Beneficiation of a Sedimentary Phosphate Ore by a Combination of Spiral Gravity and Direct-Reverse Flotation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
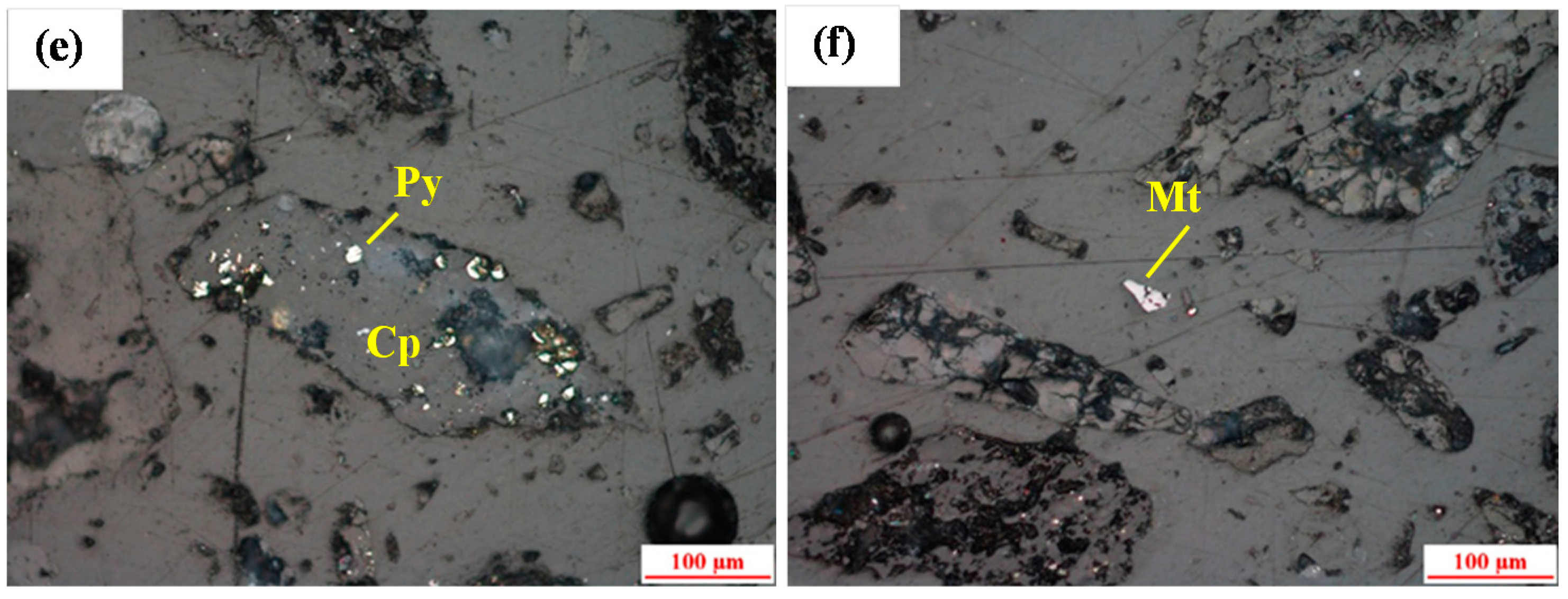
