Organic Materials and Their Effects on Lead–Zinc Mineralization in the Xicheng Belt, Western Qinling (China): A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pb–Zn Deposits in the Xicheng Belt
2.1. Geologic Settings
2.2. Pb–Zn Deposits
2.3. Forming Mechanism
3. Organic Materials (Types and Features)
3.1. Overall Characteristics of Organic Matter
3.2. Characteristics and Evolution of Sulfur Compounds
4. Effects on the Mineralization of Pb–Zn Ore Formation
4.1. Formation of H2S
4.2. Adsorption of Lead and Zinc by Organic Matter
4.3. Complexation and Reduction of Organic Matter
5. Discussion and Outlook for Xicheng
5.1. Existing Research Characteristics and Issues
5.2. Key Aspects of Xicheng Organic Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, R.L.; Guo, D.B.; Chen, X.F.; Hu, P.C.; Zhang, C.X.; Feng, F.; Xia, X.Y.; Cao, H.W.; Yang, M.X.; Yang, L.J. Research Progress and Prospecting Directions of edimentary-Hosted Lead-Zinc Deposits in the Qinling etallogenic Belt, China. Geol. J. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.L.; Qi, S.J.; Li, Y.; Xue, C.J. Genesis of albitites in Changba Pb-Zn Ore deposit. Geol. Geochem. 1998, 2, 29–33, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, D.P.; Wei, Z.G. Fault controlling in Luoba lead-zinc deposit, Gansu province. Geol. Prospect. 2005, 6, 41–44, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.L.; Sun, B.N.; Yan, D.F.; Dong, C.; Hou, S.G.; Gao, H.G. The Tectonic Evolution of the Xicheng Ore Concentrated Area in Oinling Mountain and Its Relation to Lead-Zinc Mineralization. Acta Geol. Sin. 2012, 86, 1291–1297, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, C.Q. Editorial for Special Issue “Genesis and Evolution of Pb-Zn-Ag Polymetallic Deposits”. Minerals 2024, 14, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.J.; Dai, S.; Guo, D.B.; Li, H.L.; Cao, X.F.; Yi, Y.L.; Ma, Z.T.; Ma, Y.Z. Mineralization of gold and antimony in Pb-Zn deposit periphery of Luoba, West Qinling, China: Evidence from in situ trace elements and C-O-S isotopes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2025, 41, 1367–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.L. Preliminary discussion on geological characteristics and genesis of lead-zinc deposits in Xicheng area, Gansu Province. Northwestern Geol. 1980, 3, 40–46, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.K. Types and genesis of Xicheng lead-zinc deposit. Geol. Prospec. 1983, 7, 2–10, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Beaudoin, G. Geological and geochemical characteristis of the Changba and Dengjiashan Pb-Zn deposits in the Qinling orogenic belt, China. In Mineral Deposit Research: Meeting the Global Challenge; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Deng, J.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Lai, X.G. Nature, diversity and temporal–spatial distributions of sediment-hosted Pb―Zn deposits in China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 327–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.P.; Zhou, Z.G.; Xiao, J.D.; Chen, B.Y.; Zhao, X.W.; Xin, J.R.; Li, X.; Du, Y.S.; Xin, W.J.; Li, G.C. Characteristics of Devonian sedimentary facies in the Qinling mountains and their tectono-palaeo geographic significance. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1989, 3, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.W.; Li, F.D.; Sun, N.Y. The basic geological features and genesis of Qinling type of Stratabound Lead-Zinc sulfide deposit. Northwest Geosci. 