Abstract
When dealing with the haziness that is intrinsic in decision analysis-driven decision making procedures, interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets (IVIFSs) can be quite effective. Our approach to solving the multiple attribute decision making (MADM) difficulties, where all of the evidence provided by the decision-makers is demonstrated as interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy (IVIF) decision matrices, in which all of the components are distinguished by an IVIF number (IVIFN), is based on Aczel–Alsina operational processes. We begin by introducing novel IVIFN operations including the Aczel–Alsina sum, product, scalar multiplication, and exponential. We may then create IVIF aggregation operators, such as the IVIF Aczel–Alsina weighted geometric operator, the IVIF Aczel–Alsina ordered weighted geometric operator, and the IVIF Aczel–Alsina hybrid geometric operator, among others. We present a MADM approach that relies on the IVIF aggregation operators that have been developed. A case study is used to demonstrate the practical applicability of the strategies proposed in this paper. By contrasting the newly developed technique with existing techniques, the method is capable of demonstrating the advantages of the newly developed approach. A key result of this work is the discovery that some of the current IVIF aggregation operators are subsets of the operators reported in this article.
MSC:
90B50; 47S40
1. Introduction
The intuitionistic fuzzy set [1] was extended by Atanassov and Gargov to the IVIFS [2], which is represented by membership and non-membership functions whose values are intervals rather than real numbers. Due to the advantages of IVIFS, several researchers have attempted to incorporate IVIF information generated by different kinds of operators to generate judgments [3,4]. For instance, Xu [5] constructed several aggregation operators for IVIFNs, including the IVIF weighted averaging (IVIFWA) operator and the IVIF hybrid averaging (IVIFHA) operator. Liu [6] presented two IVIF operators based on the power average and Heronian mean operators and then integrated IVIF information using them. Zhao and Xu [7] provided several novel IVIF aggregation operations. Yu et al. [8] created the IVIF prioritized weighted averaging/geometric operator. Chen and Han [9,10] provided a MADM approach that was built on the multiplication of IVIF values, in addition to the LP and NLP methodologies. The influenced IVIF weighted and ordered weighted geometric operators were invented by Wei et al. [11]. Li [12] suggested a MADM technique using IVIFSs based on TOPSIS-based nonlinear programming (NLP). Xu and Gou [13] discussed the IVIF aggregation operator in detail. Chen et al. [14] developed a variety of MADM techniques based on IVIFSs. The influenced IVIF hybrid Choquet integral operators developed by Meng et al. [15] were used in decision-making issues. Wang and Liu [16,17] recommended the IVIF Einstein weighted averaging and geometric operators. IVIF MADM has already been widely applied in a variety of fields, including hotel location selection [18], air quality evaluation [19], solid waste management [20], hotel location selection [18], sustainable supplier selection [21], potential partner selection [22], and weapon-group target analysis [23].
Schweizer and Sklar pioneered the idea of triangular norms in their theory of empirical metric spaces [24]. As it develops out, t-norms and their associated t-conorms are vital operations in fuzzification and other evolutionary computing, for instance, Lukasiewicz t-norm and t-conorm [25], Hamacher t-norm and t-conorm [26], Einstein t-norm and t-conorm [17], general continuous Archimedean t-norm, t-conorm [27], etc. Klement et al. [28] conducted a thorough examination of the characteristics and concept implications of triangular norms in the latest years.
1.1. Motivation of the Study
Generalizing the ideas of Menger [29] from 1942, Schweizer and Sklar [24] proposed in 1960 the concept of triangular norms, or t-norms. While their methodology was developed within the context of probabilistic metric spaces for the purpose of making generalizations the triangular inequality of metrics, however, within some years they have been considered in several other branches, most notably fuzzy set theory (there, t-norms generate the fuzzy conjunctions, generalizing the original proposal of Zadeh [30] considering the min operation when introducing the intersection of fuzzy sets). Already in the framework of probabilistic metric spaces, but later also to cover the fuzzy disjunctions, the dual operations to t-norms, namely t-conorms were considered [31]. Later, t-norms and t-conorms have been considered in several generalizations of the fuzzy set theory, including intuitionistic fuzzy set theory [1], interval-valued fuzzy set theory and fuzzy type-2 theory [32], IVIFS theory [2], etc. For more details concerning t-norms and t-conorms we highly suggest the monograph [28] due to Klement et al.
Let be a commutative, associative and monotone function. Then, if is its neutral element, for all , F is called a triangular norm (t-norm in short). Similarly, if is its neutral element, i.e., for all , then F is called a triangular t-conorm (t-conorm, in short).
