Authigenic and Detrital Minerals in Peat Environment of Vasyugan Swamp, Western Siberia †
Abstract
1. Introduction
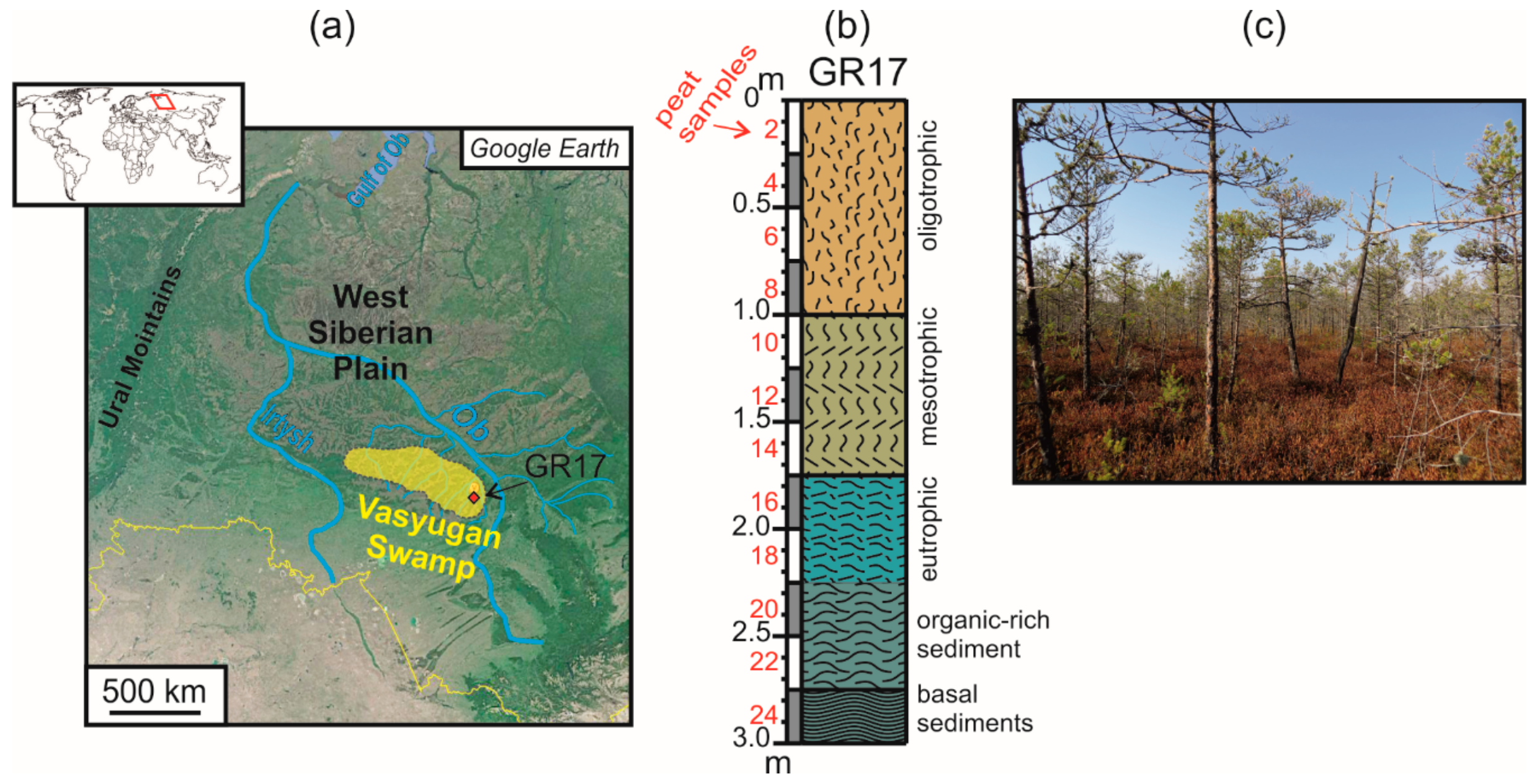
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
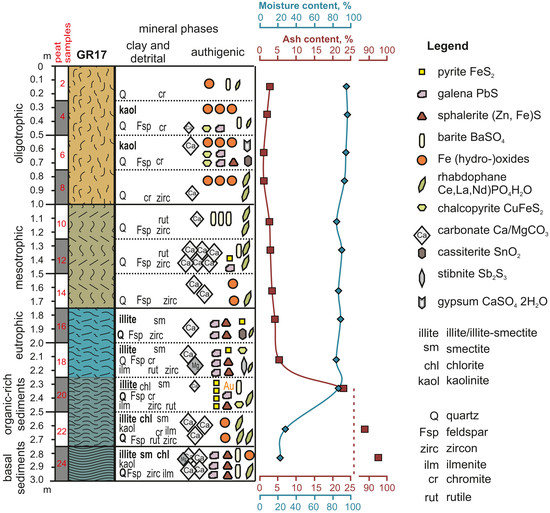
3.1. Bulk Mineral Composition of Peat Inorganic Fraction
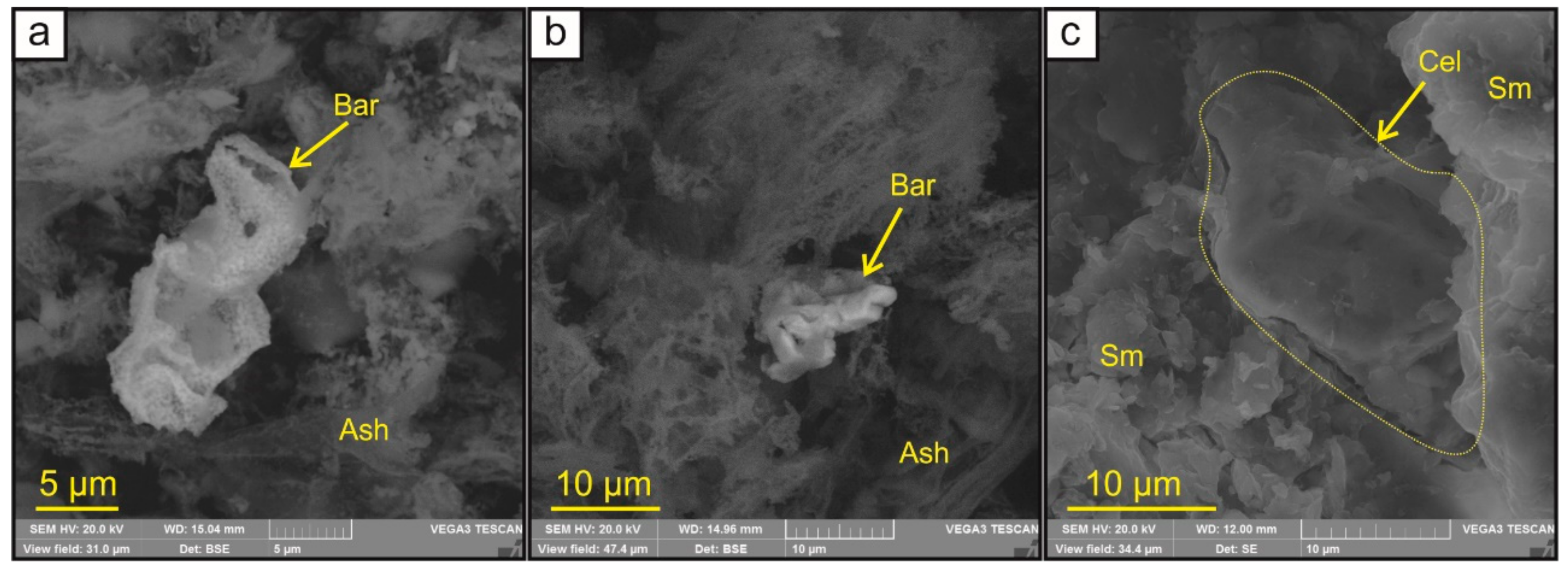
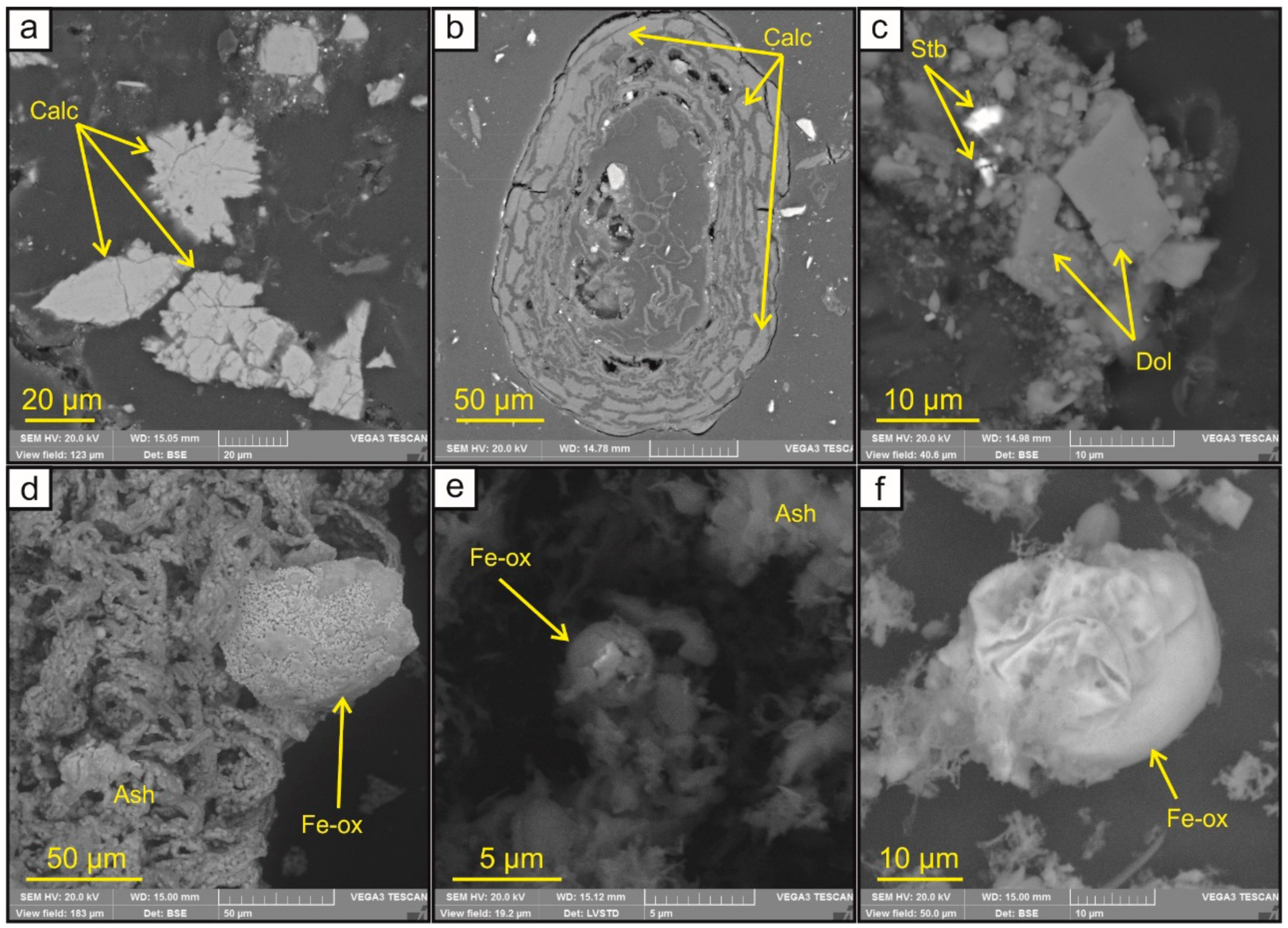
3.2. Sulfide and Sulfate Minerals
3.3. Carbonate and Fe-Bearing (Hydro-)Oxides
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction analysis |
| BSR | Bacterial sulfate reduction |
| AOM | anaerobic oxidation of methane |
References
- Inisheva, L.I.; Kobak, K.I.; Inishev, N.G. Paludification on Vasyugan Mire. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2017, 10, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvartsev, S.L.; Serebrennikova, O.V.; Zdvizhkov, M.A.; Savichev, O.G.; Naimushina, O.S. Geochemistry of wetland waters from the lower Tom basin, Southern Tomsk oblast. Geochem. Int. 2012, 50, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotyk, W. Review of the inorganic geochemistry of peats and peatland waters. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1988, 25, 95–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, P.; Shotyk, W. Geochemistry, mineralogy, and geochemical mass balance on major elements in two peat bog profiles (Jura Mountains, Switzerland). Chem. Geol. 1997, 138, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotyk, W. Peat bog archives of atmospheric metal deposition: Geochemical evaluation of peat profiles, natural variations in metal concentrations, and metal enrichment factors. Environ. Rev. 1996, 4, 149–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrovetnik, K.; Puura, E.; Neretnieks, I. Accumulation of heavy metals in Oostriku peat bog, Estonia: Site description, conceptual modelling and geochemical modelling of the source of the metals. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Buendía, A.M.; Whateley, M.K.G.; Bastida, J.; Urquiola, M.M. Origins of mineral matter in peat marsh and peat bog deposits, Spain. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2007, 71, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretennikova, E.E. Lead in the natural peat cores of ridge-hollow complex in the taiga zone of West Siberia. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 80, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabala, J.; Smieja-Król, B.; Jablonska, M.; Chrost, L. Mineral components in a peat deposit: Looking for signs of early mining and smelting activities in Silesia-Cracow region (Southern Poland). Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awid-Pascual, R.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Goemann, K.; Allen, N.; Noble, T.L.; Lottermoser, B.G.; Rodemann, T. The evolution of authigenic Zn-Pb-Fe-bearing phases in the Grieves Siding peat, western Tasmania. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2015, 170, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, Y.; Savichev, O.G.; Pasechnik, E.Y. Two decades of trends in ground water chemical composition in The Great Vasyugan Mire, Western Siberia, Russia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7329–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotyk, W.; Bicalho, B.; Cuss, C.W.; Duke, M.J.M.; Noernberg, T.; Pelletier, R.; Steinnes, E.; Zaccone, C. Dust is the dominant source of “heavy metals” to peat moss (Sphagnum fuscum) in the bogs of the Athabasca Bituminous Sands region of northern Alberta. Environ. Int. 2016, 92, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccone, C.; Pabst, S.; Senesi, G.S.; Shotyk, W.; Miano, T.M. Comparative evaluation of the mineralogical composition of Sphagnum peat and their corresponding humic acids, and implications for understanding past dust depositions. Quat. Int. 2013, 306, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrenz, M.; Druschel, G.K.; Thomsen-Ebert, T.; Gilbert, B.; Welch, S.A.; Kemner, K.M.; Logan, G.A.; Summons, R.E.; Stasio, G. De; Bond, P.L.; et al. Formation of sphalerite (ZnS) deposits in natural biofilms of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Science 2000, 290, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smieja-Król, B.; Fiałkiewicz-Kozieł, B. Quantitative determination of minerals and anthropogenic particles in some Polish peat occurrences using a novel SEM point-counting method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2573–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postma, D. Formation of siderite and vivianite and the pore-water composition of a Recent bog sediment in Denmark. Chem. Geol. 1980, 31, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.C.; Bennett, S.M.; Kramer, L.L. Sulfur mineralization in Sphagnum Peat. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1991, 22, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltman, B.; Rouwenhorst, T.G.; Van Kerkhoven, M.B.; Van Der Krift, T.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. Internal eutrophication in peat soils through competition between chloride and sulphate with phosphate for binding sites. Biogeochemistry 2000, 50, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of Pb- and Cu-contaminated soil using coal fly ash and peat. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, J.J.; Robinson, S.G.; Evans, M.G.; Yang, J.; Allott, T.E.H. Heavy metal release by peat erosion in the Peak District, southern Pennines, UK. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 2973–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenov, G.D.; Brenner, M.; Tucker, J.L. Anthropogenic versus natural control on trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope stratigraphy in peat sediments of southeast Florida (USA), 1500 AD to present. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 3549–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylander, M.E.; Martínez-Cortizas, A.; Bindler, R.; Greenwood, S.L.; Mörth, C.-M.; Rauch, S. Potentials and problems of building detailed dust records using peat archives: An example from Store Mosse (the “Great Bog”), Sweden. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 190, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuzov, S.I.; Maslov, S.G.; Finkelman, R.B.; Mezhibor, A.M.; Ilenok, S.S.; Blokhin, M.G.; Peregudina, E.V. Modes of occurrence of rare earth elements in peat from Western Siberia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotyk, W.; Weiss, D.; Kramers, J.D.; Frei, R.; Cheburkin, A.K.; Gloor, M.; Reese, S. Geochemistry of the peat bog at Etang de la Gruère, Jura Mountains, Switzerland, and its record of atmospheric Pb and lithogenic trace metals (Sc, Ti, Y, Zr, and REE) since 12,370 14C yr bp. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2337–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhibor, A.M.; Arbuzov, S.I.; Arkhipov, V.S. Trace elements in peat bogs of Tomsk Region (South Siberia, Russia). Energy Explor. Exploit. 2013, 31, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhibor, A.M.; Arbuzov, S.I.; Rikhvanov, L.P. Accumulation and average contents of trace elements in the high-moor peat of Tomsk Region (Western Siberia, Russia). Energy Explor. Exploit. 2009, 27, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.M.; Reynolds, R.C., Jr. X-ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, S. Quantitative Analysis of Clay and other Minerals in Sandstones by X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD). In Clay Mineral Cements in Sandstones; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 213–251. [Google Scholar]
