Morphology and Composition of Microspheres in Fly Ash from the Luohuang Power Plant, Chongqing, Southwestern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Samples Collection and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
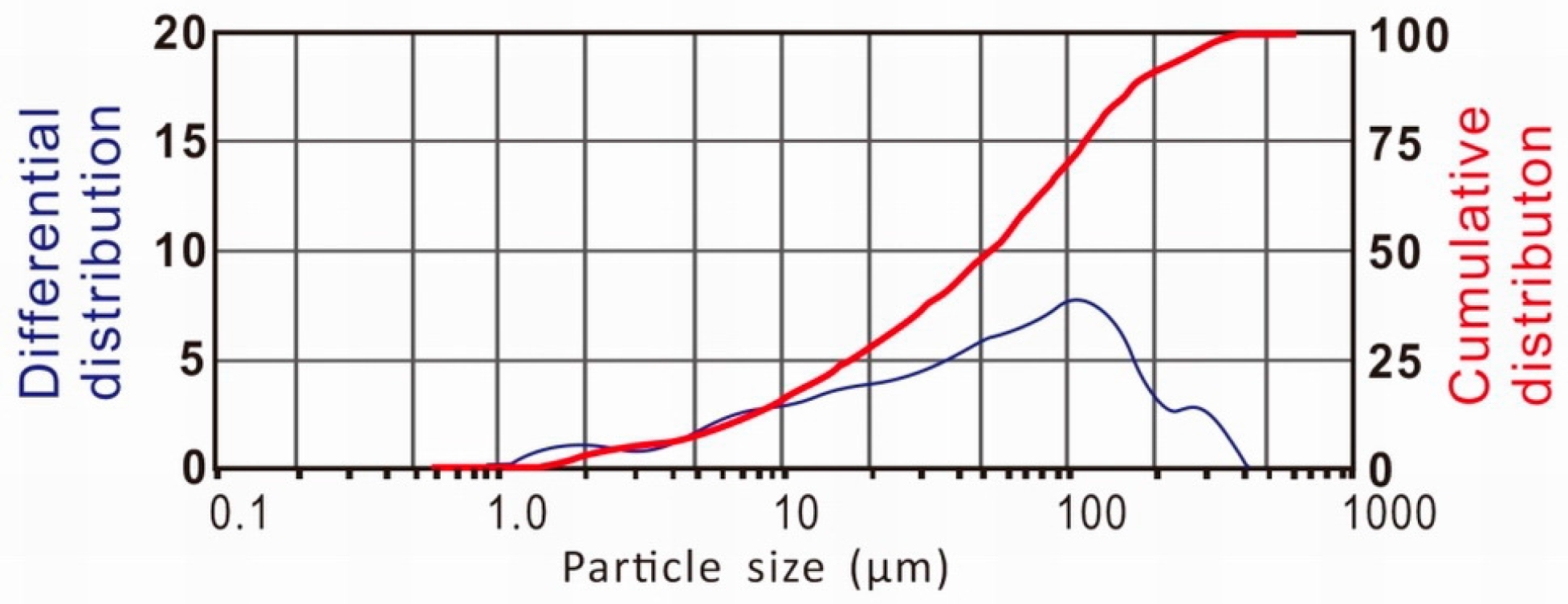
3.1. The Particle Size Distribution of the Fly Ash
3.2. Major Elements of the Fly Ash
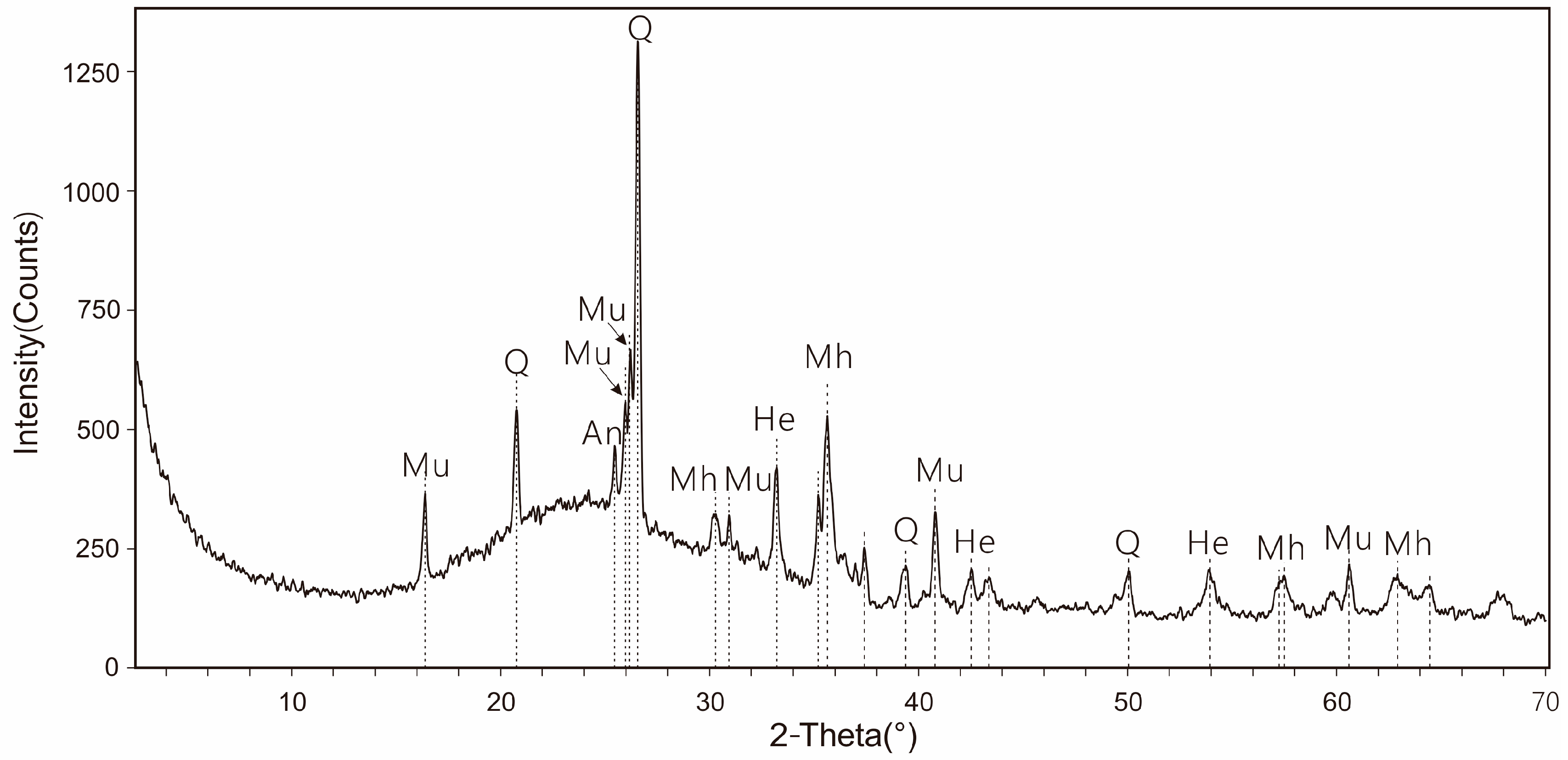
