Preparation of Direct Reduced Iron and Titanium Nitride from Panzhihua Titanomagnetite Concentrate Through Carbothermic Reduction-Magnetic Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Characterisation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Reduction Temperature
3.2. Effect of Coal Dosage
3.3. Effect of Reduction Time
3.4. Microstructure of the Reduced Composite Pellets
3.5. Separation of Metallic Iron and TiN
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The conversion of titanium to TiN is significantly affected by reduction temperature, reduction time, and coal dosage. Increasing the reduction temperature, reduction time, and coal dosage can promote the formation of TiN. Under the optimum conditions of 1300 °C reduction temperature, 26 wt % coal dosage and 90 min reduction time, titanium was almost completely transformed into TiN.
- (2)
- The SEM analysis showed that near-spherical metallic iron particles with diameters from dozens of microns to about 300 μm were formed in the reduced pellets. By contrast, the TiN particles were generally less than 10 μm. The EDS results revealed that the TiN phase contains a certain amount of vanadium and carbon, and traces of other impurities.
- (3)
- The separation results revealed metallic iron and TiN can be precisely separated through the grinding-magnetic separation process.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, F.; Chen, F.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, T.; Travyanov, A.Y.; Qiu, G. Kinetics of hydrochloric acid leaching of titanium from titanium-bearing electric furnace slag. JOM 2016, 68, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H. Principle of Blast Furnace Smelting of Vanadium-Bearing Titanomagnetite; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1996; p. 8. ISBN 9787030051189. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; An, Z.; Zhao, S. Hydrometallurgical process for recovering titanium from titanium-bearing blast furnace slag in Panzhihua Steel Plant. Nonferr. Metal. Sci. Eng. 2016, 7, 21–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Qi, T. Behaviors of vanadium and chromium in coal-based direct reduction of high-chromium vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite concentrates followed by magnetic separation. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 2015, 25, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Qi, T.; Chen, D.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y. A novel method to extract iron, titanium, vanadium, and chromium from high-chromium vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite concentrates. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 149, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, H.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, X.; Shen, Y.; Shen, F. Melting and separation behavior of slag and metal phases in metallized pellets obtained from the direct-reduction process of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 142, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Chen, F.; Zheng, F. Effects of basicity and MgO in slag on the behaviors of smelting vanadium titanomagnetite in the direct reduction-electric furnace process. Metals 2016, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Feng, K.; Yue, H. Theoretical analyses and experimental investigations of selective carbothermal reactions of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite concentrates for preparation of iron-based wear-resistant material. JOM 2016, 68, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.; Zhu, R.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Hou, J. Preparation of Fe-Ti(C,N) composites from titanomagnetite concentrate by carbothermal reduction in air atmosphere. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium 2016, 37, 46–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, C.; Yang, L.; Yan, Y.; Qian, Y. Reduction-nitridation synthesis of titanium nitride nanocrystals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 86, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, H.O. Handbook of Refractory Carbides & Nitrides: Properties, Characteristics, Processing and Apps; Noyes Publications: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 193. ISBN 081551770X. [Google Scholar]
- China Technical Committee for Standardization. GB/T 212-2008 Proximate Analysis of Coal; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Dong, X.; She, X.; Xue, Q.; Wang, J. Solid state reduction of titanomagnetite concentrate by graphite. ISIJ Int. 2013, 53, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Song, B.; Wang, L.; Qi, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Solid state reduction of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrates with pulverized coal. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welham, N.J.; Willis, P.E. Formation of TiN/TiC-Fe composites from ilmenite (FeTiO3) concentrate. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1998, 29, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Hua, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Gong, K. Synthesis of TiN from FeTiO3 by microwave-assisted carbothermic reduction-nitridation. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 583, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chou, K. A novel process to synthesize high-quality ferrovanadium nitride. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 3405–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesler, D.; Bastuck, T.; Theissmann, R.; Kruis, F.E. Plasma synthesis of titanium nitride, carbide and carbonitride nanoparticles by means of reactive anodic arc evaporation from solid titanium. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Chen, X.; Gu, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Han, P.; Yao, J.; Wang, L.; Cui, G. TiN/VN composites with core/shell structure for supercapacitors. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
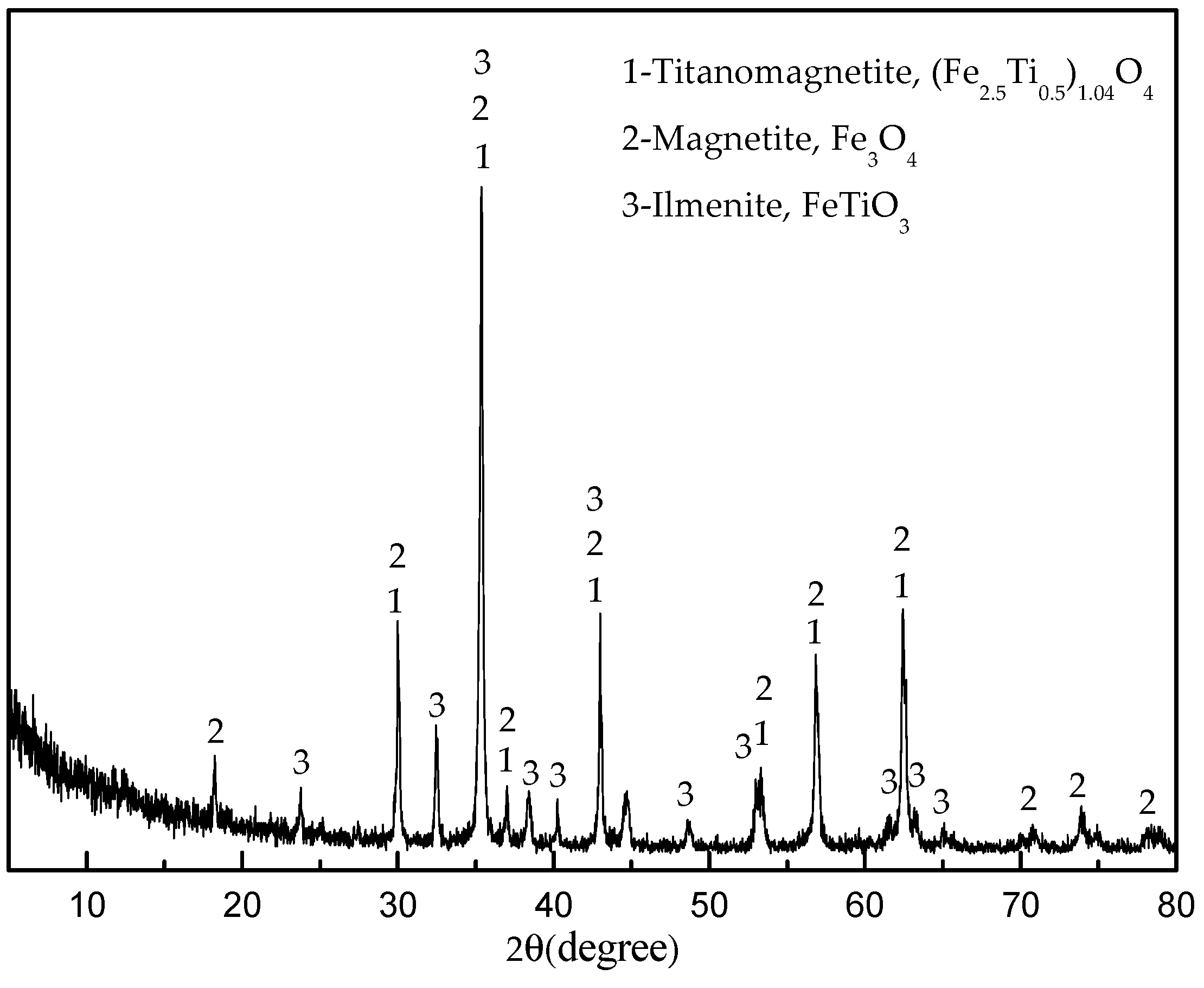
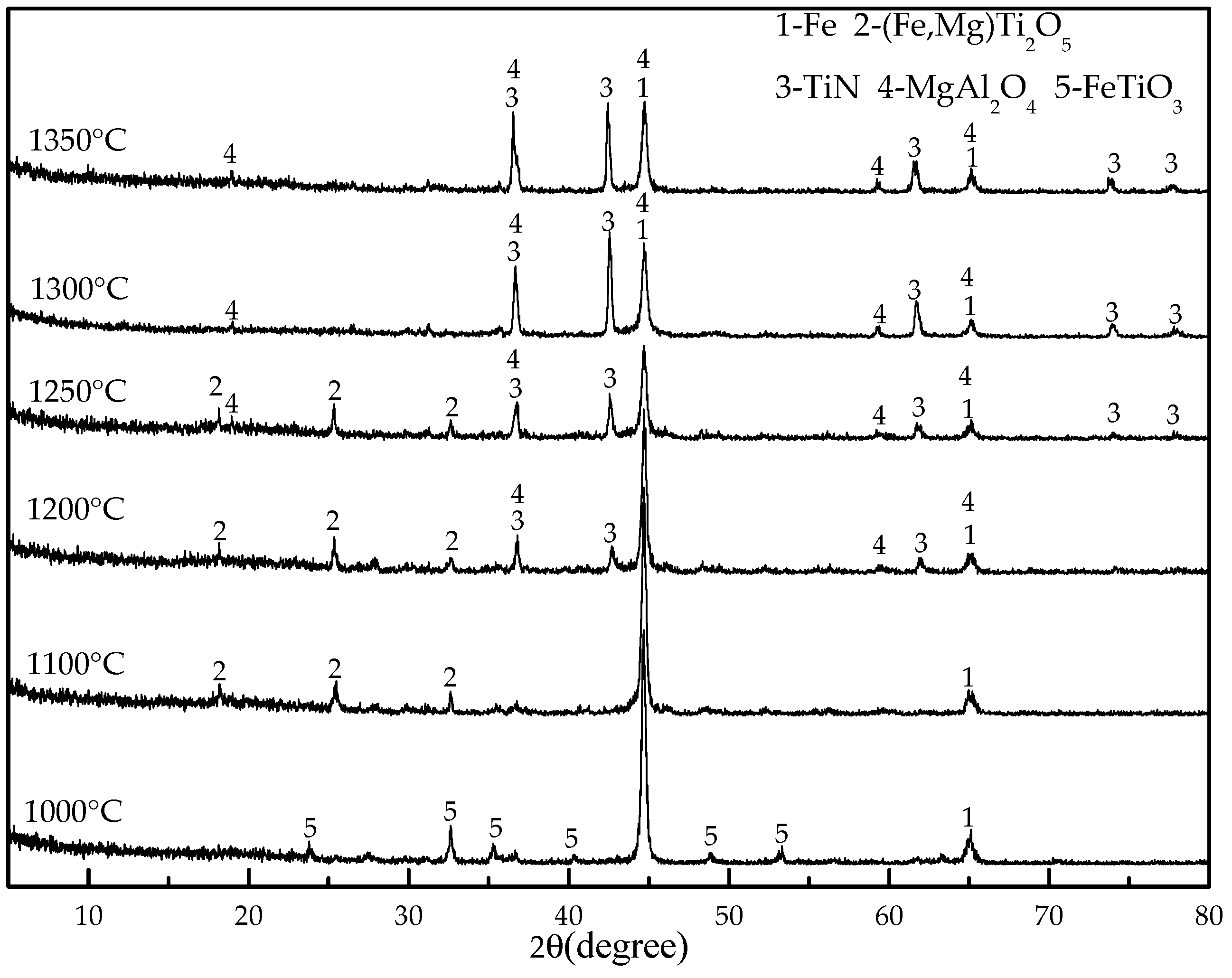
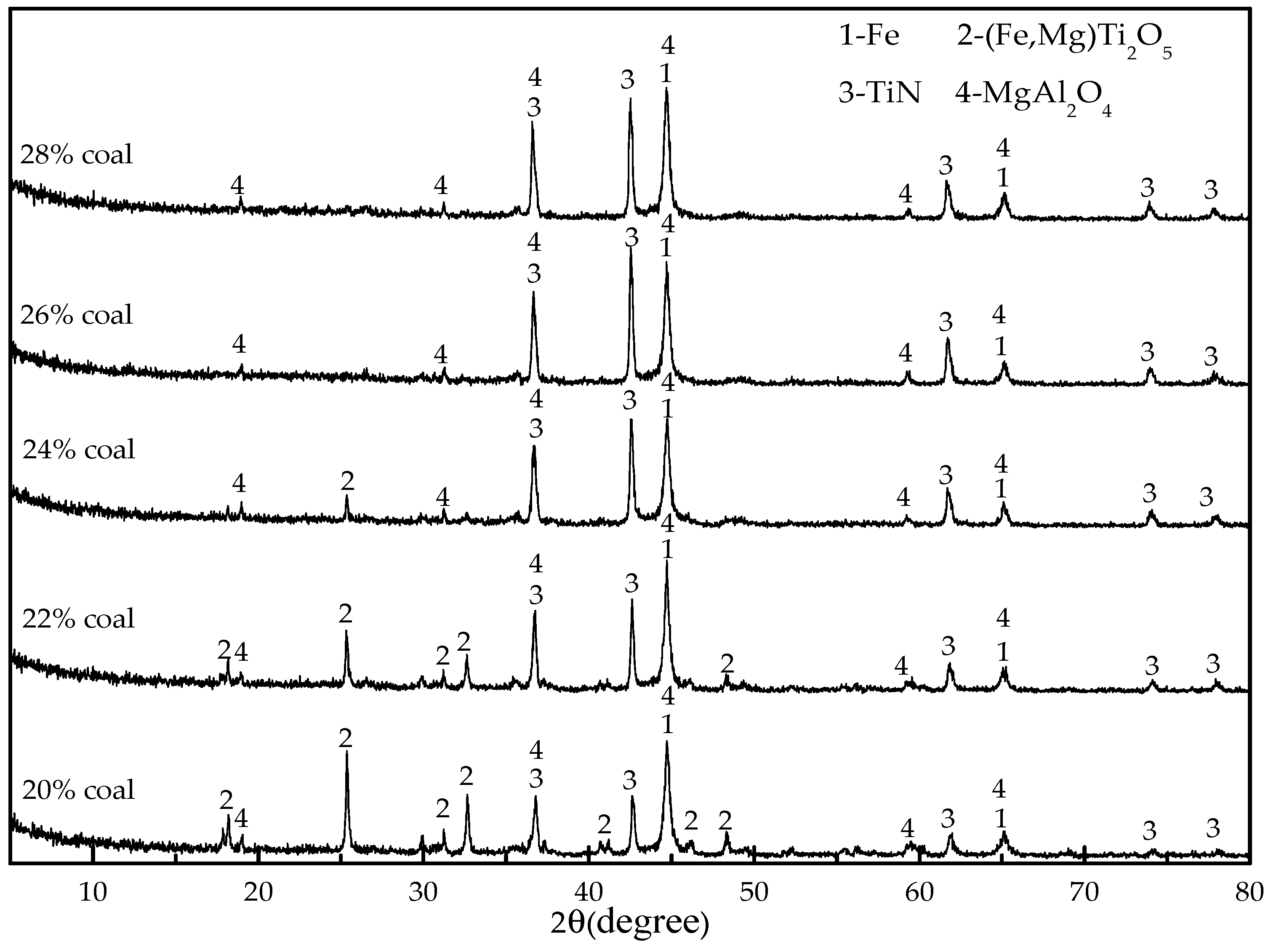
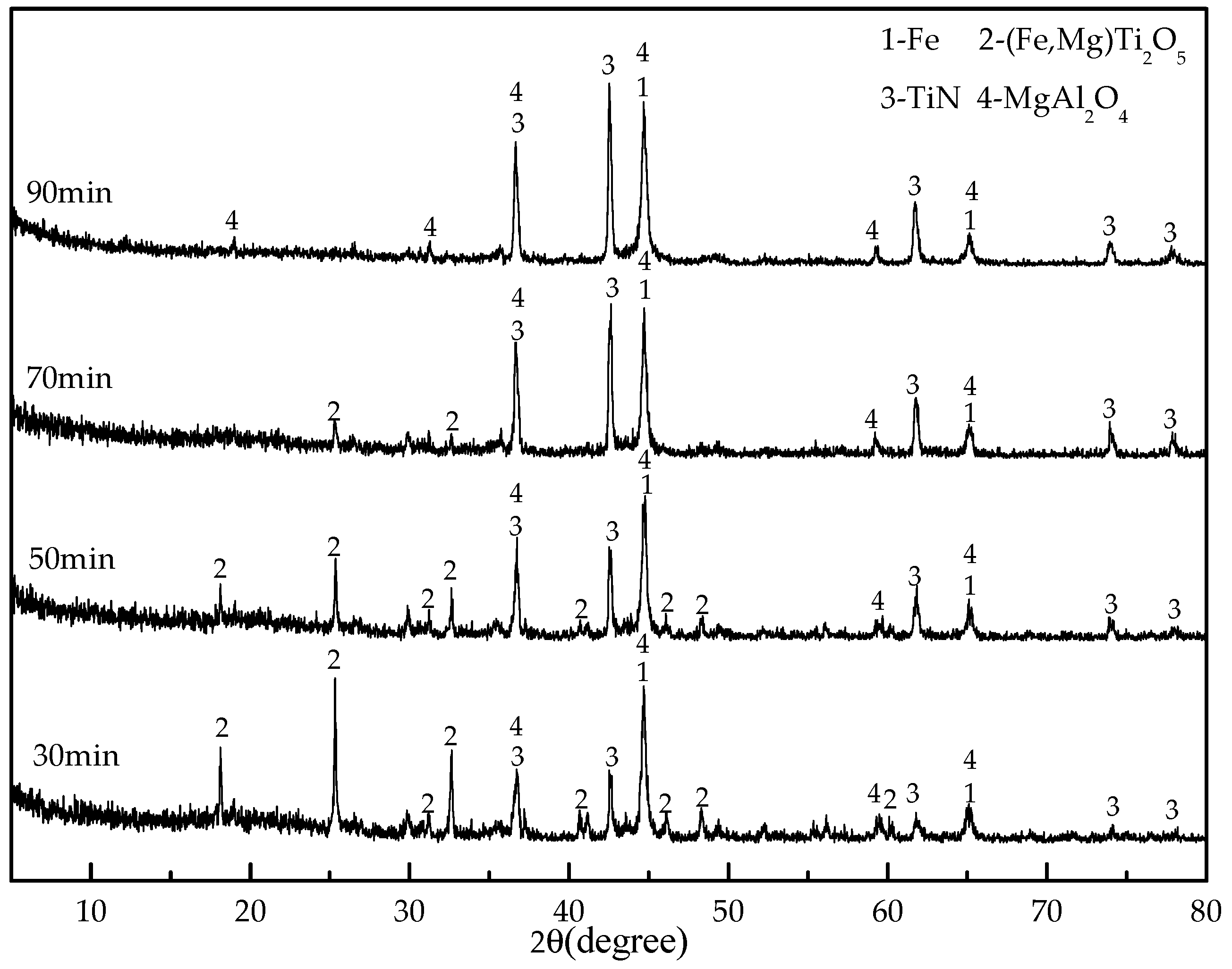
| Size (mm) | +0.28 | 0.28 + 0.15 | −0.15 + 0.10 | −0.10 + 0.074 | −0.074 + 0.056 | −0.056 + 0.038 | −0.038 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt %) | 1.27 | 8.16 | 19.50 | 16.90 | 13.54 | 17.61 | 23.02 |
| Fe | TiO2 | V2O5 | Al2O3 | MgO | SiO2 | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56.72 | 10.50 | 0.64 | 2.57 | 1.14 | 3.50 | 0.37 |
| Moisture | Cfix | Ash | Volatile | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.80 | 81.11 | 10.91 | 7.18 | 0.39 |
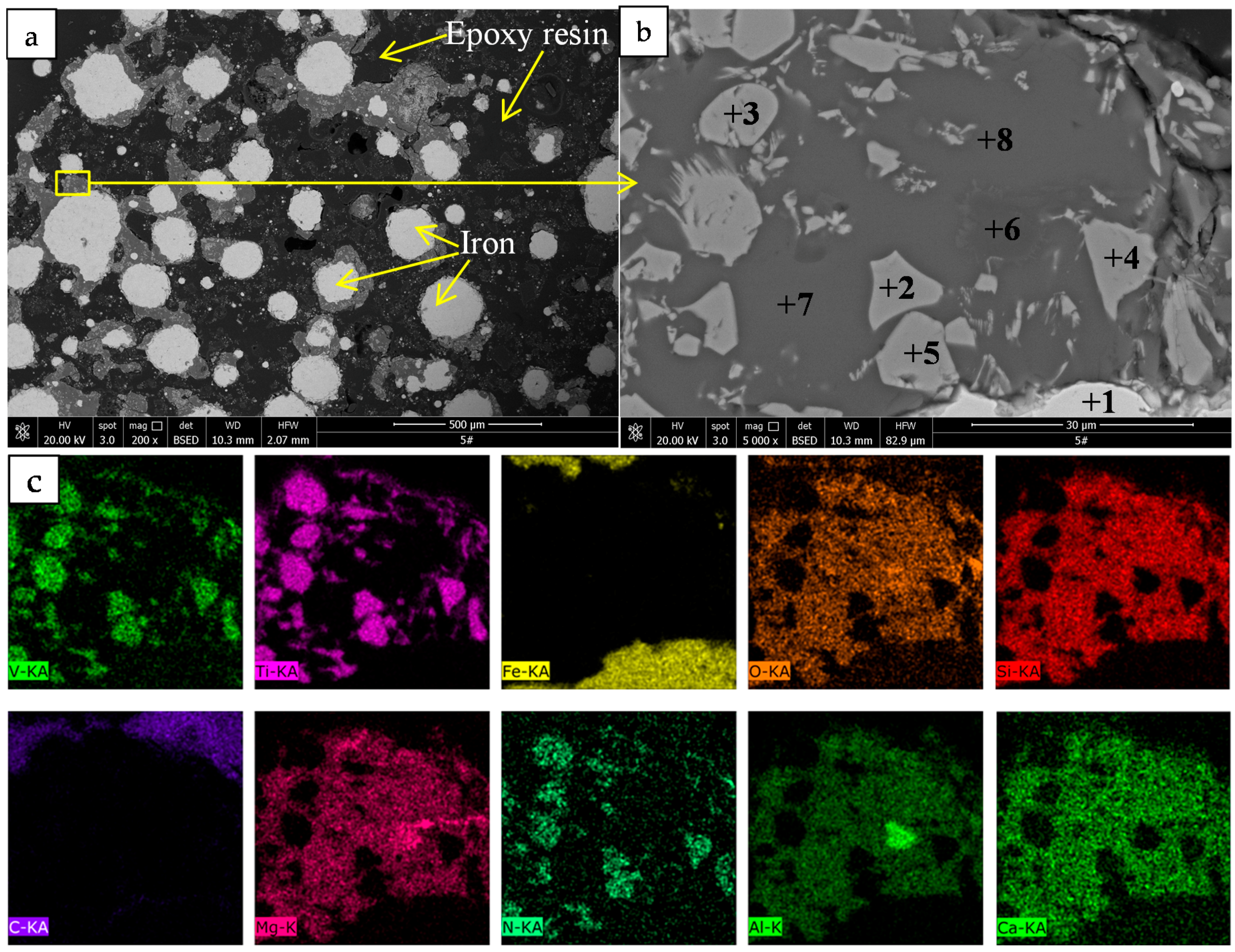
