Calcium-Bearing Minerals Transformation during Underground Coal Gasification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sample Preparation
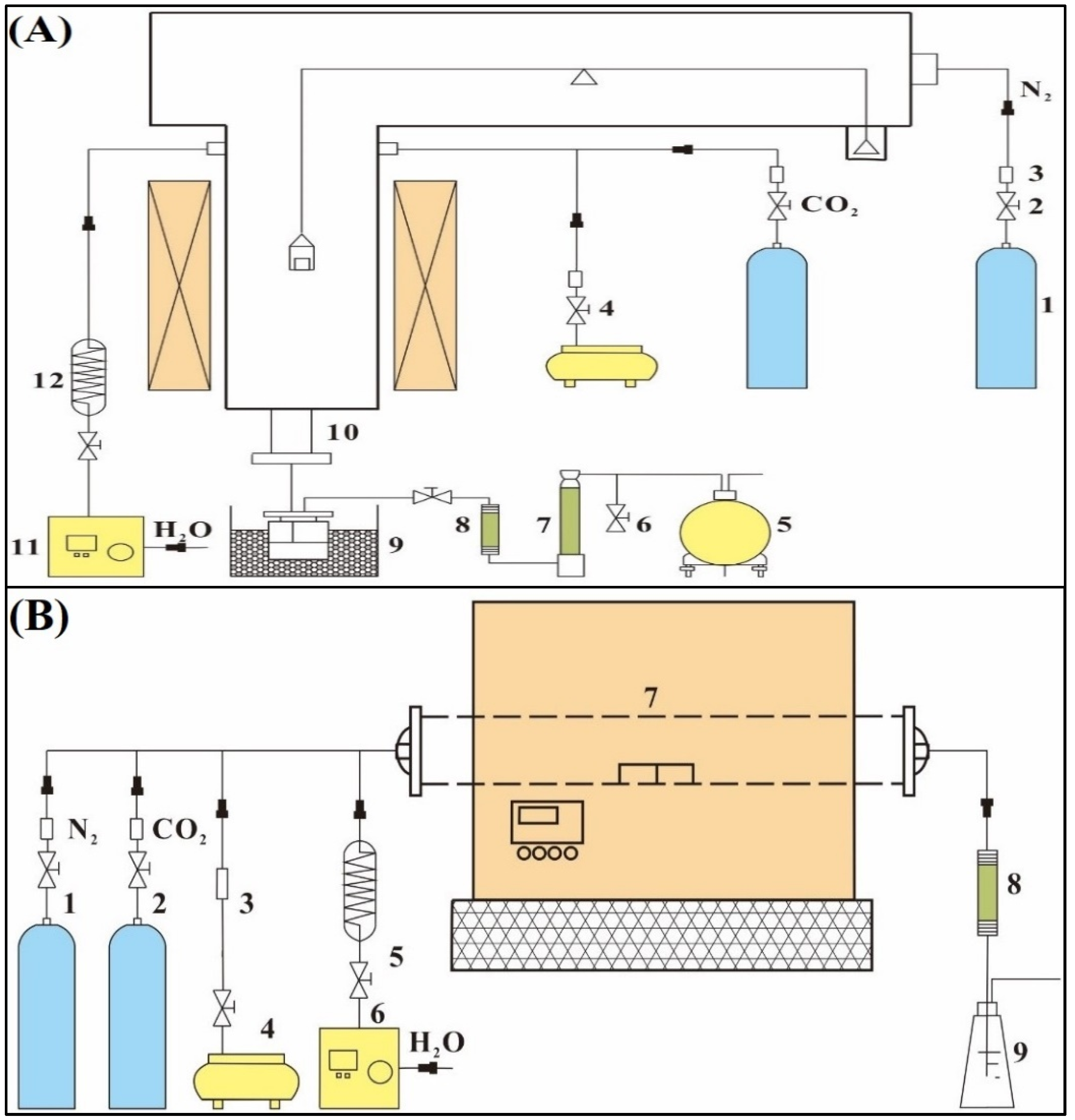
2.2. Experimental Installation and Process
2.3. Sample Characterization
2.4. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Coal Analysis
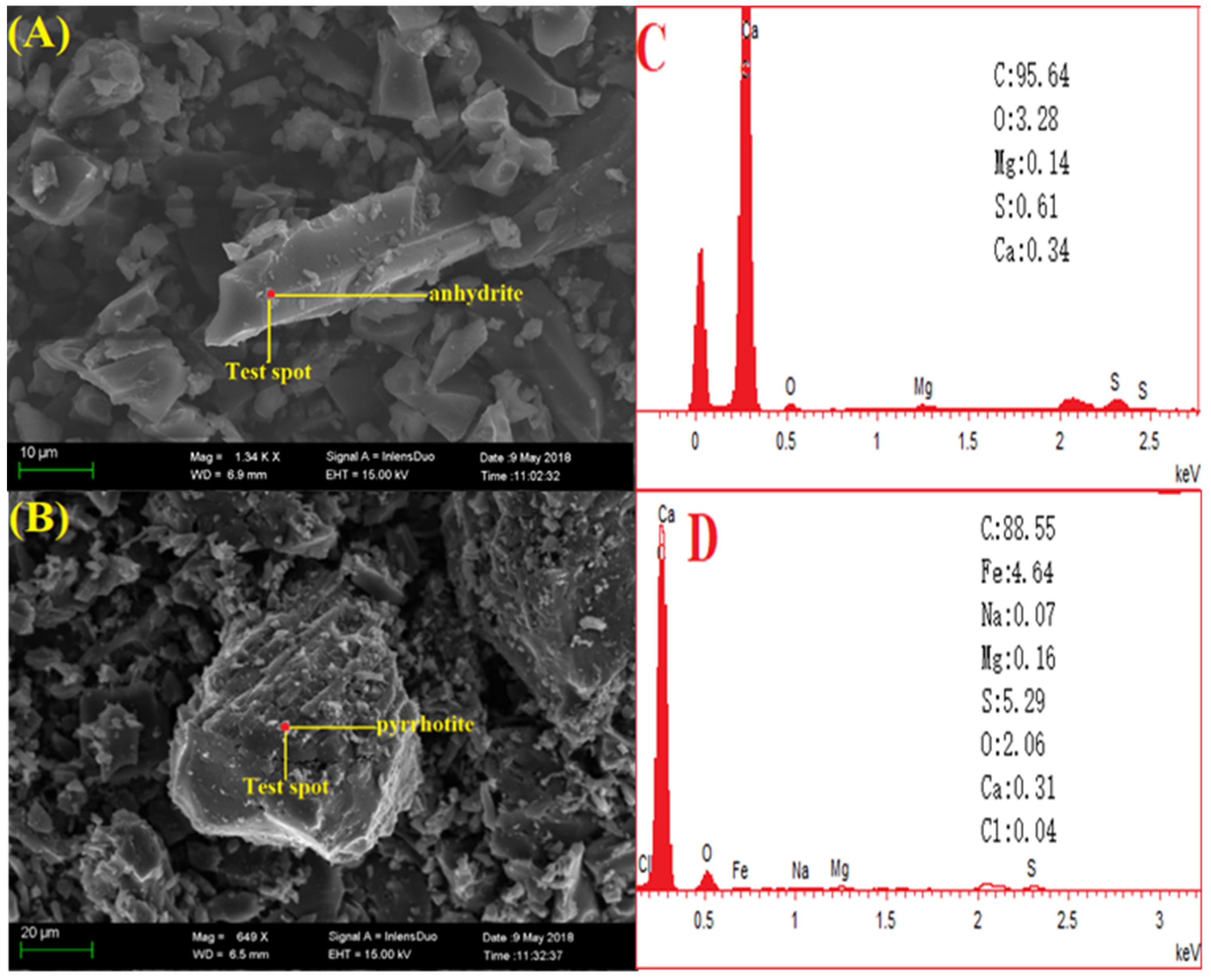
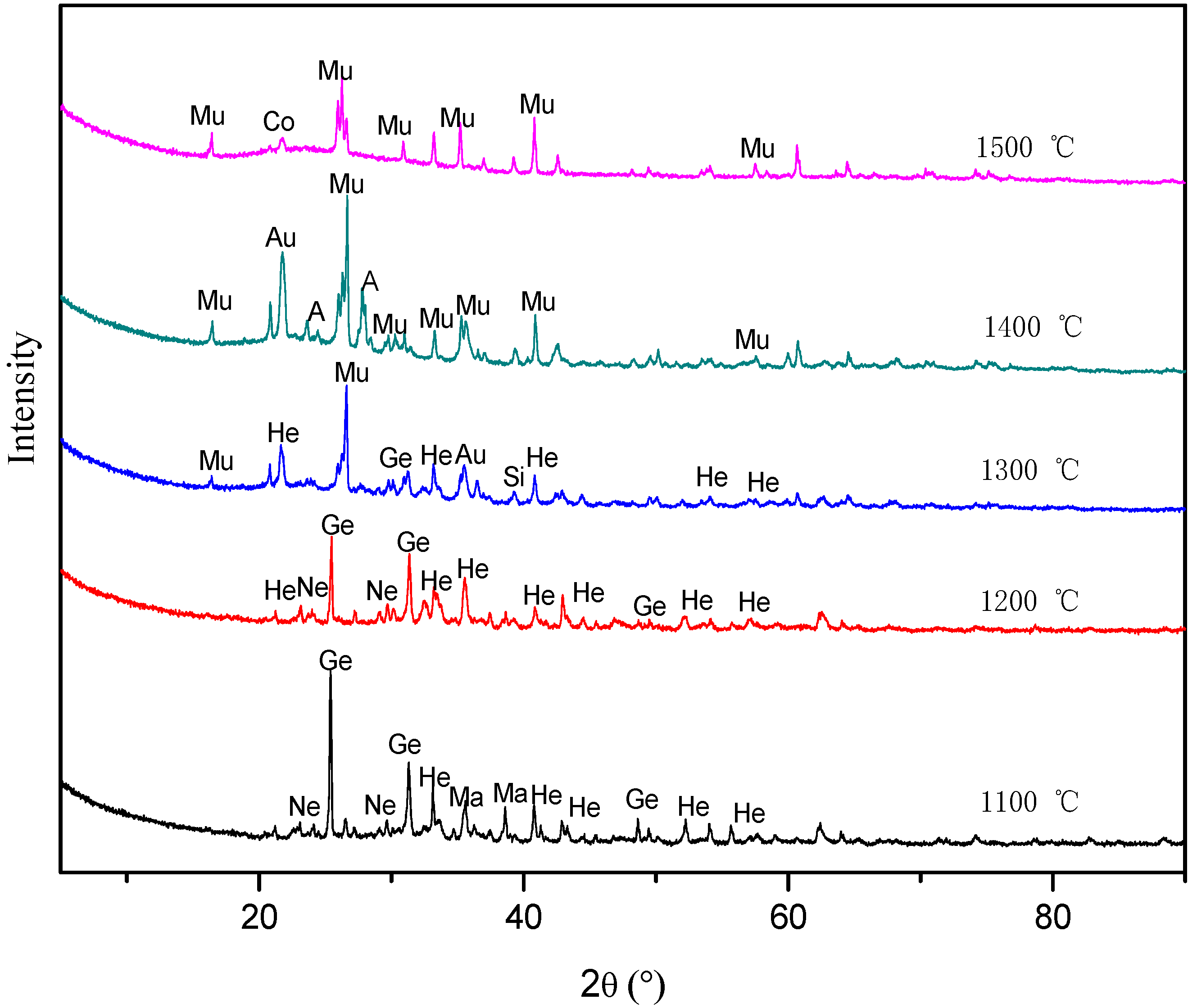
3.2. Mineral Transformation Behavior during Coal Pyrolysis
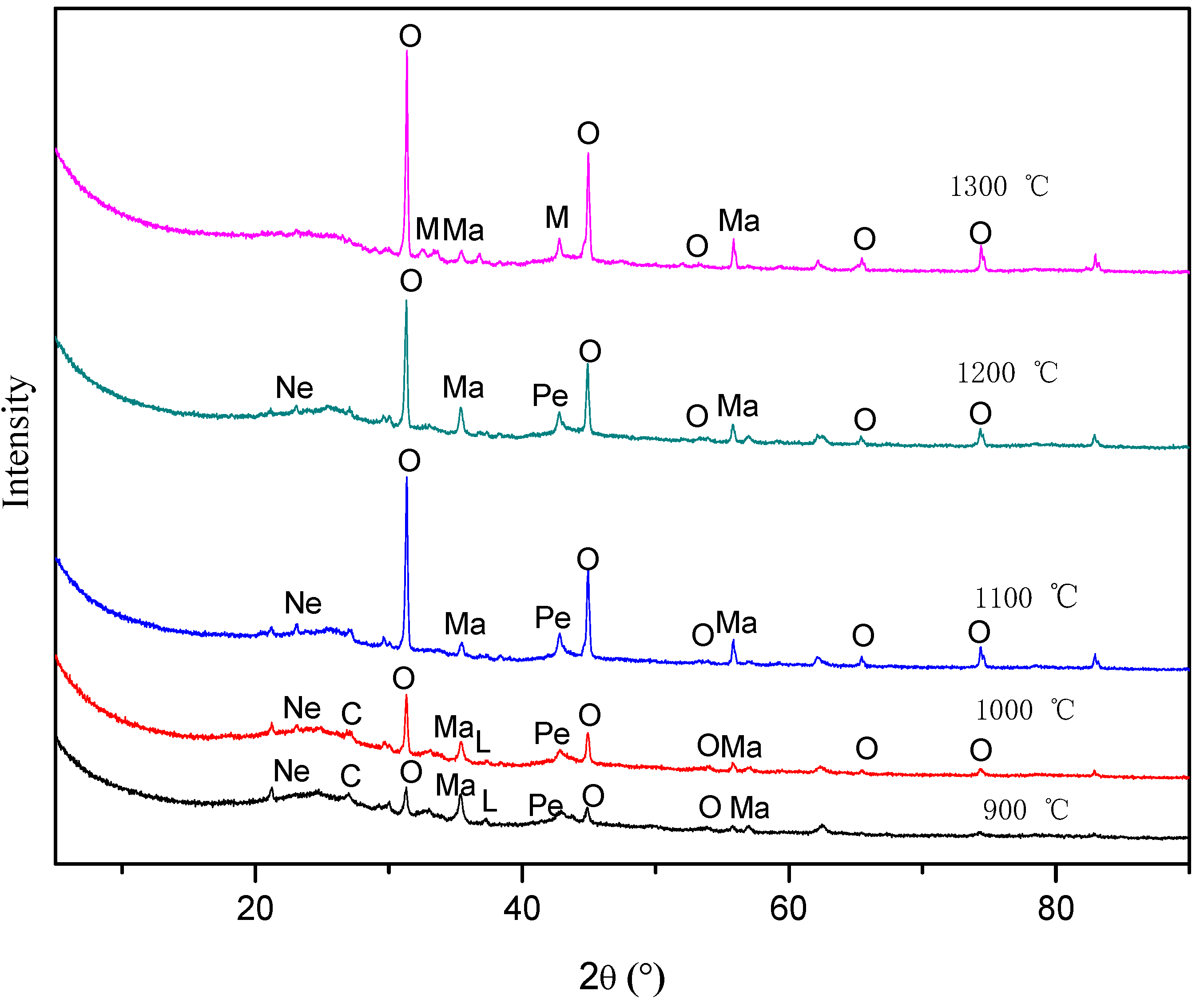
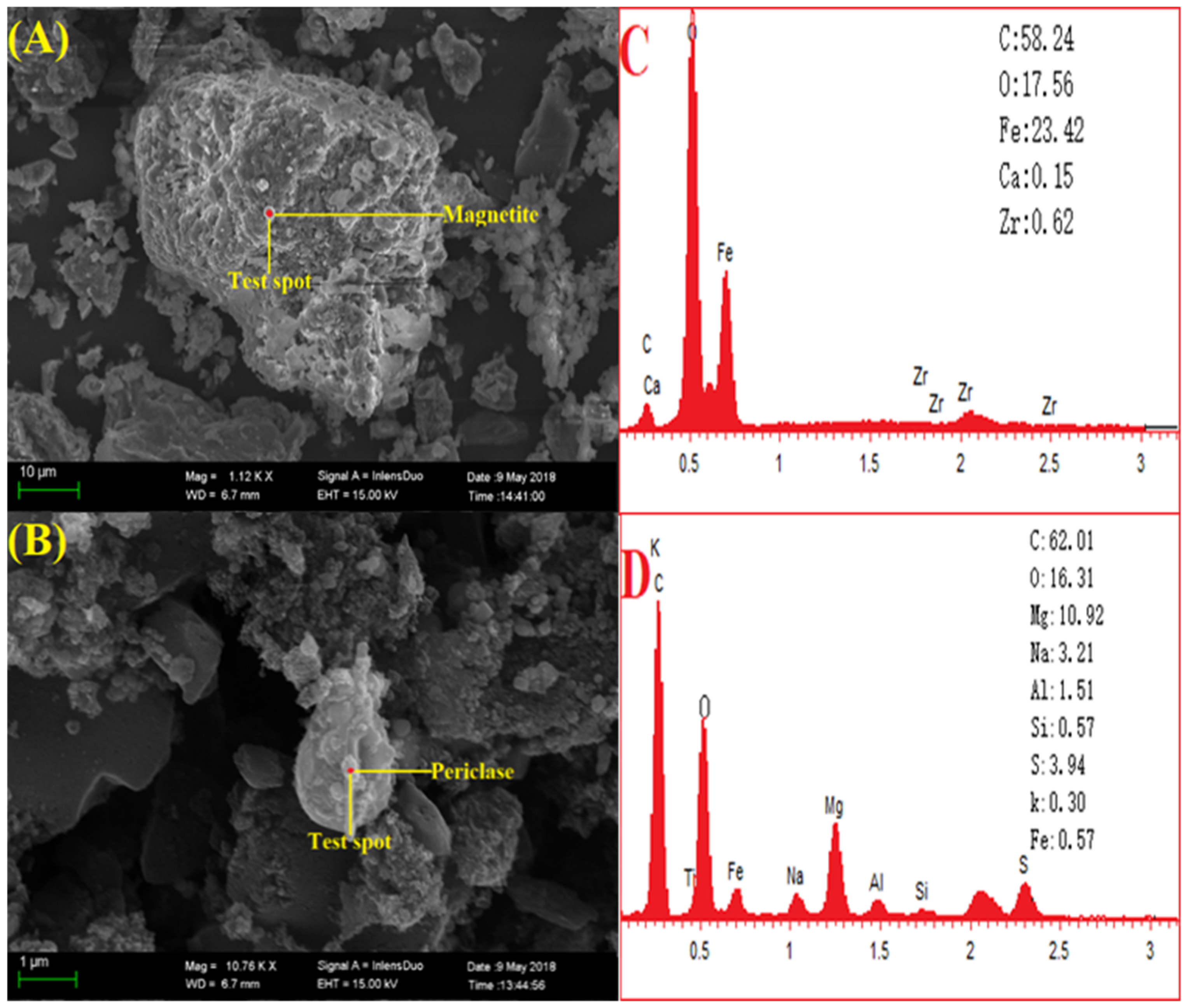
3.3. Mineral Transformation Behavior during the Semi-Coke Reduction Stage
3.4. Mineral Transformation during Residual-Coke Oxidation Process
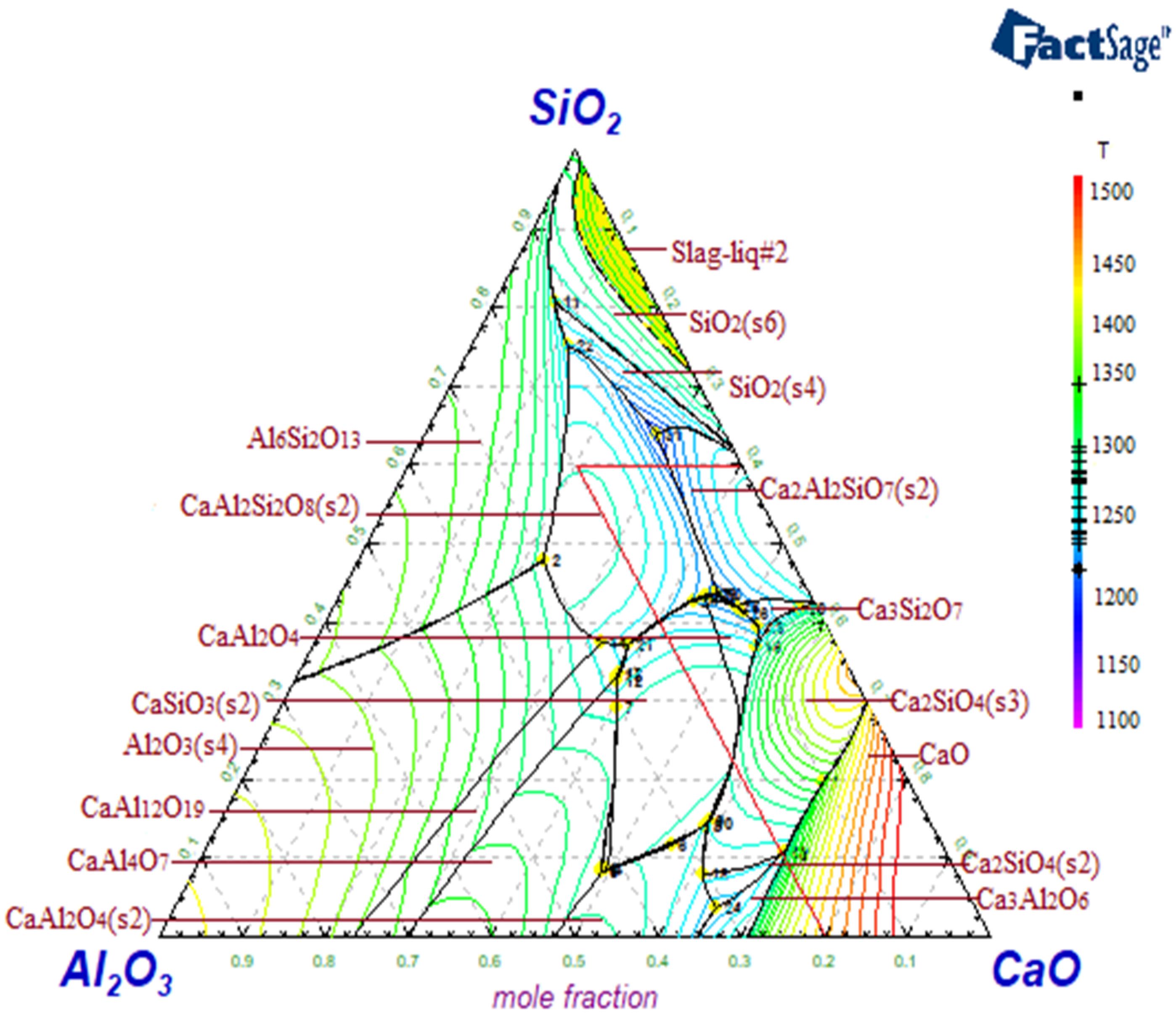
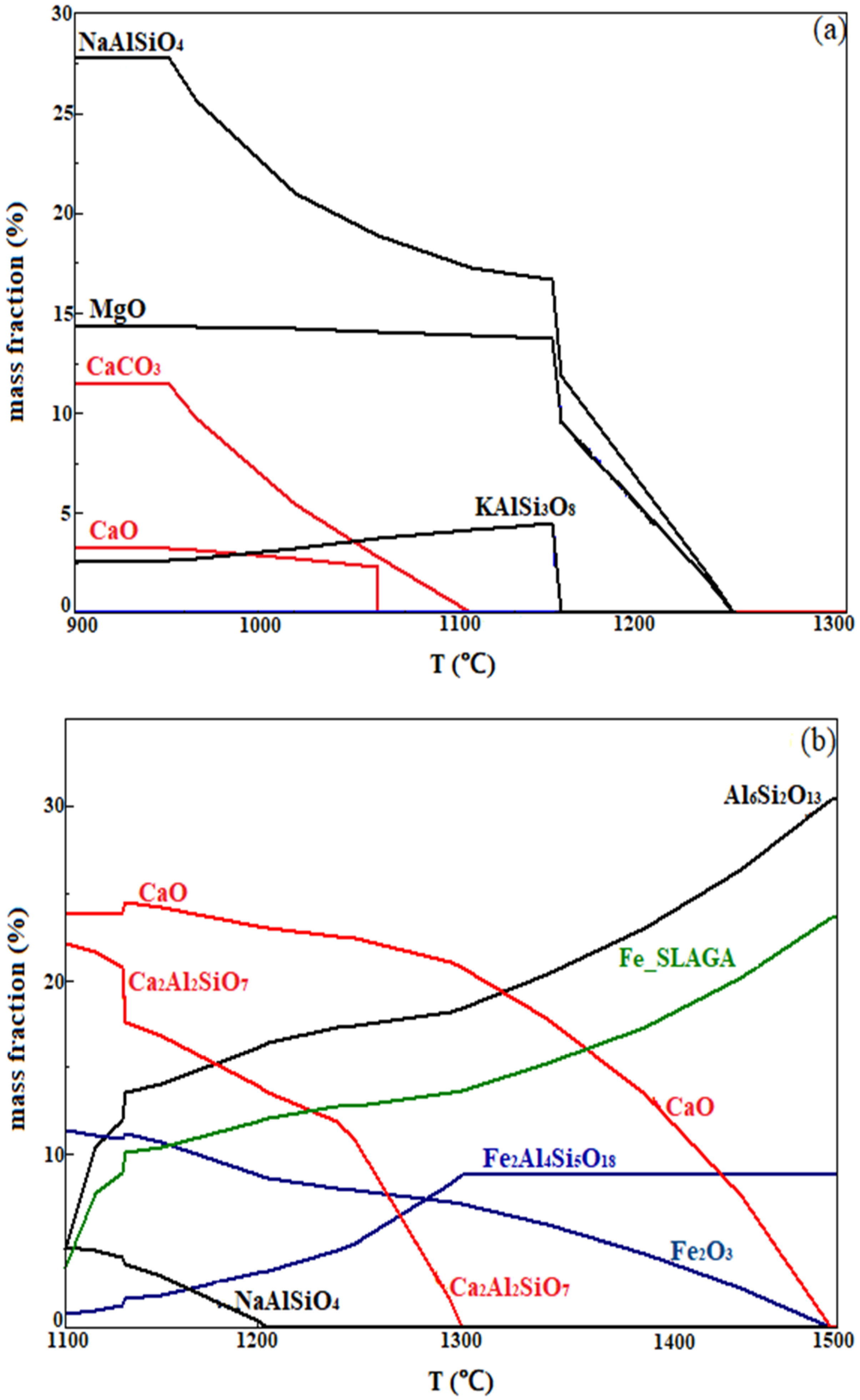
3.5. Calculation of Phase Diagrams
3.6. FactSage Equilib Calculations
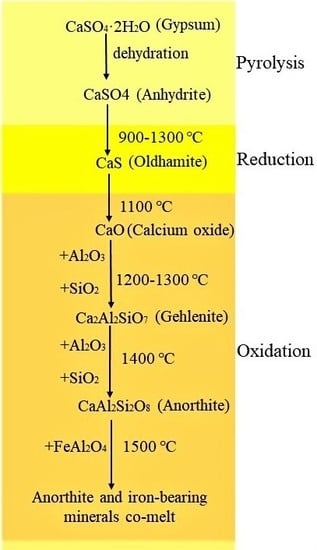
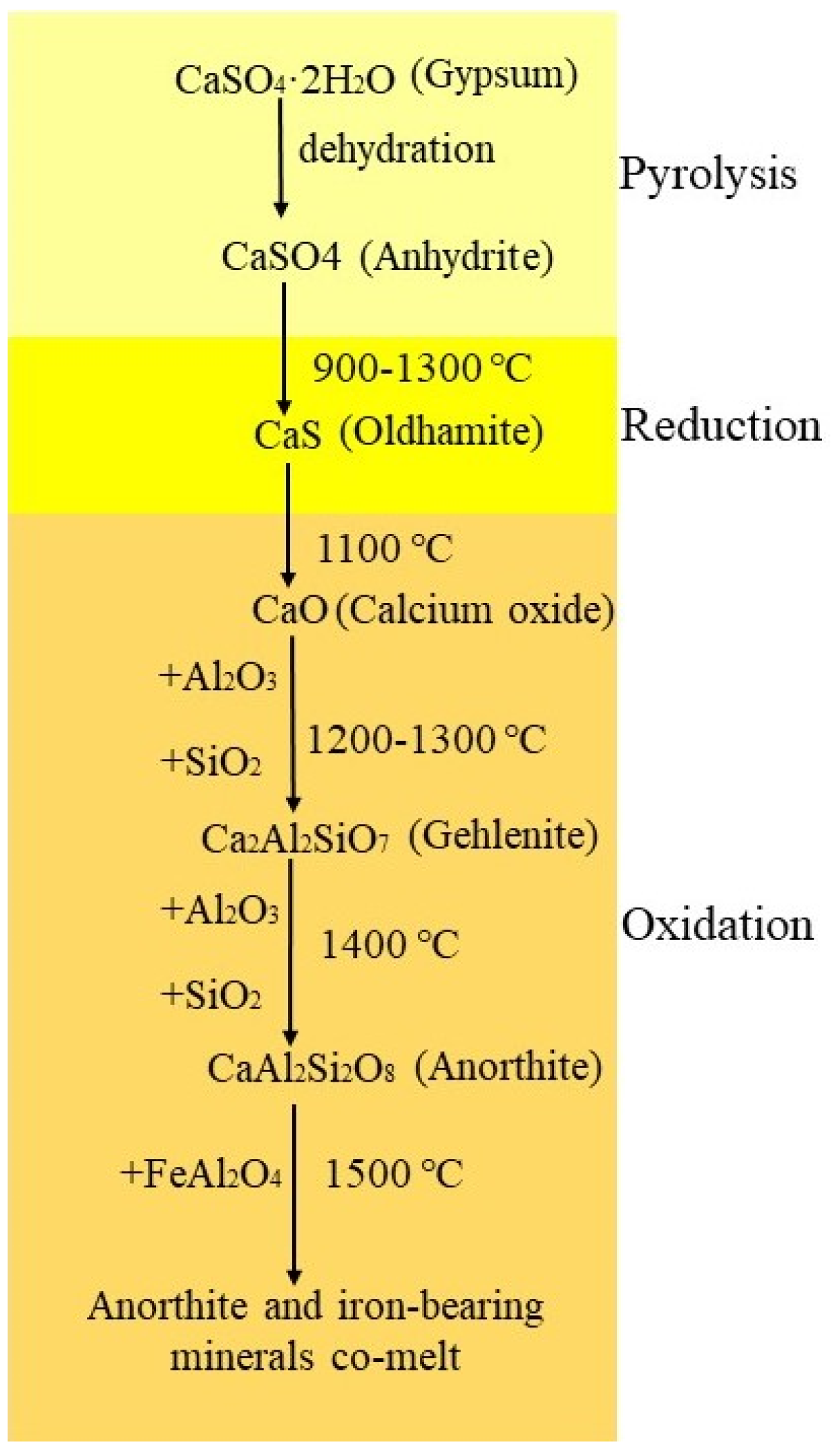
3.7. Reaction Mechanism of Minerals
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finkelman, R.B.; Dai, S.; French, D. The importance of minerals in coal as the hosts of chemical elements: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 212, 103251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, J.C.; Benson, S.A.; Laumb, M.L.; Waanders, B. Coal and coal ash characteristics to understand mineral transformations and slag formation. Fuel 2009, 88, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnefeld, F.; Leemann, A.; Lucuk, M.; Svoboda, P.; Neuroth, M. Assessment of phase formation in alkali activated low and high calcium fly ashes in building materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Xue, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xu, K.; Hu, H.; Luo, G.; Naruse, I. A novel CO2-water leaching method for AAEM removal from Zhundong coal. Fuel 2019, 237, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, S.; Huang, Q.; Yao, Q. Fine particulate formation and ash deposition during pulverized