Trace Metal Distribution in Sulfide Minerals from Ultramafic-Hosted Hydrothermal Systems: Examples from the Kairei Vent Field, Central Indian Ridge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
3. Samples and Methods
4. Results
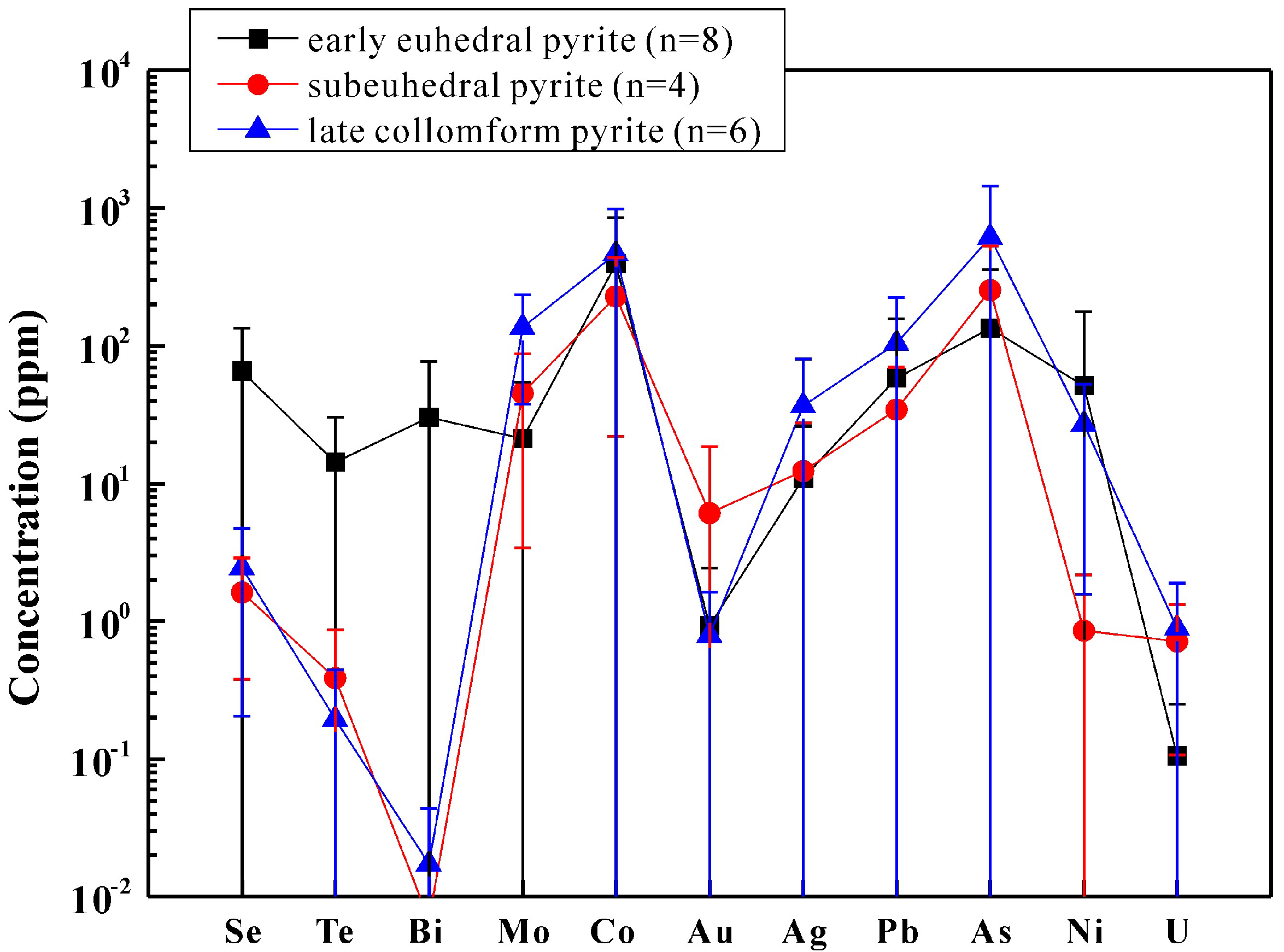
4.1. Pyrite
4.2. Chalcopyrite
4.3. Sphalerite
4.4. Bornite–Digenite Assemblage
4.5. Digenite–Covellite Assemblage
5. Discussion and Conclusions
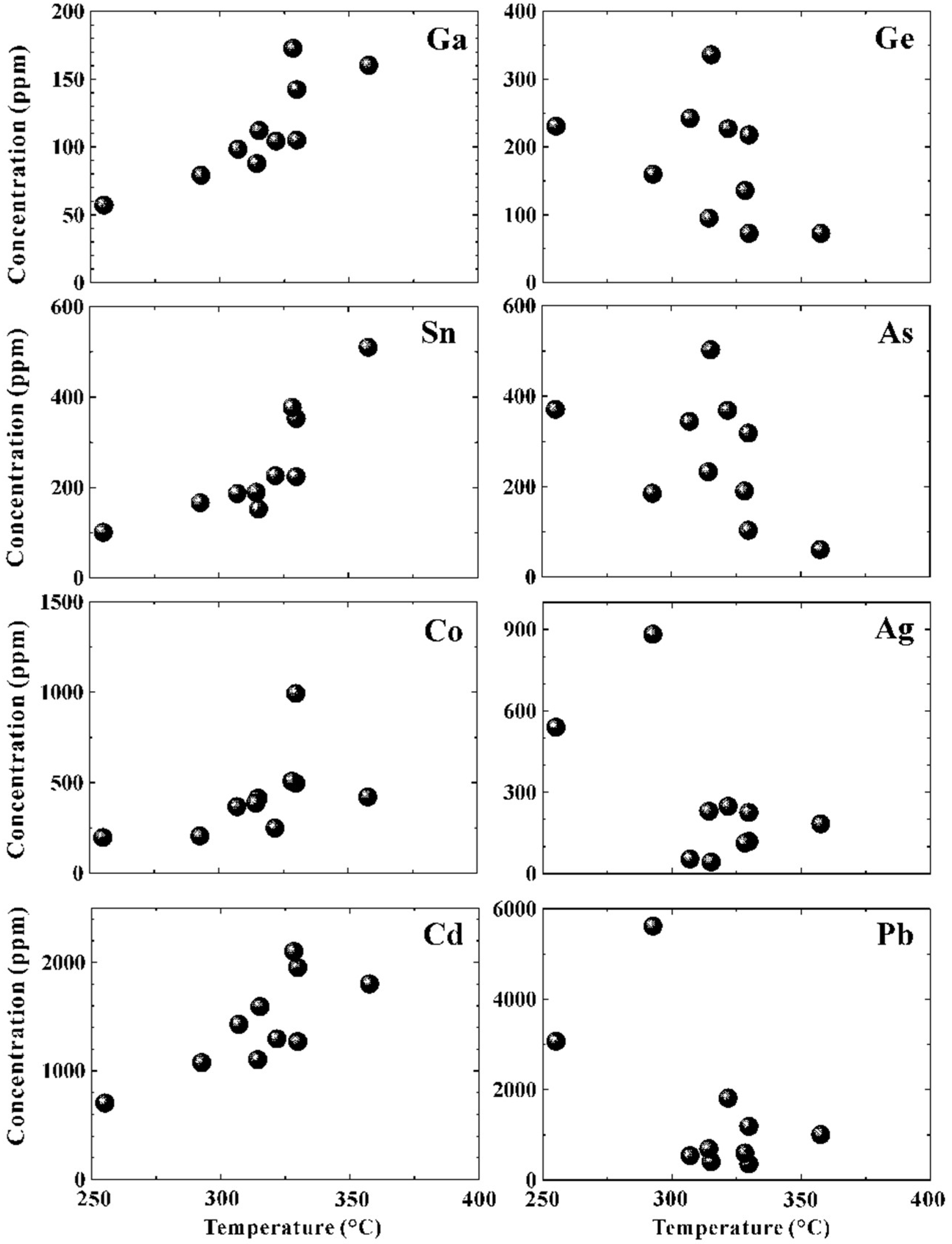
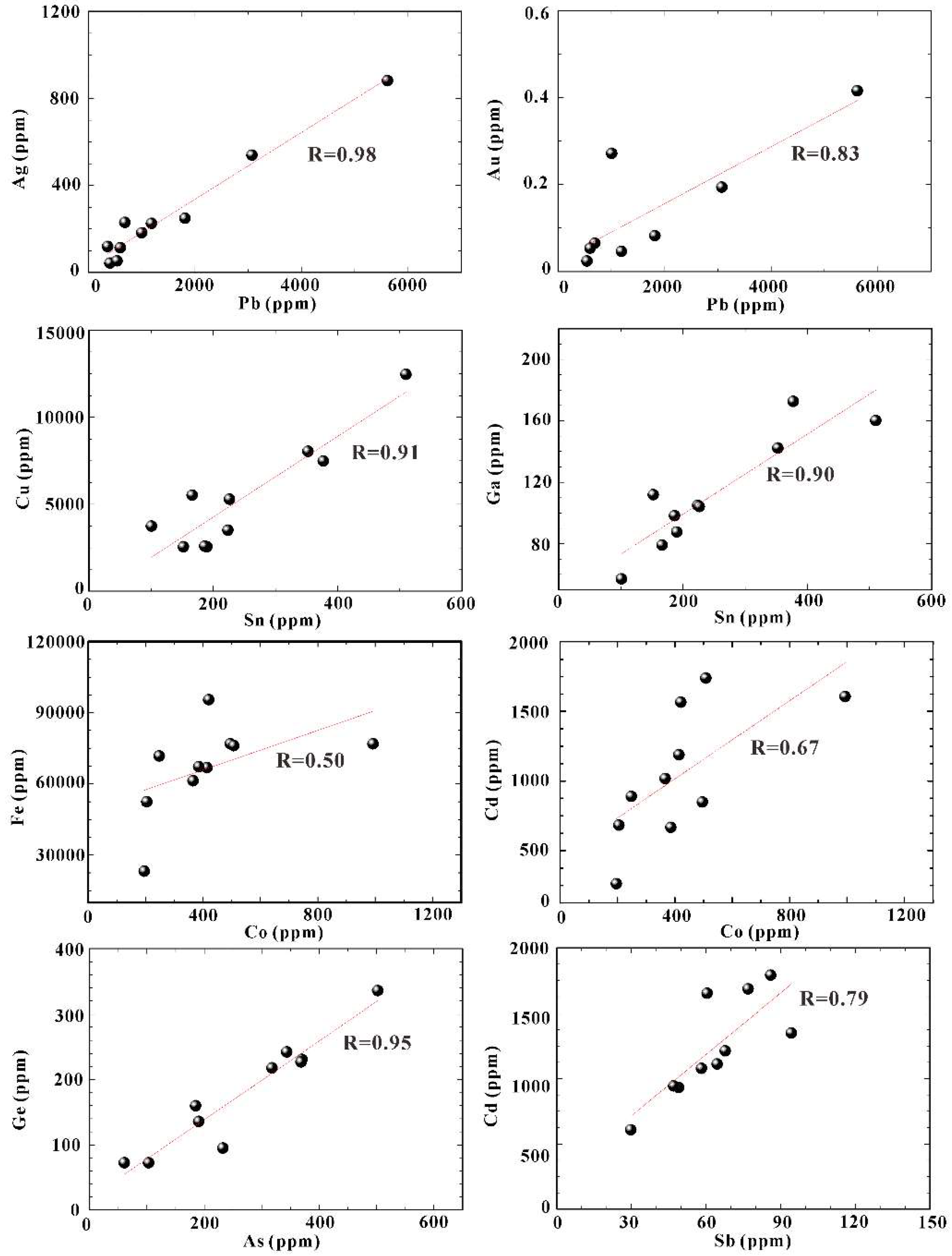
5.1. Controls on Trace Elements in Pyrite
5.2. Controls on Trace Elements in Chalcopyrite
5.3. Controls on Trace Elements in Sphalerite
5.4. Controls on Trace Elements in Bornite, Digenite, and Covellite
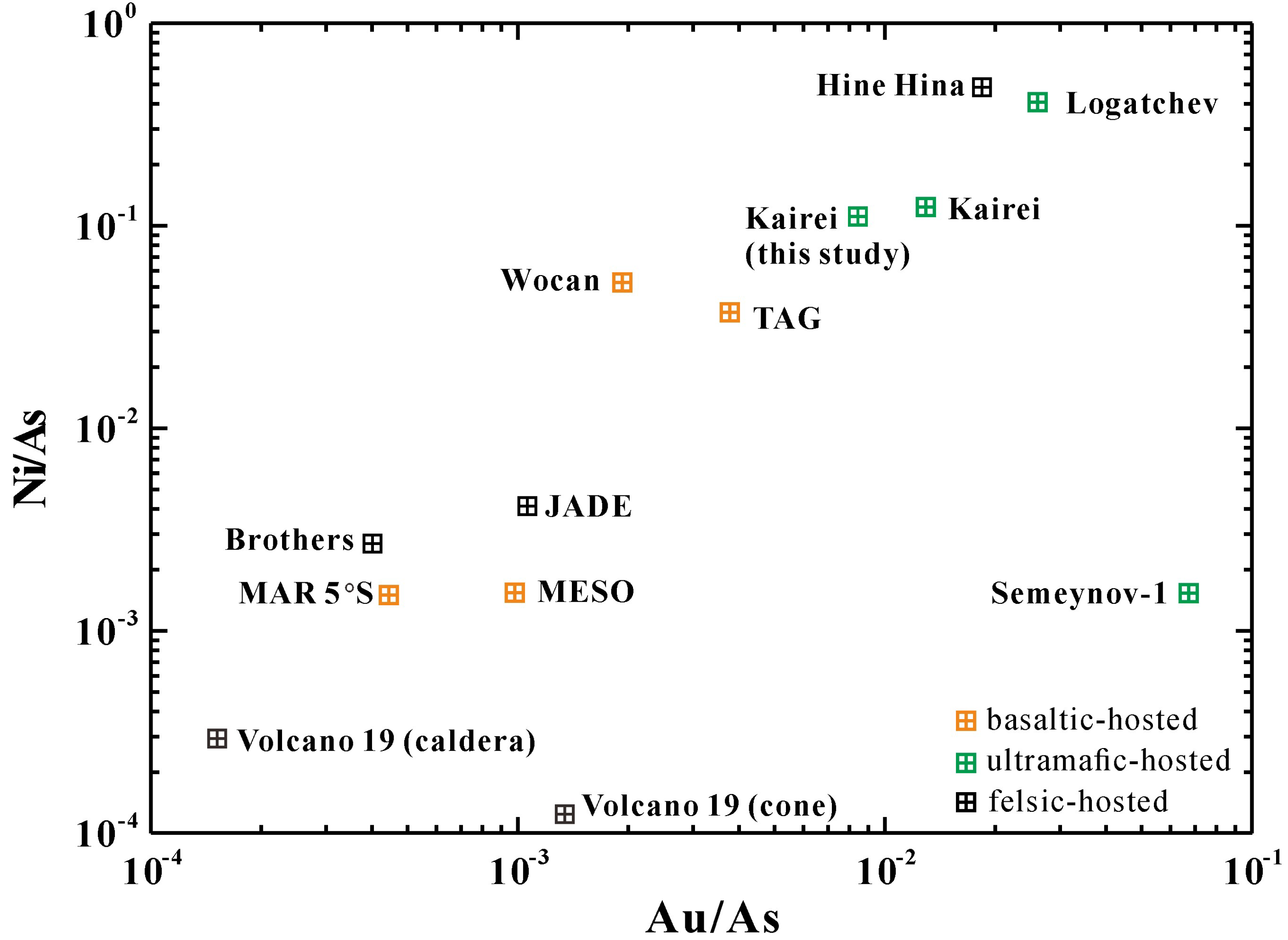
5.5. Comparison with Mafic- and Ultramafic-Hosted SMS Deposits
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hannington, M.D.; de Ronde, C.D.; Petersen, S. Sea-floor tectonics and submarine hydrothermal systems. Econ. Geol. 2005, 100, 111–141. [Google Scholar]
- Binns, R.A.; Scott, S.D. Actively forming polymetallic sulfide deposits associated with felsic volcanic rocks in the eastern Manus back-arc basin, Papua New Guinea. Econ. Geol. 1993, 88, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouquet, Y.; Pierre, C.; Etoubleau, J.; Charlou, J.L.; Ondréas, H.; Barriga, F.J.A.S.; Cherkashov, G.; Semkova, T.; Poroshina, I.; Bohn, M.; et al. Geodiversity of hydrothermal along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and ultramafic-hosted mineralization: A new type of oceanic Cu-Zn-Co-Au Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposit. In Diversity of Hydrothermal Systems on Slow Spreading Ocean Ridges; Rona, P.A., Devey, C.W., Dyment, J., Murton, B.J., Eds.; AGU: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 321–367. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Petersen, S.; Jin, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, J. Mineralogy and geochemistry of hydrothermal precipitates from Kairei hydrothermal field, Central Indian Ridge. Mar. Geol. 2014, 354, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Petersen, S.; Hannington, M.D. Hydrothermal exploration of mid-ocean ridges: Where might the largest sulfide deposits be forming? Chem. Geol. 2016, 420, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, T.; Petersen, S.; Hannington, M.D.; Grant, H.; Samson, I. The minor element endowment of modern sea-floor massive sulfides and comparison with deposits hosted in ancient volcanic successions. Rev. Econ. Geol. 2016, 18, 245–306. [Google Scholar]
- Hannington, M.D. Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 463–488. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, M.; Häckel, F.; Haase, K.M.; Schwarz-Schampera, U.; Klemd, R. Trace element systematics of pyrite from submarine hydrothermal vents. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 728–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontboté, L.; Kouzmanov, K.; Chiaradia, M.; Pokrovski, G.S. Sulfide Minerals in Hydrothermal Deposits. Elements 2017, 13, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, I.B.; Nesbitt, R.W. Trace element distributions in the chalcopyrite wall of a black smoker chimney: insights from laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 167, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lein, A.; Bogdanov, Y.; Maslennikov, V.; Li, S.; Ulyanova, N.; Maslennikova, S.; Ulyanov, A. Sulfide minerals in the Menez Gwen nonmetallic hydrothermal field (Mid-Atlantic Ridge). Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2010, 45, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Yuping, L.; Qian, Z.; Tiegeng, L.; Wei, G.; Yulong, Y.; Danyushevsky, L.V. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite from base metal deposits in South China: A LA-ICPMS study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 39, 188–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C.C.; Viljoen, F.; Petersen, S.; Vorster, C. Distribution and solubility limits of trace elements in hydrothermal black smoker sulfides: An in-situ LA-ICP-MS study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 159, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melekestseva, I.Y.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Tret’Yakov, G.A.; Nimis, P.; Beltenev, V.E.; Rozhdestvenskaya, I.I.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Belogub, E.V.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Large, R.R.; et al. Gold- and Silver-Rich Massive Sulfides from the Semenov-2 Hydrothermal Field, 13°31.13′N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge: A Case of Magmatic Contribution? Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 741–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Petersen, S.; Frische, M.; Qiu, Z.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Cui, R. Mineralogy and trace element geochemistry of sulfide minerals from the Wocan Hydrothermal Field on the slow-spreading Carlsberg Ridge, Indian Ocean. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 84, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamo, T.; Chiba, H.; Yamanaka, T.; Okudaira, T.; Hashimoto, J.; Tsuchida, S.; Ishibashi, J.; Kataoka, S.; Tsunogai, U.; Okamura, K.; et al. Chemical characteristics of newly discovered black smoker fluids and associated hydrothermal plumes at the Rodriguez Triple Junction, Central Indian Ridge. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 193, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dover, C.L.; Humphris, S.E.; Fornari, D.; Cavanaugh, C.M.; Collier, R.; Goffredi, S.K.; Hashimoto, J.; Lilley, M.D.; Reysenbach, A.L.; Shank, T.M.; et al. Biogeography and ecological setting of Indian Ocean hydrothermal vents. Science 2001, 294, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, H.; Nakamura, K.; Toki, T.; Morishita, T.; Okino, K.; Ishibashi, J.; Tsunogai, U.; Kawaguacci, S.; Gamo, T.; Shibuya, T.; et al. Geological background of the Kairei and Edmond hydrothermal fields along the Central Indian Ridge: Implications of their vent fluids’ distinct chemistry. Geofluids 2008, 8, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, R.M.; Von Damm, K.L. Geochemical controls on hydrothermal fluids from the Kairei and Edmond Vent Fields, 23°–25° S, Central Indian Ridge. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7, Q6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.S.; Karson, J.A.; Blackman, D.K.; Fruh-Green, G.L.; Butterfield, D.A.; Lilley, M.D.; Olson, E.J.; Schrenk, M.O.; Roe, K.K.; Lebon, G.T.; et al. An off-axis hydrothermal vent field near the Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 30°N. Nature 2001, 412, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douville, E.; Charlou, J.L.; Oelkers, E.H.; Bienvenu, P.; Jove Colon, C.F.; Donval, J.P.; Fouquet, Y.; Prieur, D.; Appriou, P. The rainbow vent fluids (36°14′N, MAR): The influence