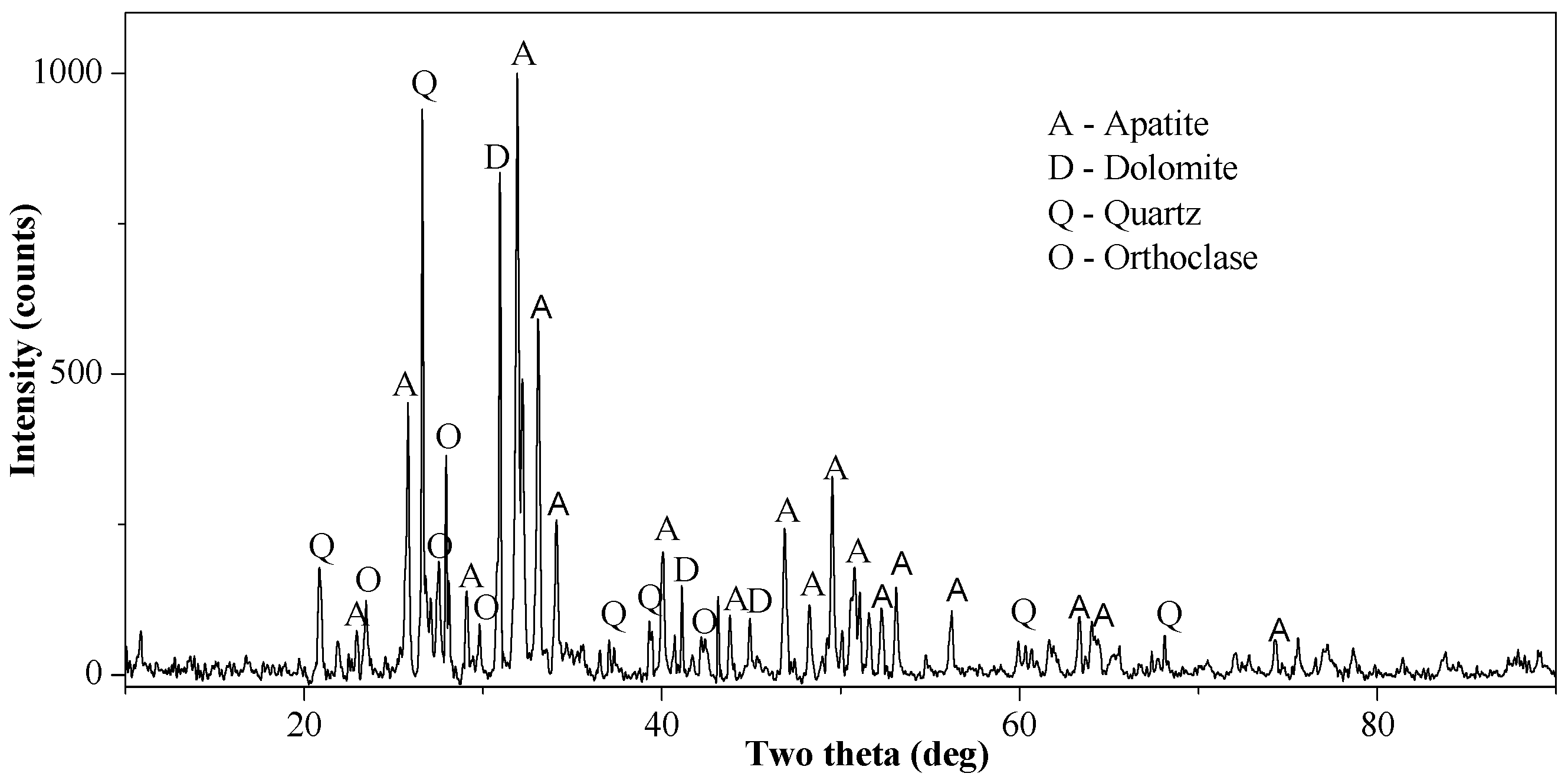
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
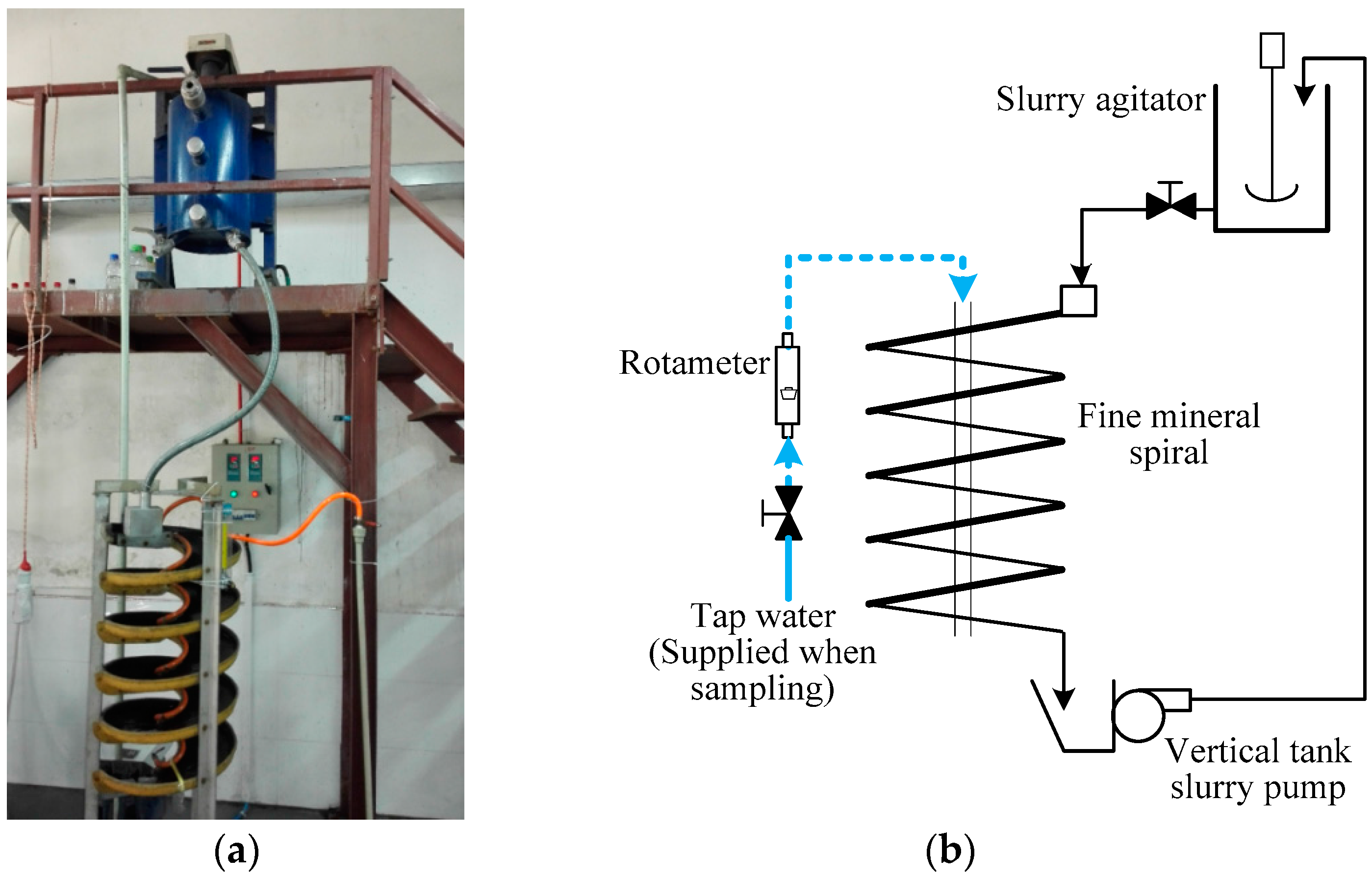
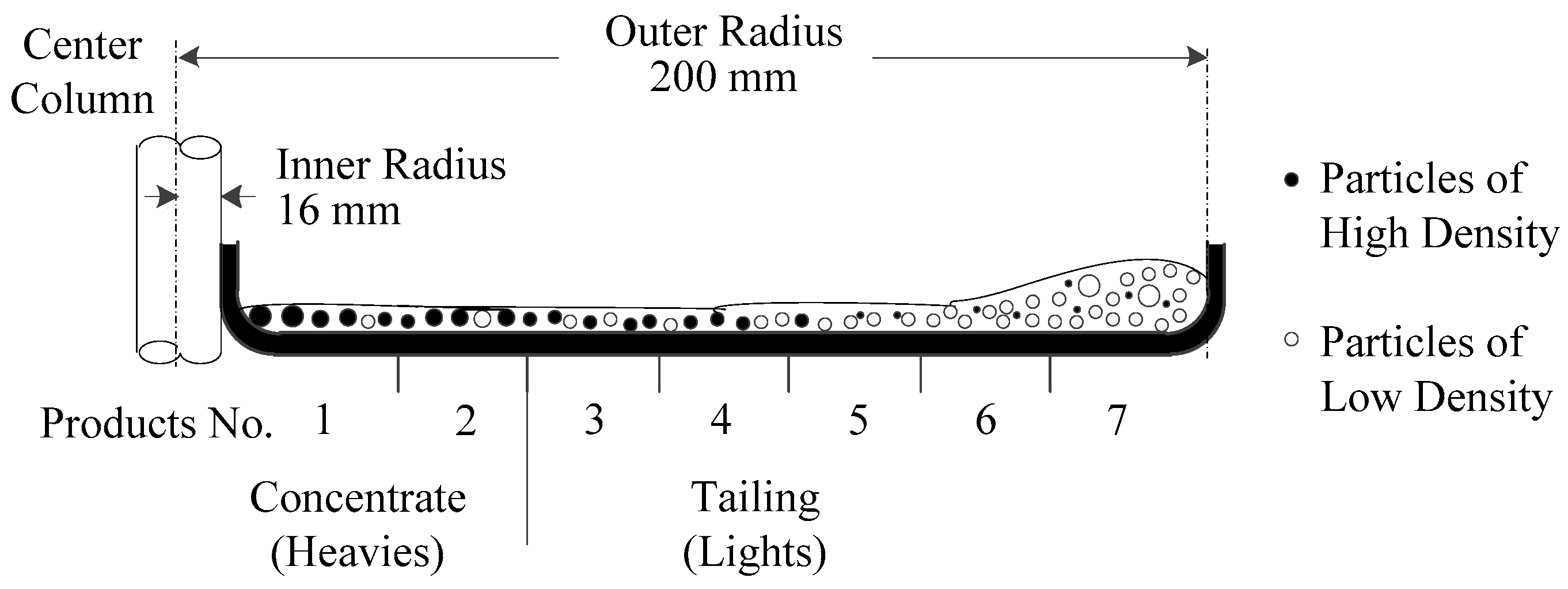
2.2.1. Gravity Separation Tests