| Point | C | N | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | Ca | Ti | V | Fe | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.61 | - * | - | - | - | - | 0.61 | - | - | 0.29 | - | 90.49 | Iron |
| 2 | 2.06 | 14.73 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.20 | 80.26 | 2.19 | 0.55 | TiN |
| 3 | 4.25 | 17.07 | 3.00 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.18 | 68.32 | 7.18 | - | TiN |
| 4 | 1.15 | 12.38 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.34 | 82.94 | 2.62 | 0.56 | TiN |
| 5 | 1.85 | 13.80 | 1.73 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.15 | 79.43 | 2.03 | 1.02 | TiN |
| 6 | 6.12 | - | 44.43 | - | 14.62 | 31.52 | - | - | - | 2.94 | 0.13 | 0.23 | Spinel |
| 7 | 6.62 | - | 45.36 | 0.76 | 10.78 | 9.57 | 16.16 | 0.91 | 7.41 | 2.15 | - | 0.28 | Slag |
| 8 | 5.78 | - | 46.17 | 0.61 | 10.85 | 9.36 | 15.99 | 0.74 | 7.97 | 2.19 | - | 0.33 | Slag |
| Element | Content in DRI (wt %) | Recovery (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| Fe | 92.88 | 92.85 |
| Ti | 1.00 | 9.00 |
| V | 0.13 | 19.40 |
| Ti | Fe | V2O5 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | MnO | Na2O | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20.21 | 9.15 | 1.11 | 11.85 | 10.07 | 7.96 | 3.51 | 0.66 | 0.41 | 1.48 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.; Wen, X.; Chen, J.; Kuang, J.; Tang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Fu, J.; Huang, W.; Qiu, T. Preparation