of ultramafic rocks and phase separation on trace metal content in Mid-Atlantic Ridge hydrothermal fluids. Chem. Geol. 2002, 184, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlou, J.L.; Donval, J.P.; Fouquet, Y.; Jean-Baptiste, P.; Holm, N. Geochemistry of high H2 and CH4 vent fluids issuing from ultramafic rocks at the Rainbow hydrothermal field (36°14′ N, MAR). Chem. Geol. 2002, 191, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlou, J.L.; Donval, J.P.; Konn, C.; Ondréas, H.; Fouquet, Y. High production and fluxes of H2 and CH4 and evidence of abiotic hydrocarbon synthesis by serpentinization in ultramafic-hosted hydrothermal systems on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. In Diversity of Hydrothermal Systems on Slow Spreading Ocean Ridges; Rona, P.A., Devey, C.W., Dyment, J., Murton, B.J., Eds.; AGU: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 265–296. [Google Scholar]
- Melchert, B.; Devey, C.W.; German, C.R.; Lackschewitz, K.S.; Seifert, R.; Walter, M.; Mertens, C.; Yoerger, D.R.; Baker, E.T.; Paulick, H.; et al. First evidence for high-temperature off-axis venting of deep crustal/mantle heat: The Nibelungen hydrothermal field, southern Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 275, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Morishita, T.; Bach, W.; Klein, F.; Hara, K.; Okino, K.; Takai, K.; Kumagai, H. Serpentinized troctolites exposed near the Kairei Hydrothermal Field, Central Indian Ridge: Insights into the origin of the Kairei hydrothermal fluid supporting a unique microbial ecosystem. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 280, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Okino, K.; Sato, T.; Sato, H.; Nakamura, K. Origin of magnetic highs at ultramafic hosted hydrothermal systems: Insights from the Yokoniwa site of Central Indian Ridge. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 441, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, T.; Hara, K.; Nakamura, K.; Sawaguchi, T.; Tamura, A.; Arai, S.; Okino, K.; Takai, K.; Kumagai, H. Igneous, alteration and exhumation processes recorded in abyssal peridotites and related fault rocks from an oceanic core complex along the Central Indian Ridge. J. Petrol. 2009, 50, 1299–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, K.; Nakamura, K.; Sato, H. Tectonic background of four hydrothermal fields along the Central Indian Ridge. In Subseafloor Biosphere Linked to Hydrothermal Systems: TAIGA Concept; Ishibashi, J., Okino, K., Sunamura, M., Eds.; Springer Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; pp. 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, W.B.F.; Carbotte, S.M.; Coplan, J.O.; O’Hara, S.; Melkonian, A.; Arko, R.; Weissel, R.A.; Ferrini, V.; Goodwillie, A.; Nitsche, F.; et al. Global Multi-Resolution Topography synthesis. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2009, 10, Q03014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Jin, X.; Qiu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Yang, H. Hydrothermal activity events at Kairei Field, Central Indian Ridge 25° S. Resour. Geol. 2012, 62, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, S.; Watters, R. Certificate of Analysis, Standard Reference Material 610; National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C.C.; McClung, C.R.; Viljoen, F. Metamorphic alteration of the massive sulfide horizon from the Salt River VMS deposit (South Africa). Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, K.P.; Stoll, B.; Herwig, K.; Willbold, M.; Hofmann, A.W.; Amini, M.; Aarburg, S.; Abouchami, W.; Hellebrand, E.; Mocek, B.; et al. MPI-DING reference glasses for in situ microanalysis: New reference values for element concentrations and isotope ratios. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7, Q02008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietzke, J.; Frische, M. Experimental evaluation of elemental behavior during LA-ICP-MS: influences of plasma conditions and limits of plasma robustness. J. Anal. At Spectrom. 2016, 31, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietzke, J.; Liebetrau, V.; Guenther, D.; Guers, K.; Hametner, K.; Zumholz, K.; Hansteen, T.H.; Eisenhauer, A. An alternative data acquisition and evaluation strategy for improved isotope ratio precision using LA-MC-ICP-MS applied to stable and radiogenic strontium isotopes in carbonates. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2008, 23, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivey, M.K.; Humphris, S.E.; Thompson, G.; Hannington, M.D.; Rona, P.A. Deducing patterns of fluid flow and mixing within the TAG active hydrothermal mound using mineralogical and geochemical data. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 12527–12555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, P.M.; Hannington, M.D.; Arribas, A., Jr. Sulfur isotopic composition of hydrothermal precipitates from the Lau back-arc: implications for magmatic contributions to seafloor hydrothermal systems. Miner. Depos. 1998, 33, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ronde, C.; Massoth, G.; Butterfield, D.; Christenson, B.; Ishibashi, J.; Ditchburn, R.; Hannington, M.; Brathwaite, R.; Lupton, J.; Kamenetsky, V.; et al. Submarine hydrothermal activity and gold-rich mineralization at Brothers Volcano, Kermadec Arc, New Zealand. Miner. Depos. 2011, 46, 541–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.J.; Rosso, K.M. Chemical bonding in sulfide minerals. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2006, 61, 231–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, A.; Paquette, J.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Crystallographic controls on trace-element incorporation in auriferous pyrite from the Pascua epithermal high-sulfidation deposit, Chile-Argentina. Can. Mineral. 2005, 43, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, M.; Alfredsson, M.; Brodholt, J.P.; Wright, K.; Catlow, C.R.A. Arsenic incorporation into FeS2 pyrite and its influence on dissolution: A DFT study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikov, V.V.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Large, R.R.; Danyushevsky, L.V. Study of trace element zonation in vent chimneys from the Silurian Yaman-Kasy volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposit (Southern Urals, Russia) using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS). Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 1111–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revan, M.K.; Genç, Y.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Large, R.R.; Danyushevsky, L.V. Mineralogy and trace-element geochemistry of sulfide minerals in hydrothermal chimneys from the Upper-Cretaceous VMS deposits of the eastern Pontide orogenic belt (NE Turkey). Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Koschinsky, A.; Garbe-Schönberg, D.; De Carvalho, L.M.; Seifert, R. Geochemistry of hydrothermal fluids from the ultramafic-hosted Logatchev hydrothermal field, 15°N on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: Temporal and spatial investigation. Chem. Geol. 2007, 242, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, W.E.; Ding, K. Phase equilibria in subseafloor hydrothermal systems: A review of the role of redox, temperature, pH and dissolved Cl on the chemistry of hot spring fluids at Mid-Ocean Ridges. In Seafloor Hydrothermal Systems, Physical, Chemical, Biological, and Geological Interactions; Humphris, S.R., Zierenberg, R.A., Mullineaux, L.S., Thomson, R.E., Eds.; AGU: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 248–272. [Google Scholar]
- Melekestseva, I.Y.; Tret’Yakov, G.A.; Nimis, P.; Yuminov, A.M.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Kotlyarov, V.A.; Beltenev, V.E.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Large, R.R. Barite-rich massive sulfides from the Semenov-1 hydrothermal field (Mid-Atlantic Ridge, 13°30.87´ N): Evidence for phase separation and magmatic input. Mar. Geol. 2014, 349, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melekestseva, I.Y.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Large, R. Covellite of the Semenov-2 hydrothermal field (13°31.13′ N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge): Enrichment in trace elements according to LA ICP MS analysis. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2017, 473, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, R.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical variations and regional diversity observed in MORB. Chem. Geol. 2010, 271, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, G.; Fouquet, Y.; Bohn, M. Distribution of selenium in high-temperature hydrothermal sulfide deposits at 13° North, East Pacific Rise. Can. Mineral. 1987, 25, 577–587. [Google Scholar]
- Hannington, M.D.; Herzig, P.M.; Scott, S.D.; Thompson, G.; Rona, P.A. Comparative mineralogy and geochemistry of gold-bearing sulfide deposits on the mid-ocean ridges. Mar. Geol. 1991, 101, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbach, P.; Fouquet, Y.; Herzig, P. Mineralization and compositional patterns in deep-sea hydrothermal systems. In Energy and mass transfer in marine hydrothermal systems; Tunnicliffe, V., Hein, J.R., Eds.; Dahlem University Press: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 85–122. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Mao, J. Textural control on gold distribution in As-free pyrite from the Dongping, Huangtuliang and Hougou gold deposits, North China Craton (Hebei Province, China). Chem. Geol. 2009, 264, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, M.; Haase, K.M.; Schwarz-Schampera, U.; Klemd, R.; Petersen, S.; Bach, W. Effects of temperature, sulfur, and oxygen fugacity on the composition of sphalerite from submarine hydrothermal vents. Geology 2014, 42, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, K.M.; Vaughan, D.J. Sulfide Mineral Surfaces. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2006, 61, 505–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgova, N.N.; Trubkin, N.V.; Borodaev, Y.S.; Cherkashev, G.A.; Stepanova, T.V.; Semkova, T.A.; Uspenskaya, T.Y. Mineralogy of massive sulfides from the Ashadze hydrothermal field, 13°N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Can. Mineral. 