coal combustion of high-sodium lignite in a down-fired furnace. Fuel 2015, 143, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Chen, L. The formation of deposits and their evolutionary characteristics during pressurized gasification of Zhundong coal char. Fuel 2018, 224, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kawa, O. Investigation on the effects of different forms of sodium, chlorine and sulphur and various pretreatment methods on the deposition characteristics of Na species during pyrolysis of a Na-rich coal. Fuel 2018, 234, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Whiddon, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cen, K. Inhibition of Sodium Release from Zhundong Coal via the Addition of Mineral Additives: Online Combustion Measurement with Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, T.; Berger, R.; Hawthorne, C.; Abanades, J.C. Lime enhanced gasification of solid fuels: Examination of a process for simultaneous hydrogen production and CO2 capture. Fuel 2008, 87, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, C.; Li, H.; Shao, X.; Zheng, C. Mineralogy and chemical composition of high-calcium fly ashes and density fractions from a coal-fired power plant in China. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qi, C.; Zhang, S.; Deng, Y. Minerals in the Ash and Slag from Oxygen-Enriched Underground Coal Gasification. Minerals 2016, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Mmbaga, J.P.; Shirazi, A.S.; Trivedi, J.; Liu, Q.; Gupta, R. Modelling underground coal gasification-A review. Energies 2015, 8, 12603–12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, W.; French, D.; Tuo, K.; Mei, X. Sequential mineral transformation during underground coal gasification with the presence of coal partings. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 208, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Nie, L. Investigation on Sodium Fate for High Alkali Coal during Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosminski, A.; Ross, D.P.; Agnew, J.B. Transformations of sodium during gasification of low-rank coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2006, 87, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosminski, A.; Ross, D.P.; Agnew, J.B. Reactions between sodium and kaolin during gasification of a low-rank coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2006, 87, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, C.; Yan, Y.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Che, D. Release and transformation of sodium during combustion of Zhundong coals. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Z. Effect of temperature on gasification performance and sodium transformation of Zhundong coal. Fuel 2017, 189, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Song, G.; Na, Y.; Song, W.; Qi, X.; Yang, Z. Transformation characteristics of Na and K in high alkali residual carbon during circulating fluidized bed combustion. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Xue, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, H.; Luo, G.; Naruse, I.; Bai, Z. Na & Ca removal from Zhundong coal by a novel CO2-water leaching method and the ashing behavior of the leached coal. Fuel 2017, 210, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhuang, X.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Li, J. Geochemistry and mineralogy of coal in the recently explored Zhundong large coal field in the Junggar basin, Xinjiang province, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 82, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM Standard D3173–11. Test Method for Moisture in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM Standard D3175–11. Test Method for Volatile Matter in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM Standard D3174–11. Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Test Method for Ash in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM Standard D3177–02. Test Methods for Total Sulfur in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; Reapproved 2007; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, P.; Wang, W.; Sang, S.; Qian, F.; Shao, P.; Zhao, X. Partitioning of hazardous elements during preparation of high-uranium coal from Rongyang, Guizhou, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 185, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, J.C.; Keyser, M.J. Influence of discard mineral matter on slag-liquid formation and ash melting properties of coal-A FACTSAGETM simulation study. Fuel 2014, 116, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, G.; Xu, J.; Liang, Q.; Liu, H. Viscosity fluctuation behaviors of coal ash slags with high content of calcium and low content of silicon. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 158, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, D.; Yang, H.; Li, S. Understanding Ash Deposition for the Combustion of Zhundong Coal: Focusing on Different Additives Effects. Energy Fuels 2018, 6, 7103–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Kong, L.X.; Bai, J.; Bai, Z.Q.; Li, W. Study on fusibility of coal ash rich in sodium and sulfur by synthetic ash under different atmospheres. Fuel 2017, 202, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.Q.; Wu, X.; De Girolamo, A.; Zhang, L. Inhibition of lignite ash slagging and fouling upon the use of a silica-based additive in an industrial pulverised coal-fired boiler. Part 1. Changes on the properties of ash deposits along the furnace. Fuel 2015, 139, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, D.; Fan, B.; Zeng, X.; Lv, W.; Chen, J. Characterization of ash particles from co-combustion with a Zhundong coal for understanding ash deposition behavior. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Xing, H.; Li, H.; Hu, H.; Li, A.; Yao, H. Improved sodium adsorption by modified kaolinite at high temperature using intercalation-exfoliation method. Fuel 2017, 191, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Song, X.