Changes and Distribution of Modes of Occurrence of Seventeen Potentially-Hazardous Trace Elements during Entrained Flow Gasification of Coals from Ningdong, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Samples
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.2.1. Proximate, Ultimate, and Total Sulfur Analyses
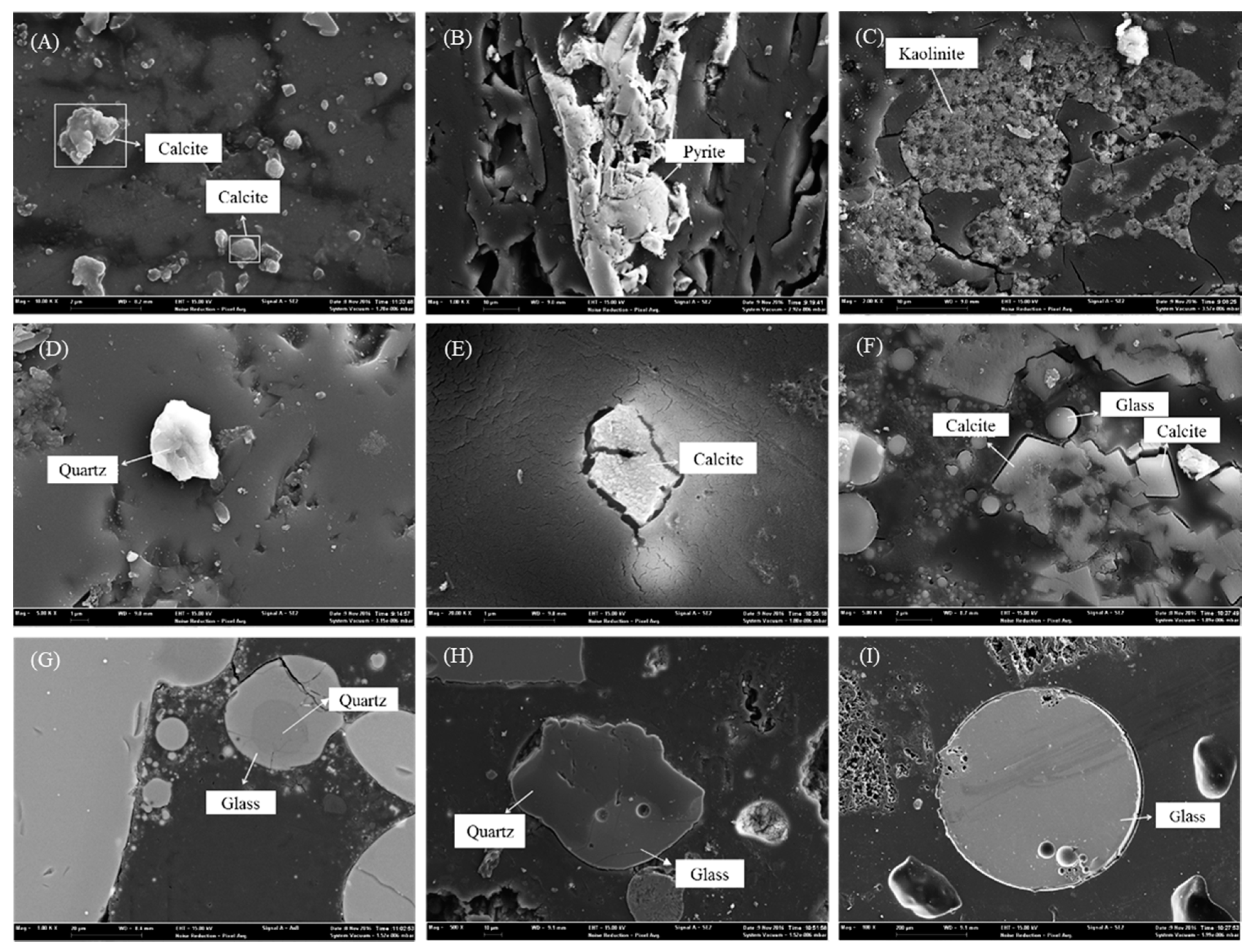
2.2.2. SEM-EDX and XRD Analyses
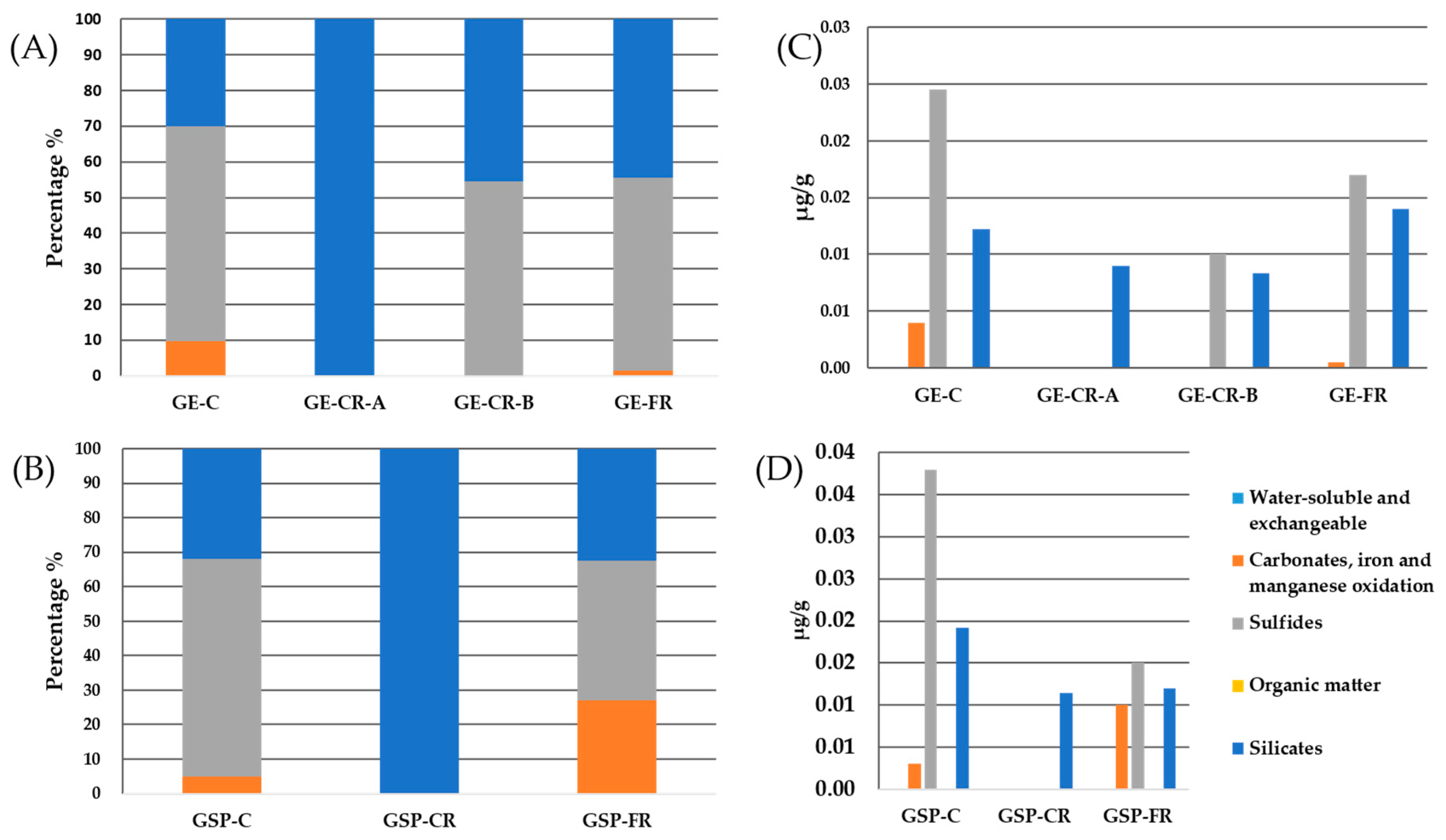
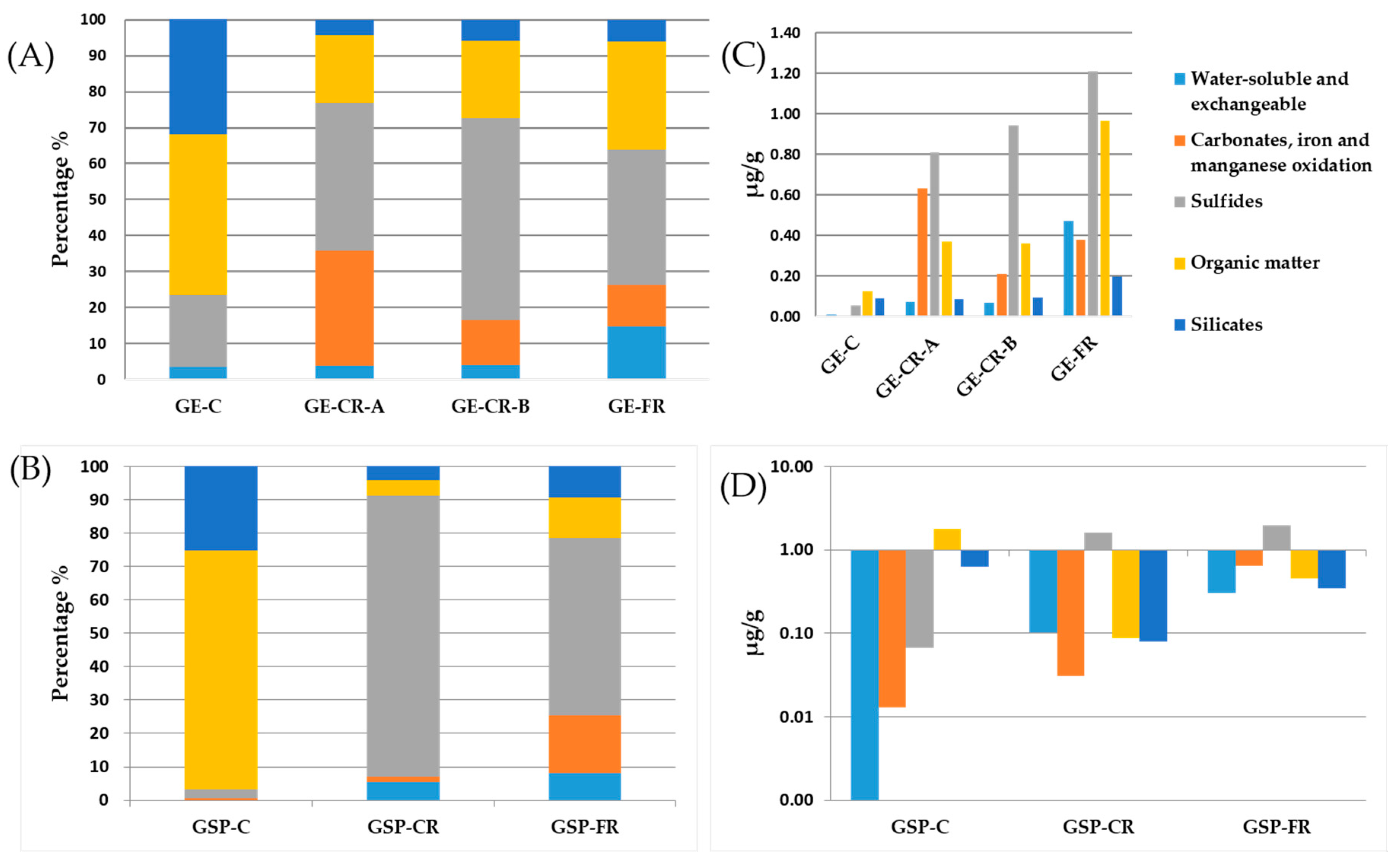
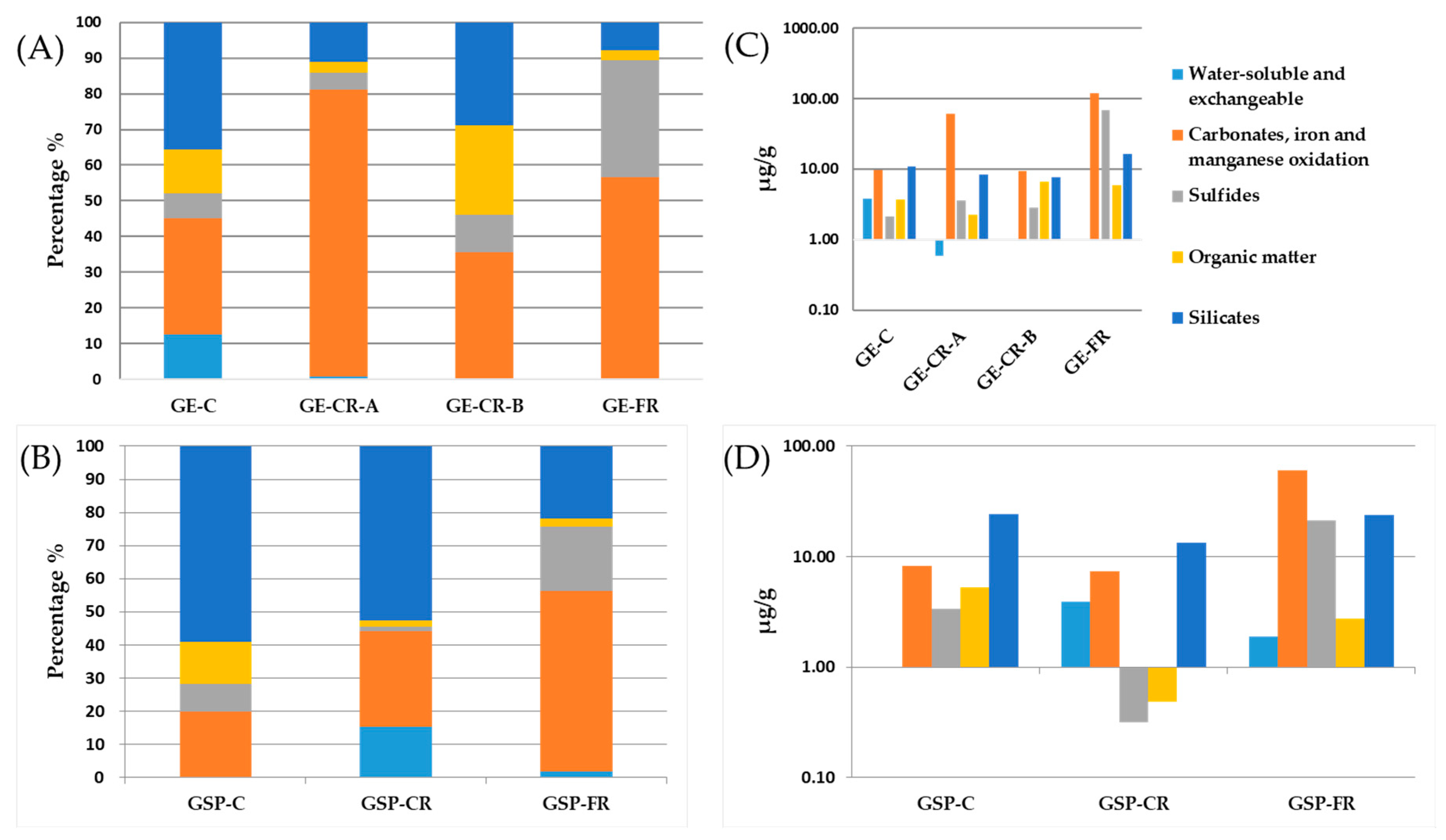
2.2.3. Protocol of Sequential Chemical Extraction
2.3.4. Trace Elements Concentration Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mineralogical Characteristics of Samples
3.2. Concentrations of the Selected Trace Elements
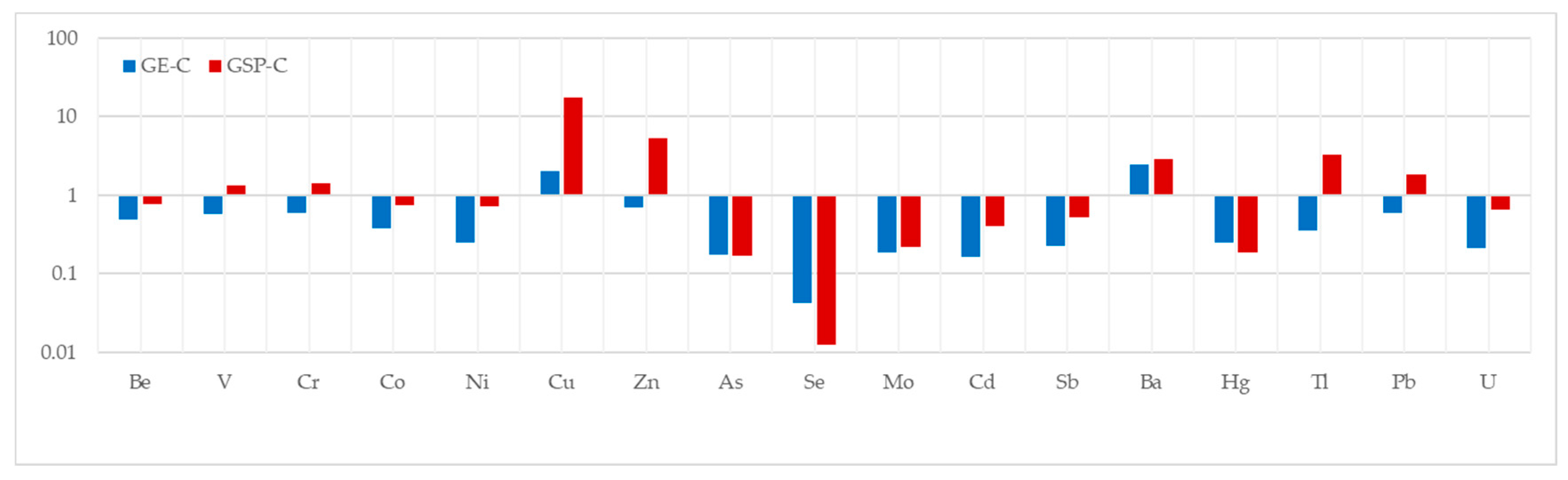
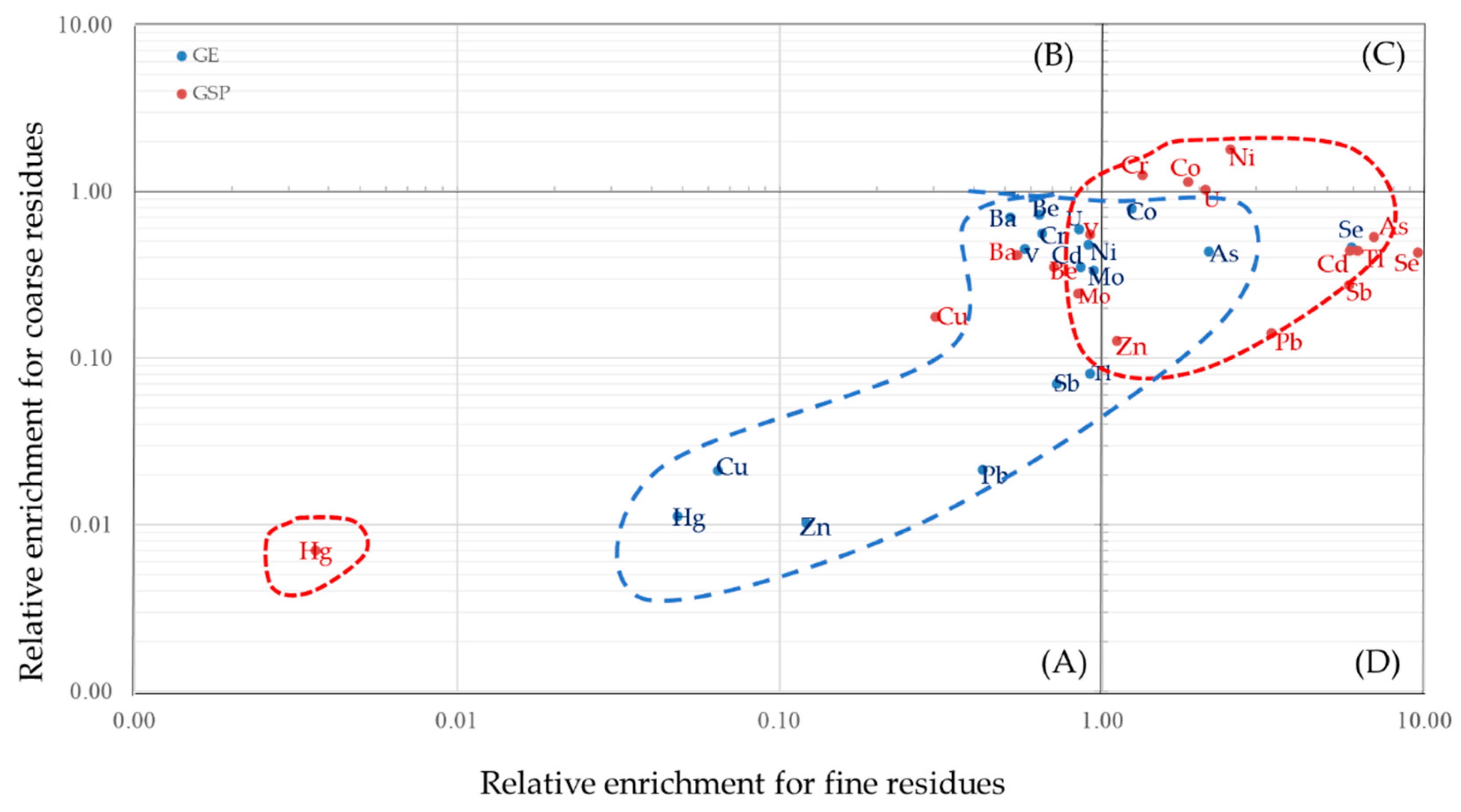
3.3. Distribution of the Selected Trace Elements Based on RE (Relative Enrichment)
3.3.1. Volatile Trace Elements
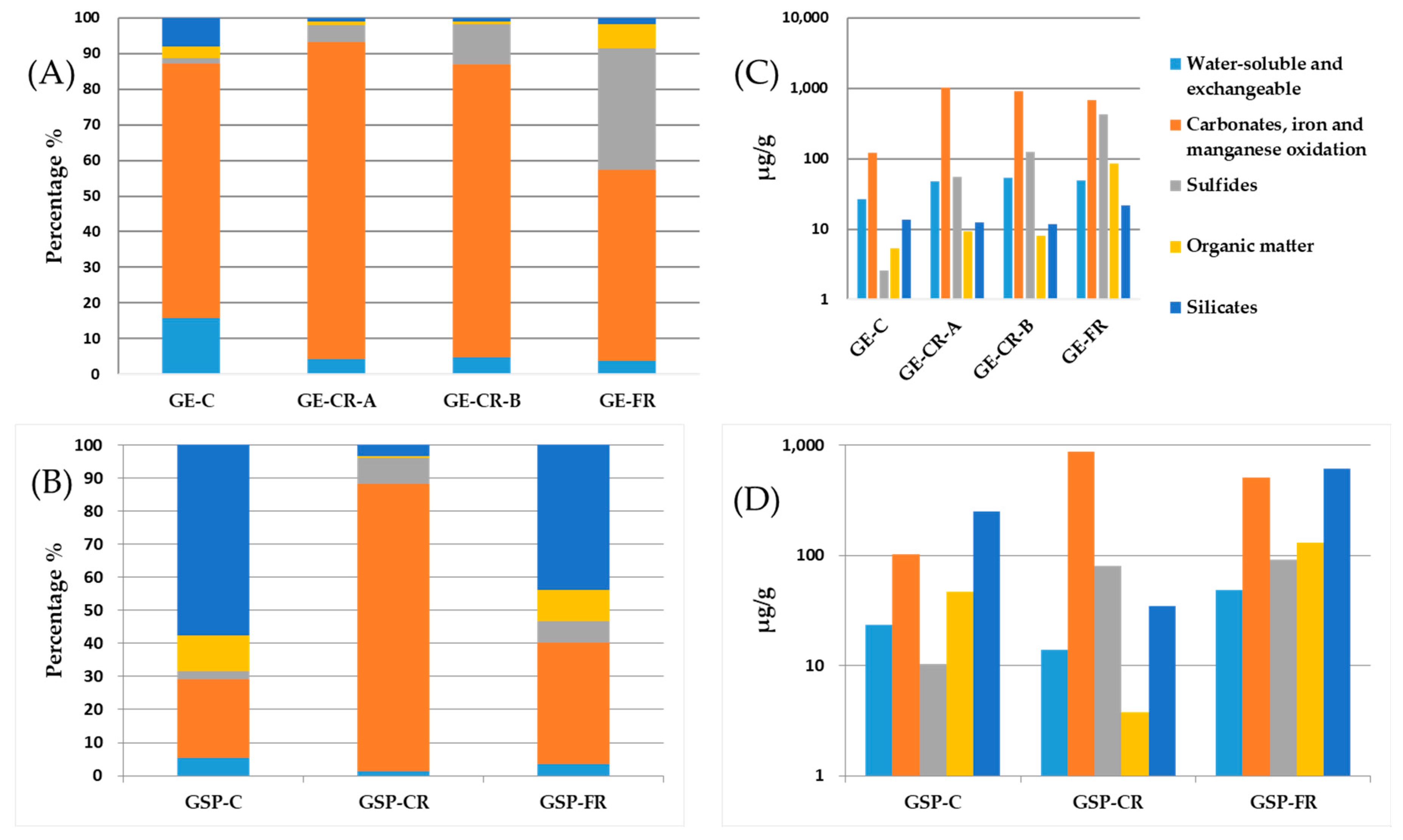
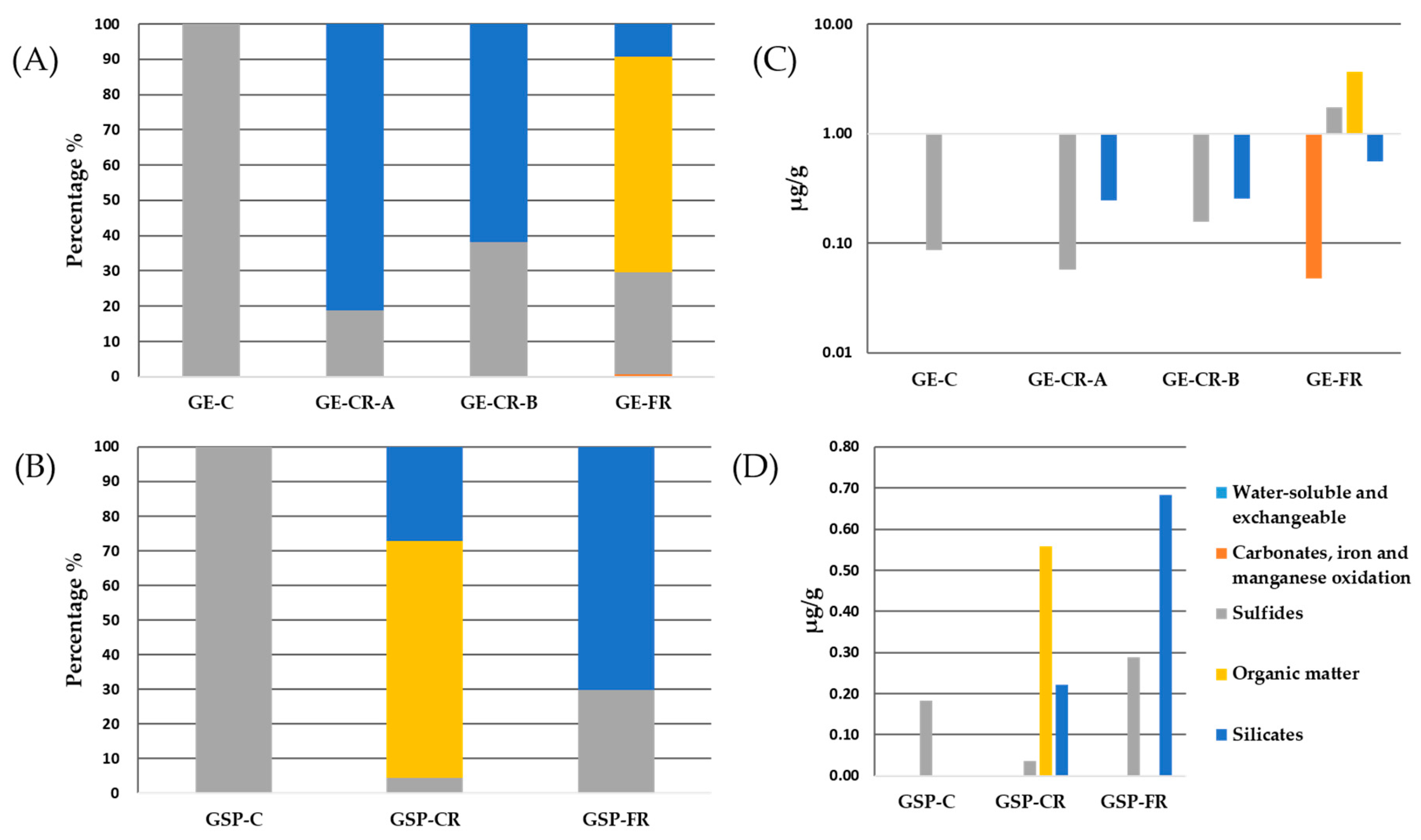
Mercury (Hg)
Molybdenum (Mo)
Barium (Ba)
Beryllium (Be)
Vanadium (V)
Copper (Cu)
3.3.2. Volatilization-Condensation Behavior of Trace Elements
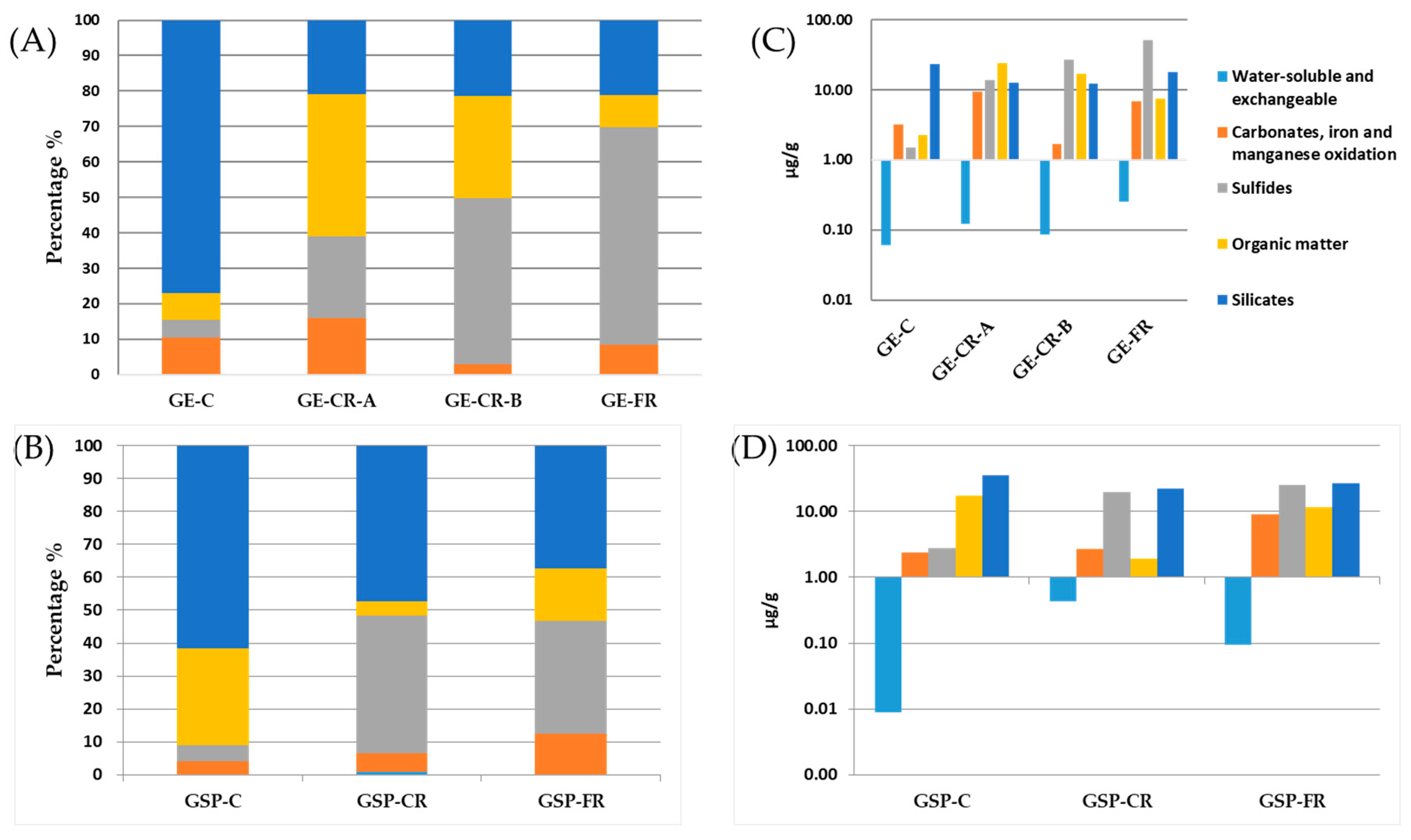
Arsenic (As)
Selenium (Se)
3.3.3. Other Trace Elements
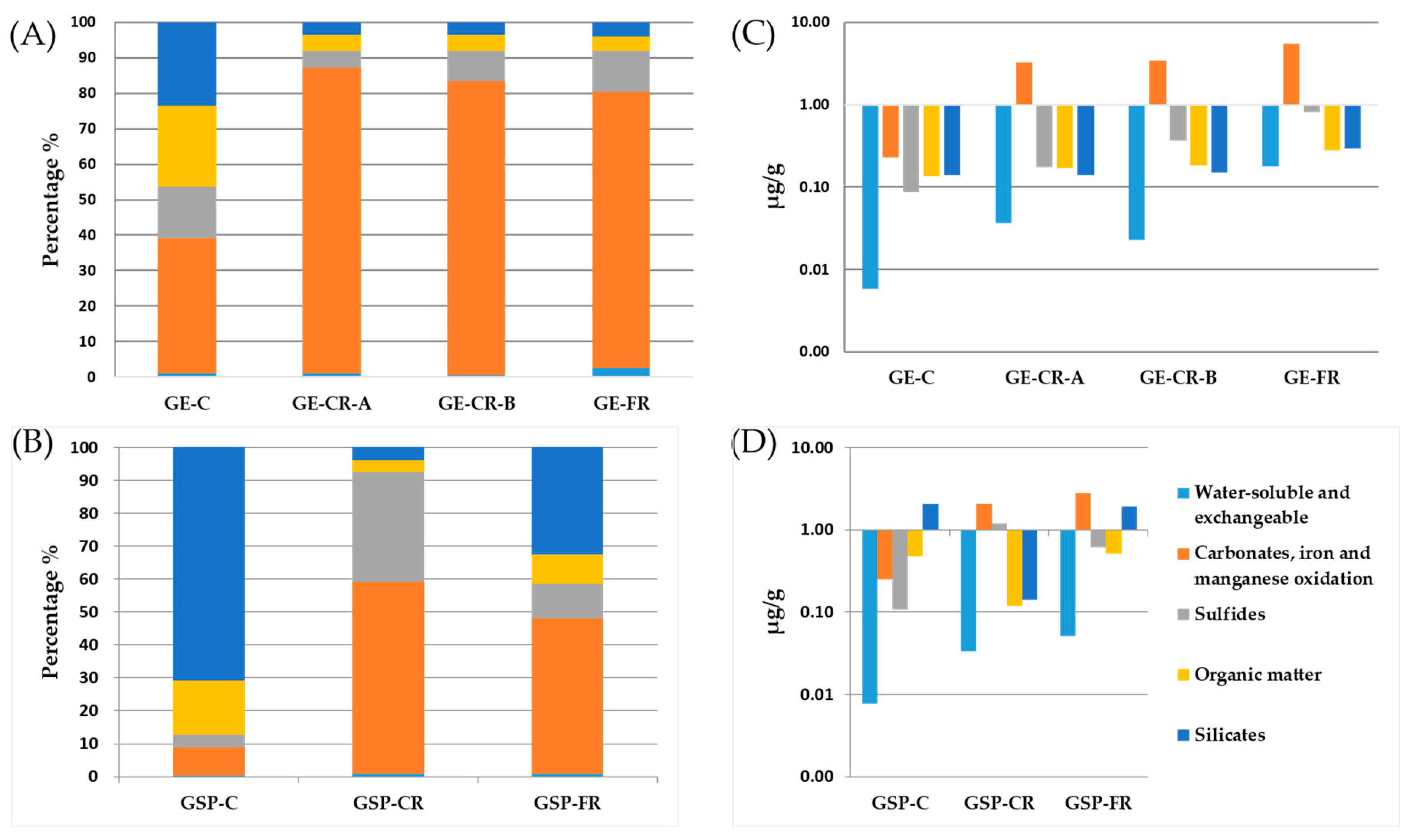
Chromium (Cr)
Uranium (U)
Nickel (Ni)
Cobalt (Co)
Cadmium (Cd)
Lead (Lead)
Antimony (Sb)
Zinc (Zn)
Thallium (Tl)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finkelman, R.B.; Tian, L. The health impacts of coal use in China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qi, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, M.; Li, Y.; Dai, S.; Finkelman, R.B. Mineralogy and geochemistry of ash and slag from coal gasification in China: A review. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 717–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronbauer, M.A.; Izquierdo, M.; Dai, S.; Waanders, F.B.; Wagner, N.J.; Mastalerz, M.; Hower, J.C.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Taffarel, S.R.; Bizani, D.; et al. Geochemistry of ultra-fine and nano-compounds in coal gasification ashes: A synoptic view. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunt, J.R.; Waanders, F.B. Volatile trace element behaviour in the Sasol®, fixed-bed dry-bottom (FBDB)™ gasifier treating coals of different rank. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboirien, B.O.; Thulari, V.; North, B.C. Enrichment of trace elements in bottom ash from coal oxy-combustion: Effect of coal types. Appl. Energy 2016, 177, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.B. The fate of trace elements during coal combustion and gasification: An overview. Fuel 1993, 72, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R. Analysis and significance of mineral matter in coal seams. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yan, R.; Zheng, C.; Qiao, Y.; Han, J.; Sheng, C. Status of trace element emission in a coal combustion process: A review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2004, 85, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.R. The fate of trace elements and bulk minerals in pulverized coal combustion in a power station. Fuel Process. Technol. 