2.2.2. Flotation Tests
3. Results
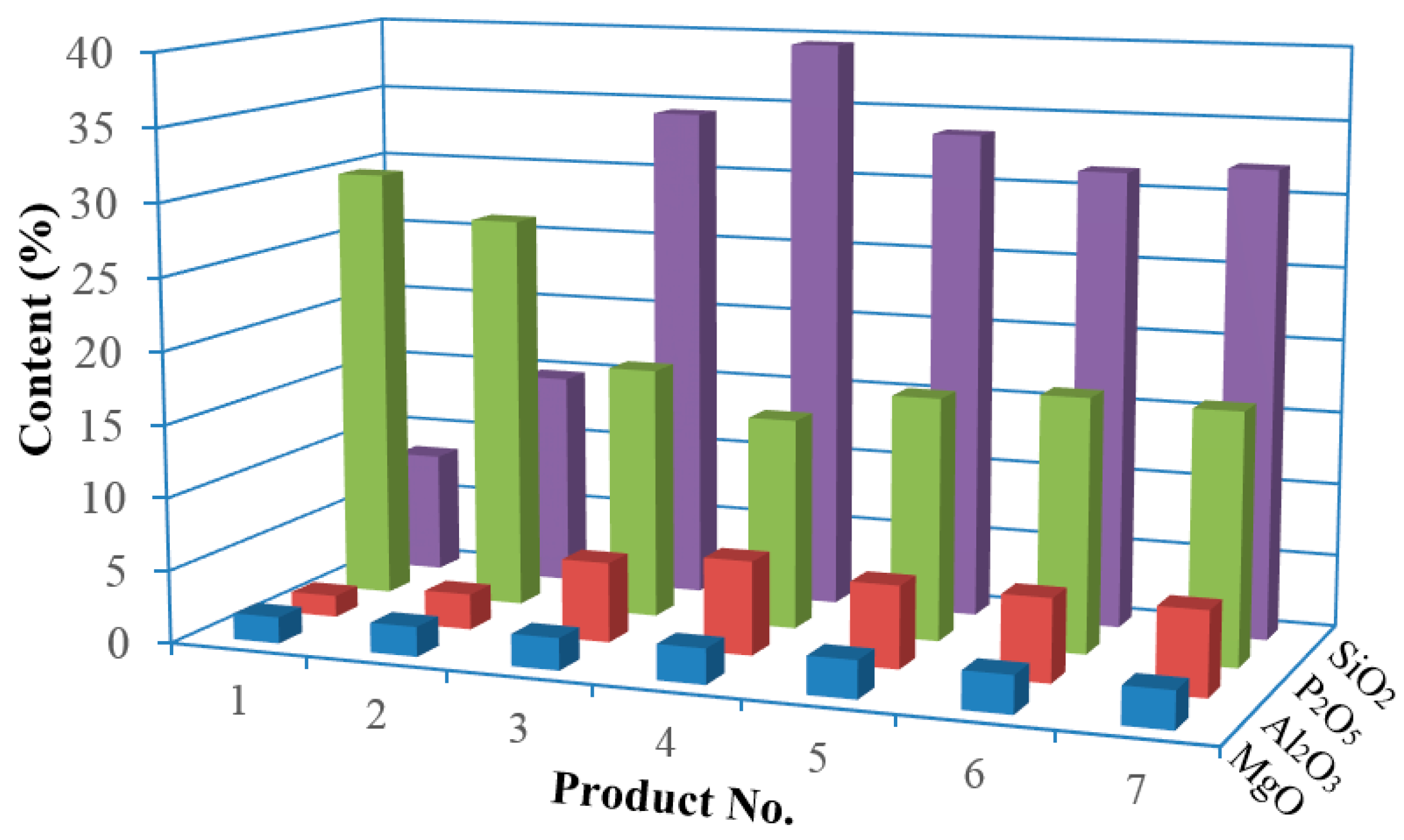
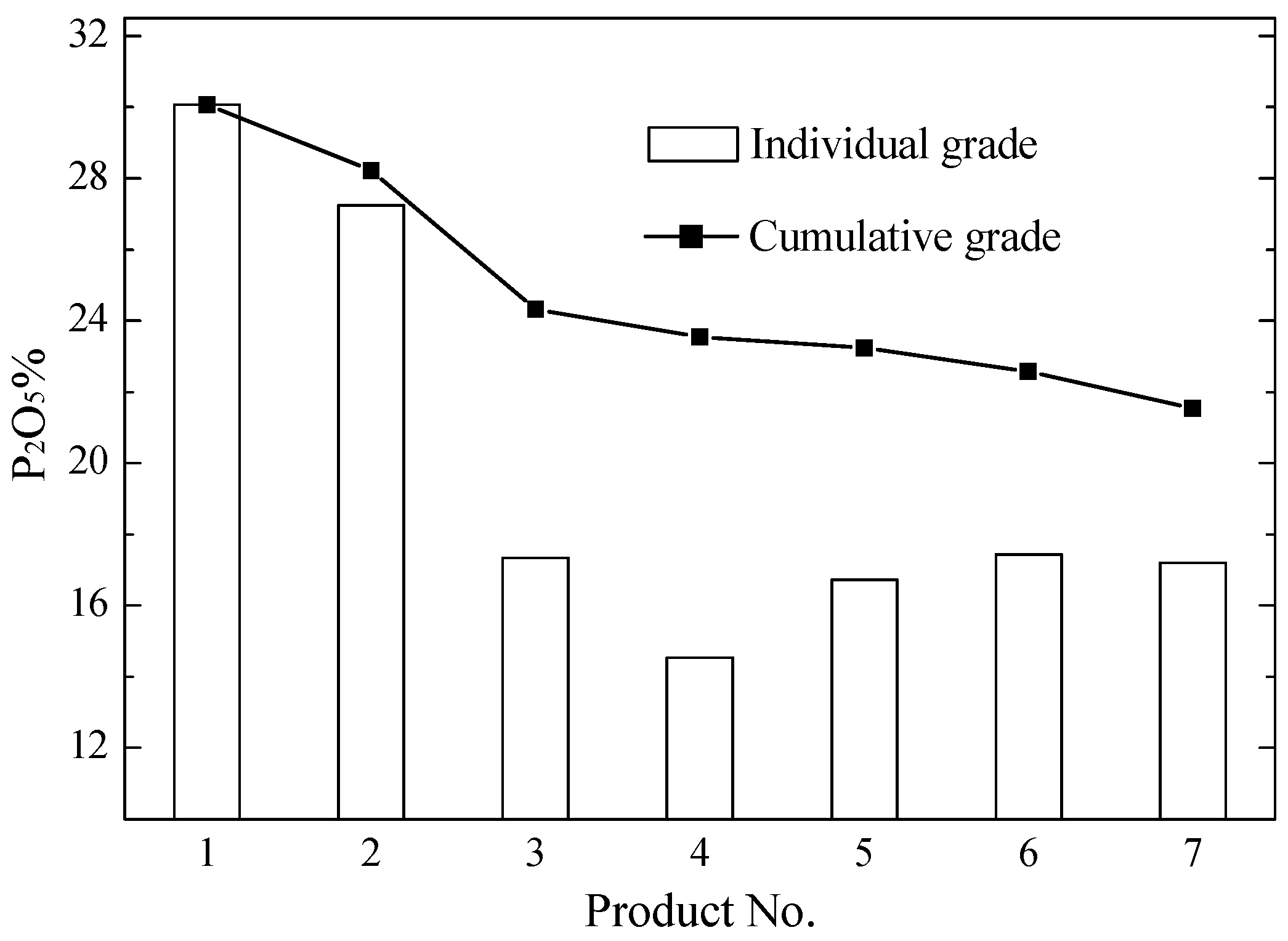
3.1. Gravity Separation Results
3.2. Flotation Tests Results
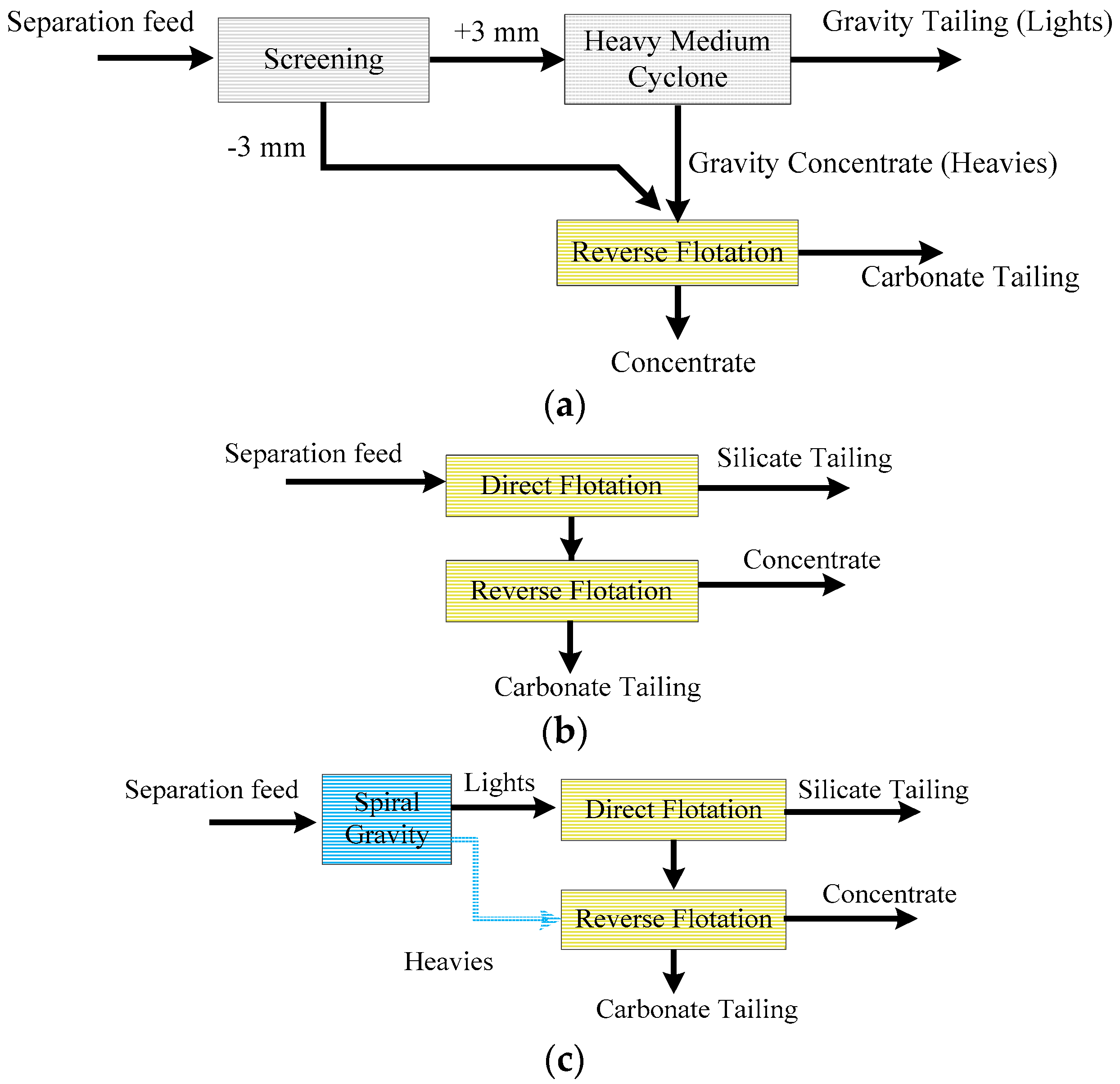