1987, 5, 83–96, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhao, H.S.; Wu, J.M. Discussion on controlling conditions of metallogenesis and enrichment regularities of mineralization of lead-zinc deposits in Changba Lijiagou area. Miner. Resour. Geol. 1988, 2, 1–9, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Discussion on the genesis of West Qinling lead-zinc deposit. Northwestern Geol. 1989, 3, 22–30+21, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Cheng, H.S.; Su, W.M.; Chen, D.Y. Source of ore-forming metals for lead-zinc deposits in the Xicheng ore field, Gansu. Sci. Geol. Sin. 1992, 2, 149–159, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.X.; Bai, R.L.; Guo, D.B.; Chen, X.F.; Yang, L.J.; Yang, M.X.; Xia, X.Y.; Wang, K.N. Tracing the Genesis and Mineralization Mechanism of the Xiejiagou Pb–Zn Deposit in Gansu, China: Insights from Trace Element Analysis, Fluid Inclusion Studies, and the Sulfur Isotopic Composition. Geol. Ore Depos. 2024, 66, 663–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L. Qinling-Type Lead-Zinc Deposits in China; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.X.; Pu, F.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Lu, J.J.; Ou, K.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.P. TI Critical metals Ga and Ge enrichment in the last-stage and low-temperature sphalerite from the Guojiagou Zn-Pb deposit, western Qinling Orogen, NW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 179, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.G.; Ni, P.; Wang, G.G.; Zhang, T. Identification and significance of methane-rich fluid inclusions in Changba Pb-Zn deposit, Gansu province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, G.Z.; Zhao, C.B. Investigating rock permeability effects on mineralization locations of the Changba-Lijiagou Pb-Zn deposit, Gansu, China: Modelling of ore-forming mechanisms through the dual length-scale approach. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 177, 106445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Han, S.J.; Zheng, Y.; Zeng, Z.J.; Chen, T.W.; Zhang, G.B. Geology, geochemistry, zircon and garnet U-Pb geochronology, and C-O-S-Pb-Hf isotopes of the Guojiagou Pb-Zn deposit, West Qinling Belt, Central China: New constraints on district-wide mineralization. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 264, 107534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.B.; Bai, R.L.; Dai, S.; Chen, X.F.; Niu, Y.J.; Shang, L.L.; Mujahed, M.A.; Guo, X.G.; Zhang, C.X.; Wang, B.L. Trace elements of sulfides in the Dengjiashan Pb–Zn deposit from West Qinling, China: Implications for mineralization conditions and genesis. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 2913–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Hu, W. Mineral Chemistry and In Situ LA-ICP-MS Titanite U-Pb Geochronology of the Changba-Lijiagou Giant Pb-Zn Deposit, Western Qinling Orogen: Implications for a Distal Skarn Ore Formation. Minerals 2024, 14, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.J.; Gao, Y.B.; Zeng, R.; Chi, G.X.; Qing, H.R. Organic petrography and geochemistry of the giant Jinding deposit, Lanping basin, northwestern Yunnan, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Disnar, J.R.; Sureau, J.F. Organic matter in ore genesis: Progress and perspectives. Org. Geochem. 