of Direct Reduced Iron and Titanium Nitride from Panzhihua Titanomagnetite Concentrate Through Carbothermic Reduction-Magnetic Separation. Minerals 2017, 7, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7110220
Yu W, Wen X, Chen J, Kuang J, Tang Q, Tian Y, Fu J, Huang W, Qiu T. Preparation of Direct Reduced Iron and Titanium Nitride from Panzhihua Titanomagnetite Concentrate Through Carbothermic Reduction-Magnetic Separation. Minerals. 2017; 7(11):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7110220
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Wen, Xiaojin Wen, Jiangan Chen, Jingzhong Kuang, Qiongyao Tang, Yuechao Tian, Jiali Fu, Weiqin Huang, and Tingsheng Qiu. 2017. "Preparation of Direct Reduced Iron and Titanium Nitride from Panzhihua Titanomagnetite Concentrate Through Carbothermic Reduction-Magnetic Separation" Minerals 7, no. 11: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7110220
APA StyleYu, W., Wen, X., Chen, J., Kuang, J., Tang, Q., Tian, Y., Fu, J., Huang, W., & Qiu, T. (2017). Preparation of Direct Reduced Iron and Titanium Nitride from Panzhihua Titanomagnetite Concentrate Through Carbothermic Reduction-Magnetic Separation. Minerals, 7(11), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7110220