To have a clear distinction for t-norms and t-conorms in notation, we will consider the traditional notation T for t-norms and S for t-conorms. Note that these two classes are dual, i.e., for any t-norm T, the function given by is a t-conorm (also called a t-conorm dual to T), and for any t-conorm S, the function determined by is a t-norm (t-norm dual to S).
It is not difficult to see that the strongest (greatest) t-norm is following the notation from [28], while the smallest t-norm is the drastic product which is vanishing on (clearly, if then for any t-norm we have . Two prototypical t-norms playing an important role both in theory and applications are the product t-norm (standard product of reals), and the Lukasiewicz t-norm given by . One of the most distinguished subclasses of the class of all t-norms is formed by the continuous Archimedean t-norms, i.e., t-norms generated by a continuous additive generator. Their importance is clearly visible when n-ary extensions of t-norms are considered. For deeper results and more details see [28]. In our paper, we will deal with some specially generated t-norms, namely with strict t-norms which are isomorphic to the product t-norm, and which are generated by decreasing bijective additive generators . In such a case, , and, considering the n-array extension (which is unique due to the associativity of t-norms), . Recall that both extremal t-norms and , as well as the product t-norm commute with the power functions, i.e., for any , they satisfy the equality . Aczel and Alsina in the early 1980s [33] have characterized all other t-norm solutions of the above functional equation, showing that these are just strict t-norms generated by additive generators , , given by . The related t-norms are denoted as and called (strict) Aczel–Alsina t-norms, and given by
Observe that including the extremal t-norms, we obtain their Aczel–Alsina family , of t-norms, which is strictly increasing and continuous in parameter ð.
Due to the duality, similar notes and examples can be introduced for t-conorms. There, the smallest t-conorms is (dual to ), and the greatest t-conorm is the drastic product , which is constant 1 on . For any t-conorm S, if , then . Dual t-conorm to (Lukasiewicz t-conorm, also called a truncated sum) is given by , and the dual t-conorm to the product (called a probabilistic sum) is given by . Continuous Archimedean t-conorms are also generated by additive generators (which are increasing), and if S is dual to a continuous Archimedean t-norm T generated by an additive generator t, then S is generated by an additive generator s given by . In particular, dual t-conorms to strict Aczel–Alsina t-noms are generated by additive generators , and they are given by
Observe that including the extremal t-conorms, we obtain their Aczel–Alsina family , of t-conorms, which is strictly decreasing and continuous in parameter ð.
Aczel-Alsina [33] came up with two new operations called Aczel–Alsina t-norm and Aczel-Alsina t-conorm. These operations have a good relationship with the deployment of parameters. Wang et al. [34] used the Aczel-Alsina triangular norm (AA t-norm) to come up with a score level convolution neural network that increases the distance between imposters and legitimate at the same time. Senapati et al. [35,36,37,38] came up with Aczel—Alsina operations depending on intuitionistic fuzzy, IVIF, hesitant fuzzy, picture fuzzy aggregation operators, and they used them to solve MADM problems. The primary objective of this insightful article is to illustrate several geometric aggregation operators using IVIF data, known to as IVIF Aczel–Alsina geometric aggregations, for the purpose of identifying the successfully guide of decisions made utilizing decision-making techniques. Unaware of the previously existing unique ways that have been developed in this domain, we have fully examined every possibility to exhibit our proposed approach, in order for it to exceed all past attempts to apprehend the system assessment problem.
1.2. Structure of This Study
The framework of the study is presented in Figure 1. The following details are presented: The next section discusses several basic concepts relating to IVIFSs. Section 3 discusses the Aczel–Alsina operational laws governing the IVIFNs. Section 4 discusses the IVIF Aczel–Alsina weighted geometric (IVIFAAWG) operator, the IVIF Aczel–Alsina order weighted geometric (IVIFAAOWG) operator, and the IVIF Aczel–Alsina hybrid geometric (IVIFAAHG) operator, as well as a few particular instances. In Section 5, we demonstrate how to use the IVIFAAWG operator to construct particular approaches for resolving multiple attribute decision-making challenges in which support and understanding are represented as IVIF values. Section 6 shows the overall methodology with a genuine scenario. Section 7 investigates the effect of a parameter on the outcome of decision-making. Section 8 provides a comparison investigation of alternative important strategies to substantiate the suggested technique’s sufficiency. Section 9 concludes this analysis and identifies potential future concerns.