1990, 16, 577–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lei, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, G.; Fu, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, J. Genetic Relationship between Mississippi Valley-Type Pb–Zn Mineralization and Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Wusihe Deposits, Southwestern Margin of the Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals 2022, 12, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williford, K.H.; Grice, K.; Logan, G.A.; Chen, J.; Huston, D. The molecular and isotopic effects of hydrothermal alteration of organic matter in the Paleoproterozoic McArthur River Pb/Zn/Ag ore deposit. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 301, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, D.L.; Song, Y.C.; Hou, Z.Q. The world-class Jinding Zn–Pb deposit: Ore formation in an evaporite dome, Lanping Basin, Yunnan, China. Miner. Depos. 2017, 52, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marikos, M.A.; Laudon, R.C.; Leventhal, J.S. Solid insoluble bitumen in the Magmont West orebody, Southeast Missouri. Econ. Geol. 1986, 81, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gize, A.P.; Barnes, H.L. The organic geochemistry of two Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc deposits. Econ. Geol. 1987, 82, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.M. Kerogen as a Source of Sulfur in MVT Deposits. Econ. Geol. 2014, 110, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender, B.D.; Shelton, K.L.; Schiffbauer, J.D. An atypical orebody in the Brushy creek mine, viburnum ternd, MVT district, Missouri early Cu-(Ni-Co)-Zn-rich ores at the lamotte sandstone/bonneterre dolomite contact. Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhu, D.Y. Hydrothermal catalytic conversion and metastable equilibrium of organic compounds in the Jinding Zn/Pb ore deposit. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 307, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.W.; Li, L.; Li, C.L.; Li, S.R.; Santosh, M.; Masroor, A.; Hou, Z.Q. The genesis of bitumen and its relationship with mineralization in the Erdaokan Ag-Pb-Zn deposit from the Great Xing’an Range, northeastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Ma, L.H. Organic Geochemistry of the Bijiashan lead-zinc deposit(II)-features of bulk organic matter and sources of ore-forming materials. Acta Mineral. Sin. 1996, 1, 82–88, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.L. Organic geochemical characters and metallogenesis of Xicheng Pb-Zn ore field, Gansu, China. Acta Geol. Gansu 1999, 2, 58–64, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.J.; Cui, Y.L. Sedimentary Environment Interpreted by the Characteristics of Organic Matters in Xicheng Ore field. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2000, 1, 125–130, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Zhu, L.D.; Pang, Y.C.; Xiong, Y.Z.; Fu, X.G. Simulation Experiment Research on Biomineralization of Xicheng Lead and Zinc Deposit, Qinling. Miner. Depos. 2002, 21, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.C.; Zhu, L.D.; Lin, L. Organic Mineralization of Lead-Zinc Deposits in Devonian System, Xicheng Ore Field. Earth Sci. 2003, 2, 201–208, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Pang, Y.C.; Zhu, D.C.; Fu, X.G.; Zhu, L.D. The role of organic fluid during the migration of ore-forming elements: A case of simulation experiment for Luoba lead-zinc deposit, Western Qinling. J. Mineral. Petrol. 2008, 2, 51–55, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.J.; Sun, Y.Z.; Tang, Y.G. Early hydrocarbon generation of algae and influences of inorganic environments during low temperature simulation. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2008, 26, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Qin, S.J.; Li, Y.H.; Lin, M.Y.; Ding, S.L. Explanation for peat-forming environments of Seam 2 and 9-2 based on the maceral composition and aromatic compounds in the Xingtai Coalfield, China. J. Coal Sci. Eng. 2009, 15, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Qin, S.J.; Zhao, C.L.; Kalkreuthc, W. Experimental study of early formation processes of macerals and sulfides. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Liu, H.; Xiao, J.F.; Fu, S.L.; Santosh, M.; Tang, Y.Y. The source of organic matterand its role in producing reduced sulfur for the giant sedimenthosted Jinding zine-lead deposit, Lanping Basin, Yunnan Southwest China. Econ. Geol. 2021, 116, 1537–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtig, N.C.; Hanley, J.J.; Gysi, A.P. The role of hydrocarbons in ore formation at the Pillara Mississippi Valley-Type Zn-Pb deposit, Canning Basin, Western Australia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 102, 875–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.C.; Yang, Z.M.; Zhuang, L.L. Enrichment of Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) deposits in the Tethyan domain linked to organic matter-rich sediments. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 2853–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.Y.; Li, S.W.; Li, R.X. Metal-organic complex as a Pb/Zn carrier in the formation of Mississippi Valley-Type (MVT) Pb-Zn deposits: A case study of the Mayuan Pb-Zn ore district, the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, Central China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 180, 106570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Mao, J.W.; Ouyang, H.G.; Sun, J. The genetic relationship between hydrocarbon systems and Mississippi Valley-type Zn-Pb deposits along the SW margin of Sichuan Basin, China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2013, 55, 941–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.J.; Chi, G.X.; Li, Z.D.; Dong, X.F. Geology, geochemistry and genesis of the Cretaceous and Paleocene sandstone- and conglomerate-hosted Uragen Zn-Pb deposit, Xinjiang, China: A review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Xiang, J.J.; Jin, Y.L.; Cen, W.P.; Zhu, G.Y.; Shen, C.B. Petroleum evolution and its genetic relationship with the associated Jinding Pb-Zn deposit in Lanping Basin, Southwest China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2024, 294, 104620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.X.; Hu, Y.Z.; Xu, S.H.; Shi, S.B.; Wen, Y.M.; Nie, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, K.; Tan, X.L.; et al. The biomarker signatures in the Niujiaotang sulfide ore field: Exploring the role of organic matter in ore formation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2026, 183, 107616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.X.; Mao, J.W.; Zhao, B.S.; Chen, B.Y.; Liu, S.W. A Review of the Role of Hydrocarbon Fluid in the Ore Formation of the MVT Pb-Zn Deposit. Adv. Earth Sci. 2021, 36, 335–345, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.X.; Dong, S.W.; Dan, L.H. Tectonically driv-en organic fluid migration in the Dabashan Foreland Belt: Evi-denced by fibrous calcite with organic inclusions. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 75, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.Y.; Li, S.W.; Li, R.X. Mineralization Process of MVT Zn-Pb Deposit Promoted by the Adsorbed Hydrocarbon: A Case Study from Mayuan Deposit on the North Margin of Sichuan Basin. Minerals 2023, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galina, V.; Janet, M.H.; Amber, J.M.; Jarrett, N.W.; Jochen, J.B. Reassessment of thermal preservation of organic matter in the Paleoproterozoic McArthur River (HYC) Zn-Pb ore deposit, Australia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104129. [Google Scholar]