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, L. Occurrence and origins of minerals in mixed-layer illite/smectite-rich coals of the Late Permian age from the Changxing Mine, eastern Yunnan, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 102, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ward, C.R.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Xue, W.; Liu, S.; Tian, H.; Sun, X. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the Pennsylvanian coal in the Adaohai Mine, Daqingshan Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China: Modes of occurrence and origin of diaspore, gorceixite, and ammonian illite. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Tang, Y.; Shao, L.; Li, S. Distribution, isotopic variation and origin of sulfur in coals in the Wuda coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 51, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Chou, C.L.; Finkelman, R.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Zhou, Y. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, W.; Bai, Z. Effects of mineral matter and coal blending on gasification. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, P.; Ward, C.R.; Tang, Y.; Song, X.; Jiang, J.; Hower, J.C.; Li, T.; Seredin, V.V.; Wagner, N.J. Elemental and mineralogical anomalies in the coal-hosted Ge ore deposit of Lincang, Yunnan, southwestern China: Key role of N2-CO2-mixed hydrothermal solutions. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 152, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y. Formation mechanism of slag during fluid-bed gasification of lignite. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, K. Sequential Transformation Behavior of Iron-Bearing Minerals during Underground Coal Gasification. Minerals 2018, 8, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Bai, J.; Li, W.; Bai, Z.; Kong, L. Mineral transformation in char and its effect on coal char gasification reactivity at high temperatures, part 1: Mineral transformation in char. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 4545–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R. Analysis and significance of mineral matter in coal seams. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, P.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G. Melting behavior of typical ash particles in reducing atmosphere. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 3527–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qi, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, M.; Li, Y.; Dai, S.; Finkelman, R.B. Mineralogy and geochemistry of ash and slag from coal gasification in China: A review. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 717–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Guo, W.; Nechaev, V.P.; French, D.; Ward, C.R.; Spiro, B.F.; Finkelman, R.B. Modes of occurrence and origin of mineral matter in the Palaeogene coal (No. 19–2) from the Hunchun Coalfield, Jilin Province, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 189, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R. Analysis, origin and significance of mineral matter in coal: An updated review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 165, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.K.; Garg, A.; Subasinghe, N.D. In situ high-temperature phase transformation studies on pyrite. Fuel 2009, 88, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhao, L.; Hower, J.C.; Johnston, M.N.; Song, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S. Petrology, mineralogy, and chemistry of size-fractioned fly ash from the Jungar power plant, Inner Mongolia, China, with emphasis on the distribution of rare earth elements. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootabadi, H.; Salamatinia, B.; Bhatia, S.; Abdullah, A.Z. Ultrasonic-assisted biodiesel production process from palm oil using alkaline earth metal oxides as the heterogeneous catalysts. Fuel 2010, 89, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Input Compositions | Reduction Stage (g) | Oxidation Stage (g) |
