Ore Genesis of the Wunuer Zn-Pb-Ag-Mo Deposit from the Central Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Constraints from Geochemical, Isotopic, and Geochronological Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regional Geology
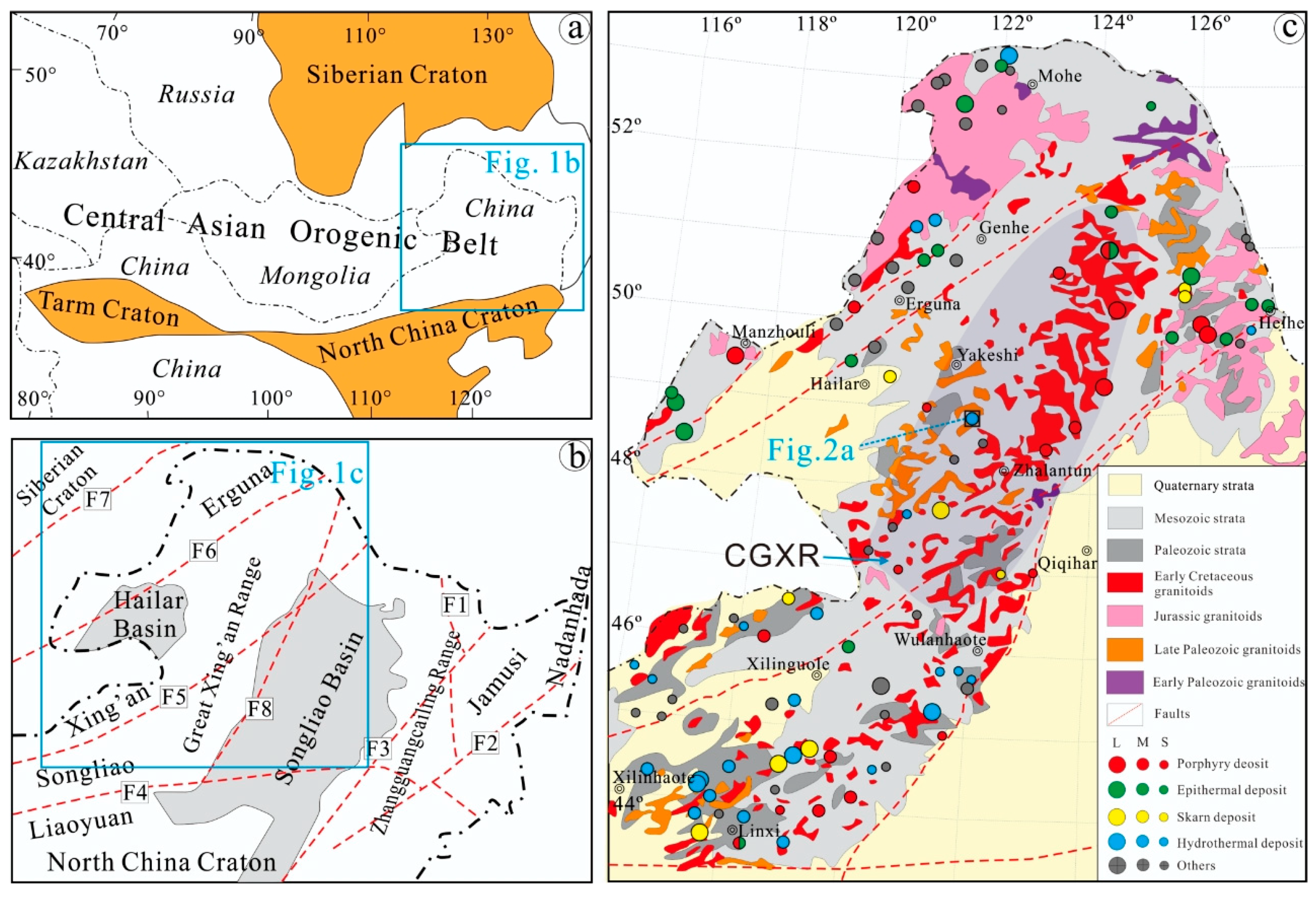
3. Deposit Geology
3.1. Stratigraphy
3.2. Structures
3.3. Igneous
3.4. Orebodies
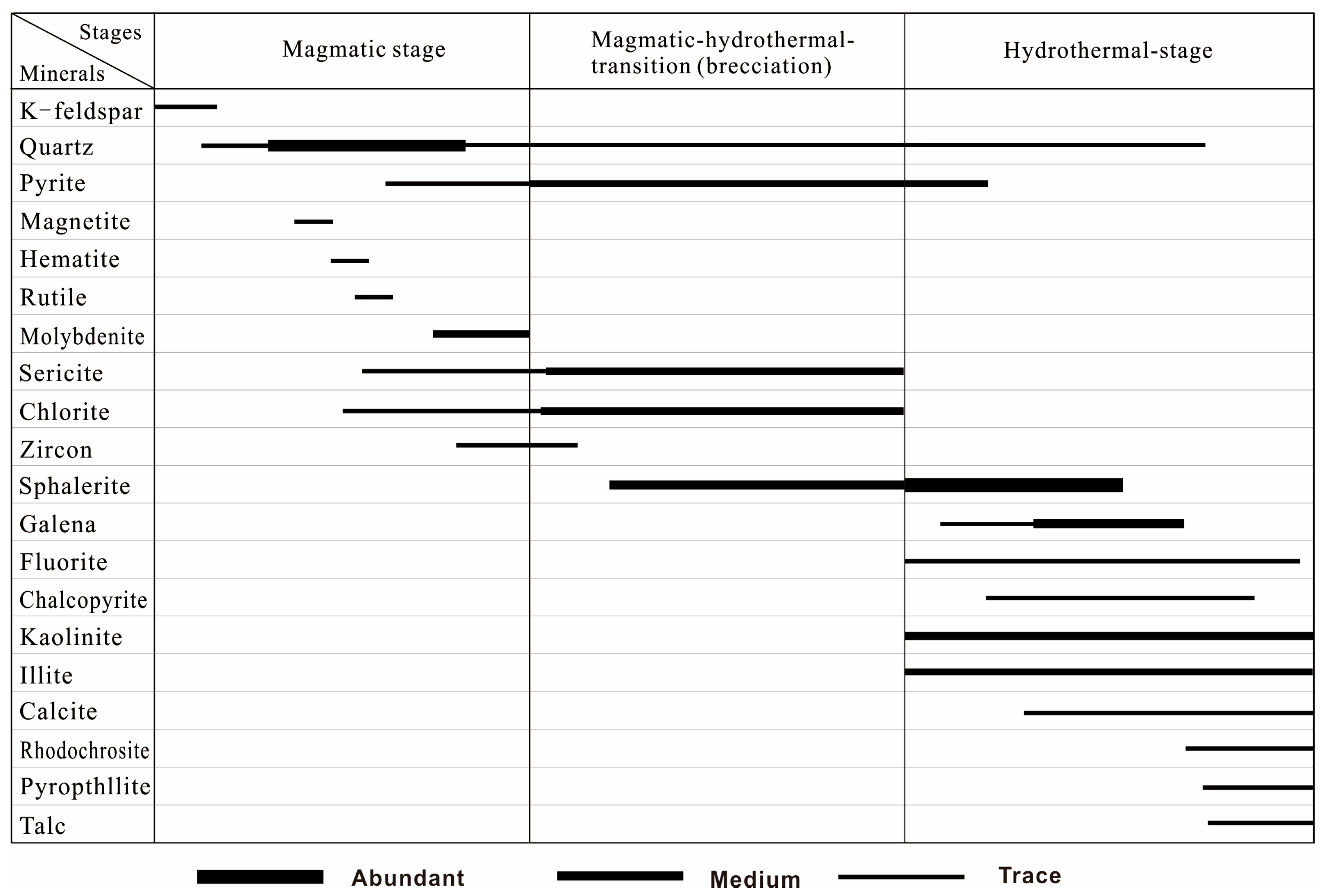
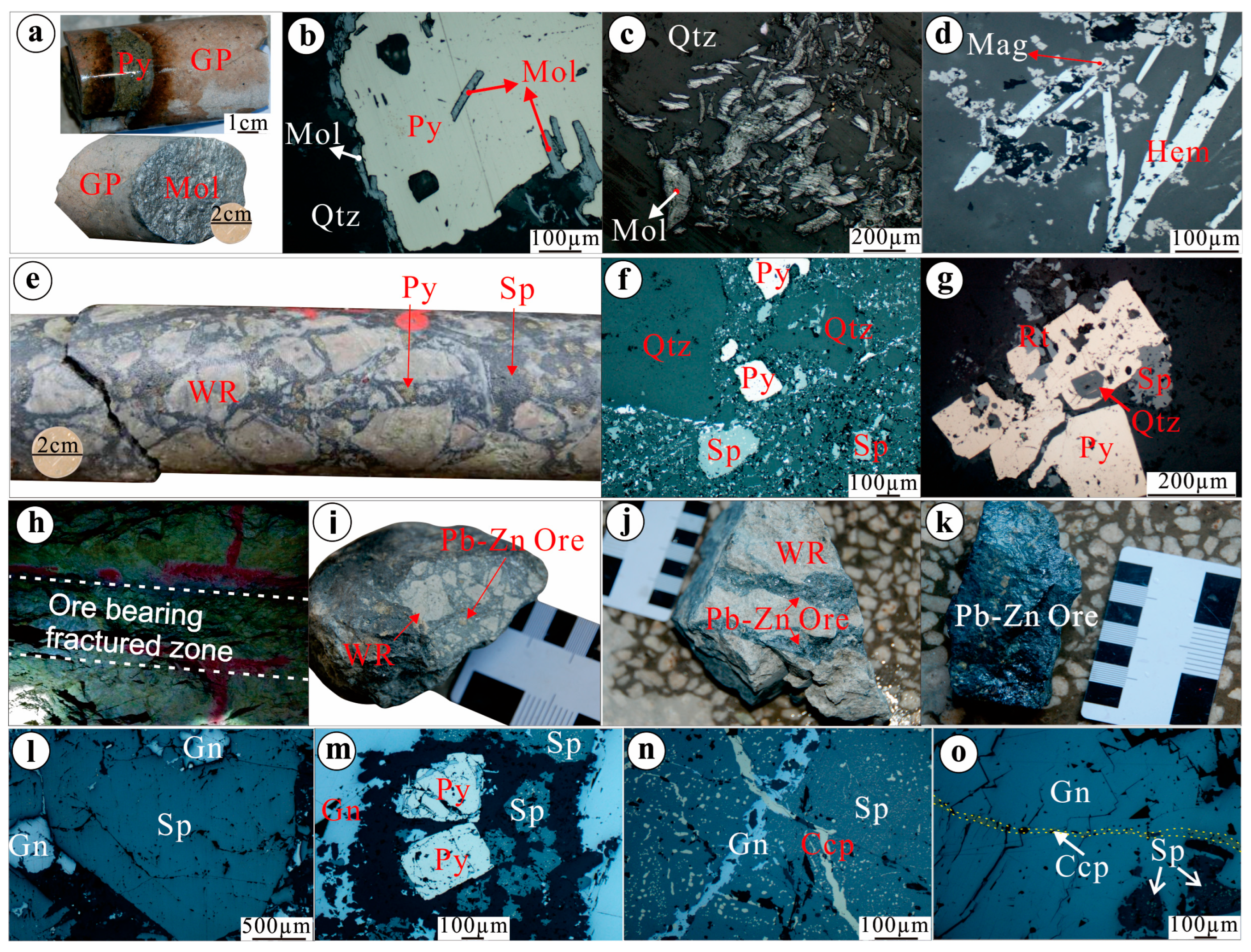
3.5. Mineralization and Alteration
4. Samples and Analytical Methods
4.1. Sample Description
4.2. Zircon U-Pb Dating and Trace Elements
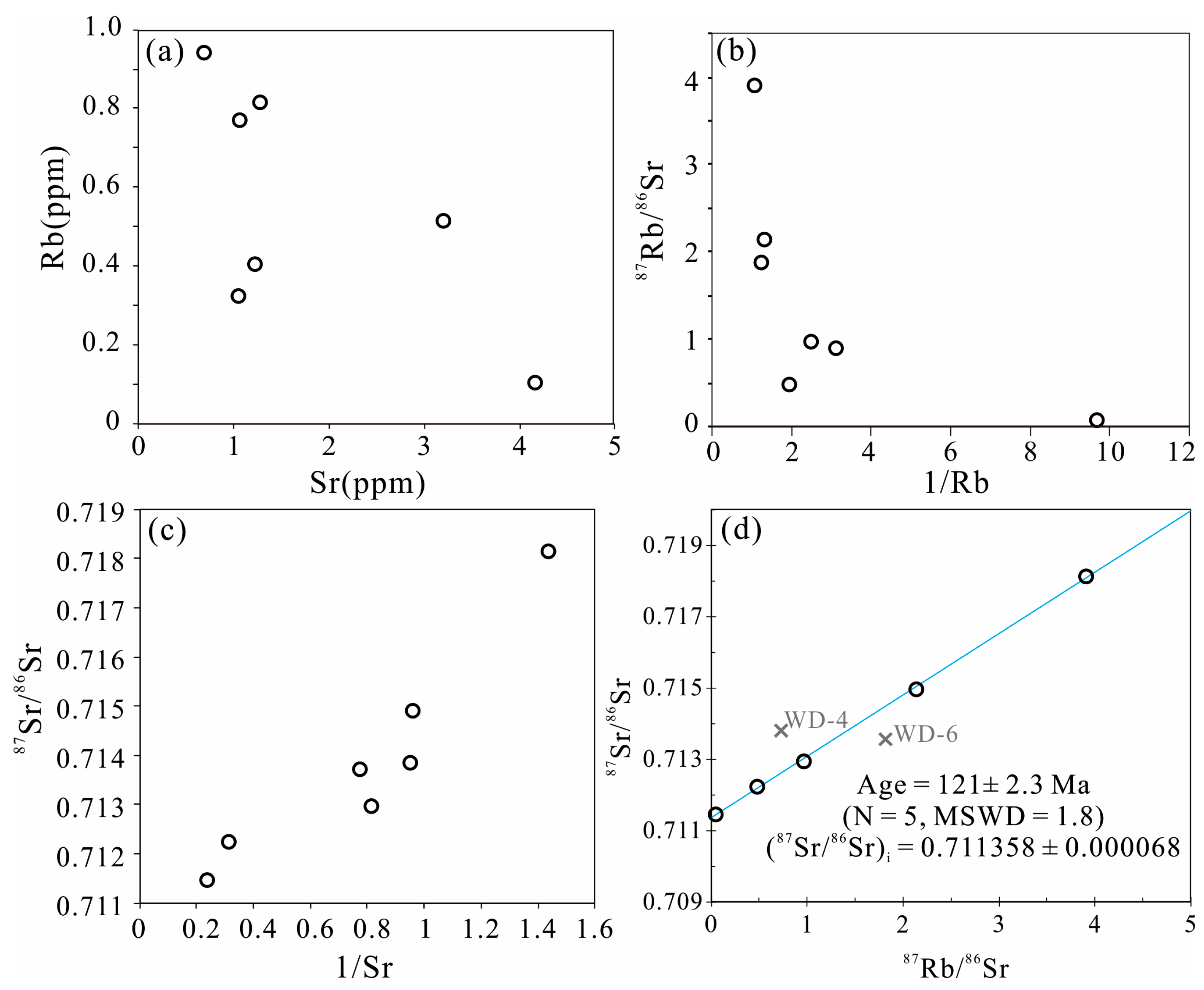
4.3. Sphalerite Rb-Sr Isochron Age
4.4. Major and Trace Elements Compositions
4.5. In Situ Zircon Hf Isotope
4.6. In Situ Sulfur Isotope Analysis
4.7. Pb Isotope Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Geochronology
5.1.1. Zircon U-Pb Dating
5.1.2. Sphalerite Rb-Sr Isochron Dating
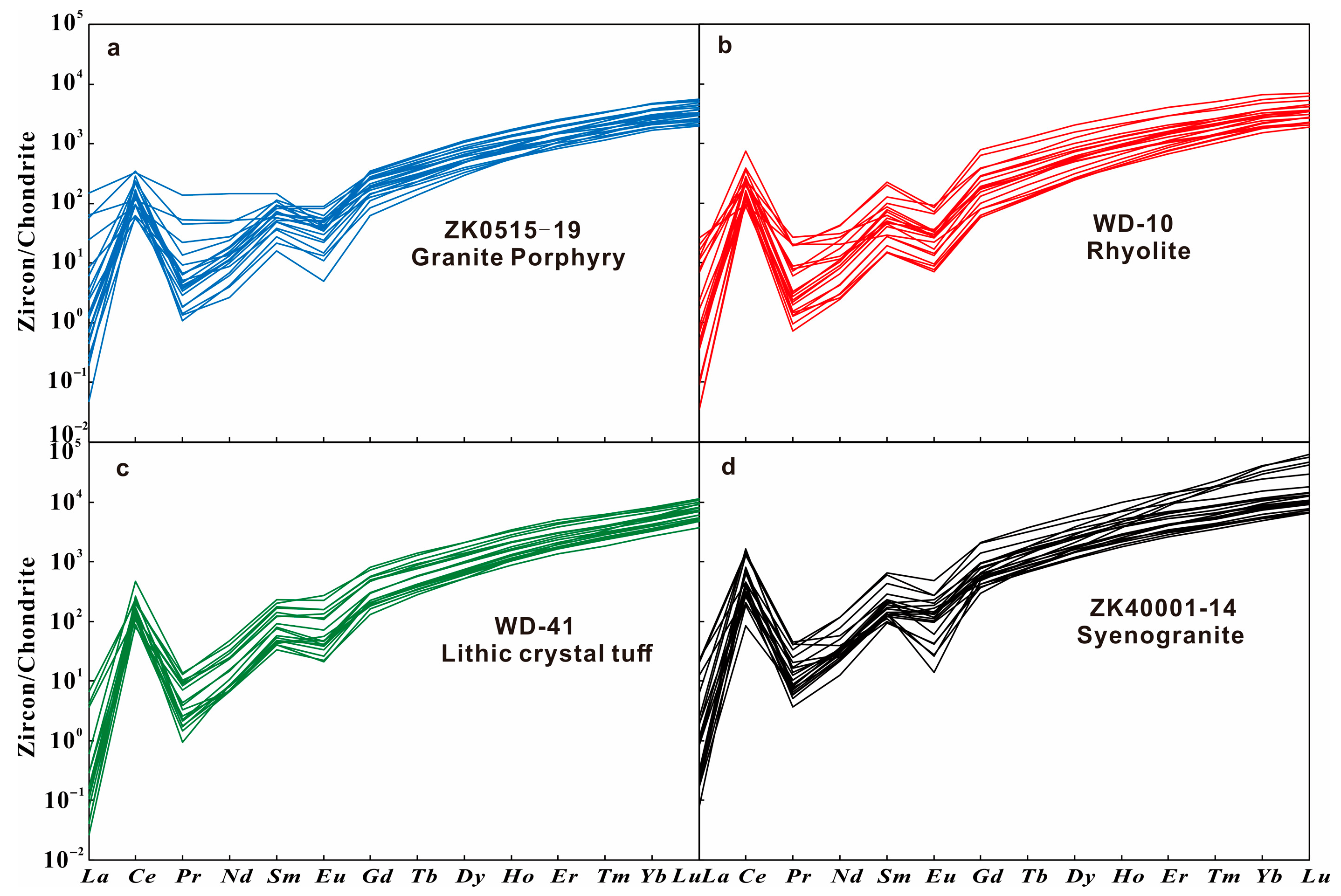
5.2. Zircon Trace Element Compositions
5.3. Whole-Rock Geochemistry
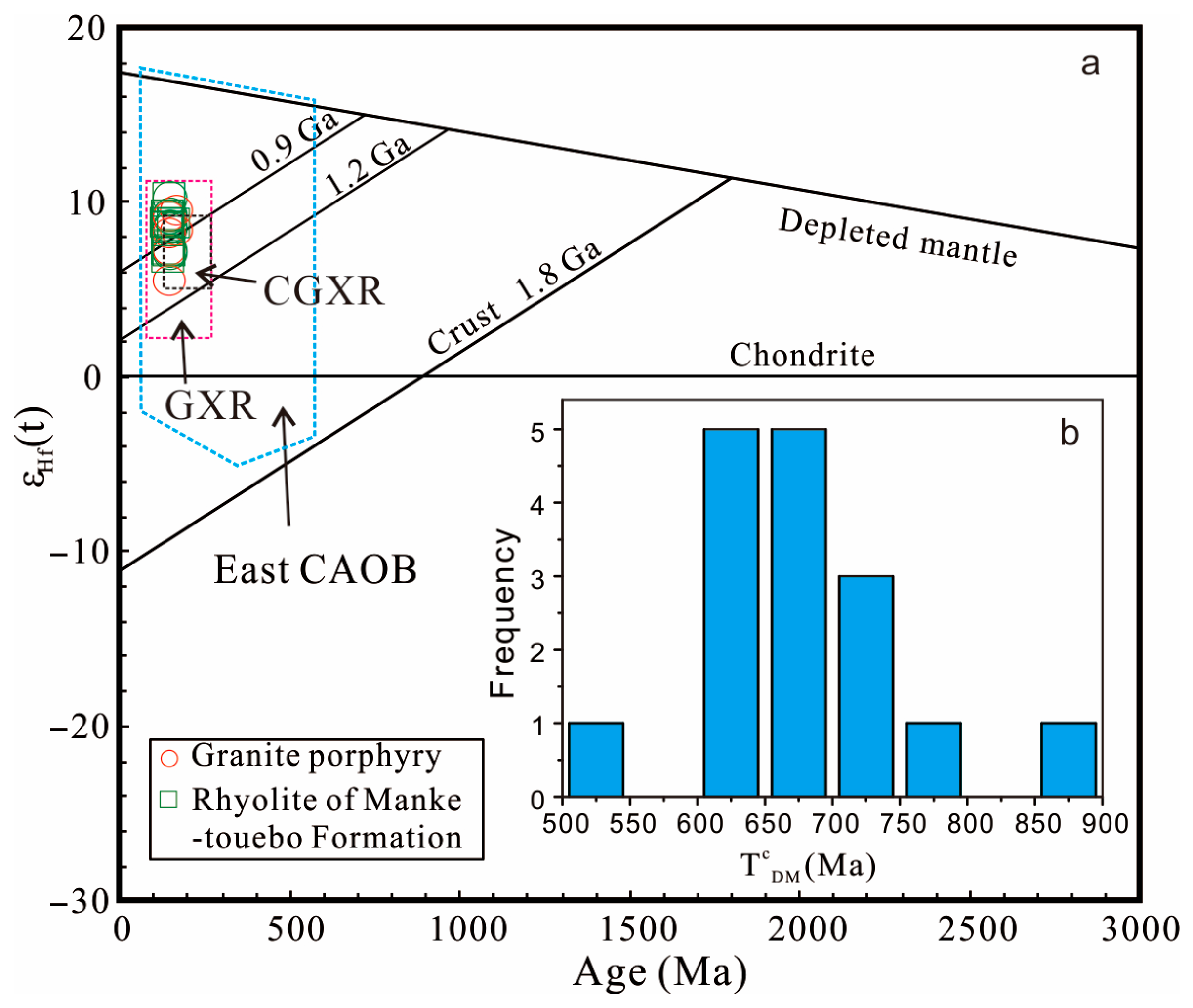
5.4. Hf-S-Pb Isotopic Compositions
6. Discussion
6.1. Timing of Magmatism and Mineralization
6.2. The Source of the Metallogenetic Material
6.3. Constraint on the Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting
6.4. Implications for REGIONAL Metallogeny
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- In this study, we have identified two mineralization events in the Wunuer Zn-Pb-Ag-Mo deposit: (a) Late Jurassic to early Cretaceous (144.8~145.8 Ma) magmatic and hydrothermal event, including the Manketouebo Formation rhyolite and the lithic crystal tuff, the ore-related granite porphyry, and the Mo mineralization of the late magmatic stage. (b) Early to middle Cretaceous (121~127.6 Ma) diagenetic and mineralization event that is composed of the hydrothermal-stage Zn mineralization and the Baiyin’gaolao Formation volcanic–sedimentary rocks.
- (2)
- The S-Pb isotope compositions of sulfides and granite porphyry intrusion imply a magmatic source of metallogenic materials for the hydrothermal Pb-Zn mineralization. The Hf-Pb isotope characteristics indicated that the granite porphyry intrusion and the Manketouebo Formation volcanic–sedimentary rocks formed simultaneously during Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous and originated from a mantle-derived juvenile component and assimilated by minor crustal material in an extensional setting.