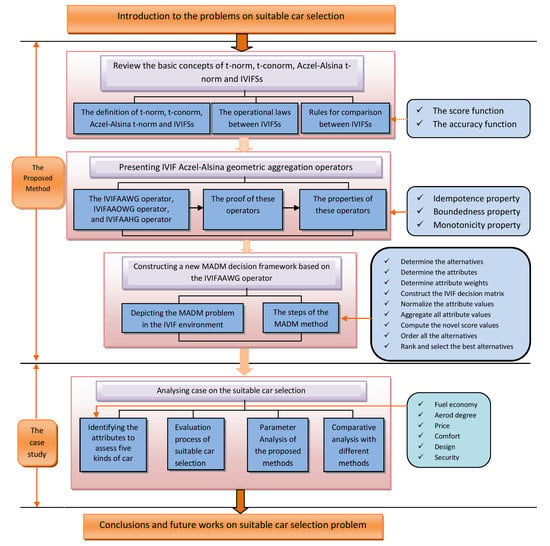
Figure 1.
The framework of the study.
2. Preliminaries
This section will summarize some major themes that will be discussed throughout the remainder of this work.
Definition 1
([2]). Assuming F is a recognized universe of discourse, an IVIFS in F is an expression given by
where , and is the set of all subintervals of . The intervals and denote the intervals of the degree of membership and degree of non-membership of the element f in the set , where and , for all , including the condition . denotes the indeterminacy degree of element f that belongs to , where and .
Assume that and are two IFSs over the universe F. The next relations and operations concerning two IVIFSs were described as follows [2,25]:
- (i)
- , if , , , and for all ;
- (ii)
- iff and ;
- (iii)
- for all ;
- (iv)
- (v)
where any pair can be utilized, T indicates a t-norm and S a so-called t-conorm dual to the t-norm T, characterized by .
For convenience, Xu [5] called an IVIFN, where , and .
For any three IVIFNs , and , Xu [5] and Xu and Chen [39] stated a few operations as follows:
- (i)
- ;
- (ii)
- ;
- (iii)
- ;
- (iv)
- ;
- (v)
- , ;
- (vi)
- , .
Several indices [5,40] were used to characterize IVIFN.
Definition 2
([40]). For any IVIFN , the score function , accuracy function , membership uncertainty index and hesitation uncertainty index of ∂ be defined as follows:
Based on these indices of IVIFNs, the total ordering [40] on IVIFNs was defined as follows.
Definition 3.
Let and be two IVIFNs, then
- (1)
- if , then ,
- (2)
- if , then
- (a)
- if , then ,
- (b)
- if , then
- (I)
- if , then ,
- (II)
- if , then
- (i)
- if , then ,
- (ii)
- if , then and are same, i.e., , , and , denoted by .
Definition 3 defines a way to compare two IVIFNs by prioritizing the functions of score, accuracy, membership uncertainty index, and hesitation uncertainty index. Because once two IVIFNs are analyzed, the sequencing is examined in the following order: general belonging degree, accuracy or hesitation level, membership uncertainty index, and hesitation uncertainty index. This comparative procedure is repeated unless one of the four functions defined in Definition 3 recognizes the two IVIFNs. When these two IVIFNs are distinguished at a particular level of severity, the computation is completed and functions with lower value levels are not computed.
Deschrijver et al. [41] designed the concept of the notion of non-empty intervals. They denoted by L the lattice of non-empty intervals with the partial order determined as and . The inferior and superior elements are denoted by the symbol and , respectively.
In this specific situation, Wang and Liu [16,17] meant by the lattice of non-empty IVIFNs with the partial order characterized as , , and , where the inferior and superior elements are and , respectively.
Remark 1.
If , then , i.e., the total order consists of the standard partial order on .
Definition 4.
is an aggregation function if it is monotone with respect to and satisfies and .
Currently, a wide number of operators are now being developed for accumulating IVIF data in [42,43]. The IVIF weighted geometric (IVIFWG) operator and the IVIF ordered weighted geometric (IVIFOWG) operator are probably the most frequently acknowledged operators for accumulating inputs, and they are discussed in details in the following.
Definition 5.
Let be an accumulation of IVIFNs and is the weight vector of so as , and . Therefore, the IVIF weighted geometric (IVIFWG) operator of dimension ℏ is a function and
.
Definition 6.
Let be a collection of IVIFNs and is the weight vector of so as , and . Then, the IVIF ordered weighted geometric (IVIFOWG) operator of dimension ℏ is a function and
.
3. Aczel–Alsina Operations of IVIFNs
This section will introduce the Aczel–Alsina operations on IVIFNs and discuss some of its fundamental properties.
If you let the t-norm T be the Aczel–Alsina product and the t-conorm S be the Aczel–Alsina sum , the generalized intersection and union over two IVIFNs E and W are the Aczel–Alsina product () and Aczel–Alsina sum () over two IVIFNs E and W, respectively, which can be seen:
Proposition 1.
Let and be two IVIFNs, and . Then, the Aczel–Alsina t-norm and t-conorm operations of IVIFNs are assigned as:
- (i)
- ,
- (ii)
- ,
Definition 7.