- Bish, D.L.; Post, J.E. Quantitative mineralogical analysis using the Rietveld full-pattern fitting method. Am. Miner. 1993, 78, 932–940. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.C. Computer programs for standardless quantitative analysis of minerals using the full powder diffraction profile. Powder Diffr. 1991, 6, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konhauser, K. Introduction to Geomicrobiology; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Yáñez, C.; Bruns, M.A.; Martínez-Villegas, N.; Martínez, C.E. Natural zinc enrichment in peatlands: Biogeochemistry of ZnS formation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 84, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontharet, S.; Pierre, C.; Blanc-Valleron, M.-M.; Rouchy, J.M.; Fouquet, Y.; Bayon, G.; Foucher, J.P.; Woodside, J.; Mascle, J. Nature and origin of diagenetic carbonate crusts and concretions from mud volcanoes and pockmarks of the Nile deep-sea fan (eastern Mediterranean Sea). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 1292–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.J.; Moore, W.S.; Kloepfer, J.; Sochaski, M.A. The flux of barium to the coastal waters of the southeastern USA: The importance of submarine groundwater discharge. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 3047–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanor, J.S.; Chan, L.-H. Non-conservative behavior of barium during mixing of Mississippi River and Gulf of Mexico waters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1977, 37, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, M.A.; Cowen, J.P. Morphological and compositional evidence for biotic precipitation of marine barite. J. Mar. Res. 1997, 55, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, P.; Reyss, J.-L.; Bonte, P.; Schmidt, S. Sr/Ba in barite: A proxy of barite preservation in marine sediments? Mar. Geol. 2003, 199, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paytan, A.; Griffith, E.M. Marine barite: Recorder of variations in ocean export productivity. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, E.M.; Paytan, A. Barite in the ocean—Occurrence, geochemistry and palaeoceanographic applications. Sedimentology 2012, 59, 1817–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, N.A.; Gleeson, S.A.; Magnall, J.M.; Creaser, R.A.; Martel, E.; Fischer, B.J.; Sharp, R. The origin of Late Devonian (Frasnian) stratiform and stratabound mudstone-hosted barite in the Selwyn Basin, Northwest Territories, Canada. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 85, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Useche, F.; Canet, C.; Barragán, R.; Alfonso, P. Bioevents and redox conditions around the Cenomanian–Turonian anoxic event in Central Mexico. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 449, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lash, G.G. Authigenic barite nodules and carbonate concretions in the Upper Devonian shale succession of western New York—A record of variable methane flux during burial. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 59, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terekhov, E.P.; Mozherovsky, A.V.; Barinov, N.N. Barites from the underwater Yamato ridge (Japan Sea) Barites from the underwater Yamato ridge (Japan Sea). Stand. Glob. J. Geol. Explor. Res. 2016, 3, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Elderfield, H.; Schultz, A. Mid-ocean ridge hydrothermal fluxes and the chemical composition of the ocean. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 191–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Bohrmann, G.; Dubé, T.E.; Poole, F.G. Formation of modern and Paleozoic stratiform barite at cold methane seeps on continental margins. Geology 2003, 31, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baioumy, H.M. Rare earth elements, S and Sr isotopes and origin of barite from Bahariya Oasis, Egypt: Implication for the origin of host iron ores. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 106, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, C.; Anadón, P.; Alfonso, P.; Prol-Ledesma, R.M.; Villanueva-Estrada, R.E.; García-Vallès, M. Gas-seep related carbonate and barite authigenic mineralization in the northern Gulf of California. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 43, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, T.M.; Wolgemuth, K. Marine barite saturation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1972, 15, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, E.; Fung, I. Methane emission from natural wetlands: Global distribution, area, and environmental characteristics of sources. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1987, 1, 61–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Sun, X.; Lu, Y.; Strauss, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, T.; Lu, H.; Peckmann, J. Iron isotope constraints on diagenetic iron cycling in the Taixinan seepage area, South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.B.; Kasten, S. Sulfur cycling and methane oxidation. In Marine Geochemistry; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germay, 2006; pp. 271–309. [Google Scholar]
- Leloup, J.; Loy, A.; Knab, N.J.; Borowski, C.; Wagner, M.; Jørgensen, B.B. Diversity and abundance of sulfate-reducing microorganisms in the sulfate and methane zones of a marine sediment, Black Sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedinger, N.; Kasten, S.; Gröger, J.; Franke, C.; Pfeifer, K. Active and buried authigenic barite fronts in sediments from the Eastern Cape Basin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 241, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogala, J.; Siavalas, G.; Christanis, K. Coal petrography, mineralogy and geochemistry of lignite samples from the Ogwashi–Asaba Formation, Nigeria. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2012, 66–67, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foscolos, A.E.; Goodarzi, F.; Koukouzas, C.N.; Hatziyannis, G. Reconnaissance study of mineral matter and trace elements in Greek lignites. Chem. Geol. 1989, 76, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Životić, D.; Stojanović, K.; Gržetić, I.; Jovančićević, B.; Cvetković, O.; Šajnović, A.; Simić, V.; Stojaković, R.; Scheeder, G. Petrological and geochemical composition of lignite from the D field, Kolubara basin (Serbia). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 111, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
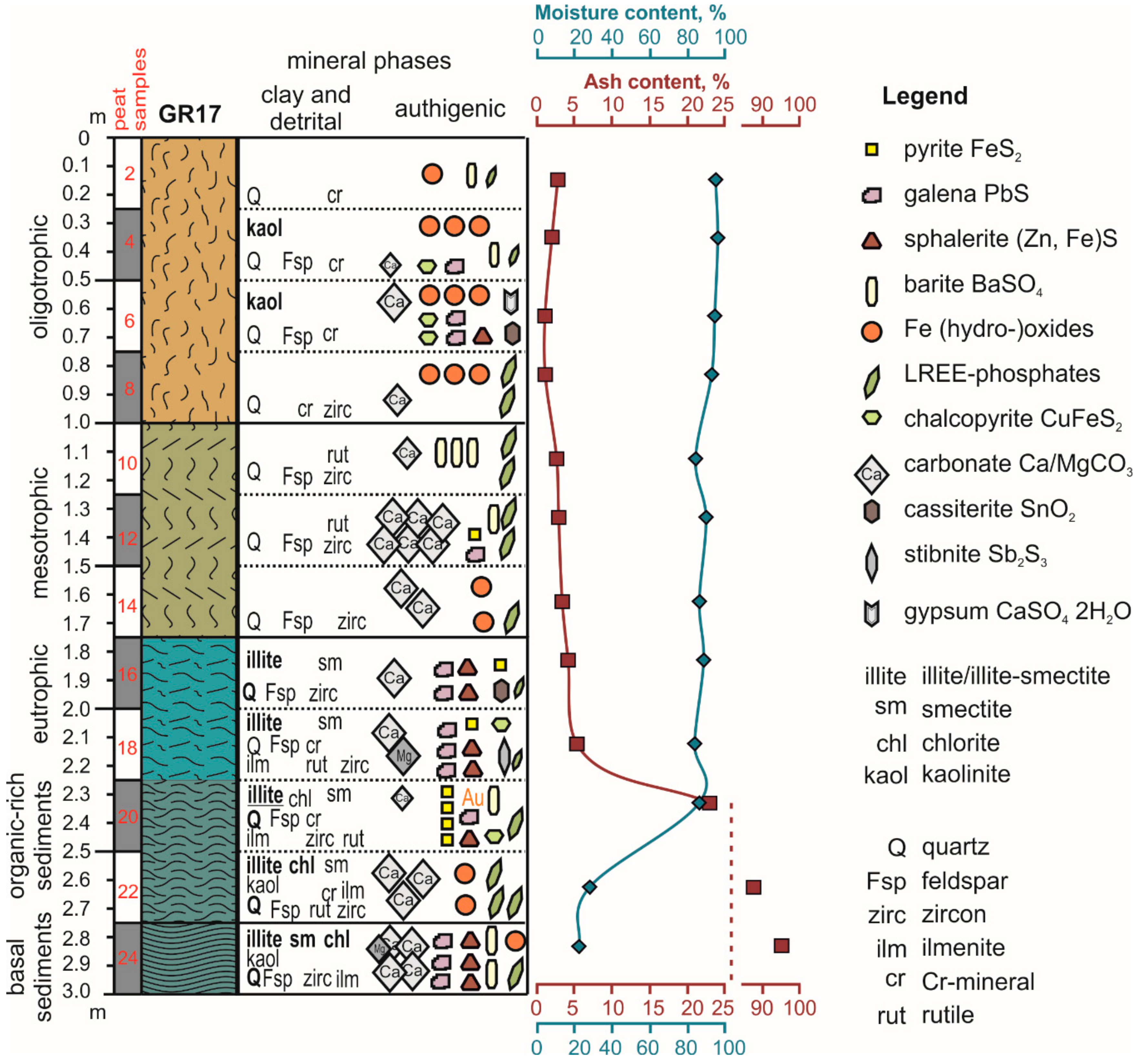


| Sample | Detrital Minerals | Clay Minerals | Authigenic Minerals | Identified by |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | quartz, chromite | Fe-(hydro-)oxides, barite, rhabdophane | SEM-EDS | |
| 4 | quartz, feldspars, chromite | kaolinite | Fe-(hydro-)oxides, rhabdophane, chalcopyrite, galena, barite, calcite | XRD, SEM-EDS |
