Investigation on Calcination Behaviors of Coal Gangue by Fluidized Calcination in Comparison with Static Calcination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials
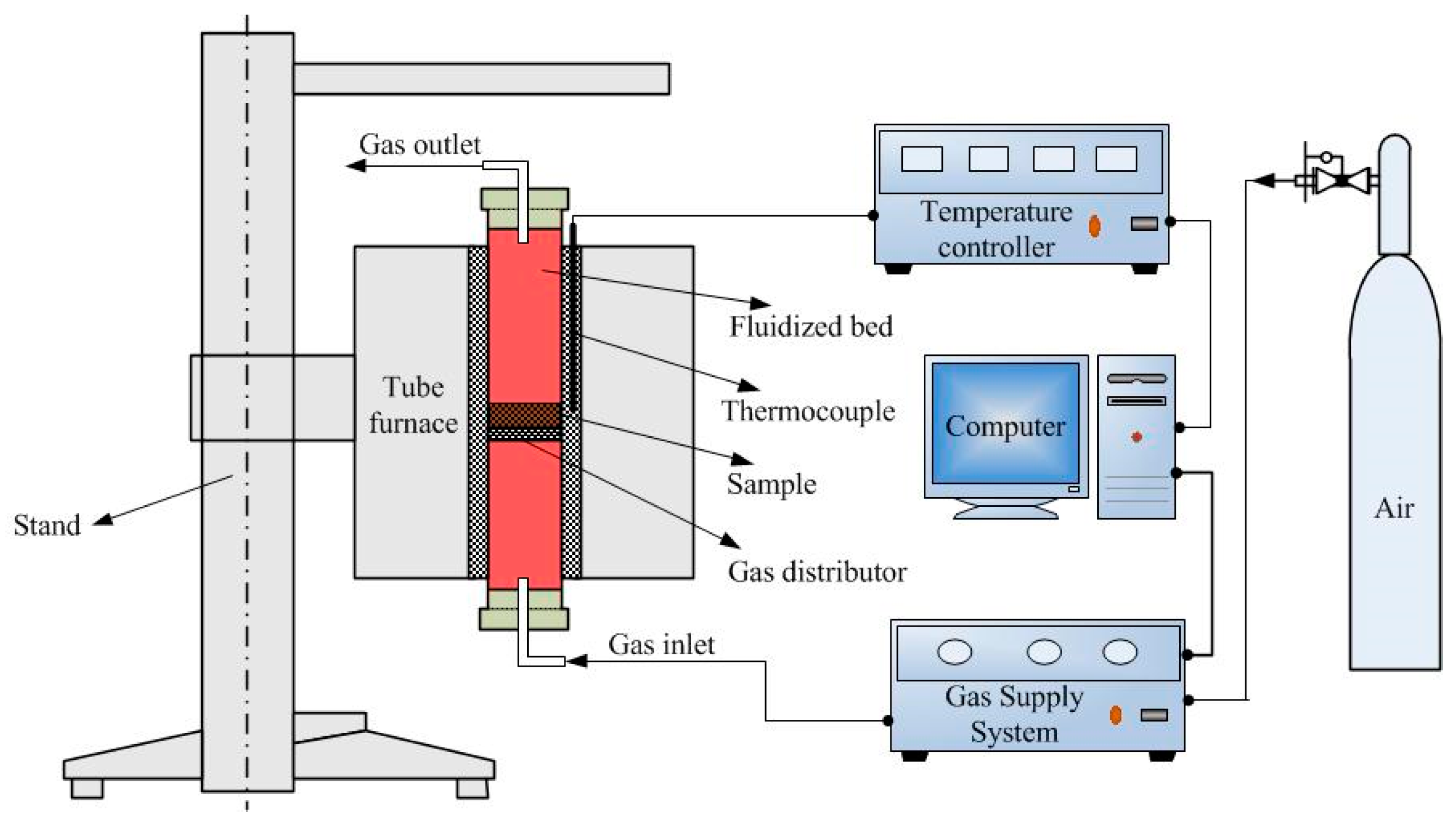
2.2. Calcination Methods