3.3. Mineral Composition of the Fly Ash
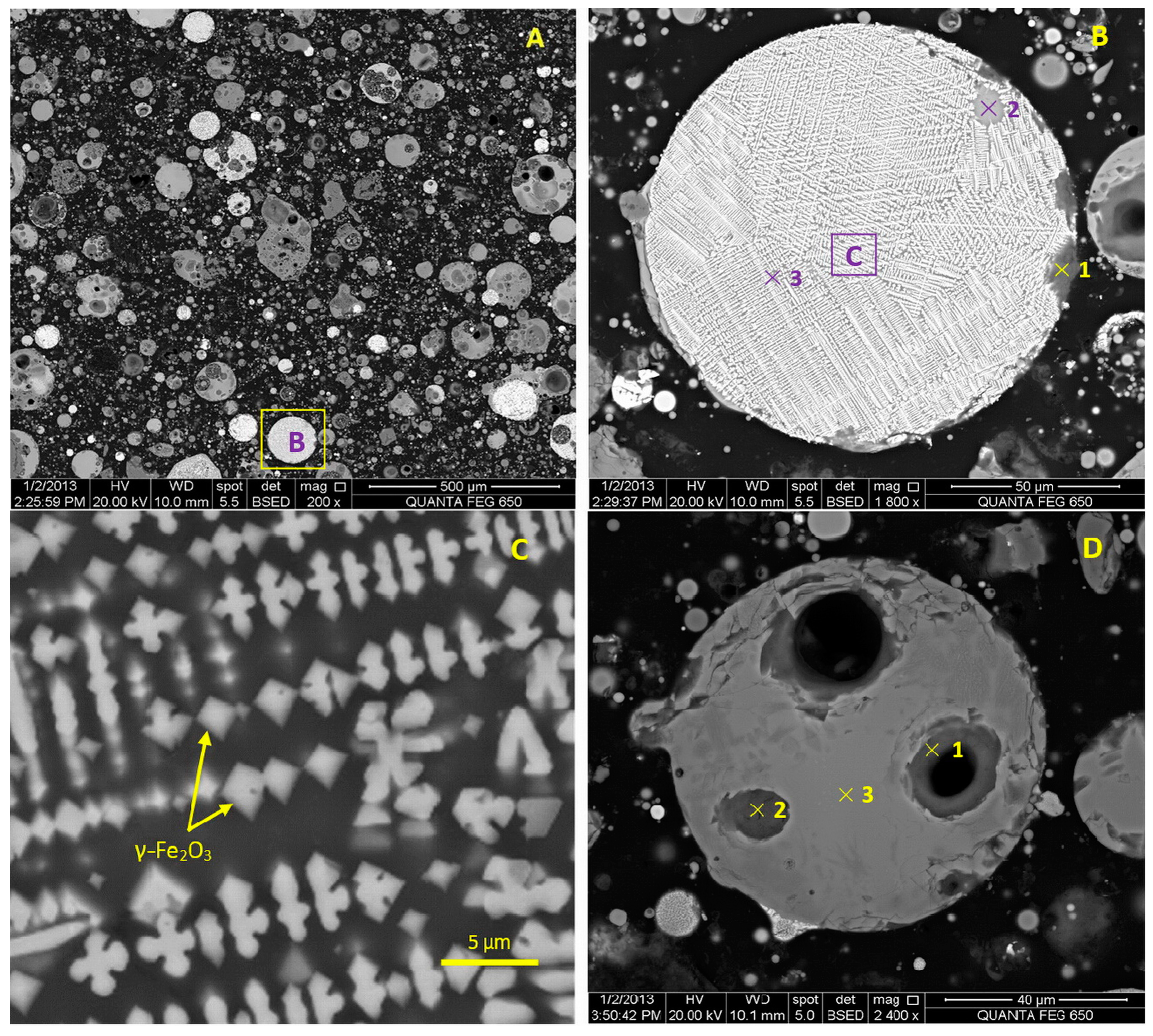
3.4. Morphology and Composition of Microspheres in the Fly Ash
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Chou, C.L.; Finkelman, R.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Zhou, Y. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, H.E.; Finkelman, R.B.; Zheng, B.S.; Zhou, D.X. Human health effects of domestic combustion of coal: A causal factor for arsenosis and fluorosis in rural China. In Proceedings of the Air Quality Conference, McLean, VA, USA, 1–4 December 1998.
- Belkin, H.E.; Finkelman, R.B.; Zheng, B.S. Geochemistry of fluoride-rich coal related to endemic fluorosis in Guizhou Province, China. In Proceedings of the Pan-Asia Pacific Conference on Fluoride and Arsenic Research, Shenyang, China, 16–20 August 1999.