- Marynowski, L.; Czechowski, F.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Phenylnaphthalenes and polyphenyls in Palaeozoic source rocks of the Holy Cross Mountains Poland. Org. Geochem. 2001, 32, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marynowski, L.; Rospondek, M.J.; Reckendorf, R.M.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Phenyldibenzofurans and phenyldibenzothiophenes in marine sedimentary rocks and hydrothermal petroleum. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.J.; Qin, S.J.; Zhao, C.L.; Sun, Y.Z.; Balaji, P.; Chang, X.C. Origin and geological implications of super high sulfur-containing polycyclic aromatic compounds in high-sulfur coal. Gondwana Res. 2021, 96, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.J.; Qin, S.J.; Shen, W.C.; Sun, Y.Z. Significant influence of different sulfur forms on Sulfur-containing polycyclic aromatic compound formation in high-sulfur coals. Fuel 2023, 332, 125999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Alexander, R.; Fazeelat, T.; Pierce, K. Geosynthesis of dibenzothiophene and alkyl dibenzothiophenes in crude oils and sediments by carbon catalysis. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.H.; Wang, T.G.; Li, M.J.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Zhang, B.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Shi, S.B.; Wang, D.W.; Deng, W.L. Dibenzothiophenes and benzo[b]naphthothiophenes: Molecular markers for tracing oil filling pathways in the carbonate reservoir of the Tarim Basin, NW China. Org. Geochem. 2016, 91, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Worden, R.H.; Jin, Z.J.; Liu, W.H.; Liu, J.; Gao, B.; Zhang, D.W.; Hu, A.P.; Yang, C. TSR versus non-TSR processes and their impact on gas geochemistry and carbon stable isotopes in Carboniferous, Permian and Lower Triassic marine carbonate gas reservoirs in the Eastern Sichuan Basin, China. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 100, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, R.H.; Smalley, P.C. H2S-producing reactions in deep carbonate gas reservoirs: Khuff Formation, Abu Dhabi. Chem. Geol. 1996, 133, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Worden, R.H.; Bottrell, S.H.; Wang, L.; Yang, C. Thermochemical sulphate reduction and the generation of hydrogen sulphide and thiols (mercaptans) in Triassic carbonate reservoirs from the Sichuan Basin, China. Chem. Geol. 2003, 202, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Qin, H.; Li, G. Fluid Mixing, Organic Matter, and the Origin of Permian Carbonate-Hosted Pb-Zn Deposits in SW China: New Insights from the Fuli Deposit. Minerals 2024, 14, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machel, H.G. Bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings—Old and new insights. Sediment. Geol. 2001, 140, 143–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Qi, H.W.; Bi, X.W.; Hu, R.Z.; Qi, L.K.; Yin, R.S.; Tang, Y.Y. Mercury and sulfur isotopic composition of sulfides from sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits in Lanping basin, Southwestern China. Chem. Geol. 2021, 559, 119910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, S.Y. Microbial geochemistry of sulfur and its implication to geology. Geol. Chem. Miner. 