2.3. Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
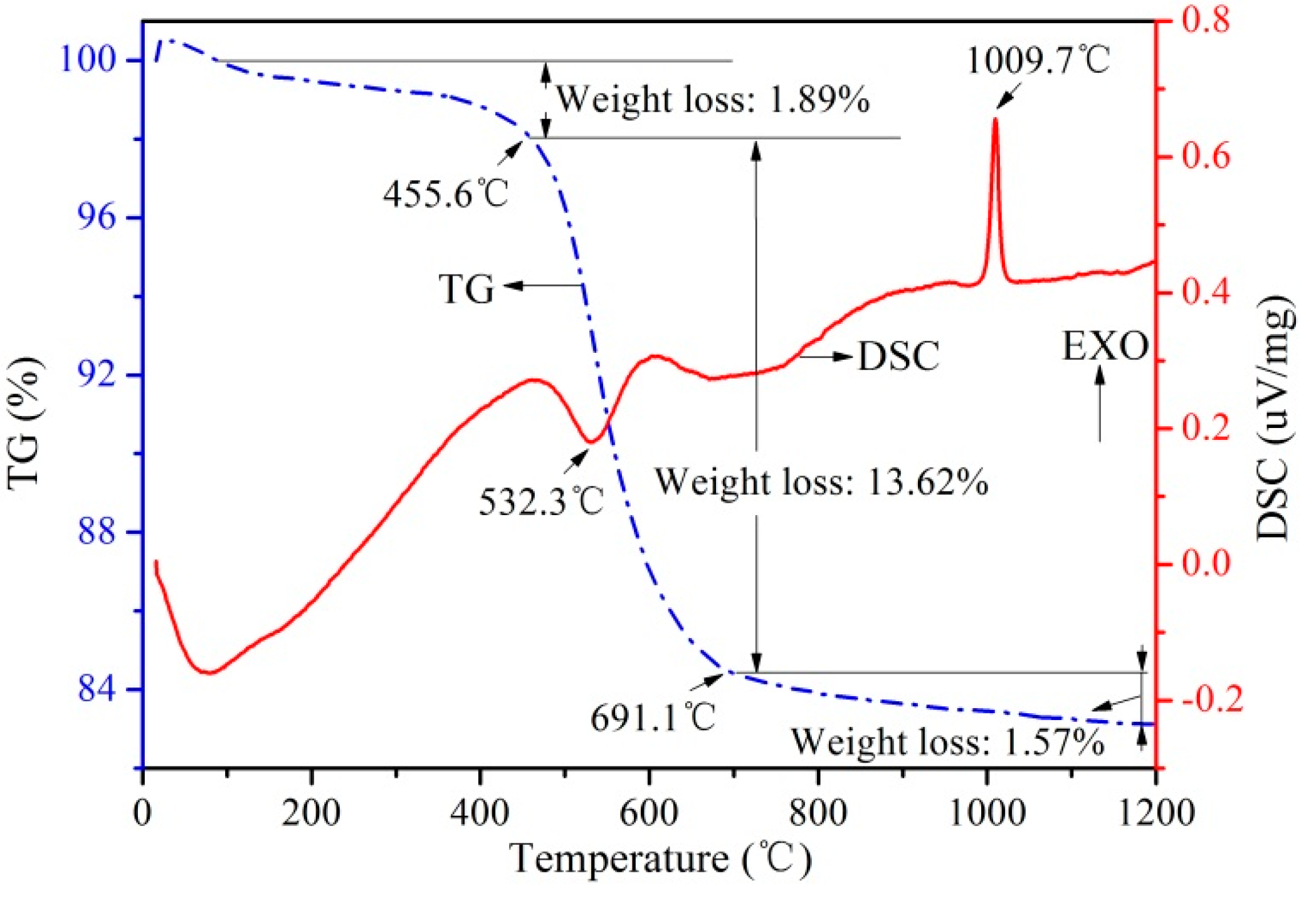
3.1. Thermal Analysis
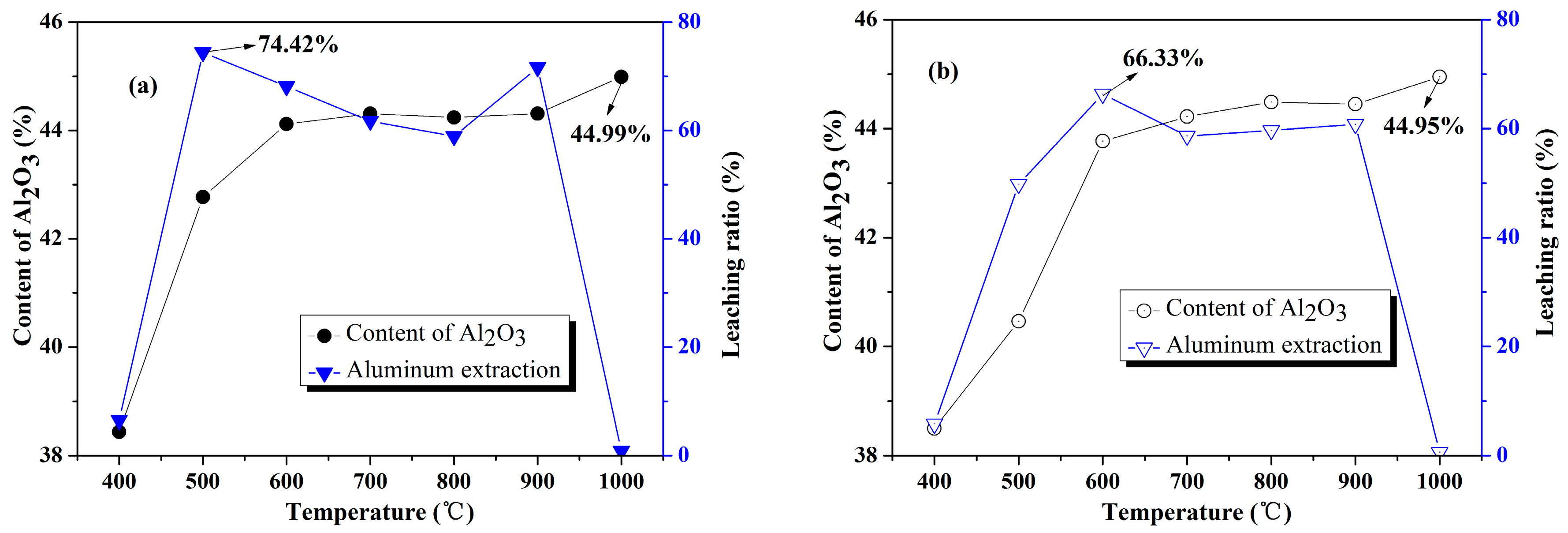
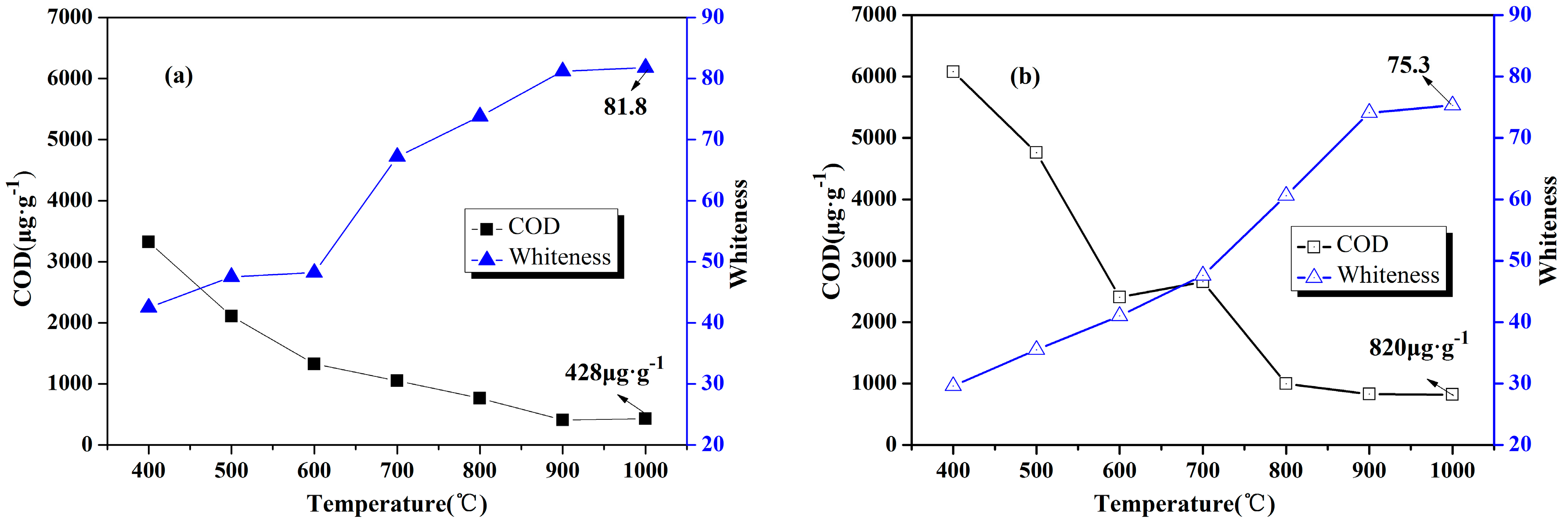
3.2. Chemical and Physical Characteristics
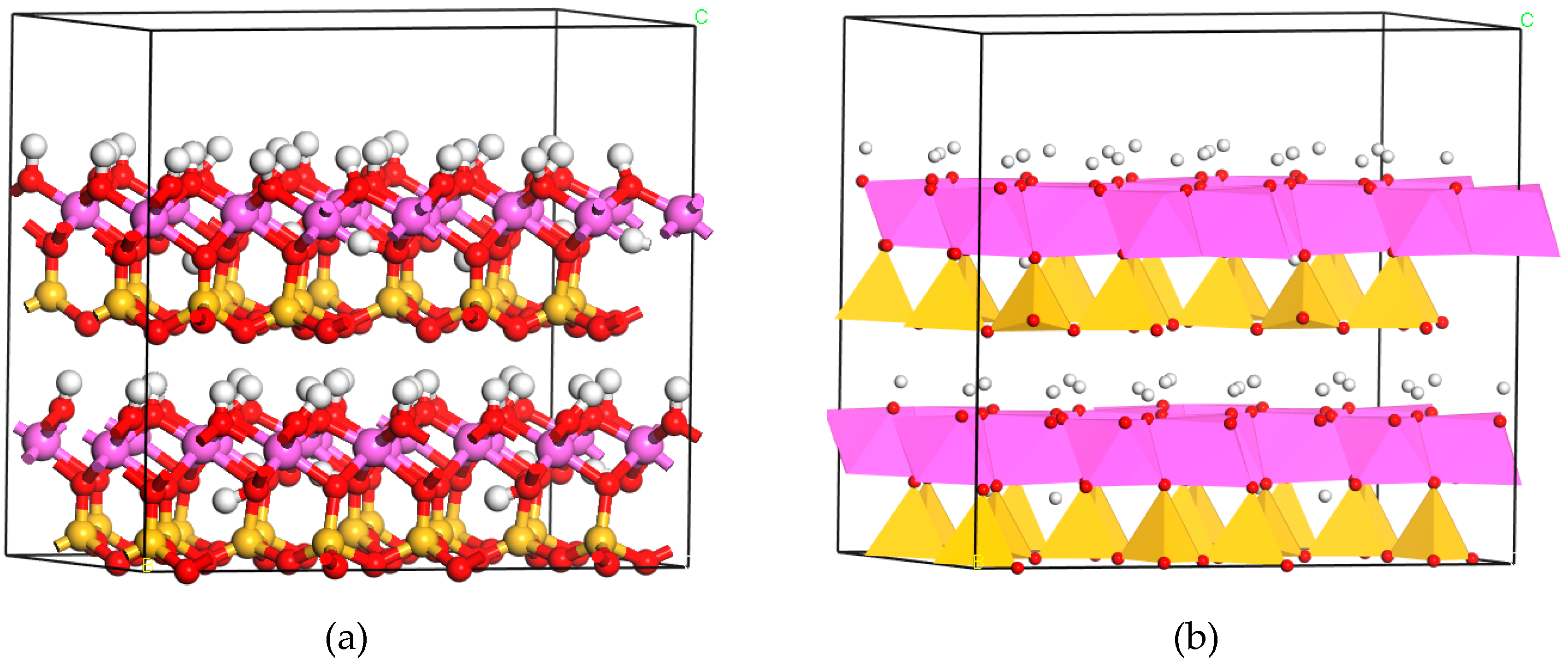