- (3)
- The Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous volcanic–subvolcanic rocks were formed in an extensional environment related to the collapse of thickened lithosphere after closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean. The formation of the late Early Cretaceous volcanic rocks was related to westward subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. This indicated the prospect of further exploration for two mineralization events in the hydrothermal polymetallic deposits of the Great Xing’an Range.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Pirajno, F.; Li, N. The Mo deposits of northeast China: A powerful indicator of tectonic settings and associated evolutionary trends. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 602–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Pei, F.; Wang, F.; Meng, E.; Ji, W.; Yang, D.; Wang, W. Spatial–temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China: Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 74, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blichert-Toft, J.; Albarède, F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth Planet Lett. 1997, 148, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Gao, S.; Ge, W.C.; Wu, F.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Wilde, S.A.; Li, M. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing’an Range, northeastern China: Implications for subduction-induced delamination. Chem. Geol. 2010, 276, 144–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhao, C.B.; Zhang, F.F.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, J.P.; Peng, R.M.; Liu, B. SIMS zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os geochronology, Hf isotope, and whole-rock geochemistry of the Wunugetushan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit and granitoids in NE China and their geological significance. Gondwana Res. 2015, 28, 1228–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Ji, W.Q.; Wang, J.M.; Yang, L. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, C.H.; Kang, H.; Wang, F.X. Metallogeny of Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt and some related problems. Miner. Depos. 