1993, 15, 101–106, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Huang, K.M.; Chen, S.K. Sulfate reduction and iron sulfide mineral formation in the southern east China sea continental slope sediment. Deep-Sea Res. Part I-Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 1837–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billon, G.; Thoumelin, G.; Barthe, J.F.; Fischer, J.C. Variations of fatty acids during the Sulphidization process in the Authie bay sediments. J. Soils Sediments 2007, 7, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.Z.; Raimondi, I.M.; Schalch, V.; Rodrigues, V.G.S. Assessment of the use of organic composts derived from municipal solid waste for the adsorption of Pb, Zn and Cd. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 226, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G.; Porter, J.F. Equilibrium parameters for the sorption of copper, cadmium and zinc ions onto peat. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 69, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddad, Z.; Gerente, C.; Andres, Y.; Cloirec, P.L. Adsorption of several metal ions onto a low-cost biosorbent: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hass, A.; Lima, I.M. Effect of feed source and pyrolysis conditions on properties and metal sorption by sugarcane biochar. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 10, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricordel, S.; Taha, S.; Cisse, I.; Dorange, G. Heavy metals removal by adsorption onto peanut husks carbon: Characterization, kinetic study and modeling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 24, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratschbacher, L.; Hacker, B.R.; Calvert, A.; Webb, L.E.; Grimmer, J.C.; Mc-williams, M.O.; Ireland, T.; Dong, S.W.; Hu, J.M. Tectonics of the Qinling (Central China): Tectonostratigraphy, geochronology, and deformation history. Tectonophysics 2003, 366, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Guo, S. Cellulose/chitin beads for adsorption of heavy metals in aqueous solution. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykova, Y.; Strömvall, A.M.; Steenari, B.M. Adsorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn on Sphagnum peat from solutions with low metal concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, W.E.; Franca, A.S.; Oliveira, L.S.; Rocha, S.D. Untreated coffee husks as biosorbents for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.C.; Aldrich, C. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions with tobacco dust. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5595–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Saeed, A.; Zafar, S.I. FTIR spectrophotometry, kinetics and adsorption isotherms modeling, ion Exchange, and EDX analysis for understanding the mechanism of the Cd2+ and Pb2+ removal by mango peel waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Guo, X.; Liang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by chemically modified orange peel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Tang, W.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of cadmium and lead sorption by Phyllostachys pubescens biochar produced under a low-oxygen pyrolysis atmosphere. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Spinks, S.C.; Glenn, M.; MacRae, C.; Pearce, M.A. How carbonate dissolution facilitates sediment-hosted Zn-Pb mineralization. Geology 2021, 49, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.B.; Xue, C.J.; Zeng, R. Geochemistry of organic matters in the Jinding zinc-lead deposit. Lanping Basin, Northwest Yunnan Province. Geochimica 2008, 3, 223–232, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.D.; Li, S.G.; Chen, Y.D.; Li, Y.J. Timing of the synorogenic granoids in the South Qinling, Central China: Constrints on the evo-lution of the Qining-Dabie orogenic belt. J. Geol. 2002, 11, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Chen, R.X.; Zhao, Z.F. Chemical geodynamics of continental subduction-zone metamorphism: Insights from studies of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling (CCSD) core samples. Tectonophysics 2009, 475, 327–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.P.; Zhang, G.W.; Neubaue, R.F.; Liu, X.M.; Johann, G.; Christoph, H. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogeny, China: Review and synthesis. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


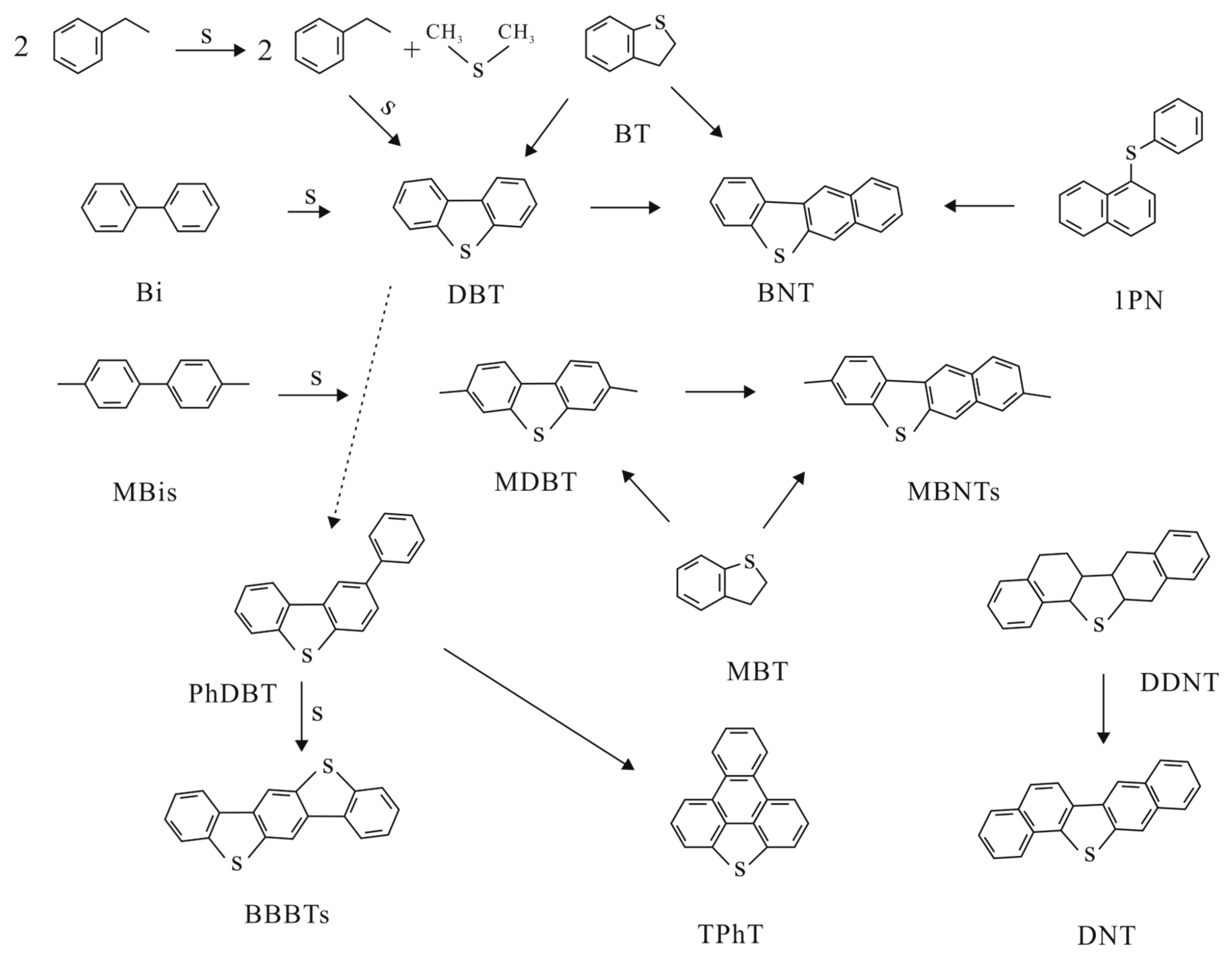
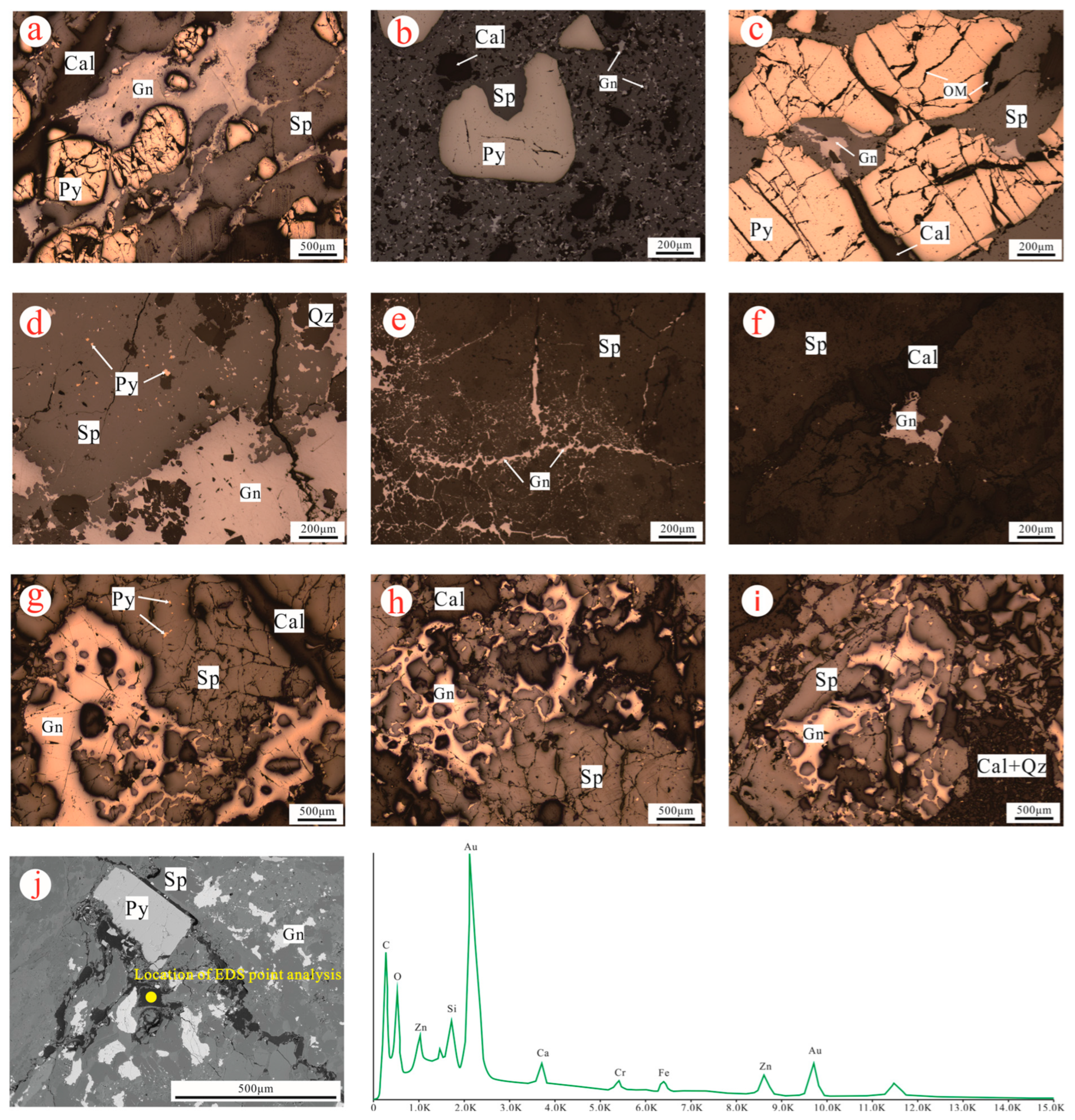
| Mineral Deposit | Lithology and Ore | Corg (%) | Relative Ore Body Position | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changba | Dolomite | 0.20 | Far Ore | [39] |
| Biotite–Quartz Schist | 0.14 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Breccia | 0.85 | | | ||
| Massive Ore | 0.32 | Near Ore | ||
| Banded Ore | 0.31 | | | ||
| Cryptocrystalline Banded Ore | 0.54 | | | ||
| Marble | 0.49 | Slightly Distant | ||
| Luoba | Carbonaceous Phyllite | 5.88 | Near Ore | [38] |
| Silicified Limestone | 0.52 | Slightly Distant | ||
| Phyllite | 0.14 | Far Ore | [39] | |
| Biogenic Limestone | 0.36 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Siliceous Rock | 0.75 | | | ||
| Ore-bearing Siliceous Rock | 0.34 | Near Ore | ||
| Bijiashan | Sericite Phyllite | 0.16 | Far Ore | [35] |
| Carbonaceous Phyllite | 0.80 | | | ||
| Ore | 2.09 | Near Ore | ||
| Phyllite | 0.31 | Far Ore | [36] | |
| Crystalline Limestone | 0.69 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Limestone | 0.82 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Siliceous Rock | 0.95 | | | ||
| Ore | 0.46 | Near Ore | ||
| Phyllite | 0.33 | Far Ore | [39] | |
| Black Siliceous Rock | 0.70 | | | ||
| Black Microcrystalline Limestone | 0.82 | Near Ore | ||
| Dengjiashan | Sericite–calcite Phyllite | 0.40 | Far Ore | [36] |
| Carbonaceous Phyllite | 0.71 | | | ||
| Crystalline Limestone | 0.86 | | | ||
| Ore | 0.98 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Limestone | 2.47 | Near Ore | ||
| Silicified Limestone | 0.19 | Far Ore | [39] | |
| Biogenic Limestone | 0.25 | | | ||
| Ore-bearing Siliceous Rock | 0.13 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Phyllite | 5.15 | Near Ore | ||
| Nanjiagou | Crystalline Limestone | 0.05 | Far Ore | [37] |
| Carbonaceous Argillaceous Striped Limestone | 0.18 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Microcrystalline Limestone | 0.11 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Micrite Limestone | 0.15 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Micrite Limestone | 0.32 | Near Ore | ||
| Yeshuihe | Lily Stem Limestone | 0.04 | Far Ore | [36] |
| Carbonaceous Limestone | 0.18 | | | ||
| Muddy Strip Carbonaceous Limestone | 0.21 | Near Ore | ||
| Carbonaceous Limestone | 0.18 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Limestone | 0.15 | Far Ore | ||
| Phyllite | 0.32 | | | ||
| Carbonaceous Phyllite | 0.24 | Near Ore |