Let be a IVIFN, and . Then, the following two operations of IVIFNs are defined as:
- (i)
- ,
- (ii)
- .
Example 1.
Let , and be three IVIFNs, then applying Aczel–Alsina operation on IVIFNs as specified in Proposition 1 and Definition 7 for and , we get
- (i)
- (ii)
- (iii)
- (iv)
- .
Theorem 1.
Let , , and be three IVIFNs, then we have
- (i)
- ;
- (ii)
- ;
- (iii)
- , ;
- (iv)
- , ;
- (v)
- , ;
- (vi)
- , .
Proof.
For the three IVIFNs , and , , and , as stated in Proposition 1 and Definition 7, we can get
- (i)
- .
- (ii)
- It is simple.
- (iii)
- Let .Then, .Using this, we get .
- (iv)
- .
- (v)
- .
- (vi)
- .
□
4. IVIF Aczel–Alsina Geometric Aggregation Operators
We demonstrate some IVIF geometric aggregation operators throughout this section using the Aczel–Alsina operations.
Definition 8.
Let ( be an accumulation of IVIFNs and be the weight vector associated with , along with and . In that case an IVIF Aczel–Alsina weighted geometric (IVIFAAWG) operator can be described as function , in which
Following that, we prove the associated theorem for the Aczel–Alsina operations on IVIFNs.
Theorem 2.
Let ( be an accumulation of IVIFNs and , then aggregated value of them utilizing the IVIFAAWG operator is also a IVIFNs, and
where function as weight vector associated with so that , and .
Proof.
We may prove Theorem 2 using the following mathematical induction method:
(i) When , rely upon Aczel–Alsina operations of IVIFNs, we acquire
Depending on Definition 7 and Proposition 1, we get
Hence, (6) is true for .
Now for , then
.
Thus, (6) is true for .
Therefore, from (i) and (ii), we may conclude that (6) holds for any ℏ. □
Theorem 3.
(Idempotency) If all are equal, i.e., for all ζ, then
Proof.
Since , then we have by Equation (6), Thus, holds. □
Theorem 4.
(Boundedness) Let be an accumulation of IVIFNs. Let and . Then,
Proof.
Let be an accumulation of IVIFNs. Let and . We have, , , , , , , , and . Hence, there have the subsequent inequalities,
Therefore, □
Theorem 5.
(Monotonicity) Let and be two sets of IVIFNs, if for all ζ, then - .
Proof.
The proof is straightforward. □
Now, we present IVIF Aczel–Alsina ordered weighted geometric (IVIFAAOWG) operator.
Definition 9.
Let be an accumulation of IVIFNs. An IVIF Aczel–Alsina ordered weighted geometric (IVIFAAOWG) operator of dimension ℏ is a mapping with the corresponding vector such that , and , as
where are the permutation of , for which for all .
We generate the following theorem on IVIFNs based on the Aczel–Alsina product.
Theorem 6.
Let be an accumulation of IVIFNs. An IVIF Aczel–Alsina ordered weighted geometric (IVIFAAOWG) operator of dimension ℏ is a mapping with the associated vector such that , and . Then,
where are the permutation of , for which for all .
Proof.
Like Theorem 2, Theorem 6 is simply obtained. □
The following characteristics can be proven well by employing the IVIFAAOWG operator.
Property 1.(Idempotency) If are identical, i.e., for every ζ, then
Property 2.(Boundedness) Let be an accumulation of IVIFNs. Let , Then,
Property 3.(Monotonicity) Suppose that and are two sets of IVIFNs and for every ζ, then
Property 4.(Commutativity) Let and be two sets of IVIFNs, then where is any permutation of .
As defined in Definition 8, the IVIFAAWG operator measures only the IVIFNs, and as defined in Definition 9, the IVIFAAOWG operator measures only the IVIFNs’ consistent positions. Following that, weights represent different aspects of both the IVIFAAWG and IVIFAAOWG operators. Nevertheless, both the operators think about just one of them. To overcome this disadvantage, in the following we will exhibit IVIF Aczel–Alsina hybrid geometric (IVIFAAHG) operator, which weights both the given IVIFN and its ordered position.
Definition 10.
Let be an accumulation of IVIFNs. An IVIFAAHG operator of dimension ℏ is a function , such that
where is the weighting vector associated with the IVIFAAHG operator, with and ; , , is any permutation of a collection of the weighted IVIFNs , such that ; is the weight vector of , with and , and ℏ is the balancing coefficient, which plays a role of balance.
The following theorem can be deduced using Aczel–Alsina operations on IVIFNs information.
Theorem 7.