- Belkin, H.E.; Finkelman, R.B.; Zheng, B.S. Human health effects of domestic combustion of coal: A causal factor for arsenic poisoning and fluorosis in rural China. Am. Geophys. Union 1999, 80, 377–378. [Google Scholar]
- Belkin, H.E.; Zheng, B.S.; Zhou, D.; Finkelman, R.B. Chronic arsenic poisoning from domestic combustion of coal in rural China: A case study of the relationship between earth materials and human health. Environ. Geochem. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B.; Orem, W.; Castranova, V.; Tatu, C.A.; Belkin, H.E.; Zheng, B.S.; Lercha, H.E.; Maharaje, S.V.; Bates, A.L. Health impacts of coal and coal use: Possible solutions. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Ma, S. The cause of endemic fluorosis in western Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Fuel 2004, 83, 2095–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, P. The sources, pathway, and preventive measures for fluorosis in Zhijin County, Guizhou, China. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Chou, C.L.; Yue, M.; Luo, K.; Ren, D. Mineralogy and geochemistry of a Late Permian coal in the Dafang Coalfield, Guizhou, China: Influence from siliceous and iron-rich calcic hydrothermal fluids. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 61, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Tang, Y.; Yue, M.; Hao, L. Concentration and distribution of elements in Late Permian coals from western Guizhou Province, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 61, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, D.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, L. Geochemistry and mineralogy of the Late Permian coals from the Songzo Coalfield, Chongqing, southwestern China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S. The occurrence of gold in fly ash derived from high-Ge coal. Miner. Deposita 2014, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S. Coal deposits as potential alternative sources for lanthanides and yttrium. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S.; Sun, Y.; Chekryzhov, I.Y. Coal deposits as promising sources of rare metals for alternative power and energy-efficient technologies. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.L.; Elseewi, A.A.; Straughan, I.R. Physical and chemical properties of fly ash from coal-fired power plants with reference to environmental impacts. In Residue Reviews; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 83–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sear, L.K.A. Properties and Use of Coal Fly Ash: A Valuable Industrial by-Product; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 2001; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez, V.A.; Arizmendi, M.A.; Vargas, G.; Almanza, J.M.; Alvarez, Q.J. Ultra-low thermal conductivity thermal barrier coatings from recycled fly-ash cenospheres. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Sun, X.; Li, Z. Unburned carbon from fly ash for mercury adsorption: I. Separation and characterization of unburned carbon. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2002, 1, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozhzhin, V.S.; Danilin, L.D.; Pikulin, I.V.; Khovrin, A.N.; Maximova, N.V.; Regiushev, S.A.; Pimenov, V.G. Functional materials on the basis of cenospheres. In Proceedings of the 2005 World of Coal Ash Conference, Lexington, KY, USA, 11–15 April 2005.
