Synthesis of Hydroxy-Sodalite/Cancrinite Zeolites from Calcite-Bearing Kaolin for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material
2.2. Synthesis of the Hydroxy-Sodalite/Cancrinite Zeolite Composite
2.3. Characterization of the Synthesized Zeolites
2.4. Synthetic Wastewater Preparation
2.5. Heavy Metal Uptake Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
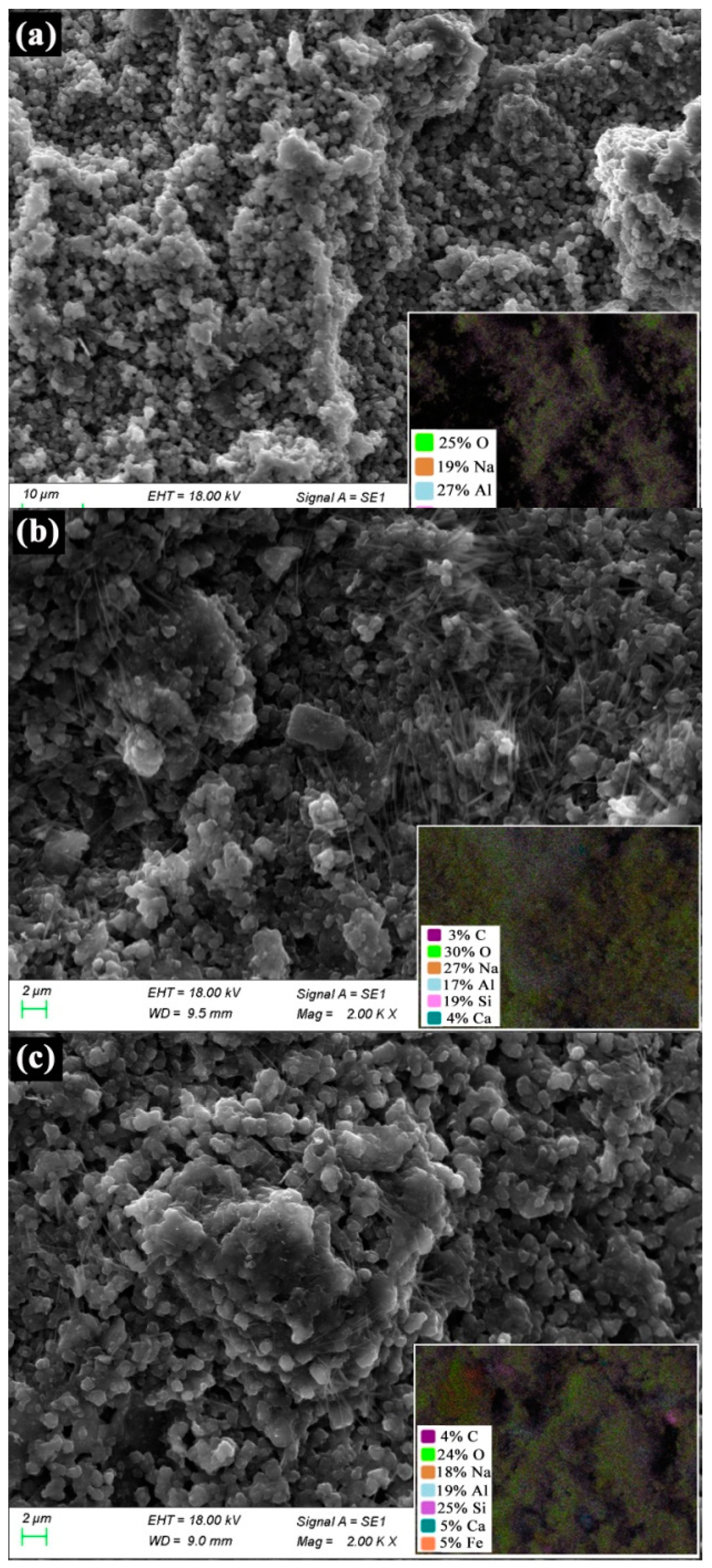
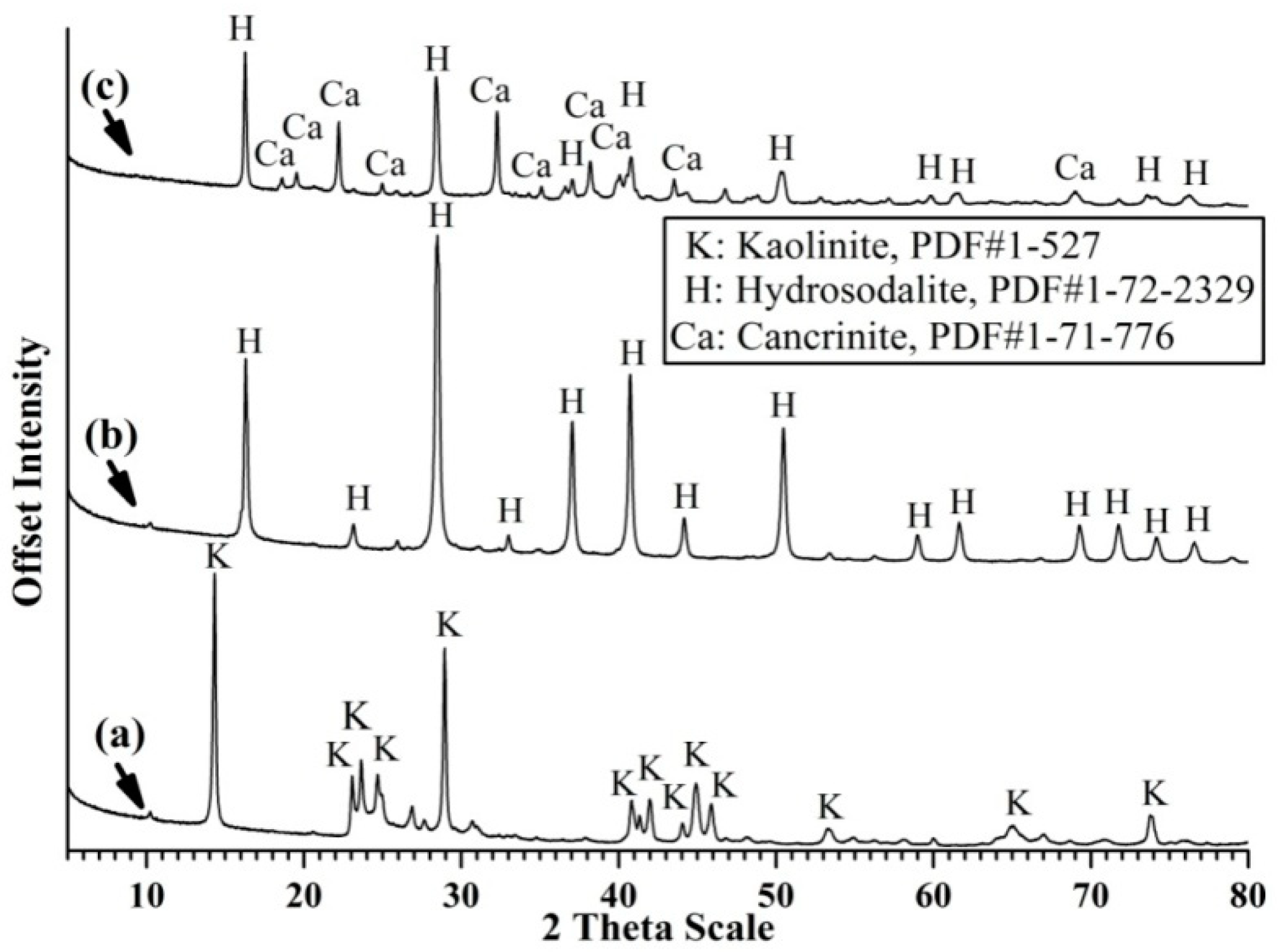
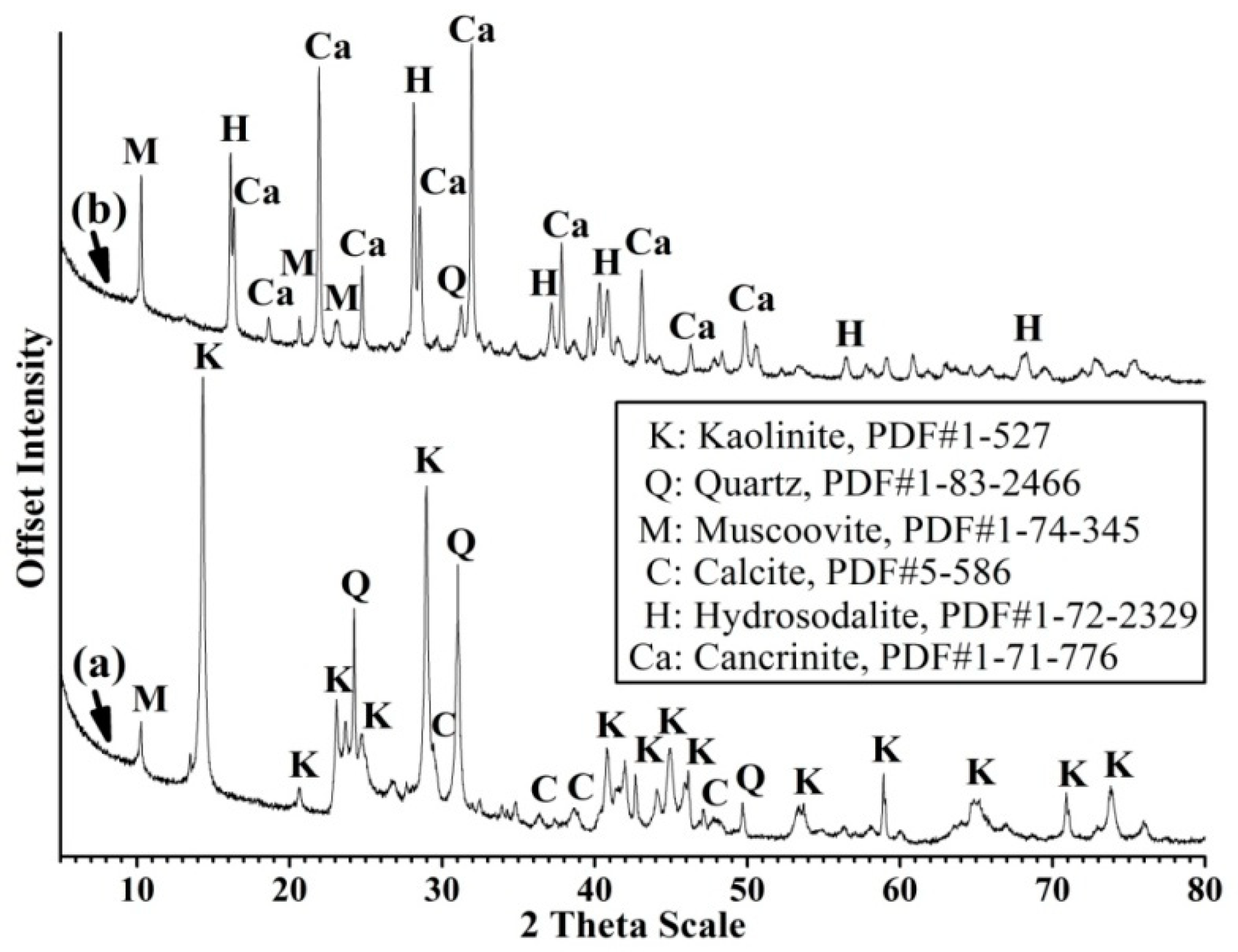
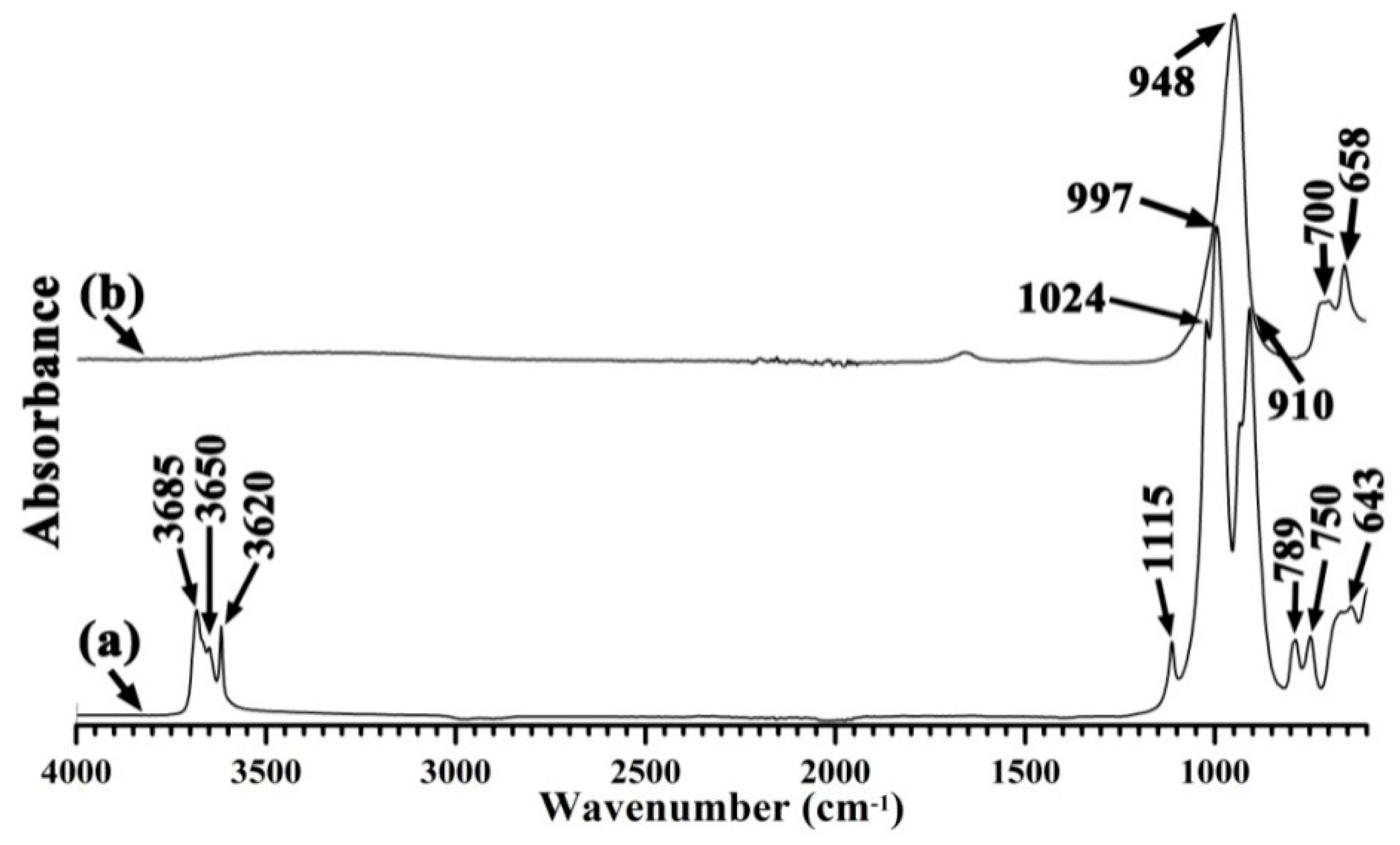
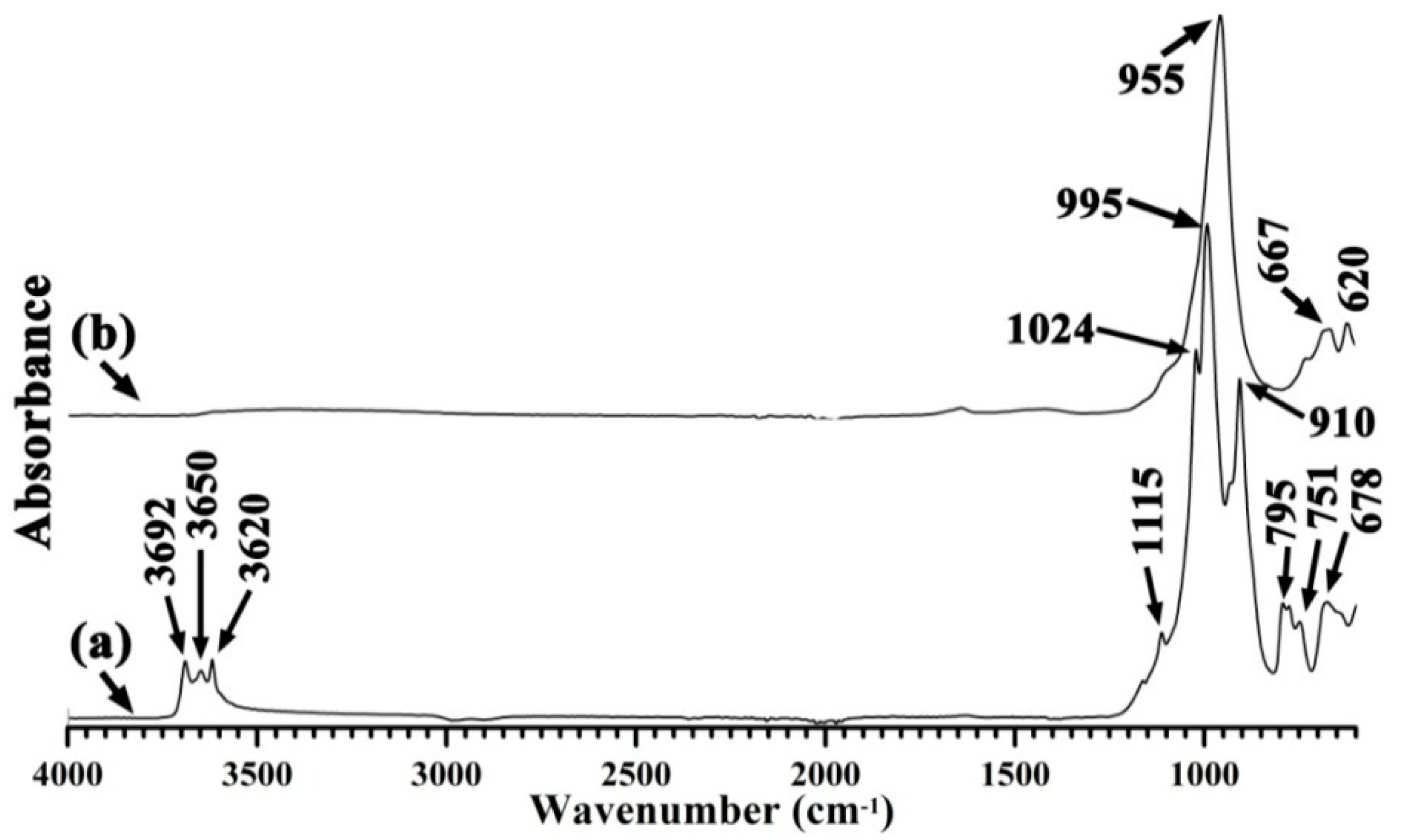
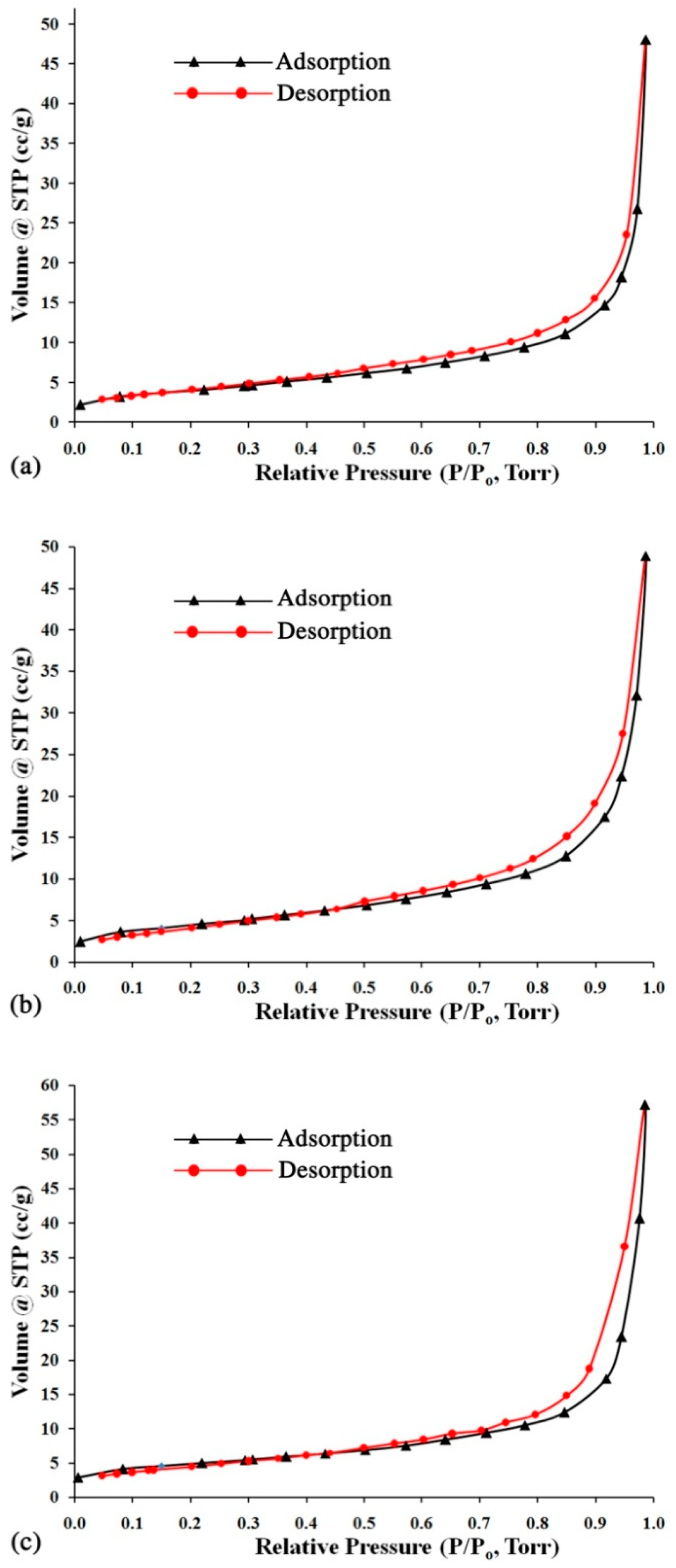