1996, 47, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Ward, C.R.; French, D.; Groves, S. Mobility of trace elements from selected Australian fly ashes and its potential impact on aquatic ecosystems. Fuel 2006, 85, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiie, R.; Taya, Y.; Ichiyanagi, T.; Ueki, Y.; Naruse, I. Emissions of particles and trace elements from coal gasification. Fuel 2013, 108, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Henke, K.R.; Dai, S.; Ward, C.R.; French, D.; Liu, S.; Graham, U.M. Chapter 2—Generation and nature of coal fly ash and bottom ash. Coal Combust. Prod. 2017, 21–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Groppo, J.G.; Graham, U.M.; Ward, C.R.; Kostova, I.; Maroto-Valer, M.M.; Dai, S. Coal-derived unburned carbons in fly ash: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 197, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoňová, L. Unburned carbon from coal combustion ash: An overview. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 134, 136–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, S.M.H.; Ghadi, A.; Baei, M.S.; Javadian, H.; Maghsudi, M.; Kazemian, H. Porous catalysts fabricated from coal fly ash as cost-effective alternatives for industrial applications: A review. Fuel 2018, 217, 320–342. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Ji, X.; Sarker, P.K.; Tang, J.; Ge, L.; Xia, M. A comprehensive review on the applications of coal fly ash. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 141, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Fernández-Turiel, J.; López-Soler, A. Trace elements in coal and their behaviour during combustion in a large power station. Fuel 1995, 74, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Jiang, J.; Hower, J.C.; Song, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gornostaeva, T.; Li, X.; et al. Composition and modes of occurrence of minerals and elements in coal combustion products derived from high-Ge coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 121, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, K.W.; French, D.H.; Farrell, O.P.; Wood, R.A.; Huggins, F.E. Modes of occurrence of trace and minor elements in some Australian coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B. Modes of Occurrence of Environmentally-Sensitive Trace Elements in Coal; Springer: Cham, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 24–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg, M.; Nordberg, G.F. Trace element research-historical and future aspects. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 38, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Finkelman, R.B. Coal as a promising source of critical elements: Progress and future prospects. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 186, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Yan, X.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Ren, D.; Finkelman, R.B. Valuable elements in Chinese coals: A review. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 590–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S.; Sun, Y.; Chekryzhov, I.Y. Coal deposits as promising sources of rare metals for alternative power and energy-efficient technologies. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, J.R.; Waanders, F.B. Trace element behaviour in the Sasol-Lurgi MK IV FBDB gasifier. Part 1—The volatile elements: Hg, As, Se, Cd and Pb. Fuel 2008, 81, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, J.R.; Waanders, F.B. Trace element behaviour in the Sasol-Lurgi MK IV FBDB gasifier. Part 2—The semi-volatile elements: Cu, Mo, Ni and Zn. Fuel 2009, 88, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, J.R.; Waanders, F.B. Trace element behaviour in the sasol-lurgi fixed-bed dry-bottom gasifier. Part 3—The non-volatile elements: Ba, Co, Cr, Mn and V. Fuel 2010, 89, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.B. Thermodynamic equilibrium study of trace element mobilisation under air blown gasification conditions. Fuel 2000, 81, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dı́az-Somoano, M.; Martı́nez-Tarazona, M.R. Trace element evaporation during coal gasification based on a thermodynamic equilibrium calculation approach. Fuel 2003, 82, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yoshihiko, N.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, M. Application of the FactSage to Predict the Ash Melting Behavior in Reducing Conditions. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 14, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, J.; Backman, R.; Hupa, M.; Moilanen, A.; Kurkela, E. Trace element behavior in the fluidized bed gasification of solid recovered fuels—A thermodynamic study. Fuel 2013, 106, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Klika, Z.; Weiss, Z.; Finkelman, R.B.; Alastuey, A.; Juan, R. Determination of element affinities by density fractionation of bulk coal samples. Fuel 2001, 80, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Li, D.; Ren, D.; Tang, Y.; Shao, L.; Song, H. Geochemistry of the late Permian No. 30 coal seam, Zhijin Coalfield of Southwest China: Influence of a siliceous low-temperature hydrothermal fluid. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Yan, X.; Ji, D.; Yang, Y.; Hu, L. Modes of occurrence of highly-elevated trace elements in superhigh-organic-sulfur coals. Fuel 2015, 156, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, D.A. The use of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA ICP-MS) for the analysis of fly ash. Fuel 2004, 83, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, D.A. The determination of trace element distributions in coals using sequential chemical leaching—A new approach to an old method. Fuel 2013, 114, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B.; Palmer, C.A.; Wang, P. Quantification of the modes of occurrence of 42 elements in coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 185, 138–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ward, C.R.; Graham, I.T.; French, D.; Dai, S.; Song, X. Modes of occurrence of non-mineral inorganic elements in lignites from the Mile Basin, Yunnan Province, China. Fuel 2018, 222, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huan, B.; Guo, X.; Finkelman, R.B. Leachability of hazardous trace elements from entrained-flow coal gasification residues in Ningdong, China. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 9703–9716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Guo, X.; Qiang, X.; Finkelman, R.B.; Han, S.C.; Huan, B.B.; Pan, X. Petrological characteristics and trace element partitioning of gasification residues from slagging entrained-flow gasifiers in Ningdong, China. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 3052–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Test Method for Moisture in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; ASTM D3173-11; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Test Method for Ash in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke from Coal; ASTM D3174-11; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Test Method for Volatile Matter in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; ASTM D3175-11; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Test Method for Total Sulfer in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke from Coal; ASTM D3177-02; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Test Methods for Instrumental Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen in Laboratory Samples of Coal; ASTM D5373-08; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Standard Practice for Preparing Coal Samples for Microscopical Analysis by Reflected Light; ASTM D2797M-11a; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Liu, J.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; French, D.; Jia, S.; Hood, M.M.; Garrison, T.M. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of Late Permian coals and host rocks from the Guxu Coalfield, Sichuan Province, China, with emphasis on enrichment of rare metals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 166, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hower, J.C.; Li, D.; Chen, W.; Zhu, X.; Zou, J. Chemical and mineralogical compositions of silicic, mafic and alkali tonsteins in the late Permian coals from the Songzao Coalfield, Chongqing, Southwest China. Chem. Geol. 2011, 282, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Classification for Quality of Coal; Part 1: Ash, 1994; Chinese Standard GB/T 15224, 1–1994; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1994. (In Chinese)
- Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Classification for Quality of Coal; Part 2: Sulfur, 2010; Chinese Standard GB/T 15224, 2–2010; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese)
- Kim, A.G.; Kazonich, G. The Silicate/non-silicate distribution of metals in fly ash and its effect on solubility. Fuel 2004, 83, 2285–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R. Analysis, origin and significance of mineral matter in coal: An updated review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 165, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matjie, R.H.; Van Alphen, C. Mineralogical features of size and density fractions in Sasol coal gasification ash, South Africa and potential by-products. Fuel 2008, 87, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matjie, R.H.; Li, Z.; Ward, C.R.; French, D. Chemical composition of glass and crystalline phases in coarse coal gasification ash. Fuel 2008, 87, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifenstein, A.P.; Kahraman, H.; Coin, C.D.A.; Calos, N.J.; Miller, G.; Uwins, P. Behaviour of selected minerals in an improved ash fusion test: Quartz, potassium feldspar, sodium feldspar, kaolinite, illite, calcite, dolomite, siderite, pyrite and apatite. Fuel 1999, 78, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Chou, C.-L.; Finkelman, R.B.; Seredin, V.V. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health and industrial utilization. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketris, M.P.; Yudovich, Y.E. Estimations of Clarkes for carbonaceous biolithes: World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 78, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Chekryzhov, I.Y.; Seredin, V.V.; Nechaev, V.P.; Graham, I.T.; Hower, J.C.; Ward, C.R.; Ren, D.; Wang, X. Metalliferous coal deposits in East Asia (Primorye of Russia and South China): A review of geodynamic controls and styles of mineralization. Gondwana Res. 2016, 29, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Finkelman, R.B. Metalliferous coals: A review of the main genetic and geochemical types. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 253–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sua’rez-Ruiz, I.; Ward, C.R. Chapter 4—Coal Combustion. In Applied Coal Petrology; Suárez-Ruiz, I., Crelling, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 84–117. [Google Scholar]