|---|---|---|
| C | 32.76 | 32.76 |
| H | 1.56 | 1.56 |
| O | 7.40 | 7.40 |
| N | 0.29 | 0.29 |
| S | 0.63 | 0.63 |
| Si | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| Al | 0.078 | 0.078 |
| Fe | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Ti | 0.0034 | 0.0034 |
| Ca | 0.34 | 0.34 |
| Mg | 0.104 | 0.104 |
| K | 0.0047 | 0.0047 |
| Na | 0.049 | 0.049 |
| Mn | 0.0012 | 0.0012 |
| P | 0.00024 | 0.00024 |
| CO2 | 151.25 | |
| H2O(g) | 192.50 | |
| O2 | 25.20 |
| Sample | Proximate Analysis/% | Ultimate Analysis/% | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Aad | Vad | FCad | Cad | Had | Oad | Nad | St,ad | ||||
| ZD-coal | 11.15 | 5.63 | 30.25 | 59.62 | 63.53 | 3.13 | 14.79 | 0.57 | 1.26 | |||
| Elemental compositions of coal ash, and loss on ignition (LOI, %) | ||||||||||||
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | MgO | K2O | Na2O | MnO2 | SO3 | P2O5 | LOI | |
| 8.82 | 5.25 | 33.69 | 16.72 | 0.20 | 6.16 | 0.20 | 2.34 | 0.07 | 24.26 | 0.02 | 1.87 | |
| Coal ash fusibility (°C) in a weakly-reducing atmosphere | ||||||||||||
| Deformation temperature (DT) | 1260 | |||||||||||
| Softening temperature (ST) | 1260 | |||||||||||
| Hemispherical temperature (HT) | 1270 | |||||||||||
| Fluid temperature (FT) | 1280 | |||||||||||
| Mineral Composition | 900 °C | 1000 °C | 1100 °C | 1200 °C | 1300 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetite | 14% | 8% | 7% | 4% | 2% |
| Oldhamite | 29% | 54% | 75% | 80% | 87% |
| Lime | 8% | 2% | - | - | - |
| Periclase | 10% | 9% | 8% | 7% | - |
| Calcite | 26% | 15% | - | - | - |
| Nepheline | 13% | 12% | 10% | 9% | - |
| Magnesite | - | - | - | - | 5% |
| Amorphous | - | - | - | - | 6% |