| Sam. | Bd1 | Bd2 | Bd6-1 | Bd4-1 | Bd4-2 | Bd6-2 | Bd9 | B3-1 | B3-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω(Ag)/10−6 | 0.440 | 0.500 | 3.790 | 0.590 | 0.450 | 0.450 | 0.360 | 0.470 | 0.570 |
| ω(Pb)/10−2 | 0.034 | 0.026 | 0.400 | 0.050 | 0.450 | 0.031 | 0.030 | 0.036 | 0.041 |
| ω(Zn)/10−2 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.390 | 0.250 | 0.033 | 0.019 | 0.010 | 0.017 | 0.020 |
| ω(N-alkanes)/% | 26.79 | 24.01 | 53.51 | 71.36 | 27.78 | 25.85 | 28.72 | 28.24 | 30.61 |
| ω(carotenes)/% | 0.004 | 0.001 | 5.084 | 0.692 | 0.014 | 1.722 | 0.646 | 2.225 | 0.001 |
| ω(terpenes)/% | 0.682 | 0.592 | 1.169 | 0.742 | 0.836 | 1.012 | 0.945 | 0.924 | 0.654 |
| ω(steranes)/% | 0.144 | 0.101 | 0.569 | 0.224 | 0.159 | 0.342 | 0.214 | 0.338 | 0.118 |
| ω(terpenes)/w(steranes) | 4.753 | 5.897 | 2.055 | 3.307 | 5.274 | 2.961 | 4.417 | 2.731 | 5.530 |
| ω(tricyclic terpanes)/ω(tetracyclic terpanes) | 62.84 | 85.57 | 20.03 | 17.59 | 73.19 | 42.87 | 56.27 | 45.49 | 77.78 |
| ω(∑C22−)/ω(∑C22+) | 3.881 | 6.249 | 1.485 | 0.683 | 6.965 | 4.250 | 4.486 | 5.853 | 7.911 |
| ω(C20 + C21)/ω(C23 + C24) | 1.319 | 1.725 | 0.901 | 1.036 | 1.754 | 1.164 | 1.429 | 1.419 | 1.705 |
| No. | Reaction Equation |
|---|---|
| 1 | Alkanes → Biodegradation of hydrocarbons |
| 2 | Crude oil → Light crude oil + H2S (+PS) + CH4 |
| 3a | 4R-CH3 + 3SO42− + 6H+ → 4R-COOH + 4H2O + 3H2S |
| 3b | R-CH3 + 2R-CH2 + CH4 +3SO42− + 5H+ → 3R-COOH + HCO3− + 3H2O + 3H2S |
| 3c | 2CH2O + SO42− → 2HCO3− + H2S |
| 4a | 2 H2S + O2 → 2S0+ 2H2O |
| 4b-1 | 3H2S + SO42− + 2H+ → 4S0 + 4H2O |
| 4b-2 | H2S + SO42− + 2H+ → S0 + 2H2O + SO2 |
| 4c | H2S + Hydrocarbons → S0 + Transforming hydrocarbons |
| 4d | S2− → S0 |
| 5 | S0 + CH2O + 2H2O + OH− → 3H2S + HCO3− |
| 6 | Hydrocarbons + SO42− → Transforming hydrocarbons + Solid asphalt + HCO3-(CO2) + H2S(HS−) + Heat of reaction |
| Reactive Material | Metal Ion Affinity Order | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Peanut husks carbon | Pb > Cd > Ni > Zn | [75] |
| Sugar beet pulp | Pb > Cu > Zn > Cd > Ni | [76] |
| Cellulose/chitin beads | Pb > Cd > Cu | [77] |
| Sphagnum temperate peat (Sweden) | Pb > Cu > Ni > Cd > Zn | [78] |
| Untreated coffee husks | Cu > Cr > Cd > Zn | [79] |
| Tobacco dust | Pb > Cu> Cd > Ni ≈ Zn | [80] |
| Mango peel waste | Pb > Cd | [81] |
| Grafted copolymerization-modified orange peel | Pb > Cd> Ni | [82] |
| Phyllostachys pubescens biochar | Pb > Cd | [83] |
| Old sugarcane bagasse steam activated biochar | Cd > Cu> Pb | [74] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Niu, Y.; Dai, S.; Guo, D.; Yi, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, H. Organic Materials and Their Effects on Lead–Zinc Mineralization in the Xicheng Belt, Western Qinling (China): A Review. Minerals 2026, 16, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010035
Niu Y, Dai S, Guo D, Yi Y, Ma Z, Li H. Organic Materials and Their Effects on Lead–Zinc Mineralization in the Xicheng Belt, Western Qinling (China): A Review. Minerals. 2026; 16(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Yongjie, Shuang Dai, Dongbao Guo, Yalong Yi, Zhitao Ma, and Hailiang Li. 2026. "Organic Materials and Their Effects on Lead–Zinc Mineralization in the Xicheng Belt, Western Qinling (China): A Review" Minerals 16, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010035
APA StyleNiu, Y., Dai, S., Guo, D., Yi, Y., Ma, Z., & Li, H. (2026). Organic Materials and Their Effects on Lead–Zinc Mineralization in the Xicheng Belt, Western Qinling (China): A Review. Minerals, 16(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010035