- Helble, J.J.; Mojtahedi, W.; Lyyränen, J. Trace element partitioning during coal gasification. Fuel 1996, 75, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meij, R. Trace element behavior in coal-fired power plants. Fuel Process. Technol. 1994, 39, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, M.A.; Hughes, R.W. Partitioning of inorganic elements in pilot-scale and demonstration-scale entrained-flow gasifiers. Fuel 2014, 127, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Y.; Anthony, E.J.; Zhao, C. Partitioning of trace elements, As, Ba, Cd, Cr, Cu, Mn and Pb, in a 2.5 MW th pilot-scale circulating fluidised bed combustor burning an anthracite and a bituminous coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 146, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.J.; Coertzen, M.; Matjie, R.H.; Dyk, J. Chapter 5—Coal Gasification. In Applied Coal Petrology; Suárez-Ruiz, I., Crelling, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 119–144. [Google Scholar]
- Yudovich, Y.E.; Ketris, M.P. Mercury in coal: A review: Part 1. Geochemistry. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 62, 107–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, X.; Seredin, V.V.; Hower, J.C.; Ward, C.R.; O’Keefe, J.M.K.; Huang, W.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Petrology, mineralogy and geochemistry of the Ge-rich coal from the Wulantuga Ge ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, China: New data and genetic implications. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 90, 72–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B. Modes of occurrence of potentially hazardous elements in coal: Levels of confidence. Fuel Process. Technol. 1994, 39, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaine, D. J. Chapter 3-Mode of occurrence of trace elements in coal. In Trace Elements in Coal; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 13, pp. 27–49. [Google Scholar]
- Huggins, F.E.; Huffman, G.P. How do lithophile elements occur in organic association in bituminous coals? Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 58, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, G.; Chou, C.-L. Abundance and modes of occurrence of mercury in some low-sulfur coals from China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 73, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Guo, S. Modes of occurrence and thermal stability of mercury in different samples from Guandi coal preparation plant. Fuel 2017, 200, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Yao, H.; Xu, M.; Gupta, R.; Xu, Z. Identifying modes of occurrence of mercury in coal by temperature programmed pyrolysis. Proc. Combust Inst. 2011, 33, 2763–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B. Mode of occurrence of accessory sulfide and selenide minerals in coal. In Neuviene Congress International de Stratigraphic et de Geologic du Carbonifere. Compte Rendu; Cross, A.T., Ed.; University Press: Carbondale, IL, USA, 1985; Volume 4, pp. 