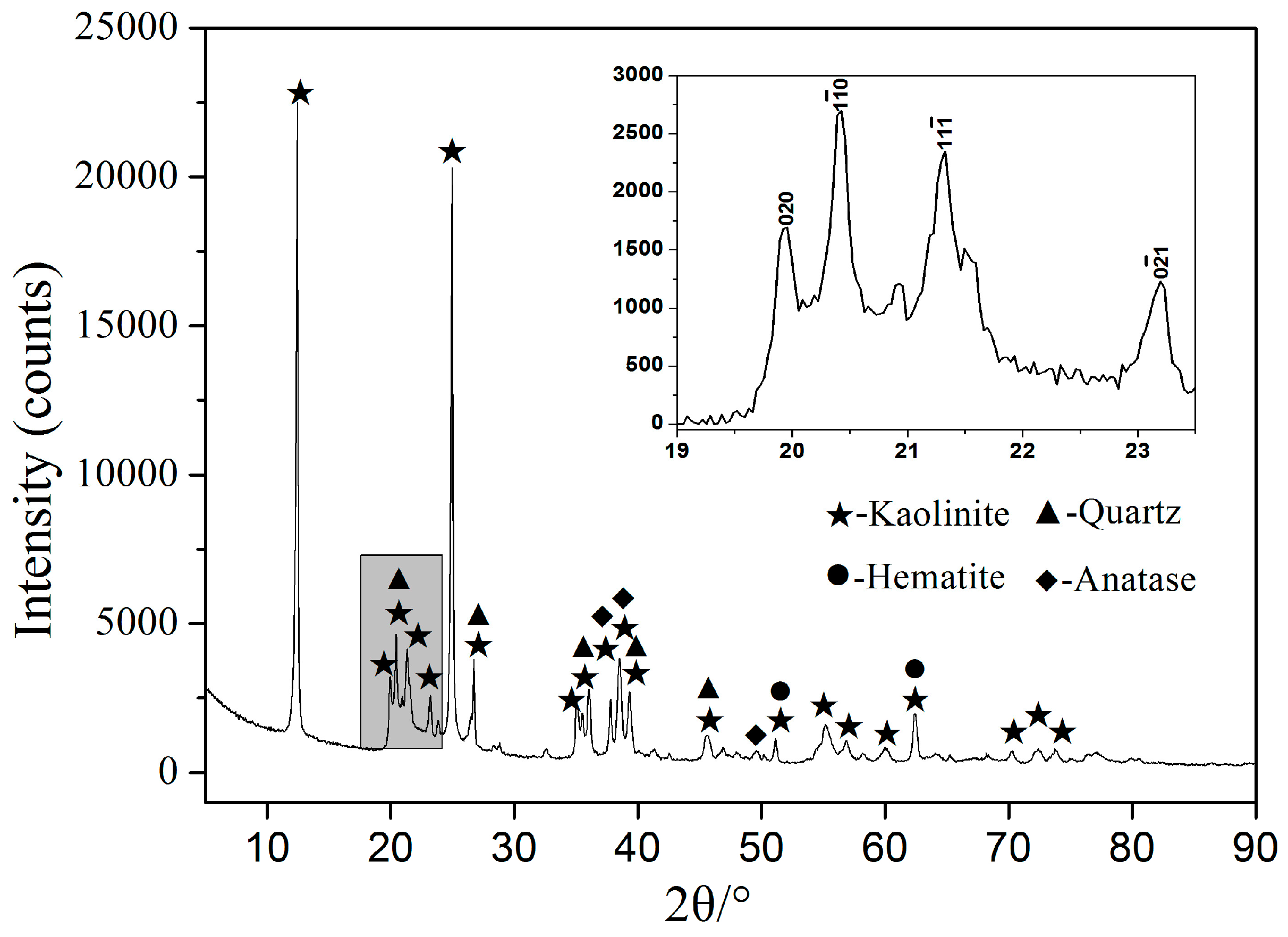
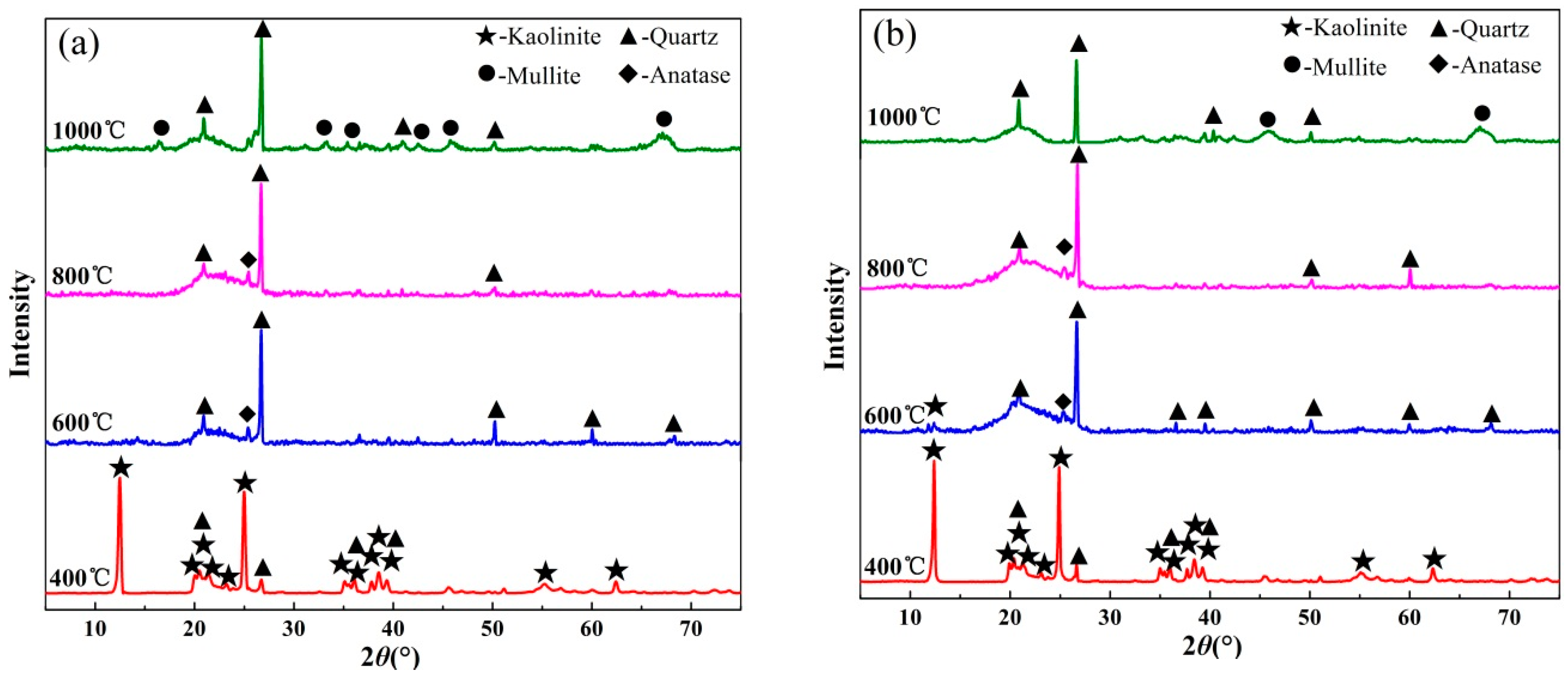
3.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
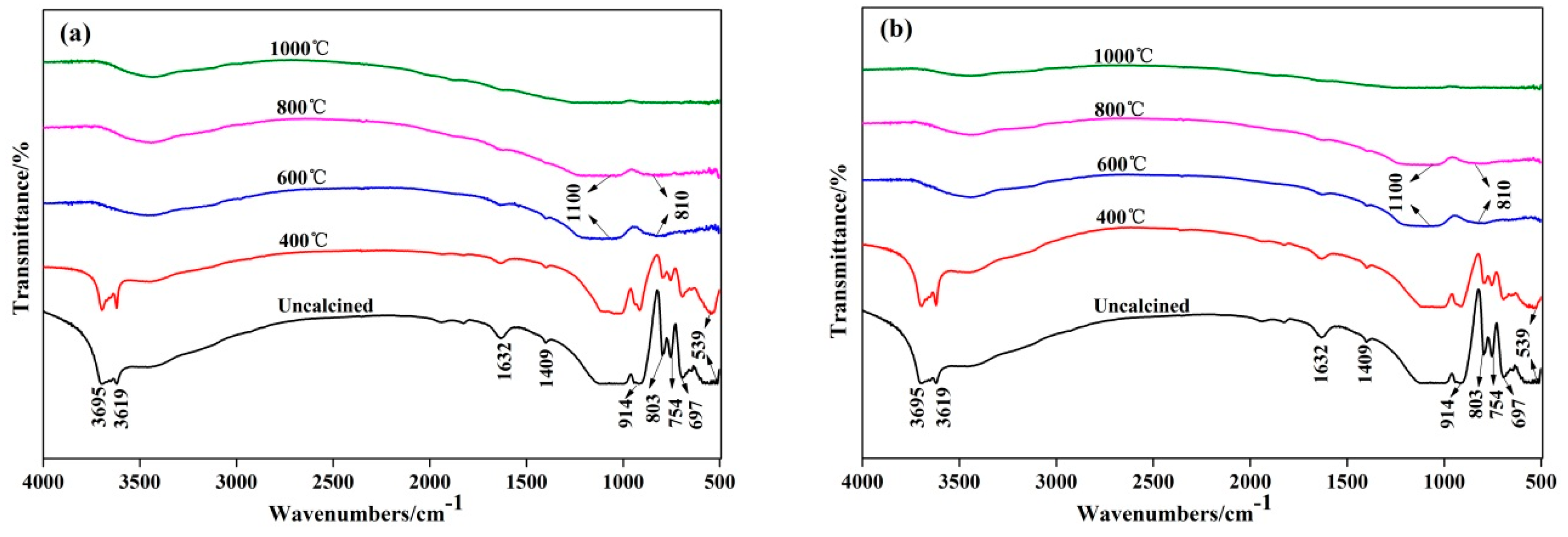
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
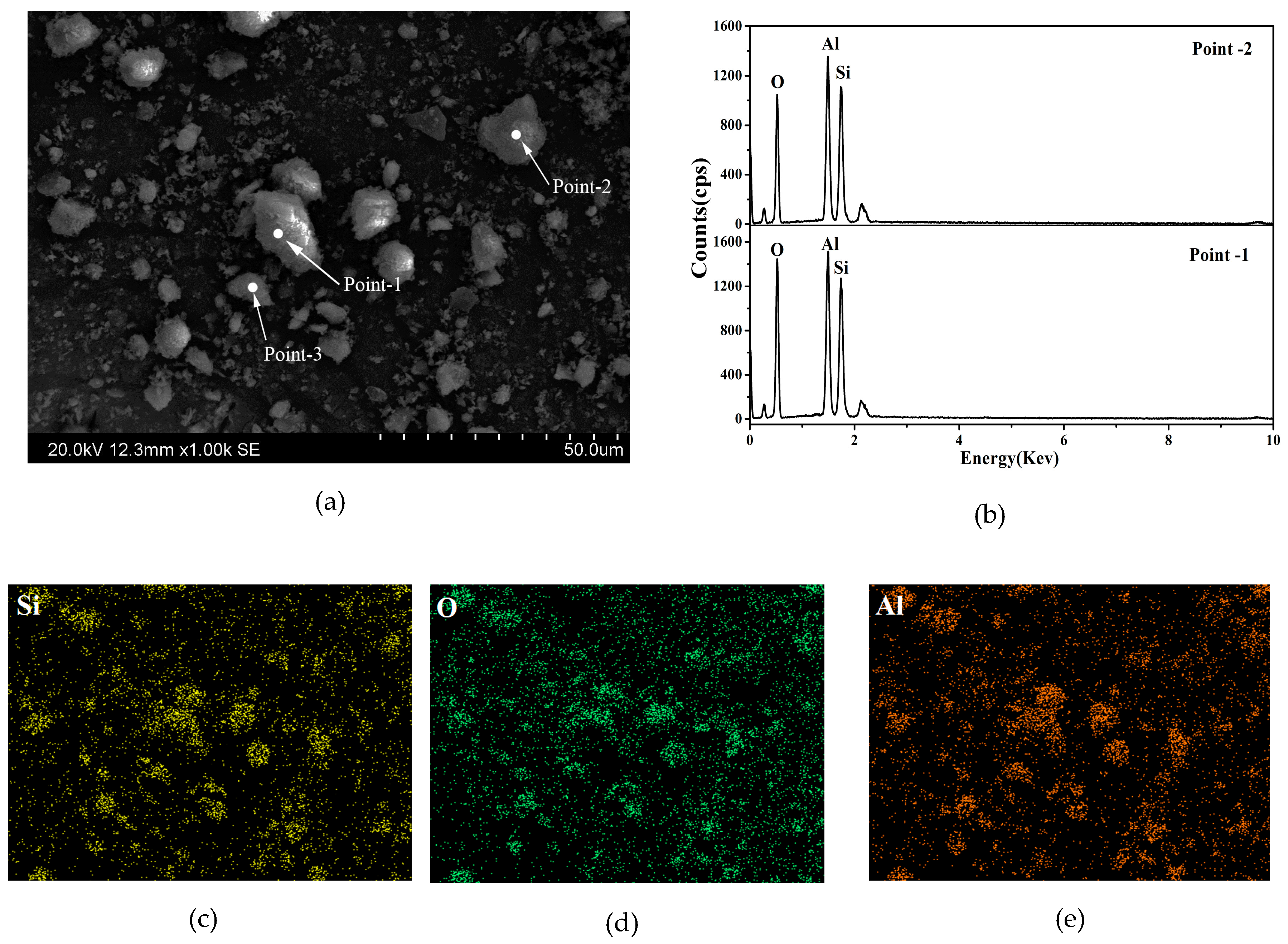