2008, 46, 545–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Gilbert, S. Minor and trace elements in bornite and associated Cu–(Fe)-sulfides: A LA-ICP-MS study Bornite mineral chemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 6473–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, J.L.; Shanks, W.C., III; Seyfried, W.E., Jr. Massive sulfide deposition and trace element remobilization in the Middle Valley sediment-hosted hydrothermal system, northern Juan de Fuca Ridge. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2863–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melekestseva, I.Y.; Zaykov, V.V.; Nimis, P.; Tret’Yakov, G.A.; Tessalina, S.G. Cu–(Ni–Co–Au)-bearing massive sulfide deposits associated with mafic–ultramafic rocks of the Main Urals Fault, South Urals: Geological structures, ore textural and mineralogical features, comparison with modern analogs. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 52, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salters, V.J.M.; Stracke, A. Composition of the depleted mantle. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2004, 5, Q5B–Q7B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.M.; Klein, E.M. Composition of the Oceanic Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 457–496. [Google Scholar]
- Hannington, M.D.; Tivey, M.K.; Larocque, A.C.L.; Petersen, S.; Rona, P.A. The occurrence of gold in sulfide deposits of the TAG hydrothermal field, Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Can. Mineral. 1995, 33, 1285–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanov, Y.A.; Lein, A.; Maslennikov, V.; Li, S.; Ul’yanov, A. Mineralogical-geochemical features of sulfide ores from the Broken Spur hydrothermal vent field. Oceanology 2008, 48, 679–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

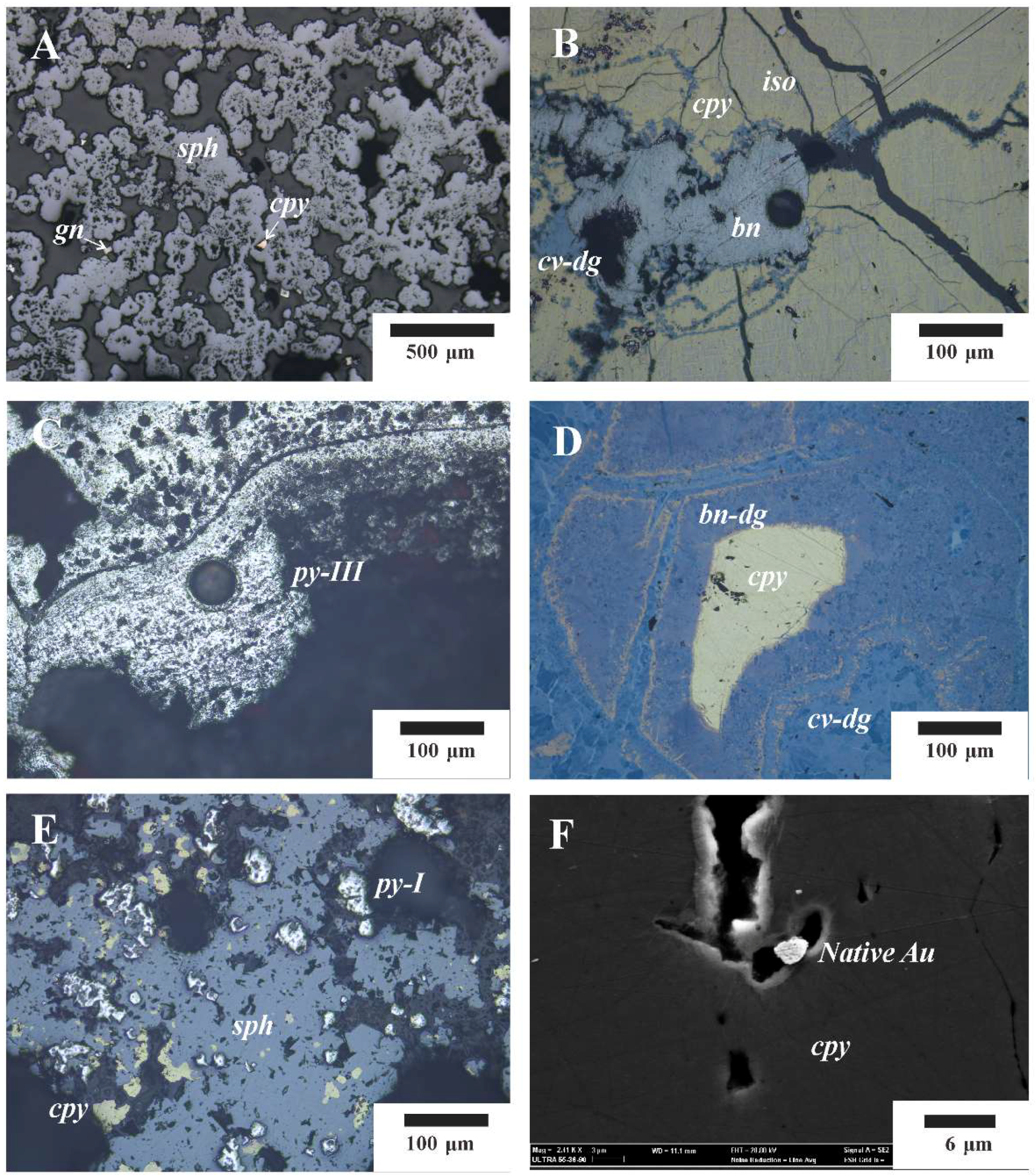
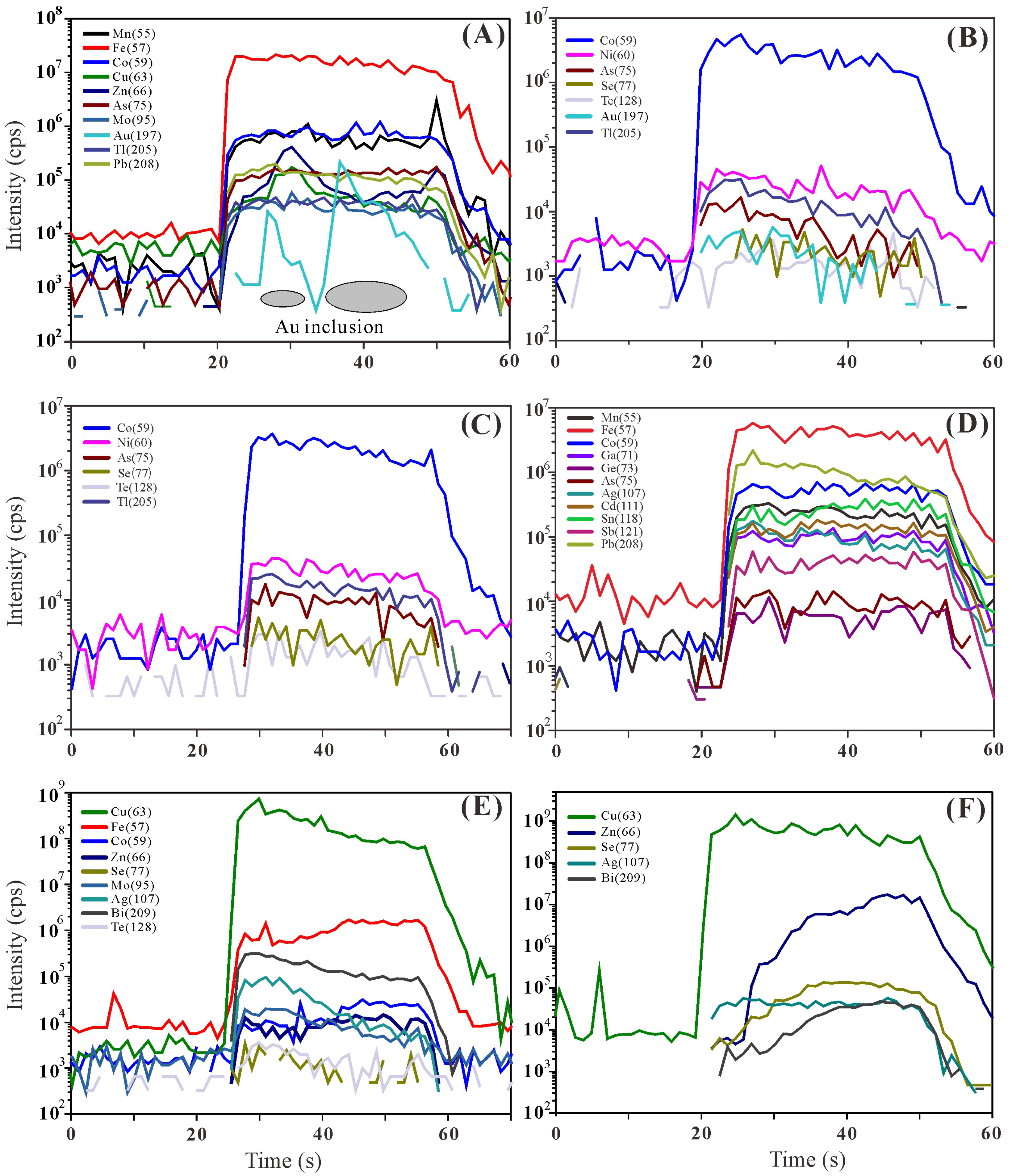
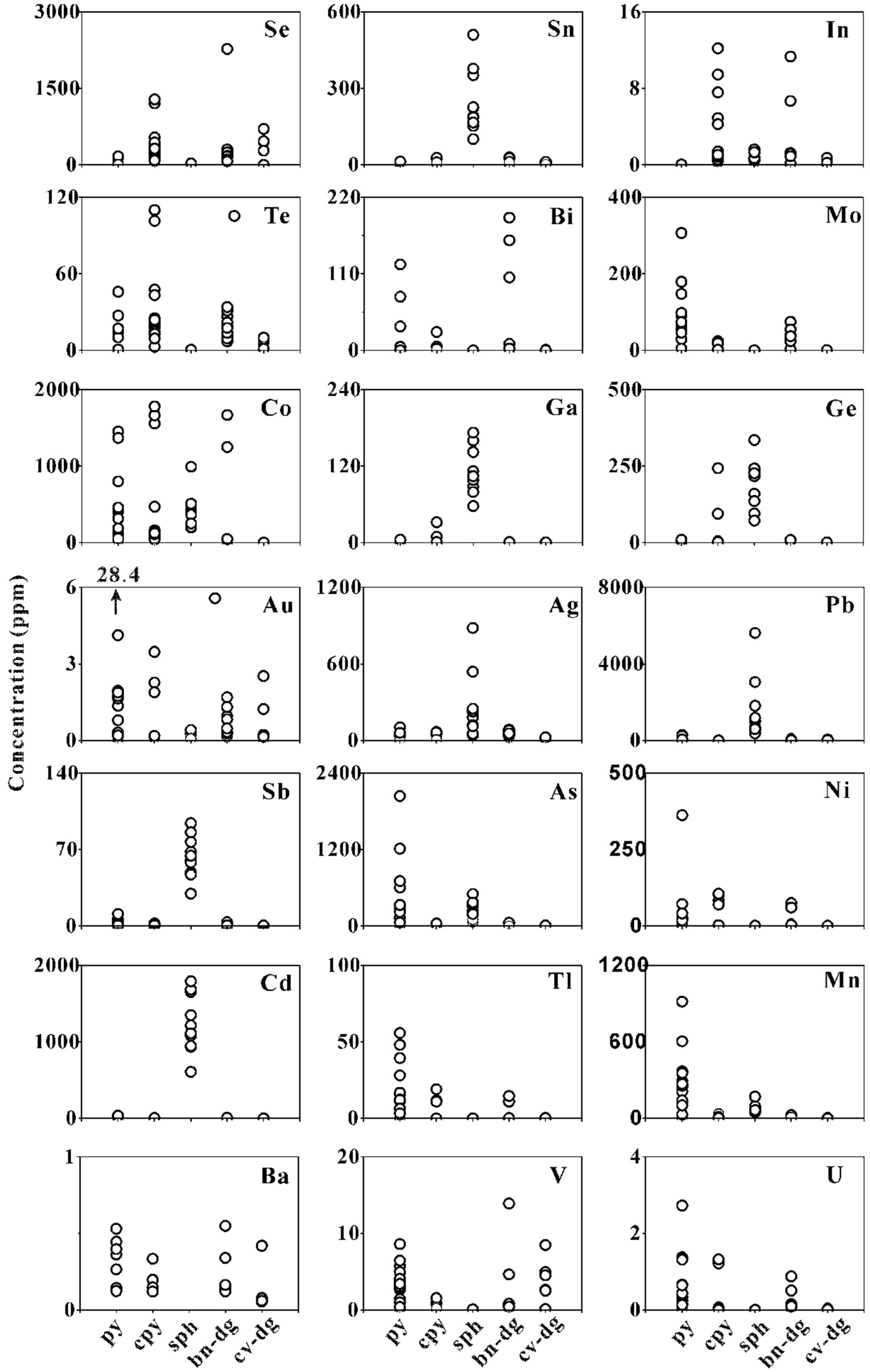
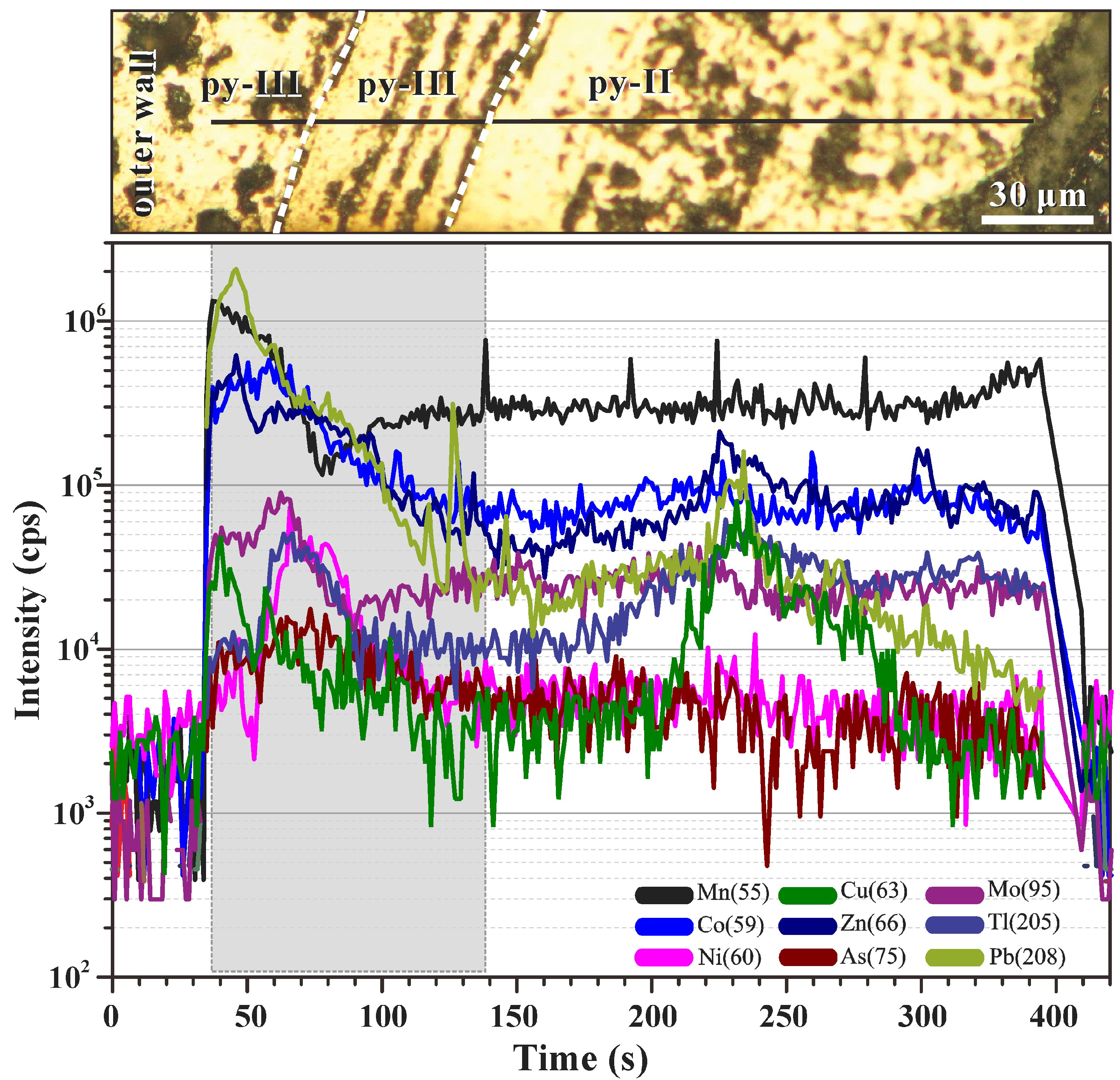

| Sampling Station | Longitude (E) | Latitude (S) | Depth (m) | Type of Samples | Mineral Assemblage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17A-TVG7-1 | 70°02.408′ | 25°19.252′ | 2430 | Cu-rich massive sulfides | cpy+bn+dg+py+(sph+iso+cv+id) |
| 17A-TVG7-3 | 70°02.408′ | 25°19.252′ | 2430 | Breccias | q+opal-A+tl+sph+py |
| 17A-TVG9 | 70°02.420′ | 25°19.221′ | 2437 | Zn-rich chimney | sph+py+mar+cpy |
| 19III-TVG6 | 70°02.440′ | 25°19.230′ | 2443 | Cu-rich massive sulfides | cpy+dg+bn+cv+py+iso+id |
| 19III-TVG7 | 70°02.410′ | 25°19.220′ | 2440 | Cu-rich massive sulfides | cpy+dg+bn+cv+py+id |
| Mineral | ppm (n) | Se | Sn | Te | Bi | Mo | Co | Ga | Ge | Au | Ag | Pb | Sb | As | Ni | Cd | Tl | Mn | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| py all | avg.(19) | 28.7 | 1.54 | 6.19 | 12.8 | 64.0 | 374 | 0.50 | 1.97 | 2.26 | 19.5 | 66.7 | 1.79 | 318 | 30.5 | 5.44 | 13.5 | 213 | 0.52 |
| SD | 53.6 | 3.15 | 12.3 | 32.7 | 78.4 | 416 | 1.17 | 2.81 | 6.42 | 28.5 | 93.7 | 2.71 | 525 | 82.5 | 8.73 | 17.2 | 235 | 0.71 | |
| py-I | avg.(8) | 65.3 | 1.37 | 14.3 | 30.4 | 21.4 | 395 | 0.47 | 1.92 | 0.93 | 11.0 | 58.4 | 0.72 | 135 | 51.4 | 4.08 | 5.52 | 64.1 | 0.11 |
| SD | 68.8 | 2.24 | 16.1 | 46.3 | 33.2 | 452 | 0.94 | 2.71 | 1.50 | 15.1 | 98.3 | 1.06 | 224 | 126 | 7.87 | 7.65 | 102 | 0.14 | |
| py-II | avg.(5) | 1.63 | 0.57 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 45.7 | 230 | 0.24 | 1.73 | 6.13 | 12.4 | 34.6 | 1.41 | 254 | 0.86 | 2.27 | 27.2 | 387 | 0.72 |