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Xie, P.; Ward, C.R.; Yan, X.; Guo, W.; French, D.; Graham, I.T. Anomalies of rare metals in Lopingian super-high-organic-sulfur coals from the Yishan Coalfield, Guangxi, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, W.; Wang, P. Enrichment of U–Se–Mo–Re–V in coals preserved within marine carbonate successions: Geochemical and mineralogical data from the Late Permian Guiding Coalfield, Guizhou, China. Miner. Deposita 2015, 50, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortenski, J. Trace elements in coal ashes from Sofia Pliocene Basin. Tendencias Del Mercado Del Arte 1986, 47, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Wang, P.; Ward, C.R.; Tang, Y.; Song, X.; Jiang, J.; Hower, J.C.; Li, T.; Seredin, V.V.; Wagner, N.J.; et al. Elemental and mineralogical anomalies in the coal-hosted Ge ore deposit of Lincang, Yunnan, southwestern China: Key role of N2-CO2-mixed hydrothermal solutions. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 152, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Xie, P.; Jia, S.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Yan, X.; French, D. Enrichment of U-Re-V-Cr-Se and rare earth elements in the Late Permian coals of the Moxinpo Coalfield, Chongqing, China: Genetic implications from geochemical and mineralogical data. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Yang, J.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Liu, H.; Garrison, T.M.; French, D.; O’Keefe, J.M.K. Geochemical and mineralogical evidence for a coal-hosted uranium deposit in the Yili Basin, Xinjiang, northwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, F.E.; Huffman, G.P. Modes of occurrence of trace elements in coal from XAFS spectroscopy. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1996, 32, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudovich, Y.E.; Ketris, M.P. Arsenic in coal: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 61, 141–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zeng, R.; Sun, Y. Enrichment of arsenic, antimony, mercury and thallium in a Late Permian anthracite from Xingren, Guizhou, Southwest China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 66, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolker, A.; Palmer, C.A.; Bragg, L.J.; Bunnell, J.E. Arsenic in Coal. In U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2006; pp. 2005–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Gong, M.; Lester, E.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Z. Characterization of residual carbon from entrained-bed coal water slurry gasifiers. Fuel 2007, 86, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.; Rubel, A.; Groppo, J.; Geertsema, A. Advanced gasification by-product utilization. In Office of Scientific & Technical Information Technical Reports; Univ of Kentucky Research Fdn: Lexington, KY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Huang, S.; Ji, L.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J. Structure characteristics and gasification activity of residual carbon from entrained-flow coal gasification slag. Fuel 2014, 122, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zeng, C.; Mao, Y.