| 6 | quartz, feldspars, chromite | kaolinite | Fe-(hydro-)oxides, chalcopyrite, galena, sphalerite, cassiterite, gypsum, calcite | XRD, SEM-EDS |
| 8 | quartz, zircon, chromite | Fe-(hydro-)oxides, rhabdophane, calcite | SEM-EDS | |
| 10 | quartz, feldspars, rutile, zircon | barite, rhabdophane, calcite | SEM-EDS | |
| 12 | quartz, feldspars, rutile, zircon | calcite, rhabdophane, barite, pyrite, galena, | XRD, SEM-EDS, Raman | |
| 14 | quartz, feldspars, zircon | calcite, Fe-(hydro-)-oxides, rhabdophane | SEM-EDS, Raman | |
| 16 | quartz, feldspars, zircon | illite, smectite | galena, sphalerite, pyrite, cassiterite, rhabdophane, calcite | XRD, SEM-EDS |
| 18 | quartz, feldspars, chromite, ilmenite, rutile, zircon | illite, smectite | galena, sphalerite, pyrite, chalcopyrite, rhabdophane, stibnite, calcite, dolomite | XRD, SEM-EDS |
| 20 | quartz, feldspars, chromite, ilmenite, rutile, zircon | illite, smectite, chlorite | pyrite, barite, galena, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, rhabdophane, gold, calcite | XRD, SEM-EDS |
| 22 | quartz, feldspars, chromite, ilmenite, rutile, zircon | illite, smectite, chlorite | calcite, Fe-(hydro-)oxides, rhabdophane | XRD, SEM-EDS, Raman |
| 24 | quartz, feldspars, ilmenite, zircon | illite, smectite, chlorite | calcite, galena, sphalerite, barite, dolomite, Fe-(hydro-)oxides, rhabdophane | XRD, SEM-EDS, Raman |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudmin, M.; Ruban, A.; Savichev, O.; Mazurov, A.; Dauletova, A.; Savinova, O. Authigenic and Detrital Minerals in Peat Environment of Vasyugan Swamp, Western Siberia. Minerals 2018, 8, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110500
Rudmin M, Ruban A, Savichev O, Mazurov A, Dauletova A, Savinova O. Authigenic and Detrital Minerals in Peat Environment of Vasyugan Swamp, Western Siberia. Minerals. 2018; 8(11):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110500
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudmin, Maxim, Aleksey Ruban, Oleg Savichev, Aleksey Mazurov, Aigerim Dauletova, and Olesya Savinova. 2018. "Authigenic and Detrital Minerals in Peat Environment of Vasyugan Swamp, Western Siberia" Minerals 8, no. 11: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110500
APA StyleRudmin, M., Ruban, A., Savichev, O., Mazurov, A., Dauletova, A., & Savinova, O. (2018). Authigenic and Detrital Minerals in Peat Environment of Vasyugan Swamp, Western Siberia. Minerals, 8(11), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110500