2018, 37, 671–711. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2005, 21, 169–188. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.R.; Tang, L.; Zhang, S.T.; Santosh, M.; Spencer, C.J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.L.; Sun, Y.Q. Genesis of the Bianjiadayuan Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit, Inner Mongolia, China: Constrains from in-situ sulfur isotope and trace element geochemistry of pyrite. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1863–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.G.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Liu, J.J.; Tombros, S.F.; Cook, N.J. Mineralogical, Fluid Inclusion, and Multiple Isotope (H-O-S-Pb) Constraints on the Genesis of the Sandaowanzi Epithermal Au-Ag-Te Deposit, NE China. Econ. Geol. 2018, 113, 1359–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, S.; Xin, W. Geochronology and geochemistry of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous granitoids in the northern Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Petrogenesis and implications for late Mesozoic tectonic evolution. Lithos 2018, 312–313, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Breiter, K.; Ouyang, H.; Liu, J. Ore-formation mechanism of the Weilasituo tin-polymetallic deposit, NE China: Constraints from bulk-rock and mica chemistry, He-Ar isotopes, and Re-Os dating. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 109, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Bagas, L.; Hu, P.; Han, N.; Chen, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Kang, H. Zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of the highly fractionated granite with tetrad REE patterns in the Shamai tungsten deposit in eastern Inner Mongolia, China: Implications for the timing of mineralization and ore genesis. Lithos 2016, 261, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Mao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Su, H. Late Mesozoic metallogeny and intracontinental magmatism, southern Great Xing’an Range, northeastern China. Gondw. Res. 2015, 27, 1153–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, A.; Sun, Y. U-Pb, Re-Os, and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of porphyry Sn ± Cu ± Mo and polymetallic (Ag-Pb-Zn-Cu) vein mineralization at Bianjiadayuan, Inner Mongolia, northeast China: Implications for discrete mineralization events. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 2041–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.G.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Liu, J.J.; Selby, D.; Voudouris, P.C.; Tombros, S.; Li, K.; Li, P.L.; Sun, H.J. The Genesis of the Giant Shuangjianzishan Epithermal AgPb-Zn Deposit, Inner Mongolia, Northeastern China. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Mao, J.W.; Wu, X.L.; Ouyang, H.G. Geochronology and geochemistry constraints of the Early Cretaceous Taibudai porphyry Cu deposit, northeast China, and its tectonic significance. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 103, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMSG (Inner Mongolia Sixth Geological and Mineral Exploration and Development Co., Ltd.). Detailed Survey Report of Molybdenum, Silver, Lead, and Zinc Deposits on the North Bank of Wunu’er River, Yakeshi City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region; IMSG: Hohhot, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Lü, X.; Wang, X. Textural, chemical, isotopic and microthermometric features of sphalerite from the Wunuer deposit, Inner Mongolia: Implications for two stages of mineralization from hydrothermal to epithermal. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 6936–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Windley, B.F.; Hao, J.; Zhai, M.G. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture. Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt. Tectonics 2003, 22, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Ge, W.C.; Zhang, Y.B.; Grant, M.L.; Wilde, S.A.; Jahn, B.M. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Sun, D.; Li, H.; Jahn, B.; Wilde, S. A-type granites in northeastern China: Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis. Chem. Geol. 2002, 187, 143–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lv, X.; Cheng, C.; Gun, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zang, S. Geochronological and geochemical characteristics of the rhyolites in Taerqi of middle Da Hinggan Mountains and their geological significance. Geol. Bull. China 2016, 35, 906–918. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Sun, D.; Han, J.; Li, G.