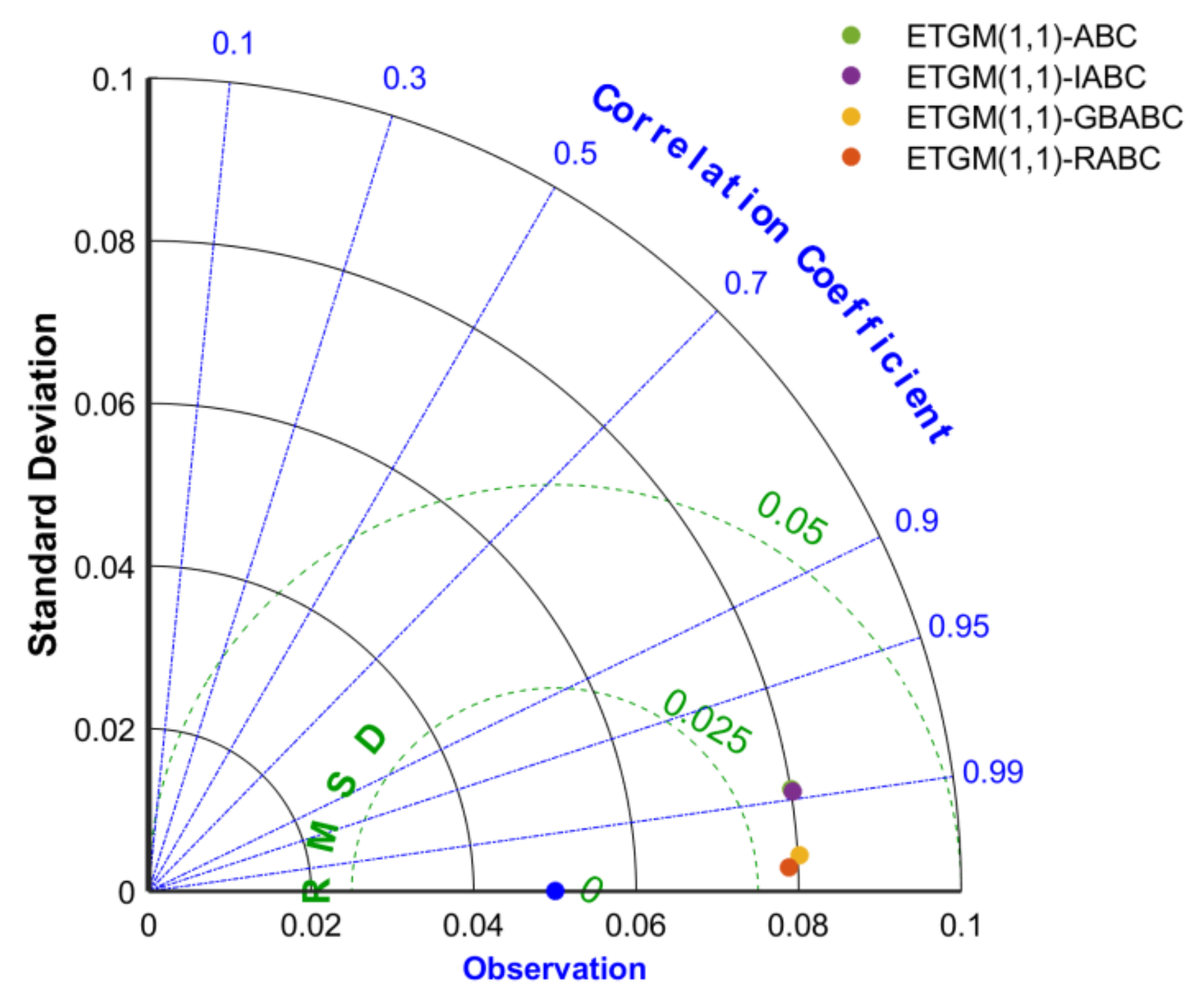
4.4.2. Comparison of ETGM(1,1)-ABC Variants
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, K.; Wu, J.; Quan, K. Review on Evaluation Technology of Oil-Gas Pipelines with Corrosion Defect. Surf. Technol. 2018, 47, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Obaseki, M. Diagnostic and prognostic analysis of oil and gas pipeline with allowable corrosion rate in Niger Delta Area, Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2019, 23, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.D.; Wang, C.H.; Yamaguchi, D.; Nagai, M.; Masuda, S. A study on the corrosion process of gas pipeline applying grey dynamic model. Int. J. Reliab. Saf. 2010, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, N.B.; Pedapati, S.R.; Othman, A.R.; Bingi, K.; Abd Dzubir, F.A. An intelligent model to predict the life condition of crude oil pipelines using artificial neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 14771–14792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, K.; He, L.; Liu, J.; Gong, J. An optimization of artificial neural network modeling methodology for the reliability assessment of corroding natural gas pipelines. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, N.B.; Pedapati, S.R.; Taqvi, S.A.A.; Othman, A.R.; Abd Dzubir, F.A. A feed-forward back propagation neural network approach to predict the life condition of crude oil pipeline. Processes 2020, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Zhang, L.; Tao, G. Study on corrosion rate of buried gas steel pipeline in Nanjing based on the GM (1, N) optimization model. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 490, 022025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hao, B. Prediction of Submarine Pipeline Corrosion Based on the Improved Grey Prediction Model. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1894, 012106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhengshan, L.U.O.; Hongwei, Y. GM-RBF model based error compensation for prediction of submarine pipeline corrosion. China Saf. Sci. J. 2018, 28, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Ding, H.; Miao, K.; Zhang, X.; Xu, T.; Li, G. Grey Relational Analysis and Fuzzy Neural Network Method for Predicting Corrosion Rate of Marine Pipeline. Int. J. High. Educ. Teach. Theory 2021, 2, 210. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhang, Y. Combined Grey Prediction and Neural Network Model for Oil and Gas Pipeline Wall Thinning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2033, 012210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, E.; Liu, W.; Qiao, W. A new hybrid algorithm model for prediction of internal corrosion rate of multiphase pipeline. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 85, 103716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Khan, F.; Han, Z. A data-driven corrosion prediction model to support digitization of subsea operations. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 153, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Anyaoha, U.; Liu, Z.; Tsukada, K. Analysis of magnetic-flux leakage (MFL) data for pipeline corrosion assessment. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyani, M.; Bahaari, M.R. A new approach for finite element based reliability evaluation of offshore corroded pipelines. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2021, 193, 104449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deif, S.; Daneshmand, M. Multiresonant chipless RFID array system for coating defect detection and corrosion prediction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 8868–8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Shi, Y.; Pun, C.M.; Kwong, S. An improved artificial bee colony algorithm with its application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezočnik, L.; Fister, I.; Podgorelec, V. Swarm intelligence algorithms for feature selection: A review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Gao, H.; Qiu, J.; Yang, Y.; Qu, X.; Wang, Y.; Bi, Z. Grey model optimized by particle swarm optimization for data analysis and application of multi-sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Squires, M.; Tao, X.; Elangovan, S.; Gururajan, R.; Zhou, X.; Acharya, U.R. A novel genetic algorithm based system for the scheduling of medical treatments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 195, 116464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Shang, S.; Cai, X.; Zhao, H.; Song, Y.; Xu, J. An improved differential evolution algorithm and its application in optimization problem. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 5277–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Tang, H.; Niu, B. Evolutionary state-based novel multi-objective periodic bacterial foraging optimization algorithm for data clustering. Expert Syst. 2022, 39, e12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, G.; Coello, C.A.C.; Cruz-Reyes, L.; Fernandez, E.R.; Gómez Santillán, C.G.; Rangel-Valdez, N. Preference incorporation into many-objective optimization: An Ant colony algorithm based on interval outranking. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 69, 101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Guo, H.; Mao, S. The modeling mechanism, extension and optimization of grey GM (1, 1) model. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 1896–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Ying-Gan, T.; Xin-Ping, G. Optimum design of fractional order PID controller for an AVR system using an improved artificial bee colony algorithm. Acta Autom. Sin. 2014, 40, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.X.; Xu, Y.M. Improvement of GM (1, 1) model based on data transformation. J. Geomat. 2019, 44, 122–124. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. Forecasting clean energy consumption in China by 2025: Using improved grey model GM (1, N). Sustainability 2020, 12, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- XieXun, Q.I.N.; WenBin, L.I.U.; LiangChao, C. Pipeline corrosion prediction based on an improved artificial bee colony algorithm and a grey model. J. Beijing Univ. Chem. Technol. 2021, 48, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H. Gaussian bare-bones artificial bee colony algorithm. Soft Comput. 2016, 20, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
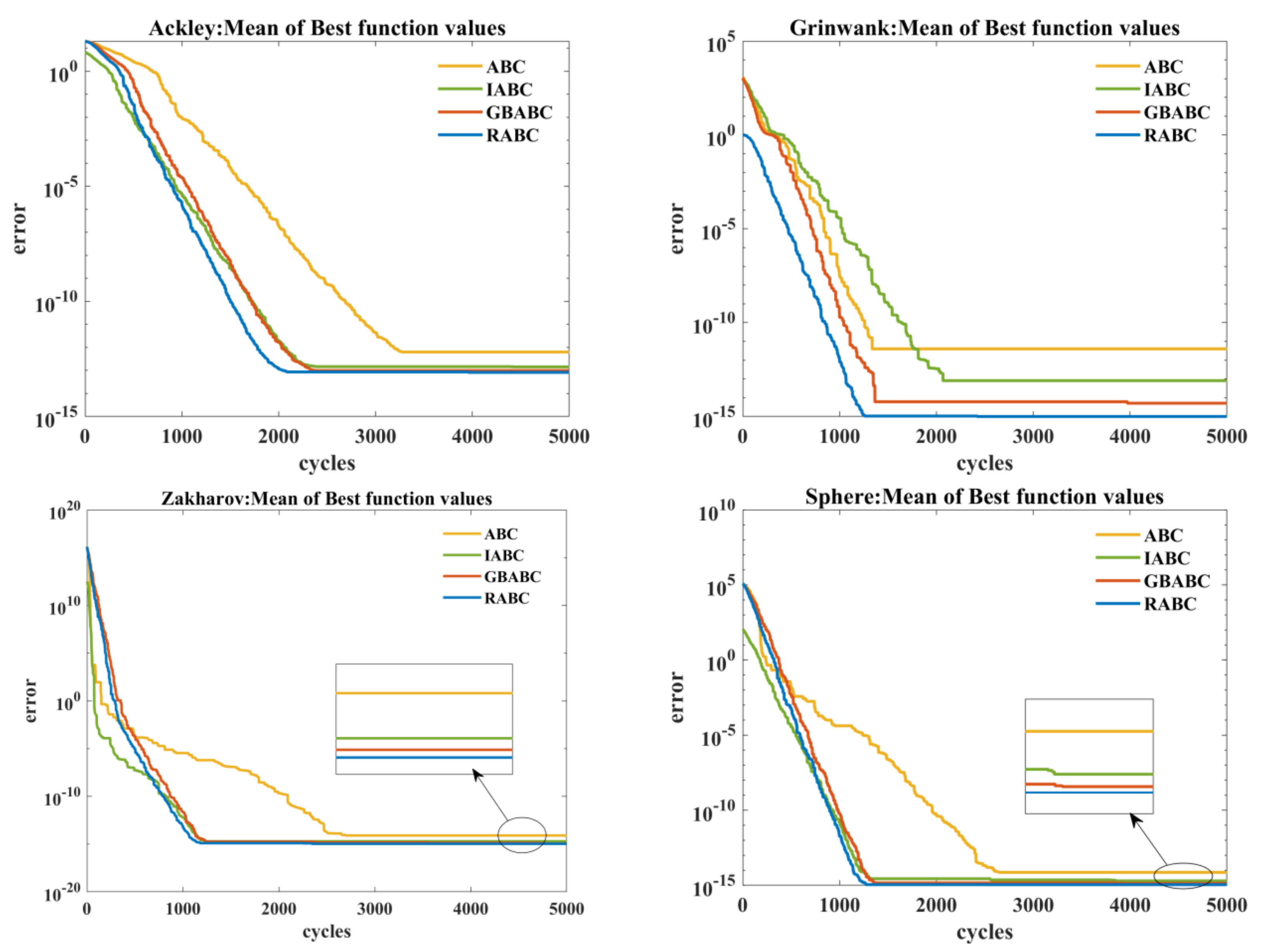
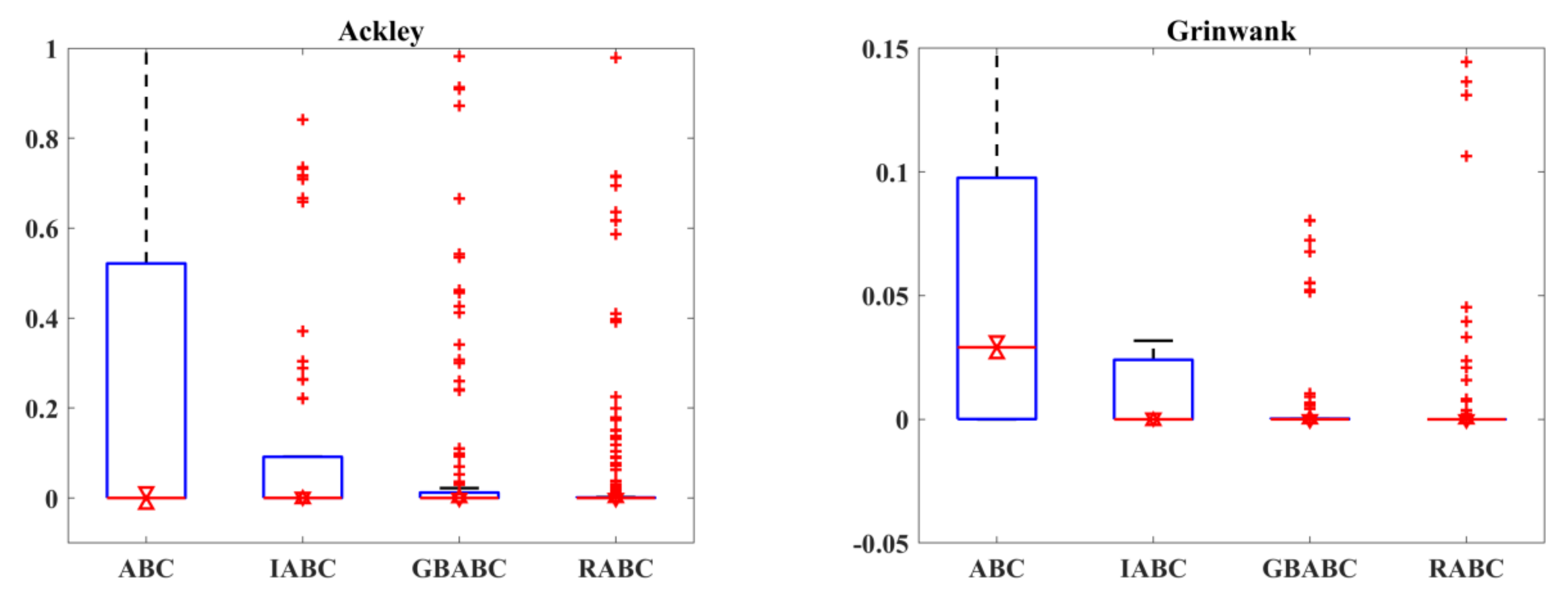
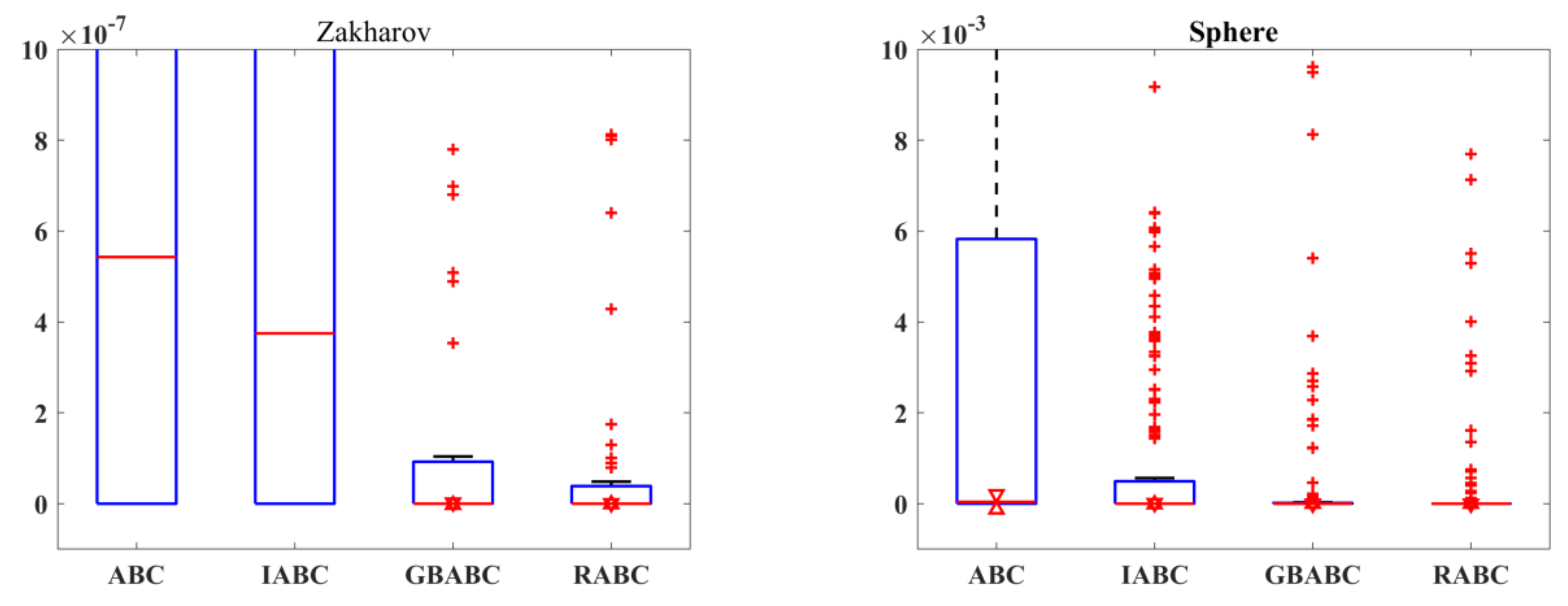



| Function | Name | Definition Domain | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Ackley | (−15, 30) | 0 |
| F2 | Griewank | (−600, 600) | 0 |
| F3 | Zakharov | (−5, 10) | 0 |
| F4 | Sphere | (−100, 100) | 0 |