| SD | 1.25 | 0.59 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 42.2 | 208 | 0.41 | 1.94 | 12.5 | 15.1 | 35.4 | 1.18 | 277 | 1.32 | 1.84 | 25.1 | 311 | 0.61 | |
| py-III | avg.(6) | 2.47 | 2.57 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 136 | 466 | 0.76 | 2.24 | 0.79 | 36.8 | 105 | 3.53 | 614 | 27.2 | 9.88 | 12.7 | 266 | 0.90 |
| SD | 2.26 | 5.11 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 98.3 | 520 | 1.80 | 3.88 | 0.84 | 43.5 | 119 | 4.26 | 836 | 25.6 | 12.2 | 13.7 | 193 | 0.99 | |
| cpy | avg.(16) | 363 | 10.2 | 29.7 | 2.77 | 4.08 | 445 | 3.05 | 22.8 | 0.50 | 14.0 | 4.7 | 0.31 | 8.6 | 23.3 | 3.61 | 2.61 | 11.2 | 0.25 |
| SD | 369 | 7.3 | 32.5 | 6.44 | 8.0 | 621 | 8.07 | 63.2 | 1.06 | 22.7 | 9.4 | 0.62 | 17.8 | 40.9 | 2.74 | 5.84 | 11.9 | 0.50 | |
| sph | avg.(10) | 21.3 | 248 | 0.26 | 0.05 | b.d.l. | 423 | 112 | 179 | 0.12 | 264 | 1529 | 63.4 | 267 | 1237 | 0.06 | 80.2 | b.d.l. | |
| SD | 3.04 | 126 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 229 | 36.3 | 86.3 | 0.14 | 259 | 1657 | 19.2 | 137 | 381 | 0.12 | 34.2 | ||||
| bn–dg | avg.(10) | 372 | 11.3 | 19.2 | 47.1 | 23.4 | 301 | 0.49 | 1.66 | 0.64 | 52.0 | 23.8 | 0.74 | 16.9 | 14.7 | 3.27 | 2.63 | 13.4 | 0.19 |
| SD | 671 | 9.55 | 9.19 | 74.8 | 26.8 | 619 | 0.36 | 2.68 | 0.54 | 23.3 | 32.1 | 1.01 | 23.3 | 28.2 | 3.77 | 5.46 | 10.1 | 0.28 | |
| cv–dg | avg.(9) | 211 | 1.94 | 2.53 | 0.24 | b.d.l. | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.49 | 14.92 | 6.6 | 0.09 | 1.12 | 0.16 | 0.99 | 0.02 | 2.62 | 0.01 |
| SD | 260 | 3.61 | 3.51 | 0.48 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.81 | 10.51 | 14.5 | 0.15 | 2.74 | 0.42 | 1.70 | 0.04 | 3.18 | 0.02 |
| Region | Vent Field | Hosted Rock | Minerals | n | Co | Ni | As | Se | Sb | Te | Au | Source * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Indian Ridge | Kairei | Ultramafic | py | 19 | 374 | 30.5 | 318 | 28.7 | 1.79 | 6.19 | 2.26 | 1 |
| Kairei | Ultramafic | cpy | 16 | 445 | 23.3 | 8.6 | 363 | 0.31 | 29.7 | 0.50 | 1 | |
| Kairei | Ultramafic | sph | 10 | 423 | 267 | 21.3 | 63.4 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 1 | ||
| Kairei | Ultramafic | bn-dg | 10 | 301 | 14.7 | 16.9 | 372 | 1.06 | 19.2 | 0.64 | 1 | |
| Kairei | Ultramafic | cv-dg | 9 | 0.33 | 0.16 | 1.12 | 211 | 0.09 | 2.52 | 0.49 | 1 | |
| Kairei | Ultramafic | py | 39 | 279 | 22.2 | 179 | 9.49 | 1.89 | 2.31 | 2 | ||
| MESO | Basaltic | py | 77 | 392 | 1.41 | 909 | 745 | 9.21 | 0.89 | 2 | ||
| Carlsberg Ridge | Wocan | Basaltic | py | 19 | 110 | 11.8 | 224 | 36.4 | 3.91 | 1.40 | 0.43 | 3 |
| Wocan | Basaltic | dg | 11 | 0.09 | 1.51 | 16.6 | 0.90 | 2.96 | 0.10 | 0.56 | 3 | |
| Wocan | Basaltic | bn | 11 | 0.11 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 2.54 | 5.17 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 3 | |
| Wocan | Basaltic | sph | 17 | 0.06 | 0.15 | 726 | 0.37 | 86.0 | 0.20 | 0.42 | 3 | |
| Wocan | Basaltic | cpy | 22 | 0.11 | 0.41 | 235 | 52.4 | 23.0 | 0.88 | 0.49 | 3 | |
| Mid-Atlantic Ridge | Logatchev | Ultramafic | py | 34 | 102 | 19.3 | 47.2 | 9.56 | 12.2 | 1.23 | 2 | |
| Logatchev | Ultramafic | cc | 15 | 42.5 | 87.9 | 17.8 | 4.40 | 4.92 | 4 | |||
| Logatchev | Ultramafic | cpy | 29 | 92.4 | 119 | 22.0 | 39.2 | 3.12 | 4 | |||
| Logatchev | Ultramafic | cc-cv | 12 | 6.75 | bdl | 1.38 | 7.30 | 0.55 | 4 | |||
| Logatchev | Ultramafic | py | 23 | 326 | 15.5 | 11.2 | 0.58 | 4.18 | 4 | |||
| Logatchev | Ultramafic | sph | 10 | 214 | 1.68 | 233 | 0.73 | 3.73 | 4 | |||