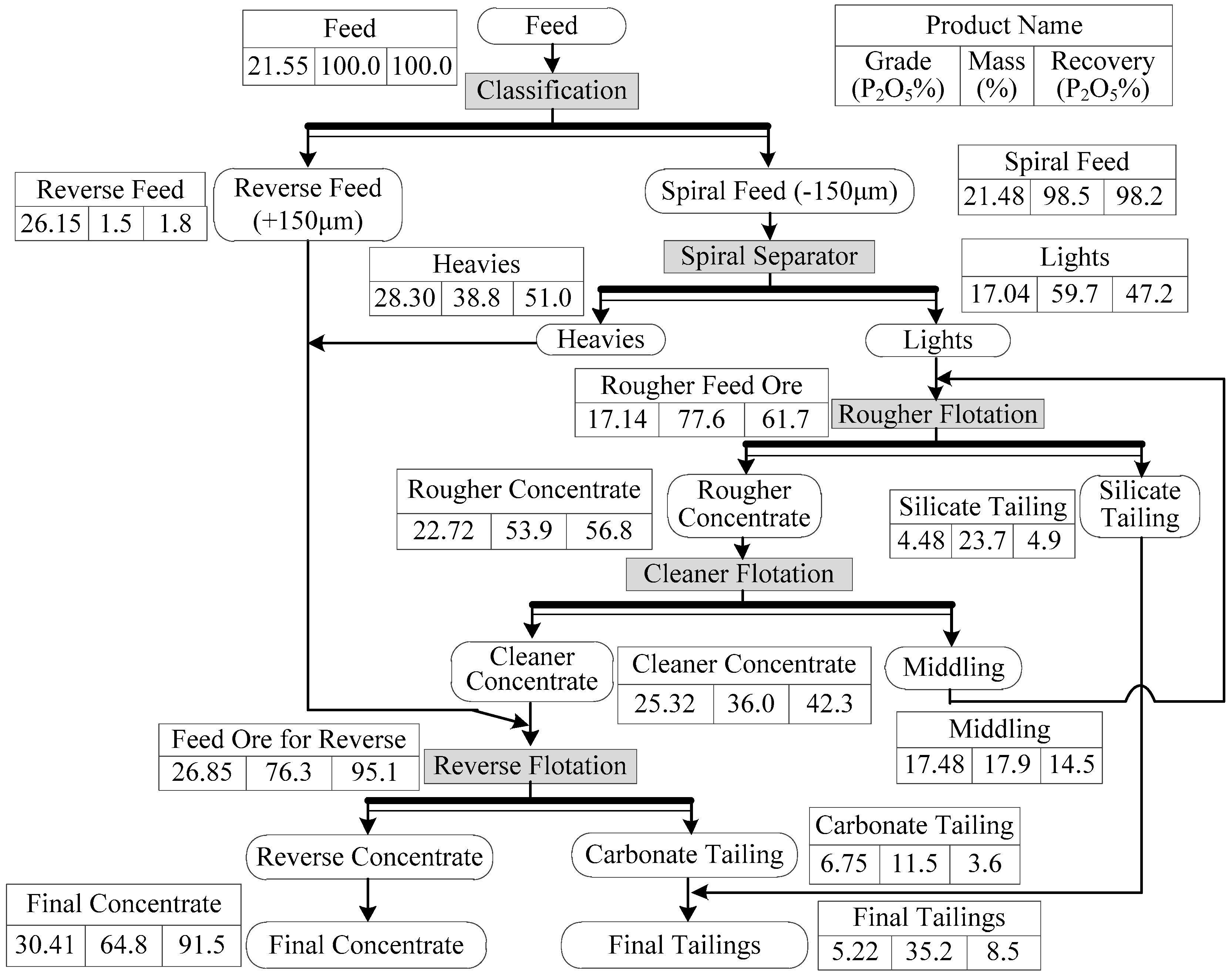
3.3. Flowsheet Test Results
4. Conclusions
- The results of this study showed that the fine spiral of a 0.36 P/D ratio was an useful separator for pre-recovery of collophanite from Yichang ultra-fine sedimentary phosphate ore. A final concentrate with a grade of 30.41% P2O5 and a recovery of 91.5% can be produced by a combined process of gravity and direct-reverse flotation.