| Function | ABC | IABC | GBABC | RABC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Mean Std | 6.33345e-13 4.89751e-14 | 1.42997 e-13 1.00486 e-14 | 9.85936e-14 8.65746e-15 | 8.26357e-14 4.29453e-15 |
| F2 | Mean Std | 4.01418e-12 3.77788e-12 | 8.13825e-14 8.65482e-15 | 5.10703e-15 5.80934e-15 | 1.16573 e-15 2.35514 e-16 |
| F3 | Mean Std | 8.04328e-15 7.47394e-15 | 1.8455 e-15 1.5451 e-16 | 1.14164e-15 5.13749e-17 | 1.07917e-15 8.23919e-17 |
| F4 | Mean Std | 7.29812e-15 8.75926e-17 | 1.96226 e-15 1.98675 e-16 | 1.34151e-15 1.24779e-17 | 1.10285e-15 1.03897e-17 |
| Working Months | Actual Wall Thickness/mm | Working Months | Actual Wall Thickness/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.03 | 10 | 9.64 |
| 2 | 10.01 | 11 | 9.58 |
| 3 | 9.95 | 12 | 9.53 |
| 4 | 9.92 | 13 | 9.51 |
| 5 | 9.85 | 14 | 9.49 |
| 6 | 9.82 | 15 | 9.45 |
| 7 | 9.76 | 16 | 9.38 |
| 8 | 9.71 | 17 | 9.31 |
| 9 | 9.69 | 18 | 9.27 |
| Working Months | Actual Wall Thickness/mm | ETGM(1,1) | GM(1,1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted Value/mm | Absolute Error/mm | Predicted Value/mm | Absolute Error/mm | ||
| 13 | 9.51 (9.506) | 9.5085 | 0.0025 | 9.4911 | 0.0189 |
| 14 | 9.49 (9.461) | 9.4652 | 0.0042 | 9.4457 | 0.0443 |
| 15 | 9.45 (9.417) | 9.4222 | 0.0052 | 9.4005 | 0.0495 |
| 16 | 9.38 (9.372) | 9.3794 | 0.0074 | 9.3556 | 0.0244 |
| 17 | 9.31 (9.328) | 9.3367 | 0.0087 | 9.3108 | 0.0008 |
| 18 | 9.27 (9.283) | 9.2943 | 0.0113 | 9.2663 | 0.0037 |
| Working Months | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Wall Thickness with ET | 9.506 | 9.461 | 9.417 | 9.372 | 9.328 | 9.283 | |
| ETGM(1,1)-ABC | Predicted value/mm | 9.5085 | 9.4648 | 9.4223 | 9.3790 | 9.3369 | 9.2939 |