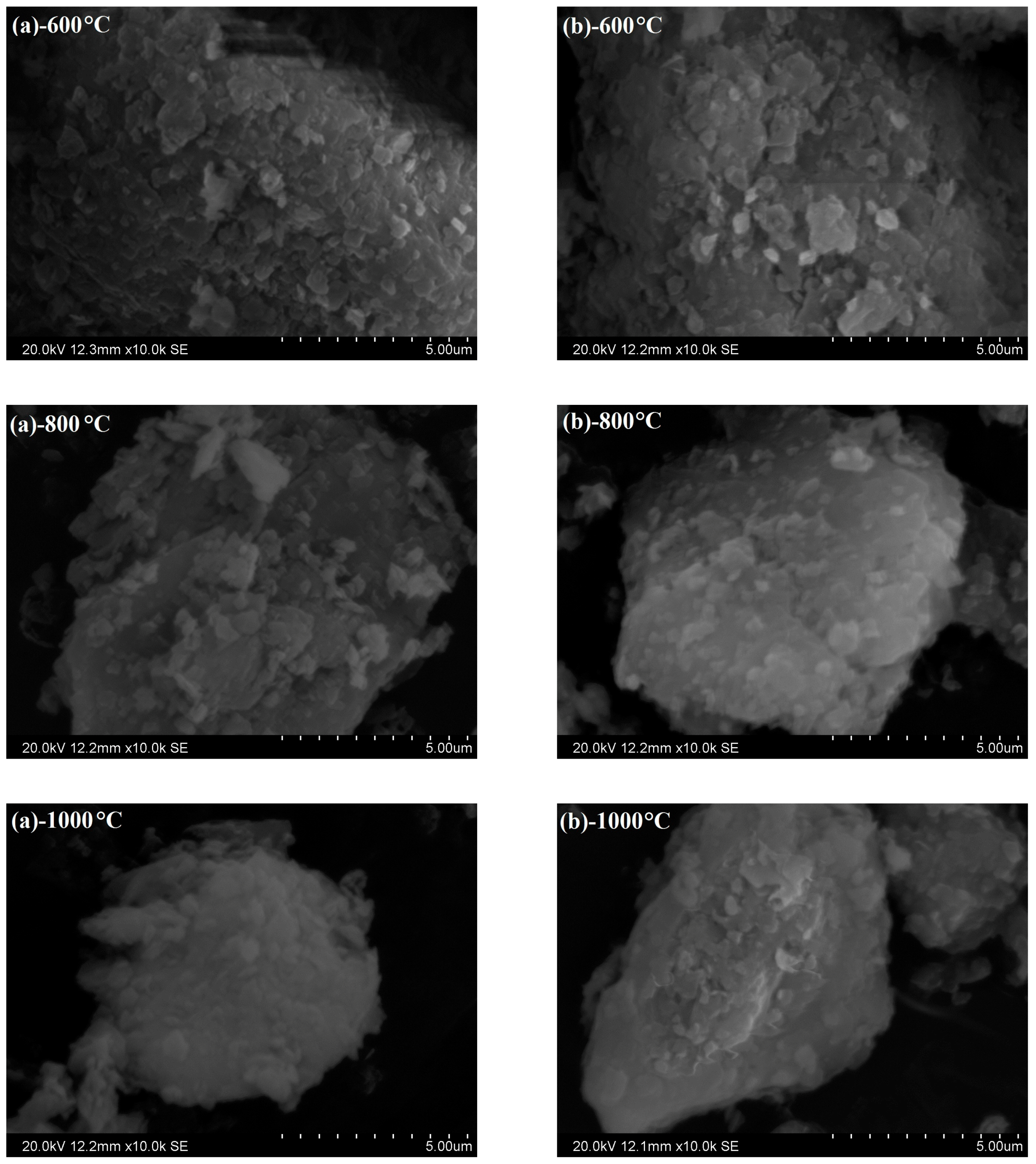
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Kaolinite, quartz, unburned carbon and organic matter were the main mineral compositions in the raw coal gangue. TG-DSC analysis indicates that kaolinite begins to decompose into amorphous meta-kaolinite at 450 °C and transforms to mullite as temperature reaches up to 1000 °C.
- (2)
- According to chemical and physical characteristics of calcined products, fluidized calcination products could obtain higher activity, higher whiteness and lower COD under same calcination temperature compared with static calcination.
- (3)
- XRD analysis illustrated that kaolinite peaks at 12.4° disappeared completely at 600 °C and more mullite peaks presence at 1000 °C by fluidized calcination, which was proved by the disappearance of O–H stretching vibration in infrared spectra results. Morphology evolution analysis showed that fluidized calcination could accelerate crystal phase transformation and improve the activity of calcined products.