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, B.; Yang, D. Ages and petrogenesis of the Late Mesozoic igneous rocks associated with the Xiaokele porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, NE China and their geodynamic implications. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 107, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Yang, J.; Fan, X.; Wei, W.; Mei, W.; Ruan, B. Geology and Genesis of Lead-Zinc Polymetallic Deposits in the Great Xing’an Range. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 4399–4427. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lv, X.B.; Li, J.; Gun, M.C. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting of Intermediate-Felsic Volcanics in Ta’erqi Area, Central Great Xing’an Range. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 4446–4462. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Watanabe, K.; Yonezu, K. Zircon morphology, geochronology and trace element geochemistry of the granites from the Huangshaping polymetallic deposit, South China: Implications for the magmatic evolution and mineralization processes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 60, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M. Metallogenic Epoch of Dajing Copper-Polymetallic Deposit of Inner Mongolia and Discussion of Metallogenic Process. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Han, Y.; Shi, C.L.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.Y. Zircon U-Pb age and geological background of rhyolite from Baiyingaolao Formation in Wunuer area, Great Xing’an Range. Geol. China 2023, 50, 1532–1541. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zong, K.; Klemd, R.; Yuan, Y.; He, Z.; Guo, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z. The assembly of Rodinia: The correlation of early Neoproterozoic (ca. 900 Ma) high-grade metamorphism and continental arc formation in the southern Beishan Orogen, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB). Precambrian Res. 2017, 290, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Mineralogical studies of zircon origin and constraints on the interpretation of U-Pb age. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1589–1604. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. Isoplot 3.75: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berk. Geochronol. Center Spec. Publ. 2012, 5, 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Lü, X.; Wei, W.; Mei, W.; Fan, X.; Sun, B. Origin of the Haobugao skarn Fe-Zn polymetallic deposit, Southern Great xing’an range, NE China: Geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope constraints. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 94, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, X.; Yuan, H.; Hattendorf, B.; Günther, D.; Chen, L.; Hu, S. Determination of Forty Two Major and Trace Elements in USGS and NIST SRM Glasses by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Geostand. Newslett. 2002, 26, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Tong, X.; Yang, L. Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmer cone and jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation multiple collector ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, E.; Munker, C.; Mezger, K. Calibration of the lutetium-hafnium clock. Science 2001, 293, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Yang, T.; Cook, N.J. Sulfur isotope fractionation in pyrite during laser ablation: Implications for laser ablation multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry mapping. Chem. Geol. 2017, 450, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todt, W.; Cliff, R.A.; Hanser, A.; Hofmann, A.W. Evaluation of a 202Pb-205Pb double spike for high-precision lead isotope analysis. Am. Geophys. Union. Geophys. Monogr. 1996, 95, 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Belousova, E.A.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Fisher, N.L. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2002, 143, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluaiton, Presentation Interdretation; Longman Scientific & Technical: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 1–352. [Google Scholar]
- Maniar, P.D.; Piccoli, P.M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geol. Society of Am. Bull. 1989, 101, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.B.W.; Tindle, A.G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, W.F.; Sun, S.S. The composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 1995, 120, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlik, M.; Raith, J.G.; Gerdes, A. U-Pb, Lu-Hf and trace element characteristics of zircon from the Felbertal scheelite deposit (Austria): New constraints on timing and source of W mineralization. Chem. Geol. 2016, 421, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.F. GeoKit—A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Geochimica 2004, 33, 459–464. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Xia, B.; Xiao, Z.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, G. The characteristics of epithermal hydrothermal deposit and its prospecting direction. Geol. Resour. 2001, 10, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 1–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H. Sulfur and Carbon Isotopes. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits, 3rd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 517–612. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.; Zhang, C.; Wan, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G. Experimental calibration of sulfur isotope geothermometers for sphalerite-galena. Acta Geol. Sin. 2003, 37, 1392. [Google Scholar]
- Ridley, J.; Diamond, L. Fluid chemistry of orogenic lode gold deposits and implications for genetic models. Hagemann S G and Brown P E. Gold in 2000. Boulder Colo. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2000, 13, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Hu, R.; Bi, X.; Peng, J.; Tang, Q. A review on the sources of ore-forming materials traced by lead isotopes in ores. Geol. Geochim. 2002, 31, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, C.; Bagas, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, N.; Kang, H.; Wang, Z. Two mineralization events in the Baiyinnuoer zn-pb deposit in Inner Mongolia, China: Evidence from field observations, S-Pb isotopic compositions and U-Pb zircon ages. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 144, 339–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Lü, X.; Yang, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.; Adam, M.M.A. Geology, geochemistry and fluid inclusions of the Bianjiadayuan Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, Inner Mongolia, NE China: Implications for tectonic setting and metallogeny. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 71, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q. What drove late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract? Tectonophysics 2003, 369, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Mao, J.; Lyckberg, P. Geochronology and isotope geochemistry of the A-type granites from the Huanggang Sn-Fe deposit, southern Great Hinggan Range, NE China: Implication for their origin and tectonic setting. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 49, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Günther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.; Chen, H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tong, Y.; Xiao, W. Rollback, scissor-like closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean and formation of an orocline: Magmatic migration based on a large archive of age data. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, X.; Tang, J. Late Mesozoic stratigraphic framework of the Great Xing’an Range, NE China, and overprinting by the Mongol–Okhotsk and Paleo-Pacific tectonic regimes. Gondwana Res. 2024, 134, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, W.; Liu, H.; Chang, Y.; Cao, X. Ore Genesis of the Wunuer Zn-Pb-Ag-Mo Deposit from the Central Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Constraints from Geochemical, Isotopic, and Geochronological Features. Minerals 2025, 15, 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121291
Mei W, Liu H, Chang Y, Cao X. Ore Genesis of the Wunuer Zn-Pb-Ag-Mo Deposit from the Central Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Constraints from Geochemical, Isotopic, and Geochronological Features. Minerals. 2025; 15(12):1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121291
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Wei, Hongyu Liu, Yiming Chang, and Xiaofeng Cao. 2025. "Ore Genesis of the Wunuer Zn-Pb-Ag-Mo Deposit from the Central Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Constraints from Geochemical, Isotopic, and Geochronological Features" Minerals 15, no. 12: 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121291
APA StyleMei, W., Liu, H., Chang, Y., & Cao, X. (2025). Ore Genesis of the Wunuer Zn-Pb-Ag-Mo Deposit from the Central Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Constraints from Geochemical, Isotopic, and Geochronological Features. Minerals, 15(12), 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121291