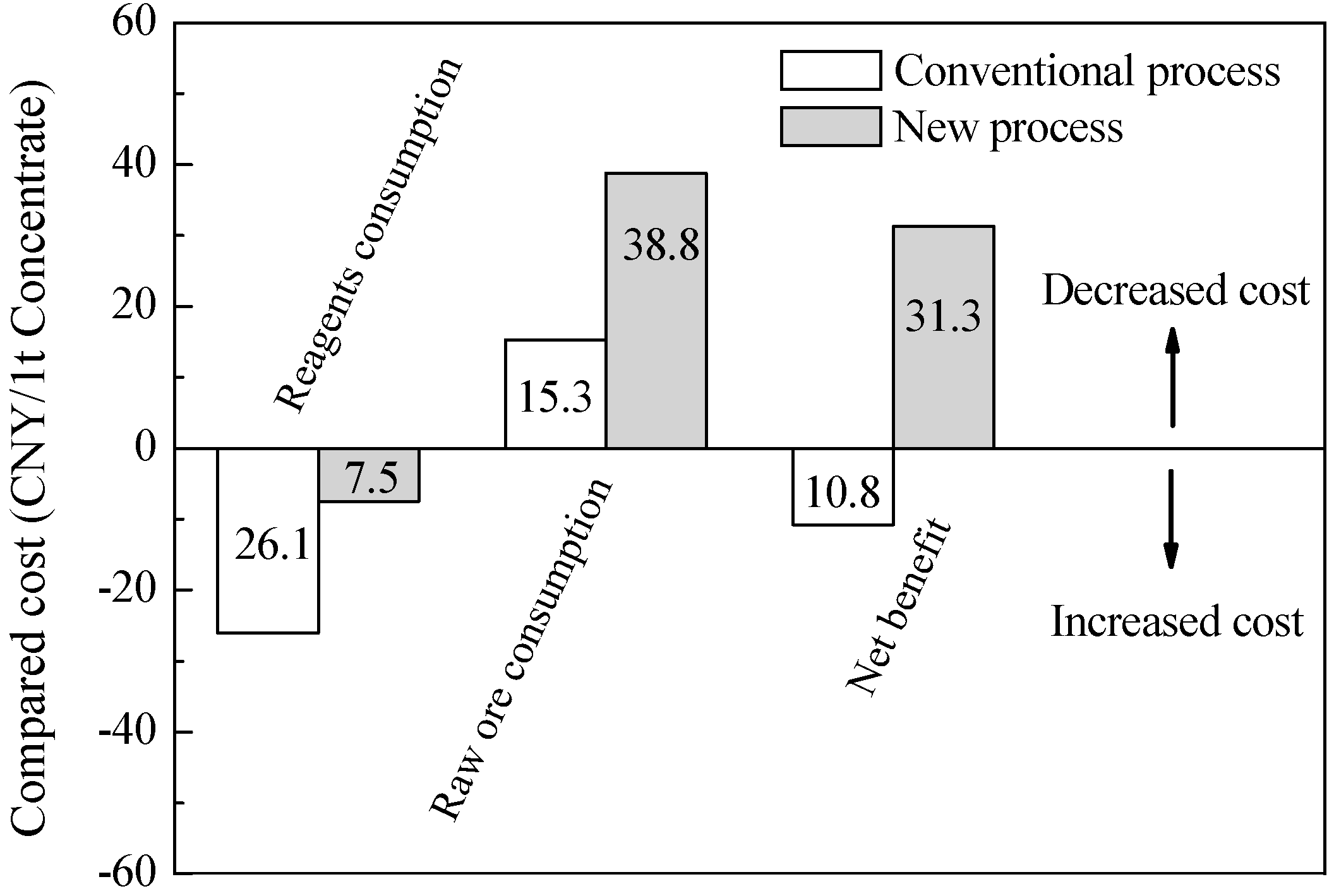
- Compared to the actual process applied during the year 2014, the use of gravity concentrator in the flowsheet achieved significant cost savings. The net benefit is 31.3 CNY/1 t concentrate and boosts the profits by 39%, whilst the conventional process costs 10.8 CNY more than the actual process for producing 1 t of concentrate.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shariati, S.; Ramadi, A.; Salsani, A. Beneficiation of low-grade phosphate deposits by a combination of calcination and shaking tables: Southwest Iran. Minerals 2015, 5, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkhani, M.; Noaparast, M.; Shafaei, S.Z.; Amini, A.; Amini, E.; Abdollahi, H. Double reverse flotation of a very low grade sedimentary phosphate, rich in carbonate and silicate. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 100, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, J. Separation strategies for Jordanian phosphate rock with siliceous and calcareous gangues. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 97, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouzeid, A.Z.M. Physical and thermal treatment of phosphate ores—An overview. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2008, 85, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS). Mineral Information. Phosphate Rock. Available online: http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/phosphate_rock/ (accessed on 18 April 2016).