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Wang, T. The surface characteristics and reactivity of residual carbon in coal gasification slag. Energy Fuel 2010, 24, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasachar, S.; Boni, A.A. A kinetic model for pyrite transformations in a combustion environment. Fuel 1989, 68, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasachar, S.; Helble, J.J.; Boni, A.A. Mineral behavior during coal combustion 1. Pyrite transformations. Prog. Energy Combust. 1990, 16, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Wedel, S.; Hansen, J.P. Decomposition and oxidation of pyrite. Prog. Energy Combust. 2006, 32, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.K.; Garg, A.; Subasinghe, N.D. In situ, high-temperature phase transformation studies on pyrite. Fuel 2009, 88, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Helble, J.J.; Bool, L.E.; Sarofim, A.F. Iron transformations during combustion of pittsburgh no. 8 coal. Fuel 2009, 88, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Bai, Z.Q.; Yan, J.C.; Bai, J.; Li, W. Transformations of pyrite in different associations during pyrolysis of coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 131, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, G.B.; Finkelman, R.B. Selenium mobilization in a surface coal mine, Powder River Basin, Wyoming. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1992, 19, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Chou, C.-L.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the No. 6 Coal (Pennsylvanian) in the Junger Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 66, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B. Modes of occurrence of trace elements in coal. In US Geol Surv Open-File Rep; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1981; pp. 81–99. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, F. Mineralogy, elemental composition and modes of occurrence of elements in Canadian feed-coals. Fuel 2002, 81, 1199–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Robertson, J.D. Clausthalite in coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2003, 53, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







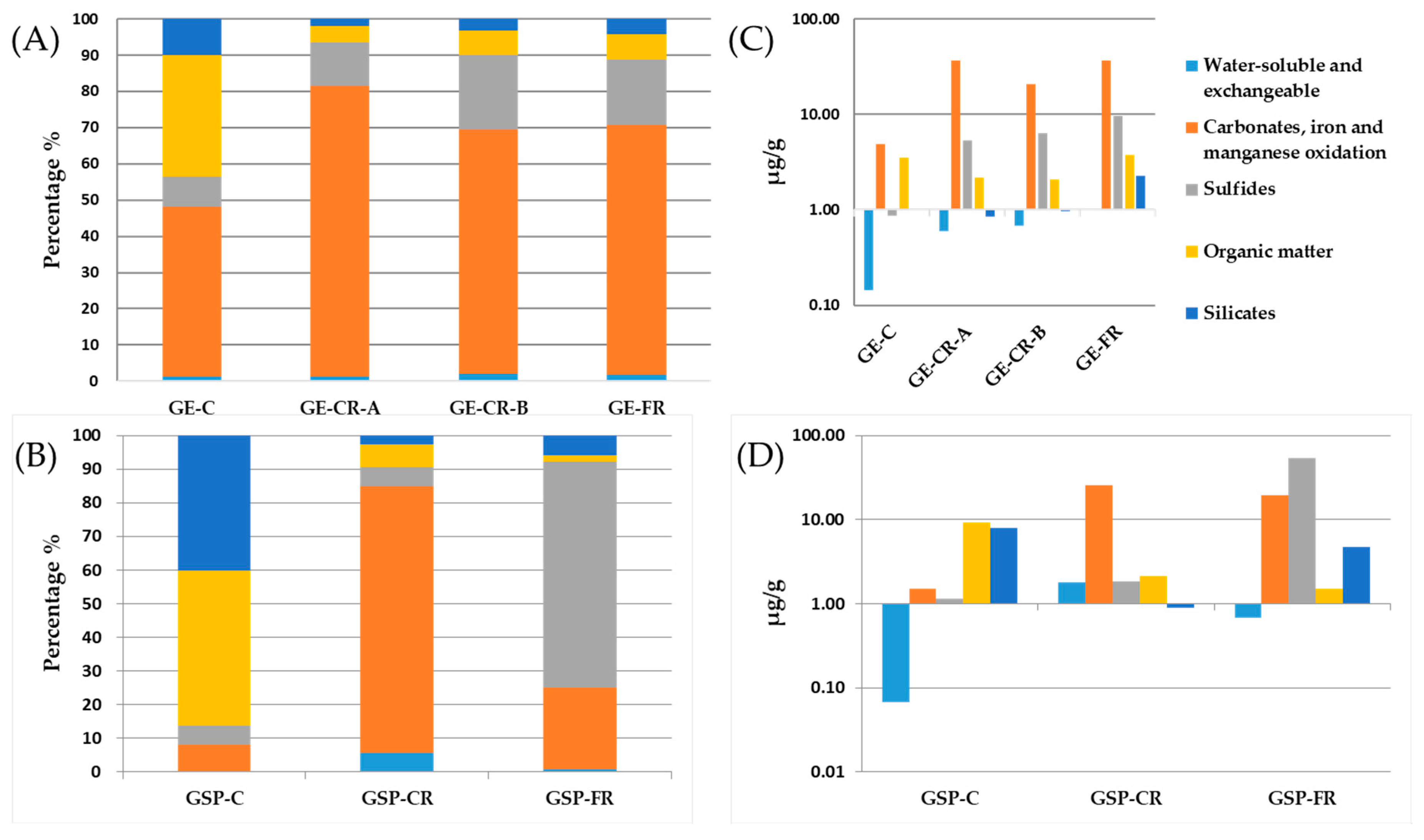

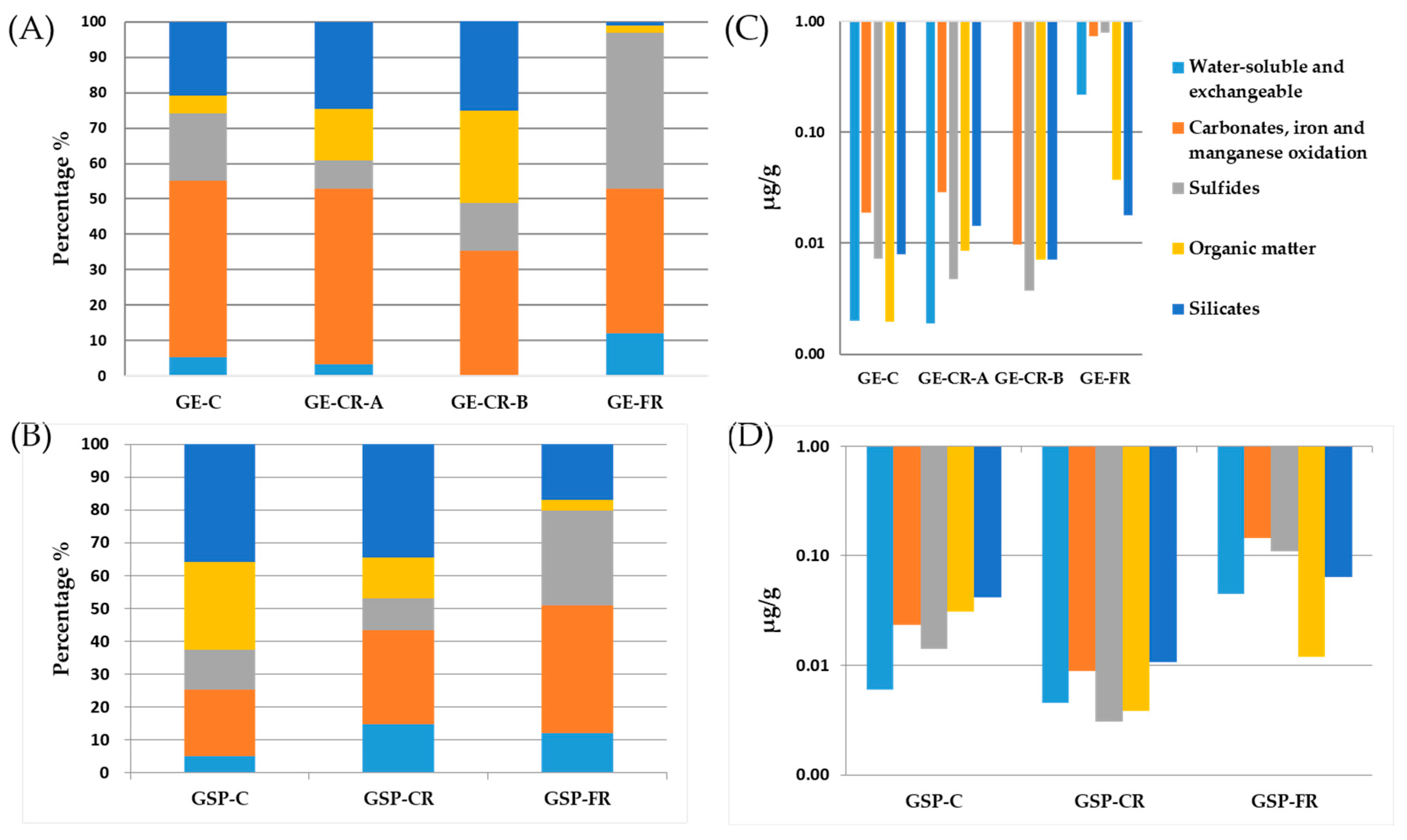
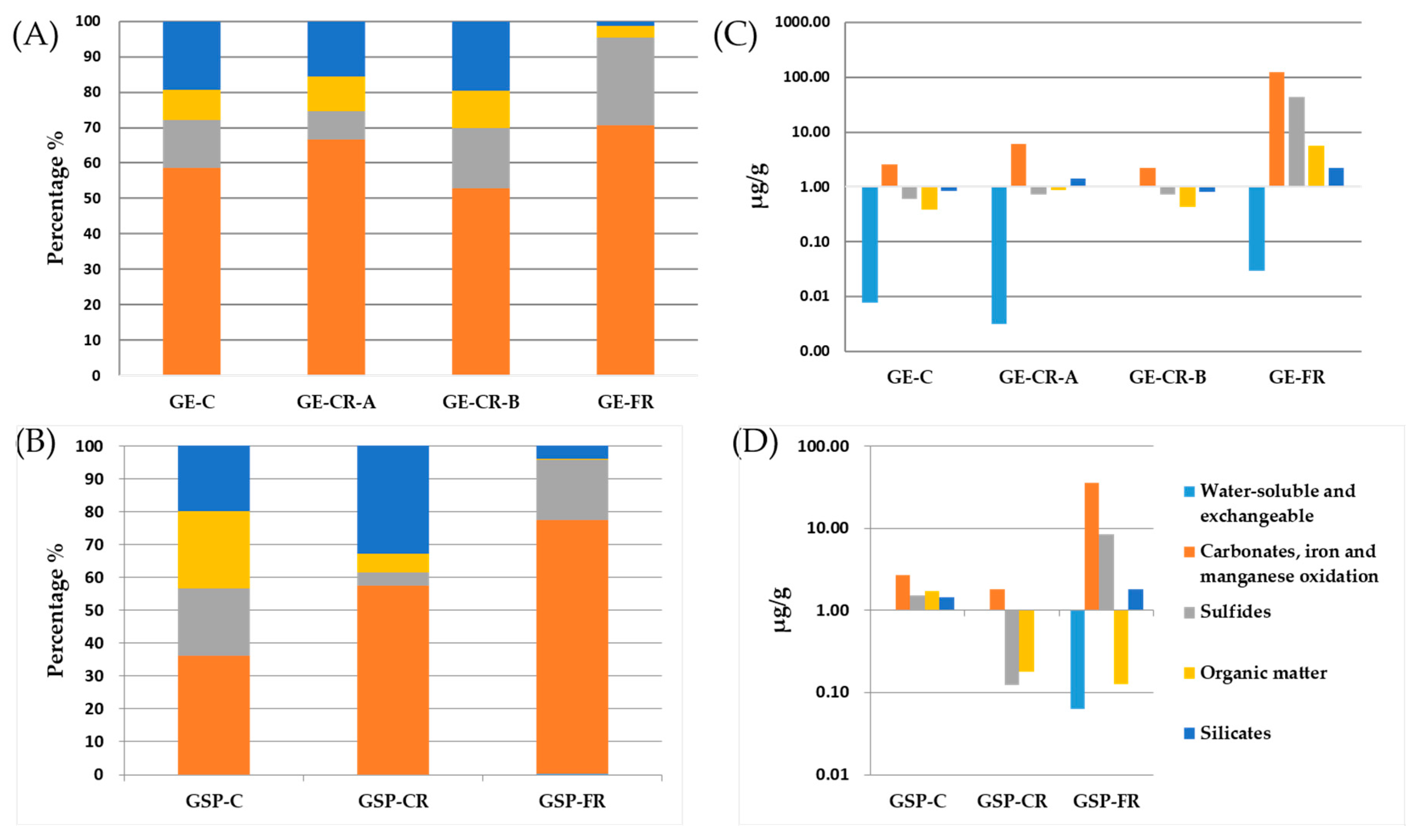
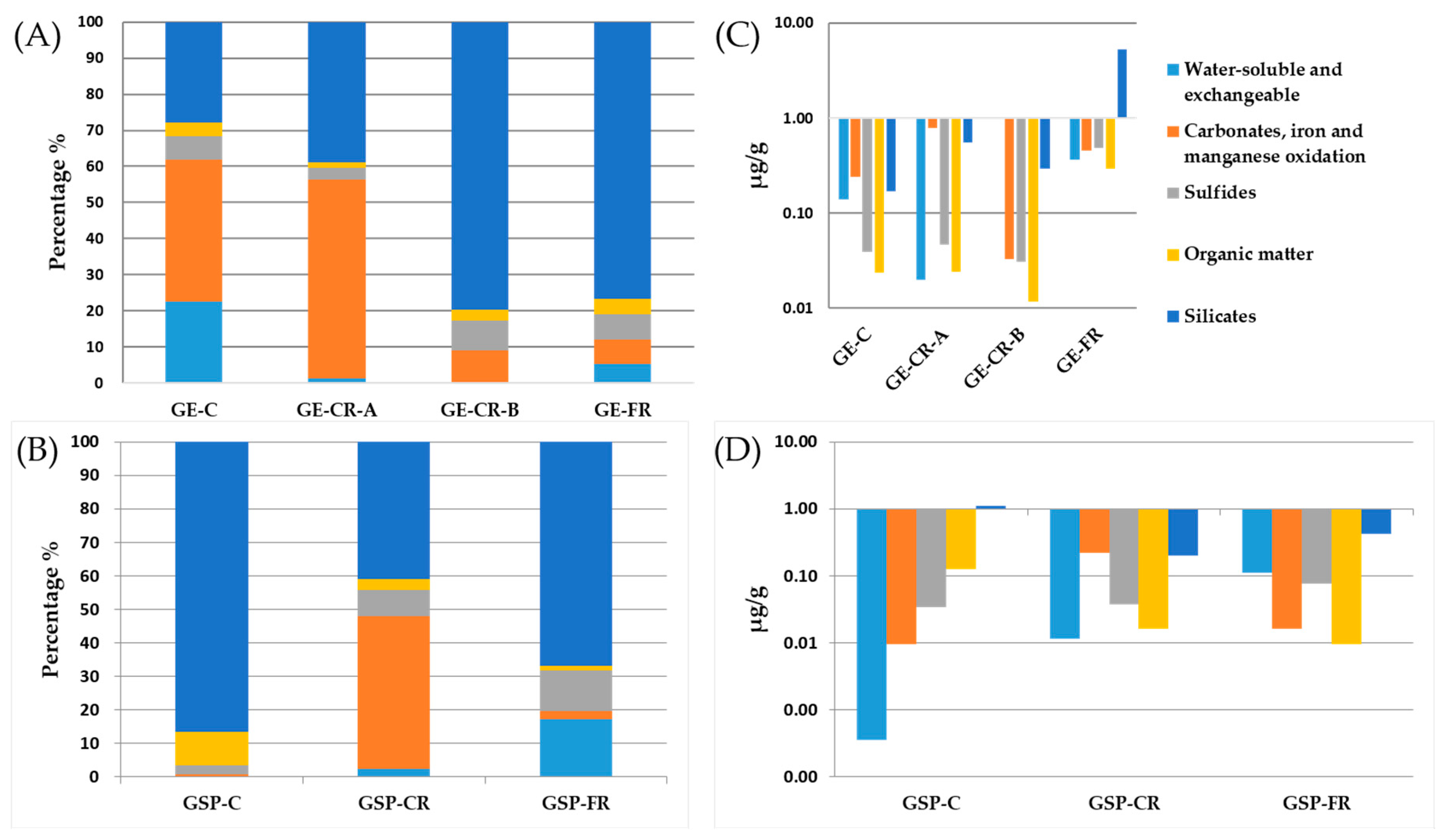

| Gasification Technology | Feed Coal | Gasification Residues | Feed Coal Mine | Status of Feed Coal | Gasification Agent | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GE1 | GE-C3 | GE-CR4-A | YCW 6 | CWS 8 | Oxygen | 1250 | 4.3 |
| GE-CR-B | |||||||
| GE-FR5 | |||||||
| GSP2 | GSP-C | GSP-CR | MHJ 7 | PC 9 | Oxygen + Steam | 1350–1450 | 3.8–4.0 |
| GSP-FR |
| Samples | Mad | Ad | V | FCd | St,d | Cdaf | Hdaf | Ndaf | Odaf * | Pdaf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GE-C | 5.34 | 10.1 | 32.44 a | 60.73 | 0.73 | 78.93 | 4.47 | 0.82 | 14.96 | 0.01 |
| GE-CR-A | 5.78 | 72.17 | 4.01 b | 23.82 | 0.55 | 95.87 | 0.29 | 0.68 | 1.15 | 0.06 |
| GE-CR-B | 5.91 | 49.84 | 6.21 b | 43.96 | 0.71 | 94.06 | 0.38 | 0.56 | 3.61 | 0.03 |
| GE-FR | 9.88 | 69.34 | 6.77 b | 23.89 | 1.08 | 92.14 | 0.36 | 0.59 | 3.39 | 0.12 |
| GSP-C | 6.9 | 16.24 | 35.88 a | 53.71 | 1.22 | 77.58 | 4.74 | 1.01 | 15.2 | 0.02 |
| GSP-CR | 0.07 | 96.97 | 1.06 b | 1.97 | 0.35 | 75.91 | 6.6 | 1.65 | 4.29 | 3.77 |
| GSP-FR | 2.26 | 67.12 | 2.72 b | 30.16 | 0.68 | 93.22 | 0.91 | 0.43 | 3.41 | 0.34 |
| Inorganic Matter | Feed Coal | Gasification Residues | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GE-C | GSP-C | GE-CR-A | GE-CR-B | GE-FR | GSP-CR | GSP-FR | |
| Quartz | 27.9 | 34.9 | 18.7 | 13.3 | 75.9 | 55.2 | 35.2 |