Let ( be an accumulation of IVIFNs and . Their aggregated value by IVIFAAHG operator is still a IVIFN, and
where is the weighting vector associated with the IVIFAAHG operator, with and ; , , is any permutation of a collection of the weighted IVIFNs , such that ; is the weight vector of , with and , and ℏ is the balancing coefficient, which plays a role of balance.
Proof.
Like Theorem 2, Theorem 7 is simply obtained. □
Theorem 8.
The IVIFAAWG and IVIFAAOWG operators are both variants of the IVIFAAHG operator.
Proof.
(1) Assume . Then,
(2) Let . Then, and
which completes the proof. □
5. MADM Methods Influenced by IVIFAAWG Operator
In this section, we shall take advantage of the IVIFAAWG operator to create a way for addressing MADM difficulties with IVIF information.
For a MADM issue, let function as the set of alternatives and function as the set of attributes, and attributes weight vector is , fulfilling and . We explicit the assessment information of the alternative concerning the criterion by , and is definitely an IVIF decision matrix. Hence, the MADM issue with IVIFNs may be discussed in the following matrix form, acknowledged by Equation (7).
where every one of the components is certainly an IVIFN, where is the positive membership degree because of which alternative fulfills the attribute that has been appropriated by the decision-makers, and gave the degree that the alternative does not fulfill the attribute that has been distributed by the decision-maker, where , and , .
The methodology dependent on IVIFAAWG operator to find out the MADM difficulties with IVIF data explicitly incorporates these steps:
- Step 1.
- Modify decision matrix into the normalization matrix .where is the complement of , such that .
In fact, if all the attributes are the same type, then there is no need to normalize them, but if it is found that there are two types of attributes then we will convert cost attributes to benefit attributes. Then, will be transformed into IVIF decision matrix .
- Step 2.
- Make use of the decision data expressed in matrix , and the operator IVIFAAWG to get the overall preference values of the alternative , i.e.,
- Step 3.
- Rank all of the alternatives in order of preference. Make use of the method in Definition 3 to rank the entire rating values and rank all the alternatives as per ˜ in descending order. Lastly, we choose the advantageous alternative(s) with the highest rating value.
- Step 4.
- End.
6. Numerical Example
This section contains an interesting explanation demonstrating the systematic methodology for choosing an appropriate car.
6.1. Problem Description
Consider a consumer who is considering purchasing a car. There are five distinct types of cars (alternatives) . The consumer considers six attributes while deciding which vehicle to buy (adapted from Herrera and Martinez [44]): : Fuel economy; : Aerod degree; : Price; : Comfort; : Design; and : Security. The weight vector of the attributes is . Expect that the features of the alternatives are addressed by the IVIFNs, as demonstrated in the IVIF decision matrix (Table 1).

Table 1.
IVIF decision matrix.
6.2. The IFAAWG Operator-Based Technique
To determine one of most perfect car , we employ the IFAAWG operator to construct a MADM theory using intuitionistic fuzzy information, which is frequently evaluated as follows:
- Step 1. Because the attributes are classified into two types, we begin by converting the attribute of the cost type into the attribute of the benefit type by employing Equation (8). At that point, is changed into the normalized decision matrix (Table 2).
 Table 2. Normalized IVIF decision matrix.
Table 2. Normalized IVIF decision matrix. - Step 2. Assume that . The IVIFAAWG operator is used to know the overall alternative values for five alternatives ,,,,,.
- Step 3. We evaluate the score values of the universal IVIFNs utilizing Equation (2) as , , , , .
- Step 4. Ranking these five alternatives according to the score values of the overall IVIFNs as .
- Step 5. Thus, the best car is .
7. The Impact of the Parameter ð in This Technique
To show how the different values of the parameter ð affect the alternatives, we use different values of the parameter ð to categorize the alternatives. The IVIFAAWG operator is used to rank the alternatives , and they are shown in Table 3 and shown in Figure 2. Clearly, when the value of ð for IVIFAAWG operator starts growing, the score values of the possible alternatives decrease, but the ranking stays the same: . Thus, the most important alternative is .

Table 3.
Ranking order of the alternatives with various parameter ð by IVIFAAWG operator.
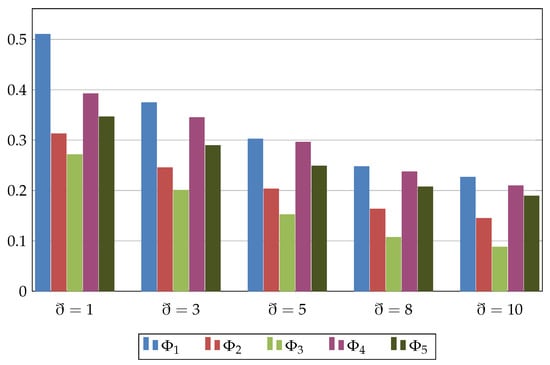
Figure 2.