- (4)
- Combustion of carbon/organic matter and dehydroxylation were more quickly and effectively by fluidized calcination, due to the high efficiency of heat and mass transfer, which could produce product with excellent performance and stable quality.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, G.; Yun, F.; Long, Z.Y.; Sen, Y.; Song, Z. Study on the property and reuse of coal gangue in Liupanshui, Guizhou Province, China. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2013, 27, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Yang, H.M. Composite of coal-series kaolinite and capric—Lauric acid as form-stable phase-change material. Energy Technol. 2015, 3, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.C.; Liu, G.J.; Fang, T.; Lam, P.K.S. Investigation on thermal and trace element characteristics during co-combustion biomass with coal gangue. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.H.; Dong, X.X.; Chai, B.; Yang, Y. Evaluation of particle size distribution of coal gangue through fractal method in Dongkuang mine, Heshan, China. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Lao, X.B.; Wu, J.F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, K. Microstructural evolution, phase transformation, and variations in physical properties of coal series kaolin powder compact during firing. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 115, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperinck, S.; Raiteri, P.; Marks, N.; Wright, K. Dehydroxylation of kaolinite to metakaolin—A molecular dynamics study. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Yuan, W.; Li, L.; Hu, J.; Xu, L. Effects of Er(NO3)3, Nd(No3)3 and Y(No3)3 on kinetics of dehydroxylation of kaolinite. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.F.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.F.; Zhang, J.S.; Frost, R.L. A spectroscopic comparison of selected Chinese kaolinite, coal bearing kaolinite and halloysite—A mid-infrared and near-infrared study. Spectrochim. Acta A 2010, 77, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.F.; Liu, Q.F.; Yang, J.; Frost, R.L. Thermogravimetric analysis of selected coal-bearing strata kaolinite. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 507–508, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Sun, H.H.; Tie, X.C.; Xia, X.J. Dissolution properties of calcined gangue. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. B 2006, 13, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.B.; Zou, J.J.; Jiang, Y.S.; Huang, T.P.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, C.D. Thermal activation of coal fly ash by sodium hydrogen sulfate for alumina extraction. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 4315–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.P.; Fang, M.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Chen, K.; Li, W.J.; Liu, Y.G. Phase transformation of coal gangue by aluminothermic reduction nitridation: Influence of sintering temperature and aluminum content. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.C.; Liu, G.J.; Yan, Z.C.; Fang, T.; Wang, R.W. Transformation behavior of mineral composition and trace elements during coal gangue combustion. Fuel 2012, 97, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.C.; Si, P.; Yu, J.G. A systematic investigation into the extraction of aluminum from coal spoil through kaolinite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8541–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wan, J.; Sun, H.; Li, L. Investigation on the activation of coal gangue by a new compound method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Lv, H.; Yang, X.; Cheng, F. AlCl3⋅6H2O recovery from the acid leaching liquor of coal gangue by using concentrated hydrochloric inpouring. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Role of additives in improved thermal activation of coal fly ash for alumina extraction. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 110, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Cheng, F. Dissolution kinetics of aluminum and iron from coal mining waste by hydrochloric acid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, Y.; Wei, X. Phase transformation in suspension roasting of oolitic hematite ore. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 4560–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, R.; Cizer, O.; Horckmans, L.; Durdzinski, P.T.; Dierckx, P.; Nielsen, P.; van Balen, K.; Vandewalle, L. Properties and pozzolanic reactivity of flash calcined dredging sediments. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 129, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Building Materials Industry Standard of China. The Determination of COD Value of Fiber Glass Raw Materials and Ingredients; JC/T 2156-2012; Ministry of Industry and Information Technology: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Xiao, J.; Li, F.C.; Zhong, Q.F.; Bao, H.G.; Wang, B.J.; Huang, J.D.; Zhang, Y.B. Separation of aluminum and silica from coal gangue by elevated temperature acid leaching for the preparation of alumina and SiC. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Frost, R.L.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J. Infrared and infrared emission spectroscopic study of typical Chinese kaolinite and halloysite. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 77, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Zhang, N.; Yao, Y.; Sun, H.H.; Feng, H. Micro-structural characterization of the hydration products of bauxite-calcination-method red mud-coal gangue based cementitious materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Cao, Y.D.; Dong, H.J.; Zhang, J.S.; Sun, C.B. Effect of calcination condition on the microstructure and pozzolanic activity of calcined coal gangue. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 146, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Ou, X.M.; Qiang, Y.H.; Niu, J.N.; Komarneni, S. Thermal decomposition behavior and de-intercalation mechanism of acetamide intercalated into kaolinite by thermoanalytical techniques. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.E.; Kearley, G.J.; Provis, J.L.; Riley, D.P. Inelastic neutron scattering analysis of the thermal decomposition of kaolinite to metakaolin. Chem. Phys. 2013, 427, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacek, P.; Soukal, F.; Opravil, T.; Havlica, J.; Brandstetr, J. The kinetic analysis of the thermal decomposition of kaolinite by DTG technique. Powder Technol. 2011, 208, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, K.; Cui, L.; Cheng, F. Improved extraction of alumina from coal gangue by surface mechanically grinding modification. Powder Technol. 2016, 302, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Hao, Z. The thermal activation process of coal gangue selected from zhungeer in china. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.C.; Liu, G.J.; Cheng, S.W.; Fang, T.; Lam, P.K.S. Thermochemical and trace element behavior of coal gangue, agricultural biomass and their blends during co-combustion. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | P | S | C | VM | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37.06 | 46.3 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 0.055 | 0.046 | 0.072 | 0.022 | 0.007 | 0.038 | 1.63 | 1.17 | 15.64 |
| Elements | Content (wt %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Point-1 | Point-2 | Point-3 | |
| O | 52.98 | 62.90 | 49.29 |
| Al | 22.77 | 18.20 | 24.24 |
| Si | 24.25 | 18.90 | 26.47 |
| Al/Si | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.92 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Gao, P.; Gong, G. Investigation on Calcination Behaviors of Coal Gangue by Fluidized Calcination in Comparison with Static Calcination. Minerals 2017, 7, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7020019
Yuan S, Li Y, Han Y, Gao P, Gong G. Investigation on Calcination Behaviors of Coal Gangue by Fluidized Calcination in Comparison with Static Calcination. Minerals. 2017; 7(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Shuai, Yanjun Li, Yuexin Han, Peng Gao, and Guichen Gong. 2017. "Investigation on Calcination Behaviors of Coal Gangue by Fluidized Calcination in Comparison with Static Calcination" Minerals 7, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7020019
APA StyleYuan, S., Li, Y., Han, Y., Gao, P., & Gong, G. (2017). Investigation on Calcination Behaviors of Coal Gangue by Fluidized Calcination in Comparison with Static Calcination. Minerals, 7(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7020019