| Potassium feldspar | - | 3.2 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Plagioclase | - | 1.6 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Calcite | 6.4 | 1.4 | 12.6 | 40.4 | 9.8 | - | 45.1 |
| Siderite | 7 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pyrite | 5.4 | 1.6 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Clay minerals | 53.3 | 57.4 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gehlenite | - | - | 58.8 | 5.3 | 5.4 | - | - |
| Melilite | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - |
| Glass | - | - | 9.9 | 41 | 2.9 | 44.8 | 19.7 |
| TEs | Feed Coal | Gasification Residues | Coal [56] | Hard Coal Ash [57] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GE-C | GSP-C | GE-CR-A | GE-CR-B | GE-FR | GSP-CR | GSP-FR | |||
| Be | 1.04 | 1.63 | 2.61 | 3.47 | 5.09 | 7.07 | 4.32 | 2.11 | 12 ± 1 |
| V | 20.1 | 46 | 79.4 | 80.4 | 127 | 124 | 110 | 35.1 | 170 ± 10 |
| Cr | 9.1 | 21.7 | 81.1 | 67.5 | 83.4 | 72.4 | 58.6 | 15.4 | 120 ± 5 |
| Co | 2.66 | 5.23 | 21.5 | 19 | 33.8 | 24.5 | 26.7 | 7.08 | 37 ± 2 |
| Ni | 3.36 | 9.82 | 42.7 | 34.1 | 57.7 | 28.1 | 36.9 | 13.7 | 100 ± 5 |
| Cu | 35.5 | 310 | 44.7 | 47.4 | 74.3 | 38.7 | 82.6 | 17.5 | 110 ± 5 |
| Zn | 29 | 221 | 26 | 25.4 | 222 | 13.5 | 111 | 41.4 | 170 ± 10 |
| As | 0.655 | 0.633 | 2.47 | 4.7 | 31.4 | 1.64 | 5.62 | 3.79 | 46 ± 5 |
| Se | 0.105 | 0.031 | 0.32 | 0.508 | 6.86 | 0.085 | 0.76 | 2.47 | 10.0 ± 0.7 |
| Mo | 0.572 | 0.674 | 0.996 | 1.55 | 3.32 | 1.34 | 2.63 | 3.08 | 14 ± 1 |
| Cd | 0.041 | 0.101 | 0.128 | 0.07 | 1.65 | 0.212 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 1.2 ± 0.3 |
| Sb | 0.189 | 0.443 | 0.37 | 0.449 | 7.56 | 0.184 | 1.33 | 0.84 | 7.5 ± 0.6 |
| Ba | 388 | 457 | 1141 | 1140 | 1456 | 1902 | 984 | 159 | 980 ± 60 |
| Hg | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.163 | 0.87 ± 0.07 |
| Tl | 0.169 | 1.52 | 0.532 | 0.655 | 7.22 | 0.729 | 5.77 | 0.47 | 4.6 ± 0.4 |
| Pb | 8.94 | 27.6 | 8.95 | 7.31 | 206 | 3.52 | 48.6 | 15.1 | 55 ± 6 |
| U | 0.513 | 1.58 | 3.73 | 3.9 | 7.37 | 5.59 | 5.56 | 2.43 | 15 ± 1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.; Guo, X.; Pan, X.; Finkelman, R.B.; Wang, Y.; Huan, B.; Wang, S. Changes and Distribution of Modes of Occurrence of Seventeen Potentially-Hazardous Trace Elements during Entrained Flow Gasification of Coals from Ningdong, China. Minerals 2018, 8, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8050202
Tang Y, Guo X, Pan X, Finkelman RB, Wang Y, Huan B, Wang S. Changes and Distribution of Modes of Occurrence of Seventeen Potentially-Hazardous Trace Elements during Entrained Flow Gasification of Coals from Ningdong, China. Minerals. 2018; 8(5):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8050202
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yuegang, Xin Guo, Xi Pan, Robert B. Finkelman, Yafeng Wang, Binbin Huan, and Shaoqing Wang. 2018. "Changes and Distribution of Modes of Occurrence of Seventeen Potentially-Hazardous Trace Elements during Entrained Flow Gasification of Coals from Ningdong, China" Minerals 8, no. 5: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8050202
APA StyleTang, Y., Guo, X., Pan, X., Finkelman, R. B., Wang, Y., Huan, B., & Wang, S. (2018). Changes and Distribution of Modes of Occurrence of Seventeen Potentially-Hazardous Trace Elements during Entrained Flow Gasification of Coals from Ningdong, China. Minerals, 8(5), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8050202