- Li, W.; Gao, H.; Luo, Y.; Gao, J. Status, trends and suggestions of phosphorus ore resources at home and abroad. China Min. Mag. 2015, 6, 6–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Sandenbergh, R. Improvement of phosphate ore flotation performance through sized flotation. In Proceedings of the International Mineral Processing Congress (IMPC), Brisbane, Australia., 6–10 September 2010.
- Abouzeid, A.Z.M.; Negm, A.T.; Elgillani, D.A. Upgrading of calcareous phosphate ores by flotation: Effect of ore characteristics. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 90, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Cheng, J.; Wen, S.; Li, C.; Bai, S.; Liu, D. A mixed collector system for phosphate flotation. Miner. Eng. 2015, 78, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, J. Phosphatic Fertilizer; Chemical Industry Press of China: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 92–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, T.R.; Yehia, A.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Yassin, K.E. A modification in the flotation process of a calcareous-siliceous phosphorite that might improve the process economics. Miner. Eng. 2014, 69, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Gan, S.; Zeng, X.; Yu, Y. Double reverse flotation process of collophanite and regulation froth action. Trans. Nonferr. Metals Soc. China 2008, 18, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M. Test on gravity-flotation complex process of mid-low grade phosphate rock in Dianchi region. Ind. Miner. Process. 2004, 5, 3–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Wei, M. Progress in beneficiation of phosphorite ores. Min. Metall. 2010, 4, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Le, H.; Shao, T. Promoting of heavy medium cyclone and new technology application. Coal Sci. Technol. 2008, 5, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mishara, B.K.; Tripathy, A. A preliminary study of particle separation in spiral concentrators using DEM. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 94, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Godivalla, K.M.; Panda, L.; Bhattacharya, K.K.; Singh, R.; Mehrotra, S.P. Mathematical modeling of separation characteristics of coal-washing spiral. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 84, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, R.G.; MacHunter, D.M.; Gates, P.J.; Palmer, M.K. Gravity separation of ultra-fine (−0.1 mm) minerals using spiral separators. Miner. Eng. 2000, 1, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Z. Development of BL1500-A spiral chute and its application in tailings retreatment. Min. Metall. 2001, 4, 24–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.J.; Zhang, Y.M. Experiments of acid pellet using treated pyrite slag and its commercial application. Res. Iron Steel 2005, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, P.C.; Meloy, T.P. Spirals observed. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1998, 53, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Bai, G.; Yuan, Z. Minerals and Rocks; Chemical Industry Press of China: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 169–200. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


| Component | P2O5 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 21.54 | 25.28 | 4.56 | 2.30 | 2.24 | 31.77 |
| Mineral | Collophanite | Quartz | Clay | Dolomite | Pyrite | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 52.5 | 16.3 | 14.1 | 10.3 | 2.0 | 4.8 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.14 | 2.54 | 2.1–2.7 | 2.82 | 4.92 | - |