3.1. Characterization of the Synthesized Zeolite
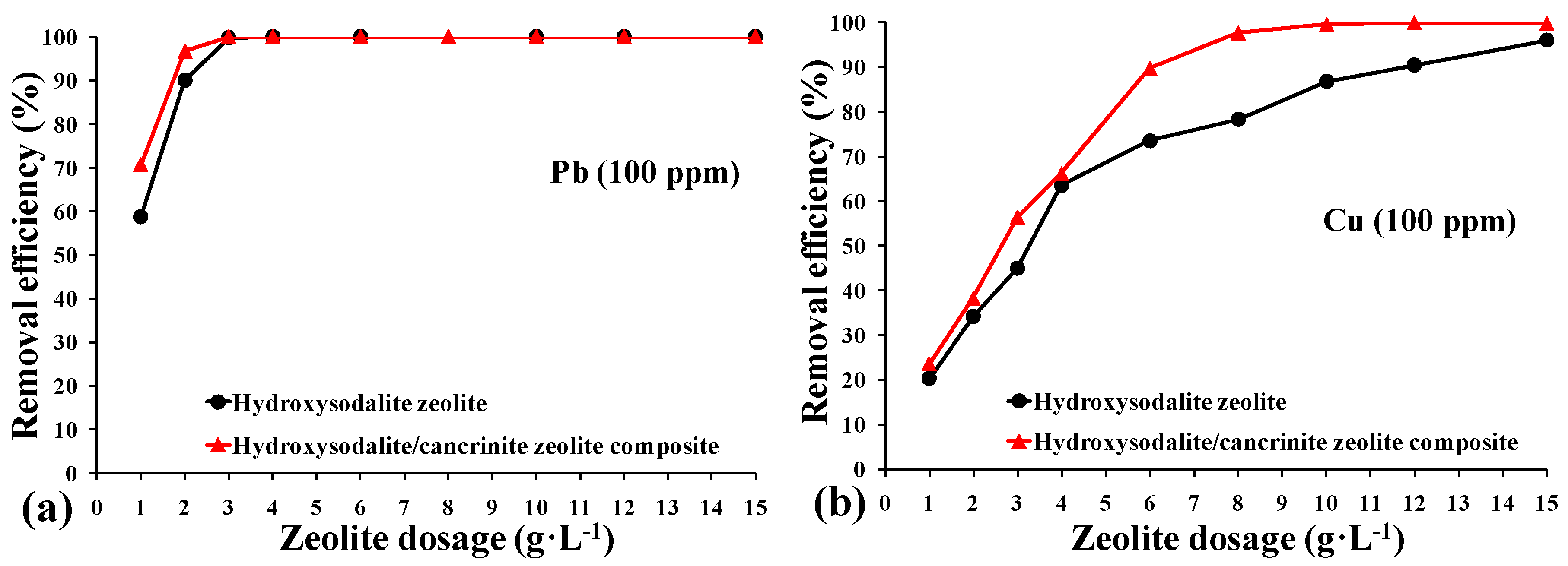
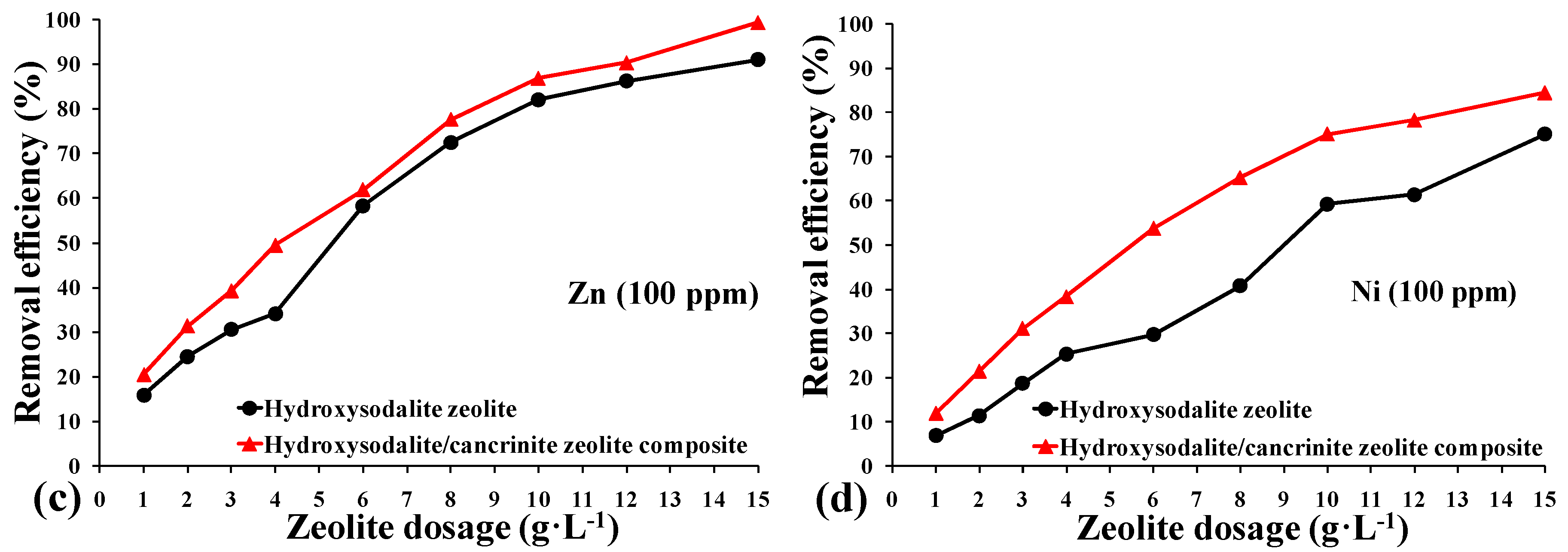
3.2. Metal Uptake Behavior of the Synthesized Zeolites
4. Implications for Water Purification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdulla, F.A.; Alfarra, A.; Abu Qdais, H.; Sonneveld, B.G.J.S. Evaluation of wastewater treatment plants in Jordan and suitability for reuse. Acad. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halalsheh, M.; Kassab, G. Policy and the governance framework for wastewater irrigation: Jordanian experience. In Safe Use of Wastewater in Agriculture; Hettiarachchi, H., Ardakanian, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Ali, I.; Saleh, T.A.; Nayak, A.; Agarwal, S. Chemical treatment technologies for waste-water recycling—An overview. Rsc Adv. 2012, 2, 6380–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, N.M.; Sahu, J.N.; Abdullah, E.C.; Jayakumar, N.S. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using carbon nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2014, 43, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Incorporating First Addendum. 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/gdwq0506.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2018).