Score values belonging to the alternatives for various values ð by IVIFAAWG operator.
Additionally, Figure 2 reveals that when the value of ð is changed in the example, the ranking results remain identical, demonstrating the resilience of the IVIFAAWG operators.
8. Sensitivity Analysis (SA) of Criteria Weights
To investigate the effect of criteria weights on ranking order, we present a sensitivity investigation. This is done using 24 different weight sets, namely— (Table 4) formed by considering all possible combinations of the criteria weights , , , , , and . This is especially valuable for achieving a more broad scope of criteria weights for taking a gander at the affectability of the created model. The scores of alternatives are accumulated in Figure 3, and their respective ranking orders are indexed in Table 5. Upon examining the ranking order of alternatives, it is seen that holds the first rank in 100% of the scenarios when the IVIFWG operator (taking ) is applied. Hence, the priority of alternatives acquired by utilizing our developed method is credible.

Table 4.
Various weight sets of criteria.
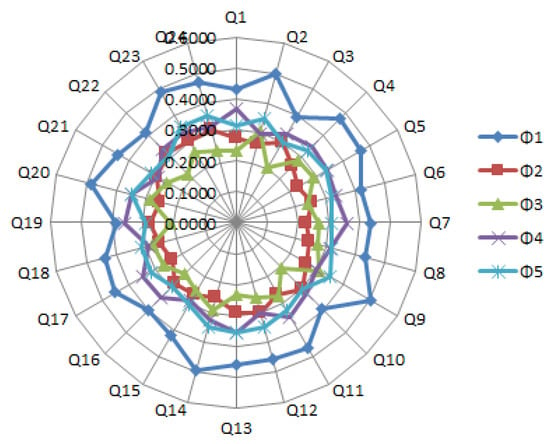
Figure 3.
Utility values of alternatives for distinct sets of weighted criteria.

Table 5.
Priority order of alternatives for diverse weight sets.
9. Comparison Study
Following that, we will compare and contrast our proposed approach with some other conventional methods such as the IVIF weighted averaging (IVIFWA) operator [5], the IVIF weighted geometric (IVIFWG) operator [39], the IVIF Einstein weighted geometric () operator [16], and the IVIF Einstein weighted averaging () operator [17]. The comparison findings are given in Table 6 and Table 7, and they are depicted in Figure 4 visually. If you look at Table 3 and Table 6, you can see that the IVIFWG operator is a special case of the IVIFAAWG operator, and that this happens when .

Table 6.
Comparative assessment using a few popular methodologies.

Table 7.
Qualitative evaluations of the current methods.
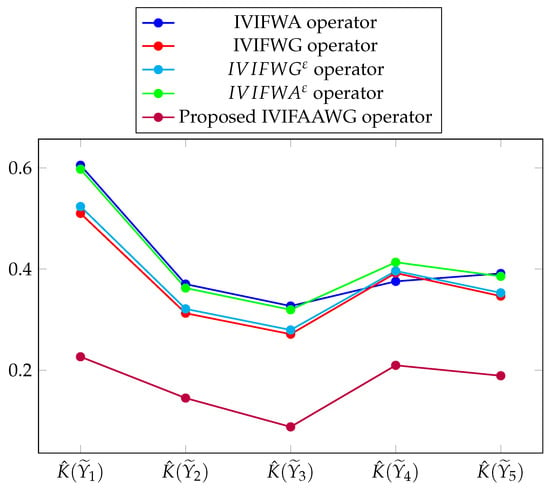
Figure 4.
Comparison analysis with a few prevailing techniques.
As a consequence, our recommended procedures for resolving IVIF MADM problems are frequently more extensive and adaptable than some of the techniques now in use.