- Wasekar, P.A.; Pravin, G.K.; Shashank, T.M. Effect of cenosphere concentration on the mechanical, thermal, rheological and morphological properties of nylon 6. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2012, 11, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, M.V.; Sharma, M.; Sailaja, R.R.N.; Anantha, P.; Sampathkumaran, P.; Seetharamu, S. Mechanical and thermal characteristics of high density polyethylene-fly ash cenospheres composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharonova, O.M.; Anshits, N.N.; Oruzheinikov, A.I.; Akimochkina, G.V.; Salanov, A.N.; Nizovshii, A.I.; Semenova, O.N.; Anshits, A.G. Composition and morphology of magnetic microspheres in power plant fly ash of coal from the Ekibastuz and Kuznetsk basins. Chem. Sustain. 2003, 11, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, G.L.; Chang, D.P.Y.; Brummer, M. Fly ash collected from electrostatic precipitators: Microcrystalline structures and the mystery of the spheres. Science 1976, 192, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodarzi, F.; Sanei, H. Plerosphere and its role in reduction of emitted fine fly ash particles from pulverized coal-fired power plants. Fuel 2009, 88, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Q.; Guo, X.; Zheng, C. Chemical composition and evolution mechanism of ferrospheres in fly ash from coal combustion. Proc. CSEE 2006, 26, 82. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, F. Characteristics and composition of fly ash from Canadian coal-fired power plants. Fuel 2006, 85, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Shi, Q. Determination of content and properties of microspheres in fly ash. Fly Ash 1997, 6, 13–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Standardization Administration of P.R. China; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the P.R. China. Chinese National Standard GB/T 212-2008, Proximate Analysis of Coal; Standand Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 3–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hower, J.C.; Li, D.; Chen, W.; Zhu, X. Chemical and mineralogical compositions of silicic, mafic, and alkali tonsteins in the Late Permian coals from the Songzao Coalfield, Chongqing, Southwest China. Chem. Geol. 2011, 282, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell: London, UK, 1985; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R.; Spears, D.A.; Booth, C.A.; Staton, I.; Gurba, L.W. Mineral matter and trace elements in coals of the Gunnedah Basin, New South Wales, Australia. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 40, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Liu, J.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; French, D.; Jia, S.; Hood, M.M.; Garrison, T.M. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of Late Permian coals and host rocks from the Guxu Coalfield, Sichuan Province, China, with emphasis on enrichment of rare metals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Li, T.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Song, X.; Song, W.; Zhao, C. Origin of minerals and elements in the Late Permian coals, tonsteins, and host rocks of the Xinde Mine, Xuanwei, eastern Yunnan, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 121, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R.; French, D. Determination of glass content and estimation of glass composition in fly ash using quantitative X-Ray diffractometry. Fuel 2006, 85, 2268–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Liu, J.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Xie, P.; Jiang, Y.; Hood, M.M.; O’Keefee, J.M.K.; Song, H. Petrological, geochemical, and mineralogical compositions of the low-Ge coals from the Shengli Coalfield, China: A comparative study with Ge-rich coals and a formation model for coal-hosted Ge ore deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 71, 318–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Hower, J.C.; Ward, C.R.; Guo, W.; Song, H.; O’Keefe, J.M.K.; Xie, P.; Hood, M.M.; Yan, X. Elements and phosphorus minerals in the middle Jurassic inertinite-rich coals of the Muli Coalfield on the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 144–145, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardon, S.M.; Hower, J.C.; O’Keefe, J.M.K.; Marks, M.N.; Hedges, D.H. Coal combustion by-product quality at two stoker boilers: Coal source vs. fly ash collection system design. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 75, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G.; Karayigit, A.I.; Bulut, Y.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Phase-mineral and chemical composition of composite samples from feed coals, bottom ashes and fly ashes at the Soma power station, Turkey. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 61, 35–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhao, L.; Peng, S.; Chou, C.L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, Y. Abundances and distribution of minerals and elements in high-alumina coal fly ash from the Jungar Power Plant, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 81, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ward, C.R.; French, D.; Graham, I.T. Mineralogical composition of Late Permian coal seams in the Songzao Coalfield, southwestern China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 116, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Li, D.; Chou, C.L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Zhua, X.; Xing, Y.; et al. A high-pyrite semianthracite of Late Permian age in the Songzao Coalfield, southwestern China: Mineralogical and geochemical relations with underlying mafic tuffs. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 83, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Li, D.; Chou, C.L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, D.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Y. Mineralogy and geochemistry of boehmite-rich coals: New insights from the Haerwusu Surface Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 74, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, E.I.; Allouche, E.N.; Eklund, S. Factors affecting the suitability of fly ash as source material for geopolymers. Fuel 2010, 89, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groppo, J.; Honaker, R. Economical recovery of fly ash-derived magnetics and evaluation for coal cleaning. In Proceedings of the WOCA 09 The World of Coal Ash, Lexington, KY, USA, 4–7 May 2009.