| Mineral Composition | 1100 °C | 1200 °C | 1300 °C | 1400 °C | 1500 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetite | 7% | - | - | - | - |
| Hematite | 23% | 20% | 8% | - | - |
| Gehlenite | 43% | 57% | 11% | - | - |
| Nepheline | 27% | 23% | - | - | - |
| Augite | - | - | 22% | 8% | - |
| Sillimanite | - | - | 23% | - | - |
| Anorthite | - | - | - | 31% | - |
| Cordierite | - | - | - | - | 8% |
| Mullite | - | - | 29% | 40% | 60% |
| Amorphous | - | - | 7% | 21% | 32% |
| Reaction | △G/KJ | △H/KJ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 °C | 1200 °C | 1300 °C | 1400 °C | 1500 °C | 1100 °C | 1200 °C | 1300 °C | 1400 °C | 1500 °C | |
| 3Al2O3 + 2SiO2 → Al6Si2O13 | −18.9 | −21 | −25 | −28 | −31 | 22.59 | 22.6 | 22.7 | 22.8 | 22.82 |
| CaO + Al2O3 + 2SiO2 → CaAl2Si2O8 | −134 | −136 | −139 | −141 | −144 | −101 | −100 | −99 | −98 | −96 |
| 2CaO + Al2O3 + SiO2 → Ca2Al2SiO7 | −166 | −170 | −173 | −176 | −179 | −124 | −125 | −126 | −127 | −128 |
| CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3 | −87.6 | −87.5 | −87.4 | −87.3 | −87.1 | −90.2 | −90 | −89 | −89.5 | −89.2 |
| Na2O + Al2O3 + 2SiO2 → 2NaAlSiO4 | −360 | −363 | −365 | −368 | −370 | −322 | −323 | −324 | −325 | −326 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Ma, W. Calcium-Bearing Minerals Transformation during Underground Coal Gasification. Minerals 2019, 9, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9110708
Liu S, Ma W. Calcium-Bearing Minerals Transformation during Underground Coal Gasification. Minerals. 2019; 9(11):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9110708
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuqin, and Weiping Ma. 2019. "Calcium-Bearing Minerals Transformation during Underground Coal Gasification" Minerals 9, no. 11: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9110708
APA StyleLiu, S., & Ma, W. (2019). Calcium-Bearing Minerals Transformation during Underground Coal Gasification. Minerals, 9(11), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9110708