10. Conclusions
We began this study by extending the Aczel–Alsina t-norm and t-conorm to IVIF scenarios, defining and examining a few additional working principles for IVIFNs. Then, in light of these new operating laws, different new aggregation operators, such as the IVIFAAWG operator, the IVIFAAOWG operator, and the IVIFAAHG operator, were devised to accommodate situations in which the specified assertions are IVIFNs. The fundamental characteristics of the recommended operators are examined, as well as their specific situations. We provide a realistic approach to MADM difficulties with IVIFNs depending on the IFAAWG operator. Furthermore, an exemplary scenario of choosing suitable cars is utilized to demonstrate the developed model, and a comparative study with some other methods is undertaken to show the recommended operators’ distinct advantages. In future studies, we plan to extend the challenge further by introducing new characteristics, including the use of probabilistic aggregations. Additionally, we will discuss additional decision-making aspects like cluster analysis, performance analysis [45], sustainable city logistics [46], risk investment assessment [47], Wireless Sensor Networks [48], capital budgeting techniques [49], home buying process [50], and other domains in uncertain environment [51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S. and R.M.; methodology, T.S. and V.S.; validation, V.S.; formal analysis, V.S. and R.A.; investigation, R.M.; data curation, R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, T.S. and A.I.; writing—review and editing, T.S. and R.C.; supervision, R.M.; project administration, V.S.; funding acquisition, A.I. and R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The author, Rifaqat Ali, extends his appreciation to Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, for funding this work through General Research Project under grant number (GRP/93/43). The author, Aiyared Iampan, is thankful to the revenue budget in 2022, School of Science, University of Phayao, for supporting this research. The author, Radko Mesiar, is thankful to the Slovak Research and Development Agency for supporting this research through Grant Number APVV-18-0052.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| IVIF | interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy |
| IVIFS | interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set |
| IVIFN | interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy number |
| MADM | multiple attribute decision making |
| IVIFWA | IVIF weighted averaging |
| IVIFHA | IVIF hybrid averaging |
| IVIF Einstein weighted averaging | |
| IVIF Einstein weighted geometric | |
| IVIFAAWG | IVIF Aczel-Alsina weighted geometric |
| IVIFAAOWG | IVIF Aczel-Alsina order weighted geometric |
| IVIFAAHG | IVIF Aczel-Alsina hybrid geometric |
References
- Attanassov, K.T. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.T.; Gargov, G. Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1989, 31, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliakov, G.; Bustince, H.; James, S.; Calvo, T.; Fernandez, J. Aggregation for Atanassov’s intuitionistic and interval valued fuzzy sets: The median operator. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2012, 20, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Wang, H.P.; Lu, Y.Y. A multicriteria group decision-making approach based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets: A comparative perspective. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 7647–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. Methods for aggregating interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information and their application to decision making. Control Decis. 2007, 22, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P. Multiple attribute group decision making method based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy power Heronian aggregation operators. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 108, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, Z. Group decision making with density-based aggregation operators under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environments. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 27, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wu, Y.; Lu, T. Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy prioritized operators and their application in group decision making. Know-Based Syst. 2012, 30, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Han, W.H. A new multiattribute decision making method based on multiplication operations of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy values and linear programming methodology. Inf. Sci. 2018, 429, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Han, W.H. Multiattribute decision making based on nonlinear programming methodology, particle swarm optimization techniques and interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy values. Inf. Sci. 2019, 471, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Wang, X. Some geometric aggregation operators based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their application to group decision making. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security (CIS 2007), Harbin, China, 15–19 December 2007; pp. 495–499. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.F. TOPSIS-based nonlinear-programming methodology for multiattribute decision making with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2010, 18, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gou, X. An overview of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information aggregations and applications. Granul. Comput. 2017, 2, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Kuo, L.W.; Zou, X.Y. Multiattribute decision making based on Shannon’s information entropy, non-linear programming methodology, and interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy values. Inf. Sci. 2018, 465, 404–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Q. Induced Atanassov’s inter-valvalued intuitionistic fuzzy hybrid Choquet integral operators and their application in decision making. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2014, 7, 524–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X. The multi-attribute decision making method based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy Einstein hybrid weighted geometric operator. Comput. Math. Appl. 2013, 66, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X. Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy hybrid weighted averaging operator based on Einstein operation and its application to decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2013, 25, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.H. Autocratic multiattribute group decision making for hotel location selection based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Inf. Sci. 2018, 427, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Cheng, S.H.; Tsai, W.H. Multiple attribute group decision making based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators and transformation techniques of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy values. Inf. Sci. 2016, 367–368, 418–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, L.; Zulkifli, N.; Liao, H.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Al-Barakati, A. An interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy DEMATEL method combined with Choquet integral for sustainable solid waste management. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intel. 2019, 82, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Quan, M.