- Huang, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhang, J. Research on the building electromagnetic wave absorber mixing high-iron fly ash. J. China Coal Soc. 2010, 35, 135–139. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.P.; Huggins, F.E. Reactions and transformations of coal mineral matter at elevated temperatures. Am. Chem. Soc. Symp. Ser. 1986, 301, 100–113. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.P.; Huggins, F.E.; Shah, N.; Shah, A. Behavior of basic elements during coal combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1990, 16, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, R.S.V.; D’Almeida, J.R.M.; Abreu, E.S.V. Proceedings of the Third Ibero-American Polymer Symposium; Wiley-VCH: Vigo, Spain, 1992; pp. 531–532. [Google Scholar]
- D’Almeida, J.R.M. An analysis of the effect of the diameters of glass microspheres on the mechanical behavior of glass-microsphere/epoxy-matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 2087–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blissett, R.S.; Rowson, N.A. A review of the multi-component utilisation of coal fly ash. Fuel 2012, 97, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seames, W.S. An initial study of the fine fragmentation fly ash particle mode generated during pulverized coal combustion. Fuel Process. Technol. 2003, 81, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, E.V.; Kalugin, V.M.; Nigmatulina, E.N.; Volkova, N.I.; Frenkel, A.E.; Maksimova, N.V. Ferrospheres from fly ashes of Chelyabinsk coals: Chemical composition, morphology and formation conditions. Fuel 2002, 81, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LOI | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | MnO | Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.01 | 0.77 | 1.21 | 21.59 | 48.27 | 0.13 | 0.78 | 1.21 | 5.72 | 1.78 | 0.09 | 14.09 |
| Mineral Phase | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| Glass | 79.5 |
| Mullite | 8.3 |
| Maghemite | 4.6 |
| Quartz | 5.1 |
| Hematite | 1.9 |
| Anhydrite | 0.7 |
| Detection Spot * | Elements (at. %) Detected by EDS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Al | Fe | Ca | Ti | Na | Mg | K | O ** | |
| B1 | 44.82 | 1.64 | 5.14 | 0.83 | - | - | - | - | 47.57 |
| B2 | 26.51 | 9.28 | 10.09 | 4.24 | 0.49 | - | 0.44 | - | 48.93 |
| B3 | 4.40 | 6.50 | 40.07 | 1.15 | 0.31 | - | 0.94 | - | 46.63 |
| D1 | 46.54 | 1.63 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 51.82 |
| D2 | 47.19 | 0.98 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 51.83 |
| D3 | 24.02 | 15.97 | 3.92 | 1.48 | 2.50 | 1.07 | 0.67 | 1.07 | 49.29 |
| E1 | 26.84 | 16.24 | 1.88 | 1.92 | 2..22 | 0.58 | 1.89 | 1.35 | 47.09 |
| E2 | 29.87 | 22.19 | 4.30 | - | 0.99 | 0.47 | 1.16 | 1.07 | 47.59 |
| F1 | 22.68 | 6.60 | 23.71 | 0.40 | - | - | - | - | 46.61 |
| F2 | 1.75 | - | 98.25 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Sun, Q.; Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Zou, J. Morphology and Composition of Microspheres in Fly Ash from the Luohuang Power Plant, Chongqing, Southwestern China. Minerals 2016, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020030
Liu H, Sun Q, Wang B, Wang P, Zou J. Morphology and Composition of Microspheres in Fly Ash from the Luohuang Power Plant, Chongqing, Southwestern China. Minerals. 2016; 6(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huidong, Qi Sun, Baodong Wang, Peipei Wang, and Jianhua Zou. 2016. "Morphology and Composition of Microspheres in Fly Ash from the Luohuang Power Plant, Chongqing, Southwestern China" Minerals 6, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020030
APA StyleLiu, H., Sun, Q., Wang, B., Wang, P., & Zou, J. (2016). Morphology and Composition of Microspheres in Fly Ash from the Luohuang Power Plant, Chongqing, Southwestern China. Minerals, 6(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020030