| Absolute error/mm | 0.0025 | 0.0038 | 0.0053 | 0.0070 | 0.0089 | 0.0109 | |
| ETGM(1,1)-IABC | Predicted value/mm | 9.5084 | 9.4647 | 9.4222 | 9.3789 | 9.3367 | 9.2938 |
| Absolute error/mm | 0.0024 | 0.0037 | 0.0052 | 0.0069 | 0.0087 | 0.0108 | |
| ETGM(1,1)-GBABC | Predicted value/mm | 9.5075 | 9.4636 | 9.4208 | 9.3842 | 9.3348 | 9.2915 |
| Absolute error/mm | 0.0015 | 0.0026 | 0.0038 | 0.0052 | 0.0068 | 0.0085 | |
| ETGM(1,1)-RABC | Predicted value/mm | 9.5066 | 9.4626 | 9.4198 | 9.3762 | 9.3338 | 9.2907 |
| Absolute error/mm | 0.0006 | 0.0016 | 0.0028 | 0.0042 | 0.0058 | 0.0077 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Du, H.; Cui, Q.; Liu, P.; Ma, X.; Wang, H. Pipeline Corrosion Prediction Using the Grey Model and Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. Axioms 2022, 11, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11060289
Li S, Du H, Cui Q, Liu P, Ma X, Wang H. Pipeline Corrosion Prediction Using the Grey Model and Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. Axioms. 2022; 11(6):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11060289
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shiguo, Hualong Du, Qiuyu Cui, Pengfei Liu, Xin Ma, and He Wang. 2022. "Pipeline Corrosion Prediction Using the Grey Model and Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm" Axioms 11, no. 6: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11060289
APA StyleLi, S., Du, H., Cui, Q., Liu, P., Ma, X., & Wang, H. (2022). Pipeline Corrosion Prediction Using the Grey Model and Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. Axioms, 11(6), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11060289