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, Z.L. A new integrated MCDM model for sustainable supplier selection under interval-valued intuitionistic uncertain linguistic environment. Inf. Sci. 2019, 486, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, X. A programming-based algorithm for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 144, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Chang, T.; Pan, J.; Hao, N.; Yang, G. A decision variable-based combinatorial optimization approach for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy MAGDM. Inf. Sci. 2019, 484, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, B.; Sklar, A. Statistical metric spaces. Pacific J. Math. 1960, 10, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deschrijver, G.; Cornelis, C.; Kerre, E.E. On the representation of intuitionistic fuzzy t-norms and t-conorms. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2004, 12, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Some Hamacher aggregation operators based on the interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and their application to group decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 22, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D. Group decision making under interval-valued multiplicative intuitionistic fuzzy environment based on Archimedean t-conorm and t-norm. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2015, 30, 590–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, E.P.; Mesiar, R.; Pap, E. Triangular Norms; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Menger, K. Statistical metrics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1942, 8, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inform. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweizer, B.; Sklar, A. Associative functions and statistical triangle inequalities. Publ. Math. Debrecen 1961, 8, 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Goguen, J.A. L-fuzzy sets. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1967, 8, 145–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aczel, J.; Alsina, C. Characterization of some classes of quasilinear functions with applications to triangular norms and to synthesizing judgements. Aequationes Math. 1982, 25, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, Q.; El-Latif, A.A.A.; Yan, X.; Niu, X. A Novel Hybrid Multibiometrics Based on the Fusion of Dual Iris, Visible and Thermal Face Images. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Biometrics and Security Technologies, Chengdu, China, 2–5 July 2013; pp. 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Chen, G.; Yager, R.R. Aczel-Alsina aggregation operators and their application to intuitionistic fuzzy multiple attribute decision making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 1529–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Chen, G.; Mesiar, R.; Yager, R.R. Novel Aczel–Alsina operations-based interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operatorsandtheir applications in multiple attribute decision-making process. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Chen, G.; Mesiar, R.; Yager, R.R.; Saha, A. Novel Aczel-Alsina operations-based hesitant fuzzy aggregation operators and their applications in cyclone disaster assessment. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2022, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T. Approaches to multi-attribute decision-making based on picture fuzzy Aczel–Alsina average aggregation operators. Comp. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, J. On geometric aggregation over interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD 07), Haikou, China, 24–27 August 2007; Volume 2, pp. 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, K.W.; Wang, W. An approach to multiattribute decision making with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy assessments and incomplete weights. Inf. Sci. 2009, 179, 3026–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deschrijver, G.; Kerre, E. On the relationship between some extensions of fuzzy set theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2003, 133, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, D.L.; Bustince, H.; Fernandez, J.; Indurain, E.; Kolesarova, A.; Mesiar, R. Construction of admissible linear orders for interval-valued Atanassov intuitionistic fuzzy sets with an application to decisionmaking. Inf. Fusion 2016, 27, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, L.; Bustince, H.; Pekala, B.; Bentkowska, U.; Da Silva, I.; Bedregal, B.; Mesiar, R.; Ochoa, G. Interval-valued Atanassov intuitionistic OWA aggregations using admissible linear orders and their application to decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 24, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, E.; Martinez, L. An approach for combining linguistic and numerical information based on 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model in decision-making. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl. Based Syst. 2000, 8, 539–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, I.; Rashid, T. Group decision making using intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy sets. Int. J. Fuzzy Log. Intell. 2014, 14, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, A.; Simic, V.; Senapati, T.; Dabic-Miletic, S.; Ala, A. A dual hesitant fuzzy sets-based methodology for advantage prioritization of zero-emission last-mile delivery solutions for sustainable city logistics. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Liu, Y.; Senapati, T.; Garg, H.; Rong, Y. An extended MABAC method based on prospect theory with unknown weight information under Fermatean fuzzy environment for risk investment assessment in B&R. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, L.; Sen, S.; Tiwary, K.; Samanta, S.; Senapati, T. Modified Floyd-Warshall’s algorithm for maximum connectivity in Wireless Sensor Networks under uncertainty. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2022, 2022, 5973433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, D.; Sari, I.U.; Senapati, T. Extension of capital budgeting techniques using interval-valued Fermatean fuzzy sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 42, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrar, M.; Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Abbas, F. Fuzzy parameterized bipolar fuzzy soft expert set and its application in decision making. Int. J. Fuzzy Log. Intell. 2019, 19, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, A.; Senapati, T.; Yager, R.R. Hybridizations of generalized Dombi operators and Bonferroni mean operators under dual probabilistic linguistic environment for group decision-making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 6645–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Yager, R.R. Fermatean fuzzy weighted averaging/geometric operators and its application in multi-criteria decision-making methods. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intel. 2019, 85, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Yager, R.R. Some new operations over Fermatean fuzzy numbers and application of Fermatean fuzzy WPM in multiple criteria decision making. Informatica 2019, 30, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senapati, T.; Yager, R.R. Fermatean fuzzy sets. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesiar, R.; Kolesarova, A.; Senapati, T. Aggregation on lattices isomorphic to the lattice of closed subintervals of the real unit interval. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Chen, G. Picture fuzzy WASPAS technique and its application in multi-criteria decision-making. Soft Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Chen, G. Some novel interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy aggregation operator based on Hamacher triangular norms and their application in MADM issues. Comp. Appl. Math. 2021, 40, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Yager, R.R.; Chen, G. Cubic intuitionistic WASPAS technique and its application in multi-criteria decision-making. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 8823–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).