- Jeuland, M. Challenges to wastewater reuse in the Middle East and North Africa. Middle East Dev. J. 2015, 7, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.R.; Salleh, N.M.; Othman, M.H.D.; Matsuura, T.; Ali, M.H.; Puteh, M.H.; Jaafar, J. The adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) in aqueous solution by novel natural zeolite based hollow fibre ceramic membrane. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, E.; Rokhmat, M.; Abdullah, M. Reduction of seawater salinity by natural zeolite (Clinoptilolite): Adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics and kinetics. Desalination 2017, 409, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, L.; Xue, Q.; Liu, J.; Hou, L.; Ding, L. Removal of ammonium from swine wastewater by zeolite combined with chlorination for regeneration. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 160, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.M.; Khoury, H.N.; Tuffaha, R. Mo and Ni removal from drinking water using zeolitic tuff from Jordan. Minerals 2016, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuna, Z. Review of the natural, modified, and synthetic zeolites for heavy metals removal from wastewater. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelić, S.K.; Medica, J.S.; Gumbarević, D.; Filošević, A.; Pržulj, N.; Pavelić, K. Critical Review on Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, C.J. Properties and applications of zeolites. Sci. Prog. 2010, 93, 223–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Bai, X.; Kang, Y.; Hao, W.; Li, R. Effective removal of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions by mesoporous LTA zeolite. Desalination 2014, 341, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.M.; Selim, A.Q.; Mohamed, E.A.; Wahed, M.S.A.; Seliem, M.K.; Sillanpӓӓ, M. Adsorption characteristics of Na-A zeolites synthesized from Egyptian kaolinite for manganese in aqueous solutions: Response surface modeling and optimization. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 140, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauanov, Z.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.; Inglezakis, V.J. Synthetic coal fly ash-derived zeolites doped with silver nanoparticles for mercury (II) removal from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belviso, C.; Cavalcante, F.; Di Gennaro, S.; Lettino, A.; Palma, A.; Ragone, P.; Fiore, S. Removal of Mn from aqueous solution using fly ash and its hydrothermal synthetic zeolite. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 137, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.B.G.; Arshad, S.E. Hydrothermally synthesized zeolites based on kaolinite: A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 97, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Yuan, P.; Zhu, H.; Bao, X. Template-free synthesis and catalytic applications of microporous and hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites from natural aluminosilicate minerals. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 10069–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaifan, M.; Khoury, H.; Aldabsheh, I.; Rahier, H.; Hourani, M.; Wastiels, J. Hydrated lime/potassium carbonate as alkaline activating mixture to produce kaolinitic clay based inorganic polymer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 126, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghrib, Y.; Frini-Srasra, N.; Srasra, E.; Martínez-Triguero, J.; Corma, A. Synthesis of cocrystallized USY/ZSM-5 zeolites from kaolin and its use as fluid catalytic cracking catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, M.; Hopa, Ç.; Yilmaz, Z.; Güler, H. The effect of alkali concentration and solid/liquid ratio on the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite NaA from natural kaolinite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 86, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panitchakarn, P.; Laosiripojana, N.; Viriya-umpikul, N.; Pavasant, P. Synthesis of high-purity Na-A and Na-X zeolite from coal fly ash. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wdowin, M.; Franus, M.; Panek, R.; Badura, L.; Franus, W. The conversion technology of fly ash into zeolites. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunecki, P.; Panek, R.; Wdowin, M.; Franus, W. Synthesis of faujasite (FAU) and tschernichite (LTA) type zeolites as a potential direction of the development of lime Class C fly ash. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 166, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaifan, M.; Rahier, H.; Barhoum, A.; Khoury, H.; Hourani, M.; Wastiels, J. Development of inorganic polymer by alkali-activation of untreated kaolinitic clay: Reaction stoichiometry, strength and dimensional stability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; López-Soler, A.; Plana, F.; Andrés, J.M.; Juan, R.; Ruiz, C.R. A fast method for recycling fly ash: Microwave-assisted zeolite synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2527–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaqour, F.; Ismeik, M.; Esaifan, M. Alkali activation of natural clay using a Ca (OH)2/Na2CO3 alkaline mixture. Clay Miner. 2017, 52, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zheng, Y. Removal of lead, copper, nickel, cobalt, and zinc from water by a cancrinite-type zeolite synthesized from fly ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 145, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhade, A.V.; Kshirsagar, T.A.; Dholi, A.G.; Agashe, J.A. Removal of heavy metals Cd2+, Pb2+, and Ni2+ from aqueous solutions using synthesized azide cancrinite, Na8 [AlSiO4]6(N3)2.4 (H2O)4.6. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackbarth, K.; Gesing, T.M.; Fechtelkord, M.; Stief, F.; Buhl, J.C. Synthesis and crystal structure of carbonate cancrinite Na8 [AlSiO4]6CO3 (H2O)3.4, grown under low-temperature hydrothermal conditions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 30, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, H. Verified Synthesis of Zeolitic Materials; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Smith, P.; Wingate, C.; De Silva, L. The effect of calcium and temperature on the transformation of sodalite to cancrinite in Bayer digestion. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 105, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Mirza, A. Facile one pot green synthesis of Chitosan-Iron oxide (CS-Fe2O3) nanocomposite: Removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) from synthetic and industrial wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Mirza, A. Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cu (II) by Alginate-Au-Mica bionanocomposite: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuabonah, E.I.; Agunbiade, F.O.; Alfred, M.O.; Adewumi, T.A.; Okoli, C.P.; Omorogie, M.O.; Taubert, A. Facile synthesis of new amino-functionalized agrogenic hybrid composite clay adsorbents for phosphate capture and recovery from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Warr, L.N.; Hilder, E.F.; Goswami, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Churchman, J.G.; Vasilev, K.; Pan, G.; Naidu, R. Biocompatible functionalisation of nanoclays for improved environmental remediation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3740–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, S.; Ghannam, A.; Madanat, M.; Sahawneh, J. Mineral Status and Future Opportunity. Amman, Internal Report: Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources. Amman, Jordan. 2015. Available online: http://www.memr.gov.jo/EchoBusV3.0/SystemAssets/PDFs/AR/MineralTR/kaolin.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Khoury, H.; El-Sakka, W. Mineralogical and industrial characterization of the BatnEl-Ghoul clay deposits, southern Jordan. Appl. Clay Sci. 1986, 1, 321–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietel, J.; Steudel, A.; Warr, L.N.; Emmerich, K. Crystal chemistry of Na-rich rectorite from North Little Rock, Arkansas. Clay Miner. 2015, 50, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Guo, F.; Shao, Z.; Wu, J. Zeolite Synthesized from Coal Fly Ash Produced by a Gasification Process for Ni2+ Removal from Water. Minerals 2018, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaifan, M.; Hourani, M.; Khoury, H.; Rahier, H.; Wastiels, J. Synthesis of hydroxysodalite zeolite by alkali-activation of basalt powder rich in calc-plagioclase. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriaa, A.; Saad, K.B.; Hamzaoui, A.H. Synthesis and characterization of cancrinite-type zeolite, and its ionic conductivity study by AC impedance analysis. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 86, 2024–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, E.R., Jr. Phenomenological theory of ion solvation. Effective radii of hydrated ions. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golomeova, M.; Zendelska, A.; Blažev, K.; Krstev, B.; Golomeov, B. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using clinoptiloliteand stilbite. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hu, Y. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by zeolite synthesized from fly ash. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2778–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukelic, D.; Boskovic, N.; Agarski, B.; Radonic, J.; Budak, I.; Pap, S.; Sekulic, M.T. Eco-design of a low-cost adsorbent produced from waste cherry kernels. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Weight Percentage (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | K2O | MgO | TiO2 | Na2O | L.O.I | Total | Si/Al | |
| China Clay | 39.4 | 48.0 | - | 0.5 | 1.0 | - | 0.1 | 0.1 | 13.6 | 102.7 | 1.1 |
| Calcite bearing kaolin | 25.2 | 53.3 | 5.3 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 11.1 | 99.5 | 1.9 |
| Specimen | Unit | Mix Composition | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | NaOH | Water | Calcite | |||
| China Clay + NaOH | (fraction) | 100 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 200 |
| (mass %) | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 1.0 | |
| (grams) | 50 | 25 | 25 | 0 | 100 | |
| China Clay + calcite + NaOH | (fraction) | 100 | 50 | 50 | 8 | 208 |
| (mass %) | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 1.0 | |
| (grams) | 48 | 24 | 24 | 4 | 100 | |
| Calcite-bearing kaolin + NaOH | (fraction) | 90.5 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 9.5 a | 200 |
| (mass %) | 0.45 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.05 a | 1.0 | |
| (grams) | 45.25 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 4.75 a | 100 | |
| Sample | SBET a (m2·g−1) | SDR b (m2·g−1) | SBJH c (m2·g−1) | Vmicro b (m3·g−1) | Dmicro b (nm) | Vmeso c (m3·g−1) | Dmeso c (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China Clay + NaOH | 14.5 | 17.1 | 13.1 | 0.06 | 2.1 | 0.07 | 19.3 |
| China Clay + calcite + NaOH | 16.0 | 18.5 | 15.4 | 0.07 | 2.0 | 0.07 | 20.5 |
| Calcite-bearing kaolin + NaOH | 16.9 | 20.2 | 20.3 | 0.07 | 1.8 | 0.09 | 21.1 |
| Materials | Rate in US$/kg | Quantity in kg | Total Cost in US$ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcite-bearing kaolin 1 | 0.13 | 0.8 | 0.10 |
| Kaolin grinding and packing cost 1 | 0.30 | - | 0.30 |
| Sodium hydroxide solution (50% wt/wt) 2 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.40 |
| Transportation | 0.30 | - | 0.30 |
| Cost of electric power consumed | 0.55 | - | 0.55 |
| Labor cost | 0.35 | - | 0.35 |
| Total cost/kg of composite | 2.0 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esaifan, M.; Warr, L.N.; Grathoff, G.; Meyer, T.; Schafmeister, M.-T.; Kruth, A.; Testrich, H. Synthesis of Hydroxy-Sodalite/Cancrinite Zeolites from Calcite-Bearing Kaolin for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Media. Minerals 2019, 9, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9080484
Esaifan M, Warr LN, Grathoff G, Meyer T, Schafmeister M-T, Kruth A, Testrich H. Synthesis of Hydroxy-Sodalite/Cancrinite Zeolites from Calcite-Bearing Kaolin for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Media. Minerals. 2019; 9(8):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9080484
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsaifan, Muayad, Laurence N. Warr, Georg Grathoff, Tammo Meyer, Maria-Theresia Schafmeister, Angela Kruth, and Holger Testrich. 2019. "Synthesis of Hydroxy-Sodalite/Cancrinite Zeolites from Calcite-Bearing Kaolin for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Media" Minerals 9, no. 8: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9080484
APA StyleEsaifan, M., Warr, L. N., Grathoff, G., Meyer, T., Schafmeister, M.-T., Kruth, A., & Testrich, H. (2019). Synthesis of Hydroxy-Sodalite/Cancrinite Zeolites from Calcite-Bearing Kaolin for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Media. Minerals, 9(8), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9080484