| Height | Pitch (P) | Outer Diameter (D) | Inner Radius | Radial Width | Trough Slope Angle (θ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 850 mm | 144 mm | 400 mm | 16 mm | 184 mm | 8° |
| Size Fraction (μm) | wt % | P2O5 | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % Dist. | % | % Dist. | % | % Dist. | % | % Dist. | ||
| +150 | 1.5 | 26.14 | 1.8 | 0.74 | 0.5 | 3.81 | 1.3 | 21.75 | 1.3 |
| −150 + 74 | 28.6 | 24.12 | 31.8 | 1.30 | 16.5 | 3.90 | 24.6 | 24.35 | 28.4 |
| −74 + 45 | 23.6 | 23.39 | 25.5 | 2.30 | 24.2 | 4.18 | 21.8 | 22.28 | 21.5 |
| −45 + 38 | 7.7 | 22.00 | 7.8 | 2.88 | 9.8 | 4.34 | 7.30 | 23.22 | 7.2 |
| −38 + 25 | 6.1 | 20.54 | 5.8 | 3.29 | 9.0 | 4.66 | 6.30 | 22.87 | 5.7 |
| −25 | 32.5 | 18.18 | 27.3 | 2.77 | 40.0 | 5.38 | 38.6 | 26.97 | 35.8 |
| Feed | 100.0 | 21.67 | 100.00 | 2.25 | 100.0 | 4.53 | 100.0 | 24.50 | 100.0 |
| Products | Product No. | wt % | P2O5 | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % Rec. | % | % Rec. | % | % Rec. | % | % Rec. | |||
| Heavies | 1 | 13.9 | 30.07 | 19.3 | 1.81 | 11.2 | 1.48 | 4.8 | 8.37 | 4.6 |
| 2 | 26.4 | 27.25 | 33.5 | 2.05 | 24.2 | 2.45 | 15.2 | 14.80 | 15.6 | |
| Total | 40.3 | 28.22 | 52.8 | 1.97 | 35.4 | 2.12 | 20.0 | 12.59 | 20.2 | |
| Lights | 3 | 22.6 | 17.34 | 18.2 | 2.20 | 22.2 | 5.49 | 29.2 | 34.34 | 30.9 |
| 4 | 5.3 | 14.53 | 3.5 | 2.44 | 5.7 | 6.44 | 7.9 | 39.50 | 8.3 | |
| 5 | 3.4 | 16.72 | 2.6 | 2.60 | 3.9 | 5.66 | 4.5 | 33.64 | 4.5 | |
| 6 | 9.0 | 17.43 | 7.3 | 2.59 | 10.5 | 5.70 | 12.1 | 31.49 | 11.4 | |
| 7 | 19.4 | 17.20 | 15.5 | 2.58 | 22.3 | 5.78 | 26.3 | 32.10 | 24.7 | |
| Total | 59.7 | 17.03 | 47.2 | 2.43 | 64.6 | 5.71 | 80.0 | 33.59 | 79.8 | |
| Feed | 100.0 | 21.54 | 100.0 | 2.24 | 100.0 | 4.26 | 100.0 | 25.13 | 100.0 | |
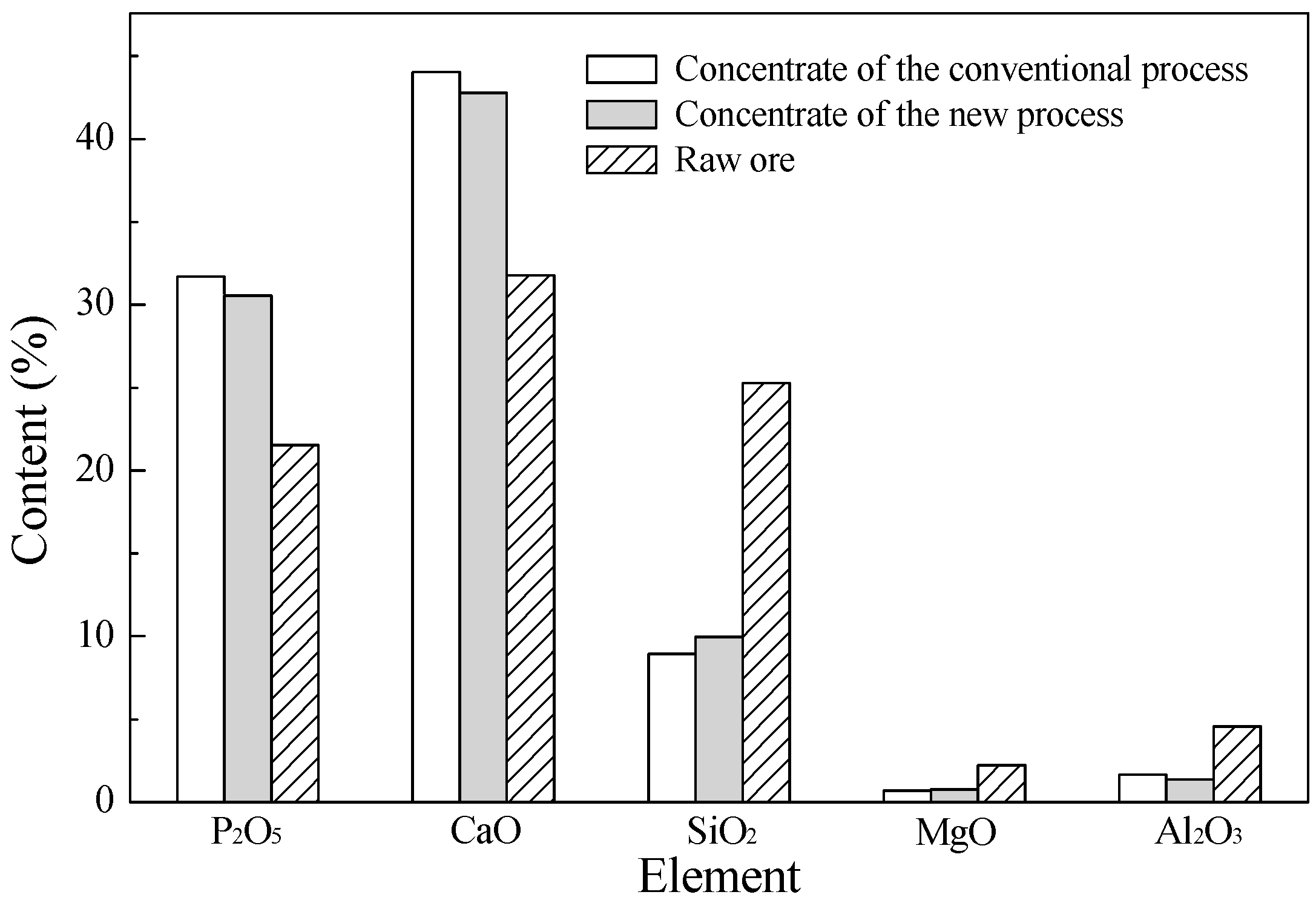
| Process | Product | wt % | P2O5 | MgO | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % Rec. | % | % Rec. | |||
| Conventional | Concentrate | 58.82 | 31.69 | 86.05 | 0.72 | 19.36 |
| Carbonate | 9.16 | 5.60 | 2.37 | 15.50 | 64.93 | |
| Silicate | 25.58 | 4.28 | 5.05 | 0.83 | 9.70 | |
| Middling | 6.44 | 21.94 | 6.53 | 2.04 | 6.01 | |
| Total | 100 | 21.66 | 100 | 2.21 | 100 | |
| New | Concentrate | 60.80 | 30.56 | 86.28 | 0.78 | 21.41 |
| Carbonate | 8.44 | 5.91 | 2.32 | 15.93 | 60.53 | |
| Silicate | 21.33 | 3.78 | 3.74 | 0.95 | 9.11 | |
| Middling | 9.43 | 17.48 | 7.66 | 2.11 | 8.95 | |
| Total | 100 | 21.53 | 100 | 2.22 | 100 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Cai, Z.; Chen, T.; Sun, K. Beneficiation of a Sedimentary Phosphate Ore by a Combination of Spiral Gravity and Direct-Reverse Flotation. Minerals 2016, 6, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020038
Liu X, Zhang Y, Liu T, Cai Z, Chen T, Sun K. Beneficiation of a Sedimentary Phosphate Ore by a Combination of Spiral Gravity and Direct-Reverse Flotation. Minerals. 2016; 6(2):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020038
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin, Yimin Zhang, Tao Liu, Zhenlei Cai, Tiejun Chen, and Kun Sun. 2016. "Beneficiation of a Sedimentary Phosphate Ore by a Combination of Spiral Gravity and Direct-Reverse Flotation" Minerals 6, no. 2: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020038
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, Y., Liu, T., Cai, Z., Chen, T., & Sun, K. (2016). Beneficiation of a Sedimentary Phosphate Ore by a Combination of Spiral Gravity and Direct-Reverse Flotation. Minerals, 6(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020038