| Semeynov-1 | Ultramafic | py | 21 | 2.07 | 0.81 | 510 | 9.20 | 0.51 | 33.1 | 5 | ||
| Semeynov-2 | Ultramafic | cpy | 5 | 340 | 13.0 | 1144 | 288 | 25.0 | 42.0 | 0.15 | 6 | |
| Semeynov-2 | Ultramafic | sph-wurt | 6 | 84.0 | 0.20 | 424 | 129 | 214 | 8.51 | 3.00 | 6 | |
| Semeynov-2 | Ultramafic | cv-A | 8 | 21.0 | 3.00 | 421 | 1024 | 579 | 97.0 | 173 | 6 | |
| Semeynov-2 | Ultramafic | cv-B | 3 | 9.00 | 1.00 | 82.0 | 222 | 81.0 | 48.0 | 72.0 | 6 | |
| Turtle Pits | Basaltic | cpy | 15 | 37.9 | 204 | 0.46 | 4.73 | 0.06 | 4 | |||
| Turtle Pits | Basaltic | py | 40 | 224 | 25.2 | 4.94 | 1.20 | 0.25 | 4 | |||
| Turtle Pits | Basaltic | sph | 20 | 147 | 28.2 | 47.9 | 0.62 | 0.36 | 4 | |||
| TAG | Basaltic | py | 61 | 269 | 2.28 | 60.9 | 43.4 | 1.55 | 0.23 | 2 | ||
| 5°S | Basaltic | py | 34 | 602 | 1.12 | 742 | 30.1 | 4.57 | 0.33 | 2 | ||
| Valu Fa Ridge | Hine Hina | Basaltic–andesitic | py | 65 | 144 | 16.0 | 33.2 | 26.5 | 1.50 | 0.61 | 2 | |
| Okinawa Though | Jade | Basaltic–rhyolitic | py | 39 | 2.22 | 2.84 | 688 | 44.9 | 18.0 | 0.73 | 2 | |
| Kermadec Arc | Brothers | Dacitic | py | 77 | 210 | 2.42 | 896 | 481 | 2.97 | 0.36 | 2 | |
| Tonga Arc | Volcano 19 (cone) | Basaltic-basaltic andesitic | py | 114 | 16.1 | 1.13 | 9100 | 11.0 | 34.3 | 12.2 | 2 | |
| Volcano 19 (caldera) | Basaltic-basaltic andesitic | py | 76 | 0.80 | 3.01 | 10240 | 623 | 1.55 | 2 | |||
| Manus Basin | PacManus-RR | Basaltic–rhyolitic | py | 58 | 2635 | 7.39 | 188 | 1.10 | 7.71 | 4 | ||
| PacManus-RR | Basaltic–rhyolitic | cpy | 75 | 470 | 23.5 | 84.5 | 0.32 | 4.84 | 4 | |||
| PacManus-RR | Basaltic–rhyolitic | sph | 52 | 1664 | 3.57 | 1576 | 0.02 | 43.3 | 4 | |||
| PacManus-SM | Basaltic–rhyolitic | cc | 5 | 749 | 304 | 0.69 | 4.16 | 4 | ||||
| PacManus-SM | Basaltic–rhyolitic | cpy | 25 | 15237 | 1.39 | 875 | 1.66 | 4.99 | 4 | |||
| PacManus-SM | Basaltic–rhyolitic | py | 5 | 5390 | 5.97 | 29.4 | 8.16 | 4 | ||||
| PacManus-SM | Basaltic–rhyolitic | sph | 6 | 17269 | 9.42 | 167 | 2.45 | 4 | ||||
| MORB | 56 | 200 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 14 × 10−3 | 4.9 × 10−3 | 1.2 × 10−3 | 7 | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Petersen, S.; Frische, M.; Qiu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, P. Trace Metal Distribution in Sulfide Minerals from Ultramafic-Hosted Hydrothermal Systems: Examples from the Kairei Vent Field, Central Indian Ridge. Minerals 2018, 8, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110526
Wang Y, Han X, Petersen S, Frische M, Qiu Z, Cai Y, Zhou P. Trace Metal Distribution in Sulfide Minerals from Ultramafic-Hosted Hydrothermal Systems: Examples from the Kairei Vent Field, Central Indian Ridge. Minerals. 2018; 8(11):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110526
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yejian, Xiqiu Han, Sven Petersen, Matthias Frische, Zhongyan Qiu, Yiyang Cai, and Peng Zhou. 2018. "Trace Metal Distribution in Sulfide Minerals from Ultramafic-Hosted Hydrothermal Systems: Examples from the Kairei Vent Field, Central Indian Ridge" Minerals 8, no. 11: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110526
APA StyleWang, Y., Han, X., Petersen, S., Frische, M., Qiu, Z., Cai, Y., & Zhou, P. (2018). Trace Metal Distribution in Sulfide Minerals from Ultramafic-Hosted Hydrothermal Systems: Examples from the Kairei Vent Field, Central Indian Ridge. Minerals, 8(11), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110526





